Abstract
Luminescent solar concentrators (LSCs) are considered promising in their application as building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPVs). However, they suffer from low performance, especially in large-area devices. One of the key issues is the self-absorption of the luminophores. In this report, we focus on the study of self-absorption in perovskite-based LSCs. Perovskite nanocrystals (NCs) are emerging luminophores for LSCs. Studying the self-absorption of perovskite NCs is beneficial to understanding fundamental photon transport properties in perovskite-based LSCs. We analyzed and quantified self-absorption properties of perovskite NCs in an LSC with the dimensions of 6 in × 6 in × 1/4 in (152.4 mm × 152.4 mm × 6.35 mm) using three approaches (i.e., limited illumination, laser excitation, and regional measurements). The results showed that a significant number of self-absorption events occurred within a distance of 2 in (50.8 mm), and the photo surface escape due to the repeated self-absorption was the dominant energy loss mechanism.
1. Introduction
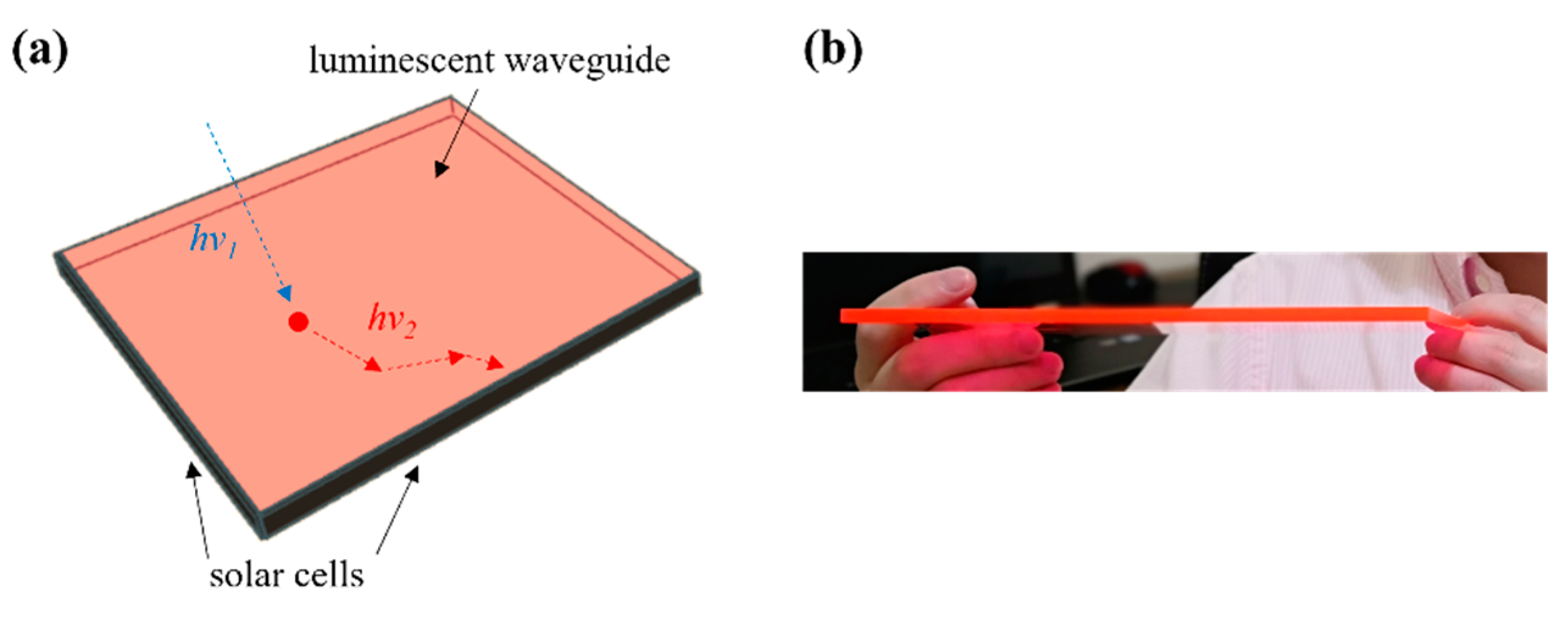
The research on building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPVs) is under vigorous development in recent years, as it becomes more urgent for the transformation of conventional buildings that are based on fossil energy to zero-energy buildings that can generate on-site energy from renewable sources [1,2,3]. The technology of luminescent solar concentrators (LSCs) is considered one of the promising approaches to imparting architectural functionalities to conventional solar cells (i.e., silicon-based solar cells) [4,5,6]. The typical structure of LSCs was introduced in the 1970s, which consists of a planar waveguide containing luminophores and solar cells attached to the edge of the waveguide [7,8] as shown in Figure 1. The main working mechanism of LSCs is that the luminescent light produced from the luminophores follows total internal reflection (TIR) inside the waveguide and transports to the edge-attached solar cells [9,10]. This design has the solar cells hidden on the edge of the waveguide while allowing the waveguide to be different colors, shapes, and transparencies [11,12,13]. This design also brings unique functionalities that make LSCs utilized in a variety of areas not only for buildings but also for other architectures [14,15,16] and other applications [17].
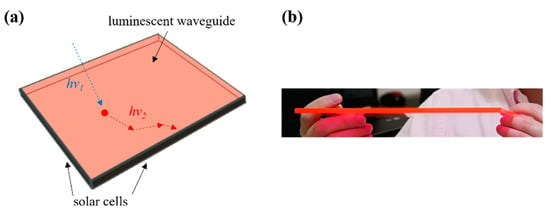
Figure 1.
