Breastfeeding, Walking Onset, and Abdominal Obesity Are Determinants of Physical Fitness among Latin American and Spanish Schoolchildren: A Cross-Cultural Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials and Procedures
2.2.1. Anthropometric Measures
2.2.2. Physical Fitness
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Strength and Limitations
4.2. Practical Application
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palacios, G.; Pedrero-Chamizo, R.; Palacios, N.; Maroto-Sánchez, B.; Aznar, S.; González-Gross, M. Biomarkers of Physical Activity and Exercise. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ortega, F.; Leskošek, B.; Blagus, R.; Gil-Cosano, J.; Mäestu, J.; Tomkinson, G.; Ruiz, J.; Mäestu, E.; Starc, G.; Milanovic, I.; et al. European Fitness Landscape for Children and Adolescents: Updated Reference Values, Fitness Maps and Country Rankings Based on Nearly 8 Million Test Results from 34 Countries Gathered by the FitBack Network. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Román, P.; Consuegra González, P.; Martínez-Redondo, M.; Cardona Linares, A.; Salas-Sánchez, J.; Lucena Zurita, M.; Manjón Pozas, D.; Pérez Jiménez, I.; Aragón-Vela, J.; García-Pinillos, F.; et al. Complex Gait in Preschool Children in a Dual-Task Paradigm Is Related to Sex and Cognitive Functioning: A Cross-Sectional Study Providing an Innovative Test and Reference Values. Mind Brain Educ. 2020, 14, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Ruiz, J.; Castillo, M.; Sjöström, M. Physical Fitness in Childhood and Adolescence: A Powerful Marker of Health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambalis, K.; Mourtakos, S.; Panagiotakos, D.; Sidossis, L. Exclusive Breastfeeding Is Favorably Associated with Physical Fitness in Children. Breastfeed. Med. 2019, 14, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenni, O.; Chaouch, A.; Caflisch, J.; Rousson, V. Infant Motor Milestones: Poor Predictive Value for Outcome of Healthy Children. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, e181–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Mei, Q.; Yu, P.; Gao, Z.; Hu, Q.; Fekete, G.; István, B.; Gu, Y. Biomechanical Characteristics of the Typically Developing Toddler Gait: A Narrative Review. Children 2022, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.; Hyler-Both, D.; Danley, T.; Wallace, G. Biomechanics of Growth and Development in the Healthy Human Infant: A Pilot Study. J. Osteopath. Med. 2002, 102, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Messerli-Bürgy, N.; Kakebeeke, T.H.; Meyer, A.H.; Arhab, A.; Zysset, A.E.; Stülb, K.; Leeger-Aschmann, C.S.; Schmutz, E.A.; Kriemler, S.; Puder, J.J.; et al. Walking Onset: A Poor Predictor for Motor and Cognitive Skills in Healthy Preschool Children. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group; de Onis, M. Motor Development Study: Windows of Achievement for Six Gross Motor Development Milestones. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 450, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, G.; Jones, P.; Kuh, D.; Richards, M. Infant Developmental Milestones and Subsequent Cognitive Function. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuh, D.; Hardy, R.; Butterworth, S.; Okell, L.; Richards, M.; Wadsworth, M.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A. Developmental Origins of Midlife Physical Performance: Evidence from a British Birth Cohort. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar Cordero, M.; Baños, M.; Baena García, L.; Mur Villar, N.; Guisado Barrilao, R.; Sánchez López, A. Breastfeeding as a Method to Prevent Cardiovascular Diseases in the Mother and the Child. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Ness, A.; Gunnell, D.; Emmett, P.; Smith, G. Does Breast-Feeding in Infancy Lower Blood Pressure in Childhood? Circulation 2004, 109, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, D.; Cooper, A.; Bain, C.; Davey Smith, G.; Irwin, A.; Riddoch, C.; Ness, A. Associations of Birth Size and Duration of Breast Feeding with Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Childhood: Findings from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 23, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafa, M.; Heshmati, J.; Sadeghi, H.; Shidfar, F.; Namazi, N.; Baradaran, H.; Heydarpour, B.; Jalili, Z. Is Exclusive Breastfeeding and Its Duration Related to Cardio Respiratory Fitness in Childhood? J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heshmati, J.; Sepidarkish, M.; Shidfar, F.; Shokri, F.; Vesali, S.; Akbari, M.; Omani-Samani, R. Effect of Breastfeeding in Early Life on Cardiorespiratory and Physical Fitness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Breastfeed. Med. 2018, 13, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labayen, I.; Ruiz, J.; Ortega, F.; Loit, H.; Harro, J.; Villa, I.; Veidebaum, T.; Sjostrom, M. Exclusive Breastfeeding Duration and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Children and Adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.; Møller, L.; Brønd, J.; Jepsen, R.; Grøntved, A. Association between Parent and Child Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Lee, H.; Lumeng, J. Obesity-Associated Biomarkers and Executive Function in Children. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Padovani, P.; Rujinski, S.; Nicolosu, D.; Toma, C.; Turcu, A.; Cioboata, R. The Increase in Childhood Obesity and Its Association with Hypertension during Pandemics. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano-Ruiz, P.; García-Hermoso, A.; García-Prieto, J.; Sánchez-López, M.; Vizcaíno, V.; Solera-Martínez, M. Predictive Ability of Waist Circumference and Waist-to-Height Ratio for Cardiometabolic Risk Screening among Spanish Children. Nutrients 2020, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Román, P.; Guzmán-Guzmán, I.P.; Antonio Párraga-Montilla, J.; Caamaño-Navarrete, F.; Salas-Sánchez, J.; Palomino-Devia, C.; Reyes-Oyola, F.A.; Álvarez, C.; de la Casa-Pérez, A.; Cardona Linares, A.; et al. Healthy Lifestyles and Physical Fitness Are Associated with Abdominal Obesity among Latin-American and Spanish Preschool Children: A Cross-Cultural Study. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, A. Waist-to-Height Ratio—Time for a New Obesity Metric? Indian J. Pediatr. 2022, 89, 534–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Silva Dos Santos, S.; Santos, A.; Seabra, A.; Vale, S. Association between Sedentary Behavior Time and Waist-to-Height Ratio in Preschool Children. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2016, 28, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebeile, H.; Kelly, A.; O’Malley, G.; Baur, L. Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Epidemiology, Causes, Assessment, and Management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, C.; Kinmonth, H.; Dixon, J. The Social, Cultural and Familial Contexts Contributing to Childhood Obesity. In Global Perspectives on Childhood Obesity, Current Status, Consequences and Prevention; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeeg, D.; Christensen, U.; Lundby-Christensen, L.; Grabowski, D. Contextual Complexities in Implementing a Family-Based Childhood Obesity Intervention: The Perspectives of Enrolled Children and Their Parents. Children 2020, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, J.; Schwartz, S. Conceptual Considerations in Studies of Cultural Influences on Health Behaviors. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.; et al. Global, Regional and National Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adults 1980–2013: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP UNDP (United Nations Development Programme). Human Development Report 2021–2022: Uncertain Times, Unsettled Lives: Shaping Our Future in a Transforming World; UNDP: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, G.; Farías-Valenzuela, C.; Guzmán-Habinger, J.; Drenowatz, C.; Marques, A.; Kovalskys, I.; Gómez, G.; Rigotti, A.; Cortés, L.; Yépez García, M.; et al. Relationship between Socio-Demographic Correlates and Human Development Index with Physical Activity and Sedentary Time in a Cross-Sectional Multicenter Study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, A.; Hallal, P. Temporal Trends in Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes Ferrari, G.; Kovalskys, I.; Fisberg, M.; Gómez, G.; Rigotti, A.; Cortés Sanabria, L.; Yépez García, M.; Pareja Torres, R.; Herrera-Cuenca, M.; Zimberg, I.Z.; et al. Original Research Socio-Demographic Patterning of Self-Reported Physical Activity and Sitting Time in Latin American Countries: Findings from ELANS. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.; Riley, L.; Bull, F. Worldwide Trends in Insufficient Physical Activity from 2001 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 358 Population-Based Surveys with 1·9 Million Participants. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1077–e1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curilem Gatica, C.; Almagià Flores, A.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, F.; Yuing Farias, T.; Berral de la Rosa, F.; Martínez Salazar, C.; Jorquera Aguilera, C.; Bahamondes Ávila, C.; Solís Urra, P.; Cristi Montero, C.; et al. Assessment Body Composition in Children and Teens: Guidelines and Recommendations. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 734–738. [Google Scholar]
- Alves Junior, C.; Mocellin, M.; Andrade Gonçalves, E.; Silva, D.A.S.; Trindade, E.B.S.M. Anthropometric Indicators as Body Fat Discriminators in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Román, P.; García Pinillos, F.; Pantoja Vallejo, A.; Berrios Aguayo, B. Creativity and Physical Fitness in Primary School-aged Children. Pediatr. Int. 2017, 59, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.; España-Romero, V.; Ortega, F.; Sjöström, M.; Castillo, M.; Gutierrez, A. Hand Span Influences Optimal Grip Span in Male and Female Teenagers. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2006, 31, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Román, P.; Mora-López, D.; García-Pinillos, F. Effects of a Physical Activity Programme in the School Setting on Physical Fitness in Preschool Children. Child. Care. Health Dev. 2018, 44, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The Multistage 20 Metre Shuttle Run Test for Aerobic Fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical Scaling with Applications in Physical Work and the Perception of Exertion. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1990, 16, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, C.; Cordovil, R.; Rodrigues, L.; Gao, Z.; Goodway, J.; Sacko, R.; Nesbitt, D.; Ferkel, R.; True, L.; Stodden, D. Motor Competence and Health-Related Fitness in Children: A Cross-Cultural Comparison between Portugal and the United States. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bann, D.; Scholes, S.; Fluharty, M.; Shure, N. Adolescents’ Physical Activity: Cross-National Comparisons of Levels, Distributions and Disparities across 52 Countries. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, N.; Yaali, R.; Amani-Shalamzari, S.; Clark, C. The Effect of 8 Weeks of Child Designed vs Teacher Designed Games on Physical Fitness and Creativity in Children 8–10 Years. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 259, 114030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, R.; Bouzas, C.; Albertos, I.; García, C.; García, Á.; Prieto, T.; Velázquez, J.; Sánchez-Jiménez, E.; Rodríguez, R.; Martín, F.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life in Spanish Schoolchildren and Its Association with the Fitness Status and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Cumillaf, A.; Bizzozero-Peroni, B.; Tomkinson, G.; Brazo-Sayavera, J. Physical Fitness of Latin America Children and Adolescents: A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhurandhar, E. The Food-Insecurity Obesity Paradox: A Resource Scarcity Hypothesis. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 162, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, C.; Ravanbakht, S.; Flower, K.; Yin, H.S.; Rothman, R.; Sanders, L.; Delamater, A.; Perrin, E. Associations between Food Insecurity and Parental Feeding Behaviors of Toddlers. Acad. Pediatr. 2020, 20, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqout, M.; Michels, N.; Ahrens, W.; Börnhorst, C.; Molnár, D.; Moreno, L.; Eiben, G.; Siani, A.; Papoutsou, S.; Veidebaum, T.; et al. Associations between Exclusive Breastfeeding and Physical Fitness during Childhood. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artero, E.; Ortega, F.; España-Romero, V.; Labayen, I.; Huybrechts, I.; Papadaki, A.; Rodriguez, G.; Mauro, B.; Widhalm, K.; Kersting, M.; et al. Longer Breastfeeding Is Associated with Increased Lower Body Explosive Strength during Adolescence. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidelman, A.; Schanler, R. Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, S.; Griffiths, L.; Dezateux, C.; Law, C.; Peckham, C.; Butler, N.; Cole, T.; Bedford, H.; Tate, A.; Walton, S.; et al. The Impact of Maternal Employment on Breast-Feeding Duration in the UK Millennium Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, L.; Tate, A.; Dezateux, C.; Bartington, S.; Bedford, H.; Cole, T.; Hawkins, S.; Law, C.; Peckham, C.; Samad, L.; et al. Do Early Infant Feeding Practices Vary by Maternal Ethnic Group? Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caamaño-Navarrete, F.; Guzmán-Guzmán, I.; Palomino-Devia, C.; Reyes-Oyola, F.; Bustos-Barahona, R.; Jerez-Mayorga, D.; Delgado-Floody, P. The Association between Modifiable Lifestyle Behaviour in Latin-American Schoolchildren with Abdominal Obesity and Excess Weight. A Comparison of Chile and Colombia. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2022, 69, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaoutis, G.; Georgoulis, M.; Psarra, G.; Milkonidou, A.; Panagiotakos, D.; Kyriakou, D.; Bellou, E.; Tambalis, K.; Sidossis, L. Association of Anthropometric and Lifestyle Parameters with Fitness Levels in Greek Schoolchildren: Results from the EYZHN Program. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 325014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medrano, M.; Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Oses, M.; Villanueva, A.; Cabeza, R.; Idoate, F.; Sanz, A.; Rodríguez-Vigil, B.; Ortega, F.; Ruiz, J.; et al. Associations of Fitness and Physical Activity with Specific Abdominal Fat Depots in Children with Overweight/Obesity. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
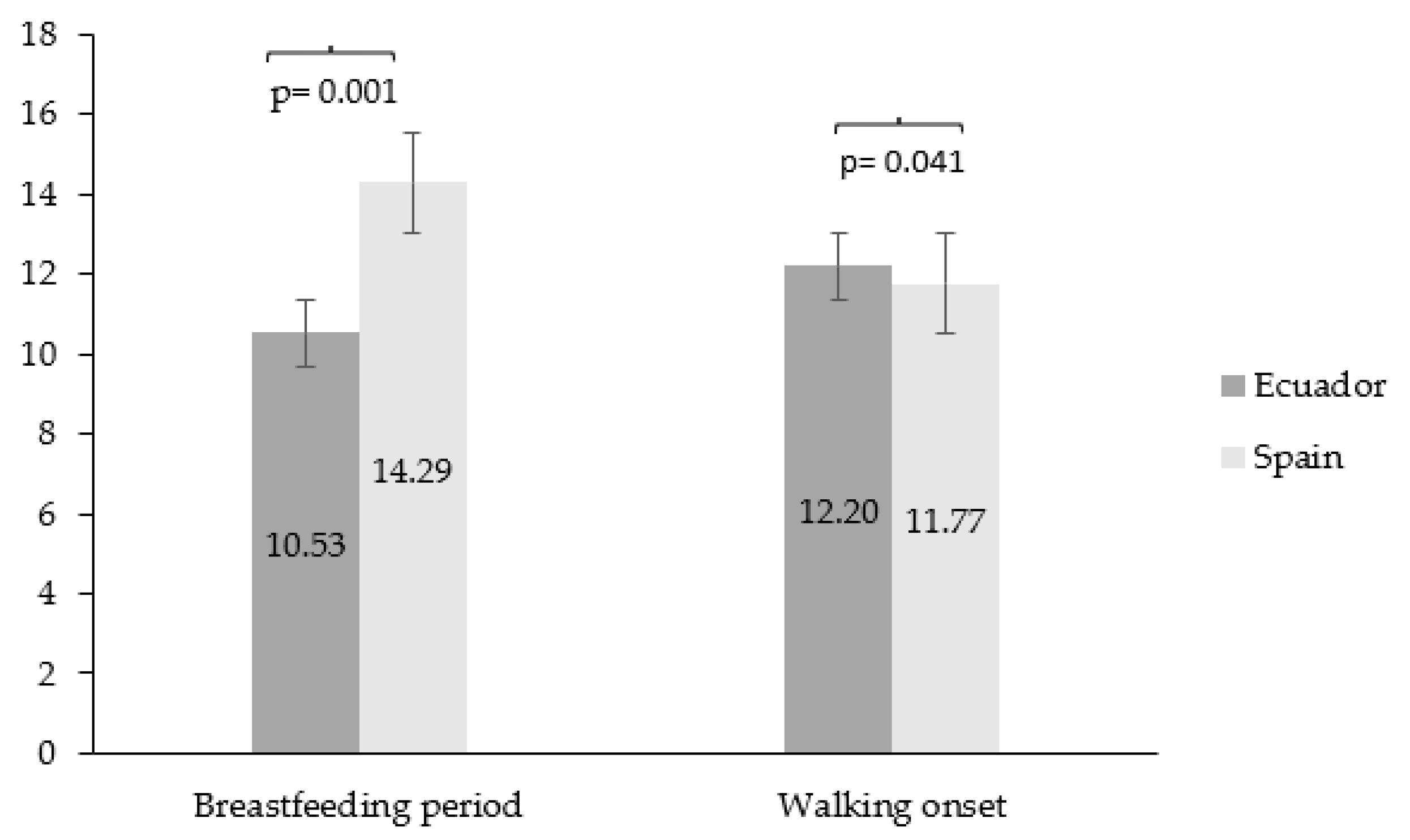
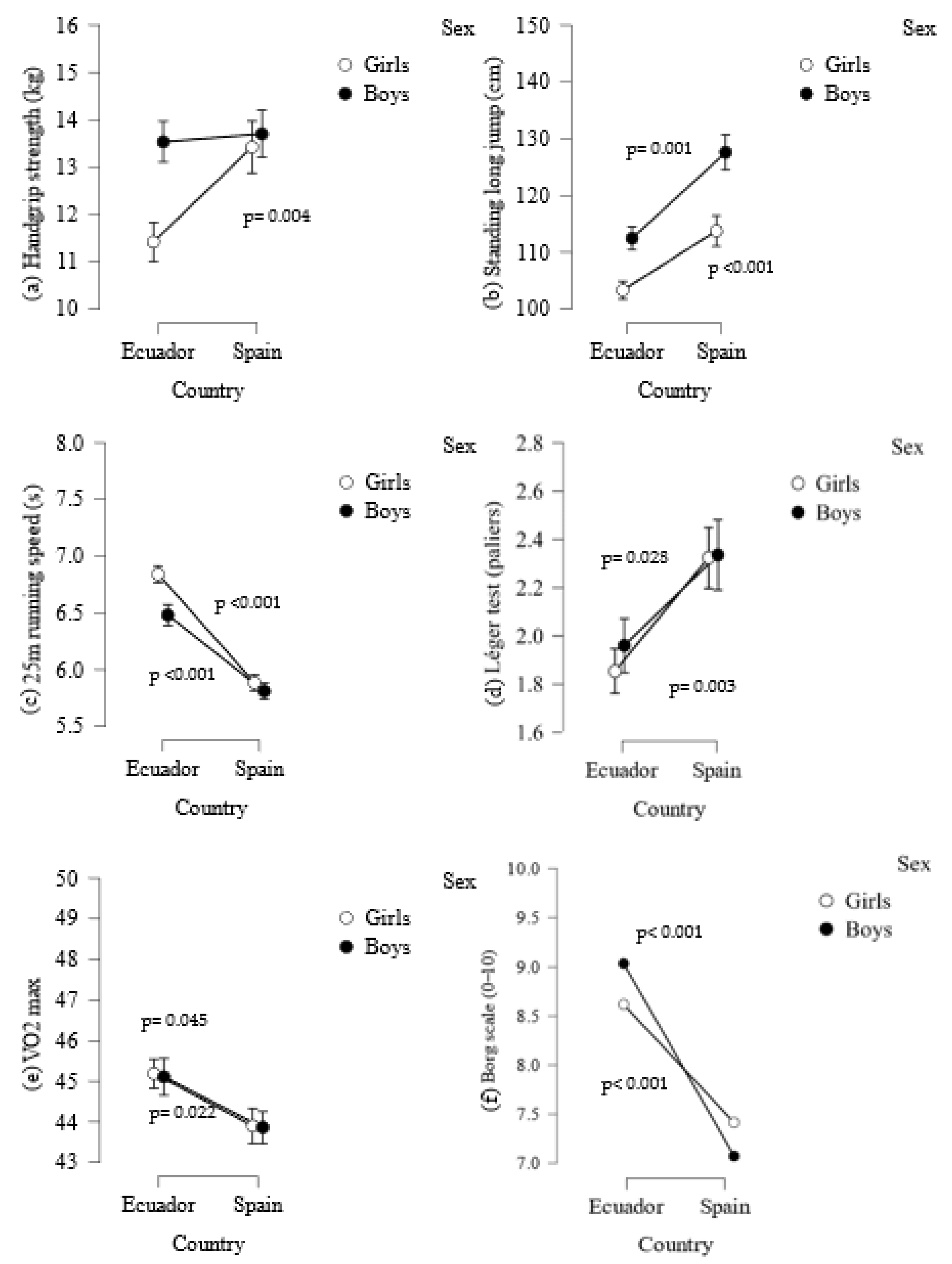
| ALL | Ecuador | Spain | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | (n = 352) | (n = 176) | (n = 176) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-Value | Cohen’s d | ||||
| Age (years) | 8.54 | (1.79) | 8.47 | (1.74) | 8.61 | (1.85) | 0.460 | 0.078 |
| Weight (kg) | 34.99 | (11.06) | 34.64 | (10.49) | 35.35 | (11.64) | 0.549 | 0.064 |
| Height (m) | 1.35 | (0.12) | 1.33 | (0.11) | 1.36 | (0.13) | 0.046 | 0.249 |
| BMI (kg/) | 18.73 | (4.19) | 19.04 | (4.35) | 18.42 | (4.02) | 0.164 | 0.148 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 63.66 | (10.56) | 64.55 | (11.04) | 62.77 | (10.0) | 0.115 | 0.169 |
| WtHR (WC/height) | 0.47 | (0.07) | 0.46 | (0.09) | 0.47 | (0.06) | 0.754 | 0.131 |
| Underweight | 4 | 1.1% | 3 | 1.7% | 1 | 0.6% | 0.696 | |
| Healthy weight | 213 | 60.5% | 105 | 59.7% | 108 | 61.4% | ||
| Overweight | 96 | 27.3% | 50 | 28.4% | 46 | 26.1% | ||
| Obese | 39 | 11.1% | 18 | 10.2% | 21 | 11.9% | ||
| Handgrip strength (kg) | 13.02 | (4.52) | 12.46 | (4.09) | 13.57 | (4.87) | 0.021 | 0.247 |
| Standing long jump (cm) | 114.49 | (24.46) | 107.83 | (17.57) | 121.15 | (28.32) | <0.001 | 0.566 |
| 25 m running speed (s) | 6.25 | (0.83) | 6.66 | (0.79) | 5.84 | (0.65) | <0.001 | 1.136 |
| Léger test (periods) | 2.11 | (1.15) | 1.89 | (1.05) | 2.33 | (1.21) | <0.001 | 0.389 |
| max. (mL· 1·) | 44.51 | (3.88) | 43.88 | (3.85) | 45.15 | (3.83) | 0.002 | 0.331 |
| Physical fitness Z score | 0.04 | (0.99) | −0.25 | (0.73) | 0.33 | (1.13) | <0.001 | 0.611 |
| Borg scale | 8.02 | (1.82) | 7.23 | (2.03) | 8.82 | (1.13) | <0.001 | 0.970 |
| Variables | BMI | Handgrip Strength | Standing Long Jump | 25 m Running Speed | Léger Test | Max | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjus Ted | Raw | Adjus Ted | Raw | Adjus Ted | Raw | Adjus Ted | Raw | Adjus Ted | Raw | Adjus Ted | Raw | |||
| Breastfeeding period | Ecuador | β | −0.139 | −0.131 | 0.008 | 0.135 | 0.238 | 0.310 | −0.316 | −0.409 | 0.209 | 0.246 | 0.150 | 0.008 |
| p-value | 0.071 | 0.085 | 0.891 | 0.075 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.919 | ||
| Spain | β | −0.168 | −0.153 | 0.043 | 0.015 | 0.143 | 0.103 | −0.206 | −0.188 | 0.060 | 0.051 | 0.042 | 0.075 | |
| p-value | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.444 | 0.847 | 0.021 | 0.178 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.792 | 0.505 | 0.377 | 0.327 | ||
