Abstract
Background: The detailed relationship between apical periodontitis and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening is still unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between maxillary posterior teeth periapical odontogenic lesions and maxillary sinus mucosal (MSM) thickening by using volumetric 3D CT analysis. Methods: A total of 83 subjects with apical periodontitis around maxillary posterior teeth and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening were selected. 3D models of maxillary sinus mucosa and apical lesions were reconstructed from CT, and their volume, mean diameter were calculated. Results: Mean MSM thickening was 8.81 ± 12.59 mm with an average volume of 5092.58 ± 7435.38 mm3. Men had higher MSM thickening than women. Mean diameter of apical lesion was 5.94 ± 2.68 mm; average volume was 200.5 ± 197.29 mm3. Mean distance between MSM and apical lesion was 1.83 ± 2.07 mm. Mucosal volume was the highest in the S1 and D1 configuration and the lowest in R3. Reducing the distance between apical lesion and MSM by each millimetre, the volume of MSM increases by 759.99 mm3. Conclusions: Volumetric CT analysis is a circumstantial method to evaluate the association between maxillary posterior teeth apical periodontitis and MSM thickening. This relationship is not related to the size of the apical lesion but depends on their anatomical position and the distance from the maxillary sinus mucosa.
1. Introduction
Apical periodontitis (AP) is an inflammation and destruction of periapical tissues. It occurs as a sequence of various infectious or physical insults to the dental pulp or the damaging effects of root canal filling materials.
Microorganisms from the infected root canals produce a sufficient amount of endotoxins, which egress in high concentrations into the periapical area.
The microbial factors and host defence destroy much of the periapical tissue, resulting in a formation of various kinds of periapical lesions, such as reactive granulomas and cysts [1].
Moreover, a close anatomical proximity of the maxillary posterior lateral teeth to the maxillary sinuses renders them vulnerable to this periodontal inflammation [2].
Infection from periapical lesion can affect the maxillary sinus mucosa via bone marrow, blood vessels and lymphatics. The upper posterior roots and the floor of the maxillary sinus are separated by a thin cortical bone and, not rarely, solely by the sinus mucosa, which facilitates the spread of infection into sinus [3].
Research by Tian et al. revealed that the average distance between the floor of maxillary sinus and the roots of molar/premolar teeth varies between 0.5 ± 2.9 and 5.5 ± 4.8 mm depending on tooth group. [4]
Conventional diagnostics (i.e., intraoral and panoramic radiographs) show a limited reliability in the maxillary posterior area, while computed tomography and cone-beam computed tomography is now widely used for imaging studies of the oral cavity and the maxillofacial region. In comparison with conventional diagnostics, CT provides a superior diagnostic accuracy in defining periodontal bone defects and the soft-tissue morphology of the maxillary sinus floor [2].
To date, most researchers have measured the structures (periapical lesions and sinus mucosal thickening) in a two-dimensional view (mm). Volumetric analysis of these structures is a new, perspective method which is able to evaluate the precise extent of the disease. Therefore, our aim was to establish a significant connection between the parameters of periapical lesions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening by using 3D CT volumetric analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
The materials for this retrospective study and ethical approval was obtained from the local Lithuanian University of Health Sciences Centre of Bioethics: Number P2-86/2004. The bioethics committee’s permission was given for the large research into upper airways diseases, which also includes exploration of odontogenic sinusitis using CT and other methods, testing surgical techniques and gathering patients’ clinical data.
CT images of adults (≥18 years) who were treated in the Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) and Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery departments (Lithuanian University of Health Sciences Kaunas Clinics, Kaunas, Lithuania) were retrospectively examined. CT prescriptions were due to implant treatment planning and paranasal sinus diseases. The image inclusion criteria were:
- Good quality imaging of the posterior maxillary teeth;
- Periapical lesion on the maxillary molar or premolar tooth on the right or/and left side.
Exclusion criteria were:
- No rhinogenic paranasal sinus pathology (polyps, mucoceles, OMC obstruction from nasal cavity side, non-odontogenic fungus balls);
- No sign of acute sinusitis, including air-fluid level and thickening of all the sinus walls;
- No prescription of CT due to the oral and maxillofacial developmental problems or trauma.
Every image was analysed by oral surgeon in consultation with oral radiologist.
2.1. Evaluation Method of Periapical Lesions
Periapical lesion was defined as periapical radiolucency in connection with the apical part of the root of at least twice the width of the periodontal ligament space. It should be visible in at least two CT sections.
Periapical lesions were allocated according to the Venskutonis et al. periapical and endodontic status scale (PESS COPI) index: S—the size of the lesion, R—relationship between the root and the lesion, D—location of bone destruction (contact of radiolucency with important anatomic structures or the destruction of cortical bone) [5]. The details of the COPI index are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Complex Periapical Index (COPI) evaluation scale.
2.2. Evaluation Method for Mucosal Thickening
Primary maxillary sinus mucosa thickening (MT) was analysed in axial, coronal and sagittal CT views. Afterwards, segmentation of 3D maxillary sinus mucosa from the floor of maxillary sinus to the lower margin of the orbital floor was performed.
