Abstract
Ghrelin and its growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) have been found in the placenta, both in endothelial and trophoblast cells. Ghrelin has been shown to decrease blood pressure in several systems and improve endothelial function by stimulating VEGF production. Because locally increased Ghrelin was detected in the preeclamptic fetoplacental unit, we hypothesized its involvement in the fibrinolysis and vascular tone typically observed in preeclamptic patients. This study aimed to evaluate the synthesis of plasminogen activators (PAs), PA inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and urokinase-type PA (uPA) receptor (uPAR) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) since the components of the PA/plasmin system are vital players in the extracellular matrix remodeling process necessary for angiogenesis. HUVECs were treated for 24 h with increasing concentrations of Ghrelin (10−11–10−7 M) or IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL). PAs, PAI-1, and uPAR mRNAs were determined by real-time PCR and PA activity was determined by casein underlay. We demonstrated an increase in uPA, tissue-type PA (tPA), and uPAR mRNA; a reduction in PAI-1 mRNA in HUVECs treated with Ghrelin; and an increase in total uPA activity. In conclusion, our results suggest a potential compensatory physiological mechanism for Ghrelin in response to the maternal endothelial dysfunction observed in the preeclamptic fetoplacental unit.
1. Introduction
Ghrelin is a 28-amino-acid hormone produced primarily by the stomach and small intestine. Ghrelin is involved in a series of metabolic functions, mainly stimulating the release of GH by the pituitary gland through its growth hormone (GH) secretagogue receptor (GHSR). Two identified transcript variants are expressed in several tissues: GHSR type 1a, the fully functional receptor, and type 1b, the biologically inactive receptor, is expressed in various peripheral human tissues, including kidney, heart, and blood vessels [1]. Ghrelin has also been found in the human placenta [2], where its expression varies with the pregnancy proceeding. It is highly expressed in the first trimester, peaks in the second trimester, and drops to its lowest in the third trimester [3]. The presence of Ghrelin and its functional receptor GHSR-1a in the placenta and the pregnancy-related changes of Ghrelin expression in the placenta suggest a functional role for Ghrelin in placental formation, differentiation, and function [4]. The presence of Ghrelin in cord blood has been found to be inversely correlated with birth weight [5], suggesting a role in the control of fetal growth and prevention of the development of metabolic diseases often associated with large birth weight [6]. Moreover, Ghrelin protein can be detected in trophoblast cells, mainly localized in the cytotrophoblast cells [3], thus indicating that Ghrelin may play a physiological role in healthy pregnancy and embryo implantation [7]. Placental Ghrelin may have an immunomodulatory role in pregnancy. Tolerance, immunosuppression, and immunomodulation must be established for a successful pregnancy. Hattori [8] found the expression of Ghrelin and its receptor in human immune cells. In addition, Dixit [9] demonstrated that Ghrelin exerts inhibitory effects on the expression and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF-alpha.
The placenta is known to be a source of hormonal and non-hormonal substances with angiogenic and vasoactive properties that play an important role in maintaining pregnancy, maternal adaptations, and mother-fetus interaction [10]. Moreover, endothelial integrity, regular fibrinolytic activity, and substances influencing the vascular tone are important to ensure normal vascular function. Alterations in blood flow may be responsible for placental infarction and fetal growth restriction observed in some pregnancy diseases mainly characterized by vascular disorders [11]. Vaso-regulatory imbalance in favor of vasoconstriction and endothelial dysfunction are among the significant characteristics of preeclampsia (PE) [12,13]. Ghrelin could be involved in these functions since it has been shown to positively influence endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. Increasing production of pro-inflammatory molecules has been shown in several diseases such as metabolic syndrome, atherosclerosis, and hypertension, and inflammation is one of the first events leading to endothelial dysfunction. Ghrelin has been shown to play an important role in controlling endothelial dysfunctions and decreasing blood pressure in several systems [14,15,16]. Its action is mediated by the stimulation of the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), thus increasing NO production. In human aortic endothelial cells, it has been shown that Ghrelin stimulates NO production via phosphorylation of eNOS, PI 3-kinase, and AKT through its receptor GHSR-1a [17]. However, the action of Ghrelin can also be mediated via NO-independent mechanisms [1,18]. Moreover, Ghrelin improves endothelial function by promoting angiogenesis through the Jagged1/Notch2/VEGF pathway [3].
