Device-Free Indoor Location Estimation System Using Commodity Wireless LANs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Channel Sounding Using IEEE 802.11n Wireless LANs
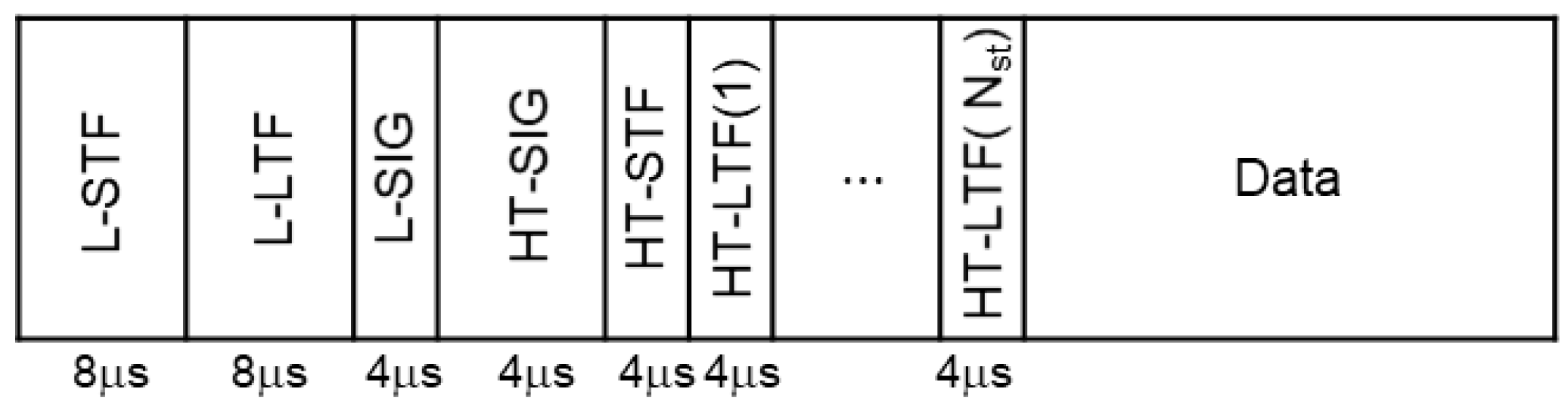
2.1. IEEE 802.11n
2.2. CSI Acquisition
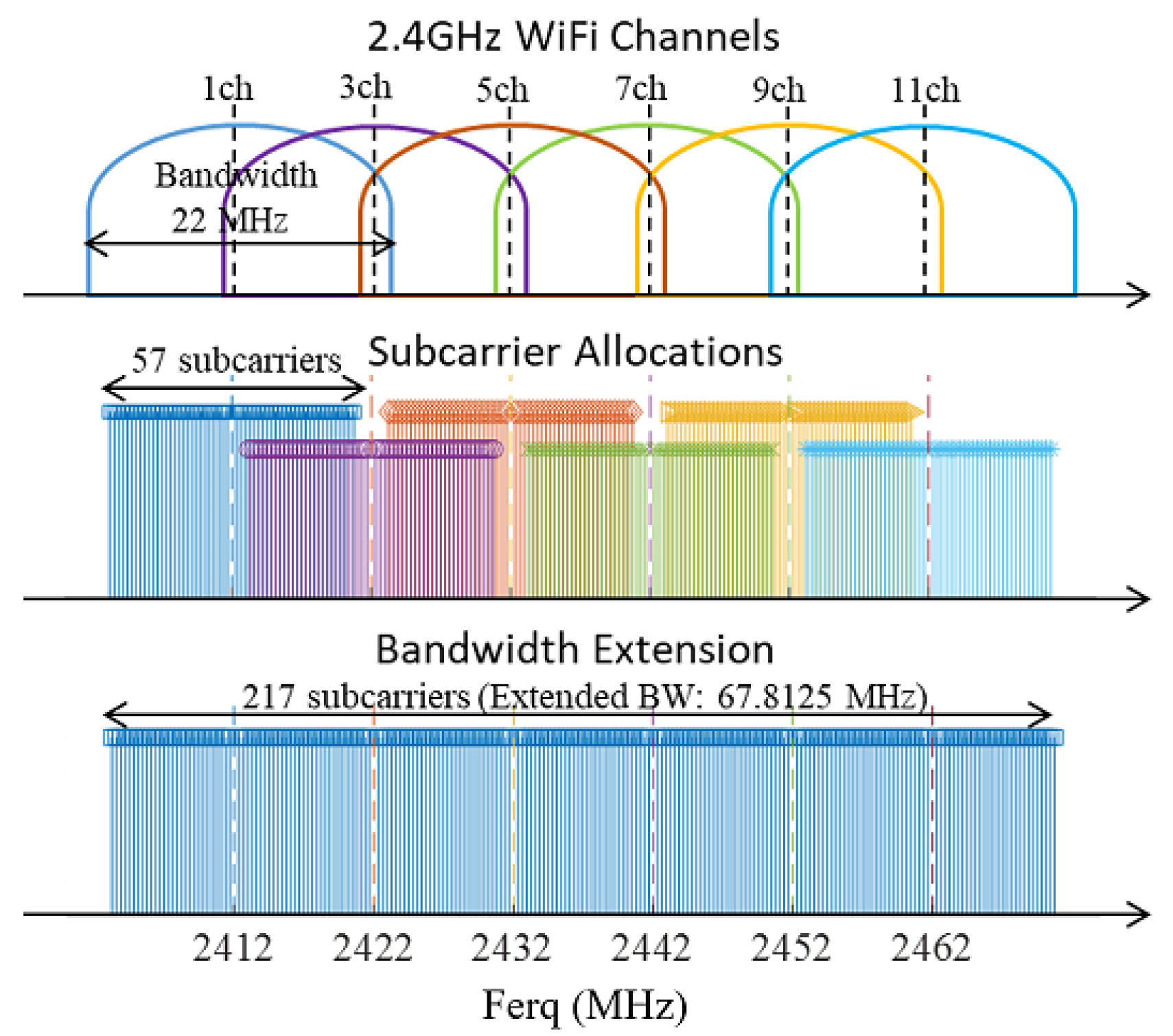
2.3. MIMO Channel Sounding
2.4. Developed System
2.4.1. System Configuration
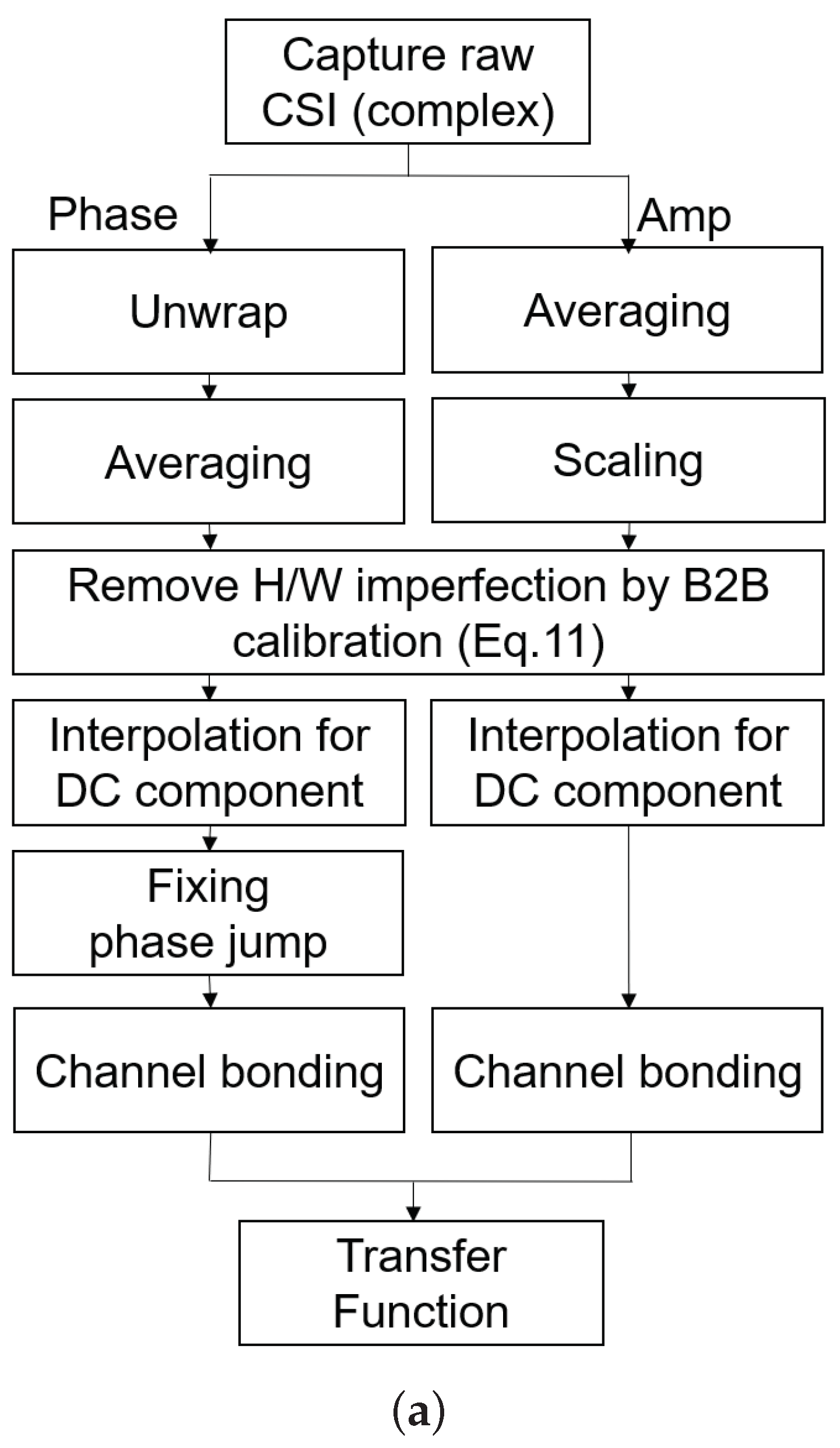
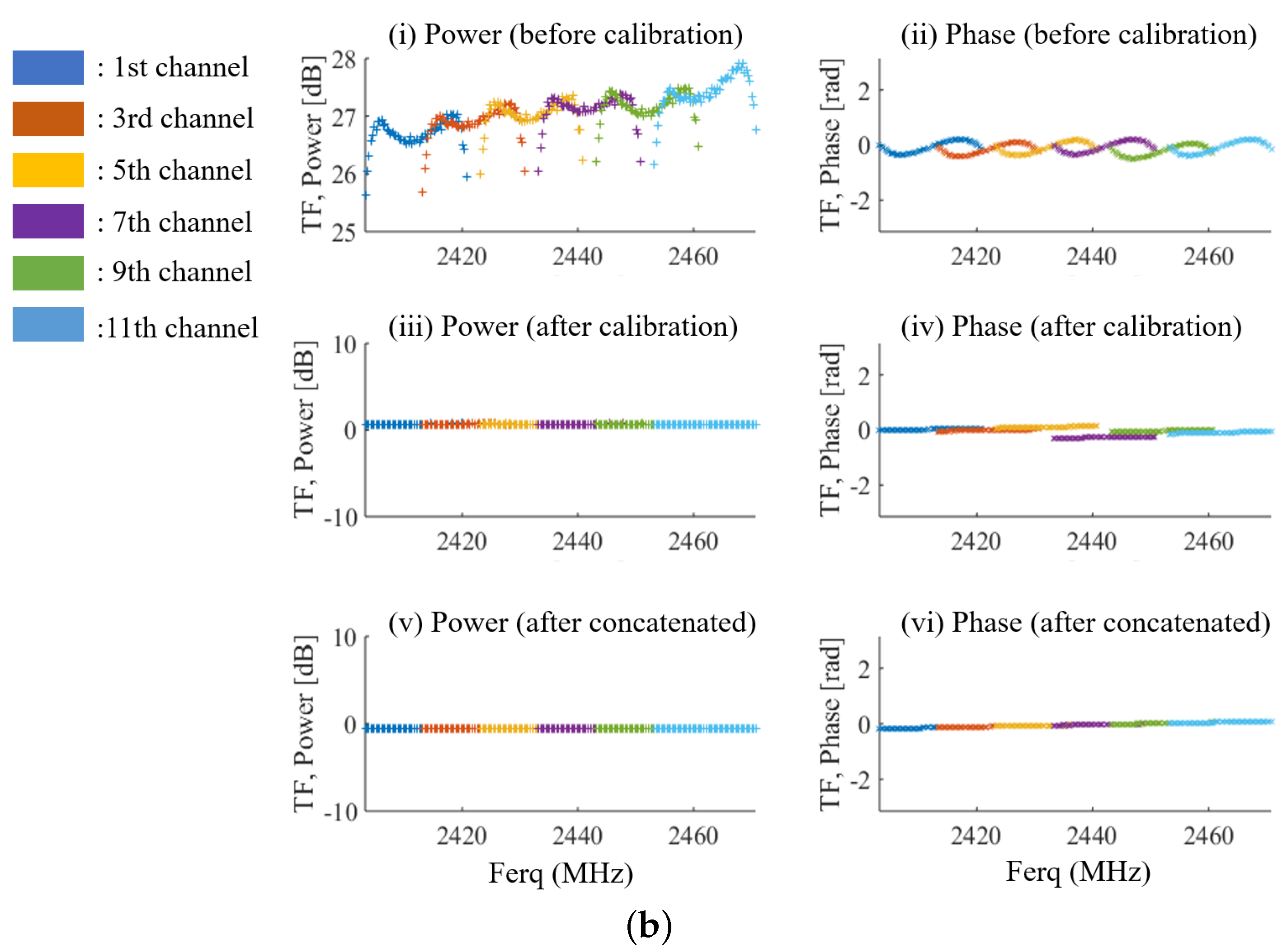
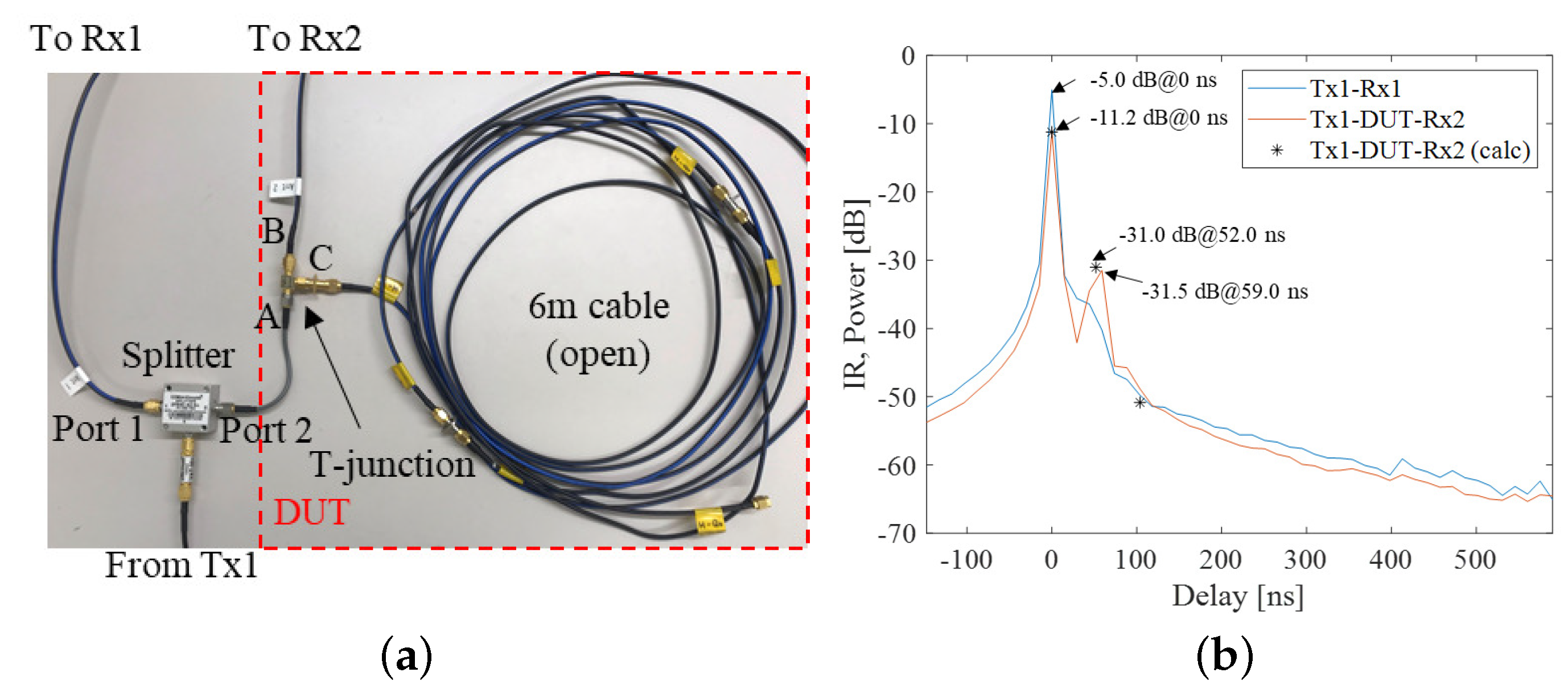
2.4.2. Back-To-Back Calibration
2.5. Evaluation
3. DF Indoor Location Estimation
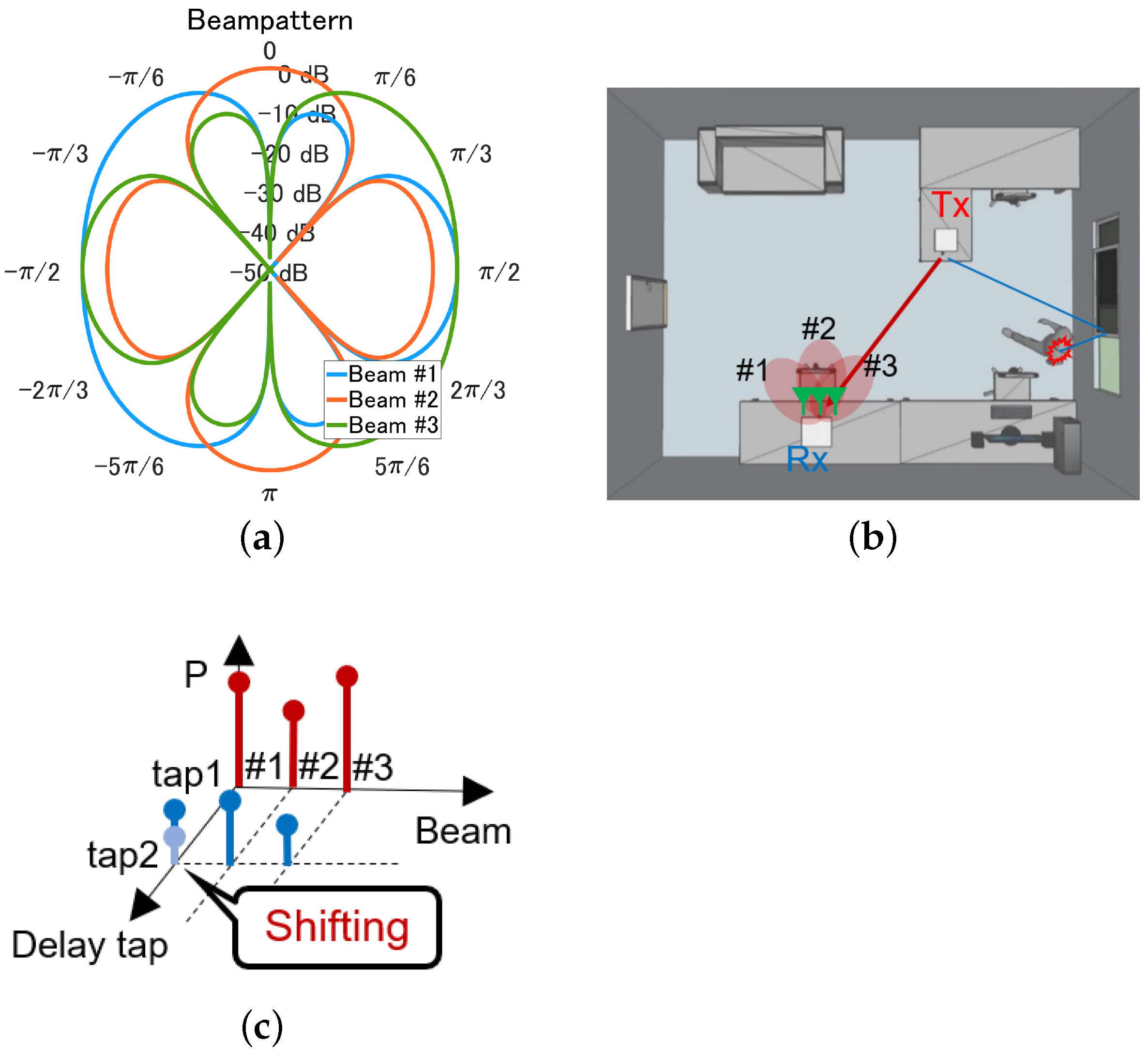
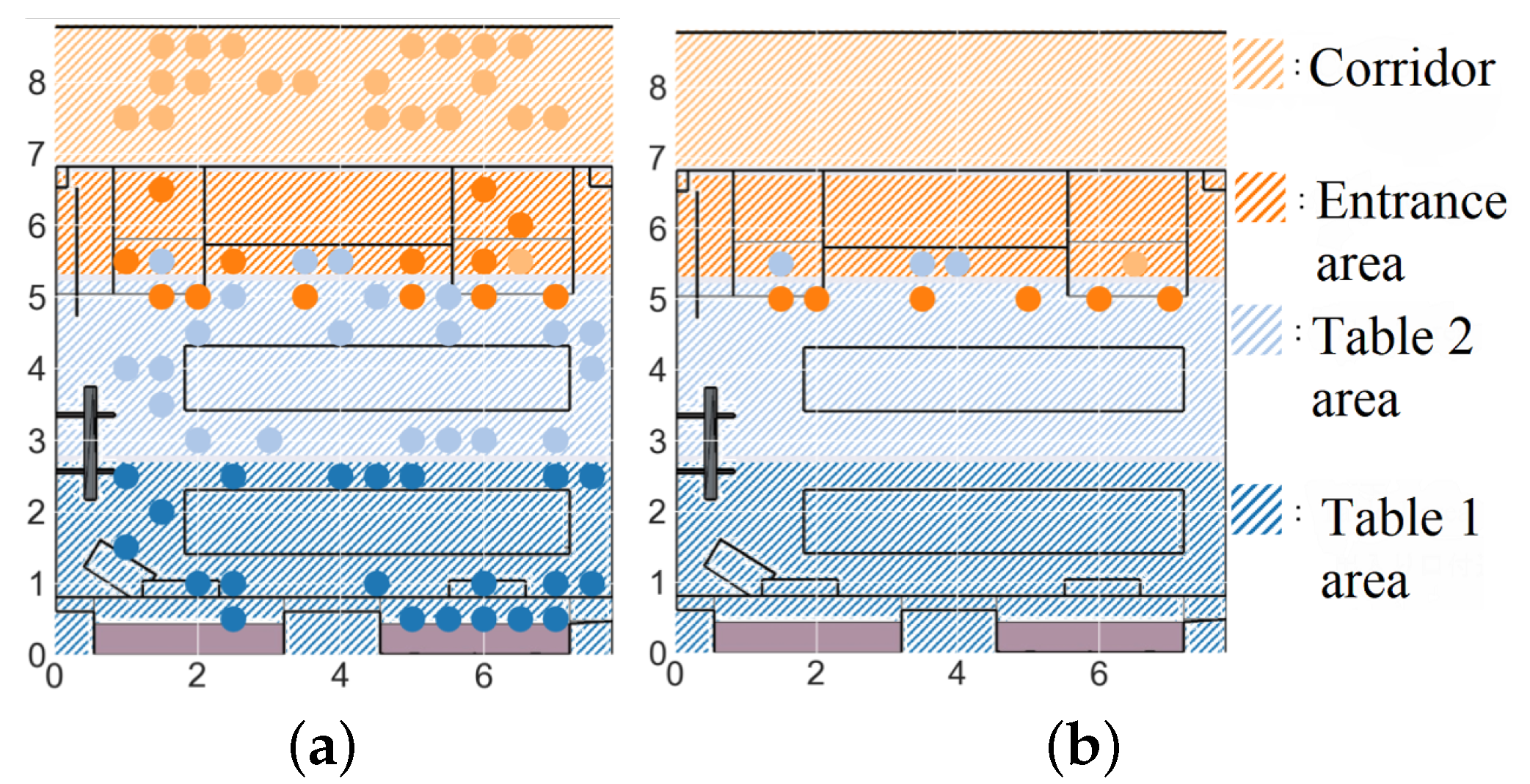
3.1. Experiment Scenario
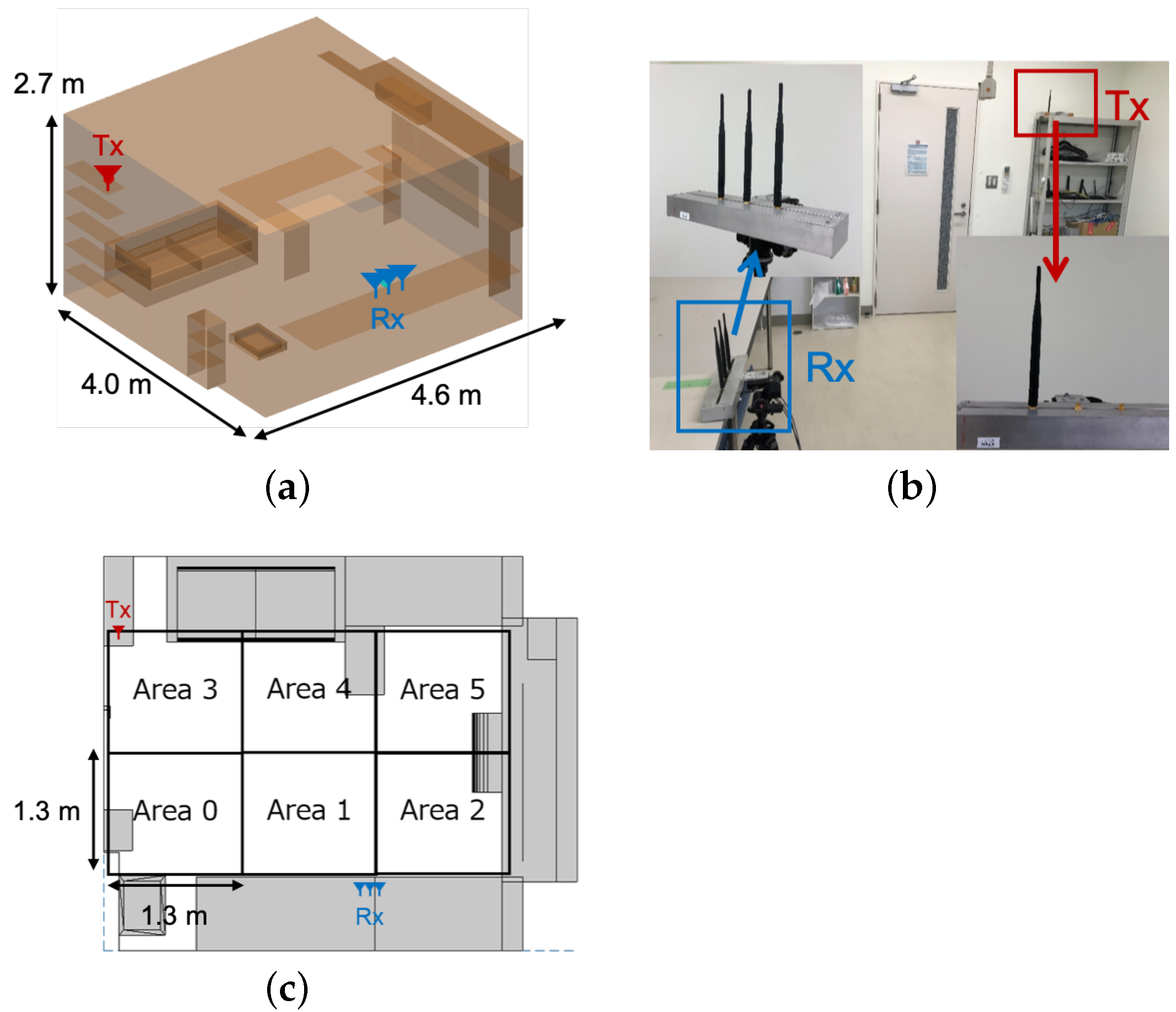
3.1.1. Small Office
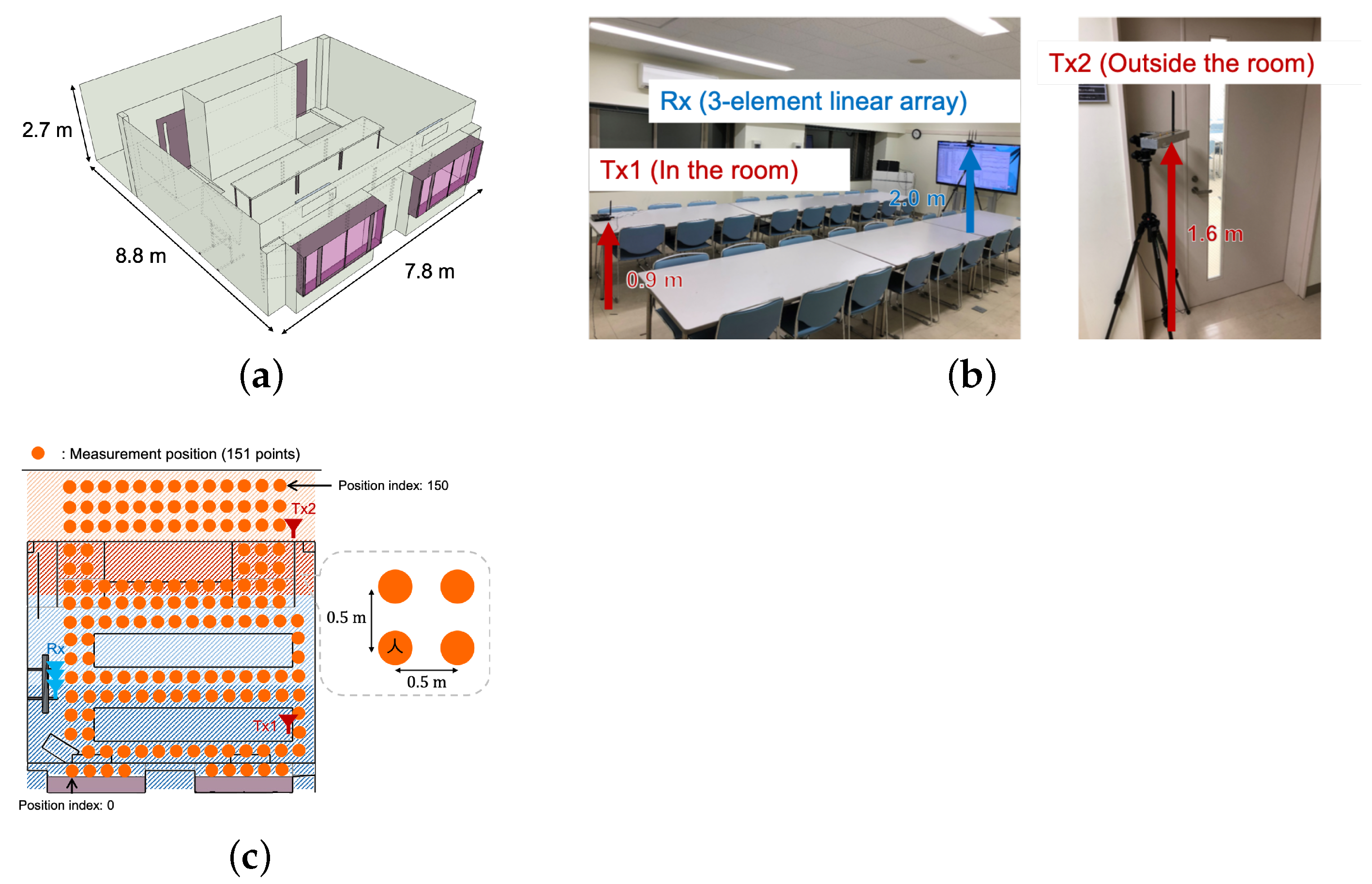
3.1.2. Conference Room
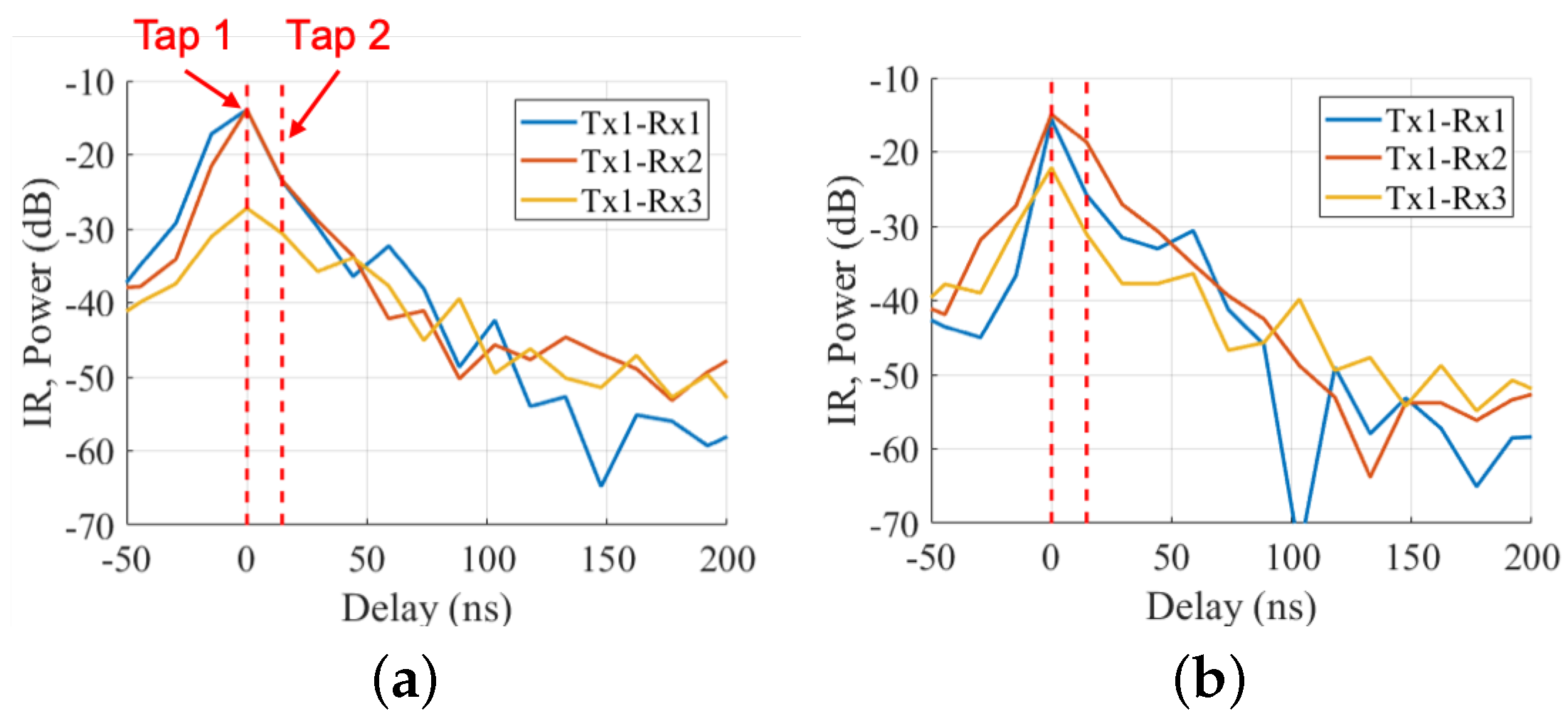
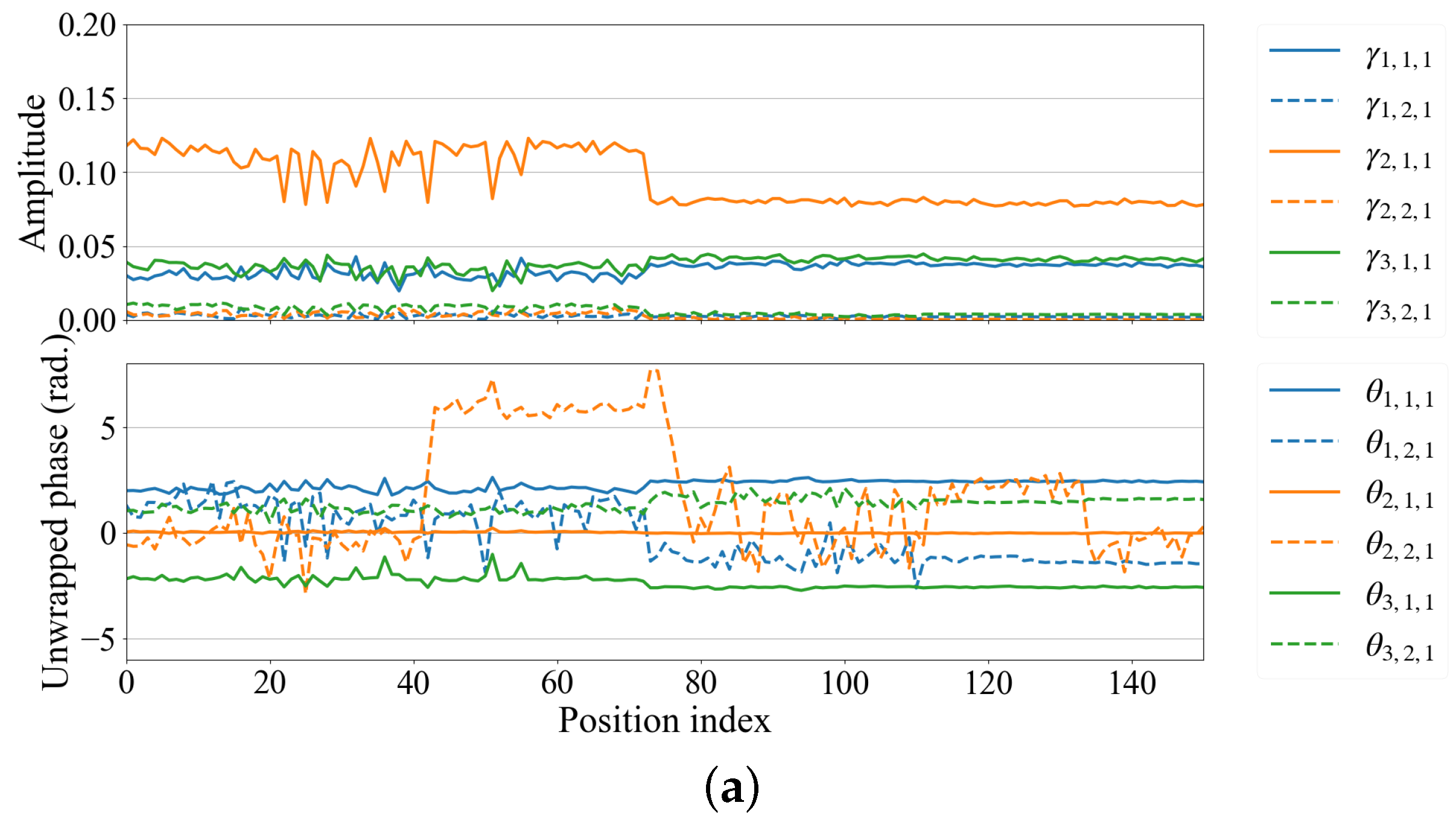
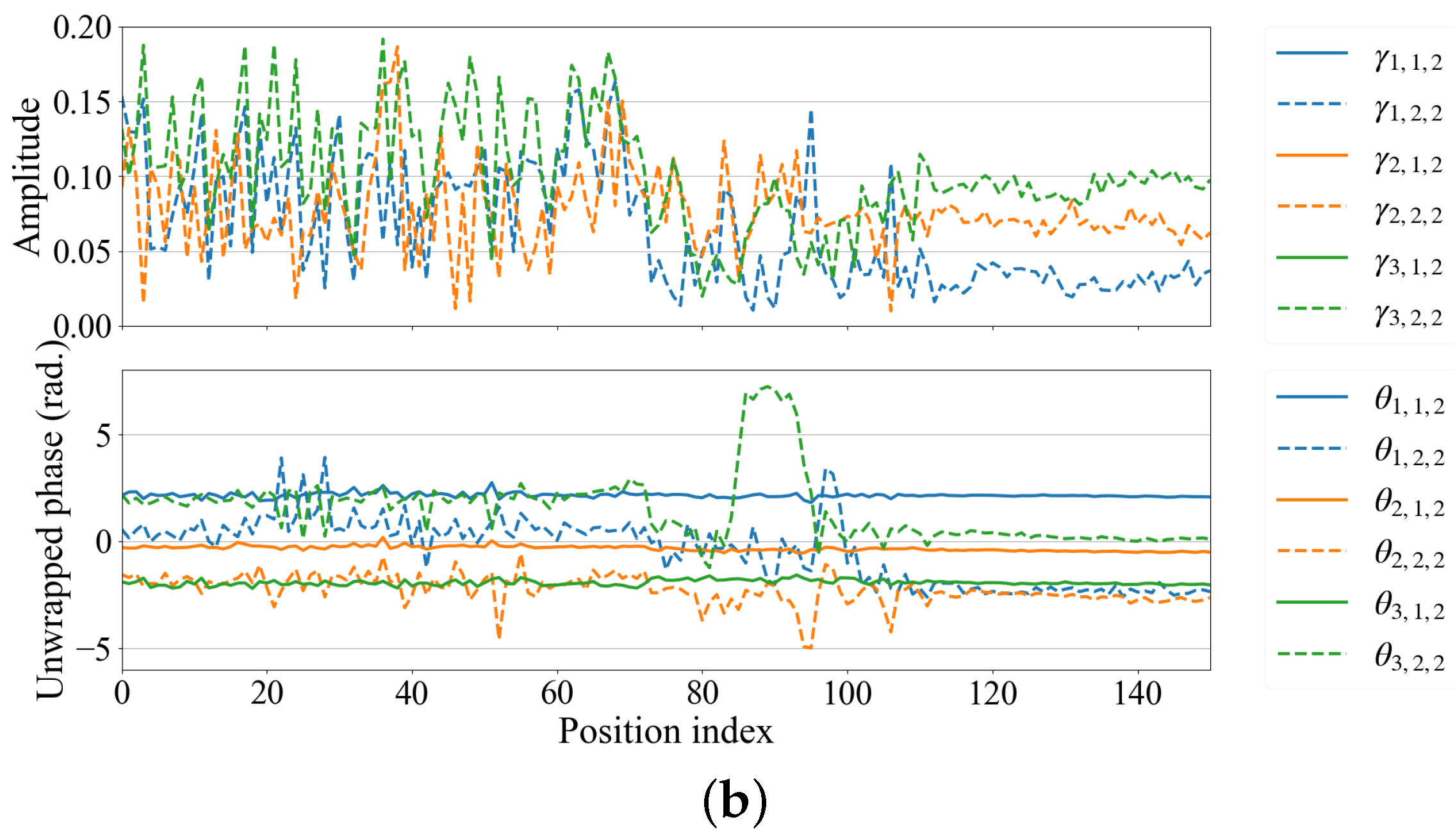
3.2. Signal Processing
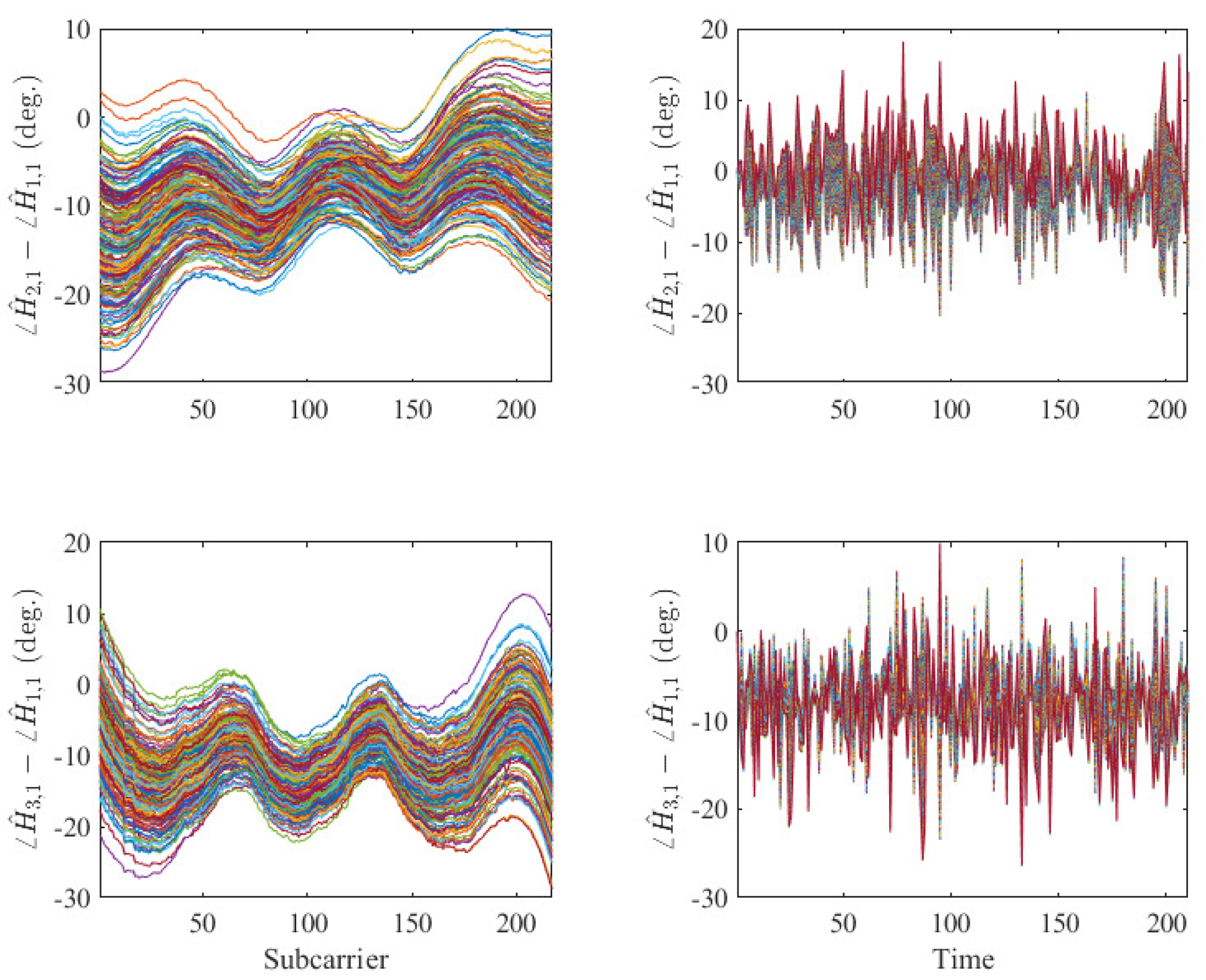
3.2.1. Existing Method
3.2.2. Proposed Method
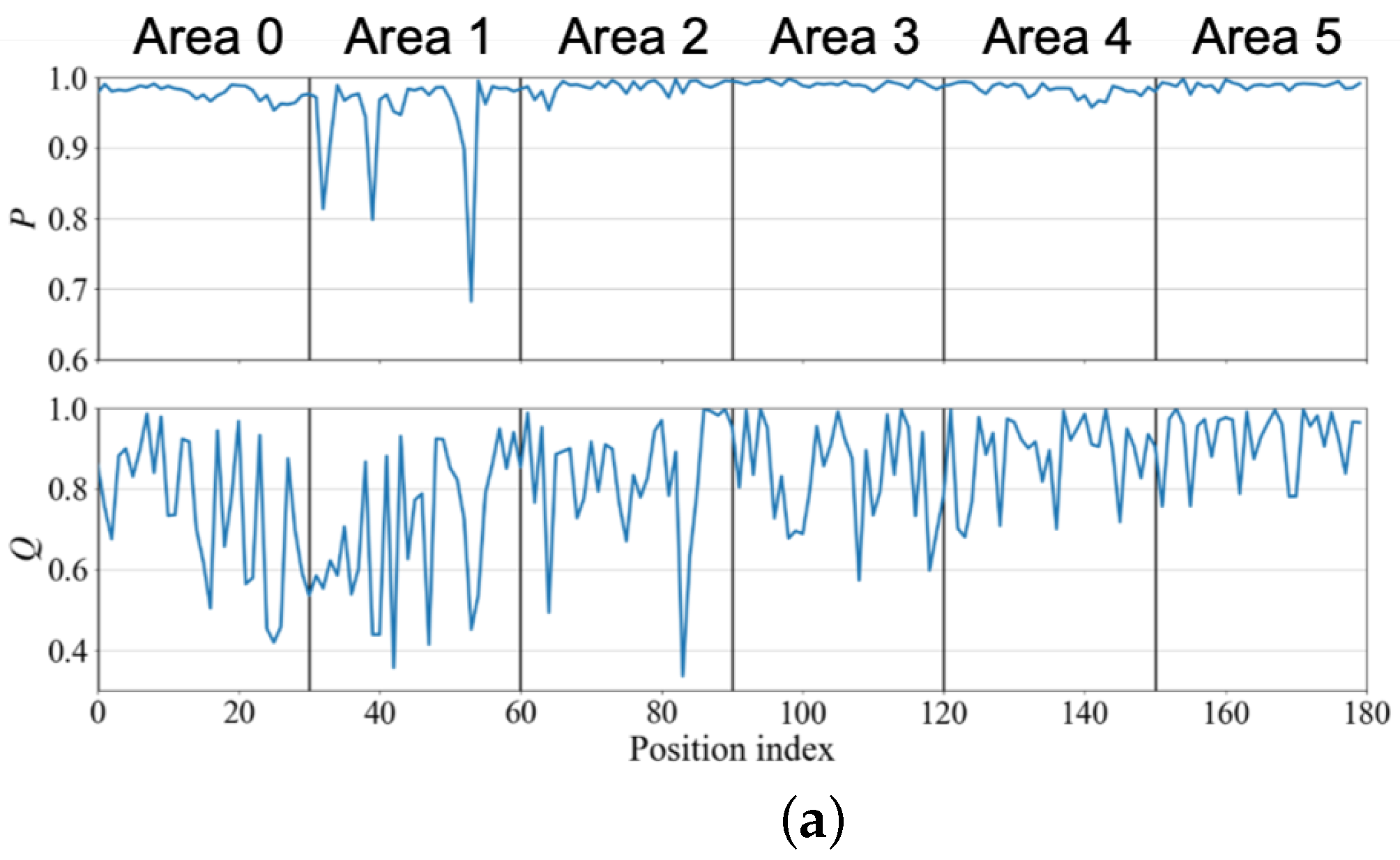
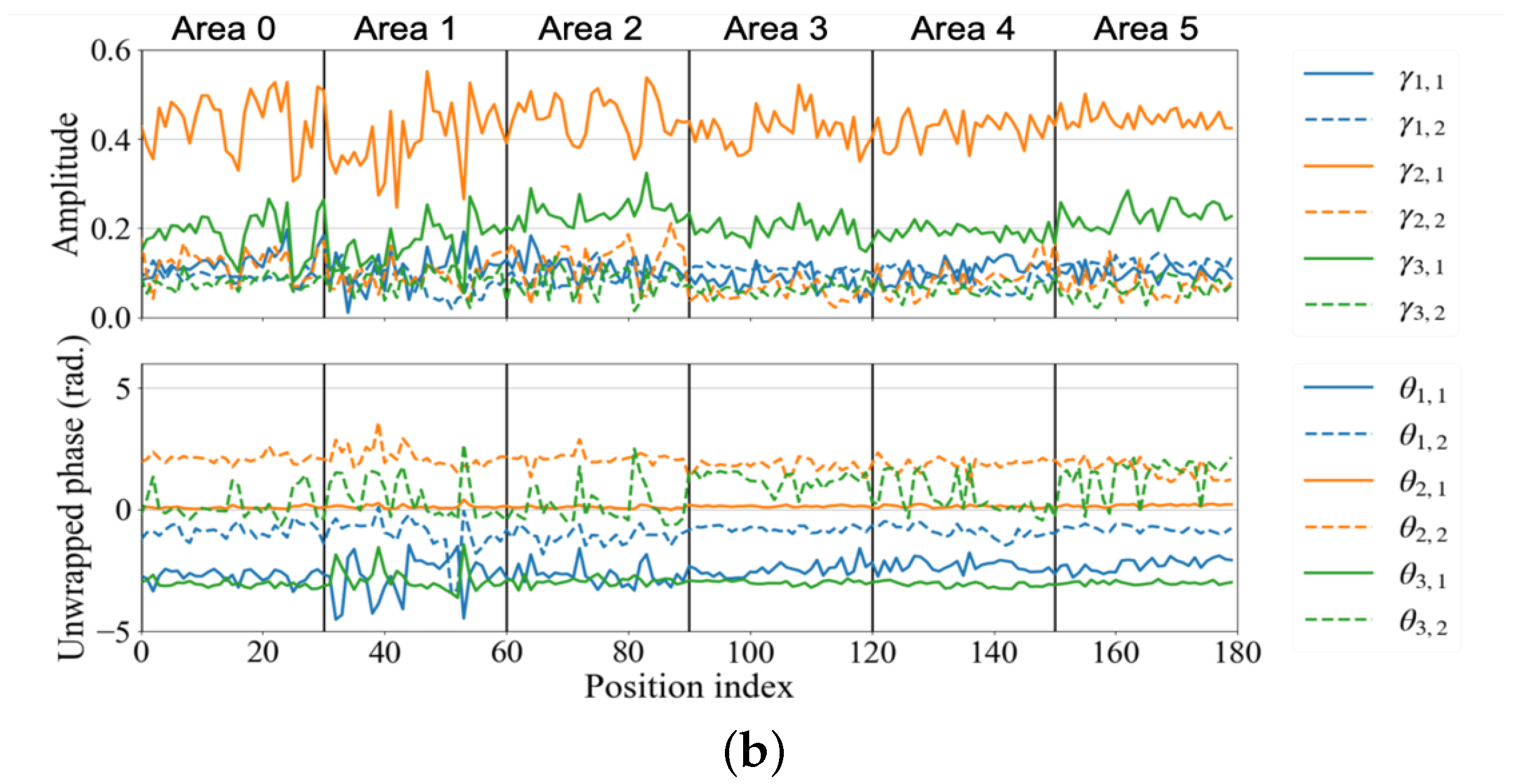
