Resource Allocation Using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Networks in Industry 5.0 Scenario
Abstract
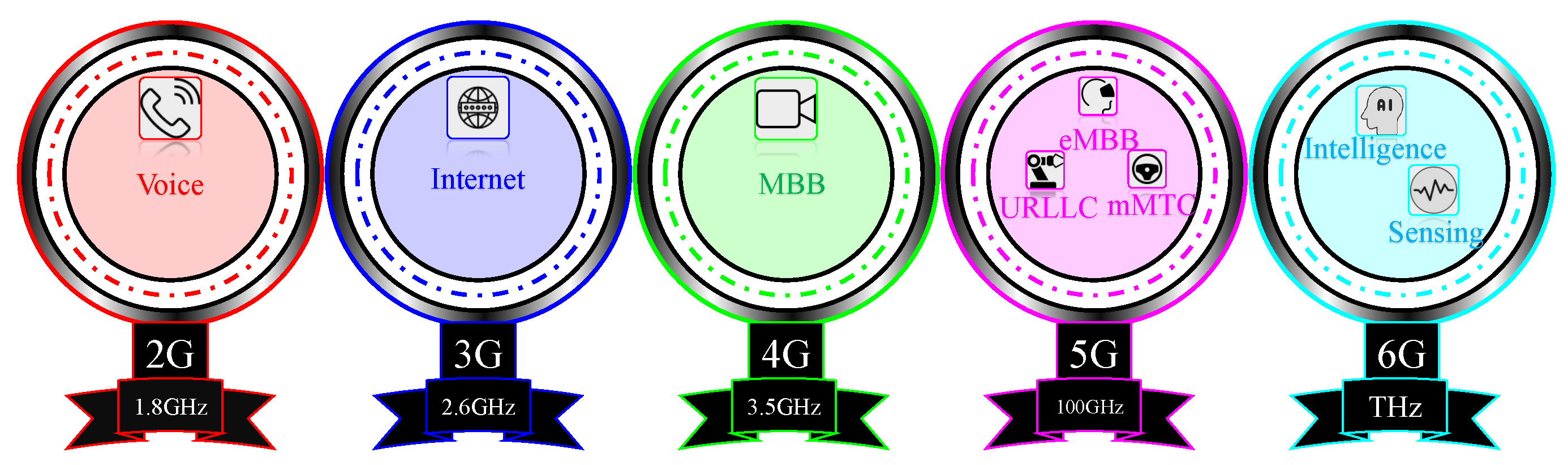
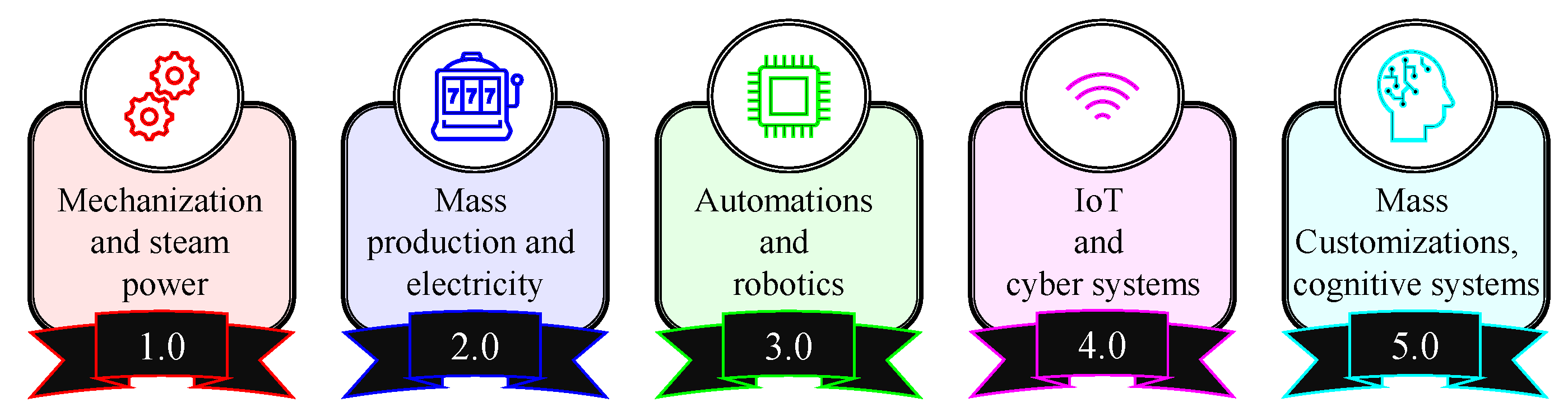
:1. Introduction
- We formulate an optimization problem in the RIS-assisted wireless network in the industry 5.0 scenario.