The increased blood pressure in hypertension has been correlated with alterations in fibrinolytic activity [19]. The endothelium controls intravascular thrombosis by secreting molecules that prevent blood clot formation. Among these molecules, the plasminogen/plasmin system plays an important role in the dissolution of blood clots and the control of atherosclerosis, hemostasis, and thrombosis [20]. The plasminogen/plasmin system is composed of the inactive proenzyme plasminogen, which is converted into plasmin by the plasminogen activators (PAs): urokinase-type (uPA) and tissue-type (tPA) [21]. Plasmin, besides fibrin degradation, can degrade proteins of the extracellular matrix, directly and indirectly, by activating matrix metalloproteases [22,23]. Specific PA inhibitors (PAIs), PAI-1 and PAI-2, balance PA activity, thus limiting plasminogen activation and plasmin formation [24]. The PAI-1 inhibitor is predominantly a regulator of uPA, to which it binds covalently. PAI-1 at high levels prevents angiogenesis and tumorigenesis while facilitating tumor growth and angiogenesis at physiological levels [25]. Furthermore, in the absence of PAI, both tumor growth and angiogenesis are blocked. PAI-1 knockout mice have reduced vascularization on both the maternal and fetal sides of the placenta [26]. In addition, although tPA and uPA are secreted proteases, both can bind to the cell surface via specific cell surface receptors, thus protecting them from the inhibitory actions of the abundant plasma inhibitors [21].
The abnormal growth of the fetus requires an adequate supply of maternal blood brought into the placenta’s intervillous spaces. Therefore, the placenta, during its development, undergoes important morphological modifications associated with remodeling of uterine and fetal tissue and vascularization. As described above, the plasminogen/plasmin system has been associated with tissue remodeling and vessel formation. Moreover, the production of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors has been demonstrated by the trophoblast at the time of implantation when vessel remodeling is observed [7]. Frequently, in many diseases characterized by vascular disorders, endothelial injury also results in a dysregulation of the fibrinolytic system. For instance, in PE, a significant reduction in uPA concentrations in maternal plasma has been described [27,28,29], whereas PAI-1 levels were significantly increased [30]. Similar alterations have been found in umbilical cord circulation [31].
It has been demonstrated that human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) express mRNA for Ghrelin and both subtypes of GHSR receptors [32]. These findings suggest that these endothelial cells represent not only the site of synthesis but also a target of action of Ghrelin, which may exert a possible paracrine/autocrine action on this endothelium. Hence, there is an increased interest in the effects of Ghrelin on HUVECs, which, therefore, represent a good model for studying endothelial functions in the feto-mother unit.
Based on these data, this study aimed to verify whether Ghrelin could act on the protagonists of cell invasion and angiogenesis by evaluating its ability to influence the expression of uPA, tPA, PAI-1, and uPAR in HUVECs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Ghrelin (#031-40) was obtained from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Burlingame, CA, USA. Trypsin, antibiotics, and Hank’s balanced salt solution were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Interleukin-1β (IL-1β; #1 457 756), was obtained from Roche Diagnostics (Indianapolis, IN, USA). Heparin was obtained from Parke-Davis Spa (Lainate, MI, Italy). Medium 199 and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were purchased from Life Technologies, Inc. (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rome, Italy).
2.2. Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell Cultures
Human umbilical cords were obtained from healthy women who underwent uncomplicated term pregnancies. After collection, the umbilical cord was rapidly immersed in sterile saline solution (0.9% NaCl) and immediately processed for endothelial cell isolation as previously described [33]. The endothelial cells showed the typical cobblestone aspect and by immunostaining with an antibody versus factor VIII-related antigen [33].
After isolation, cells were plated on tissue culture flasks (25 cm2), grown in medium 199 containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS, antibiotics, endothelial cell growth factor, and heparin, and cultured in 5% CO2/95% air at 37 °C; cells reached confluence after 1–3 days of culture. Confluent cells were detached with trypsin and plated in 60 mm dishes.
Informed consent was obtained from each patient.
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and Quantification
To evaluate tPA, uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 expression, HUVECs were plated in 60 mm tissue culture dishes. Once grown to confluence, the cells were incubated with fresh serum-free medium alone (controls) or containing IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL) as a positive control or with Ghrelin (10−11–10−7 M) with or without IL-1β. After 24 h, HUVECs were treated for total RNA extraction. Total RNA was extracted using TRI-Reagent (Sigma-Aldrich). Total RNA was reverse-transcribed in a final volume of 20 μL using the M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase kit (Invitrogen, Milan, Italy) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The presence of transcripts for uPA, uPAR, tPA, and PAI-1 was evaluated by SYBR Green Real-Time PCR on an Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR System using SYBR Green Universal PCR Master Mix (EuroClone, Milan, Italy), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Each sample was normalized to its RPLP0 content [34]. The results were calculated using the ΔΔCt method and were expressed as fold increase with respect to C, arbitrarily set at 1. The primers utilized are shown in Table 1. The primers’ specificity was confirmed by melting curves.