(a) The working mechanism of LSCs and (b) a luminescent waveguide showing light concentration on the edge.
There is no doubt that luminophores are important for achieving high-performance LSCs. To date, many efforts have been made to develop luminophores with advanced spectroscopic properties [18,19,20,21,22]. One promising type of luminophores is perovskite nanocrystals (NCs), which are organic–inorganic hybrids [23,24,25]. The utilization of perovskite NCs in LSCs is summarized in several recent reviews [26,27,28]. Although significant breakthroughs have been made in developing perovskite NCs for LSCs, there remain practical issues to applying perovskite NCs in large-area LSCs [29]. One of the key issues is the self-absorption of the perovskite NCs [30]. Repeated self-absorption of the luminophores during photon transport leads to an increased probability of photon loss through surface escape and Stokes loss [31].
In this report, we studied the self-absorption of perovskite NCs in LSCs using three approaches (i.e., limited illumination, laser excitation, and regional measurements). The results revealed the fundamentals of the self-absorption of perovskite NCs and provided useful information to develop novel perovskite NCs as well as LSCs.
2. Experimental
2.1. Device Fabrication
An LSC with the dimensions of 6 in × 6 in × 1/4 in (152.4 mm × 152.4 mm × 6.35 mm) was fabricated in this study. The fabrication procedure was according to a previous report [32], where a thin (thickness: approximately 15 μm; density: 1.18 g cm−3) polymer (poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)) layer containing perovskite (CsPbI3) NCs was sandwiched between two clear acrylic sheets, and four gallium arsenide (GaAs) solar cells connected in parallel were used to attach to the waveguide. Liquid optically clear adhesives (refractive index: 1.52@590 nm; cure by heating at 50 °C for 1 day) were used for index matching between the solar cells and the waveguide. The perovskite NCs were synthesized according to the literature [33], and the concentration of the perovskite NCs was 1 wt % in the thin polymer layer.
2.2. Luminophore and Device Characterization
The absorption and emission spectra of the perovskite NCs in the thin polymer film were measured using a Varian Cary 5000 UV–Visible–NIR spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) and an ISS PC1 photon-counting spectrofluorometer (ISS, Inc., Champaign, IL, USA), respectively. The photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of the perovskite NCs in the thin polymer film was measured using an integrating sphere connected to a Hamamatsu C9920-12 external quantum efficiency (EQE) measurement system (Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., Hamamatsu City, Shizuoka, Japan). The I–V curves of the solar cells and the LSC were measured with a Keithley 2401 SourceMeter (Keithley Instruments, Cleveland, OH, USA). The EQE of the solar cells and the LSC were measured on an Enlitech QE-R3011 system (Enlitech, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan). The AM1.5G sunlight (1000 W m−2) was provided by an OAI class AAA solar simulator (OAI, Milpitas, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectroscopic and PV Properties
