Software-Defined Visible Light Communication for Internet of Things: A Low-Complexity Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An SD-VLC system is proposed on the PYNQ platform, enabling reconfigurability and low complexity suitable for IoT scenarios.
- CAP modulation is employed to simplify hardware design while maintaining high spectral efficiency under IM/DD constraints.
- A lightweight adaptive equalizer based on the SDLMS algorithm is integrated to enhance signal quality with minimal computational overhead.
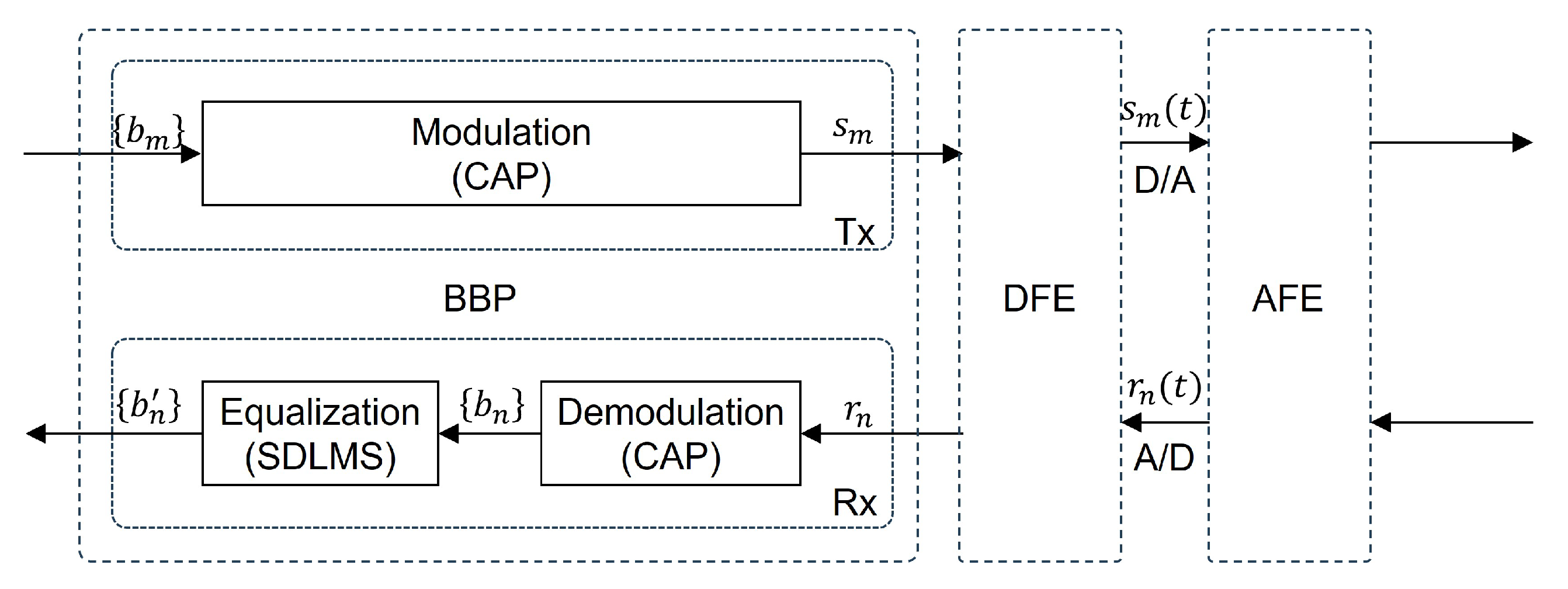
2. Architecture of SD-VLC System for IoT Applications
3. Modeling of BBP Unit in SD-VLC System
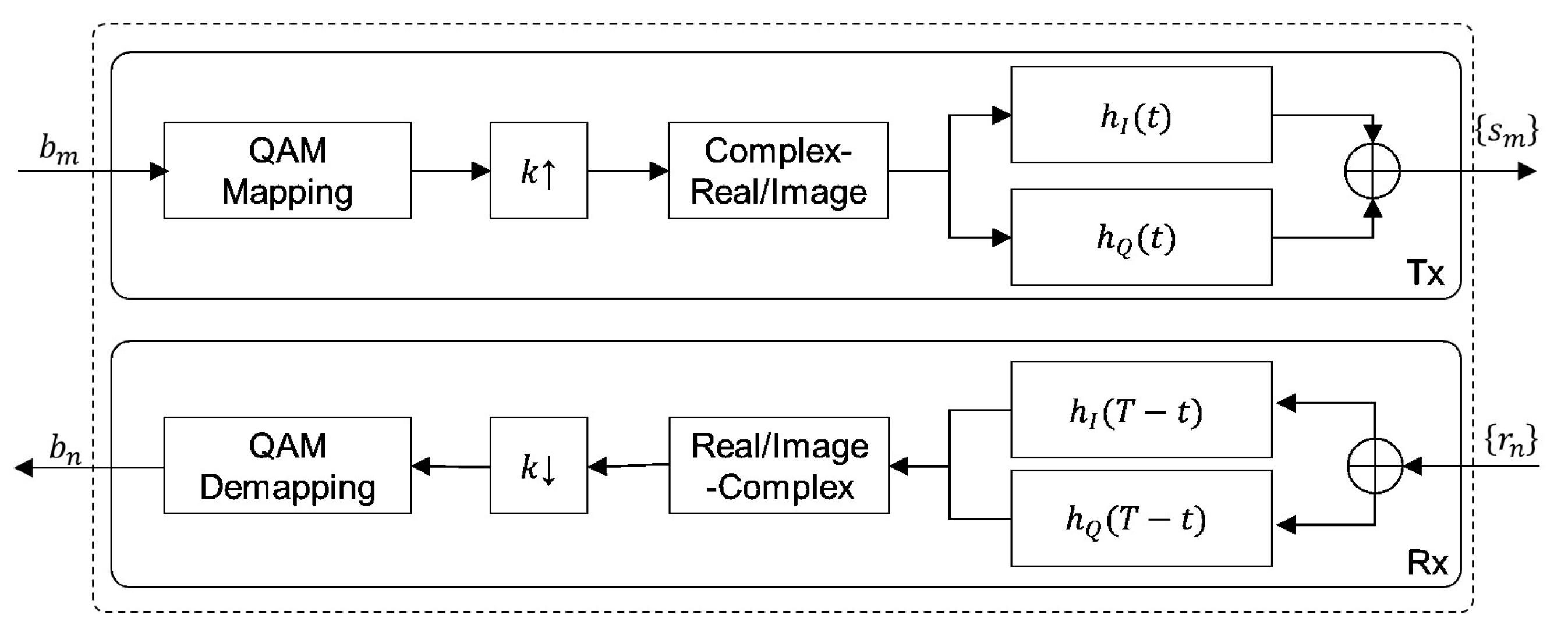
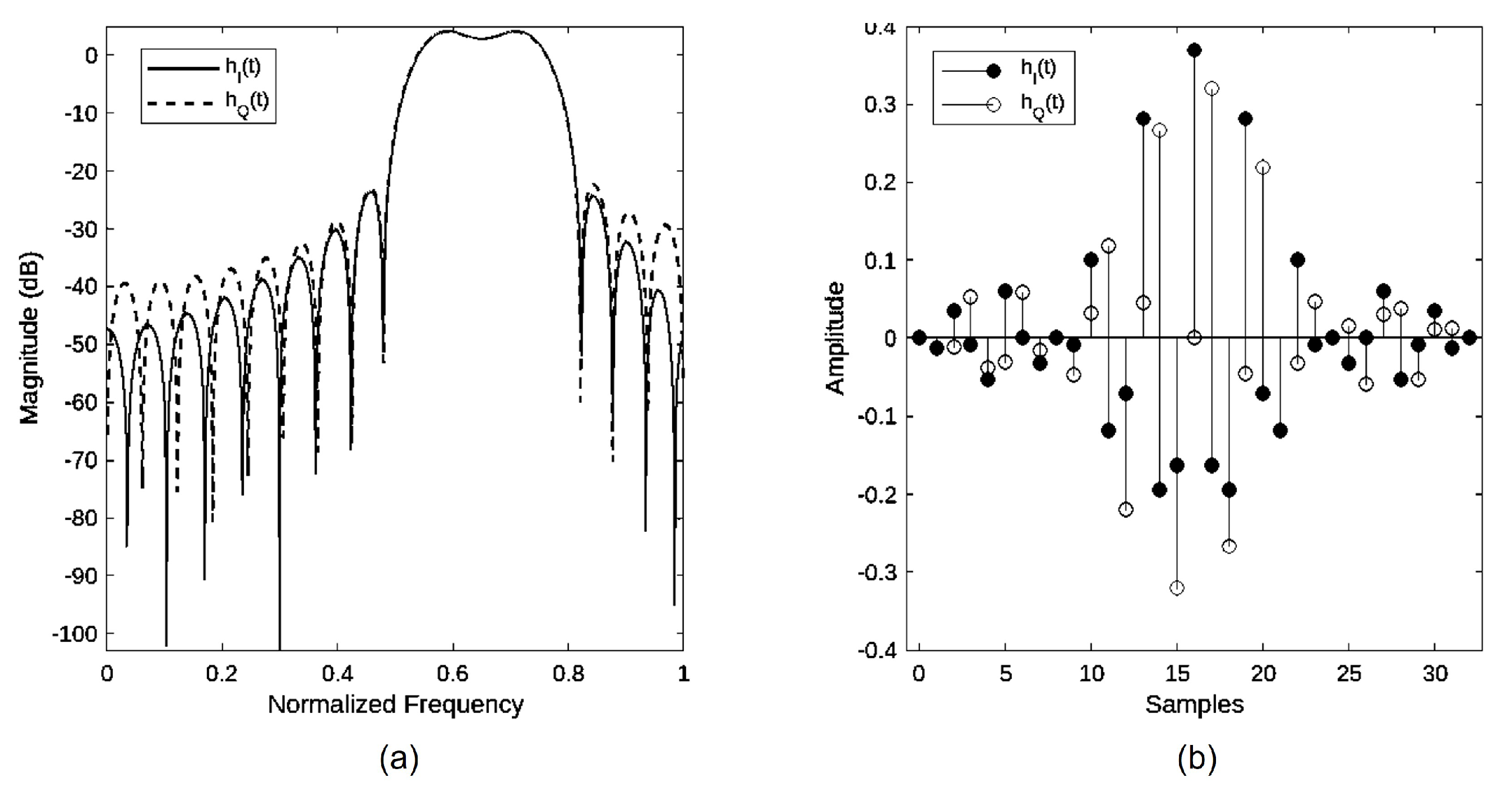
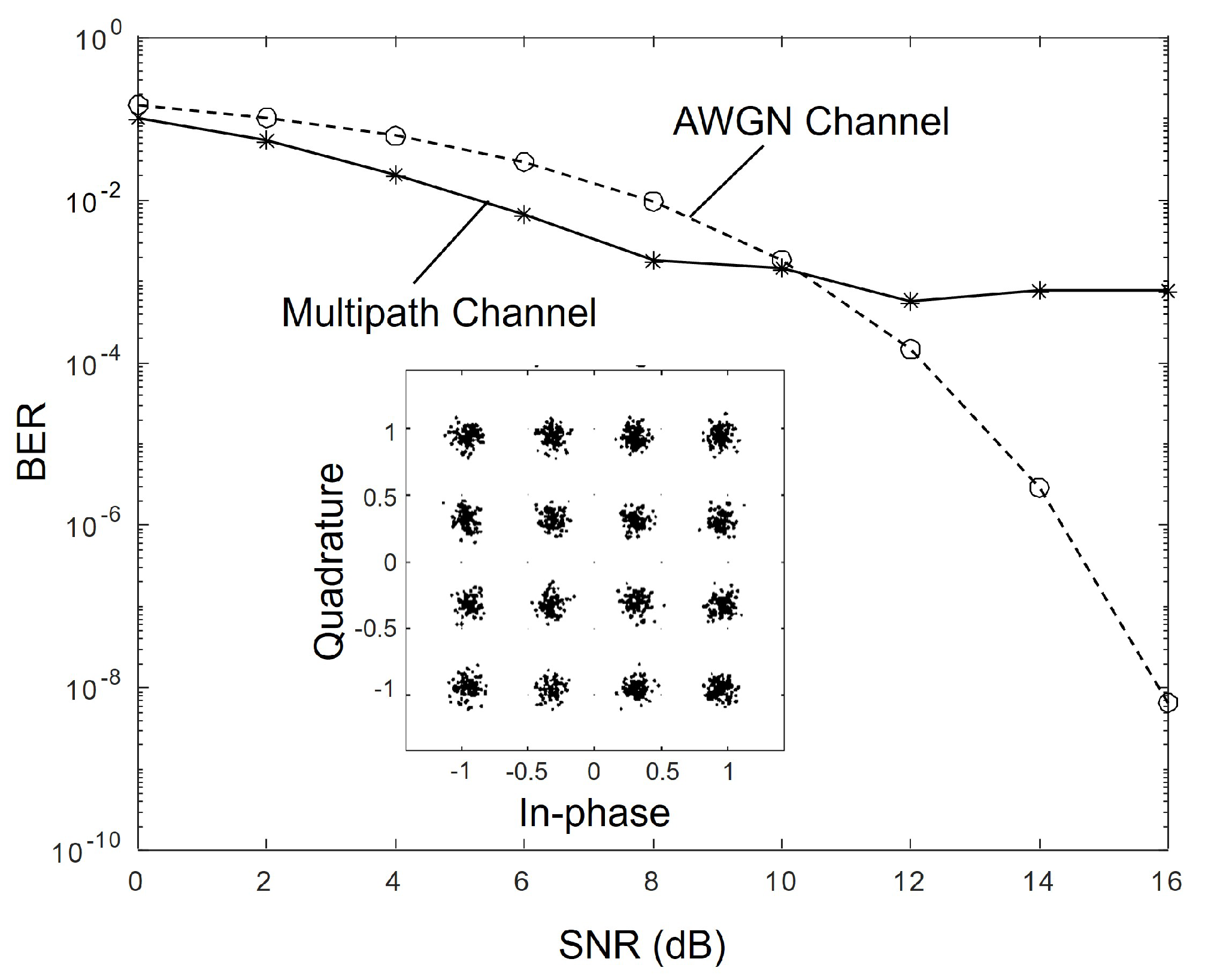
3.1. Performance Analysis of CAP Modulation
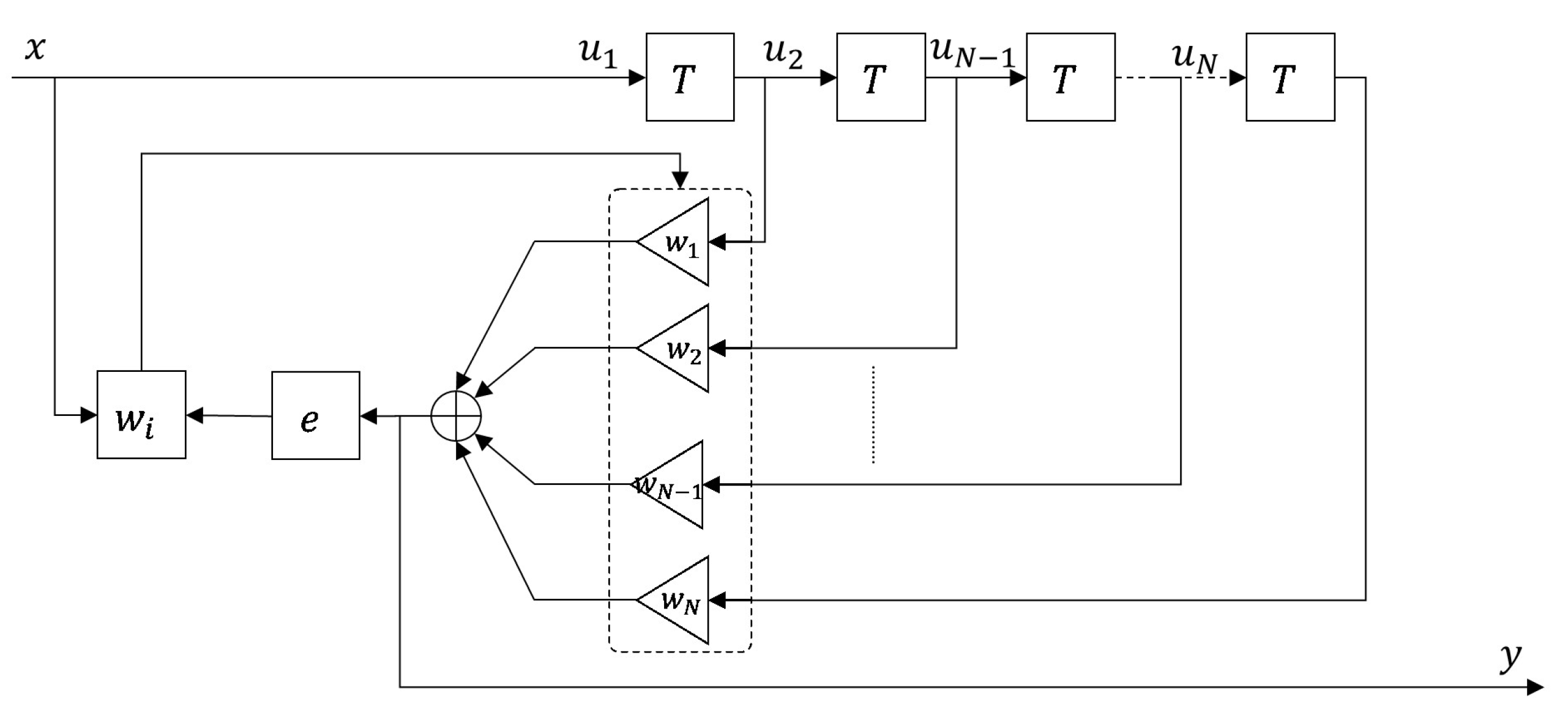
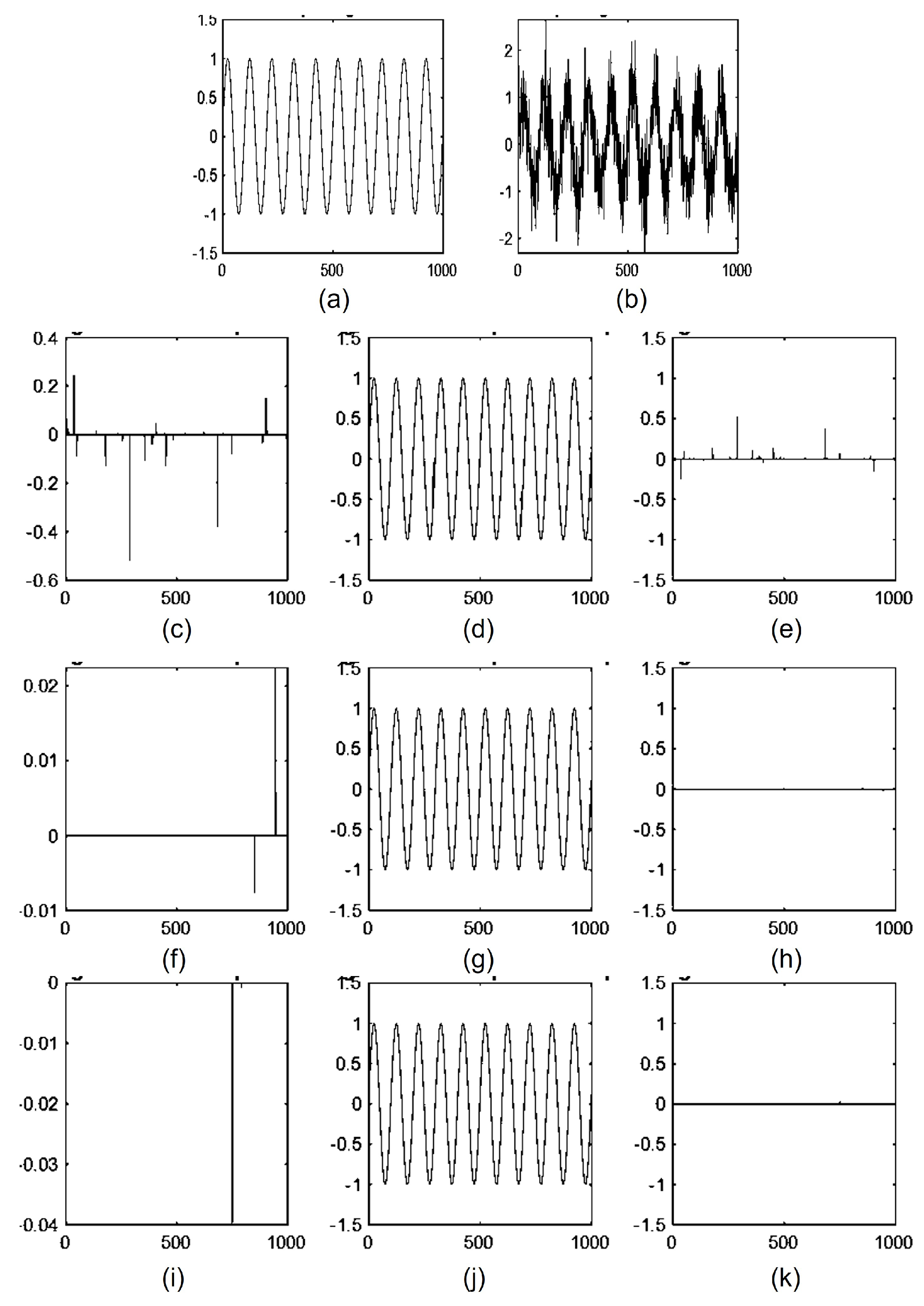
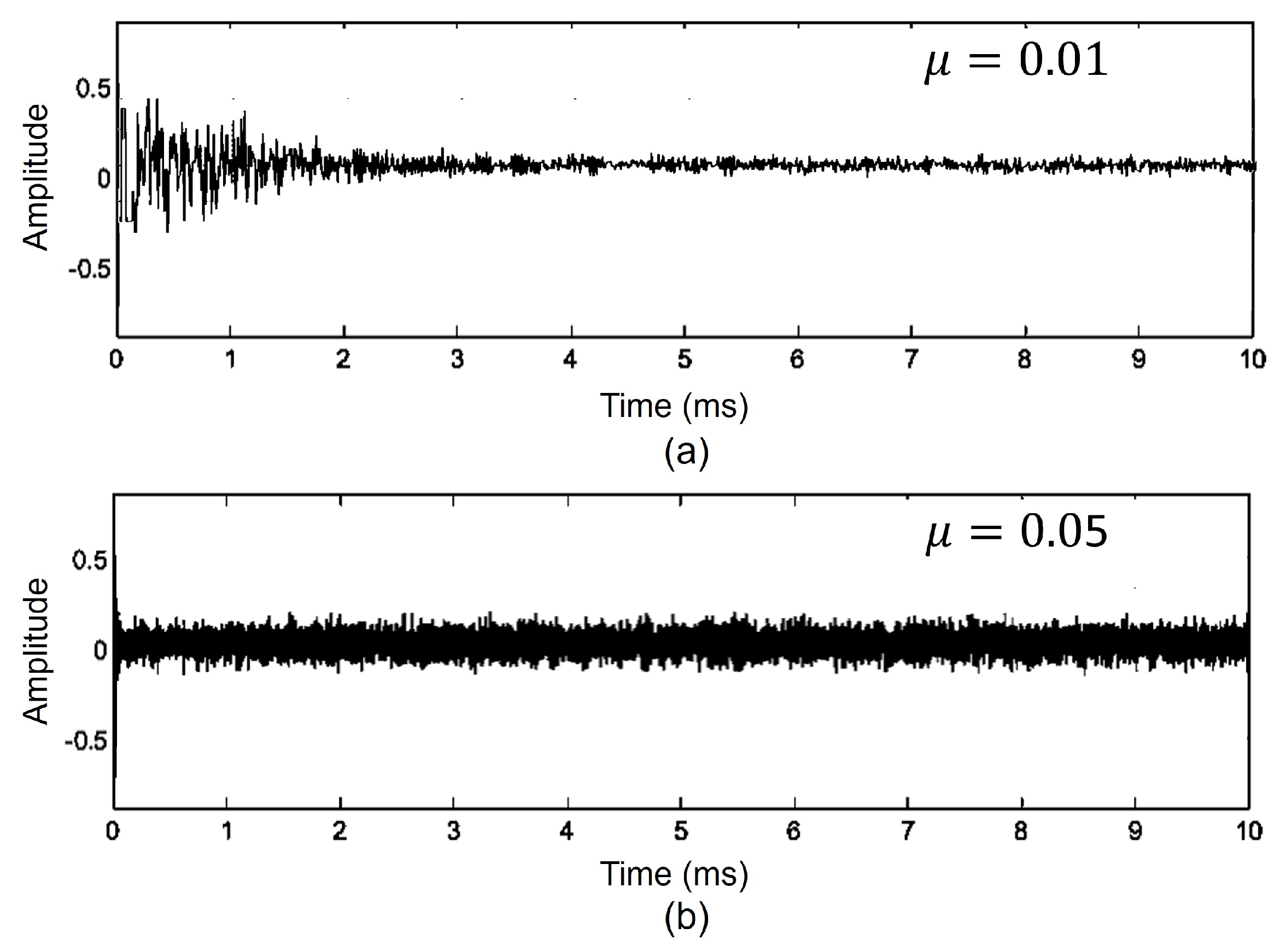
3.2. Performance Analysis of SDLMS Equalization
4. Modeling of CAP16 Modulator and SDLMS Equalizer for SD-VLC System
