Synthesis and In Silico Evaluation of GABA, Pregabalin and Baclofen N-Heterocyclic Analogues as GABAB Receptor Agonists
Abstract
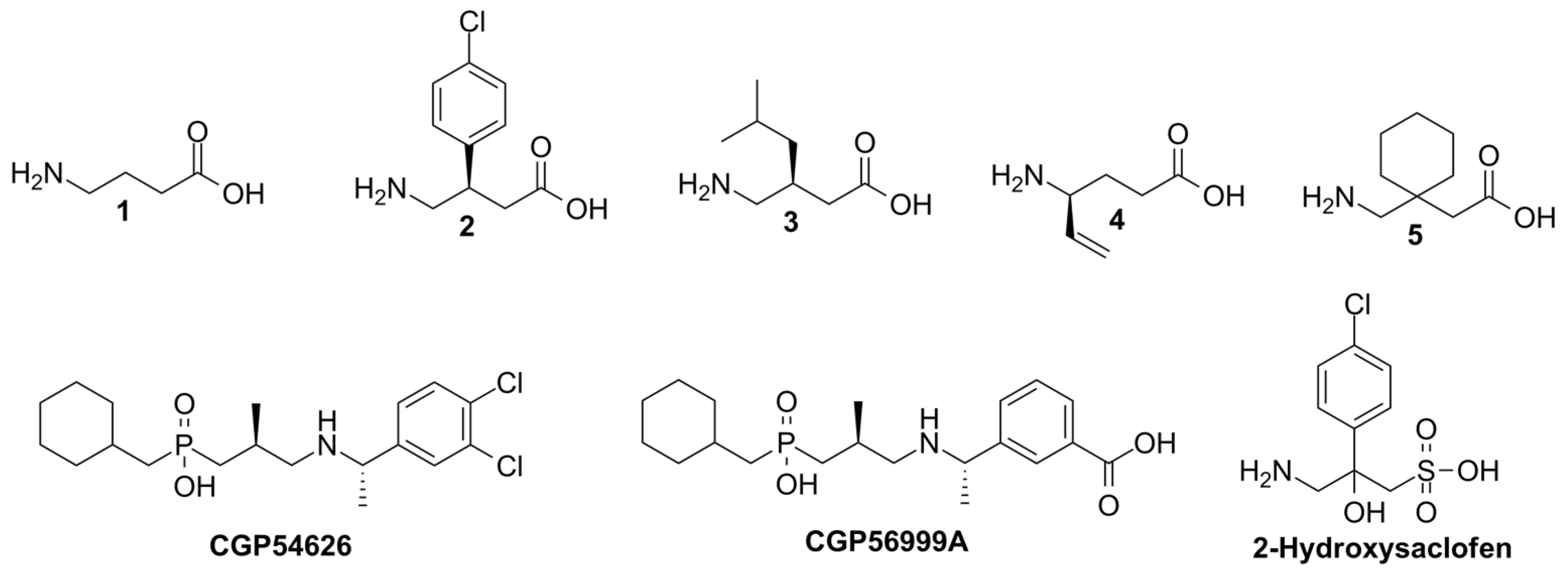
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
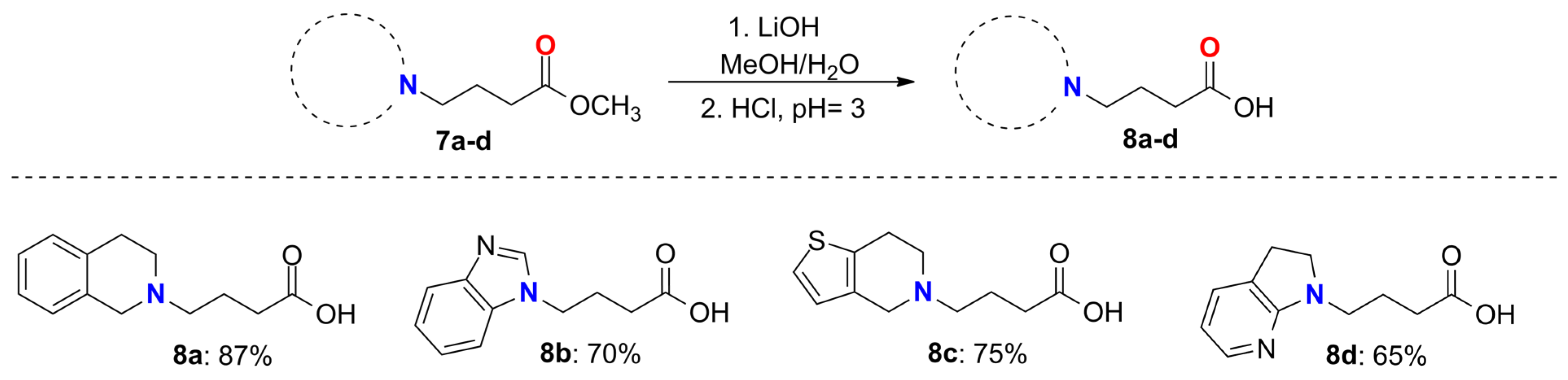
2.2. General Method for the N-Alkylation Reaction. Synthesis of Compounds 7a–d
2.3. General Method for the Synthesis of Compounds 8a–d
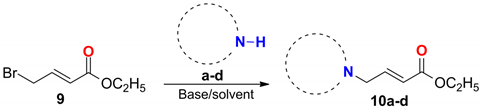
2.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 10a–d
2.5. General Procedure for the 1,4-Addition Reactions
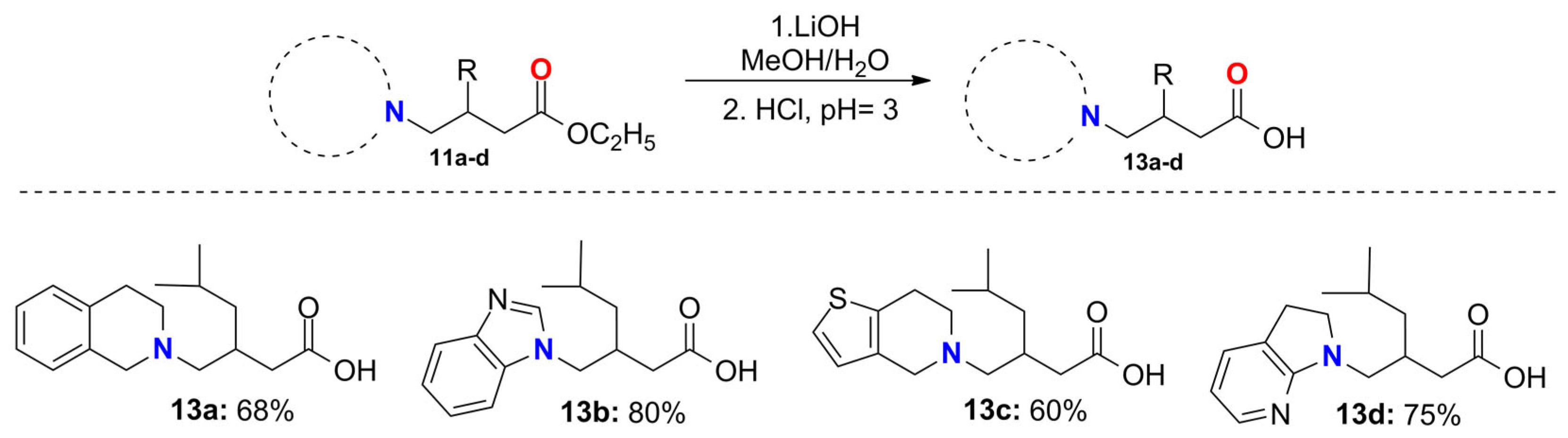
2.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Pregabalin Analogs 13a–d
2.7. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Baclofen Analogs 14a, 14b and 14d
2.8. Computational Details
2.8.1. Chemical-Structure Optimization
2.8.2. Molecular Docking
2.8.3. QSAR Analysis
2.8.4. Molecular Docking Re-Evaluation
2.8.5. Molecular Similarity Analysis
2.8.6. Drug-Likeness Prediction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of GABA Analogs
3.2. Synthesis of Pregabalin and Baclofen Analogs
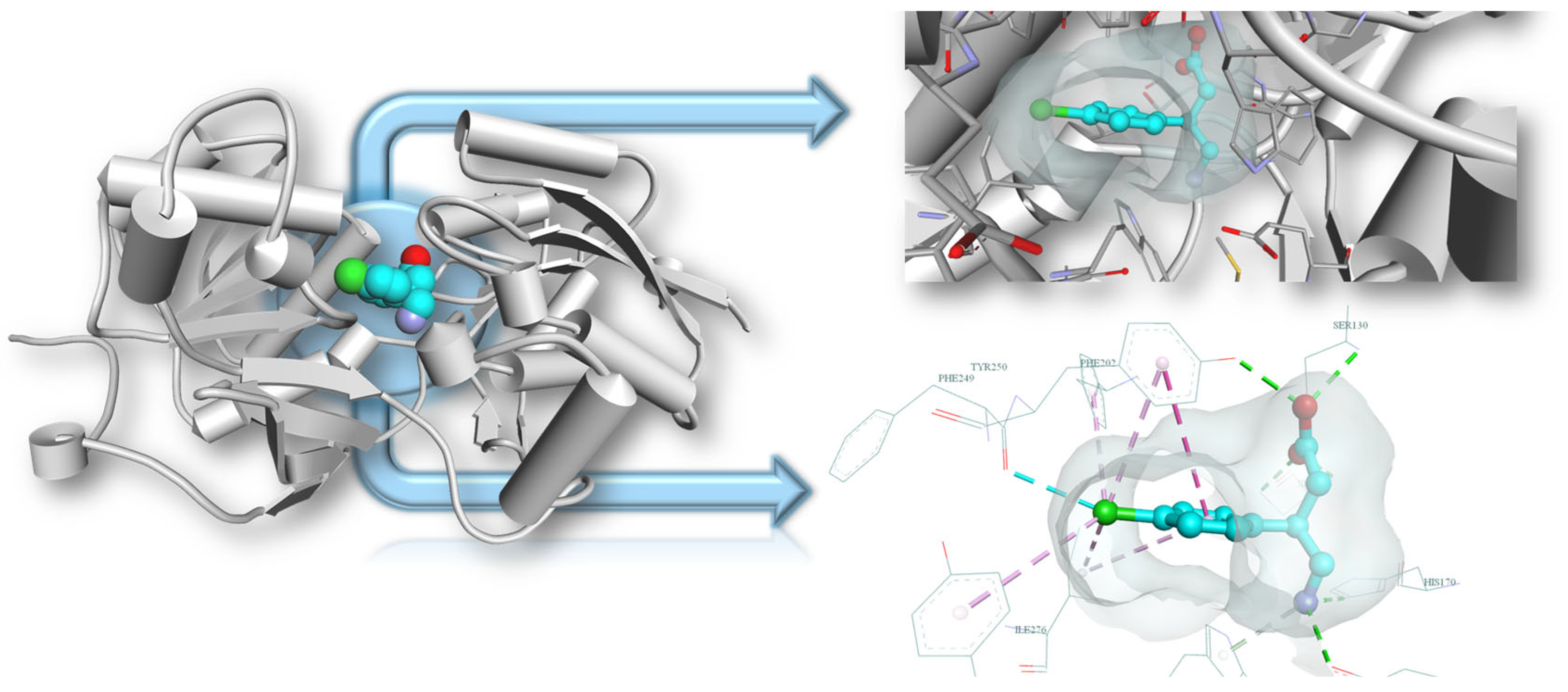
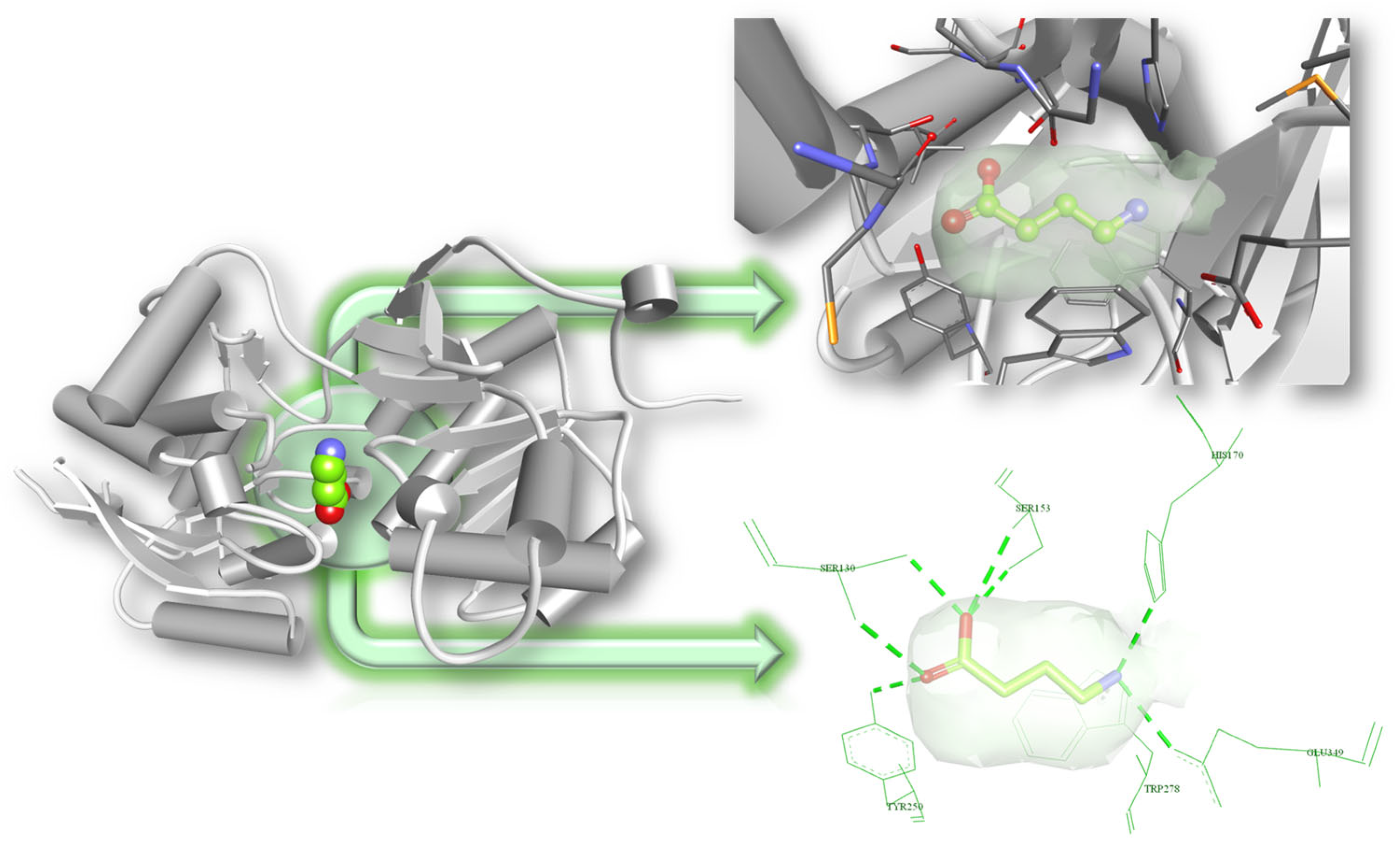
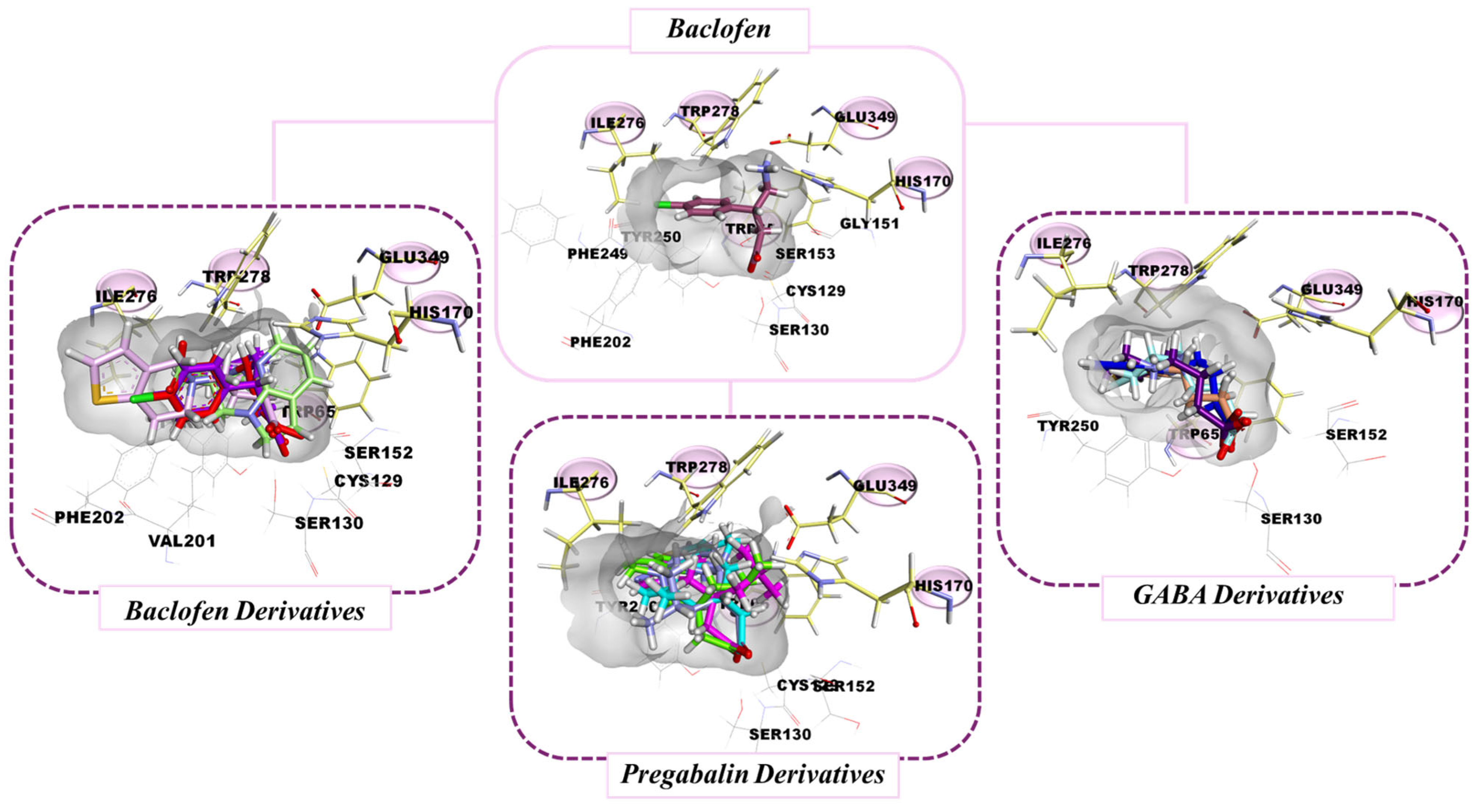
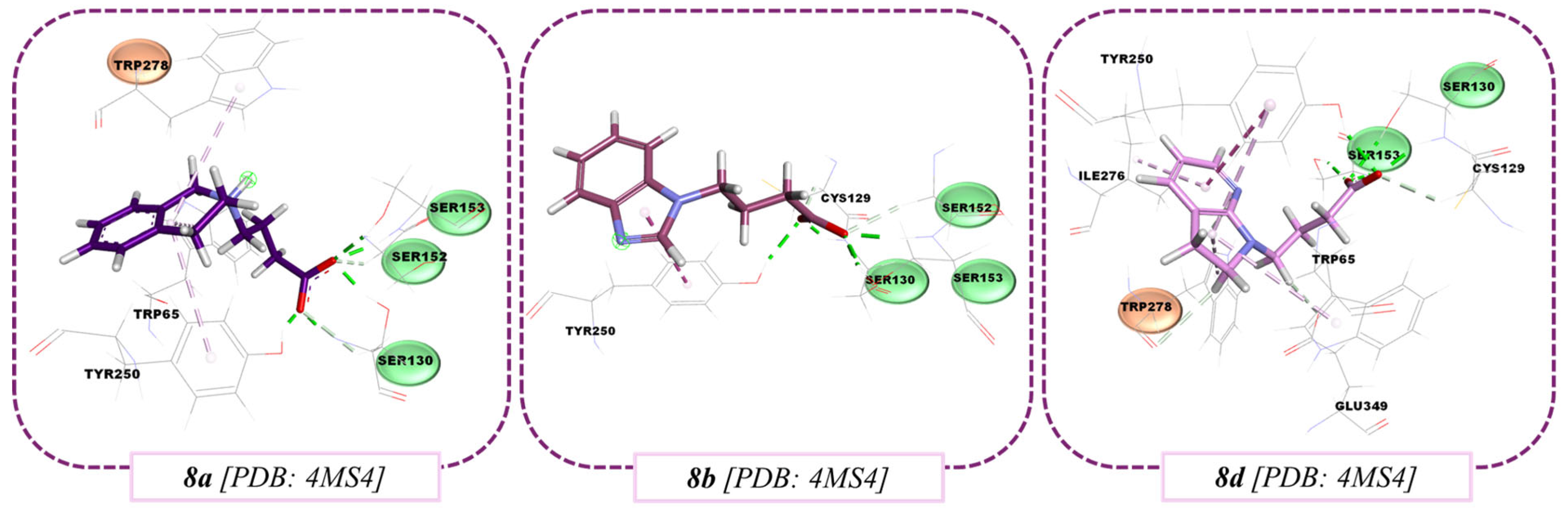
3.3. Molecular Docking Results
3.4. QSAR Study
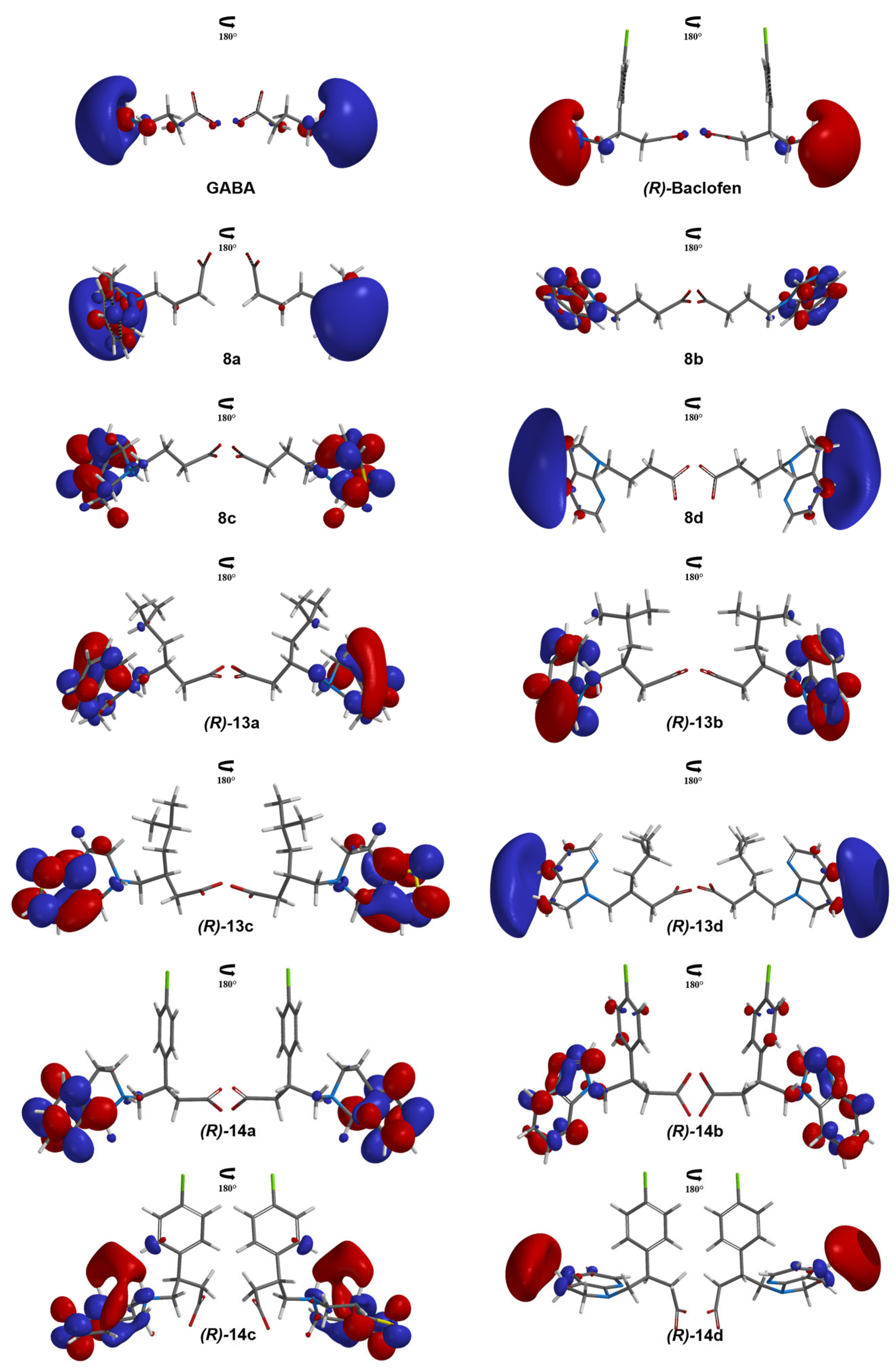
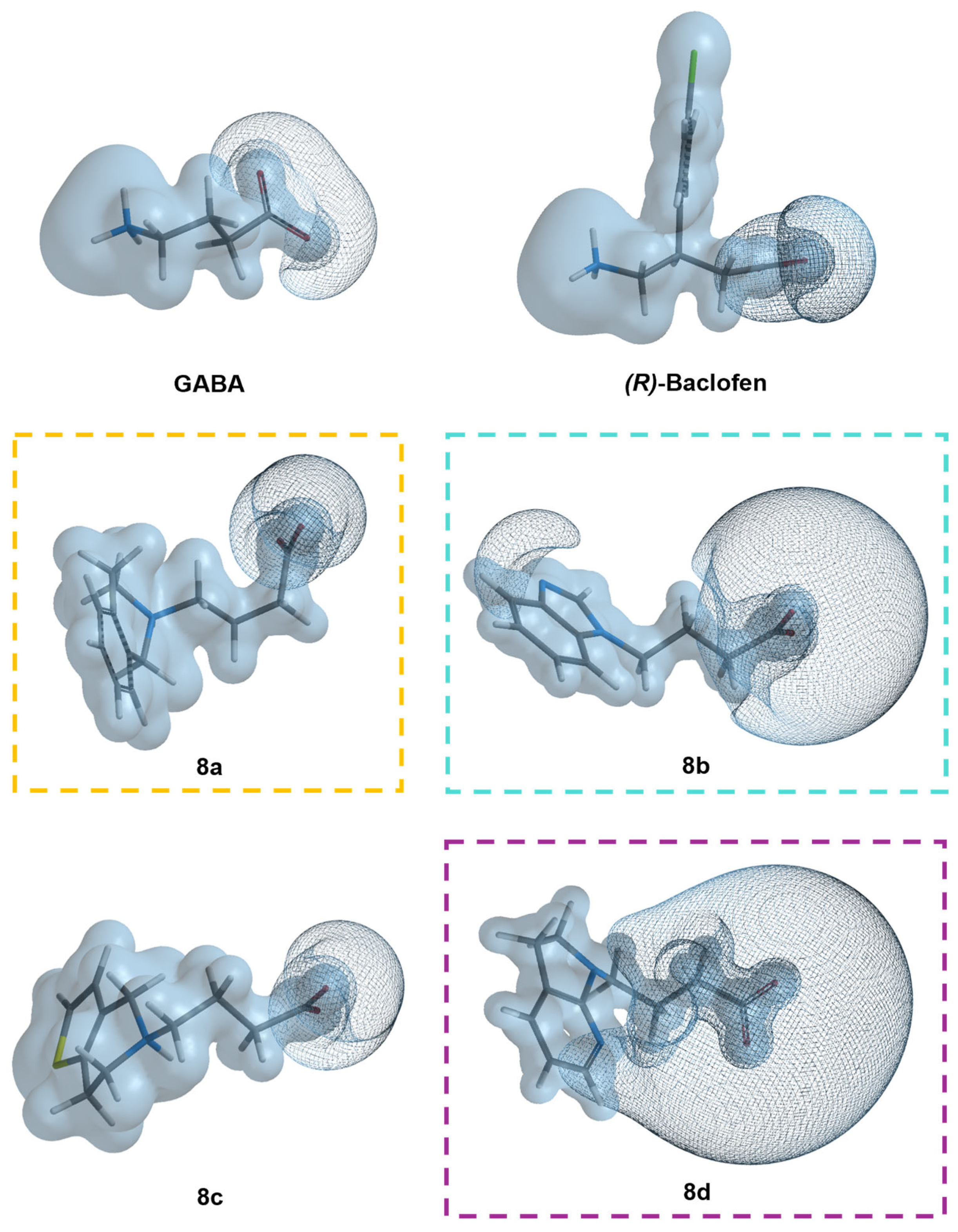
3.5. Molecular Similarity Analysis Results
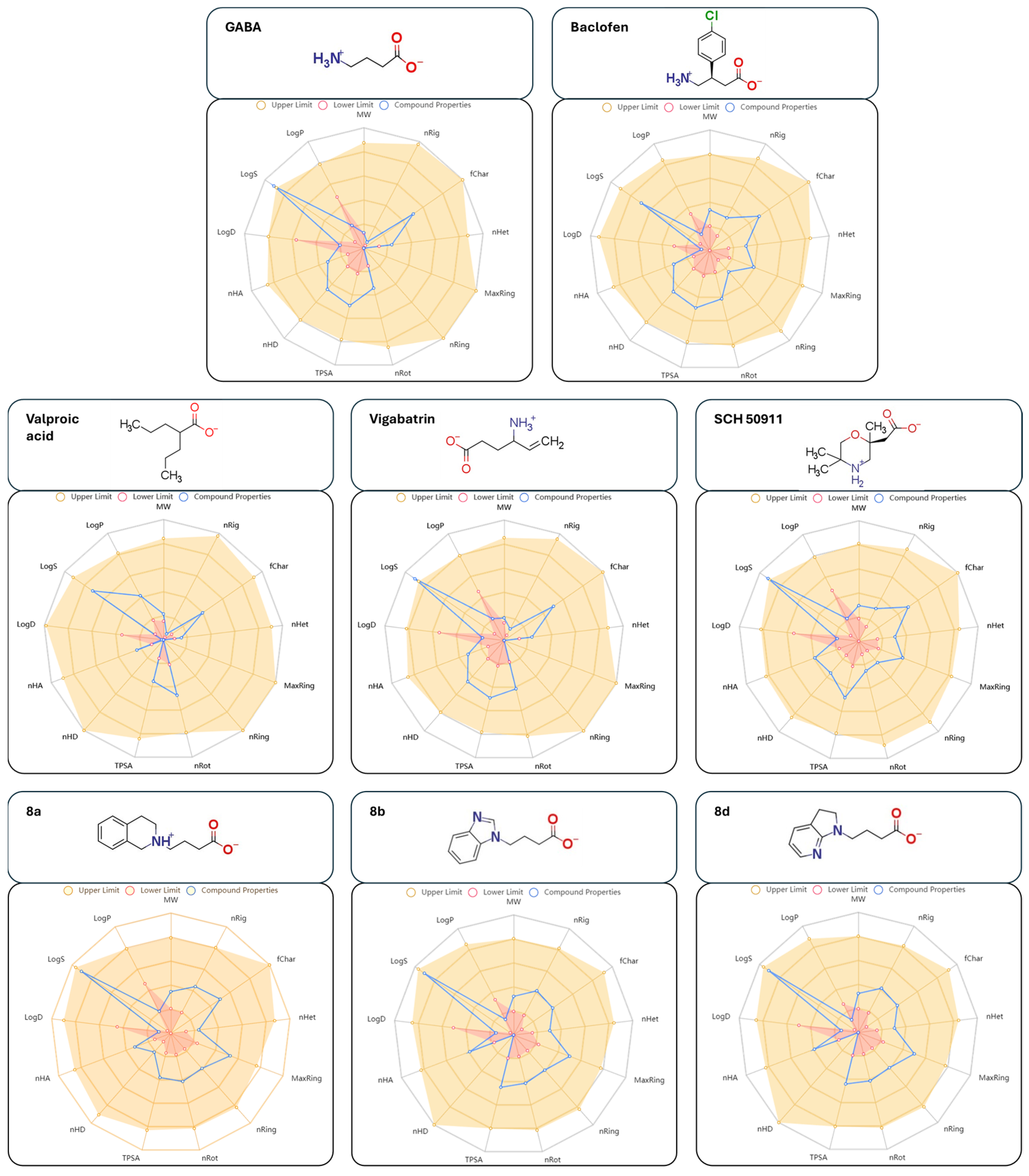
3.6. Drug-Likeness Prediction Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smart, T.G.; Stephenson, A. A half century of γ-aminobutyric acid. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2019, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jembrek, M.J.; Vlainić, J. GABA receptors: Pharmacological potential and pitfalls. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 4943–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaflesh, S.; Qaswal, A.B.; Suleiman, A.; Alali, O.; Zayed, F.M.; Al-Adwan, M.A.O.; Ali, M.B. GABA Receptors Can Depolarize the Neuronal Membrane Potential via Quantum Tunneling of Chloride Ions: A Quantum Mathematical Study. Cells 2022, 11, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbison, A.; Moenter, S.M. Depolarising and hyperpolarising actions of GABAA receptor activation on gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neurones: Towards an emerging consensus. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, 23, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettler, B.; Kaupmann, K.; Mosbacher, J.; Gassmann, M. Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABAB receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 835–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinard, A.; Seddik, R.; Bettler, B. GABAB receptors: Physiological functions and mechanisms of diversity. Adv. Pharmacol. 2010, 58, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.A.; Borowsky, B.; Tamm, J.A.; Craig, D.A.; Durkin, M.M.; Dai, M.; Gerald, C. GABAB receptors function as a heterodimer assembly of the subunit GABABR1 and GABABR2. Nature 1998, 396, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G. G protein-coupled receptor hetero-dimerization: Contribution to pharmacology and function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, G.Y.K.; Clark, J.; Coulombe, N.; Ethier, N.; Hebert, T.E.; Sullivan, R.; O′neill, G.P. Identification of a GABAB receptor subunit, gb2, required for functional GABAB receptor activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 247, 7607–7610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froestl, W. Chemistry and pharmacology of GABAB receptor ligands. Adv. Pharmacol. 2010, 58, 19–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowery, N.G.; Bettler, B.; Froestl, W.; Gallagher, J.P.; Marshall, F.; Raiteri, M.; Bonner, T.I.; Enna, S.J. International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian γ-Aminobutyric AcidB Receptors: Structure and Function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenseth, L.S.M.; Gabrielsen, M.; Sylte, I. The GABAB Receptor-Structure, Ligand Binding and Drug Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapin, I. Phenibut (β-phenyl-GABA): A tranquilizer and nootropic drug. CNS Drug Rev. 2006, 7, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H. Arbaclofen placarbil decreases reflux with good tolerability in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 16, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, A.P.; Aso, E.; Maldonado, R.; Balerio, G.N. Baclofen and 2-hydroxysaclofen modify acute hypolocomotive and antinociceptive effects of nicotine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, M.; Frankowska, M. GABA(B) receptors in drug addiction. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fransson, B.; Silberg, D.G.; Niazi, M.; Miller, F.; Ruth, M.; Holmberg, A.A. Effect of food on the bioavailability of lesogaberan given as an oral solution or as modified-release capsules in healthy male volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 50, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froestl, W.; Mickel, S.J.; von Sprecher, G.; Diel, P.J.; Hall, R.G.; Maier, L.; Strub, D.; Melillo, V.; Baumann, P.A.; Bernasconi, R. Phosphinic acid analogues of GABA. 2. Selective, orally active GABAB antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 3313–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, P.; Deshmukh, R. Therapeutic potential of GABAB receptor ligands in drug addiction, anxiety, depression and other CNS disorders. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 110, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria-Horner, B.A.; Pohl, R.B. Pregabalin: A new anxiolytic. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2003, 12, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachem, E.B. Mechanism of action of vigabatrin: Correcting misperceptions. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2011, 124, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikyurt, I.K.; Mutlu, O.; Ulak, G.; Akar, F.Y.; Erden, F. Gabapentin, A GABA analogue, anhances cognitive performance in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 492, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Roy, K.K.; Hockerman, G.H.; Doerksen, R.J.; Colby, D.A. Activation of the γ-aminobutyric acid type B (GABAB) receptor by agonists and positive allosteric modulators: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6336–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajcy, K.; Lochynski, S.; Librowski, T. A role of GABA analogues in the treatment of neurological diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomtsyan, A. Heterocycles in drugs and drug discovery. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2012, 48, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.D.; MacCoss, M.; Lawson, A.D.G. Rings in Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5845–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Gudiño, E.; Guevara-Salazar, J.A.; Bahena-Herrera, J.R.; Trujillo-Ferrera, J.G.; Martínez-Campos, Z.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Santiago, A.; Pastor, N.; Fernández-Zertuche, M. Novel-Substituted Heterocyclic GABA Analogues. Enzymatic Activity against the GABA-AT Enzyme from Pseudomonas fluorescens and In Silico Molecular Modeling. Molecules 2018, 23, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lozada, J.; Tovar-Gudiño, E.; Guevara-Salazar, J.A.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Santiago, A.; Pastor, N.; Fernández-Zertuche, M. QSAR and Molecular Docking Studies of the Inhibitory Activity of Novel Heterocyclic GABA Analogues over GABA-AT. Molecules 2018, 23, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Peralta, L.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Santiago, A.; Pastor, N.; Guevara-Salazar, J.A.; Fernández-Zertuche, M. 1,4-Disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole GABA Analogues: Synthesis, In Vitro Evaluation, Quantum QSAR and Molecular Docking against Pseudomonas fluorescens GABA-AT. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Peralta, L.; Fernández-Zertuche, M.; Guevara-Salazar, J.A.; Moran-Díaz, J.R.; Hernández-Domínguez, L.E.; Razo-Hernández, R.S. 1,5-Disubstituted-1,2,3-Triazoles as GABA analogues: Synthesis, QSAR and biological evaluation as Pseudomonas fluorescens GABA-AT inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2024, 165, 134300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, C.; Brameld, K.A.; Graton, J.; Questel, J.Y.; Renault, E. The pKBHX Database: Toward a Better Understanding of Hydrogen-Bond Basicity for Medicinal Chemists. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4073–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meanwell, N.A. Synopsis of Some Recent Tactical Application of Bioisosteres in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2529–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jampilek, J. Heterocycles in Medicinal Chemistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitaku, E.; Smith, D.T.; Njardarson, J.T. Analysis of the Structural Diversity, Substitution Patterns, and Frequency of Nitrogen Heterocycles among U.S. FDA Approved Pharmaceuticals. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10257–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Campos, Z.; Pastor, N.; Pineda-Urbina, K.; Gómez-Sandoval, Z.; Fernández-Zertuche, M.; Razo-Hernández, R.S. In silico structure-based design of GABAB receptor agonists using a combination of docking and QSAR. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 94, 1782–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Campos, Z.; Palacios-Can, F.J.; López-Cortina, S.T.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Fernández-Zertuche, M. Design and synthesis of 3,5-disubstituted isoxazoles by Cu-mediated 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition and their in silico evaluation as potential GABAB receptor modulators. Tetrahedron 2024, 168, 134336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Neto, J.X.; Bezerra, K.S.; Barbosa, E.D.; Oliveira, J.I.N.; Manzoni, V.; Soares-Rachetti, V.P.; Albuquerque, E.L.; Fulco, U.L. Exploring the binding mechanism of GABAB receptor agonists and antagonists through in silico simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartan’24, v. 1.2.0; Wavefunction, Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2024.
- Geng, Y.; Bush, M.; Mosyak, L.; Wang, F.; Fan, Q.R. Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human GABAB receptor. Nature 2013, 504, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for main group elements Na to Bi. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Olson, R.M.; Kelly, C.P.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Self-consistent reaction field model for aqueous and nonaqueous solutions based on accurate polarized partial charges. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 2011–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, A. AlvaDesc: A Tool to Calculate and Analyze Molecular Descriptors and Fingerprints. In Ecotoxicological QSARs; Roy, K., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petijean, M. Applications of the radius-diameter diagram to the classification of topological and geometrical shape of chemical compounds. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1992, 32, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randic, M. Novel shape descriptors for molecular graphs. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2001, 41, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, D.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Millán-Pacheco, C.; Leyva-Peralta, M.A.; Peña-Morán, O.A.; Sánchez-Carranza, J.N.; Rodríguez-López, V. Ligand-Based Drug Design of Genipin Derivatives with Cytotoxic Activity against HeLa Cell Line: A Structural and Theoretical Study. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Yin, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. ADMETlab 2.0: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions of ADMET properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W5–W14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like Properties and the Causes of Poor Solubility and Poor Permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, S.; Doerksen, R.J. Topological polar surface area: A useful descriptor in 2D-QSAR. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Allory, L.; Mozziconacci, J.C.; Arnoult, E.; Baurin, N.; Marot, C. Preparation of a Molecular Database from a Set of 2 Million Compounds for Virtual Screening Applications: Gathering, Structural Analysis and Filtering; Institut de Chimie Organique et Analytique, Universite d’Orleans: Orleans, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan, V.N.; Wendoloski, J.J. A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. J. Comb. Chem. 1999, 1, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ChemAxon. MarvinSketch (Product Version 24.1.2) Computer Software. 2024. Available online: https://chemaxon.com/marvin (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Gaikwad, S.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Vilariño, D.; Lasanta, G.; Villaverde, C.; Mouriño, A.; Verlinden, L.; Verstuyf, A.; Peluso-Iltis, C.; Rochel, N.; et al. Lithocholic acid-based design of noncalcemic vitamin D receptor agonists. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 111, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Base | Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Solvent | Yield (%) |
