Modeling and Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control of Input-Affine Polynomial Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Periodic Event-Triggered Output-Feedback Control
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- .
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- Step 1.
- Offline Design:
- (a)
- Verify system representation, ensure C is full row rank, and decompose .
- (b)
- Define parameters (h, , , ), formulate SOS constraints from Theorem 2.
- (c)
- Solve via SOSTOOLS [27] to obtain matrices and compute gain
- (d)
- Derive triggering matrices and store all parameters.
- Step 2.
- Online Execution (during each verification period h):
- (a)
- Measure the system output , compute error .
- (b)
- Check trigger:
- (c)
- If triggered, update and hold constant until the next verification instant ; else, maintain previous input.
- Step 3.
- Repeat Step 2 at each subsequent verification instant.
3. Event-Triggered State-Feedback Control
3.1. Event-Triggered Stabilization
3.2. Lower Bound for Inter-Event Times
- Step 1.
- Offline Design:
- (a)
- Formulate SOS constraints based on Theorem 3 to ensure asymptotic stability under the triggering condition Equation (39).
- (b)
- Solve the SOS optimization using SOSTOOLS [27] to obtain matrices and polynomial certificates.
- (c)
- Compute the controller gain as
- (d)
- Verify a positive minimum inter-event time using Theorem 4 to exclude Zeno behavior.
- Step 2.
- Online Execution (during each verification period h):
- (a)
- At each verification instant , measure the state .
- (b)
- Evaluate the triggering condition:
- (c)
- If the triggering condition is satisfied, update the control input , and hold it constant until the next verification instant ; else, maintain previous input.
- Step 3.
- Repeat Step 2 at each subsequent verification instant.
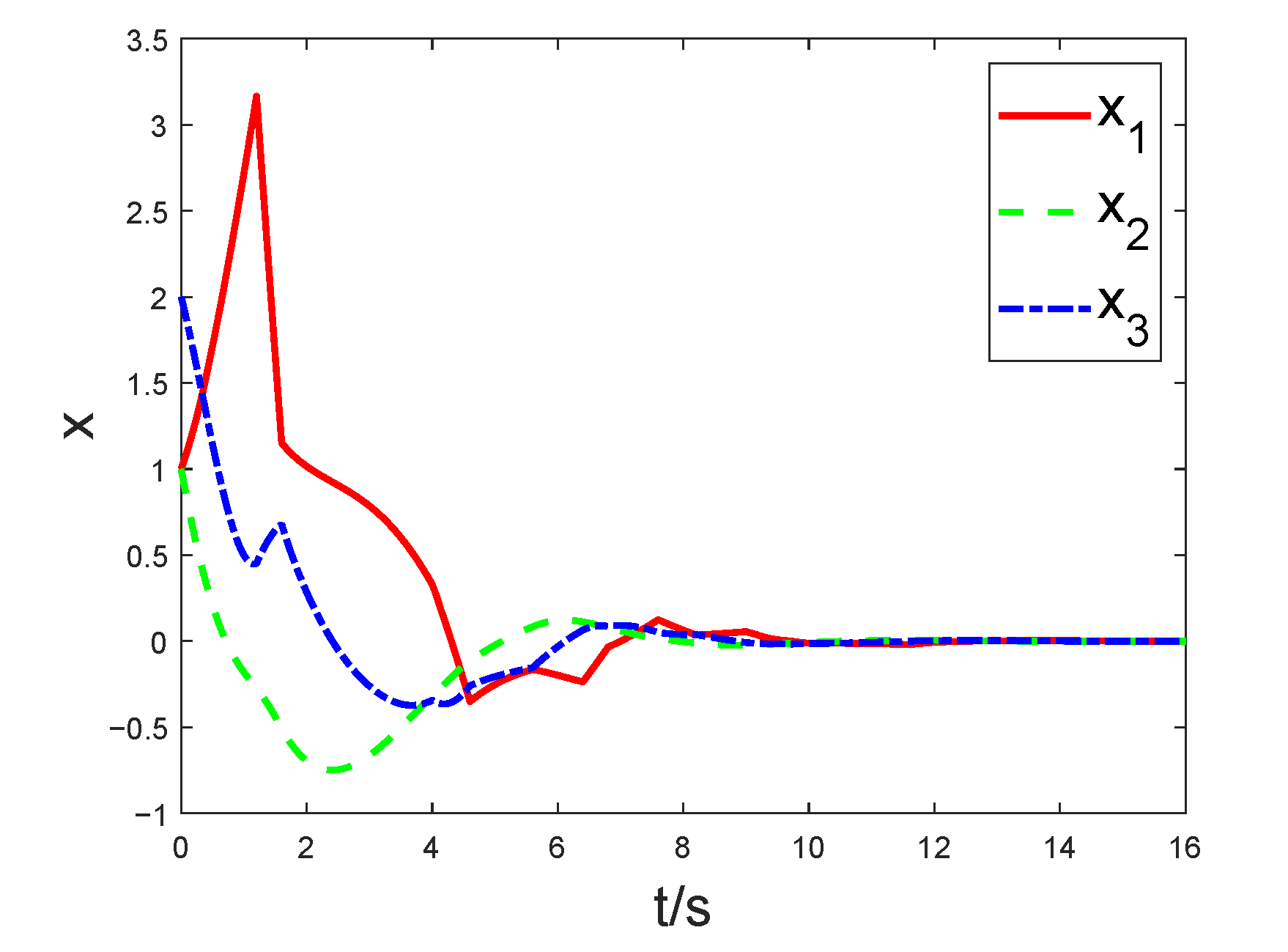
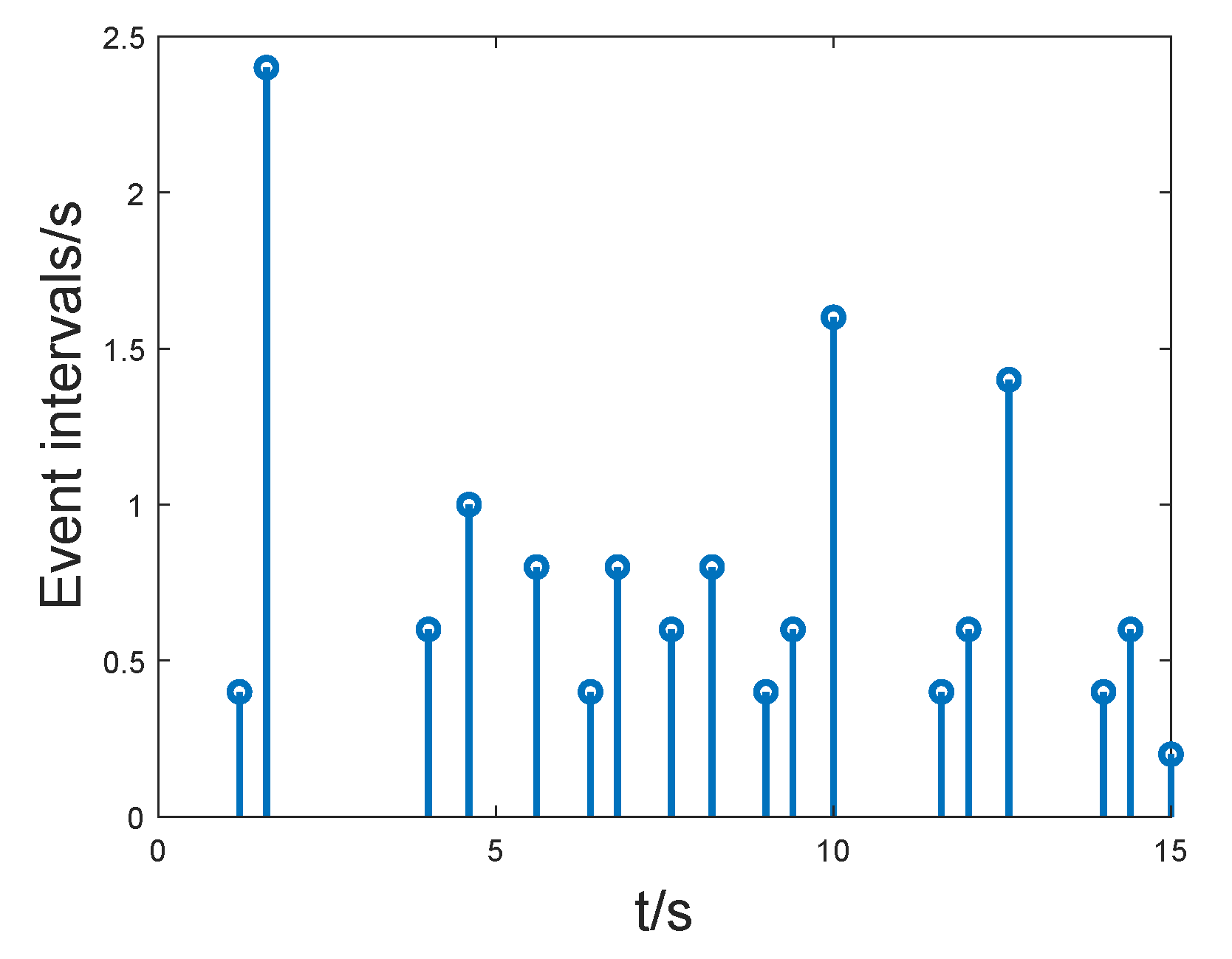
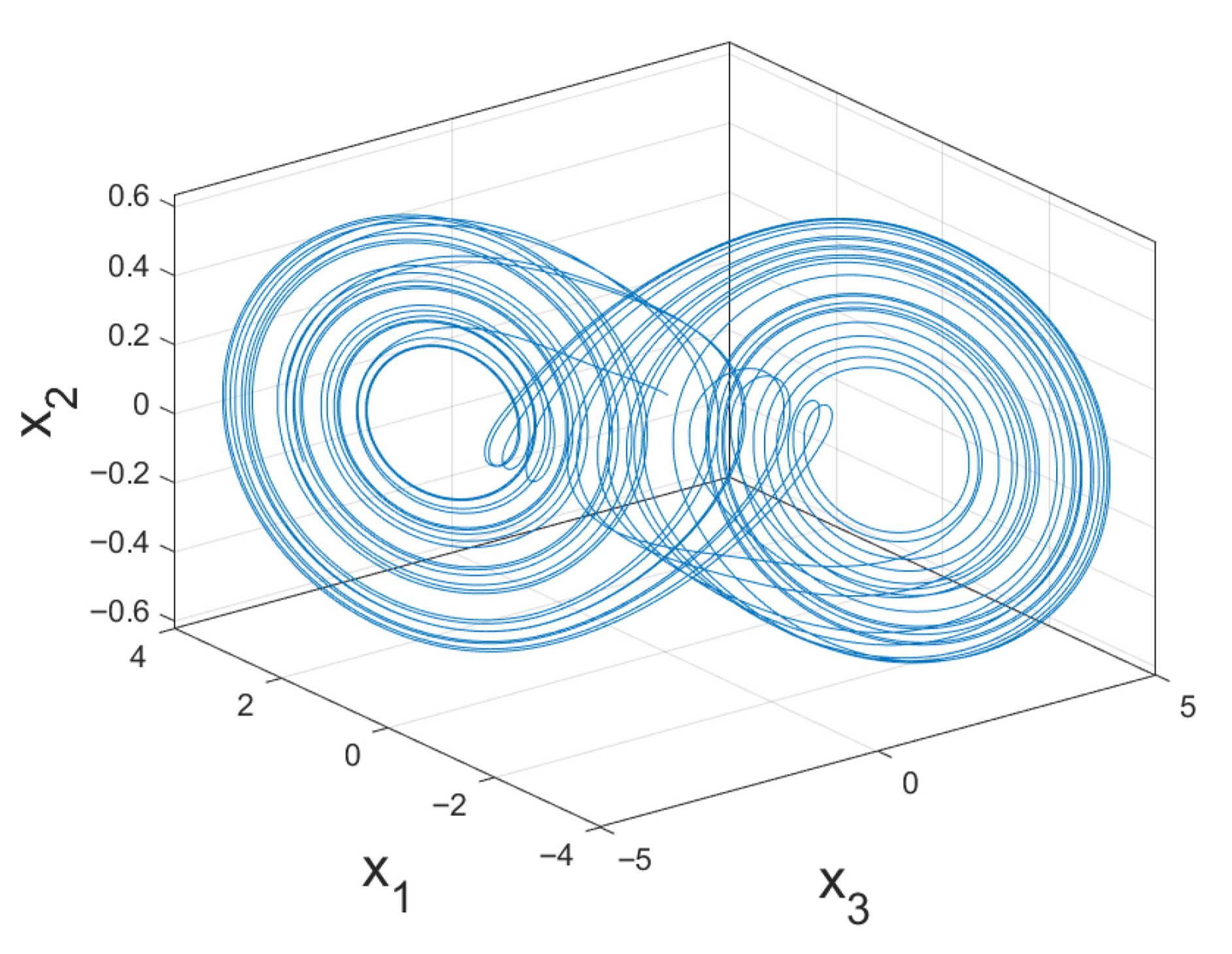
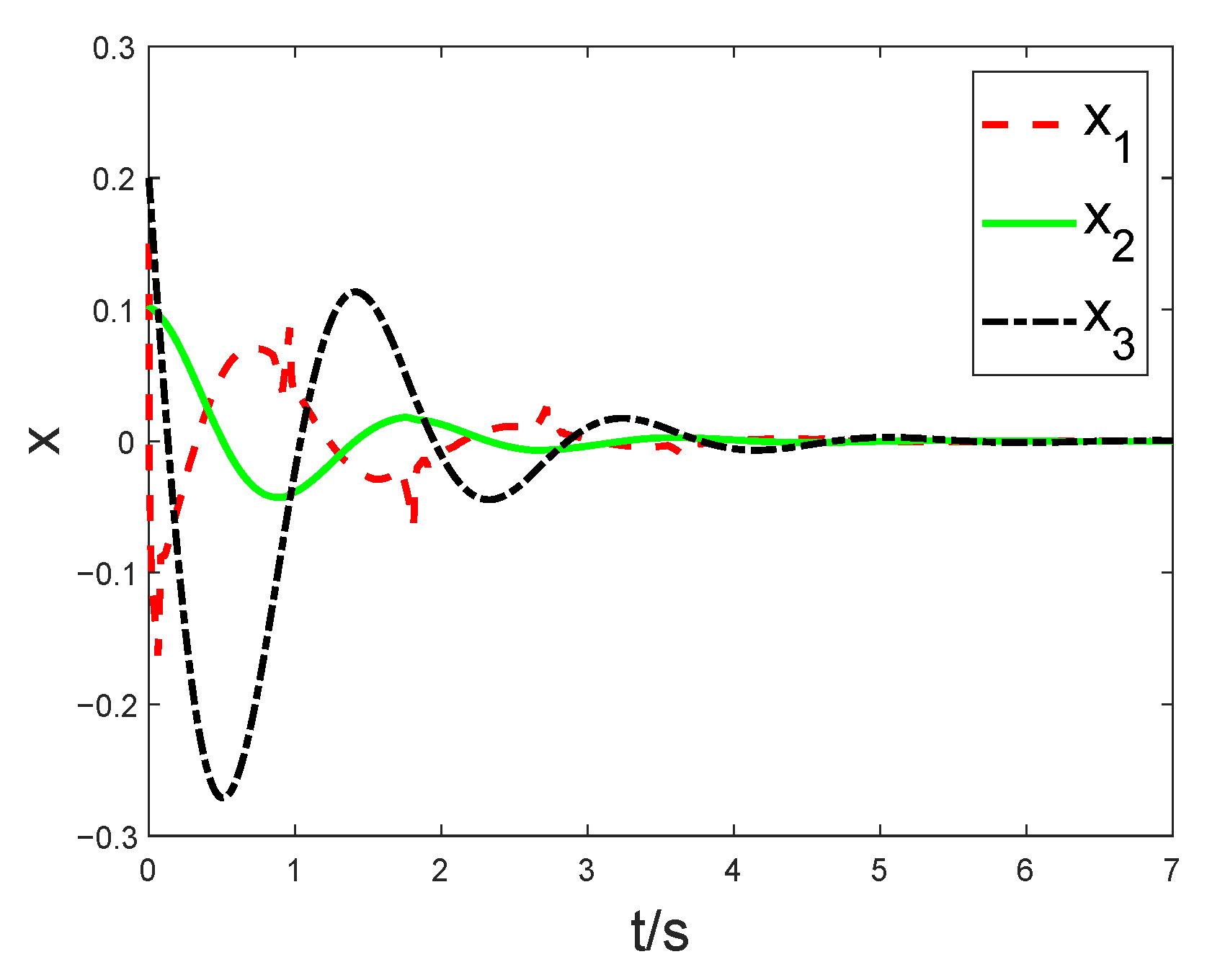
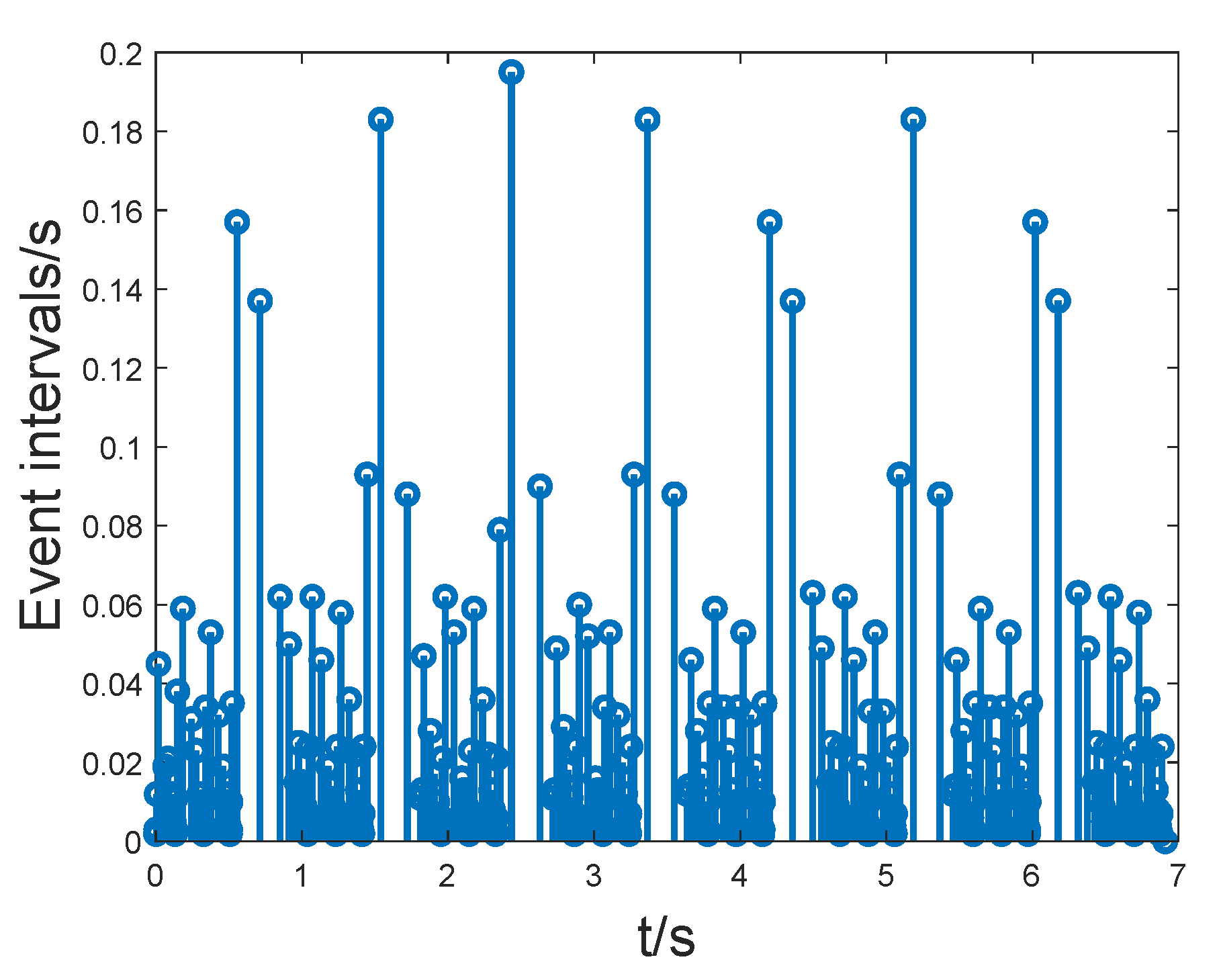
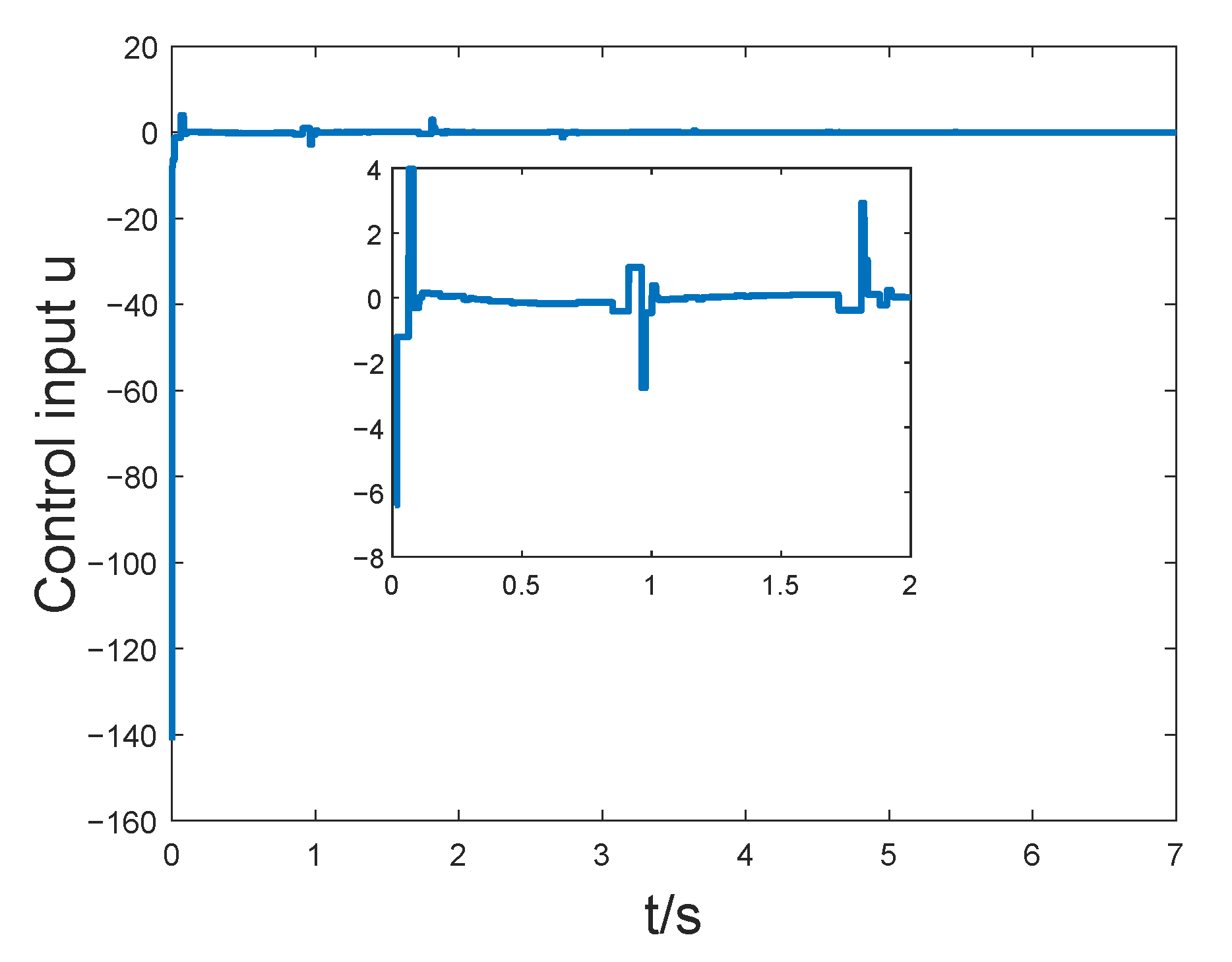
4. Numerical Examples
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ichihara, H. Optimal control for polynomial systems using matrix sum of squares relaxations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, A.; Dang, T.; Dorigo, L.; Dreossi, T.; Piazza, C.; Pippia, E. Parameter synthesis of polynomial dynamical systems. Inf. Comput. 2022, 289, 104941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, T.; Hein, N.; Sottile, F. Certification for polynomial systems via square subsystems. J. Symb. Comput. 