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komine, T.; Nakagawa, M. Fundamental Analysis for Visible-Light Communication System Using LED Lights. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2004, 50, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wook, H.B.C.; Haruyama, S.; Nakagawa, M. Visible Light Communication with LED Traffic Lights Using 2-Dimensional Image Sensor. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2006, 89, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C. What Is Lifi? J. Light. Technol. 2015, 34, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchardt, H.; Serafimovski, N.; Tsonev, D.; Videv, S.; Haas, H. VLC: Beyond Point-to-Point Communication. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chow, C.-W. Real-Time White-Light Phosphor-LED Visible Light Communication (VLC) with Compact Size. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 26192–26197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, L.U. Visible light communication: Applications, architecture, standardization and research challenges. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2017, 3, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewobi, S.S.; Djouani, K.; Kurien, A.M. Visible Light Communications for Internet of Things: Prospects and Approaches, Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions. Technologies 2022, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Joint Resource Management for Intelligent Reflecting Surface—Aided Visible Light Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 6508–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Chi, X.; Zhao, L.; Chaaban, A. Secure Visible Light Communications via Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiatmas, A.; Baggen, C.P.; Willems, F.M.; Linnartz, J.-P.M.; Bergmans, J.W. An Illumination Perspective on Visible Light Communications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Roy, B. An Approach to Ensure Joint Illumination & Communication Performance of a Forward Error Corrected Indoor Visible Light Communication (VLC) System in Presence of Ambient Light Interference. J. Opt. Commun. 2024, 44, s1767–s1776. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdenko, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Dao, T.; Chowdhury, K.; Leeser, M. Hardware-Software Codesign of Wireless Transceivers on Zynq Heterogeneous Systems. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2017, 6, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobai, R.; Sekanina, L. Towards Evolvable Systems Based on the Xilinx Zynq Platform. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Evolvable Systems (ICES), Singapore, 16–19 April 2013; pp. 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Šiaučiulis, M.; Northcote, D.; Goldsmith, J.; Crockett, L.H.; Kaladè, Š. 100 GBit/s RF Sample Offload for RFSoC Using GNU Radio and PYNQ. In Proceedings of the 2023 21st IEEE Interregional NEWCAS Conference (NEWCAS), Edinburgh, UK, 26-28 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, S.U. Adaptive Equalization. Proc. IEEE 1985, 73, 1349–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yi, X.; Wang, J.J.; Li, J. LED Modulation Characteristics in a Visible-Light Communication System. Opt. Photonics J. 2013, 3, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yan, B.; Teng, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, G. Improving The 3 dB Bandwidth of Medium Power GaN-Based LEDs through Periodic Micro via-Holes for Visible Light Communications. Opt. Commun. 2017, 392, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, M.; Kuboki, T.; Kato, K. Dimmable Optical OFDM Based on Discrete Hartley Transform for Indoor Visible Light Illumination and Communication. In Proceedings of the 2018 23rd Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 2–6 July 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Che, M.; Kuboki, T.; Kato, K. Proposal of Cost-Efficient and Low-Complexity Platform for Software Defined Visible Light Communication. In Proceedings of the 2017 22nd Microoptics Conference (MOC), Tokyo, Japan, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 330–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bamiedakis, N.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H. Carrierless amplitude and phase modulation in wireless visible light communication systems. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, C. Pairwise Coded m CAP with Chaotic Dual-Mode Index Modulation for Secure Bandlimited VLC Systems. Photonics 2022, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, M.; Othman, M.; Ridzuan, N.M.; Abdullah, M.; Mohamad, R.; Kanesan, T. Simulation of High Dimensionality Carrierless Amplitude Phase (CAP) Modulation Technique. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on Photonics (ICP), Kuching, Malaysia, 14–16 March 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Che, M.; Kuboki, T.; Kato, K. Trellis Coded Three Dimensional Carrierless Amplitude and Phase Modulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 