Table 1.
Sequence of oligonucleotides used as real-time PCR primers.
2.4. Gel Electrophoresis and Casein Underlay
For PA enzymatic activity detection, HUVECs were plated in 35 mm tissue culture dishes. Once grown to confluence, the cells were incubated with fresh serum-free medium alone (controls) or containing IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL) as a positive control or with Ghrelin (10−11–10−7 M). After 24 h of treatment, aliquots of conditioned media and cell homogenates were separated by electrophoresis in 8% polyacrylamide slab gels in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS-PAGE) under nonreducing conditions according to the procedure of Laemmli [35]. PA was then visualized by placing the Triton-X-washed gel on a casein agar-plasminogen underlay, incubated at 37 °C in humidified chambers, and at the end photographed under dark-field illumination, as previously described [36]. Molecular weights were calculated from the position of prestained markers that were subjected to electrophoresis in parallel lines. The lytic zones were plasminogen-dependent. Densitometric analysis of the bands was performed using ImageJ software1.52a (NIH).
2.5. Dissociation of High-Molecular-Weight PA Forms
To dissociate tPA and uPA from the PAI inhibitors, media were treated with neutrophilic agents to convert the PA high molecular bands into the active forms of PAs [37]. The medium was mixed with an equal volume of 2% SDS in TRIS-HCl pH 7.5. After 30 min incubation at room temperature, 1 M hydroxylamine (Sigma-Aldrich) was added to the sample and incubated for an additional 90 min at room temperature. Samples were dialyzed against 0.1% SDS, 0.065 M Tris-HCl pH 6.8 and then analyzed for PA activity by gel electrophoresis and casein underlay.
2.6. Data Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA followed by the Tukey–Kramer test for comparisons of multiple groups. Values with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Ghrelin on uPA, uPAR, tPA, PAI-1 mRNA Expression
To determine whether Ghrelin was able to affect the mRNA levels of molecules of the plasminogen/plasmin system, HUVECs obtained from six separate cord preparations were plated in 60 mm dishes and cultured for 24 h in medium alone (C), IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL), or in the presence of increasing concentrations of Ghrelin (ranging from 10−11 to 10−7 M). Two 60 mm dishes for each experimental group were utilized in each independent experiment. At the end of culture, total RNA was extracted and analyzed by RT-PCR. As expected, IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL) increased uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 mRNA levels. As shown in Figure 1A,B,D, treatment of HUVECs with Ghrelin caused a dose-dependent increase in uPA, uPAR, and tPA mRNA levels, while PAI-1 mRNA was decreased (Figure 1C).
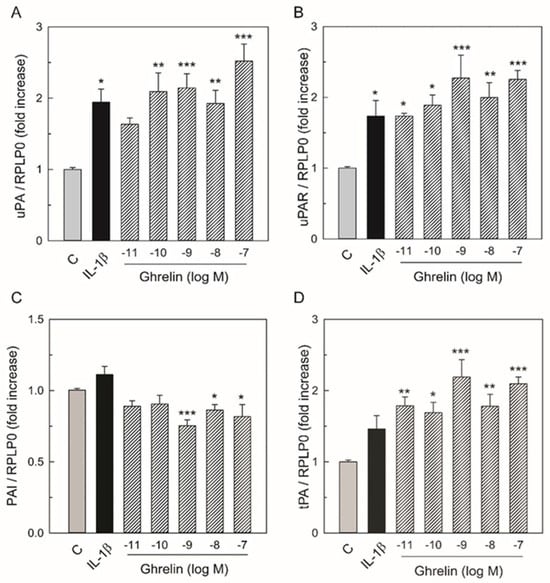
Figure 1.
Effect of IL-1β and Ghrelin on uPA (A), uPAR (B), PAI-1 (C), and tPA (D) mRNA levels in HUVECs. Total RNA was prepared from HUVECs cultured for 24 h with either medium alone as control (C), IL-1β 0.1 ng/mL, or increasing Ghrelin concentrations. Total RNA was subjected to real-time PCR using the specific primer sets shown in Table 1. The levels of the transcripts were normalized with the house-keeping gene (RPLP0). Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of six separate experiments using total RNA preparations from different cords. Results are expressed as fold increase with respect to the control set equal to 1. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 vs. C values.
