Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
Normal Insulin Function
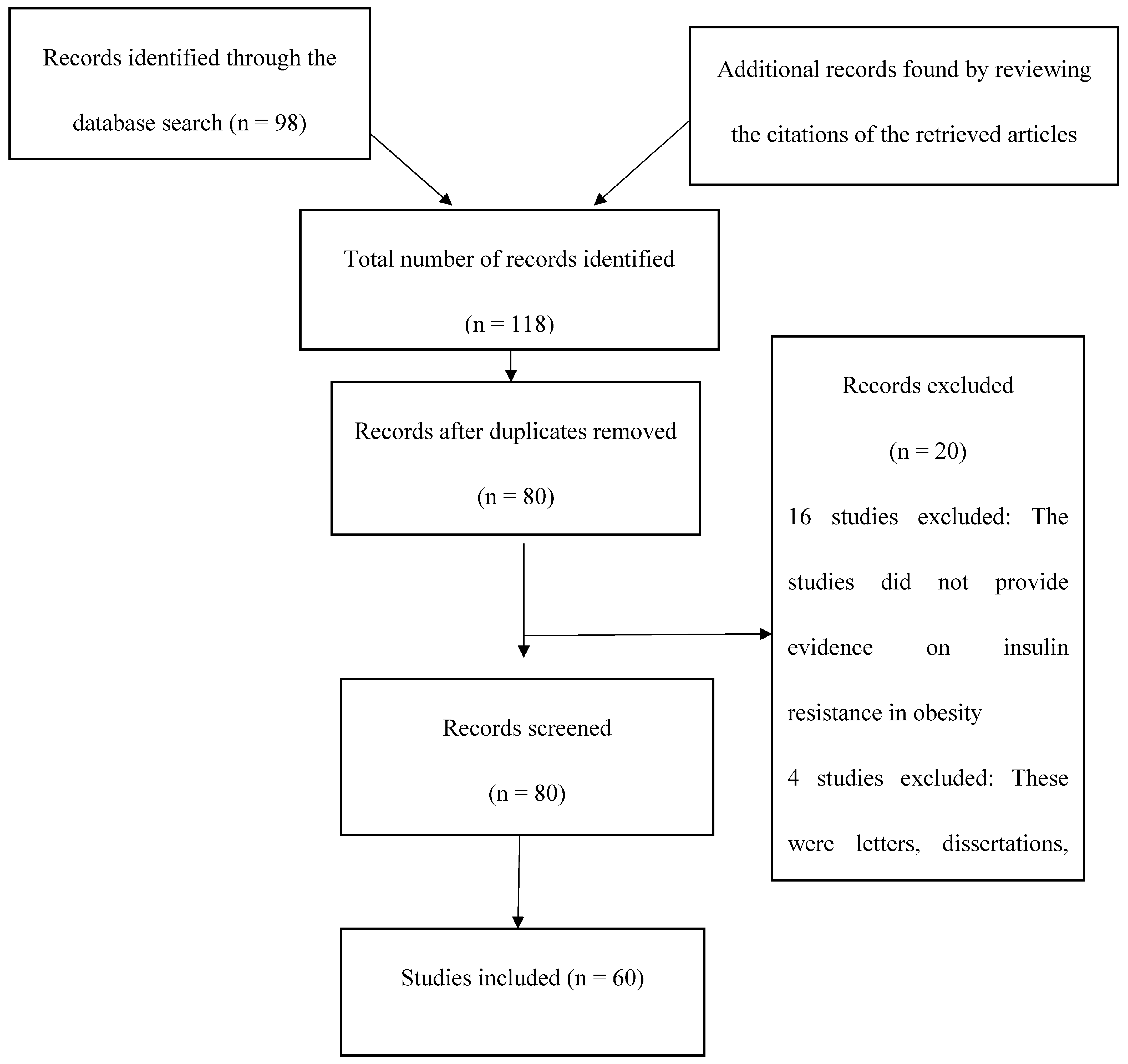
2. Methodology
2.1. Arteriosclerosis in Obesity and Diabetes
2.2. Inflammatory Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance
2.3. Neural Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance
2.4. Biochemical Mechanisms: Ectopic Fat, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Akt | Agder Kollektivtrafikk/Protein kinase B |
| ATF-6 | Transcription factor 6 |
| CaV1.2 | Cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CPT-1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 |
| HbA1c | Glycosylated hemoglobin |
| IRS-1 | Inhibiting insulin receptor substrate 1 |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead box protein O1 |
| GSK3 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 |
| IκB | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| IKBKB | Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase beta |
| IKKβ | IκB kinase β |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IRE-1 | Inositol-requiring kinase/endoribonuclease 1 |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| IRS-1 | Insulin receptor substrate 1 |
| IRS-2 | Insulin receptor substrate 2 |
| JNK | Jun N-terminal kinases |
| JNK1 | JUN N-terminal kinase1 |
| NF-Κb | Nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| p38 MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 |
| PERK | Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α |
| PGC-1β | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1β |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOCS | Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins |
| SOCS-1 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins 1 |
| SOCS-3 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins 3 |
| SOCS-6 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins 6 |
| TNF-a | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TZD | Thiazolidinedione |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| β cells | Beta cells |
References
- He, Q.; Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Yun, Z.; Ye, J. Regulation of HIF-1α activity in adipose tissue by obesity-associated factors: Adipogenesis, insulin, and hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E877–E885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; McGuinness, O.P. Inflammation during obesity is not all bad: Evidence from animal and human studies. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 304, E466–E477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Chan, Z.; Chooi, Y.C.; Choo, J.; Sadananthan, S.A.; Chang, A.; Sasikala, S.; Michael, N.; Velan, S.S.; Magkos, F. Regulation of glucose metabolism in nondiabetic, metabolically obese normal-weight Asians. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E494–E502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röder, P.V.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gaetano, A.; Gaz, C.; Palumbo, P.; Panunzi, S. A unifying organ model of pancreatic insulin secretion. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckwith, S. The relationship between diabetes and atherosclerosis. Br. J. Card. Nurs. 2014, 9, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakami, N. Mechanism of Development of Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Liang, F. Mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 508409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H. Nutrition and Diabetes Mellitus: How are They Interlinked? Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2016, 26, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feve, B.; Bastard, J.P. The role of interleukins in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Chen, S. Role of inflammatory mechanisms in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Chen, S. IL-1Ra and its delivery strategies: Inserting the association in perspective. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2951–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaroop, J.J.; Rajarajeswari, D.; Naidu, J.N. Association of TNF-alpha with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Kitade, H.; Ni, Y.; Ota, T. Roles of chem Okines and chemokine receptors in obesity-associated insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitade, H.; Sawamoto, K.; Nagashimada, M.; Inoue, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sai, Y.; Takamura, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Ginsberg, H.N.; et al. CCR5 plays a critical role in obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by regulating both macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Harris, S.B.; Retnakaran, R.; Gerstein, H.C.; Perkins, B.A.; Zinman, B.; Hanley, A.J. White blood cell subtypes, insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction in high-risk individuals—The PROMISE cohort. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, C.A.; Burgos, X.; Ellis, C.J.; Zubia, R.Y.; Ontiveros, D.; Reyes, H.; Lozano, C. Associations of insulin resistance with cardiovascular risk factors and inflammatory cytokines in normal-weight Hispanic women. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, M.A.; Alipour, A.; Klop, B.; van de Geijn, G.J.; Janssen, H.W.; Njo, T.L.; van der Meulen, N.; Rietveld, A.P.; Liem, A.H.; Westerman, E.M.; et al. Glucose-dependent leukocyte activation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, familial combined hyperlipidemia, and healthy controls. Metabolism 2015, 64, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Farha, M.; Behbehani, K.; Elkum, N. Comprehensive analysis of circulating adipokines and hsCRP association with cardiovascular disease risk factors and metabolic syndrome in Arabs. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.L.; Donohoe, C.L.; Lysaght, J.; Reynolds, J.V. Visceral obesity, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and cancer. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamodi, Z.; Al-Habori, M.; Al-Meeri, A.; Saif-Ali, R. Association of adipokines, leptin/adiponectin ratio and C-reactive protein with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, W.; Farwa, U.; Khan, F.R. The metabolic syndrome and inflammation: The role of insulin resistance and increased adiposity. Oman Med. J. 2015, 30, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Kim, Y.B. Molecular mechanism of insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2010, 25, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: Integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveyenko, A.V.; Liuwantara, D.; Gurlo, T.; Kirakossian, D.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; White, M.F.; Copps, K.D.; Volpi, E.; Fujita, S.; et al. Pulsatile portal vein insulin delivery enhances hepatic insulin action and signaling. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2269–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Leavens, K.F.; Hunter, R.W.; Koren, S.; von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, A.; Lu, M.; Satapati, S.; Chu, Q.; Sakamoto, K.; Burgess, S.C.; et al. A noncanonical, GSK3-independent pathway controls postprandial hepatic glycogen deposition. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wan, M.; Leavens, K.F.; Chu, Q.; Monks, B.R.; Fernandez, S.; Ahima, R.S.; Ueki, K.; Kahn, C.R.; Birnbaum, M.J. Insulin regulates liver metabolism in vivo in the absence of hepatic Akt and Foxo1. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.J.; Camporez, J.P.G.; Kursawe, R.; Titchenell, P.M.; Zhang, D.; Perry, C.J.; Jurczak, M.J.; Abudukadier, A.; Han, M.S.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Cell 2015, 160, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogan, J.S.; Rubin, B.R.; Yu, C.; Löffler, M.G.; Orme, C.M.; Belman, J.P.; McNally, L.J.; Hao, M.; Cresswell, J.A. Endoproteolytic cleavage of TUG protein regulates GLUT4 glucose transporter translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 23932–23947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S. Physiological regulation of lipoprotein lipase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruud, J.; Steculorum, S.M.; Brüning, J.C. Neuronal control of peripheral insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, E.D.; Liu, T.; Kong, X.; Sohn, J.W.; Vong, L.; Deng, Z.; Lee, C.E.; Lee, S.; Williams, K.W.; Olson, D.P.; et al. Melanocortin 4 receptors in autonomic neurons regulate thermogenesis and glycemia. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.W.; Elias, C.F.; Fukuda, M.; Williams, K.W.; Berglund, E.D.; Holland, W.L.; Cho, Y.R.; Chuang, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Choi, M.; et al. Direct insulin and leptin action on pro-opiomelanocortin neurons is required for normal glucose homeostasis and fertility. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Gortan Cappellari, G.; Ragni, M.; Nisoli, E. Insulin resistance in obesity: An overview of fundamental alterations. Eat. Weight Disord. 2018, 23, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.P.; David Cheng, T.Y.; Tsai, S.P.; Chan, H.T.; Hsu, H.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Eriksen, M.P. Are Asians at greater mortality risks for being overweight than Caucasians? Redefining obesity for Asians. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 12, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, P.C.; Dekkers, O.