Abstract
The supramolecular interactions in water between β-cyclodextrin and the open and closed photochromic forms of two bis-cationic dithienylethenes, characterized by different electronic properties, were investigated aiming at underlying the key aspects of the recognition process. The dithienylethene equipped with the cyclopentenyl unit showed a difference in binding free energies to the β-cyclodextrin between the open and closed photochromic forms of about 1 kJ/mol. Conversely, the dithienylethene equipped with the perfluorinated cyclopentenyl unit not only was a better guest but showed a three times higher difference in the binding of free energies between the open and closed isomers.
1. Introduction
The study and the development of new light-triggered systems are highly encouraged by the outstanding and growing opportunities presented by the realization of light-responsive catalysts [1,2,3,4], polymers [5,6], biomaterials [7,8], and in general photo-modulable molecular devices. Nowadays, a new frontier is achievable in combining well-known photochromic units with different supramolecular hosts and, on this regard, one of the most promising and thoroughly investigated combination is the association between the E and Z forms of the azobenzene unit [9] with cyclodextrins [10]. Among the different achievements obtained by these systems, developments in the fields of photoswitchable supramolecular hydrogels [11], UV responsive supramolecular nanofibers [12] and photoswitchable catalysts [13] clearly state the advances reached in the comprehension and design of such approach.
When other photochromes are considered, such as spiropyranes [14,15], spirooxazines [16] and diarylethenes [17], the advances reached in incorporating these moieties within the molecular structure of ligands [18,19,20,21,22,23,24], macrocycles [25], catalysts [1,3], data-storage systems [26,27], bio-compounds [28], photoswitchable cation chemosensors [29], and others are remarkable and their behaviour and application within supramolecular systems are emerging as new and highly prospective research fields. For instance, Ma and co-workers developed a photochromic supramolecular polymer based on a dithienylethene derivative and p-sulfonate-calixarene unit that showed the light driven switch of the morphology [30]. A dithienylethene-tethered β-cyclodextrin dimer as a photoswitchable host [31] have been reported to show reversible binding of meso-tetrakis(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphyrin. However, as long as the dithienylethene units acts as a guest for different host systems is concerned, different results emerged. In fact, when a similar photochrome was included within a hydrogen-bonded hexameric host based on the self-assembly of resorcin [4] arene unit in organic solvents, its photochromic behavior resulted inhibited [32]. Conversely cyclodextrins, β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) in particular, showed not only to be suitable hosts but also to speed up the photochromic process [33,34]. Moreover, mechanically interlocked molecules (MIMs) based on the threading of cyclodextrins with axle molecular units have inspired the realization of many molecular systems displaying redox and photochemical control of the shuttling of the CD and its pirouette movement [35,36,37,38]. Overall, it is clearly evident that deep investigations on the host-guest interactions between the photochrome and the hosting system are important for their implementation into photo-reversible systems and molecular devices.
For the development of new, highly performing systems based on the simple interaction between β-CD and the dithienylethene units, it is of primary importance to deeply investigate the process in terms of binding constants and to understand how the molecular pattern of the dithienylethene affects the binding constants in terms of magnitude and difference between open and closed forms.
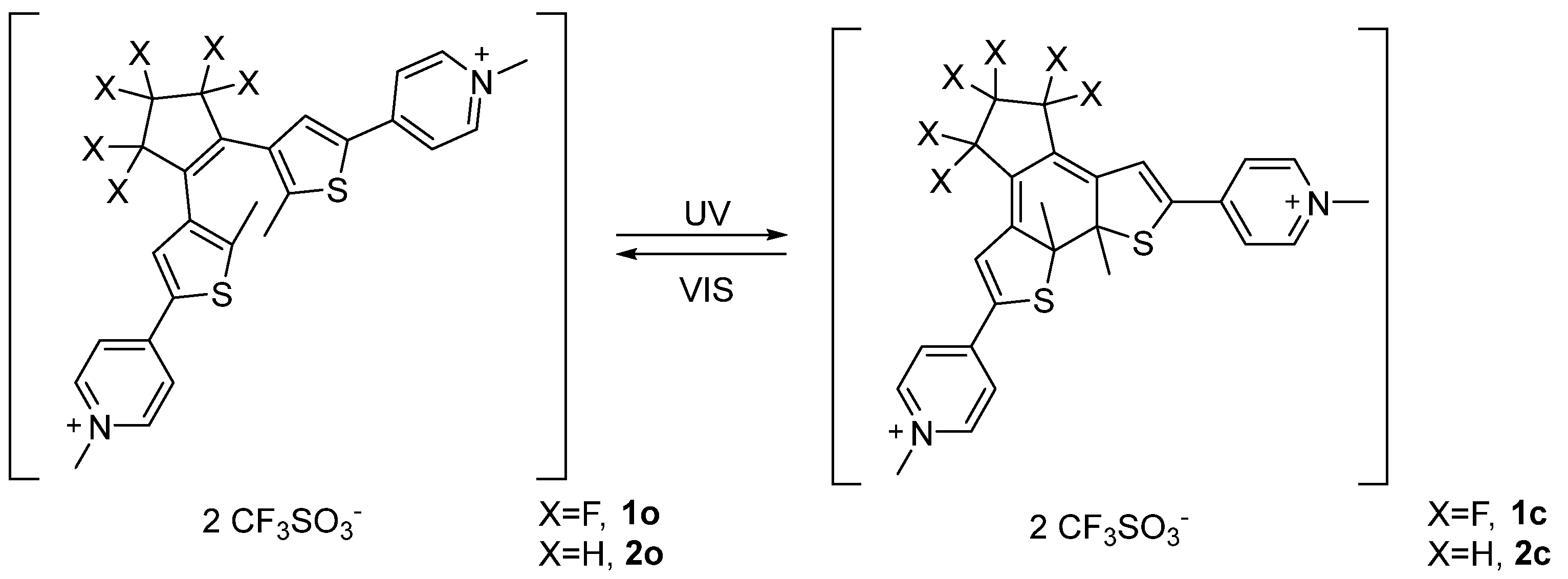
In the present contribution, we report about the supramolecular recognition exerted by β-CD on the different photochromic forms of two well- known and easily achievable bis-cationic diarylethenes, reported in Scheme 1, bearing methyl-pyridinium units and differing on the nature of cyclic perfluorinated 1 and regular 2 cyclopentenyl backbone in between the two thiophene moieties. Job’s plots of compounds 1o-c and 2o-c in the presence of β-CD, together with 2D-NMR (NOESY and DOSY) elucidated the stoichiometry and inclusion behavior, while titration of the photochromes with the β-CD provided the association constants (KAss) and therefore the binding free energies (ΔG°).