3.2. Effects of Ghrelin on uPA, tPA, and PAI-1 Production
To investigate whether Ghrelin could modulate PA activity in HUVECs, the cells were cultured for 24 h medium alone (C), IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL), and Ghrelin (10−8–10−7 M). PA activity was assayed in the conditioned media (Figure 2A) and cell lysates (Figure 2B) with casein underlay. As shown in Figure 2A, in the conditioned medium, we observed a band with an apparent molecular mass of about 55 kDa, corresponding to human uPA. A lower band at 33 kDa represents one of the two chains present in uPA after its activation [38]. This band contains the proteolytic domain and is evidenced in the gel at 33 kDa. No bands were observed at the molecular mass of 68 kDa corresponding to human tPA. Both Ghrelin and IL-1β induced uPA activity. In addition, a doublet at higher molecular weight was present in the casein underlay, suggesting the presence of PAI-PA complexes.
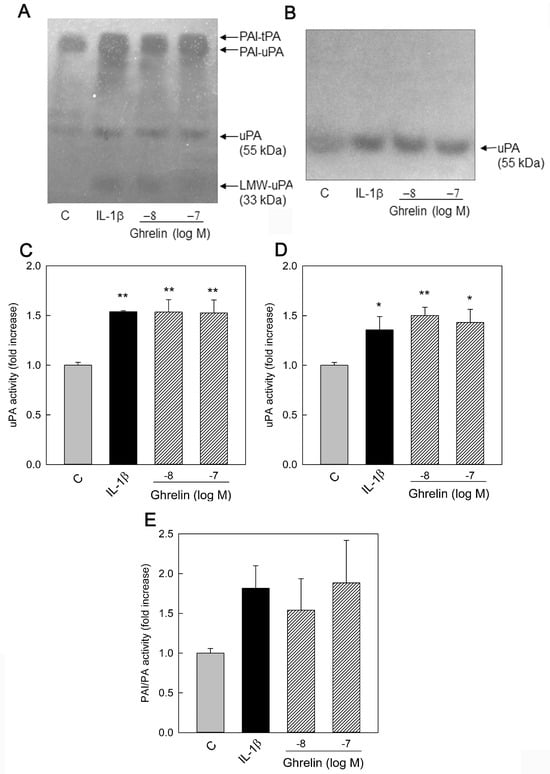
Figure 2.
Effect of Ghrelin on HUVEC PAs and PAI production. HUVECs were cultured for 24 h with medium alone (C), IL-1β (0.1 ng/mL), and Ghrelin (10−8–10−7 M). Aliquots of conditioned media (20 μL) (A) and cell lysate (15 μL) (B) were analyzed by zymography. The photographs were taken after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C. The figures shown are representative zymographies of four independent experiments. LMW–uPA (low–molecular–weight uPA). All bands were plasminogen-dependent. PA activity was measured by densitometric scanning of zymographies. Data represent the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. Values are reported as fold increase with respect to the control set equal to 1. (C) uPA activity in conditioned media (55 kDa), (D) uPA activity in cell lysates, and (E) PA activity associated with PAI in conditioned media. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. C values.
When cell lysates were examined (Figure 2B), only the uPA band was present. Despite the presence of tPA-mRNA in the cells, no free tPA activity was present in both medium and cell lysates.
PA activity was measured by densitometric scanning of zymographies. As shown in Figure 2, uPA activity increased in the conditioned medium (Figure 2C) and cell lysate (Figure 2D). The activity at higher molecular weight increased after stimulation with Ghrelin (Figure 2E). However, this last measure might not represent the actual amount of the enzyme bound to the PAI since PAs are tightly bound to their inhibitor, and the dissociation under the condition of these experiments is casual and never complete.
3.3. PAI and PA Dissociation
In order to understand if the tPA is absent because it is all bound to its inhibitor, conditioned media were treated with nucleophilic reagents to dissociate PAI and PAs [37]. The presence of PAs was evidenced by gel electrophoresis and casein underlay. After 60 min of incubation at 37 °C, in the presence of 0.1% SDS and 1.5 M NH4OH, we observed the dissociation of these high-molecular-weight bands into bands at MW 68 and 55 kDa, corresponding to tPA and uPA proteins, respectively. The results are shown in Figure 3. The treatment of the conditioned medium resulted in the dissociation of these proteins into their respective 68 and 55 kDa forms. After dissociation, we observed an increase in tPA activity (Figure 3B) and a slight decrease in uPA activity (Figure 3C) in response to both stimulations. However, these values did not reach significance.
