- Article
Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Internet of Things Networks: A Comparative Analysis of Machine and Deep Learning Techniques
- Akeem Abimbola Raji and
- Thomas Otieno Olwal
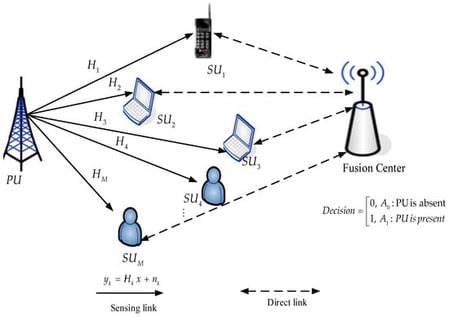
The proliferation of data-intensive IoT applications has created unprecedented demand for wireless spectrum, necessitating more efficient bandwidth management. Spectrum sensing allows unlicensed secondary users to dynamically access idle channels assigned to primary users. However, traditional sensing techniques are hindered by their sensitivity to noise and reliance on prior knowledge of primary user signals. This limitation has propelled research into machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) solutions, which operate without such constraints. This study presents a comprehensive performance assessment of prominent ML models: random forest (RF), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and support vector machine (SVM) against DL architectures, namely a convolutional neural network (CNN) and an Autoencoder. Evaluated using a robust suite of metrics (probability of detection, false alarm, missed detection, accuracy, and F1-score), the results reveal the clear and consistent superiority of RF. Notably, RF achieved a probability of detection of 95.7%, accuracy of 97.17%, and an F1-score of 96.93%, while maintaining excellent performance in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions, even surpassing existing hybrid DL models. These findings underscore RF’s exceptional noise resilience and establish it as an ideal, high-performance candidate for practical spectrum sensing in wireless networks.
6 February 2026