Scheme 1.
Bis-cationic dithienylethenes bearing fluorinated 1 and non-fluorinated 2 cyclopentenyl units in their open (1o and 2o) and closed (1c and 2c) forms chosen for the evaluation of the host–guest interactions with β-CD.
2. Materials and Methods
1H-NMR, 13C{1H}-NMR and 19F{1H}-NMR were recorded at 298 K with a BRUKER AVANCE spectrometer operating respectively at 400, 100 and 376 MHz, respectively. 1H-NMR DOSY spectra were recorded using 15 increments of gradient field strength from 2000 to 25,000 G∙cm−1, 2 ms diffusion gradient length and 100 ms diffusion delay. NOESY 1H-NMR spectra were recorded using 500 ms mixing time. TLC analyses were performed on TLC Polygram ® Sil G/UV254 of 0.25 mm thickness and flash-chromatography separations were performed on silica gel Merk 60, 230–400 mesh. Solvents and reactants were used purchased. Irradiation at 365 nm was performed with a Wood lamp, omnilux 25 W, irradiance at 365 nm 10 W/m2 (10 cm) while irradiation in the visible region was performed with a visible light lamp (120 W). 1 [39] and 2 [29,40] were prepared following the experimental procedure reported in the literature.
3. Results and Discussion
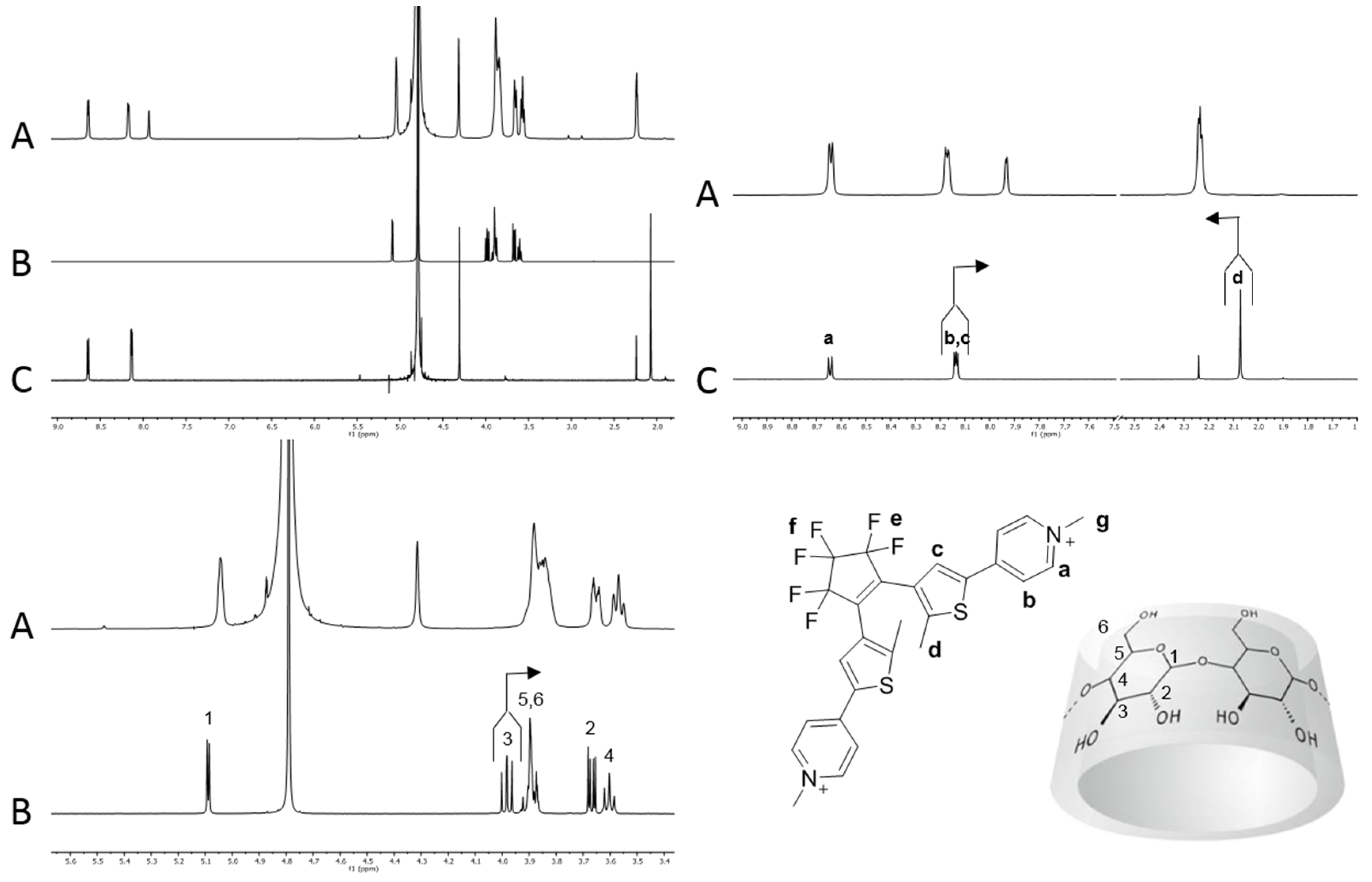
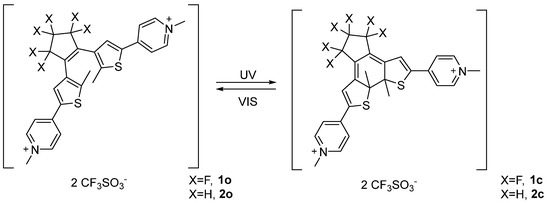
Compound 1 and 2 both showed good solubility in deuterium oxide and fast interconversion on the NMR timescale between the parallel and anti-parallel forms of the open isomers (1H-NMR at 400 MHz) as demonstrated by the observation of a single set of resonances. Upon addition of 1 equivalent of β-CD to a solution of 1o (7.00·10−3 M) 1H-NMR analysis revealed a slight chemical shift variation of selected peaks with respect to the pure chemical species (Figure 1). More precisely, the thiophenic proton c of compound 1o was shifted to higher fields while the methyl resonance d on the thiophene ring moved to lower fields. The pyridinium protons g, a and b did not show remarkable variations with respect to the free photochromic unit in solution (Figure 1). As long as the host resonances are considered, all β-CD proton signals resulted broadened. Interestingly, protons 3 moved to lower chemical shifts leading to coalescence with protons 5 and 6. These chemical shift variations suggest the encapsulation of the thiophene ring fragment within the β-CD and therefore the formation of the inclusion complex between 1o and β-CD (1o@β-CD). Indeed, shielding of the protons pointing inside the cavity is expected as a consequence of the ring-current of the aromatic moiety [41], while the de-shielding effect observed for the thiophenic methyl unit d is due to its proximity to the hydroxyl units. A similar behaviour was reported for the β-CD interaction with a benzo[b]thiophene based dithienylethenes, which showed inclusion of the hetero-aromatic fragment [33]. Additionally, 19F-NMR analysis revealed down-field shift of the fluorine atoms present in the allylic positions (e) and up-shield shift of the f ones (see Supporting Information, Figure S12).