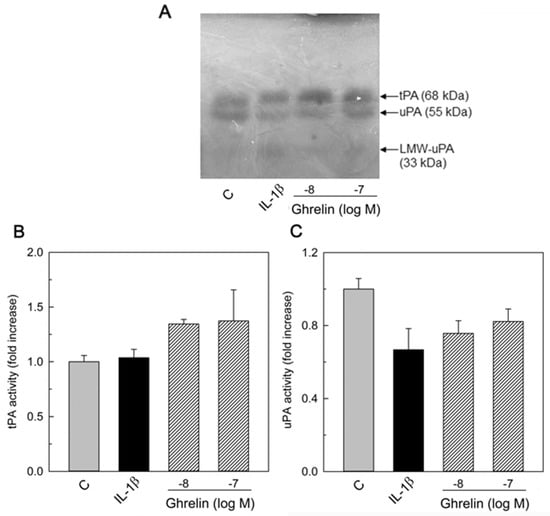
Figure 3.
Effect of treatment with neutrophilic agents to convert the PA high molecular bands into the active forms of PAs. HUVEC-conditioned media were treated as described in the Section 2 and analyzed by zymography. The photographs were taken after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C. (A) representative zymography of three independent experiments. LMW–uPA (low–molecular–weight uPA). PA activity was measured by densitometric scanning of zymographies. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Values are reported as fold increase with respect to the control set equal to 1. (B) tPA activity (68 kDa) and (C) uPA activity (55 kDa) after dissociation from PA/PAI complex.
4. Discussion
Ghrelin is present in the human placenta, and it has been shown to increase in pregnancy-induced hypertension [39] and in mild and severe PE compared to healthy controls [40]. Ghrelin is a potent vasodilator in humans capable of reversing the effects of endothelin-1 both in in vitro and in vivo studies with trials carried out on volunteers where intravenous injection of the peptide leads to a reduction in blood pressure in the middle artery [41,42]. This ability, together with the high levels of Ghrelin circulating in human plasma, considerably higher than those of other vasoactive peptides, and with the localization of GSH-R in the cardiovascular system, suggest that Ghrelin may have a vasodilatory role in the regulation of vascular tone. Moreover, Ghrelin activates the Jagged1/Notch2 pathway, inducing increased VEGF, which decreases in PE [3], showing a positive effect on hypertension in pregnancy.
In this study, we show that Ghrelin modulates the PA/plasmin system component in endothelial cells obtained from the human umbilical cord (HUVECs). The decrease in PAI-1 and the concomitant increase in uPA let us hypothesize a net increase in the proteolytic activity, thus favoring angiogenesis and tissue remodeling during placenta formation [28].
The components of the PA/plasmin system are vital players in the extracellular matrix remodeling process necessary for angiogenesis [43]. Ghrelin has been shown to affect HUVEC proliferation, migration, and tube formation [3], therefore promoting angiogenesis. Frequently, in many diseases characterized by vascular disorders such as PE, endothelial injury also results in a dysregulation of the fibrinolytic system [44]. The impairment of fetoplacental vascular function(s) is associated with maternal endothelial cell dysfunction and altered expression of PA system components. Higher levels of tPA and PAI-1 and lower levels of uPA and PAI-2 have been detected in plasma of women with severe PE [27,28,29,30]. Moreover, Roes et al. [31] found that in PE, the fetal fibrinolytic system was also affected. In fact, they found a very high increase in PAI-1 levels and a decrease in uPA levels in the umbilical cord of preeclamptic patients, suggesting a decreased fibrinolysis in the fetal circulation.
We demonstrated that Ghrelin significantly increased the expression of uPA-, its receptor uPAR-, and tPA-mRNA. Conversely, Ghrelin had an inhibitory effect on PAI-1 mRNA expression. It is known that the extracellular enzymatic activity produced by endothelial cells represents the net expression of activity resulting from the interplay between plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors [45]. Therefore, the presence of mRNA might not reflect the levels of proteins nor their activity as proteolytic enzymes. For this reason, we analyzed PA activity in media and cell lysates. As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, different results were obtained when we observed enzymatic activity. Casein underlay showed an increase in uPA activity in HUVECs after Ghrelin treatment, both in conditioned media and in cell lysates. Conversely, despite the presence of tPA-mRNA, we could not detect tPA activity either in conditioned media or cell lysates. When we analyzed the conditioned media with casein underlay, we observed the presence of high-MW bands that suggested the presence of PAI/PAs complexes. Therefore, in our media, the absence of tPA activity could be ascribed to the inhibitory action of PAI, and in particular of PAI-1, which is the major form of PAI secreted by endothelial cells [46]. In fact, after the treatment of conditioned media with nucleophilic reagents to dissociate PAI and PAs, it was possible to observe the presence of both uPA and tPA with casein underlay.
