RFID-Enabled Electronic Voting Framework for Secure Democratic Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory of Work
2.1. Overview of Electronic Voting Systems
2.2. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology
2.3. Cryptographic Security and Authentication Models in E-Voting
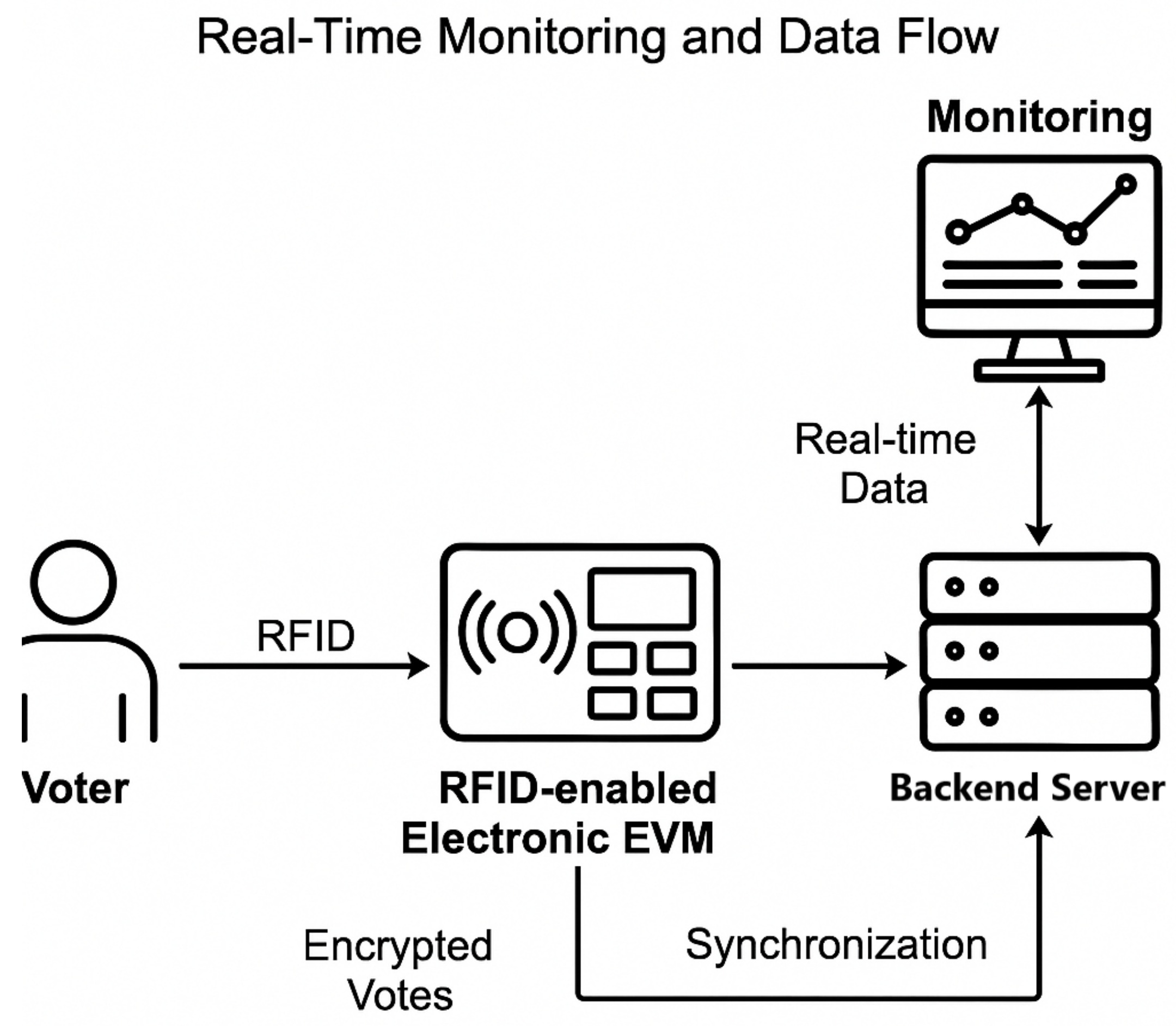
2.4. Secure Storage, Real-Time Monitoring and Comparative Analysis of RFID Voting
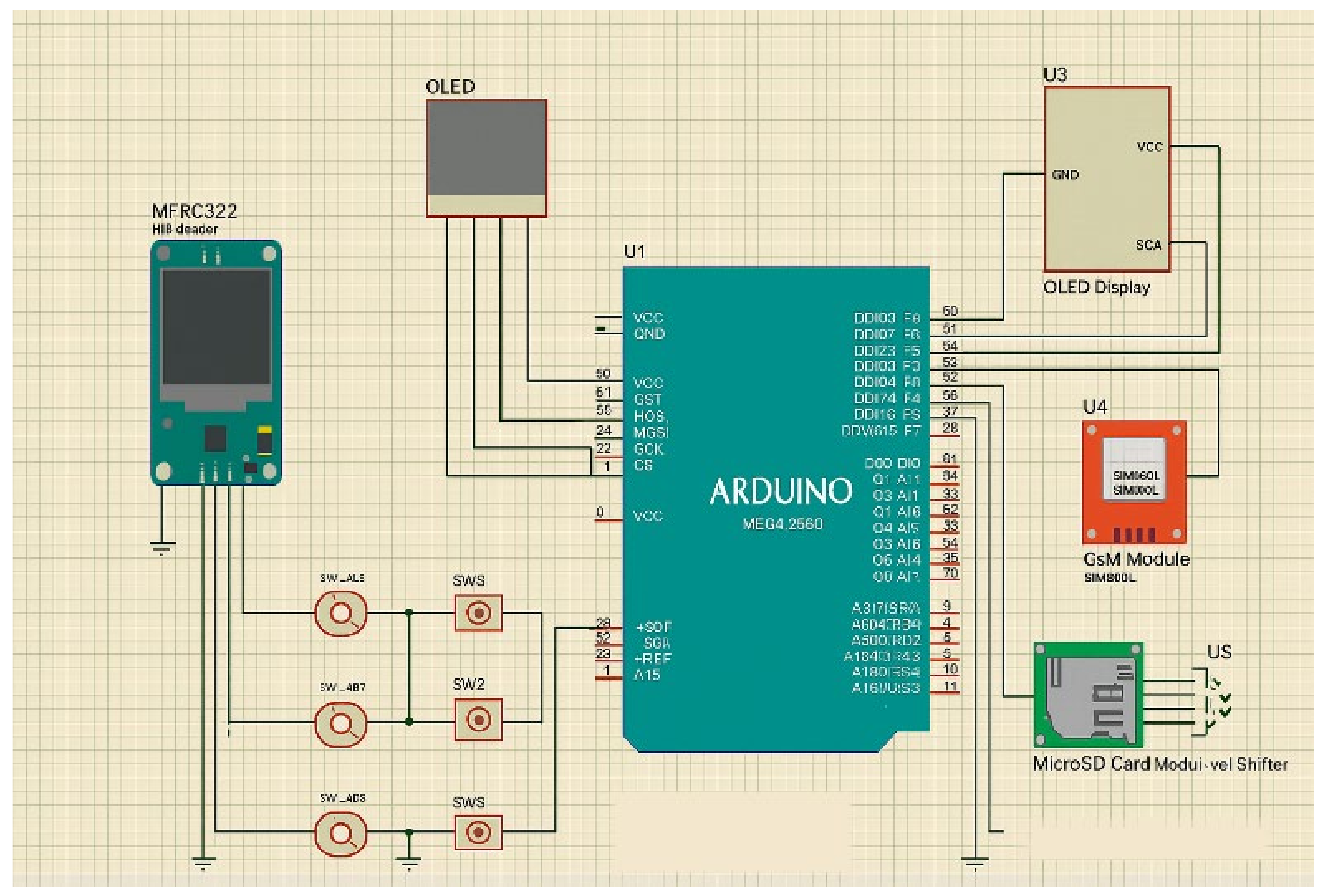
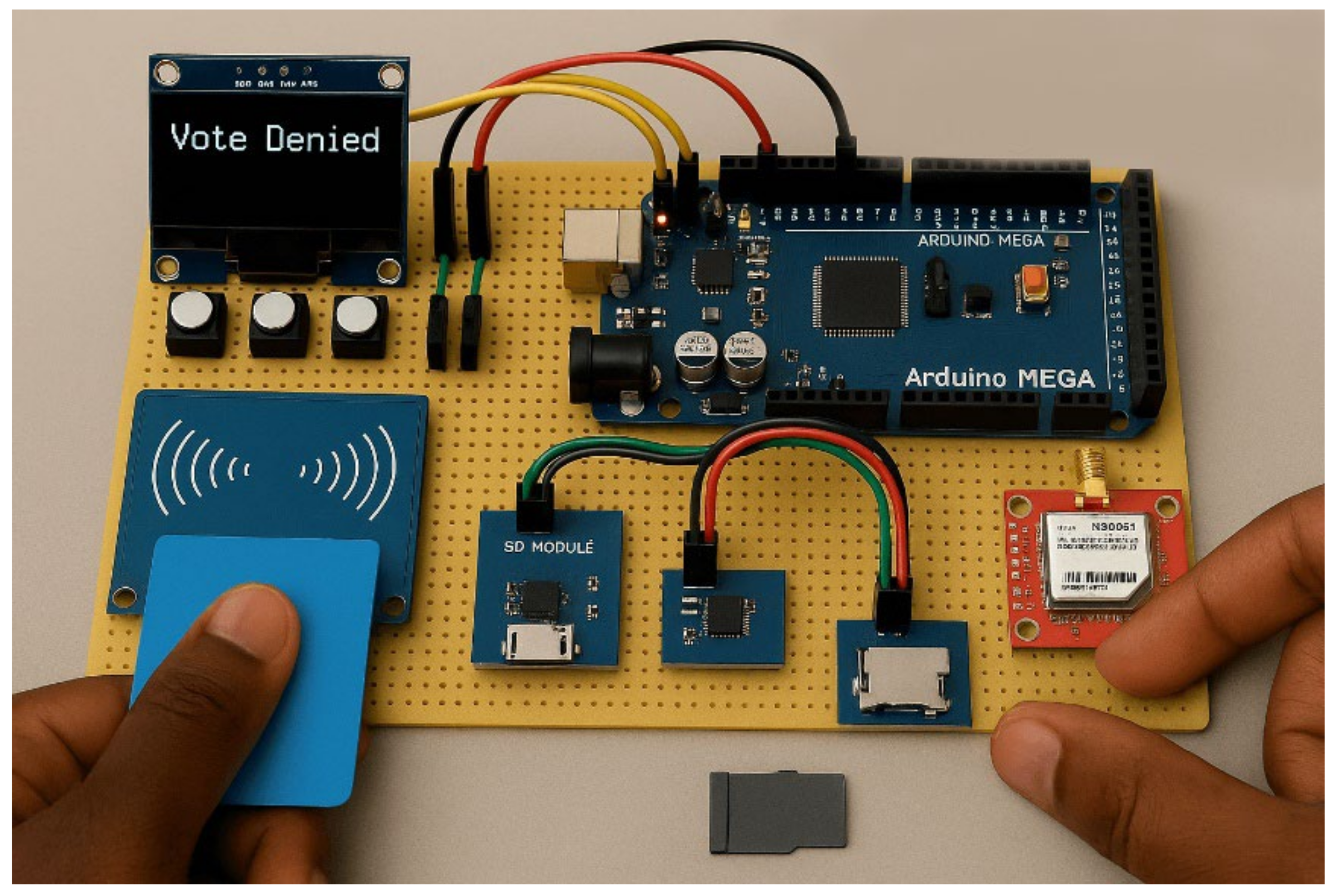
3. System Architecture and Implementation Procedure
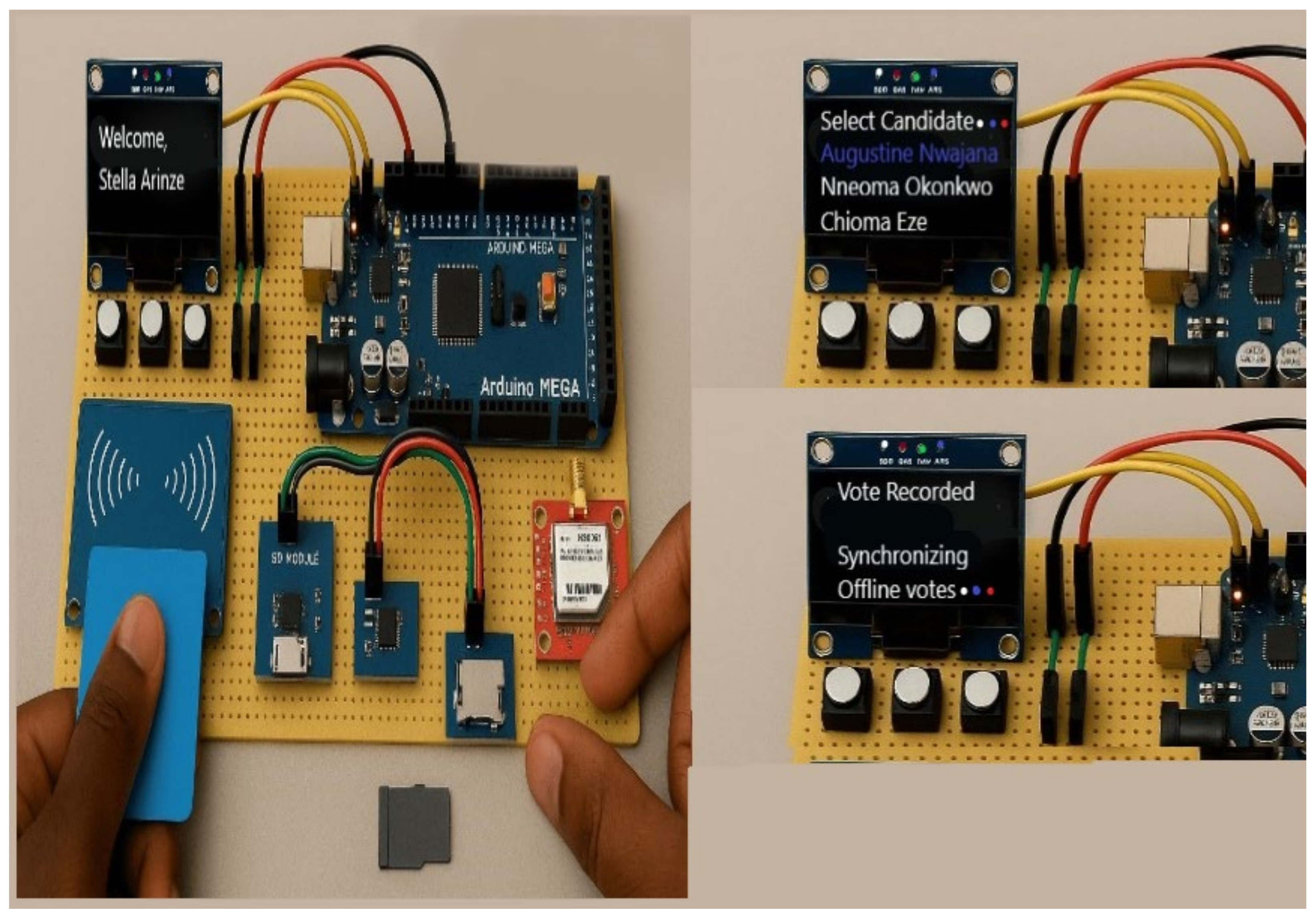
3.1. Device Setup
3.2. Voter List Upload and Verification
3.3. Card Authentication and Voter Authentication
3.4. Threat Model and Security Goals
3.5. Vote Casting and Encryption
3.6. Storage, Synchronization, and Backend Scalability
3.7. Voter Verifiability and Logging
4. Result Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhary, N.; Agarwal, S.; Lavania, G. Smart Voting System through Facial Recognition. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 7–10. Available online: https://ijsrcse.isroset.org/index.php/j/article/view/308 (accessed on 13 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Deb, D.; Engelsma, J.J. Biometrics: Trust, but Verify. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoze, S.; Omaji, S.; Edegbe, G.N. Machine Learning-Based Multimodal Biometric Authentication System (Facial and Fingerprint Recognition) for Online Voting Systems. ABUAD J. Eng. Res. Dev. (AJERD) 2025, 8, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, M.; Njilla, L.; Huang, C.; Geng, T. Blockchain-Based E-Voting Mechanisms: A Survey and a Proposal. Network 2024, 4, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanka, A.I.; Cheung, R.C. A systematic review of blockchain scalability: Issues, solutions, analysis and future research. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 195, 103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, A.; Yajam, H.; Akhaee, M.A.; Asghari, R. A scalable decentralized privacy-preserving e-voting system based on zero-knowledge off-chain computations. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2023, 79, 103645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, M.G. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Based Voting System Using Internet of Thing. Autom. Control. Intell. Syst. 2025, 13, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.N.V.; Melanka, J.P.H.C. Use of RFID Technology to Enhance Electoral Integrity. Int. J. Res. Sci. Innov. 2024, 11, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidynov, T.; Goranin, N.; Satybaldina, D.; Nurusheva, A. A Systematic Literature Review of Current Trends in Electronic Voting System Protection Using Modern Cryptography. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Kaur, A.; Agarwal, P.; Idrees, S.M. Enhancing Security and Transparency in Online Voting through Blockchain Decentralization. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.; Qu, Y. Enhancing Vulnerability Assessments for Electronic Voting Systems through an Augmented CVSS 3.1 Model. European J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2025, 9, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian Berenjestanaki, M.; Barzegar, H.R.; El Ioini, N.; Pahl, C. Blockchain-Based E-Voting Systems: A Technology Review. Electronics 2024, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohize, H.O.; Onumanyi, A.J.; Umar, B.U.; Ajao, L.A.; Isah, R.O.; Dogo, E.M.; Nuhu, B.K.; Olaniyi, O.M.; Ambafi, J.G.; Sheidu, V.B.; et al. Blockchain for securing electronic voting systems: A survey of architectures, trends, solutions, and challenges. Clust. Comput. 2025, 28, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinze, S.N.; Okafor, P.U.; Obi, E.R.; Nwajana, A.O. Implementation of Radio Frequency Identification Technology for a Secure and Intelligent Shopping Cart. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2025, 14, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Gao, T.; Shu, F.; Lei, X.; Wu, Y.; Gui, G.; Wang, J. A Novel RFID Authentication Protocol Based on A Block-Order-Modulus Variable Matrix Encryption Algorithm. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gaabouri, I.; Senhadji, M.; Belkasmi, M.; El Bhiri, B. A Systematic Literature Review on Authentication and Threat Challenges on RFID Based NFC Applications. Future Internet 2023, 15, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ullah, S.; Ahmad, T.; Jawad, K.; Buriro, A. Enhancing Security and Privacy in Healthcare Systems Using a Lightweight RFID Protocol. Sensors 2023, 23, 5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.K.; Tiwari, U.; Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, S. AES Based Online Voting System. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamani, K.; Monisha, R. Physical Layer Security Using Cross Layer Authentication for AES-ECDSA Algorithm. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 215, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapurna, K.; Chandrani, V.; Mounika, P.; Sree, P.T. Design of Authenticated Radio Frequency Identification based Electronic Voting Machine. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 20–22 January 2021; pp. 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, N.; Wang, B. Efficient Electronic Voting System Based on Homomorphic Encryption. Electronics 2024, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.N.; Hridoy, M.W.; Mizanur Rahman, M.; Islam, M.R.; Banik, S. Highly secured and effective management of app-based online voting system using RSA encryption and decryption. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madueke, O.; Enyiazu, C. Electoral Integrity and Election Management in Nigeria: The Case of the 2023 General Election. World Aff. 2025, 188, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, J.N.; Okodugha, A.; Okuboarere, A.G. Design and Implementation of a Radio Frequency Identification based Enhanced Electronic Voting Machine (EEVM) for Free and Fair Elections. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2022, 184, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagde, Y.; Karanje, K.; Dhage, S.; Gajare, M.P. Design and Development of Biometric based Electronic Voting System. Int. J. Innov. Res. Technol. (IJIRT) 2024, 11, 759–766. Available online: https://ijirt.org/article?manuscript=167201 (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Russo, A.; Anta, A.F.; Vasco, M.I.G.; Romano, S.P. Chirotonia: A Scalable and Secure e-Voting Framework based on Blockchains and Linkable Ring Signatures. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Melbourne, Australia, 6–8 December 2021; pp. 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabia, F.; Sara, A.; Taoufiq, G. ZkSNARKs and Ticket-Based E-Voting: A Blockchain System Proof of Concept. Data Metadata 2024, 3, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



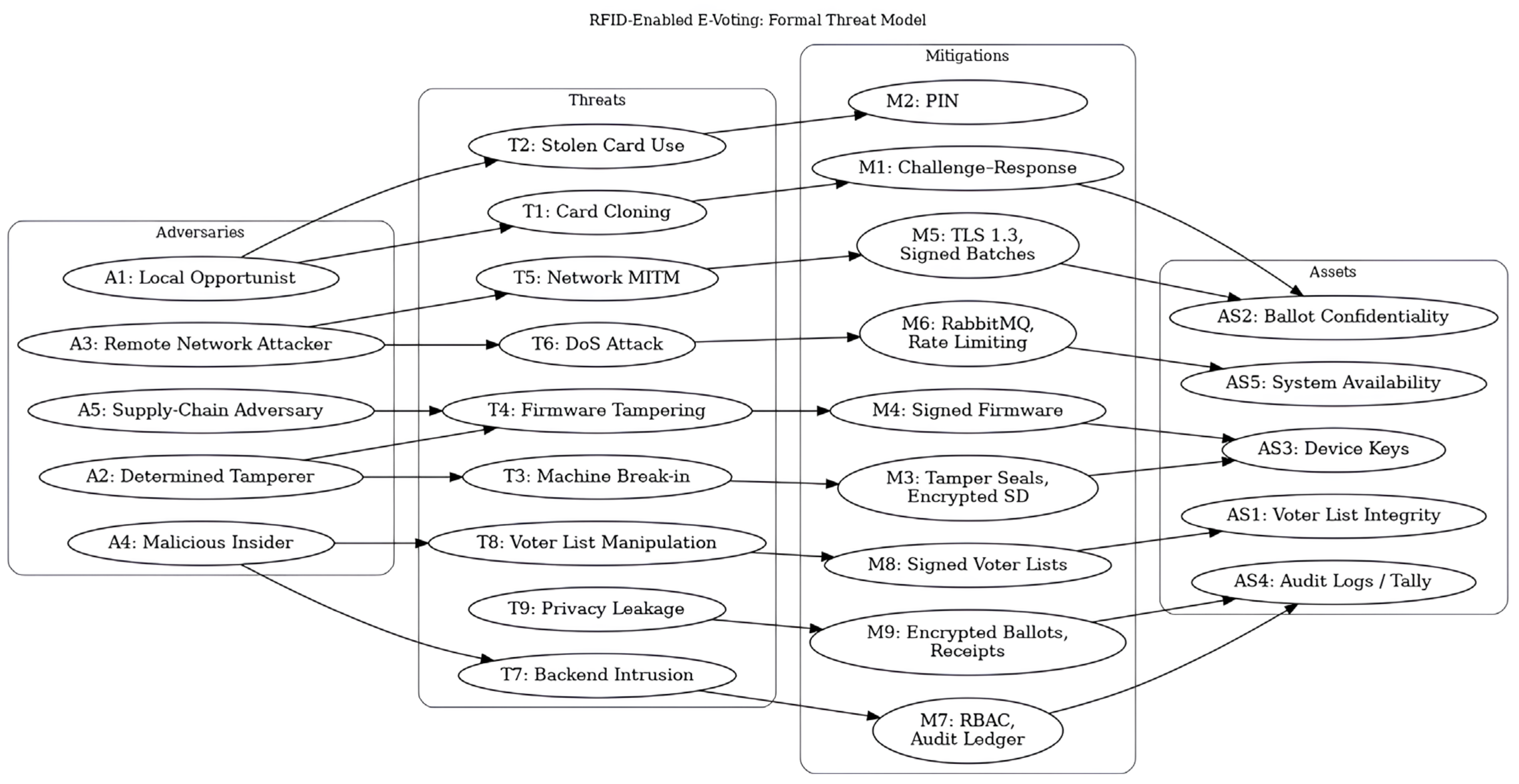

| Threat ID | Threat Description | Mitigation Implemented | Validation/Test Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Card cloning/replay—attacker duplicates card UID | Challenge–response protocol using per-card secret and random nonce | Tested with cloned UID cards → rejected due to invalid challenge-response |
| T2 | Stolen card impersonation—fraudulent voter uses stolen card | Second-factor authentication (PIN or biometric) required in addition to card | Tested with correct card but invalid PIN → access denied |
| T3 | Machine break-in/SD theft—attacker physically opens device | Tamper-evident seals; SD content encrypted; keys in secure microcontroller memory | Tamper test: SD removed → ciphertext unreadable; device logged tamper |
