The Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Contributes to cAMP-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. RNA Isolation for Quantitative RT-PCR
2.4. siRNA-Mediated Depletion of uPA
2.5. Protein Purification and Western Blots
2.6. Progesterone Quantification
2.7. Plasmids
2.8. Cell Transfections and Luciferase Assays
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Plau Expression Is Increased by Forskolin Treatment, and This Increase Is Blunted by AMPK Activation
3.2. Urokinase Is Implicated in Steroidogenesis
3.3. The cAMP Responsive Region Is Located within the Proximal Plau Promoter
3.4. KLF6 and SP1 Activate the Plau Promoter
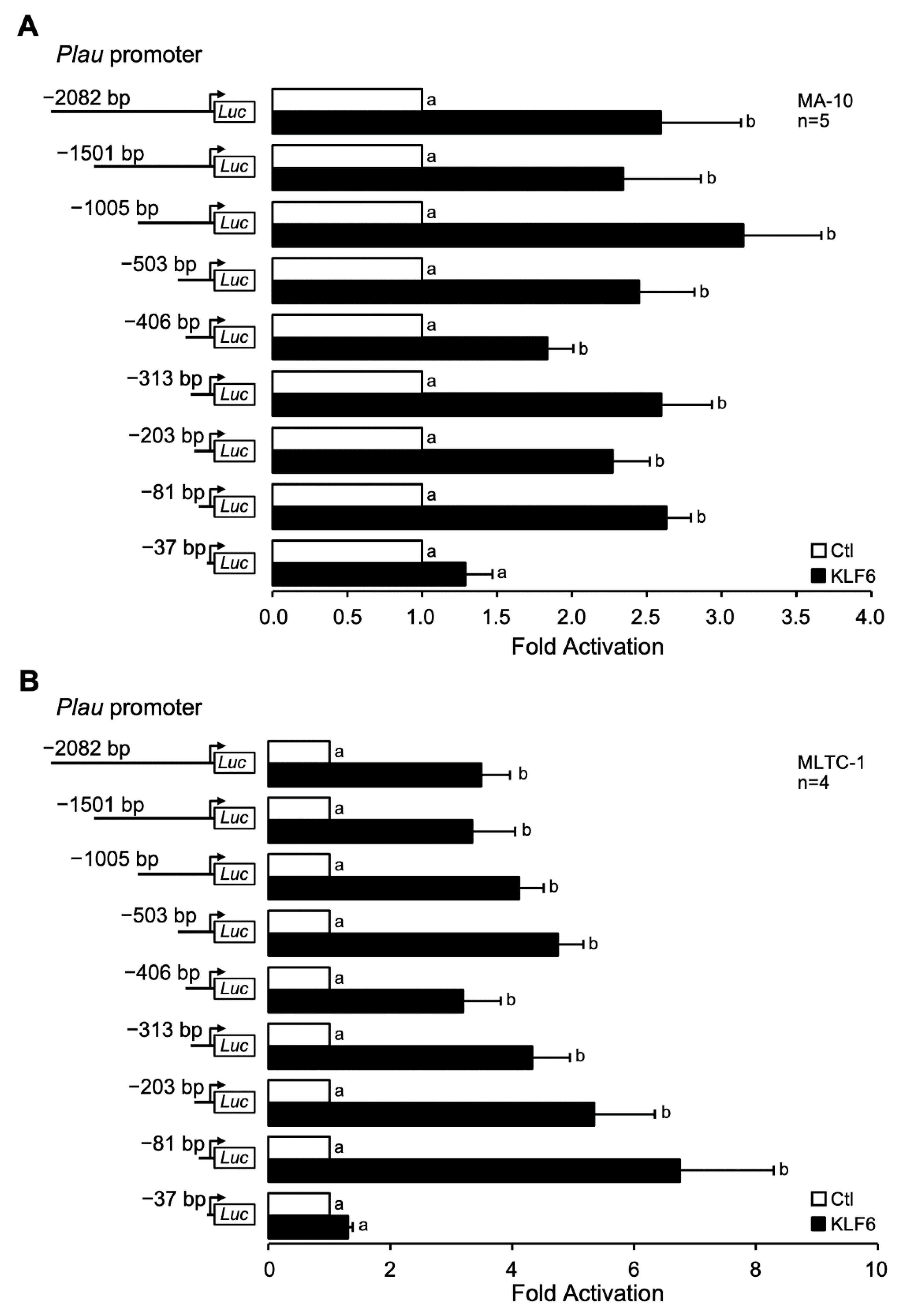
3.5. KLF6-Dependent Activation of the Plau Promoter Requires the Proximal −81/−37 bp Region
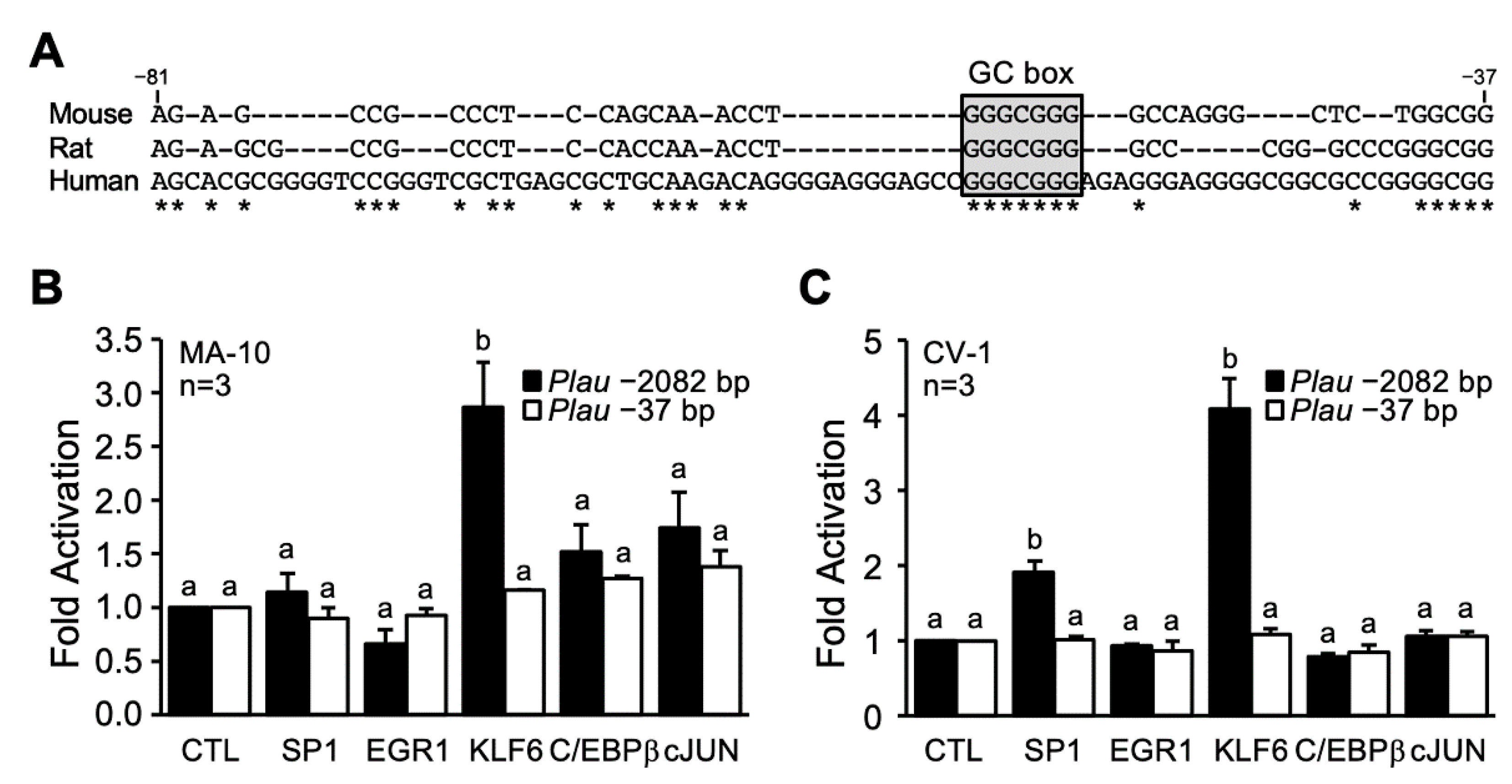
3.6. The GC Box in the Proximal Promoter Contributes to KLF6- and cAMP-Dependent Activation of the Plau Promoter
4. Discussion
4.1. uPA Contributes to Leydig Cell Steroidogenesis
4.2. Hormonal- and KLF6-Dependent Regulation of Plau Expression in Leydig Cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leydig, F. Zur anatomie der mannlichen geschlechtsorgane und analdrusen der saugethiere. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1850, 2, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bouin, P.; Ancel, P. Recherches sur les cellules interstitielles du testicule des mammiferes. Arch. Zool. Exp. Gen. 1903, 1, 437–523. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, P.F.; Irby, D.C.; De Kretser, D.M. Conversion of cholesterol to androgens by rat testes: Comparison of interstitial cells and seminiferous tubules. Endocrinology 1969, 84, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, L.L.; Eik-Nes, K.B. On the formation of testosterone by the perfused rabbit testis. Can. J. Biochem. 1966, 44, 1327–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufau, M.L.; Tsuruhara, T.; Horner, K.A.; Podesta, E.; Catt, K.J. Intermediate role of adenosine 3′:5′-cyclic monophosphate and protein kinase during gonadotropin-induced steroidogenesis in testicular interstitial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 3419–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tremblay, J.J. Molecular regulation of steroidogenesis in endocrine Leydig cells. Steroids 2015, 103, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattos, K.; Viger, R.S.; Tremblay, J.J. Transcription factors in the regulation of leydig cell gene expression and function. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 881309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B.J.; Wells, J.; King, S.R.; Stocco, D.M. The purification, cloning, and expression of a novel luteinizing hormone-induced mitochondrial protein in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Characterization of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 28314–28322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu-Albergine, M.; Tsai, L.-C.L.; Patrucco, E.; Beavo, J.A. cAMP-specific phosphodiesterases 8A and 8B, essential regulators of Leydig cell steroidogenesis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 81, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdou, H.S.; Bergeron, F.; Tremblay, J.J. A cell-autonomous molecular cascade initiated by AMP-activated protein kinase represses steroidogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 4257–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crippa, M.P. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, D.; Franco, P.; Stoppelli, M.P. Modulation of cellular function by the urokinase receptor signalling: A mechanistic view. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 818616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canipari, R.; Strickland, S. Studies on the hormonal regulation of plasminogen activator production in the rat ovary. Endocrinology 1986, 118, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, R.; Miskin, R.; Tsafriri, A. Follicular plasminogen activator: Involvement in ovulation. Endocrinology 1985, 116, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettle, J.A.; Waller, E.K.; Fritz, I.B. Hormonal stimulation alters the type of plasminogen activator produced by Sertoli cells. Biol. Reprod. 1986, 34, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vihko, K.K.; Toppari, J.; Saksela, O.; Suominen, J.J.; Parvinen, M. Testicular plasminogen activators during postnatal development in the rat. Acta Endocrinol. 1986, 112, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolli, R.; Monaco, L.; Di Bonito, P.; Canipari, R. Hormonal regulation of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activator in rat Sertoli cells. Biol. Reprod. 1995, 53, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odet, F.; Verot, A.; Le Magueresse-Battistoni, B. The mouse testis is the source of various serine proteases and serine proteinase inhibitors (SERPINs): Serine proteases and SERPINs identified in Leydig cells are under gonadotropin regulation. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4374–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.M.; Liu, Y.X. Expression of plasminogen activator and inhibitor, urokinase receptor and inhibin subunits in rhesus monkey testes. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 3, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.R.; Paulsen, D.B.; Sehgal, I.; Hosgood, G. Immunohistochemical staining of urokinase plasminogen activator-like and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor-like proteins in the urinary tract of healthy dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1628–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, M.; Lecander, I.; Abrahamsson, P.A. Factors of the plasminogen activator system in human testis, as demonstrated by in-situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1999, 5, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibañez-Tallon, I.; Ferrai, C.; Longobardi, E.; Facetti, I.; Blasi, F.; Crippa, M.P. Binding of Sp1 to the proximal promoter links constitutive expression of the human uPA gene and invasive potential of PC3 cells. Blood 2002, 100, 3325–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, P.; Piscitelli, D.; Albanesi, C.; Blasi, F.; Geremia, R.; Rossi, P. Identification of 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-inducible nuclear factors binding to the human urokinase promoter in mouse Sertoli cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Xiong, Z.; Yi, Y.; Xiong, C.; Huang, D.; Zhao, H. Transcriptional activation and regulation of urokinase plasminogen activator inducted by LPS through MyD88-independent pathway in rat Sertoli cells. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2021, 59, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatzakis, C.; Papadopoulos, V. Differential utilization of the promoter of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor by steroidogenic versus nonsteroidogenic cell lines and the role of Sp1 and Sp3 in the regulation of basal activity. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergeron, F.; Bagu, E.T.; Tremblay, J.J. Transcription of platelet-derived growth factor receptor α in Leydig cells involves specificity protein 1 and 3. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 46, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampidonis, A.D.; Theodorou, G.; Pecorini, C.; Rebucci, R.; Baldi, A.; Politis, I. Cloning of the 5′ regulatory regions and functional characterization of the core promoters of ovine PLAU (u-PA) and SERPIN1 (PAI-1). Gene 2011, 489, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benasciutti, E.; Pagès, G.; Kenzior, O.; Folk, W.; Blasi, F.; Crippa, M.P. MAPK and JNK transduction pathways can phosphorylate Sp1 to activate the uPA minimal promoter element and endogenous gene transcription. Blood 2004, 104, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, P.; Grimaldi, P.; Blasi, F.; Geremia, R.; Verde, P. Follicle-stimulating hormone and cyclic AMP induce transcription from the human urokinase promoter in primary cultures of mouse Sertoli cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1990, 4, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kojima, S.; Hayashi, S.; Shimokado, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimada, J.; Crippa, M.P.; Friedman, S.L. Transcriptional activation of urokinase by the Krüppel-like factor Zf9/COPEB activates latent TGF-beta1 in vascular endothelial cells. Blood 2000, 95, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa, K.; Imataka, H.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kusume, H.; Abe, H.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. cDNA cloning and transcriptional properties of a novel GC box-binding protein, BTEB2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tremblay, M.A.; Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; Robert, N.M.; Bergeron, F.; Tremblay, J.J. KLF6 cooperates with NUR77 and SF1 to activate the human INSL3 promoter in mouse MA-10 Leydig cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Han, Y.; Xiong, C.-L.; Li, H.-G.; Hu, L.; Zhang, L. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: A new target for male contraception? Asian J. Androl. 2015, 17, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Hu, L.; Xiong, C.-L. Tissue-specific inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression in the testes of mice by inducible lentiviral RNA interference causes male infertility. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2017, 29, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vihko, K.K.; Penttilä, T.L.; Parvinen, M.; Belin, D. Regulation of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activator gene expression in the rat seminiferous epithelium. Mol. Endocrinol. 1989, 3, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huarte, J.; Vassalli, J.D.; Belin, D.; Sakkas, D. Involvement of the plasminogen activator/plasmin proteolytic cascade in fertilization. Dev. Biol. 1993, 157, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascoli, M. Characterization of several clonal lines of cultured Leydig tumor cells: Gonadotropin receptors and steroidogenic responses. Endocrinology 1981, 108, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, H.S.; Villeneuve, G.; Tremblay, J.J. The calcium signaling pathway regulates Leydig cell steroidogenesis through a transcriptional cascade involving the nuclear receptor NR4A1 and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daems, C.; Di-Luoffo, M.; Paradis, É.; Tremblay, J.J. MEF2 cooperates with forskolin/cAMP and GATA4 to regulate Star gene expression in mouse MA-10 Leydig cells. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; Robert, N.M.; Martin, L.J.; Brousseau, C.; Tremblay, J.J. The nuclear receptor NR2F2 activates Star expression and steroidogenesis in mouse MA-10 and MLTC-1 Leydig cells. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hébert-Mercier, P.-O.; Bergeron, F.; Robert, N.M.; Mehanovic, S.; Pierre, K.J.; Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; de Mattos, K.; Brousseau, C.; Tremblay, J.J. Growth hormone-induced STAT5B regulates Star gene expression through a cooperation with cJUN in mouse MA-10 Leydig cells. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqab267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehanovic, S.; Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; de Mattos, K.; Talbot, P.; Viger, R.S.; Tremblay, J.J. Identification of novel genes and pathways regulated by the orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII in mouse MA-10 Leydig cells. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 105, 1283–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehanovic, S.; Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; Viger, R.S.; Tremblay, J.J. The nuclear receptor COUP-TFII regulates Amhr2 gene transcription via a GC-rich promoter element in mouse Leydig cells. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 2236–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enangue Njembele, A.N.; Demmouche, Z.B.; Bailey, J.L.; Tremblay, J.J. Mechanism of action of an environmentally relevant organochlorine mixture in repressing steroid hormone biosynthesis in Leydig cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enangue Njembele, A.N.; Bailey, J.L.; Tremblay, J.J. In vitro exposure of Leydig cells to an environmentally relevant mixture of organochlorines represses early steps of steroidogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enangue Njembele, A.N.; Tremblay, J.J. Mechanisms of MEHP inhibitory action and analysis of potential replacement plasticizers on Leydig cell steroidogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.J.; Viger, R.S. Transcription factor GATA-4 enhances Müllerian inhibiting substance gene transcription through a direct interaction with the nuclear receptor SF-1. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyssier, C.; Belguise, K.; Galtier, F.; Chalbos, D. Characterization of the physical interaction between estrogen receptor alpha and JUN proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36361–36369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Umek, R.M.; McKnight, S.L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, L.J.; Boucher, N.; El-Asmar, B.; Tremblay, J.J. cAMP-induced expression of the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 in MA-10 Leydig cells involves a CaMKI pathway. J. Androl. 2009, 30, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Boucher, N.; Brousseau, C.; Tremblay, J.J. The orphan nuclear receptor NUR77 regulates hormone-induced StAR transcription in Leydig cells through cooperation with Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stocco, D.M. Tracking the role of a Star in the sky of the new millennium. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocco, D.M. Clinical disorders associated with abnormal cholesterol transport: Mutations in the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 191, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, W.M.; Zarnegar, R.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen activators uPA and tPA. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keski-Oja, J.; Vaheri, A. The cellular target for the plasminogen activator, urokinase, in human fibroblasts—66,000 dalton protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1982, 720, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.A.; Goldfarb, R.H.; Brundage, R.; Siegal, G.P.; Terranova, V.; Garbisa, S. Effect of plasminogen activator (urokinase), plasmin, and thrombin on glycoprotein and collagenous components of basement membrane. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 4629–4636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dudek, G.A.; Kloczewiak, M.; Budzyński, A.Z.; Latallo, Z.S.; Kopeć, M. Characterisation and comparison of macromolecular end products of fibrinogen and fibrin proteolysis by plasmin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 214, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, E.S.; Pellizzari, E.; Meroni, S.; Cigorraga, S.; Lustig, L.; Denduchis, B. Effect of extracellular matrix proteins on in vitro testosterone production by rat Leydig cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2002, 61, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R.B.; Lane, T.F.; Angello, J.C.; Sage, H. Adhesion, shape, proliferation, and gene expression of mouse Leydig cells are influenced by extracellular matrix in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 1991, 44, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarinejad, V.; Tajik, P.; Movahedin, M.; Youssefi, R. Effect of extracellular matrix on testosterone production during in vitro culture of bovine testicular cells. Vet. Res. Forum 2017, 8, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naldini, L.; Tamagnone, L.; Vigna, E.; Sachs, M.; Hartmann, G.; Birchmeier, W.; Daikuhara, Y.; Tsubouchi, H.; Blasi, F.; Comoglio, P.M. Extracellular proteolytic cleavage by urokinase is required for activation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 4825–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bravo, J.; Catizone, A.; Ricci, G.; Galdieri, M. Hepatocyte growth factor-modulated rat Leydig cell functions. J. Androl. 2007, 28, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catizone, A.; Ricci, G.; Galdieri, M. Functional role of hepatocyte growth factor receptor during sperm maturation. J. Androl. 2002, 23, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricci, G.; Guglielmo, M.C.; Caruso, M.; Ferranti, F.; Canipari, R.; Galdieri, M.; Catizone, A. Hepatocyte growth factor is a mouse fetal Leydig cell terminal differentiation factor. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odet, F.; Guyot, R.; Leduque, P.; Le Magueresse-Battistoni, B. Evidence for similar expression of protein C inhibitor and the urokinase-type plasminogen activator system during mouse testis development. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, H.W.; Marshall, C.J. Regulation of cell signalling by uPAR. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, S.; Blasi, F. The urokinase receptor as an entertainer of signal transduction. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 4575–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinat, N.; Crépieux, P.; Reiter, E.; Guillou, F. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1, 2 are required for luteinizing hormone (LH)-induced steroidogenesis in primary Leydig cells and control steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) expression. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 45, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matzkin, M.E.; Yamashita, S.; Ascoli, M. The ERK1/2 pathway regulates testosterone synthesis by coordinately regulating the expression of steroidogenic genes in Leydig cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 370, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinelle, N.; Holst, M.; Söder, O.; Svechnikov, K. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases are involved in the acute activation of steroidogenesis in immature rat Leydig cells by human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4629–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.R.; Jo, Y.; Stocco, D.M. Regulation of Leydig cell steroidogenesis by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2: Role of protein kinase A and protein kinase C signaling. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 193, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.R.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Wang, X.-J.; Eubank, D.W.; Stocco, D.M. Mechanisms of epidermal growth factor signaling: Regulation of steroid biosynthesis and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in mouse Leydig tumor cells. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 67, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evaul, K.; Hammes, S.R. Cross-talk between G protein-coupled and epidermal growth factor receptors regulates gonadotropin-mediated steroidogenesis in Leydig cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27525–27533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, M.; Thomas, K.S.; O’Donnell, D.M.; Gonias, S.L. Epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent and -independent cell-signaling pathways originating from the urokinase receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Jo, M.; Cavenee, W.K.; Furnari, F.; VandenBerg, S.R.; Gonias, S.L. Crosstalk between the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and EGF receptor variant III supports survival and growth of glioblastoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15984–15989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, J.; von der Ahe, D.; Pearson, D.; Hemmings, B.A.; Shibahara, S.; Nagamine, Y. Transcriptional regulation of a plasminogen activator gene by cyclic AMP in a homologous cell-free system. Involvement of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in transcriptional control. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira-Y-Lopez, R.; Jaramillo, S.; Jing, Y. Synergistic transcriptional activation of the mouse urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) gene and of its enhancer activator protein 1 (AP1) site by cAMP and retinoic acid. Biochem. J. 1998, 331, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Purpose | Description | Template | Sequence | Temperature °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPCR | Plau | 5′-CATCCATCCAGTCCTTGCGTG-3′ 5′-CAAGTACACTGCCACCTTCAGAGT-3′ | 62.6 | |
| Star | 5′-GTTCCTCGCTACGTTCAAGC-3′ 5′-GAAACACCTTGCCCACATCT-3′ | 62.6 | ||
| Rpl19 | 5′-CTGAAGGTCAAAGGGAATGTG-3′ 5′-GGACAGAGTCTTGATGATCTC-3′ | 62.6 | ||
| Promoter Constructs | −2082/+44 bp Plau | Mouse gDNA | 5′-ATGCGGATCCTGTCCTTGGGCAAGGGAATTT-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 |
| −1501/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-TCTGGGATCCACAGTGTGGAATTGGCAACAG-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −1005/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-CATAGGATCCGCAACCACAATACCAGTGAGG-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −503/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-ATTCGGATCCTGTGGGAGCCTTTGTTAGTAGG-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −406/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-TCTGGGATCCGGACAGGTTGGAGAAGAACTG-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −313/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-TCTGGGATCCGCCGCACTAGGTGAATGAAAG-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −203/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-ATTAGGATCCAAGTTGGGAAGCAAGCGC-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −81/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-ATTAGGATCCAGAGCCGCCCTCCAGCAAA-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| −37/+44 bp Plau | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-ATTAGGATCCGGGCCCTAATAAAGGGCGAG-3′ 5′-TATAGGTACCACACGCAAGGACTGGATG-3′ | 62 | |
| Mutagenesis | GC box Mutation | −2082/+44 bp Plau | 5′-GAGCCGCCCTCCAGCAAACCTTTGCTTGGCCAGGGCTC-3′ 5‘-GAGCCCTGGCCAAGCAAAGGTTTGCTGGAGGGCGGCTC-3′ | 74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demmouche, Z.B.; Tremblay, J.J. The Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Contributes to cAMP-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Endocrines 2022, 3, 460-475. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines3030037
Demmouche ZB, Tremblay JJ. The Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Contributes to cAMP-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Endocrines. 2022; 3(3):460-475. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines3030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemmouche, Zoheir B., and Jacques J. Tremblay. 2022. "The Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Contributes to cAMP-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells" Endocrines 3, no. 3: 460-475. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines3030037
APA StyleDemmouche, Z. B., & Tremblay, J. J. (2022). The Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Contributes to cAMP-Induced Steroidogenesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Endocrines, 3(3), 460-475. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines3030037