- We propose a novel algorithm to solve the optimization problem and evaluate EE, SE, throughput, and latency.
- We allocate resources and evaluate the channel mode.
- We compare the performance of the proposed algorithm with others.
2. Related Work
3. Scenario and Problem Formulation
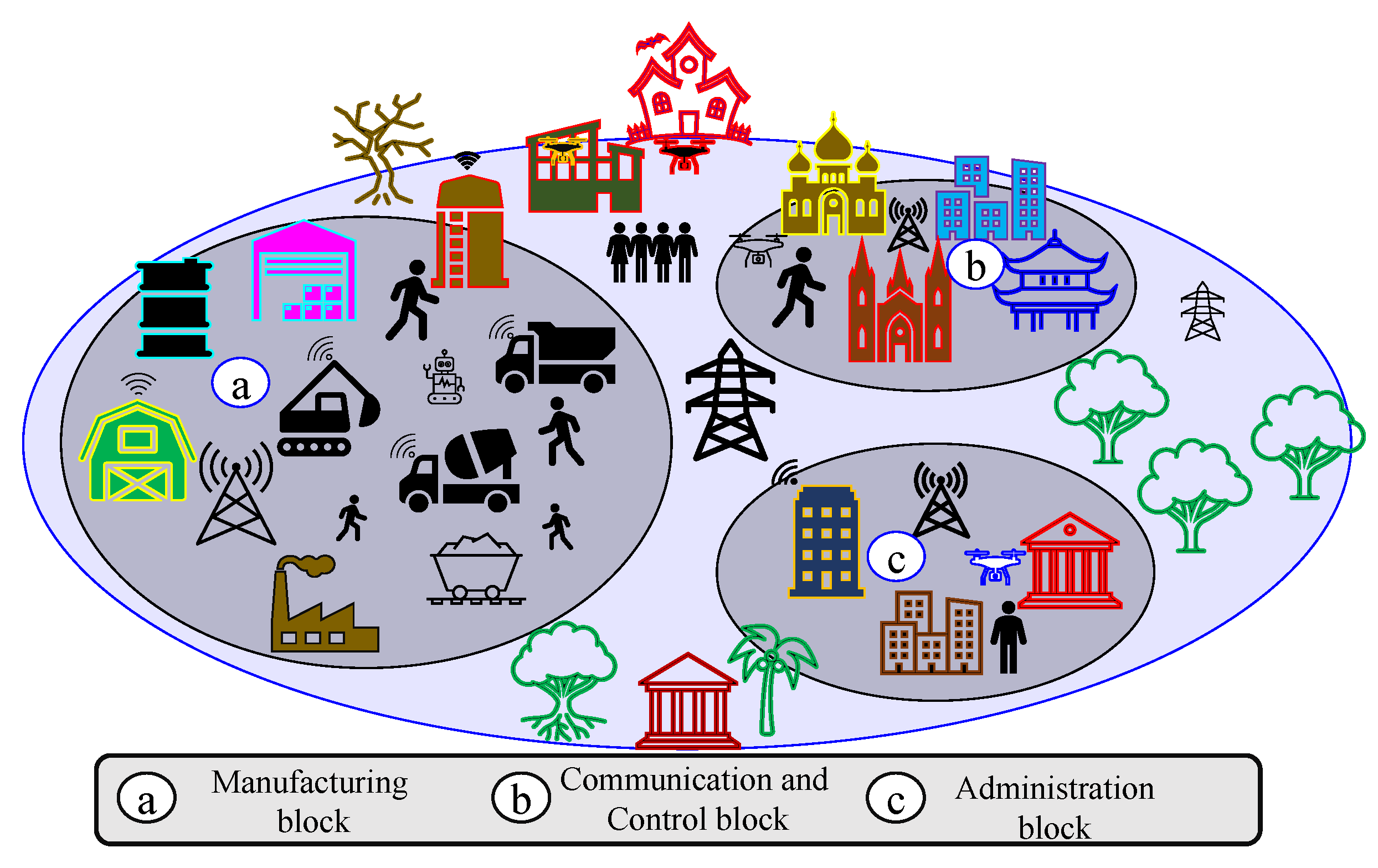
3.1. RIS-Assisted Scenario
3.2. Problem Formulation
- The power of cth connection must be greater than or equal to minimum power (8b).