2022, 109, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajna, S.; Papachristodoulou, A.; Wu, F. Nonlinear control synthesis by sum of squares optimization: A Lyapunov-based approach. In Proceedings of the 2004 5th Asian Control Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04EX904), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 20–23 July 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara, H. A convex approach to state feedback synthesis for polynomial nonlinear systems with input saturation. Sice J. Control. Meas. Syst. Integr. 2013, 6, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennawasin, T.; Kawanishi, M.; Narikiyo, T. Performance bounds for optimal control of polynomial systems: A convex optimization approach. Sice J. Control. Meas. Syst. Integr. 2011, 4, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, J.L. Robust static output feedback design for polynomial nonlinear systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2010, 20, 1637–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennawasin, T.; Banjerdpongchai, D. Design of state-feedback control for polynomial systems with quadratic performance criterion and control input constraints. Syst. Control Lett. 2018, 117, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Fault-tolerant consensus control of linear multi-agent systems with polynomial faults based on event triggered mechanism. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2025. Online First. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, P.; Kwon, O.m.; Lee, S.; Sakthivel, R.; Lee, S. Event-triggered control design with varying gains for polynomial fuzzy systems against DoS attacks. Math. Comput. Simul. 2024, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wu, L.; Liu, W. Adaptive event-triggered control for strict-feedback systems with time-varying parameters. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2024, 34, 3464–3480. [Google Scholar]
- Heemels, W.; Johansson, K.H.; Tabuada, P. An introduction to event-triggered and self-triggered control. In Proceedings of the 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Maui, HI, USA, 10–13 December 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3270–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Shi, K.; Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; Wen, S.; Tian, Z. Intelligent event-triggered control supervised by mini-batch machine learning and data compression mechanism for TS fuzzy NCSs under DoS attacks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 32, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ding, D. Dynamic Event-triggered Control and Estimation: A Survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2021, 18, 857–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhullipalla, M.H.; Yu, H.; Chen, T. A framework for distributed control via dynamic periodic event-triggering mechanisms. Automatica 2022, 146, 110548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuada, P. Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lemmon, M.D. Event design in event-triggered feedback control systems. In Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Cancun, Mexico, 9–11 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 2105–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Lunze, J.; Lehmann, D. A state-feedback approach to event-based control. Automatica 2010, 46, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eqtami, A.; Dimarogonas, D.V.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J. Event-triggered control for discrete-time systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 June–2 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 4719–4724. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, W.; Cui, B. Event-triggered feedback control for discrete-time piecewise-affine systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2018, 49, 3377–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemels, W.H.; Donkers, M.; Teel, A.R. Periodic event-triggered control for linear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 58, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.M.; Doyle, J.C. H∞ control of nonlinear systems: A convex characterization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1995, 40, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Tronfi, A. Bi-quadratic stability of uncertain nonlinear systems. In Proceedings of the IFAC Symposium on Robust Control Design, Prague, Czech Republic, 21–23 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Parrilo, P.A. Structured Semidefinite Programs and Semialgebraic Geometry Methods in Robustness and Optimization. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Hao, F. Periodic event-triggered state-feedback and output-feedback control for linear systems. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2015, 13, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, J. The Schur Complement and Symmetric Positive Semidefinite (and Definite) Matrices; Penn Engineering: Danboro, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Papachristodoulou, A.; Anderson, J.; Valmorbida, G.; Prajna, S.; Seiler, P.; Parrilo, P. SOSTOOLS version 3.00 sum of squares optimization toolbox for MATLAB. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1310.4716. [Google Scholar]
- Prajna, S.; Papachristodoulou, A.; Seiler, P.; Parrilo, P.A. SOSTOOLS and its control applications. In Positive Polynomials in Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 273–292. [Google Scholar]
- Chesi, G. LMI techniques for optimization over polynomials in control: A survey. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Packard, A. Stability region analysis using sum of squares programming. In Proceedings of the 2006 American Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 14–16 June 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Cao, J. Stabilisation and synchronisation of chaotic systems via hybrid control. Iet Control Theory Appl. 2007, 1, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Ye, Q.; Lou, X. Modeling and Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control of Input-Affine Polynomial Systems. Modelling 2025, 6, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040137
Zhang J, Lin H, Ye Q, Lou X. Modeling and Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control of Input-Affine Polynomial Systems. Modelling. 2025; 6(4):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinqi, Haojie Lin, Qian Ye, and Xuyang Lou. 2025. "Modeling and Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control of Input-Affine Polynomial Systems" Modelling 6, no. 4: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040137
APA StyleZhang, J., Lin, H., Ye, Q., & Lou, X. (2025). Modeling and Event-Triggered Output Feedback Control of Input-Affine Polynomial Systems. Modelling, 6(4), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/modelling6040137