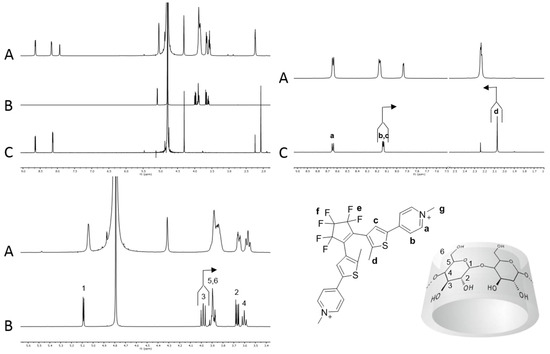
Figure 1.
Host–guest interaction between β-CD and photochrome 1o. (A) 1o (7.00·10−3 M) + β-CD (7.00·10−3 M) in D2O; (B) β-CD (7.00·10−3 M) in D2O; (C) 1o (7.00·10−3 M) in D2O.
Further addition of β-CD enhanced the chemical shift variation up to a maximum, confirming that the host-guest complexation equilibrium undergoes on a very fast exchange rate compared to NMR time scale. Additional information concerning 1o and β-CD interactions came from NOESY 1H-NMR analysis that showed weak NOE cross-peaks between protons d and c with the broad signal composed by protons 3, 5 and 6 of the host molecule (see Supporting Information, Figures S5 and S6). 1H-NMR DOSY analysis of a 1:1 mixture of β-CD and 1o showed both species diffusing at the same rate with a diffusion coefficient of 3.0·10−10 m2/s, a lower value with respect to the separate components β-CD and 1o, 3.3∙10−10 and 4.8·10−10 m2/s respectively, under identical conditions (see Supporting Information, Figure S8). From a geometrical point of view β-CD is characterized by a truncated-cone cavity with a diameter ranging between 6.0–6.5 Å and a cavity height of approximately 7.9 Å; on the other hand, 1o has a flattened cone shape characterized by an overall length of 18.2 Å, 3.6 Å width in correspondence of the thiophene ring (from proton c to S atom) and 7.0 Å width between the S atom and the most distant fluorine atoms f of the perfluorinated bridge. Furthermore, the distance between the two methyl units (on the C atom) attached to the thiophene rings is about 5.0 Å, and the pyridinium units resulted out of the thiophene plane by 22° as determined by geometric optimization performed on Gaussian at semi-empirical level PM6 in vacuum. For compounds 2o and 2c the pyridinium moiety was 10° and 35° out of the thiophene plane, respectively. This structural features, together with NOESY evidence, strongly suggests that the thiophene ring is deeply hosted inside β-CD cavity and that the perfluorinated backbone behaves as a stopper, since it is too wide to be accommodated within the cavity. The observed higher affinity towards the thiophene unit, rather than the pyridinium group, could be explained considering the relative hydrophilicity of the two groups. In fact, the inner cavity of β-CD is known to have higher affinity towards lipophilic moieties [42,43] and to bind guests mostly driven by the hydrophobic effect. This provide a suitable explanation for the deeper threatening of the thiophene unit while the pyridinium group is better located more exposed to the aqueous medium.