Changes in sinus mucosal thickening in CT were allocated into four categories (measuring from the sinus floor up to the highest extent in 2D analysis, mm): 1—up to 2 mm, 2—from 2 to 4 mm (mild maxillary mucosa thickening), 3—from 4 to 10 mm (mediocre mucosa thickening), 4—more than 10 mm (advanced mucosa thickening).
2.3. Volumetric and 2D Analysis of Periapical Lesions and Mucosal Thickening
Axial planes of CT images were imported into secondary analysis software Materialise MIMICS Version 20.0 (Materialise Interactive Medical Image Control System, Materialise NV, Leuven, Belgium). Automatically, coronal and sagittal reconstructions were created. Before transferring to the secondary software, patients’ names and surnames were changed into randomly generated identification codes, to ensure confidential analysis of CT images. MIMICS software built-in tools were used to analyse and segment periapical bone destruction around apices of the maxillary lateral teeth and the maxillary sinus mucosa. According to the analyses of the axial, coronal and sagittal planes, 3D models of these structures were segmented. 3D structure analysis algorithms were used to determine the highest diameter (mm), calculate volumes (mean mucosal volume (MMV) and mean periapical bone destruction diameter in mm3) and the nearest distances between maxillary sinus mucosa and periapical bone destruction margins (mm).
2.4. Anatomic Relationship
The anatomical relationship between maxillary lateral teeth roots and sinus floor was distributed into five categories according to Kwak [6]:
- Type I: The inferior wall of the maxillary sinus (MS) floor is located above the root apex of the buccal and palatal roots;
- Type II: The inferior wall of the MS is located below the level connecting the buccal and palatal root apices without an apical protrusion over the MS;
- Type III: An apical protrusion of the buccal root apex is observed over the inferior wall of the MS;
- Type IV: An apical protrusion of the palatal root apex is observed over the inferior wall of the MS;
- Type V: Apical protrusions of the buccal and palatal root apices are observed over the inferior wall of the MS.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
In order to determine the reproducibility of the numerical measurements taken, 25% of randomly selected cases were evaluated twice and Intra-class correlation coefficient was calculated (ICC)—the ideal reproducibility was determined (ICC = 0.999; p < 0.001). The mean differences between measurements were 0.12–0.57 mm and 0.01–5.73 mm3 per case. There were no outliers and the data were normally distributed, as assessed by boxplot and Shapiro–Francia test (p > 0.05), respectively. Descriptive analysis was carried out and central tendency and dispersion were described by mean and standard deviation (SD), unless stated otherwise. A p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. A one-way ANOVA was conducted to compare means among groups. The post-hoc Tukey HSD test was used for multiple comparisons between groups. Univariate multiple regression analysis was used to evaluate the association of the factors (sex, age, side affected, causative tooth, periapical bone destruction diameter (mm) and volume (mm3), the distance from margin of periapical bone destruction to the floor of maxillary sinus (mm), COPI index configurations and the anatomical relationship (AR)) with maxillary sinus mucosal thickening (mm3). Statistical analysis was carried out by using RStudio (version 1.2.5033 ©2009–2019 RStudio, Inc. Software).
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Periapical Bone Lesions
In total, 83 teeth with lesions and maxillary sinuses were analysed: 12 first premolars, 9 s premolars, 40 first molars, 18 s molars and 4 third molars. According to sex, women formed 65% and men 35% of cases. In 54.76% of cases, periapical bone lesion associated with mucosal thickening was around the first and second molar mesiobuccal root, and more rarely around the palatal root (40.47%) and distobuccal root (35.71%). Mean periapical bone destruction diameter was 5.94 ± 2.68 mm (1.27–15.32 mm) with an average volume of 200.5 ± 197.29 mm3 (11.23–878.45 mm3). The detailed analysis of periapical bone lesions according to COPI index is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The detailed analysis of periapical bone lesions according to the COPI index. IAS—Radiolucency is in contact with important anatomical structures; DCB—destruction of cortical bone.
The most common periapical lesion configurations were S3R1D1 (16.9%), S2R1D1 (15.7%) and S3R3D3 (10.8%). Mean distance between the floor of maxillary sinus and periapical bone destruction was 1.83 ± 2.07 mm (from 0 to 7.03 mm). Statistically significant differences in lesion diameter were found between S1 and S3, S2 and S3, R1 and R2 and R1 and R3 COPI groups (p < 0.001), while no statistically significant difference was detected within group D. Periapical bone destruction volume was statistically different between S1 and S3, S2 and S3, all R groups and D2 and D3 (p < 0.05).
