Pd-Based Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Polysaccharides Catalyst and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogel Beads with Calcium Chloride (I-CaCl2)
2.3. Preparation of Hydrogel Beads with Chitosan (I-C)
2.4. Reaction Procedure
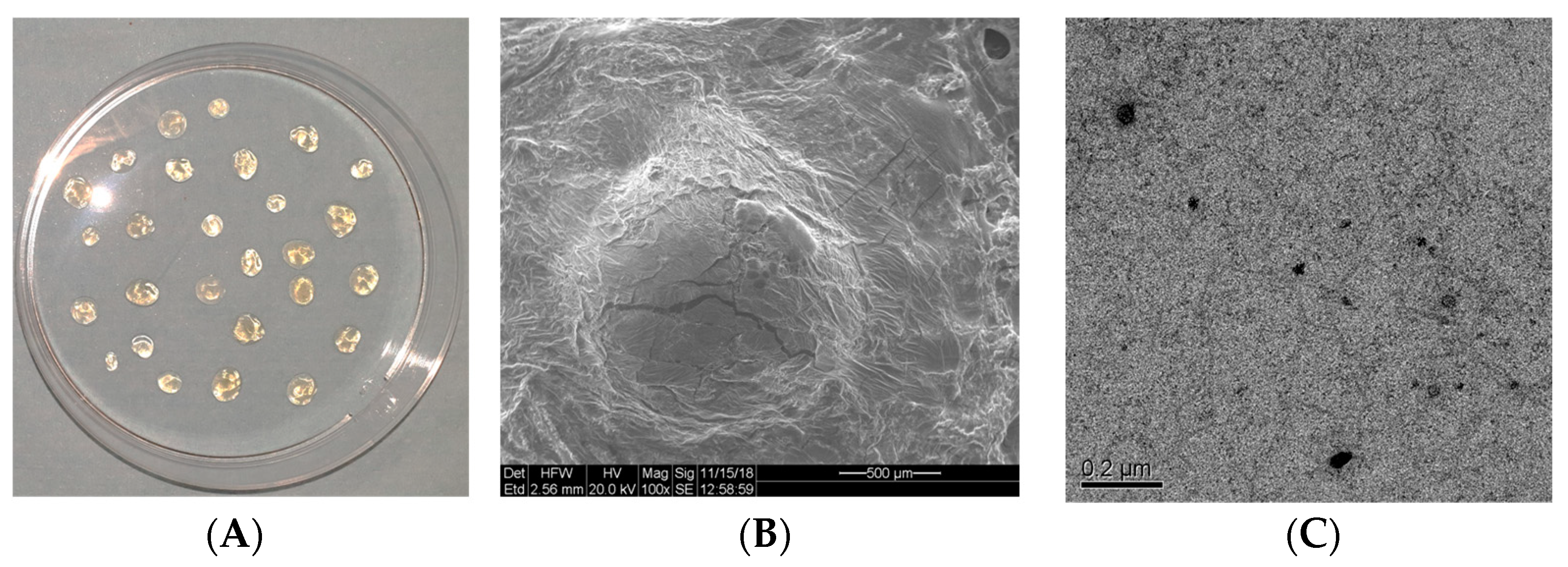
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
2.6. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopic (HRTEM) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auriemma, G.; Russo, P.; Del Gaudio, P.; García-González, C.A.; Landín, M.; Aquino, R.P. Technologies and Formulation Design of Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. Moleculs 2020, 25, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quignard, F.; Di Renzo, F.; Guibal, E. From natural polysaccharides to materials for catalysis, adsorption, and remediation. In Carbohydrates in Sustainable Development I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 165–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Pei, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q. Construction of ordered structure in polysaccharide hydrogel: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naim, S.; Samuel, B.; Chauhan, B.; Paradkar, A. Effect of potassium chloride and cationic drug on swelling, erosion and release from κ-carrageenan matrices. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, C.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Sun, T.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Yu, G. Chitosan-based nanomaterials for drug delivery. Molecules 2018, 23, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.K.; Sahoo, D.; Nayak, P.L. Chitosan-sodium alginate nanocomposites blended with cloisite 30B as a novel drug delivery system for anticancer drug curcumin. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. Technol. 2011, 2, 402–411. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, G.; Barbucci, R. Polysaccharide based hydrogels for biomedical applications. In Hydrogels; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2009; pp. 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Magnani, A.; Rappuoli, R.; Lamponi, S.; Barbucci, R. Novel polysaccharide hydrogels: Characterization and properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2000, 11, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L. Carrageenan: A review. Veterinární Medicína 2013, 58, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, W.R.; Harpell, A.R. Carrageenan. In Food Stabilisers, Thickeners and Gelling Agents; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.R.; Rajgopal, K.; Maheswari, C.U.; Kantam, M.L. Chitosan hydrogel: A green and recyclable biopolymer catalyst for aldol and Knoevenagel reactions. N. J. Chem. 2006, 30, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.; Levy-Ontman, O. Recent Developments in the Immobilization of Palladium Complexes on Renewable Polysaccharides for Suzuki–Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Halobenzenes and Phenylboronic Acids. Catalysts 2020, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.; Levy-Ontman, O. Development and application of palladium nanoparticles on renewable polysaccharides as catalysts for the Suzuki cross-coupling of halobenzenes and phenylboronic acids. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, J.-I. Enzymatic preparation of functional polysaccharide hydrogels by phosphorylase catalysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, L.R.; Rogov, A.M.; Zueva, O.S.; Zuev, Y.F. Lipase enzymatic microreactor in polysaccharide hydrogel: Structure and properties. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurettin, S. Soft and flexible hydrogel templates of different sizes and various functionalities for metal nanoparticle preparation and their use in catalysis. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1329–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Ontman, O.; Biton, S.; Shlomov, B.; Wolfson, A. Renewable polysaccharides as supports for palladium phosphine catalysts. Polymers 2018, 10, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, A.; Biton, S.; Levy-Ontman, O. Study of Pd-based catalysts within red algae-derived polysaccharide supports in a Suzuki cross-coupling reaction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37939–37948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviev, S.; Wolfson, A.; Levy-Ontman, O. Novel iota carrageenan-based RhCl3 as an efficient and recyclable catalyst in Suzuki cross coupling. Mol. Catal. 2020, 486, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviev, S.; Wolfson, A.; Levy-Ontman, O. RhCl(TPPTS)3 supported on iota-carrageenan as recyclable catalysts for Suzuki cross-coupling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48200–48204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy-Ontman, O.; Blum, D.; Golden, R.; Pierschel, E.; Leviev, S.; Wolfson, A. Palladium Based-Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Catalysts in the Suzuki Cross-Coupling Reaction. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 30, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamker, E.; Levy-Ontman, O.; Wolfson, A. Green procedure for aerobic oxidation of benzylic alcohols with palladium supported on iota-carrageenan in ethanol. Polymers 2021, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckvall, J.E. Modern Oxidation Methods; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kopylovich, M.N.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Alegria, E.C.; Martins, N.M.; Martins, L.M.; Pombeiro, A.J. Catalytic oxidation of alcohols: Recent advances. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 91–174. [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi, Y. Green Oxidative Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones. In Green Oxidation in Organic Synthesis; Ning, J., Stahl, S.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 35–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tojo, G.; Fernandez, M.I. Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes and Ketones: A Guide to Current Common Practice; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, M.; Ohmura, S.D.; Wada, M.; Miyoshi, N. Aerobic oxidation of alcohols using bismuth bromide as a catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 60, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaeta, V.R.; Rodríguez-Lugo, R.E. Aerobic oxidation reactions in the fine chemicals and pharmaceutical industries. In Catalytic Aerobic Oxidations; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 252–290. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, C. Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