| T4 | Firmware tampering—malicious code injected | Signed firmware and secure bootloader | Unsigned firmware upload attempted → device refused to start |
| T5 | Network MITM—adversary alters transmitted data | TLS 1.3 with mutual authentication; batch signatures and checksums | Packet modification during transmission → backend rejected invalid checksum |
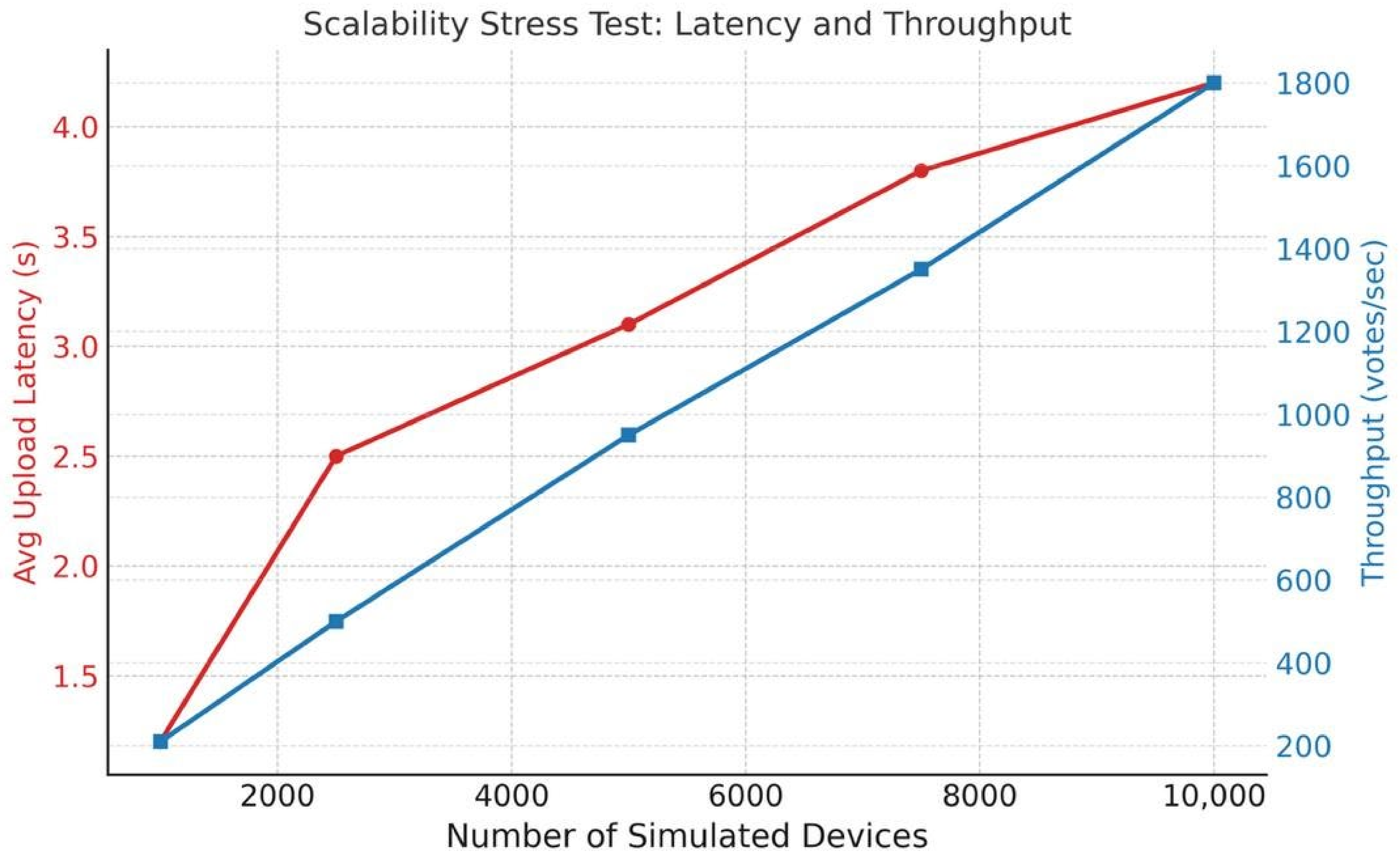
| T6 | Denial-of-Service (DoS)—API flood or RF jamming | RabbitMQ buffering, rate-limiting, offline-first storage | Stress test with 10k simulated devices → no data loss, graceful queue handling |
| T7 | Backend intrusion—attacker tampers with database | PostgreSQL cluster with RBAC, audit logs, replication | Insider attempt to modify entries → mismatched audit log flagged intrusion |
| T8 | Voter list manipulation—unauthorized edits before election | Digitally signed voter list; verified at device startup | Test with unsigned voter list → device refused to load |
| T9 | Privacy leakage—voter identity linked to choice | Encrypted ballot storage; anonymous receipt codes (commitment only) | End-to-end test: receipt showed inclusion without revealing choice |
| Feature/Metric | Flutter–Firebase Model [7] | Basic RFID Voting System [8] | RFID EVM [24] | Biometric + RFID [25] | Chirotonia Blockchain Framework [26] | zkSNARK Ticket-Based System [27] | Proposed RFID-Enabled System (This Work) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voter authentication | RFID with app/cloud account | RFID tag check only | RFID with additional local verification | Fingerprint + RFID | Cryptographic identity via linkable ring signatures (no RFID) | Cryptographic tickets with zkSNARK eligibility proofs (no RFID) | RFID challenge–response (per-card keys) + 2FA (PIN/biometric) |
| Encryption | Cloud-managed; details not specified | None | Not specified | Not specified/OS libs | On-chain crypto + linkable ring signatures | zkSNARK proofs + on-chain commitments | AES-128 (CBC, random IVs) + checksums + signed batches |
| Offline voting support | No (cloud dependent) | Limited/Not implemented | Local device operation; sync not detailed | Not specified | Requires connectivity | Requires connectivity | Full offline-first; local encrypted log; deferred sync |
| Vote synchronization | Real-time cloud writes | Not included | Not detailed (likely manual collation) | Not specified | Blockchain ledger synchronization | On-chain inclusion | Batch sync via TLS 1.3 + RabbitMQ; de-dup + integrity checks |
| Double-voting prevention | Cloud rules (per account) | Not reliable | Not detailed | Biometric re-auth; duplicates not detailed | Cryptographic uniqueness (protocol) | Cryptographic uniqueness (tickets) | Local state + server reconciliation; anti-replay |
| Tamper-proof logging | Cloud logs | Not implemented | Not specified | Not specified | Immutable blockchain log | Immutable blockchain log | Encrypted append-only logs (device ID, ts, batch ID) |