- The SINR of cth connection must be greater than or equal to minimum SINR (8c).
- The power of cth connection must be greater than or equal to zero and less than or equal to maximum (8d).
- The data rate of cth connection must be greater than or equal to minimum data rate (8e).
- No power is allocated to non-connected . denotes the maximum transmission power of cth link while represents the cth channel power having u (8f).
- The minimum power of cth must be greater than or equal to 0 (8g).
4. Proposed Method
| Algorithm 1: OAA Algorithm |
 |
4.1. Description of OAA Algorithm
- Y is the set with objective U. It possesses constraints .
- U and are continuous differentiable.
- Optimal solution obtained by fixing the X satisfies all the constraints.
- If we have solution of X, we can obtain the optimal solution of U.
4.2. Resource Allocation
| Algorithm 2: Resource Allocation Algorithm |
 |
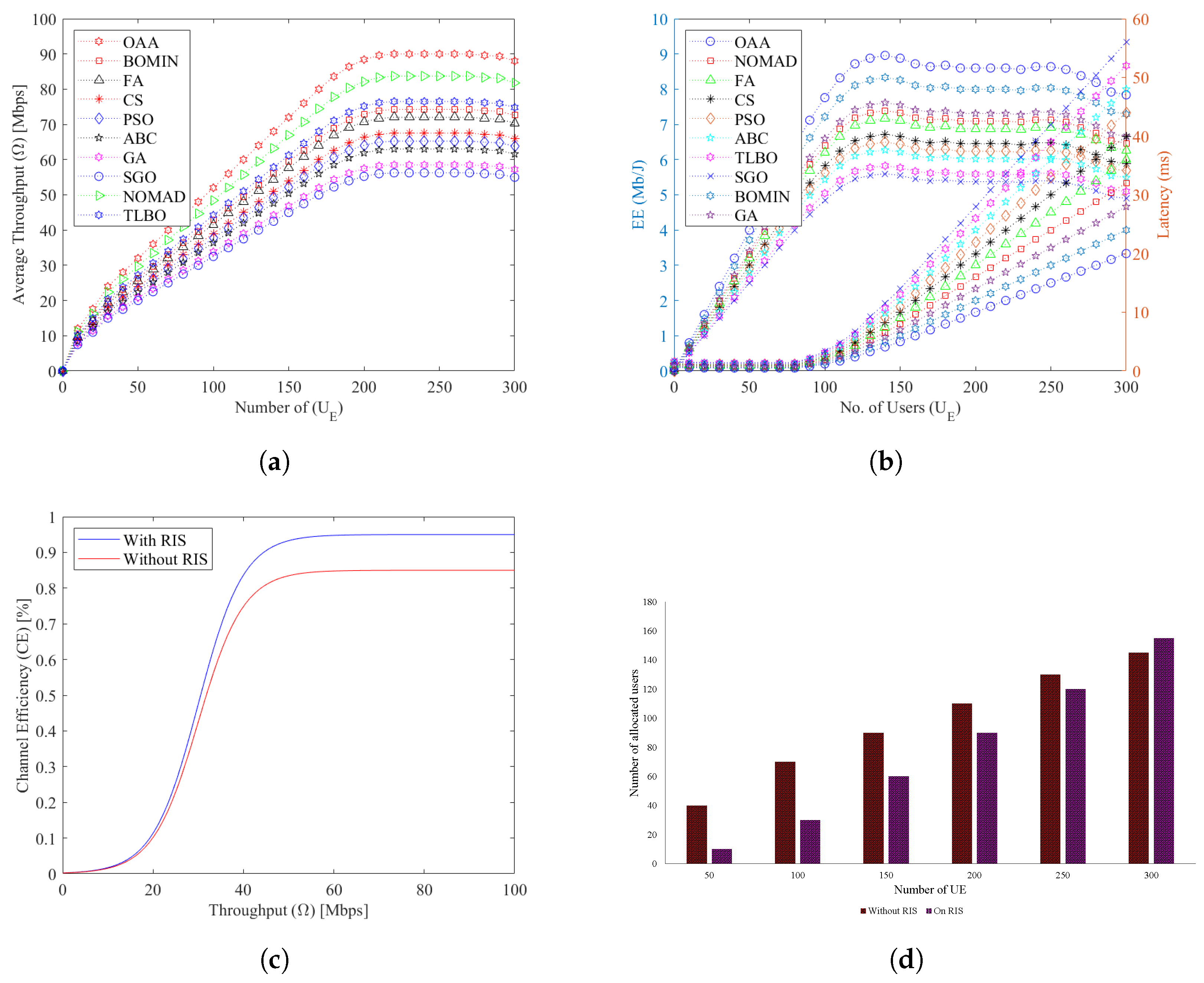
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Connell, E.; Moore, D.; Newe, T. Challenges Associated with Implementing 5G in Manufacturing. Telecom 2020, 1, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Özdogan, Ö.; Larsson, E.G. Intelligent Reflecting Surface Versus Decode-and-Forward: How Large Surfaces are Needed to Beat Relaying? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tekbıyık, K.; Kurt, G.K.; Yanikomeroglu, H. Energy-Efficient RIS-Assisted Satellites for IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, E.; Di Renzo, M.; De Rosny, J.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.-S.; Zhang, R. Wireless Communications Through Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116753–116773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tang, W.; Jin, S.; Wen, C.-K.; Ma, X. Large Intelligent Surface-Assisted Wireless Communication Exploiting Statistical CSI. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 8238–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Zappone, A.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Debbah, M.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Energy Efficiency in Wireless Communication. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di, B.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Poor, H.V. Hybrid Beamforming for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface based Multi-User Communications: Achievable Rates with Limited Discrete Phase Shifts. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ruan, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Shuang, Y.; Alù, A.; Qiu, C.-W.; Cui, T.J. Machine-learning reprogrammable metasurface imager. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaskos, C.; Nie, S.; Tsioliaridou, A.; Pitsillides, A.; Ioannidis, S.; Akyildiz, I. A New Wireless Communication Paradigm through Software-Controlled Metasurfaces. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Koutsonikolas, D.; Jornet, J.M. Enabling Indoor Mobile Millimeter-wave Networks Based on Smart Reflect-arrays. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2018—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–19 April 2018; pp. 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo, M.; Debbah, M.; Phan-Huy, D.-T.; Zappone, A.; Alouini, M.-S.; Yuen, C.; Sciancalepore, V.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Hoydis, J.; Gacanin, H.; et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable ai meta-surfaces: An idea whose time has come. EURASIP J. Wireless Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Renzo, M.; Zappone, A.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.; Yuen, C.; De Rosny, J.; Tretyakov, S. Smart Radio Environments Empowered by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: How It Works, State of Research, and The Road Ahead. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2450–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zheng, B.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Wen, M.; Chen, F.; Mumtaz, S. Adaptive Transmission for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Assisted OFDM Wireless Communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2653–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xu, D.; Schober, R. MISO Wireless Communication Systems via Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces: (Invited Paper). In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Changchun, China, 11–13 August 2019; pp. 735–740. [Google Scholar]