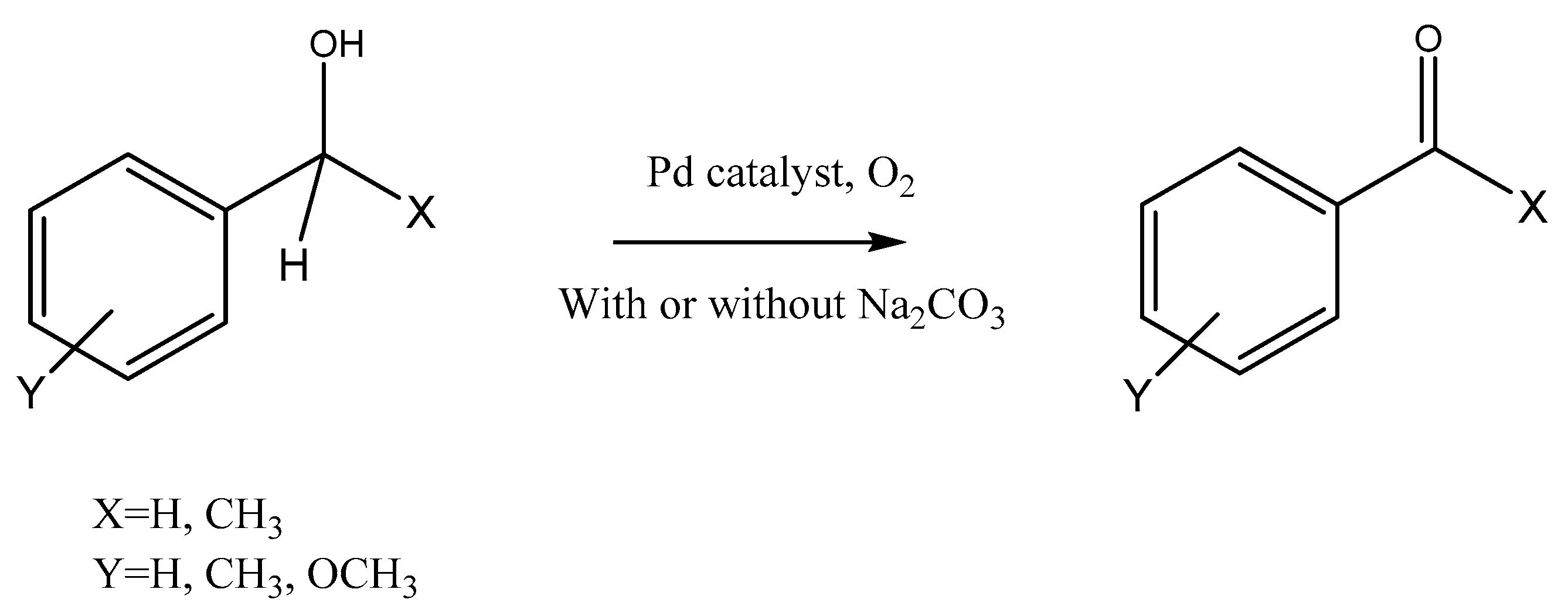
| Entry | Solvent | RP b | Pd(OAc)2 | Pd(OAc)2(TPPTS)2 | I-CaCl2 | I-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ethanol | 0.654 | 50 | 40 (78) c | 25 | 4 |
| 2 | Ethyl acetate | 0.228 | 26 | 28 (59) c | 16 | 3 |
| 3 | Petroleum ether | 0.111 | 31 | 25 (55) c | 38 | 14 |
| 4 | Hexane | 0.009 | 48 | 47 (86) c | 66 | 35 |
| Polysaccharide | Branched/Linear | Building Block | Functional Groups | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iota (I) | Linear | d-Gal-4-sulfate,3,6-anhydro-d-Gal-2-sulfate | –OH, –OSO3− | 66 71 b 40 c |
| Kappa (K) | Linear | d-Gal-4-sulfate,3,6-anhydro-d-Gal | –OH, –OSO3− | 44 |
| Alginate (A) | Linear | β-(1 → 4)-linked mannose and α-L guluronate | –OH, –COO− | 34 |
| Guar gum (G) | Branched | β-(1 → 4)-linked mannose | –OH | - |
| Entry | Mixing | Substrate | Pressure (atm) | Cycle | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 1 | 66 |
| 2 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 2 | 33 |
| 3 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 3 | 10 |
| 4 | Shaking | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 1 | 49 |
| 5 | Shaking | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 2 | 28 |
| 6 | Shaking | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 3 | 25 |
| 7 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 1 | 1 | 22 |
| 8 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 3.8 | 1 | 69 |
| 9 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 1 b | 1 | 60 |
| 10 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol | 3.8 b | 1 | 55 |
| 11 | Stirring | 1-Phenyl ethanol | 1 | 1 | 63 |
| 12 | Stirring | 4-Methylbenzyl alcohol | 1 | 1 | 69 |
| 13 | Stirring | 4-Methoxylbenzyl alcohol | 1 | 1 | 99 |
| 14 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol c | 1 | 1 | 25 |
| 15 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol c | 1 | 2 | 23 |
| 16 | Stirring | Benzyl alcohol c | 1 | 3 | 19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levy-Ontman, O.; Stamker, E.; Mor, V.; Wolfson, A. Pd-Based Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohols. Organics 2021, 2, 50-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/org2010005
Levy-Ontman O, Stamker E, Mor V, Wolfson A. Pd-Based Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohols. Organics. 2021; 2(1):50-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/org2010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevy-Ontman, Oshrat, Eliraz Stamker, Vital Mor, and Adi Wolfson. 2021. "Pd-Based Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohols" Organics 2, no. 1: 50-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/org2010005
APA StyleLevy-Ontman, O., Stamker, E., Mor, V., & Wolfson, A. (2021). Pd-Based Polysaccharide Hydrogels as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Oxidation of Aromatic Alcohols. Organics, 2(1), 50-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/org2010005