| 7a | - | 8 | r.t. | - | 72 |
| 7b | DIPEA | 72 | 60 | CH3CN | 65 |
| 7c | DIPEA | 72 | 60 | CH3CN | 70 |
| 7d | DIPEA | 72 | 60 | CH3CN | 30 |
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Base (1.1 eq) | Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Solvent | Yield (%) |
| 10a | - | 24 | r.t. | - | 65 |
| 10b | DIPEA | 48 | r.t. | CH3CN | 70 |
| 10c | DIPEA | 72 | r.t. | CH3CN | 65 |
| 10d | DIPEA | 72 | r.t. | CH3CN | 40 |
| Compound | ETRP278 | PIJ2 | PW5 | T(N..O) | ELUMO (kJ/mol) | Ypred |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (R)-Baclofen | −19.699 | 1.0000 | 0.0920 | 10 | −213.07 | 5.601 |
| GABA | −4.919 | 0.6667 | 0.0438 | 10 | −275.50 | 12.084 |
| 8a | −16.374 | 1.0000 | 0.0869 | 10 | −212.47 | 7.119 |
| 8b | −19.910 | 0.8000 | 0.0832 | 24 | 126.85 | 7.243 |
| 8c | −20.023 | 0.8000 | 0.0761 | 10 | −190.38 | 5.766 |
| 8d | −20.702 | 0.8000 | 0.0832 | 24 | 122.32 | 7.027 |
| (R)-13a | −25.100 | 1.0000 | 0.0916 | 10 | −173.77 | 4.533 |
| (R)-13b | −23.836 | 0.8000 | 0.0900 | 24 | 132.32 | 5.387 |
| (R)-13c | −21.550 | 0.8000 | 0.0834 | 10 | −187.47 | 4.412 |
| (R)-13d | −26.530 | 0.8000 | 0.0900 | 24 | 108.77 | 4.612 |
| (R)-14a | −26.520 | 1.0000 | 0.1036 | 10 | −182.49 | 2.501 |
| (R)-14b | −28.810 | 0.8333 | 0.1019 | 24 | 116.00 | 2.806 |
| (R)-14c | −22.383 | 0.8333 | 0.0970 | 10 | −188.74 | 2.673 |
| (R)-14d | −28.000 | 0.8333 | 0.1019 | 24 | 104.93 | 2.948 |
| Molecule | LogS | LogD | LogP | MW | nHA | nHD | TPSA | nROT | PAINS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABA | 0.639 | −2.143 | −2.598 | 103.06 | 3 | 3 | 67.77 | 3 | 0 |
| Baclofen | −0.674 | 0.276 | −1.127 | 213.06 | 3 | 3 | 67.77 | 4 | 0 |
| Pregabalin | 0.379 | −0.748 | −1.022 | 159.13 | 3 | 3 | 67.77 | 5 | 0 |
| Vigabatrin | 0.716 | −1.649 | −2.280 | 129.08 | 3 | 3 | 67.77 | 4 | 0 |
| Gabapentin | 0.402 | −1.145 | −0.845 | 171.13 | 3 | 3 | 67.77 | 3 | 0 |
| Valproic acid | −0.572 | −0.054 | 1.095 | 143.11 | 2 | 0 | 40.13 | 5 | 0 |
| SCH–50911 | 0.572 | −1.650 | −2.550 | 187.12 | 4 | 2 | 65.97 | 2 | 0 |
| 8a | 0.221 | −0.561 | −2.364 | 219.13 | 3 | 1 | 44.57 | 4 | 0 |
| 8b | 0.204 | −1.071 | −1.063 | 203.08 | 4 | 0 | 57.95 | 4 | 0 |
| 8c | 0.120 | −0.673 | −2.431 | 225.08 | 3 | 1 | 44.57 | 4 | 0 |