24th OptoElectronics and Communications Conference (OECC) and 2019 International Conference on Photonics in Switching and Computing (PSC), Fukuoka, Japan, 7–11 July 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Tang, D.; Huang, B.; Chen, H. 200 Mb/s Visible Optical Wireless Transmission Based on NRZ-OOK Modulation of Phosphorescent White LED and a Pre-Emphasis Circuit. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2014, 12, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Minh, H.; O’Brien, D.; Faulkner, G.; Zeng, L.; Lee, K.; Jung, D.; Oh, Y.; Won, E.T. 100-Mb/s NRZ Visible Light Communications Using a Postequalized White LED. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2009, 21, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, H. A 550 Mbit/s Real-Time Visible Light Communication System Based on Phosphorescent White Light LED for Practical High-Speed Low-Complexity Application. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 27203–27213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chi, N. A Gb/s VLC Transmission Using Hardware Preequalization Circuit. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanoglu, M.; Dalveren, Y.; Catak, F.O.; Kara, A. Modelling and Design of Pre-Equalizers for a Fully Operational Visible Light Communication System. Sensors 2023, 23, 5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, M.; Kuboki, T.; Kato, K. Nonlinear Compensation for Indoor Visible Light Communication Systems with Carrierless Amplitude and Phase Modulation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SJJA02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Chen, G.-H.; Wei, L.-Y.; Chow, C.-W.; Lu, I.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yeh, C.-H.; Liu, Y. Adaptive Filtering for White-Light LED Visible Light Communication. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 016115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| QAM | CAP | |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier Generation | Digital NCO | No carrier needed |
| Computational Complexity | High (IQ mixing + phase tracking) | Lower (FIR-based filtering) |
| Hardware Complexity | Moderate (NCO + multipliers) | Low (FIR filters only) |
| IQ Imbalance | Present (sensitive to errors) | None (no IQ separation) |
| Phase Noise Sensitivity | Moderate (requires phase tracking) | None (no explicit carrier) |
| Spectral Efficiency | Comparable to CAP | Comparable to QAM |
| Suitability for IoT VLC | Flexible | Simple |
| LMS | SDLMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Computational Complexity | (Multiplications + Additions) | (Only Additions) |
| Multiplications per Iteration | 0 | |
| Additions per Iteration | N | N |
| Convergence Speed | Rapid | Slower |
| MSE Reduction | Rapid | Slower |
| Power Consumption | High | Low |
| Suitability for IoT VLC | High Processing Demand | Low-Power Applications |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, M. Software-Defined Visible Light Communication for Internet of Things: A Low-Complexity Approach. Telecom 2025, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020031
Che M. Software-Defined Visible Light Communication for Internet of Things: A Low-Complexity Approach. Telecom. 2025; 6(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Ming. 2025. "Software-Defined Visible Light Communication for Internet of Things: A Low-Complexity Approach" Telecom 6, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020031
APA StyleChe, M. (2025). Software-Defined Visible Light Communication for Internet of Things: A Low-Complexity Approach. Telecom, 6(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020031