Urokinase PA is a secreted protein; however, once secreted, uPA can bind to its receptors on the cell membrane. The binding to the receptor protects uPA from its inhibitors but, at the same time, allows the formation of plasmin on the cell surface, focusing the extracellular matrix degradation in the pericellular space [47]. Our data showing the increased expression of uPA and its receptor uPAR align with the increase in uPA associated with cell lysates observed via casein underlay (Figure 2B). Studies on HUVECs evidenced the ability of the uPA/u-PAR complex to stimulate, in a dose-dependent manner, the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells [48]. In fact, the u-PAR receptor allows the potentiation of proteolytic activity on the cell surface [47]. Moreover, uPAR can function as a receptor for components of the extracellular matrix and also provide mitogenic signals, which induce the proliferation of invading cells [49].
Interestingly, the production of Ghrelin varies with the progression of pregnancy, increasing in the first trimester, peaking in the second trimester, and dropping to its lowest in the third trimester [3]. In early-onset PE patients (<34 weeks), Ghrelin was reduced compared to control group. This reduction was consistent with the stronger association between abnormal placental development and trophoblastic invasion and early-onset preeclampsia [50]. On the contrary, Ghrelin production is increased in late-onset PE [3]. It has been suggested that the decrease in Ghrelin may be involved in the onset of early-onset PE. At the same time, the increase in Ghrelin levels in the plasma of late-onset PE patients may be a compensatory physiological mechanism in response to maternal endothelial dysfunction [3]. As regards the embryo, the presence of Ghrelin in the placenta in the first trimester and its characteristic expression pattern, which sees it highly expressed in the cytotrophoblast cells, i.e., in the embryonic cells mainly involved in invasion, suggest an active role of the peptide in the placentation process. Studies on sheep’s placenta show that the peak expression of Ghrelin occurs in the phase of active proliferation of the placenta [51]. Therefore, our results, considering the expression of Ghrelin that parallels the process of cytotrophoblastic invasion, lead us to hypothesize that one of the roles played by the peptide in the placenta is to stimulate the production of uPA to favor the placentation process either favoring trophoblast cell migration and invasion and stimulating angiogenesis.
Oxidative stress can negatively affect the endothelium, and Ghrelin has been shown to ameliorate endothelial functions by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress via activation of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) [52,53]. Interestingly, AMKP activation has been shown to inhibit PAI-1 production via adipocytes [54] and to inhibit the NF-kb binding on PAI-1 promoter in HUVECs [55]. Therefore, it is possible to hypothesize the Ghrelin can control PA proteolytic activity by modulation of PAI-1 expression via cAMP-PKA-AMPK signaling.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we demonstrated that Ghrelin increased the production of uPA and its receptor significantly. Moreover, the proteolytic activity was further increased because of the decreased production of PAI-1 caused by Ghrelin. It is essential to know that extracellular proteolysis, necessary for normal capillary morphogenesis, requires to be appropriately balanced by protease inhibitors. Therefore, our results, together with the data showing stimulation of VEGF [3], lead us to hypothesize that one of the roles played by the peptide in the placenta is to favor the placentation process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.C., A.T. and R.A.; methodology, E.F. and G.N.; software, R.C.; validation, R.C. and R.A.; formal analysis, R.C.; investigation, E.F., G.N., R.A. and R.C.; resources, R.C.; data curation, R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, R.C.; writing—review and editing, R.A. and R.C.; supervision, R.C. and R.A.; funding acquisition, R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Sapienza University (Ateneo) #RP11916B7A9A378C to R.C.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent for anonymous cord donation was obtained from each patient.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mao, Y.; Tokudome, T.; Kishimoto, I. Ghrelin and Blood Pressure Regulation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2016, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualillo, O.; Caminos, J.; Blanco, M.; Garcia-Caballero, T.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F. Ghrelin, a novel placental-derived hormone. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fei, H. Ghrelin promotes angiogenesis by activating the Jagged1/Notch2/VEGF pathway in preeclampsia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak-Mardyla, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E. Effect of ghrelin on proliferation, apoptosis and secretion of progesterone and hCG in the placental JEG-3 cell line. Reprod. Biol. 2010, 10, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, M.I.; Lazo-de-la-Vega-Monroy, M.L.; Zaina, S.; Sabanero, M.; Daza-Benitez, L.; Malacara, J.M.; Barbosa-Sabanero, G. Association of cord blood des-acyl ghrelin with birth weight, and placental GHS-R1 receptor expression in SGA, AGA, and LGA newborns. Endocrine 2016, 53, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, S.M.A.; Kleinman, K.P.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Trends in birth weight and gestational length among singleton term births in the United States: 1990–2005. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 115, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappino, A.P.; Huarte, J.; Belin, D.; Vassalli, J.D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Saito, T.; Yagyu, T.; Jiang, B.H.; Kitagawa, K.; Inagaki, C. GH, GH receptor, GH secretagogue receptor, and ghrelin expression in human T cells, B cells, and neutrophils. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.D.; Schaffer, E.M.; Pyle, R.S.; Collins, G.D.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Palaniappan, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr.; Taub, D.D. Ghrelin inhibits leptin- and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Ida, T.; Shiimura, Y.; Matsui, K.; Oishi, K.; Kojima, M. Insights into the Regulation of Offspring Growth by Maternally Derived Ghrelin. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 852636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Trujillo, L.; Garcia-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Guijarro, L.G.; Bravo, C.; De Leon-Luis, J.A.; Saez, J.V.; Bujan, J.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Garcia-Honduvilla, N.; et al. Considering the Effects and Maternofoetal Implications of Vascular Disorders and the Umbilical Cord. Medicina 2022, 58, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathiram, P.; Moodley, J. Pre-eclampsia: Its pathogenesis and pathophysiolgy. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeldt, D.S.; Bird, I.M. Vascular adaptation in pregnancy and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R27–R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mao, S.J.; McLean, L.R.; Powers, R.W.; Larsen, W.J. Proteins of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor family stabilize the cumulus extracellular matrix through their direct binding with hyaluronic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 28282–28287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Schinzari, F.; Iantorno, M.; Rizza, S.; Melina, D.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C. Ghrelin improves endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, N.; Annambhotla, S.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Chai, H.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Growth hormone-releasing peptide ghrelin inhibits homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries and human endothelial cells. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 49, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iantorno, M.; Chen, H.; Kim, J.A.; Tesauro, M.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C.; Quon, M.J. Ghrelin has novel vascular actions that mimic PI 3-kinase-dependent actions of insulin to stimulate production of NO from endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E756–E764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, H.; Nagaya, N.; Enomoto, M.; Nakagawa, E.; Oya, H.; Kangawa, K. Vasodilatory effect of ghrelin, an endogenous peptide from the stomach. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 39, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, K.; Tengborn, L.; Smith, U. Elevated fibrinogen and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in hypertension are related to metabolic risk factors for cardiovascular disease. J. Intern. Med. 1990, 227, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, W.P.; Garg, N.; Sunkar, M. Vascular functions of the plasminogen activation system. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, K.; Andreasen, A.; Grondahl-Hansen, J.; Kristensen, P.; Nielsen, L.S.; Skriver, L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation and cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 1985, 44, 139–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.G.; Holloway, R.W.; Miller, V.A.; Waisman, D.M. Plasmin and Plasminogen System in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, M.S. Role of the matrix metalloproteinase and plasminogen activator-plasmin systems in angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1104–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, A.; Georg, B.; Lund, L.R.; Riccio, A.; Stacey, S.N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: Hormonally regulated serpins. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1990, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajou, K.; Masson, V.; Gerard, R.D.; Schmitt, P.M.; Albert, V.; Praus, M.; Lund, L.R.; Frandsen, T.L.; Brunner, N.; Dano, K.; et al. The plasminogen activator inhibitor PAI-1 controls in vivo tumor vascularization by interaction with proteases, not vitronectin. Implications for antiangiogenic strategies. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferovic, M.D.; Gupta, M.B. Increased Umbilical Cord PAI-1 Levels in Placental Insufficiency Are Associated with Fetal Hypoxia and Angiogenesis. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 7124186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.C.; Anandakumar, C.; Montan, S.; Ratnam, S.S. Plasminogen activators, plasminogen activator inhibitors and markers of intravascular coagulation in pre-eclampsia. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1993, 35, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindoff, C.; Astedt, B. Plasminogen activator of urokinase type and its inhibitor of placental type in hypertensive pregnancies and in intrauterine growth retardation: Possible markers of placental function. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1994, 171, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.H.; Koh, S.C.; Malcus, P.; SvenMontan, S.; Biswas, A.; Arulkumaran, S.; Ratnam, S.S. Preeclampsia: Haemostatic status and the short-term effects of methyldopa and isradipine therapy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 1998, 24, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelles, A.; Gilabert, J.; Aznar, J.; Loskutoff, D.J.; Schleef, R.R. Changes in the plasma levels of type 1 and type 2 plasminogen activator inhibitors in normal pregnancy and in patients with severe preeclampsia. Blood 1989, 74, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roes, E.M.; Sweep, C.G.; Thomas, C.M.; Zusterzeel, P.L.; Geurts-Moespot, A.; Peters, W.H.; Steegers, E.A. Levels of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in maternal and umbilical cord plasma in severe preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 187, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conconi, M.T.; Nico, B.; Guidolin, D.; Baiguera, S.; Spinazzi, R.; Rebuffat, P.