| 8d | 0.237 | −0.991 | −0.727 | 205.1 | 4 | 0 | 56.26 | 4 | 0 |
| (R)-13a | −0.268 | 1.496 | −0.940 | 275.19 | 3 | 1 | 44.57 | 6 | 0 |
| (R)-13b | −3.147 | 2.513 | 3.094 | 260.15 | 4 | 1 | 55.12 | 6 | 0 |
| (R)-13c | −0.350 | 1.298 | −1.057 | 281.14 | 3 | 1 | 44.57 | 6 | 0 |
| (R)-13d | −2.666 | 0.932 | 1.133 | 261.16 | 4 | 0 | 56.26 | 6 | 0 |
| (R)-14a | −0.69 | 1.793 | −0.591 | 329.12 | 3 | 1 | 44.57 | 5 | 0 |
| (R)-14b | −1.933 | 0.663 | 0.916 | 313.07 | 4 | 0 | 57.95 | 5 | 0 |
| (R)-14c | −0.482 | 1.440 | −0.846 | 335.07 | 3 | 1 | 44.57 | 5 | 0 |
| (R)-14d | −3.161 | 1.079 | 1.805 | 315.09 | 4 | 0 | 56.26 | 5 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Campos, Z.; Hernandez-Dominguez, L.E.; Romero-Rivera, F.; López-López, D.; Corona-González, M.V.; López-Cortina, S.T.; Palacios-Can, F.J.; Razo-Hernández, R.S.; Fernández-Zertuche, M. Synthesis and In Silico Evaluation of GABA, Pregabalin and Baclofen N-Heterocyclic Analogues as GABAB Receptor Agonists. Organics 2025, 6, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020013
Martínez-Campos Z, Hernandez-Dominguez LE, Romero-Rivera F, López-López D, Corona-González MV, López-Cortina ST, Palacios-Can FJ, Razo-Hernández RS, Fernández-Zertuche M. Synthesis and In Silico Evaluation of GABA, Pregabalin and Baclofen N-Heterocyclic Analogues as GABAB Receptor Agonists. Organics. 2025; 6(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Campos, Zuleyma, Luis Eduardo Hernandez-Dominguez, Fatima Romero-Rivera, Diana López-López, María Vicky Corona-González, Susana T. López-Cortina, Francisco José Palacios-Can, Rodrigo Said Razo-Hernández, and Mario Fernández-Zertuche. 2025. "Synthesis and In Silico Evaluation of GABA, Pregabalin and Baclofen N-Heterocyclic Analogues as GABAB Receptor Agonists" Organics 6, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020013
APA StyleMartínez-Campos, Z., Hernandez-Dominguez, L. E., Romero-Rivera, F., López-López, D., Corona-González, M. V., López-Cortina, S. T., Palacios-Can, F. J., Razo-Hernández, R. S., & Fernández-Zertuche, M. (2025). Synthesis and In Silico Evaluation of GABA, Pregabalin and Baclofen N-Heterocyclic Analogues as GABAB Receptor Agonists. Organics, 6(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6020013