When the closed form 1c was investigated with the β-CD, either obtained upon irradiation at 365 nm (or 254 nm) of a 1:1 solution of 1o and β-CD or by preformed 1c added to a β-CD solution, the same trend of 1H-NMR and 19F-NMR variations were observed. Interestingly, the magnitude of the chemical shift variations was less pronounced, suggesting somehow a weaker interactions between the species. NOESY 1H-NMR experiments were carried out but no evidence of cross-peaks between 1c and β-CD were detected. 1H-NMR DOSY analyses also in this case showed that for a 1:1 solution of 1c and β-CD both resonances of host and guest diffused together showing same value (3.0·10−10 m2/s). The latter value is in fact lower than determined for the free species in solution (see Supporting Information, Figure S9). This further corroborates the formation of the inclusion complex 1c@β-CD. Another proof of successful complex formation came from the 1H-NMR signals of proton c and d that resulted split into two signals as a consequence of the chiral environment of the β-CD and the racemic form of 1c (see Supporting Information, Figure S2).
As long as the geometrical features of 1c are considered, the photochrome is characterized by a flattened cone shaped geometry with a central residue 7.3 Å wide (from S atom to the most distant F atoms), sides 4.3 ÷ 3.6 Å wide and an overall length of 17.0 Å. The distance between the two thiophene methyl groups is 3.6 Å, suggesting an enhanced flatness of the molecule as a consequence of the photo-isomerization; the solid angle between the pyridinium units and the central part of the molecule resulted increased to 42°. This photo-isomer is more rigid and characterized by an extended π-system which ranges from one pyridinium unit to the other and hosts two positive charges and an electron withdrawing group.
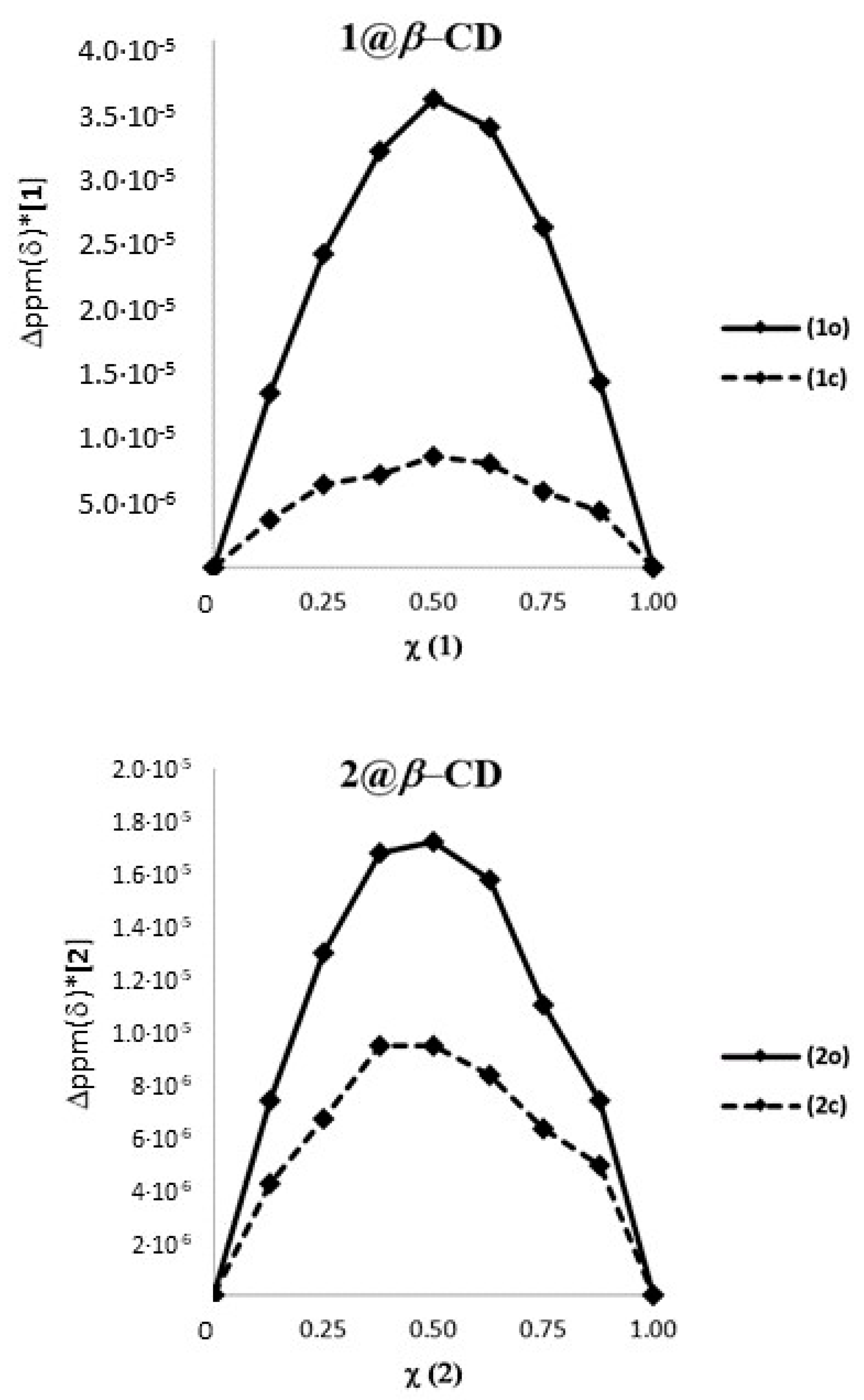
In order to ascertain the stoichiometry of the inclusion process, a Job’s plot analysis was performed using as reference the 1H-NMR resonance signal of the methyl units d attached to the thiophene ring [44]. The typical plots obtained are reported in Figure 2 and suggest a 1 to 1 stoichiometry for both 1o and 1c and an apparent ratio between the two binding constants of 4.2 (K1o@β-CD/K1c@β-CD) (see Supporting Information). 1o and 1c were then titrated with increasing amounts of β-CD until no variation of chemical shift was observed, and the data obtained by the variation of the chemical shift of proton d of the dithienylethene photo-isomers as a function of the β-CD concentration were used to calculate the association constants of the two photochromic forms with the host. The open form 1o showed an association constant of 6.1∙103 ± 0.4∙103 M−1 while the closed form 1c has a value of 1.8∙103 ± 0.2∙103 M−1, leading to a ratio K1o@β-CD/K1c@β-CD of 3.4 which is in good agreement with that determined using the Job’s plot analyses. These data clearly suggest that the open isomer 1o is a better guest than the closed isomer 1c for the β-CD cavity in water.