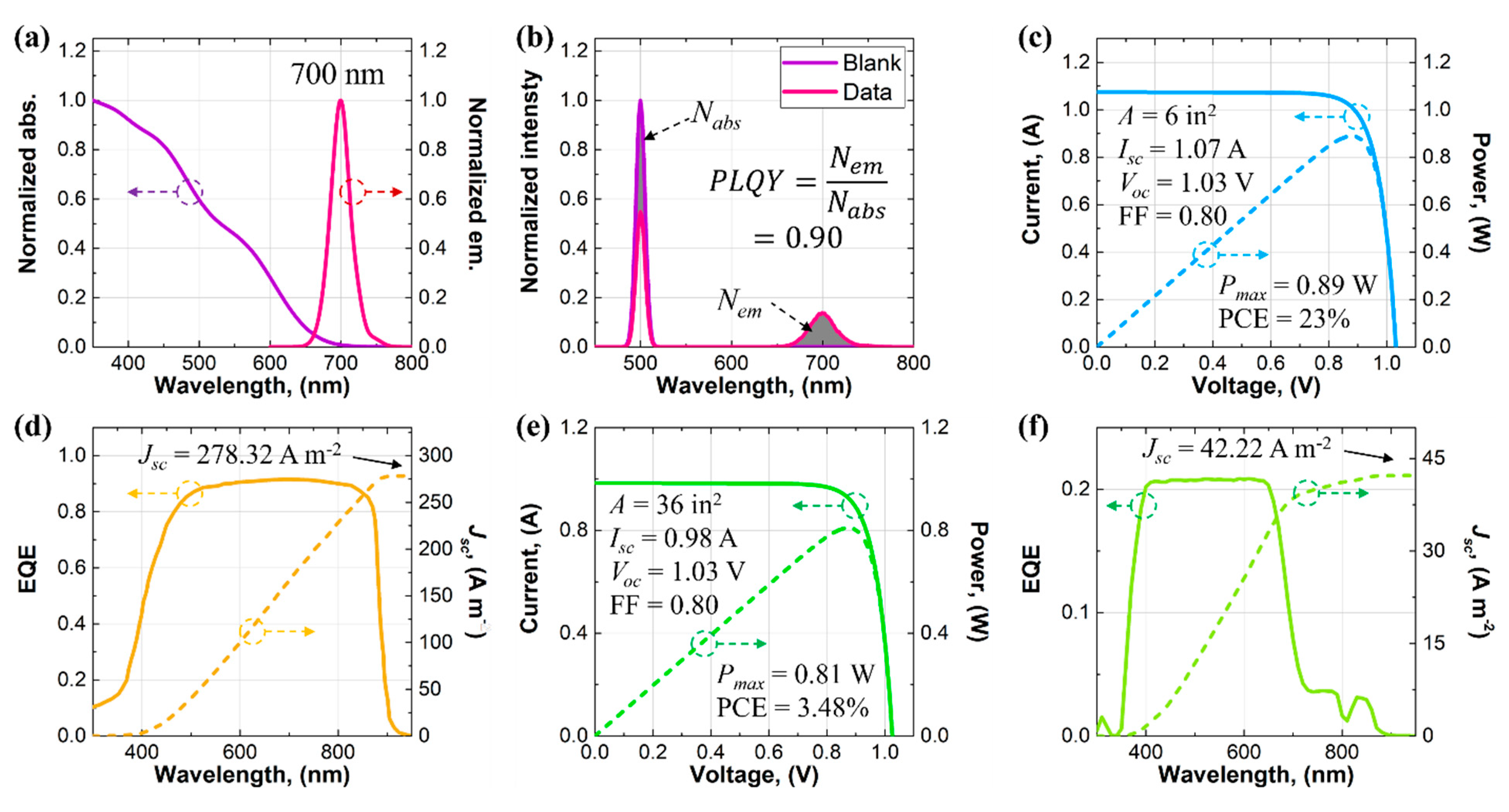
The spectroscopic properties of the perovskite NCs and the PV properties of the GaAs solar cells and the LSC were shown in Figure 2. The absorption spectrum of the perovskite NCs spanned a spectral range up to 700 nm with decreasing absorbance for increasing wavelength (see Figure 2a). Compared with other luminophores that exhibited limited absorption ranges, especially organic dyes [34,35,36], the wide absorption range of the perovskite NCs was beneficial for improving the light-harvesting capability of the LSC. The emission spectrum of the perovskite NCs was sharp and maximized at 700 nm (see Figure 2a). The PLQY of the perovskite NCs was measured in an integrating sphere using a 500 nm continuous wave (CW) laser and calculated from the ratio between the number of the emitted photons (Nem) and the number of the absorbed photons (Nabs) (see Figure 2b). The PLQY of the perovskite NCs was as high as 0.90, which was comparable to those of organic dyes [37,38,39]. In the architecture of the LSC, the total area of the four parallelly connected GaAs solar cells was 6 in2 (3870.96 mm2) (6 in × 1/4 in × 4 (152.4 mm × 6.35 mm × 4)). The solar cells exhibited a short-circuit current (Isc) of 1.07 A, an open-circuit voltage (Voc) of 1.03 V, and a fill factor (FF) of 0.80, which led to maximum electric power (Pmax) of 0.89 W and a PCE of 23% (see Figure 2c). The external quantum efficiency (EQE) of the GaAs solar cells was also measured and integrated with AM1.5G solar spectrum to afford an integrated short-circuit current density (Jsc) of 278.32 A m−2 (see Figure 2d), which matched the Jsc from the I–V measurement (276.42 A m−2). The same PV characterizations were also applied to the LSC. The LSC exhibited an Isc of 0.98 A, a Voc of 1.03 V, and an FF of 0.80, which led to a Pmax of 0.81 W and a PCE of 3.48% (see Figure 2e). The slightly lower Pmax of the LSC (0.81 W) than that of the GaAs solar cells (0.89 W) indicated that the luminescent waveguide behaved as a solar collector rather than a concentrator and, thus, the concentration ratio of the LSC was 0.91 (0.81 W/0.89 W). The EQE of the LSC was attributed to the absorption spectrum of the perovskite NCs and the EQE of the GaAs solar cells, covering the range from 400 to 700 nm. The spectral response beyond 700 nm was due to the scattering effects in the luminescent waveguide [40,41,42]. The integrated Jsc of the LSC was 42.22 A m−2, consistent with that from the I–V measurement of the LSC (42.19 A m−2).
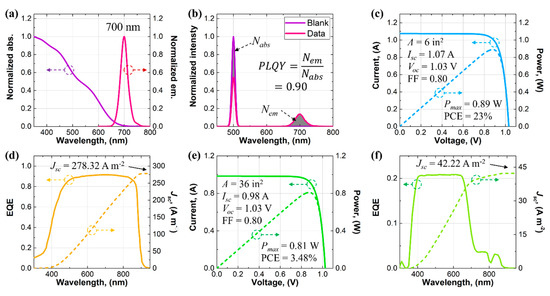
Figure 2.
(a) Normalized absorption and emission spectra and (b) results for the PLQY of the perovskite NCs. Results for the (c) I–V and (d) EQE measurements of the GaAs solar cells. Results for (e) the I–V and (f) the EQE measurements of the LSC.