| Verifiability (voter) | None reported | None | None | None | Strong protocol verifiability | Strong protocol verifiability | Anonymous receipt code + public bulletin board (inclusion only) |
| Scalability evidence | Prototype/app scale | Prototype scale | Prototype in national context | Lab prototype | Protocol/framework-level | Protocol-level | Stress-tested: 10k devices, 1M voters (PostgreSQL cluster + RabbitMQ) |
| Deployment readiness | Prototype/simulation | Basic hardware demo | Concept/prototype | Lab prototype | Research framework (not embedded) | Proof-of-concept protocol | Field-oriented; offline-capable; auditable |
| Average voting time | ~15–20 s | ~18–25 s | Not reported | Not reported | Not applicable | Not applicable | ~11.5 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arinze, S.N.; Nwajana, A.O. RFID-Enabled Electronic Voting Framework for Secure Democratic Processes. Telecom 2025, 6, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040078
Arinze SN, Nwajana AO. RFID-Enabled Electronic Voting Framework for Secure Democratic Processes. Telecom. 2025; 6(4):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040078
Chicago/Turabian StyleArinze, Stella N., and Augustine O. Nwajana. 2025. "RFID-Enabled Electronic Voting Framework for Secure Democratic Processes" Telecom 6, no. 4: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040078
APA StyleArinze, S. N., & Nwajana, A. O. (2025). RFID-Enabled Electronic Voting Framework for Secure Democratic Processes. Telecom, 6(4), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6040078