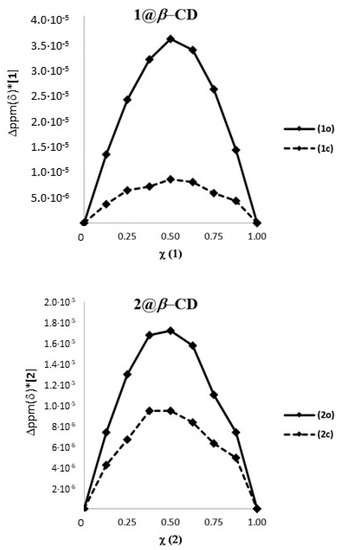
Figure 2.
Job plots of 1o-c and 2o-c in the presence of β-CD.
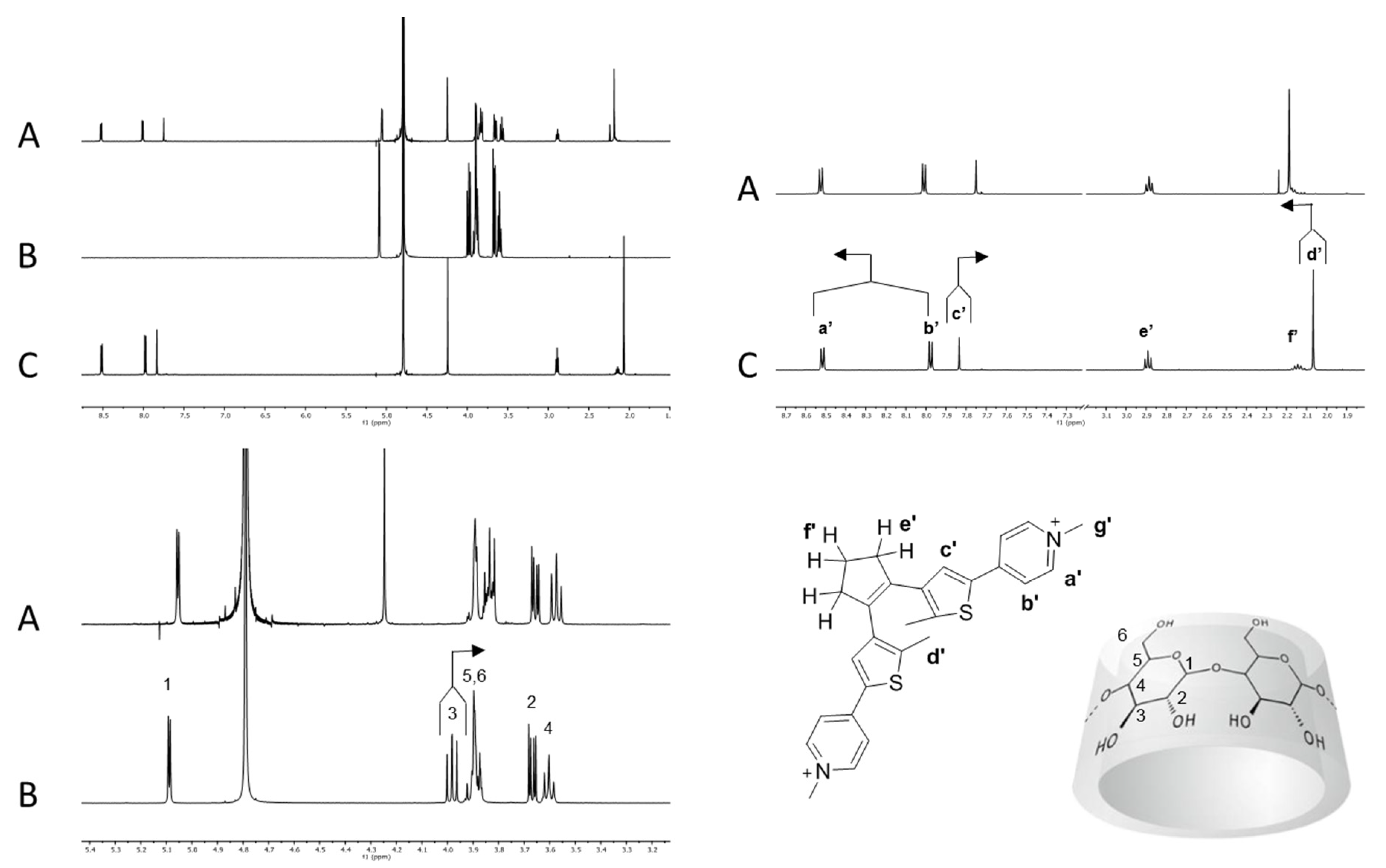
Chromophore 2 is characterized by geometrical features similar to 1 and by relevant differences in terms of electronic properties. In fact, compound 1 is endowed with an electron withdrawing perfluorinated bridging unit while compound 2 bears a cyclopentenyl moiety as substituent on the thiophenes that actually behaves as a weak electron donating group. When an equimolar solution of 2o and β-CD (7.00·10−3 M) was analyzed by 1H-NMR, the β-CD resonances resulted shifted as previously observed for 1o@β-CD, while protons a′ and b′ resulted slightly shifted to lower field and protons d′ and c′ considerably shifted to lower and higher field, respectively (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Host–guest interaction between β-CD and photochrome 2o. (A) 2o (7.00·10−3 M) + β-CD (7.00·10−3 M) in D2O; (B) β-CD (7.00·10−3 M) in D2O; (C) 2o (7.00·10−3 M) in D2O.