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Vacca, A.; Carraro, G.; Parnigotto, P.P.; et al. Ghrelin inhibits FGF-2-mediated angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Peptides 2004, 25, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, F.; Tropea, A.; Minici, F.; Orlando, M.; Lamanna, G.; Gangale, M.F.; Panetta, B.; Tiberi, F.; Vaccari, S.; Canipari, R.; et al. Effects of insulin-like growth factor I and II on prostaglandin synthesis and plasminogen activator activity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhashab, S.; Lary, S.; Ahmed, F.; Schulten, H.J.; Bashir, A.; Ahmed, F.W.; Al-Malki, A.L.; Jamal, H.S.; Gari, M.A.; Weaver, J.U. Reference genes for expression studies in hypoxia and hyperglycemia models in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. G3 2014, 4, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, D.; Godeau, F.; Vassalli, J.D. Tumor promoter PMA stimulates the synthesis and secretion of mouse pro-urokinase in MSV-transformed 3T3 cells: This is mediated by an increase in urokinase mRNA content. EMBO J. 1984, 3, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booyse, F.M.; Scheinbuks, J.; Lin, P.H.; Traylor, M.; Bruce, R. Isolation and interrelationships of the multiple molecular tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activator forms produced by cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 15129–15138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Arimura, H.; Nishida, M.; Suyama, T. Primary structure of single-chain pro-urokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 12382–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, Y.; Hosoda, H.; Shibata, K.; Makino, I.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Kawarabayashi, T. Alteration of plasma ghrelin levels associated with the blood pressure in pregnancy. Hypertension 2002, 39, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.; Ellidag, H.Y.; Ayik, H.; Bulbul, G.A.; Derbent, A.U.; Kulaksizoglu, S.; Yilmaz, N. Increased serum ghrelin in preeclampsia: Is ghrelin a friend or a foe? Ginekol. Pol. 2016, 87, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Nagaya, N.; Teranishi, Y.; Imazu, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Shokawa, T.; Kangawa, K.; Kohno, N.; Yoshizumi, M. Ghrelin improves endothelial dysfunction through growth hormone-independent mechanisms in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, K.E.; Davenport, A.P. Comparison of vasodilators in human internal mammary artery: Ghrelin is a potent physiological antagonist of endothelin-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.A.; Shaker, B.T.; Bajou, K. The Plasminogen-Activator Plasmin System in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusse, L.M.; Rios, D.R.; Pinheiro, M.B.; Cooper, A.J.; Lwaleed, B.A. Pre-eclampsia: Relationship between coagulation, fibrinolysis and inflammation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loskutoff, D.J.; Ny, T.; Sawdey, M.; Lawrence, D. Fibrinolytic system of cultured endothelial cells: Regulation by plasminogen activator inhibitor. J. Cell. Biochem. 1986, 32, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprengers, E.D.; Kluft, C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood 1987, 69, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, F.; Sidenius, N. The urokinase receptor: Focused cell surface proteolysis, cell adhesion and signaling. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, T.; Casslen, B.; Gustavsson, B.; Benraad, T.J. Human endothelial cell migration is stimulated by urokinase plasminogen activator:plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 complex released from endometrial stromal cells stimulated with transforming growth factor beta1; possible mechanism for paracrine stimulation of endometrial angiogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 1998, 59, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, R.; Gandhari, M.; Stroebel, P.; Marx, A.; Allgayer, H.; Arens, N. The urokinase-system--role of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.; Peterson, E. A critical review of early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2011, 66, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.L.; Adam, C.L.; Brown, Y.A.; Wallace, J.M.; Aitken, R.P.; Lea, R.G.; Miller, D.W. An immunohistochemical study of the localization and developmental expression of ghrelin and its functional receptor in the ovine placenta. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2007, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Pan, Z.; Ou, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Li, R.; Yang, P.; Han, W.; Guan, S.; et al. AMPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway regulated by ghrelin participates in the regulation of HUVEC and THP1 Inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 437, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F. Ghrelin improves endothelial function and reduces blood pressure in Ang II-induced hypertensive mice: Role of AMPK. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2208774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komiya, M.; Fujii, G.; Takahashi, M.; Shimura, M.; Noma, N.; Shimizu, S.; Onuma, W.; Mutoh, M. Bi-directional regulation between adiponectin and plasminogen activator-inhibitor-1 in 3T3-L1 cells. In Vivo 2014, 28, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, C.; Xin, L.; Zhong, S.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, L. Adiponectin Inhibits TNF-alpha-Activated PAI-1 Expression Via the cAMP-PKA-AMPK-NF-kappaB Axis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).