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Dieben, S.W.; Helmerhorst, F.M. PCOS, coronary heart disease, stroke and the influence of obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2011, 17, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, A.M.; Sicari, R.; Folli, F.; Gastaldelli, A. Ectopic fat storage, insulin resistance, and hypertension. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinkens, R.; Goossens, G.H.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Targeting fatty acid metabolism to improve glucose metabolism. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 715–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, S.; Samocha-Bonet, D.; Milner, K.L.; Greenfield, J.R.; Chisholm, D.J. Adiposity and insulin resistance in humans: The role of the different tissue and cellular lipid depots. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 463–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, A.; Konings, E.; Goossens, G.H.; Bouwman, F.G.; Moors, C.C.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Afman, L.A.; Müller, M.; Mariman, E.C.; Blaak, E.E. PUFAs acutely affect triacylglycerol-derived skeletal muscle fatty acid uptake and increase postprandial insulin sensitivity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Gross, M.; Lee, D.H.; Holvoet, P.; Himes, J.H.; Shikany, J.M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Oxidative stress and insulin resistance: The coronary artery risk development in young adults’ study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangvarasittichai, S. Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossarizza, A.; Ferraresi, R.; Troiano, L.; Roat, E.; Gibellini, L.; Bertoncelli, L.; Nasi, M.; Pinti, M. Simultaneous analysis of reactive oxygen species and reduced glutathione content in living cells by polychromatic flow cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 4, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.S.; Zhou, L.; Park, S.Y.; Xu, L.; Xia, X.; Ye, J.; Su, L.; Jeong, K.H.; Hur, J.H.; Oh, H.; et al. Insulin resistance and white adipose tissue inflammation are uncoupled in energetically challenged Fsp27-deficient mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, D.; Xi, Q.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Jaggar, J.H. Mitochondria control functional CaV1.2 expression in smooth muscle cells of cerebral arteries. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Manna, P.; Gachhui, R.; Sil, P.C. D-saccharic acid 1,4-lactone protects diabetic rat kidney by ameliorating hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammatory cytokines via NF-κB and PKC signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 267, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.; Deng, H.; Fukushima, A.; Cai, X.; Boivin, B.; Galic, S.; Bruce, C.; Shields, B.; Skiba, B. Reactive oxygen species enhance insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leloup, C.; Tourrel-Cuzin, C.; Magnan, C.; Karaca, M.; Castel, J.; Carneiro, L.; Colombani, A.L.; Ktorza, A.; Casteilla, L.; Pénicaud, L. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species are obligatory signals for glucose-induced insulin secretion. Diabetes 2009, 58, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangvarasittichai, S.; Poonsub, P.; Tangvarasittichai, O. Association of serum lipoprotein ratios with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 131, 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, Y.F.; Stafford, J.M.; McGuinness, O.P. Pathway-selective insulin resistance and metabolic disease: The importance of nutrient flux. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20462–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Hernández, A.; Leon-Aparicio, D.; Chavez-Reyes, J.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A.; DeJesus, S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in insulin resistance and diabetes. Cell Calcium 2014, 56, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamment, M.; Hajduch, E.; Ferré, P.; Foufelle, F. New insights into ER stress-induced insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, H.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; Qi, L. Stressed out about obesity: IRE1a-XBP1 in metabolic disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Another link between obesity and insulin resistance/inflammation? Diabetes 2009, 58, 518–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wang, C.H. ER stress in adipocytes and insulin resistance: Mechanisms and significance (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, N.; Asada, R.; Saito, A.; Kanemoto, S.; Imaizumi, K. Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes chronic inflammation in adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ozcan, U. Unfolded protein response signaling and metabolic diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Studies Related to Inflammatory Mechanisms | ||