| Walking onset | Ecuador | β | 0.061 | 0.065 | 0.058 | 0.067 | −0.201 | −0.190 | 0.232 | 0.233 | −0.182 | −0.174 | −0.128 | −0.124 |
| p-value | 0.420 | 0.390 | 0.328 | 0.377 | 0.003 | 0.012 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.017 | 0.101 | ||
| Spain | β | 0.168 | 0.162 | −0.103 | −0.167 | −0.120 | −0.199 | 0.252 | 0.284 | −0.207 | −0.222 | −0.128 | −0.625 | |
| p-value | 0.030 | 0.032 | 0.082 | 0.028 | 0.056 | 0.009 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.533 | ||
| Abdominal Obesity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Ecuador | Spain | ||
| OR (CI95%) | p-Value | OR (CI95%) | p-Value | |
| Handgrip strength (kg) | 0.979 (0.882–1.086) | 0.683 | 1.084 (1.004–1.004) | 0.039 |
| Standing long jump (cm) | 0.972 (0.950–0.996) | 0.021 | 0.985 (0.970–1.000) | 0.047 |
| 25 m running speed (s) | 2.646 (1.515–4.622) | 0.001 | 0.828 (0.509–1.347) | 0.448 |
| Léger test (periods) | 0.674 (0.487–0.934) | 0.018 | 0.688 (0.490–0.966) | 0.031 |
| max. (mL· 1·) | 0.846 (0.7363–0.972) | 0.021 | 1.024 (0.936–1.120) | 0.611 |
| Physical fitness Z score | 0.473 (0.197–1.132) | 0.093 | 0.344 (0.031–0.906) | 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade-Lara, K.E.; Cabrera Linares, J.C.; Párraga Montilla, J.A.; Mayanquer-Lara, A.; Lucena Zurita, M.; Latorre Román, P.Á. Breastfeeding, Walking Onset, and Abdominal Obesity Are Determinants of Physical Fitness among Latin American and Spanish Schoolchildren: A Cross-Cultural Study. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 318-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5030022
Andrade-Lara KE, Cabrera Linares JC, Párraga Montilla JA, Mayanquer-Lara A, Lucena Zurita M, Latorre Román PÁ. Breastfeeding, Walking Onset, and Abdominal Obesity Are Determinants of Physical Fitness among Latin American and Spanish Schoolchildren: A Cross-Cultural Study. Epidemiologia. 2024; 5(3):318-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade-Lara, Karina E., José Carlos Cabrera Linares, Juan Antonio Párraga Montilla, Alexander Mayanquer-Lara, Manuel Lucena Zurita, and Pedro Ángel Latorre Román. 2024. "Breastfeeding, Walking Onset, and Abdominal Obesity Are Determinants of Physical Fitness among Latin American and Spanish Schoolchildren: A Cross-Cultural Study" Epidemiologia 5, no. 3: 318-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5030022
APA StyleAndrade-Lara, K. E., Cabrera Linares, J. C., Párraga Montilla, J. A., Mayanquer-Lara, A., Lucena Zurita, M., & Latorre Román, P. Á. (2024). Breastfeeding, Walking Onset, and Abdominal Obesity Are Determinants of Physical Fitness among Latin American and Spanish Schoolchildren: A Cross-Cultural Study. Epidemiologia, 5(3), 318-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia5030022