3.2. Limited Illumination
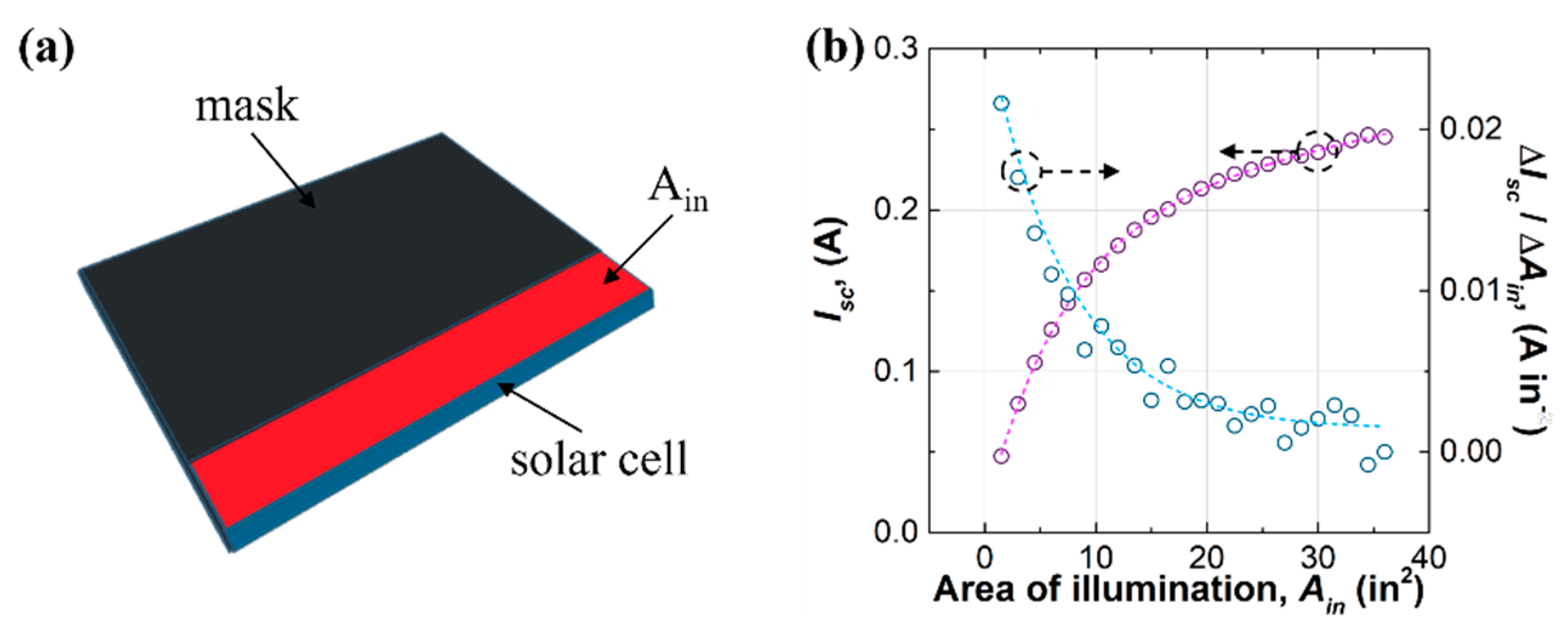
Our first approach to studying the self-absorption of the LSC was limited illumination. This approach has been employed by other studies on LSCs [43,44]. In this approach, the Isc of a solar cell was measured under a certain area of illumination (Ain), which is depicted in Figure 3. In the experimental setup, a mask was used to adjust Ain from 1.5 in2 (967.74 mm2) (1/4 in × 6 in (6.35 mm × 152.4 mm)) to 36 in2 (23,225.76 mm2) (6 in × 6 in (152.4 mm × 152.4 mm)) (see Figure 3a). One edge of the waveguide was attached with a solar cell, and the other edges were covered by blackout tapes. The results showed that Isc increased, but its increasing rate (ΔIsc/ΔAin) decreased with increasing Ain (see Figure 3b). The pattern of the increasing rate was a quasi-exponential decay, where a fast decay was observed for Ain below 10 in2 (6451.6 mm2) and a slow decay that approached zero for Ain beyond 20 in2 (12,903.2 mm2). This indicated that photons far from the solar cell cannot be efficiently delivered to the solar cell due to the photon transport loss mechanisms such as self-absorption of the luminophores and waveguide scattering.
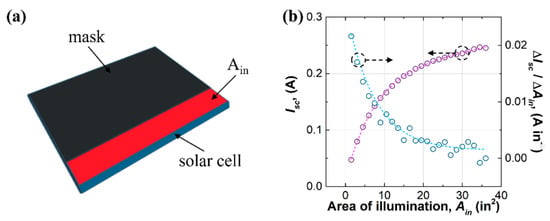
Figure 3.
(a) Device configuration and (b) results for the approach of limited illumination.
3.3. Laser Excitation
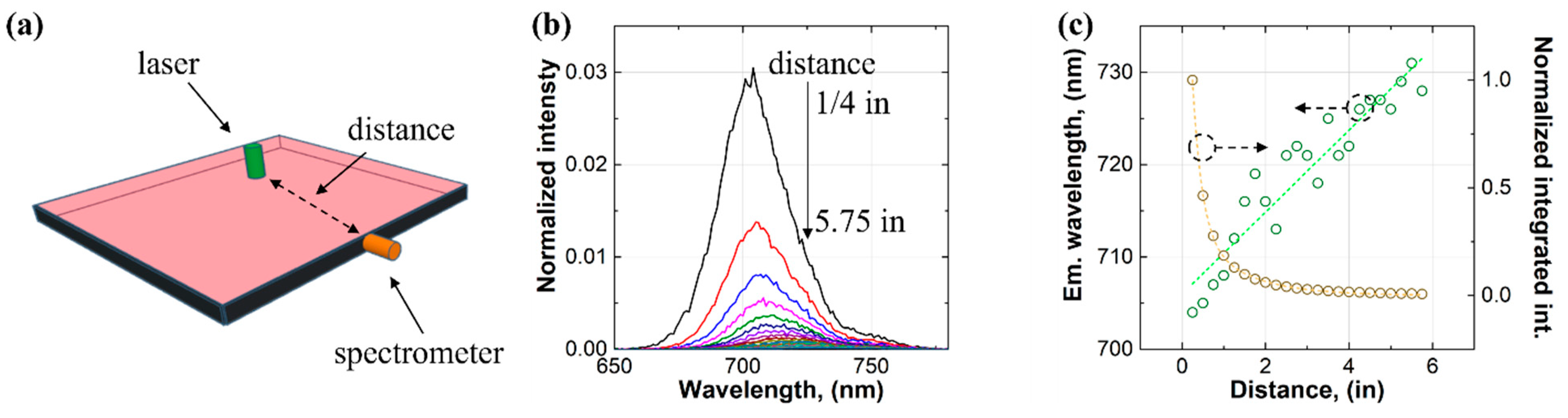
Our second approach to studying the self-absorption of the LSC was using a laser to excite the luminophores inside the waveguide and measuring the emission from the edge of the waveguide using a spectrometer [45,46], which is depicted in Figure 4. This approach allowed us to tell which photon transport loss mechanism (self-absorption of the luminophores or waveguide scattering) was dominant. In the experimental setup, the spectrometer was attached to the center of one edge of the waveguide through an optical fiber (diameter: 1/4 in (6.35 mm)), while the rest of the edge and the other three edges were covered by blackout tapes (see Figure 4a). A 500 nm CW laser was aligned with the spectrometer and moved along the centerline of the waveguide. The distance between the spectrometer and the laser was from 1/4 in (6.35 mm) to 5.75 in (146.05 mm). The results showed that with increasing the distance, the intensity of the edge emission decreased (see Figure 4b). For example, the intensity for a distance of 1/2 in (12.7 mm) was approximately half of that for a distance of 1/4 in (6.35 mm), suggestive of significant photon transport loss. The emission wavelength red-shifted and increased almost linearly with increasing distance (see Figure 4c), which indicated a high degree of self-absorption of the luminophores in the LSC. Meanwhile, the integrated intensity of the edge emission decreased rapidly for a distance shorter than 2 in (50.8 mm), and it approached zero for a distance beyond 2 in (50.8 mm). The results signified that self-absorption of the luminophores was the dominant photon transport loss mechanism in the LSC.