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Small Office
4.2. Conference Room
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rainer, M. Indoor Positioning Technologies; ETH Zurich Research Collection: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J. Global sales of video surveillance equipment projected to surpass 20 billion this year. Biometric Update, 10 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, E.; Hegarty, C. Understanding GPS Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fascista, A.; Coluccia, A.; Ricci, G. A Pseudo Maximum likelihood approach to position estimation in dynamic multipath environments. Signal Process. 2021, 181, 107907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyan, T.; Humphrey, D.; Hedle, M. WASP: A System and Algorithms for Accurate Radio Localization Using Low-Cost Hardware. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2011, 41, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hedley, M.; Collings, I.B.D. Humphrey. Indoor positioning based on ranging offset model and learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 1265–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Jeong, S.; Mok, E.; Xia, L.; Choi, C.; Pyeon, M. Application of WiFi-based indoor positioning system for labor tracking at construction sites: A case study in Guangzhou MTR. Autom. Constr. 2011, 20, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Shon, G. Indoor Localization Using Wi-Fi Based Fingerprinting and Trilateration Techiques for Lbs Applications. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, XXXVIII-4/C26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaemarungsi, K.; Krishnamurthy, P. Analysis of WLAN’s received signal strength indication for indoor location fingerprinting. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2012, 8, 292–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brena, R.F.; García-Vázquez, J.P.; Galván-Tejada, C.E.; Muñoz-Rodriguez, D.; Vargas-Rosales, C.; Fangmeyer, J. Evolution of Indoor Positioning Technologies: A Survey. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadh, S.A.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Ghourchian, N.; Allegue, M. Indoor Localization Based on Channel State Information. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Topical Conference on Wireless Sensors and Sensor Networks (WiSNet), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–23 January 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Xiao, J.; Yi, Y.; Chen, D.; Luo, X.; Ni, L. CSI-Based Indoor Localization. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2013, 24, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Mao, S.; Pandey, S. CSI-Based Fingerprinting for Indoor Localization: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altintas, B.; Serif, T. Improving RSS-Based Indoor Positioning Algorithm via K-Means Clustering. In Proceedings of the 17th European Wireless 2011–Sustainable Wireless Technologies, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 April 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, P.; Tao, X. Channel State Information Feedback with Zero-Overhead in Closed-Loop MIMO System. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2010, 93, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linux 802.11n CSI Tool. Available online: https://dhalperi.github.io/linux-80211n-csitool/ (accessed on 20 October 2019).
- Ohtsuki, T.; Hong, J. Activity Recognition Based on Array Sensor. In Proceedings of the APSIPA ASC 2011, Xi’an, China, 18–21 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa, S.; Kim, M. Intruder Detection Using Radio Wave Propagation Characteristics. In Proceedings of the ICCE-Asia 2018, Jeju, Korea, 24–26 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Standard for Information Technology– Local and Metropolitan Area Networks– Specific Requirements–Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC)and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 5: Enhancements for Higher Throughput; IEEE Std 802.11n-2009 (Amendment to IEEE Std 802.11-2007 as amended by IEEE Std 802.11k-2008, IEEE Std 802.11r-2008, IEEE Std 802.11y-2008, and IEEE Std 802.11w-2009); IEEE Std: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 29 October 2009; pp. 1–565.
- Yasushi, T.; Yusuke, A.; Yasuhiko, I. MIMO Technologies in Wireless LAN Systems. J. Inst. Image Inf. Telev. Eng. 2016, 51, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. Atheros CSI Tool. Available online: https://wands.sg/research/wifi/AtherosCSI/ (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Zhu, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chang, S. π-Splicer: Perceiving Accurate CSI Phases with Commodity WiFi Devices. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2018, 17, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lab of Innovation on Networking. π-Splicer. Available online: http://lion.sjtu.edu.cn/project/projectDetail?id=5 (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Tadayon, N.; Rahman, M.; Han, S.; Valaee, S.; Yu, W. Decimeter Ranging with Channel State Information. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 3453–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junction, T. BL41-6203-00, Orient Microwave Corp. Available online: http://www.orient-microwave.com/index.html (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Coaxial Cable Enviroflex_316. Huber+Shuner AG Corp. Available online: http://hubersuhner.com/en/ (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Vapnik, V.N.; Chervonenkis, A.Y. Pattern recognition using generalized portrait method. Autom. Remote Control 1963, 24, 774–780. [Google Scholar]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual ACM Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324 (accessed on 25 October 2019). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Duchesnay, E. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Python Software Foundation. Welcome to Python.org. Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Preferred Networks, Inc. Optuna—A Hyper Parameter Optimization Framework. Available online: https://optuna.org (accessed on 30 October 2019).




| Item | Values |
|---|---|
| Hardware | Linux (Kernel 4.1 Modified version) |
| (equipped with Rabortw AR9380 WiFi card) | |
| Software | AP (transmitter): hostapd, hostapd_cli |
| STA (receiver): WPA_supplicant | |
| 1 ch (2412 MHz), 3 ch (2422 MHz), | |
| WiFi channels | 5 ch (2432 MHz), 7 ch (2442 MHz), |
| 9 ch (2452 MHz), 11 ch (2462 MHz) | |
| Sub-carriers | 217 |
| Extend bandwidth | 67.8125 MHz (bonded by 6 channels) |
| Beacon interval | 15 ms (usually, 100 ms) |
| Packet transmission method | Send 50 packets in a row, and wait for 50 ms |
| Repeat while switching channels |
| Room Type | Small Office | Conference Room |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 4.0×4.6 () | 7.8×8.8 () |
| Bandwidth | 67.813 MHz (6 channel bonding) | |
| Transmitting antennas | 1 | 2 |
| Receiving antennas | 3-element linear array | |
| Element pattern | Omni-directional | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Kim, M.; Momose, H.; Yasukawa, S. Device-Free Indoor Location Estimation System Using Commodity Wireless LANs. Telecom 2021, 2, 181-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom2020012
Zhou Y, Kim M, Momose H, Yasukawa S. Device-Free Indoor Location Estimation System Using Commodity Wireless LANs. Telecom. 2021; 2(2):181-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom2020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuan, Minseok Kim, Hideaki Momose, and Satoru Yasukawa. 2021. "Device-Free Indoor Location Estimation System Using Commodity Wireless LANs" Telecom 2, no. 2: 181-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom2020012
APA StyleZhou, Y., Kim, M., Momose, H., & Yasukawa, S. (2021). Device-Free Indoor Location Estimation System Using Commodity Wireless LANs. Telecom, 2(2), 181-198. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom2020012