- Basar, E. Transmission Through Large Intelligent Surfaces: A New Frontier in Wireless Communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), Valencia, Spain, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, Q.-U.-A.; Kammoun, A.; Chaaban, A.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.-S. Asymptotic Max-Min SINR Analysis of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted MISO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 7748–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzzi, S.; D’Andrea, C.; Zappone, A.; Fresia, M.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Feng, S. Resource Allocation in Wireless Networks Assisted by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 31 August–3 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.; Jung, M.; Kasgari, A.T.Z.; Saad, W.; Bennis, M. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Energy-Efficient Networking with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. In Proceedings of the ICC 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Xu, W.; Shikh-Bahaei, M. Energy Efficient Rate Splitting Multiple Access (RSMA) with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Youn, J.; Son, W.; Jung, B.C. Physical-Layer Security Improvement with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for 6G Wireless Communication Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeyemi, K.; Owolawi, P.; Olakanmi, O. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface in Wireless-Powered Interference-Limited Communication Networks. Symmetry 2021, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Chehri, A.; Fortier, P. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for 5G and beyond Wireless Communications: A Comprehensive Survey. Energies 2021, 14, 8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Xiong, J.; Ng, D.W.K.; Yuen, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, X. Energy Efficiency and Spectral Efficiency Tradeoff in RIS-Aided Multiuser MIMO Uplink Transmission. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntontin, K.; Di Renzo, M.; Lazarakis, F. On the Rate and Energy Efficiency Comparison of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces with Relays. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 21st International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 26–29 May 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, M.; Jamil, S.; Ejaz, M.T.; Abbas, M.S. Energy Efficiency Maximization in RIS-assisted Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computing, Electronic and Electrical Engineering (ICE Cube), Quetta, Pakistan, 26–27 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Kumbhar, A.; Güvenç, İ.; Sichitiu, M.L. Intelligent Interference Management in UAV-Based HetNets. Telecom 2021, 2, 472–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennaceur, J.; Ahmadi, H.; Souhi, S. Game-Theoretical Approaches for Service Provisioning in Network Virtualization: Survey, Taxonomies and Open Challenges. Telecom 2021, 2, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.N.; Nguyen, V.-D.; Dobre, O.A.; Zhao, R. Energy Efficiency Maximization in RIS-Aided Cell-Free Network With Limited Backhaul. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Basak, S.; Peters, R.A., II. Particle swarm optimization: A survey of historical and recent developments with hybridization perspectives. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2019, 1, 157–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvakumar, B.; Muneeswaran, K. Firefly Algorithm-Based Feature Selection for Network Intrusion Detection. Comput. Secur. 2019, 81, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Hao, J.; Zheng, Y. Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm for Multi-Stage Resource Leveling Problem in Sharing Logistics Network. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 142, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareli, M.; Twala, B. An Adaptive Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Optimization. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2018, 14, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Chen, D.; Xu, Q. A Survey of Teaching Learning-Based Optimization. Neurocomputing 2019, 335, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimorelli, L.; Fecarotta, O. Optimal Regulation of Variable Speed Pumps in Sewer Systems. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2020, 2, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, S.P.; Rao, K.T.; Janakiramaiah, B. Effective Allocation of Resources and Task Scheduling in Cloud Environment using Social Group Optimization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, S.; Rahman, M.; Tanveer, J.; Haider, A. Energy Efficiency and Throughput Maximization Using Millimeter Waves–Microwaves HetNets. Electronics 2022, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C.; Lera, I.; Juiz, C. Genetic Algorithm for Multi-Objective Optimization of Container Allocation in Cloud Archi-tecture. J. Grid Comput. 2018, 16, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Research | Approach | Objective | Contributions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | Throughput | SE | Latency | Channel Allocation | |||
| [6] | Gradient descent search | ✓ | × | × | × | × | 300% higher EE |
| [28] | Alternating descent algorithm | ✓ | × | × | × | × | Signification gain in EE of cell-free network |
| [18] | DRL | ✓ | × | × | × | × | EE improved up to 77% by increasing the number of RIS element |
| [19] | Dinkelbach method | ✓ | × | × | × | × | The algorithm provided a significant improvement in the EE of D2D network |
| [23] | Accelerated projected gradient | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | × | Achieved higher EE in MIMO network |
| [24] | Power consumption method | ✓ | × | × | × | × | RIS network surpasses relay one in terms of both rate and EE |
| [25] | Approximation Algorithm | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | × | Maximization of throughput and EE in the RIS-assisted wireless network |
| This paper | OAA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Improved throughput, EE, SE of the network; minimized latency |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | dBW | |
| 10 | dBm | |
| 10 | dBm | |
| 0.1 | bits/s/Hz | |
| 2 | – | |
| 300 | – | |
| 32 | – | |
| 16 | – |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamil, S.; Rahman, M.; Abbas, M.S.; Fawad. Resource Allocation Using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Networks in Industry 5.0 Scenario. Telecom 2022, 3, 163-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom3010011
Jamil S, Rahman M, Abbas MS, Fawad. Resource Allocation Using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Networks in Industry 5.0 Scenario. Telecom. 2022; 3(1):163-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom3010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamil, Sonain, MuhibUr Rahman, Muhammad Sohail Abbas, and Fawad. 2022. "Resource Allocation Using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Networks in Industry 5.0 Scenario" Telecom 3, no. 1: 163-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom3010011
APA StyleJamil, S., Rahman, M., Abbas, M. S., & Fawad. (2022). Resource Allocation Using Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-Assisted Wireless Networks in Industry 5.0 Scenario. Telecom, 3(1), 163-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom3010011