The cyclopentenyl protons e′ and f′ and the pyridinium resonances g appeared to be almost unaffected by the presence of the β-CD. Overall, these observations suggest the formation of an inclusion complex between 2o and β-CD (2o@β-CD) with similar features with respect to 1o@β-CD, namely the inclusion of the thiophene moiety, but with a less pronounced proximity between the β-CD and the cyclopentenyl backbone. This last consideration arises considering the lack of shielding/de-shielding effects, due to the binding on the resonances of protons e′ and f′, whereas the fluorinated counterparts e and f in 1o were shifted to a lower and higher field, respectively. NOESY 1H-NMR analyses revealed only a weak NOE interaction between the thiophene methyl unit d′ and the multiplets composed by the β-CD signals 3, 5 and 6, as previously observed for 1o@β-CD (see Supporting Information, Figure S7). 1H-NMR DOSY analysis of a 1:1 solution of 2o and β-CD showed a common diffusion coefficient at 3.1∙10−10 m2/s, while the free species diffused at 4.7∙10−10 and 3.3∙10−10 m2/s, respectively (see Supporting Information, Figure S10).
Photo-isomerization of 2o to 2c by irradiation at 365 nm (or 254 nm) followed by 1H-NMR analysis in the presence of β-CD again showed the splitting of signals c′ and d′ as a consequence of the chirality of the host and the racemic nature of the guest. As a general observation, the binding event produced on 2c the same trend of chemical shift variations already observed for the open isomer 2o, except for two significant variations. Signal b′, which was de-shielded in 2o@β-CD, resulted in being slightly shielded for 2c, while the cyclopentyl resonances e′ and f′ appeared at a lower field (see Supporting Information, Figure S4). These observations suggest inclusion of the thiophene and part of the pyridine moiety of 2c and the interaction of the bridging unit with the rim of the β-CD. Such behavior could be explained by the increased width of the central part of 2c with respect to 2o, which forces the β-CD to slide down towards the pyridinium moiety. Moreover, the photo-isomerization of 2o into 2c blocks the free rotation between the thiophene moiety and the cyclopentenyl unit, leading to a planar and rigid structure where the latter protons are frozen and forced to interact with the β-CD rim. NOESY 1H-NMR on 2c@β-CD did not show any appreciable NOE cross-peaks, while 1H-NMR DOSY experiments exhibited both 2c and β-CD resonances diffusing at the same rate, 3.1∙10−10 m2/s (see Supporting Information, Figure S11).
The Job plot analysis of 2@β-CD (Figure 2) suggested a 1 to 1 stoichiometry between the host and photochromic guests. Moreover, a ratio between the association constant (KAss) of 1.4 (K2o@β-CD/K2c@β-CD) was derived by the plot. Titration of 2o and 2c with β-CD, yielded values of association constant of 7.4∙102 ± 0.5∙102 M−1 and 5.3∙102 ± 0.5∙102 M−1, respectively, with a K2o@β-CD/K2c@β-CD ratio identical to that obtained from the Job plots. Table 1 summarizes the diffusion coefficients, association constants and ΔG0 of binding for 1@β-CD and 2@β-CD.

Table 1.
Empirical data obtained for 1 and 2 inclusion complexes with β-CD. a Diffusion coefficients determined by 1H-NMR DOSY; b association constants (KAss) determined by titration experiments; c free binding energies determined by association constants (KAss) and Equation: ; T = 298 K; R = 8.314772 (J∙K−1∙mol−1).
The association free energy for all supramolecular complexes is negative and ranges between −22 and −15 kJ/mol, and both isomeric forms of 1o-c and 2o-c, when in the presence of the β-CD, diffuse approximately at the same rate comparable to that of the free β-CD. As far as the association constants are concerned, the inclusion complexes 1o-c@β-CD show significantly higher binding constants compared to 2o-c@β-CD, suggesting stronger interaction between the β-CD and the fluorinated photo-modulable chromophore. Moreover, the difference in association constants between the two photochromic open and closed forms was enhanced in the case of the dithienylethene equipped with the perfluorinated bridging unit, with differences of 3 and 1 kJ/mol for 1o-c and 2o-c, respectively. The latter observation can be accounted to the different electronic properties of the four dithienylethene bis-cations. In fact, both open 1o and 2o could be approximately considered as mainly constituted by a thiophene fragment that interacts by hydrophobic effect with the β-CD, while closed 1c and 2c consist of an extended π-system, mainly ranging from one thiophene unit to the other since the pyridinium moieties are not fixed on the same plane. The π-system of 1c results in being much less electron-rich compared to 2c due to the presence of the perfluorinated bridging unit; therefore, the electron-density difference between 1o and 1c is expected to be higher than that between 2o and 2c with regard to the thiophene area. The electronic similarity in the latter case suggests that the limited binding differences observed are mainly due to structural geometric variation. Conversely, the more electron-rich 1o isomer preferably binds to β-CD compared to 1c, confirming the β-CD preference for electron-rich π-systems.