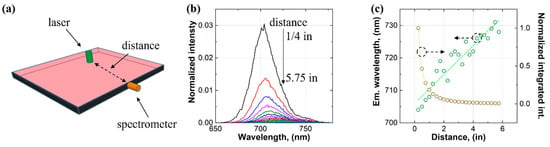
Figure 4.
(a) Device configuration, (b) edge emission spectra, and (c) the results for the approach of laser excitation.
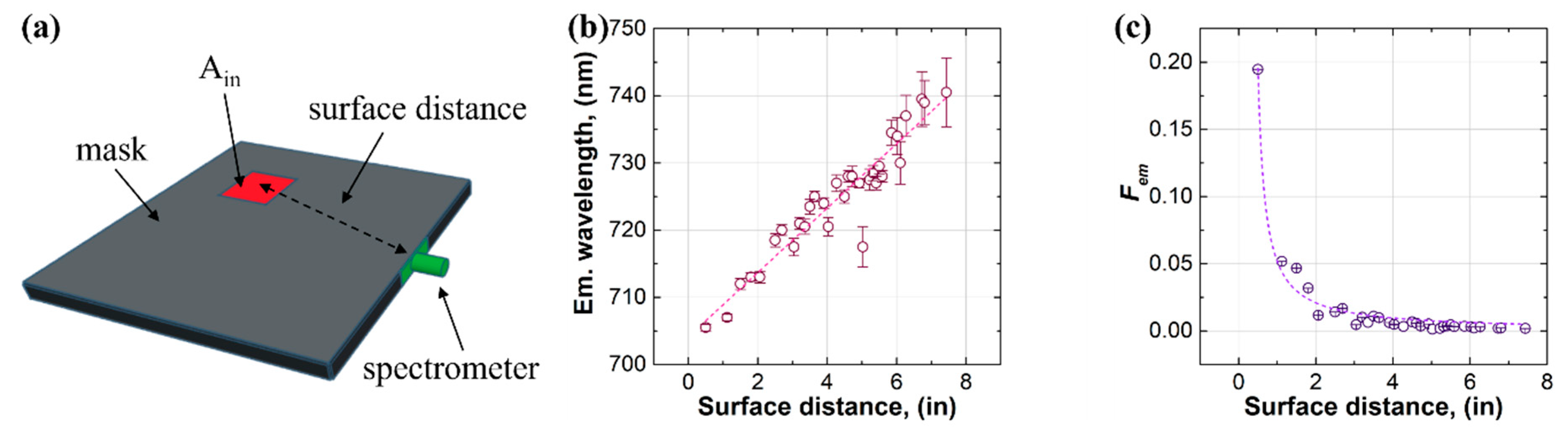
3.4. Regional Measurements
Our third approach to studying the self-absorption of the LSC was applying the methodology of regional measurements, which is depicted in Figure 5. This approach was recently developed by our group and allowed us to extract important parameters related to the photon transport of the LSC [47,48]. In the experimental setup, the spectrometer was attached to the edge of the luminescent waveguide at a certain position, and the Ain was a 1 in (25.4 mm) square (see Figure 5a). The surface distance was the lateral distance between the spectrometer and the illumination. The relationship between the peak emission wavelength and the surface distance was almost linear (see Figure 5b), and the emission factor (Fem) exhibited a quasi-exponential decay with increasing surface distance (see Figure 5c). These observations were consistent with those from the approach of laser excitation, suggestive of a high degree of self-absorption of the luminophores in the LSC. According to the analysis in the literature [47], the relationship between Fem and surface distance can be fitted by a theoretical equation to afford two important parameters related to the photon transport of the LSC, which were the number of self-absorption events at the largest photon transport length () and the critical angle for photon surface escape (θc). For the LSC in this study, the was 28.5 and the θc was 70.7°, which were much higher than those of the LSC using BASF Lumogen F Red 305 ( = 11.3 and θc = 39.3°) in the literature [47]. The results suggested that a great number of self-absorption events occurred in the LSC, causing an increasing number of photons that escaped from the surface.