| Study | Design | Key Findings |
| Chen et al. (2015) [9] | Systematic review | A wide range of inflammatory processes and molecules, such as cytokines and macrophages, increase the risk of insulin resistance |
| Rehman and Akash (2016) [10] | Systematic review | Inflammation is a critical physiological process associated with increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and white blood cells in the body |
| Xu et al. (2015) [15] | Systematic review | Inflammatory markers, such as chemokines and chemokine receptors, play a vital role in the development of insulin resistance and the progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Vella et al. (2013) [18] | Experimental study | Surrogate markers of inflammation are associated with insulin resistance and the risk of cardiovascular disease among Hispanic women |
| de Vries et al. (2015) [19] | Randomized controlled trial | Insulin resistance is associated with acute and chronic hyperglycemia and postprandial leukocyte activation |
| Al-Hamodi et al. (2014) [22] | Randomized controlled trial | A significant association exists among insulin resistance, adiposity, adipokines, C-reactive protein, and the leptin/adiponectin ratio |
| Studies Related to Neural mechanisms | ||
| Study | Design | Key Findings |
| Samuel and Shulman (2016) [26] | Systematic review | Insulin resistance is a complex disorder caused by inflammatory and neural signaling processes and substrate flux |
| Samuel and Shulman (2012) [26] | Systematic review | Insulin resistance is caused by unfolded protein response (UPR) activation, ectopic lipid metabolite accumulation, and innate immune system responses |
| Wan M et al. (2013) [29] | Systematic review | The GSK3-independent pathway and postprandial hepatic glycogen deposition contribute to the development of insulin resistance |
| Lu M et al. (2012) [30] | Experimental study (gene expression analysis) | Deletion of Akt results in the activation of FoX01–dependent gene expression and eventually insensitivity to insulin level changes |
| Kersten (2012) [33] | Systematic review | Liver-derived apolipoproteins influence the risk of insulin resistance |
| Hill et al. (2010) [36] | Systematic review | Insulin action and sensitivity are regulated by pro-opiomelanocortin neurons. These neurons also control glucose homeostasis |
| Studies Related to Cellular Mechanisms | ||
| Study | Design | Key Findings |
| Sironi et al. (2011) [40] | Systematic review | Increased uptake of fatty acids and lipids can result in obesity and the subsequent ectopic storage of fats |
| Stinkens et al. (2015) [41] | Systematic review | Fatty acid metabolism and accumulation may result in the emergence and progression of complications, such as insulin resistance |
| Tangvarasittichai (2015) [45] | Systematic review | Oxidative stress leads to dyslipidemia, β-cell dysfunction, loss of glucose tolerance, and insulin resistance |
| Cossarizza et al. (2010) [46] | Experimental study (polychromatic flow cytometry) | A significant association exists among reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress, and cell death |
| Narayanan et al. (2010) [48] | Systematic review | Mitochondria dysfunction affects the expression of CaV1.2 in muscles and contributes to the development of insulin resistance |
| Tangvarasittichai et al. (2010) [52] | Systematic review and meta-analysis | A significant association exists between the serum lipoprotein ratios and insulin resistance among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Khan and Wang (2014) [58] | Systematic review | ER stress leads to the development of insulin resistance through neural and inflammatory mechanisms |
| Kawasaki et al. (2012) [59] | Systematic review | Obesity-induced ER leads to chronic inflammation in adipose tissues and increases the risk of insulin resistance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arneth, B. Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Obesity. Endocrines 2024, 5, 153-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5020011
Arneth B. Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Obesity. Endocrines. 2024; 5(2):153-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleArneth, Borros. 2024. "Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Obesity" Endocrines 5, no. 2: 153-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5020011
APA StyleArneth, B. (2024). Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Obesity. Endocrines, 5(2), 153-165. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5020011