The higher degree of formation of the 1@β-CD, as confirmed by the free energy values, suggests that the perfluorinated ring should play some other effects. Indeed, the presence of fluorine atoms (e and f signals), included in the bridging unit of compounds 1o and 1c are likely to be involved in hydrogen bonding with the β-CD hydroxyl groups on the rim of the host structure. H-bond acceptor behavior by organic fluorine is controversial. In fact, while a 1996 report by Dunitz and Taylor, based on the statistical analysis of the Cambridge Structural Database System (CSDS), concluded that F atoms present in organic molecules hardly accept the H-bond [45], other remarkable example of such interactions have been more recently reported for X-H∙∙∙F-C (X = O, N) since then [46,47]. Carbon hybridization has been reported to affect the successful formation of such interactions, with the following success trend: sp3 > sp2 > sp [48]. We therefore believe that the formation of the inclusion complexes is driven by the encapsulation of the thiophene moieties, as for 2o and 2c, but once the inclusion complex is formed its stability could be enhanced by intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl groups in the β-CD rim and the CF2 units in allylic position e present in the perfluorinated cyclopentenyl bridge. Differently from recent observations by Branda and collaborators that underlined the importance of intramolecular H-bonding in disabling the photochromic properties of a dithienylethene based detector for organo-phosphorous nerve agents [49], the interconversion of 1o to 1c within the β-CD was possible indicating the presence of only weak H bonds between F atoms and the host structure. Since compound 1 is equipped with sp3 CF2 units pinned in a cyclic rigid moiety, it is likely to assume that involvement of these residues in H-bonding is rather limited.
4. Conclusions
The supramolecular features related to the reversible binding of two water soluble bis-cationic dithienylethene units 1 and 2 to the β-CD have been investigated, observing substantial differences in the binding affinities. Both isomeric forms of 1o-c and 2o-c were shown to spontaneously form 1:1 inclusion complexes with the β-CD. The different substitution pattern in the chromophores was shown to be crucial to obtain large association constants differences between the open and the closed isomeric forms. In this regard, the photochromic isomers of the dithienylethene equipped with a perfluorinated bridging unit (1o-c) showed an association constants ratio (K1o@β-CD/K1c@β-CD) equal to 3.4 and difference between the ΔG0 of 3 kJ/mol in the binding event with the β-CD. Conversely, the geometrically similar dithienylethene bearing the regular cyclopentenyl bridging unit (2o-c) showed only 1.4 association constants ratio and 1 kJ/mol binding free energy difference for the same supramolecular interaction. Moreover, the presence of F atoms in the backbone of 1o-c allowed inclusion complexes 3–5 kJ/mol to be obtained that were more stable than those obtained with 2o-c.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/org3020005/s1, Figure S1. Cyclodextrin recognition of photochrome 1o, 1H-NMR spectra. Figure S2. Cyclodextrin recognition of photochrome 1c, 1H-NMR spectra. Figure S3. Cyclodextrin recognition of photochrome 2o, 1H-NMR spectra. Figure S4. Cyclodextrin recognition of photochrome 2c, 1H-NMR spectra. Figure S5. Proton d area expansion of NOESY 1H-NMR of 1o + β-CD in D2O. Figure S6. Proton c area expansion of NOESY 1H-NMR of 1o + β-CD in D2O. Figure S7. Proton d′ area expansion of NOESY 1H-NMR of 2o + β-CD in D2O. Figure S8. 1o + β-CD 1H-NMR DOSY. Figure S9. 1o + β-CD 1H-NMR DOSY. Figure S10. 2o + β-CD 1H-NMR DOSY. Figure S11. 2c + β-CD 1H-NMR DOSY. Figure S12. Cyclodextrin recognition of photochrome 1o and 1c, 19F-NMR spectra. Table S1. 1o, 1c, β-CD, 1o@β-CD and 1c@β-CD diffusion coefficients. Table S2. 2o, 2c, β-CD, 2o@β-CD and 2c@β-CD diffusion coefficients. Table S3. 1o@β-CD Job’s plot data and data treatment. Table S4. 1c@β-CD Job’s plot data and data treatment. Table S5. 2o@β-CD Job’s plot data and data treatment. Table S6. 2c@β-CD Job’s plot data and data treatment. Table S7. Data from 1o titration with β-CD. Table S8. Data from 1c titration with β-CD. Table S9. Data from 2o titration with β-CD. Table S10. Data from 2c titration with β-CD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., F.F. and G.B.; formal analysis, M.B. and G.B.; investigation, M.B. and G.B.; writing—review and editing, A.S. and F.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Università Ca’ Foscari ADIR project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Università Ca’ Foscari di Venezia and Ministero Università e Ricerca for the financial support. Special acknowledgements to Claudio Santo for assistance in the calculation of the association constants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Neilson, B.M.; Bielawski, C.W. Photoswitchable Organocatalysis: Using Light To Modulate the Catalytic Activities of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12693–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Feringa, B.L. Dynamic Control of Chiral Space in a Catalytic Asymmetric Reaction Using a Molecular Motor. Science 2011, 331, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J. Recycling a Homogeneous Catalyst through a Light-Controlled Phase Tag. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4425–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, S.; Stoll, R.S. Artificial Light-Gated Catalyst Systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5054–5075. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.; Ji, X.; Xia, D.; Huang, F. A Dual-Responsive Supra-Amphiphilic Polypseudorotaxane Constructed from a Water-Soluble Pillar [7] arene and an Azobenzene-Containing Random Copolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, F.D.; Theato, P. Temperature- and light-responsive smart polymer materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7468–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.; Abell, A.D. Structural Optimization of Photoswitch Ligands for Surface Attachment of α-Chymotrypsin and Regulation of Its Surface Binding. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 6983–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ueno, S.; Komatsu, H.; Ikeda, M.; Ishizuka, K.; Iko, Y.; Tabata, K.V.; Aoki, H.; Ito, S.; et al. Photo Gel–Sol/Sol–Gel Transition and Its Patterning ofa Supramolecular Hydrogel as Stimuli-Responsive Biomaterials. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, G.M. The cis-trans isomerization of conjugated compounds. Chem. Rev. 1955, 55, 625–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolus, P.; Monti, S. Cis-Trans Photoisomerization of Azobenzene-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 5046–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamesue, S.; Takashima, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Shinkai, S.; Harada, A. Photoswitchable Supramolecular Hydrogels Formed by Cyclodextrins and Azobenzene Polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7461–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Nielsen, S.R.; Uyar, T.; Zhang, S.; Zafar, A.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F. Electrospun UV-responsive supramolecular nanofibers from a cyclodextrin–azobenzene inclusion complex. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Yan, H.; Ang, C.Y.; Nguyen, K.T.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y. Photoswitchable Supramolecular Catalysis by Interparticle Host–Guest Competitive Binding. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 13979–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordani, S.; Cejas, M.A.; Raymo, F.M. Photoinduced proton exchange between molecular switches. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 10973–10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymo, F.M.; Giordani, S. Signal Communication between Molecular Switches. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3475–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovic, G.; Krongauz, V.; Weiss, V. Spiropyrans and Spirooxazines for Memories and Switches. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.; Fukaminato, T.; Matsuda, K.; Kobatake, S. Photochromism of Diarylethene Molecules and Crystals: Memories, Switches, and Actuators. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 12174–12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; Strukul, G.; Wass, D.F.; Scarso, A. Photomodulable phosphines incorporating diarylethene moieties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10795–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, B.M.; Bielawski, C.W. Photoswitchable metal-mediated catalysis: Remotely tuned alkene and alkyne hydroborations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 32, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, B.M.; Lynch, V.M.; Bielawski, C.W. Photoswitchable N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Using Light to Modulate Electron-Donating Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10322–10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.N.; Carling, C.J.; Nagle, J.K.; Branda, N.R.; Wolf, M.O. Successful bifunctional photoswitching and electronic communication of two platinum (II) acetylide bridged dithienylethenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16644–16645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samachetty, H.D.; Lumieux, V.; Branda, N.R. Modulating chemical reactivity using a photoresponsive molecular switch. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 8292–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samachetty, H.D.; Branda, N.R. Photomodulation of Lewis basicity in a pyridine-functionalized 1,2-dithienylcyclopentene. Chem. Commun. 2005, 2840–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sud, D.; McDonald, R.; Branda, N.R. Synthesis and Coordination Chemistry of a Photoswitchable Bis(phosphine) Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 5960–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasceanu, A.; Cacciarini, M.; Brøndsted Nielsen, M. Photo/thermochromic macrocycles based on dihydroazulenes, dithienylethenes, and spiropyranes. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 6635–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szacilowski, K. Digital Information Processing in Molecular Systems. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3481–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, A.J.; Branda, N.R. 1,2-Dithienylethene Photochromes and Non-destructive Erasable Memory. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Atar, U.; Fernandes, R.; Johnsen, B.; Baillie, D.; Branda, N.R. A photocontrolled molecular switch regulates paralysis in a living organism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15966–15967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Liao, C.; Yang, Z.; Hu, F. Recent Advances in Photoswitchable Cation Chemosensors. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Tian, H. A photochromic supramolecular polymer based on bis-p-sulfonatocalix [4] arene recognition in aqueous solution. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7166–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, A.; Jukovic, A.; Lucas, L.N.; van Esch, J.; Feringa, B.L.; Huskens, J.; Reinhoudt, D.N. A dithienylethene-tethered β-cyclodextrin dimer as a photoswitchable host. Chem. Commun. 2002, 2734–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bianchini, G.; La Sorella, G.; Canever, N.; Strukul, G.; Scarso, A. Efficient isonitrile hydration through encapsulation within a hexameric self-assembled capsule and selective inhibition by a photo-controllable competitive guest. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5322–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, M.; Kato, N.; Kawauchi, S.; Imase, T.; Watanabe, J.; Irie, M. Photochromism of dithienylethenes included in cyclodextrins. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 9306–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, M.; Yamada, M.; Kato, N.; Irie, M. Photochromism of dithienylethene-bis(trimethylammonium) iodide in cyclodextrin cavities. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2000, 2, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, H. Relatively High-Yield Syntheses of Rotaxanes. Syntheses and Properties of Compounds Consisting of Cyclodextrins Threaded by, -Diaminoalkanes Coordinated to Cobalt(III)- Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A. Cyclodextrin-based molecular machines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashidzume, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. Cyclodextrin Based Rotaxanes: From Rotaxanes to Polyrotaxanes and Further to Functional Materials. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3344–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Zajicek, J.; Smith, B.D. Cyclodextrin Rotaxane with Switchable Pirouetting. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2096–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, T.C.S.; Müller, V.; Li, S.; Lincoln, P.; Andréasson, J. Enantioselective cyclization of photochromic dithienylethenes bound to DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4393–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Davidson-Rozenfeld, G.; Vàzquez-Gonzàlez, M.; Fadeev, M.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Willner, I. Reversible Modulation of DNA-Based Hydrogel Shapes by Internal Stress Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17691–17701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy; Academic Press Limited: London, UK, 1993; Volume 27, pp. 59–101. ISBN 0-12-505327-4. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G. A history of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10940–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin Del Valle, E.M. Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process Biochem. 2004, 34, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K. A Practical Guide for the Determination of Binding Constants. J. Inc. Phenom. Macroc. Chem. 2001, 39, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunitz, J.D.; Taylor, R. Organic fluorine hardly ever accepts hydrogen bonds. Chem. Eur. J. 1997, 3, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarich, T.J.; Rithner, C.D.; Miller, M.S.; Anderson, O.P.; Strauss, S.H. Significant Inter- and Intramolecular O−H···FC Hydrogen Bonding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 4280–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.R.; Mogurampelly, S.; Suryaprakash, N. Engagement of CF3 Group in N–H···F–C Hydrogen Bond in the Solution State: NMR Spectroscopy and MD Simulation Studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheneider, H.J. Hydrogen bonds with fluorine. Studies in solution, in gas phase and by computations, conflicting conclusions from crystallographic analyses. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadian, F.; Wu, T.; Branda, N.R. A ‘chemically-gated’ photoresponsive compound as a visible detector for organophosphorus nerve agents. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10954–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).