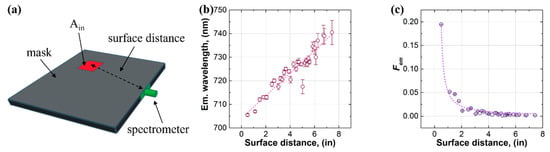
Figure 5.
(a) Device configuration, (b) edge emission wavelength, and (c) Fem with increasing surface distance for the approach of regional measurements.
3.5. Projected Performance
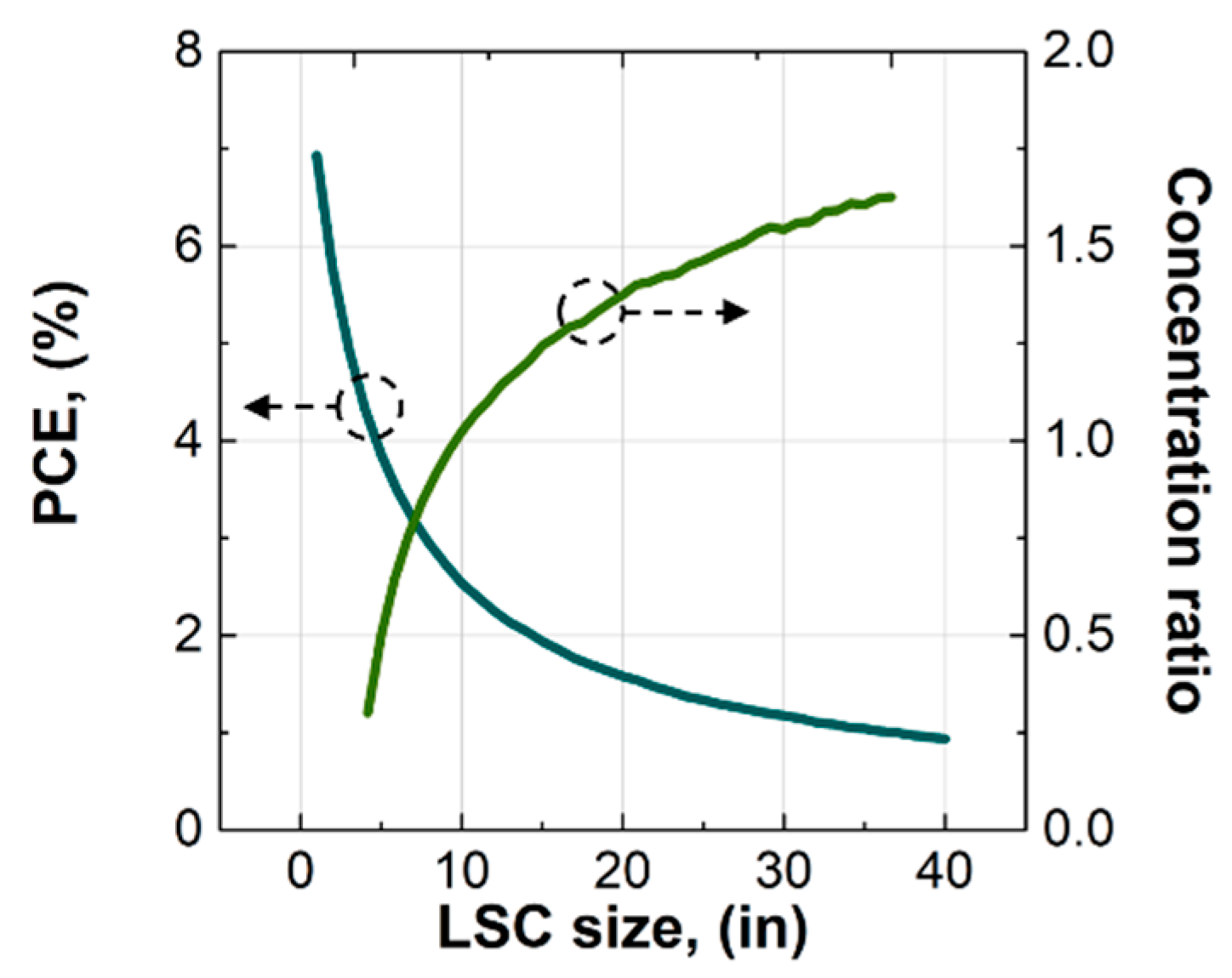
The high degree of self-absorption of the luminophores in the LSC signified that large-area LSCs based on the perovskite NCs would exhibit low performance. To verify this, we performed Monte Carlo ray-tracing simulations [49,50,51] to project the performance of the LSCs with sizes up to 40 in (1016 mm). The results in Figure 6 indicated that the PCE started to be below 2% at the size of 15 in (381 mm) and below 1% at the size of 38 in (965.2 mm). The concentration ratio started to be greater than 1, turning the LSC from a collector to a concentrator, at the size of 8 in (203.2 mm), while at the size of 40 in (1016 mm), it was just 1.63. The fast decrease in the PCE and slow increase in the concentration ratio with increasing LSC size were due to the high degree of self-absorption of the perovskite NCs in the LSC.
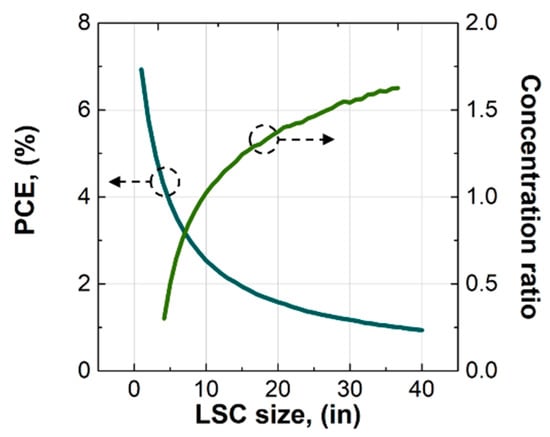
Figure 6.
Projected performance of the LSCs with sizes up to 40 in (1016 mm).
4. Conclusions
In this report, we fabricated an LSC with the dimensions of 6 in × 6 in × 1/4 in (152.4 mm × 152.4 mm × 6.35 mm) using perovskite NCs and GaAs solar cells. The LSC exhibited a PCE of 3.48% and a concentration ratio of 0.91. Three approaches were applied to study the self-absorption of the perovskite NCs in the LSC. The results for the measurements based on the approach of limited illumination showed that perovskite NCs exhibited a high degree of self-absorption, which would lead to low PCEs for large-area LSCs. Measurements based on the approach of laser excitation revealed that the self-absorption events primarily occurred within 2 in (50.8 mm). Regional measurements indicated that the was as high as 28.5 and the θc was as high as 70.7°, suggesting a significant number of self-absorption events and photon surface escape events in the LSC. The projected performance of the LSCs using Monte Carlo ray-tracing simulations signified that the PCE was below 1% for a large-area LSC with a size of 40 in (1016 mm). The strong self-absorption of the perovskite NCs in the LSC was possibly due to the large absorption tail of the material [52].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. (Yilin Li); Investigation, Y.S.; Resources, Y.S. and Y.L. (Yuxin Li); Software, Y.Z.; Writing—original draft, Y.S.; Writing—review and editing, Y.Z., Y.L. (Yuxin Li), and Y.L. (Yilin Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This work is a part of the project “Energy-Harvesting Windows and Panels”. The authors would like to thank the members of Solera City Energy and the LSC Research Collaborative for their research support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dai, Y.; Bai, Y. Performance improvement for building integrated photovoltaics in practice: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T.E.; Erban, C.; Heinrich, M.; Eisenlohr, J.; Ensslen, F.; Neuhaus, D.H. Review of technological design options for building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). Energy Build. 2021, 231, 110381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabie, H.M.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Al-Alami, A.H.; Ramadan, M.; Mushtaha, E.; Wilberforce, T.; Olabi, A.G. State-of-the-art technologies for building-integrated photovoltaic systems. Buildings 2021, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debije, M.G.; Verbunt, P.P.C. Thirty years of luminescent solar concentrator research: Solar energy for the built environment. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinardi, F.; Bruni, F.; Brovelli, S. Luminescent solar concentrators for building-integrated photovoltaics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncali, J. Luminescent solar collectors: Quo vadis? Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.H.; Lambe, J. Luminescent greenhouse collector for solar radiation. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, 2299–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzberger, A.; Greube, W. Solar energy conversion with fluorescent collectors. Appl. Phys. 1977, 14, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelder, J.S.; Zewail, A.H.; Cole, T. Luminescent solar concentrators. 1: Theory of operation and techniques for performance evaluation. Appl. Opt. 1979, 18, 3090–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelder, J.S.; Zewail, A.H.; Cole, T. Luminescent solar concentrators. 2: Experimental and theoretical analysis of their possible efficiencies. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3733–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinders, A.; Kishore, R.; Slooff, L.; Eggink, W. Luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic designs. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 8RD10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, R.; Luscombe, C.K. Review on the role of polymers in luminescent solar concentrators. J. Polym. Sci. A 2019, 57, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafiee, M.; Chandra, S.; Ahmed, H.; McCormack, S.J. An overview of various configurations of Luminescent Solar Concentrators for photovoltaic applications. Opt. Mater. 2019, 91, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, C.; Leow, S.W.; Osborn, M.; Carbone, I.; Hellier, K.; Short, M.; Alers, G.; Carter, S.A. Power generation study of luminescent solar concentrator greenhouse. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 43502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sark, W.V.; Moraitis, P.; Aalberts, C.; Drent, M.; Grasso, T.; L’Ortije, Y.; Visschers, M.; Westra, M.; Plas, R.; Planje, W. The “electric Mondrian” as a luminescent solar concentrator demonstrator case study. Sol. RRL 2017, 1, 1600015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujadas-Gispert, E.; Lenaers, W.J.H.P.; Schie, F.F.V.; Lazauskas, M.; Moonen, S.P.G.F. The gem tower: A hybrid renewable energy unit for festivals. Struct. Eng. Int. 2021, 31, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, I.; Portnoi, M.; Debije, M.G. The hidden potential of luminescent solar concentrators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2002883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, W.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Zou, G.; Zhang, Q. Luminescent solar concentrator employing rare earth complex with zero self-absorption loss. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Olsen, J.; Nunez-Ortega, K.; Dong, W.-J. A structurally modified perylene dye for efficient luminescent solar concentrators. Sol. Energy 2016, 136, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Arquer, F.P.G.D.; Walters, G.; Yang, Z.; Quan, L.N.; Kim, Y.; Sabatini, R.; Quintero-Bermudez, R.; Gao, L.; Fan, J.Z.; et al. Ultrafast narrowband exciton routing within layered perovskite nanoplatelets enables low-loss luminescent solar concentrators. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Melikov, R.; Jalali, H.B.; Karatum, O.; Srivastava, S.B.; Conkar, D.; Firat-Karalar, E.N.; Nizamoglu, S. Ecofriendly and efficient luminescent solar concentrators based on fluorescent proteins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 8710–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, D.C.J.; Goh, W.P.; Lau, H.H.; Shanmugam, J.; Chen, Y.F. CuInS2 quantum dots with thick ZnSexS1-x shells for a luminescent solar concentrator. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 6489–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdražil, L.; Kalytchuk, S.; Langer, M.; Ahmad, R.; Pospíšil, J.; Zmeškal, O.; Altomare, M.; Osvet, A.; Zbořil, R.; Schmuki, P.; et al. Transparent and low-loss luminescent solar concentrators based on self-trapped exciton emission in lead-free double perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 6445–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, R.; Zheng, W.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; et al. Stable metal-halide perovskites for luminescent solar concentrators of real-device integration. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendewala, B.; Vickers, E.T.; Nikolaidou, K.; DiBenedetto, A.; Delmas, W.G.; Zhang, J.Z.; Ghosh, S. High efficiency luminescent solar concentrator based on organo-metal halide perovskite quantum dots with plasmon enhancement. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraitis, P.; Schropp, R.E.I.; Sark, W.G.J.H.M.V. Nanoparticles for luminescent solar concentrators—A review. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kuang, D.-B.; Wu, W.-Q. A review of diverse halide perovskite morphologies for efficient optoelectronic applications. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, S.M.; Wobben, M.; Ehrler, B. Rare-earth quantum cutting in metal halide perovskites—A review. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Benetti, D.; Ma, D.; Rosei, F. Perovskite quantum dots integrated in large-area luminescent solar concentrators. Nano Energy 2017, 37, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendewala, B.; Nikolaidou, K.; Hoffman, C.; Sarang, S.; Lu, J.; Ilan, B.; Ghosh, S. The potential of scalability in high efficiency hybrid perovskite thin film luminescent solar concentrators. Sol. Energy 2019, 183, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Kate, O.M.; Hooning, K.M.; van der Kolk, E. Quantifying self-absorption losses in luminescent solar concentrators. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 5238–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Verduzco, R. High-performance hybrid luminescent-scattering solar concentrators based on a luminescent conjugated polymer. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tong, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, T.; Tan, H.; Nie, S.; Deng, Z. Efficient and stable thin-film luminescent solar concentrators enabled by near-infrared emission perovskite nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7738–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Scudiero, L.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.-J. Synthesis and characterizations of benzothiadiazole-based fluorophores as potential wavelength-shifting materials. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2012, 231, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.-J. Tuning photophysical properties of triphenylamine and aromatic cyano conjugate-based wavelength-shifting compounds by manipulating intramolecular charge transfer strength. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2013, 251, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, F.; Li, Y.; Saeed, M.A.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, S.-K. Large-area luminescent solar concentrator utilizing donor-acceptor luminophore with nearly zero reabsorption: Indoor/outdoor performance evaluation. J. Lumin. 2021, 231, 117837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Compaan, A.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.-J. Increasing the power output of a CdTe solar cell via luminescent down shifting molecules with intramolecular charge transfer and aggregation-induced emission characteristics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2907–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ablekim, T.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.J. Rational design of tetraphenylethylene-based luminescent down-shifting molecules: Photophysical studies and photovoltaic applications in a CdTe solar cell from small to large units. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 26193–26202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Olsen, J.; Dong, W.J. Enhancing the output current of a CdTe solar cell via a CN-free hydrocarbon luminescent down-shifting fluorophore with intramolecular energy transfer and restricted internal rotation characteristics. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breukers, R.D.; Smith, G.J.; Stirrat, H.L.; Swanson, A.J.; Smith, T.A.; Ghiggino, K.P.; Raymond, S.G.; Winch, N.M.; Clarke, D.J.; Kay, A.J. Light losses from scattering in luminescent solar concentrator waveguides. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 2630–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Wu, D.; Hao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, K. Scattering enhanced quantum dots based luminescent solar concentrators by silica microparticles. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 179, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. Boosting the cost-effectiveness of luminescent solar concentrators through subwavelength sanding treatment. Sol. Energy 2020, 198, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, F.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, S.K. Luminescent solar concentrators based on thermally activated delayed fluorescence dyes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3708–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.J.; Purcell-Milton, F.; McKenna, B.; Watson, T.M.; Gun’Ko, Y.K.; Evans, R.C. Large area quantum dot luminescent solar concentrators for use with dye-sensitised solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turrisi, R.; Sanguineti, A.; Sassi, M.; Savoie, B.; Takai, A.; Patriarca, G.E.; Salamone, M.M.; Ruffo, R.; Vaccaro, G.; Meinardi, F.; et al. Stokes shift/emission efficiency trade-off in donor–acceptor perylenemonoimides for luminescent solar concentrators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8045–8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Luo, J.; Shi, L.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Song, J.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Deng, Z. Fabrication of highly emissive and highly stable perovskite nanocrystal-polymer slabs for luminescent solar concentrators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4872–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. Regional measurements to analyze large-area luminescent solar concentrators. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ren, T. Spectral response of large-area luminescent solar concentrators. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 8964–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, D.; Ilan, B.; Kelley, D.F. Monte-Carlo simulations of light propagation in luminescent solar concentrators based on semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 033108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leow, S.W.; Corrado, C.; Osborn, M.; Isaacson, M.; Alers, G.; Carter, S.A. Analyzing luminescent solar concentrators with front-facing photovoltaic cells using weighted Monte Carlo ray tracing. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 214510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J. Monte-Carlo simulations of optical efficiency in luminescent solar concentrators based on all-inorganic perovskite quantum dots. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 548, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earp, A.A.; Franklin, J.B.; Smith, G.B. Absorption tails and extinction in luminescent solar concentrators. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).