3.2. Mucosal Thickening
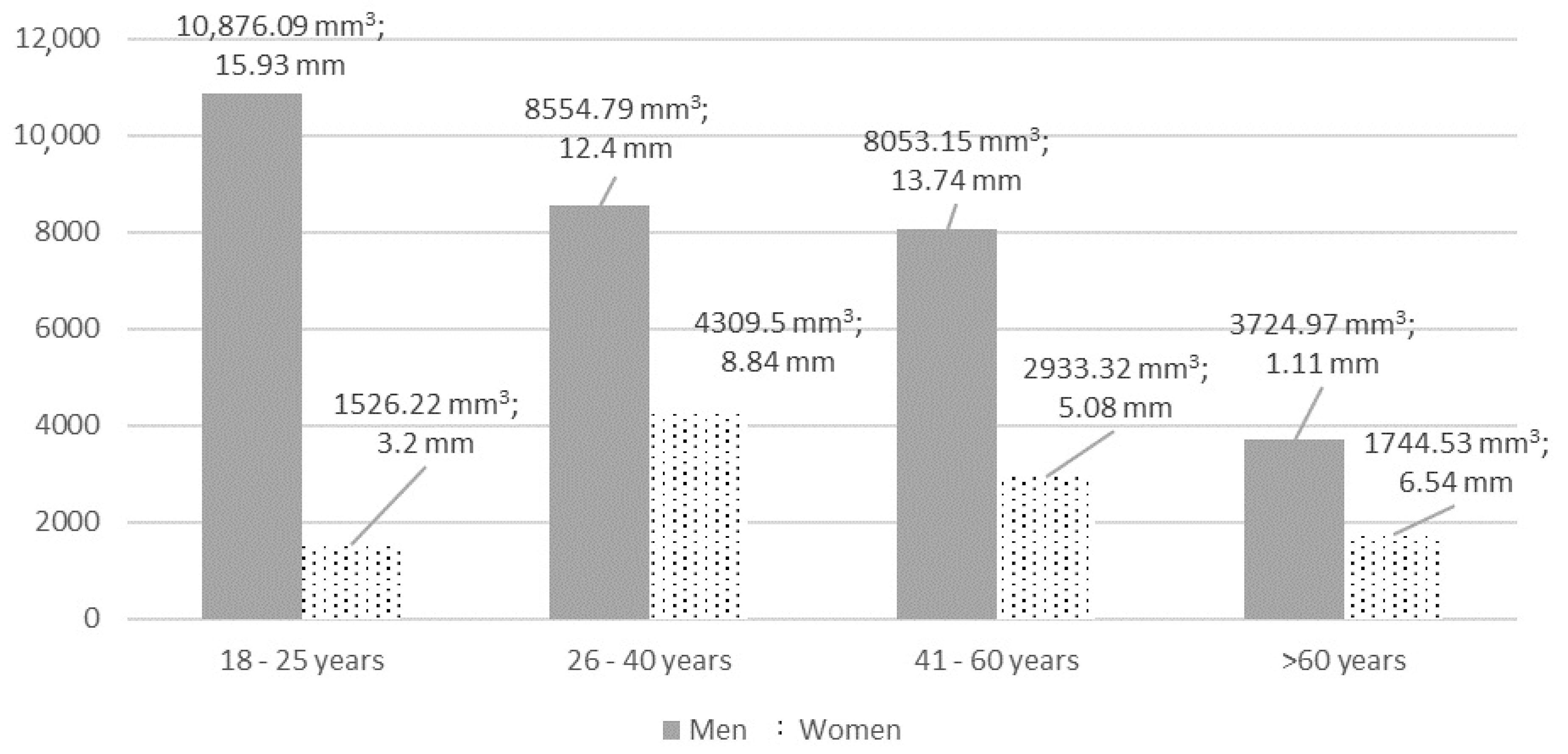
Maxillary mucosal thickening of >2 mm (type 3 or higher) was found in 41 (49.4%) cases, of which 12 (30%) were bilateral. Mean thickness of mucosa was 8.81 ± 12.59 mm (0.34 to 43.53 mm) with an average volume of 5092.58 ± 7435.38 mm3 (84.37 to 30617.08 mm3). The right maxillary sinus had a mean thickening of 10.16 ± 13.81 mm with an MMV of 5947.66 ± 8399.5 mm3, left—7.35 ± 11.1 mm and 4173.37 ± 6211.98 mm3, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences between left and right maxillary sinuses’ mucosal thickening (in mm and mm3) (p > 0.05). The detailed analysis of mucosal volume (mm3) according to the thickening group is shown in Table 3. Mean MT (mm) significantly differed between 4th and all other groups, while MMV differed also between the 3rd and 1st group. The detailed analysis of MT (volume in mm3 and thickness in mm) according to sex and age groups is shown in Figure 1.

Table 3.
The detailed analysis of MMV (mm3) according to the mucosa thickening group (mm).
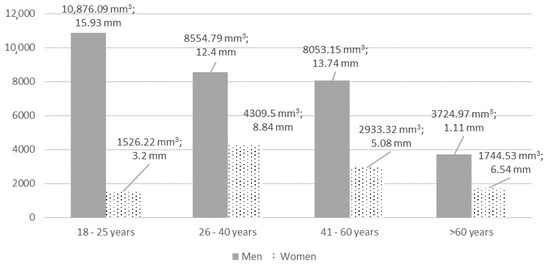
Figure 1.
The detailed analysis of MT (volume in mm3 and thickness in mm) according to sex and age. MT and MMV differences were statistically significant according to sex, p < 0.05. Differences between age groups were not statistically significant, p > 0.05.
3.3. Relationship Between Mucosal Thickening and Variables
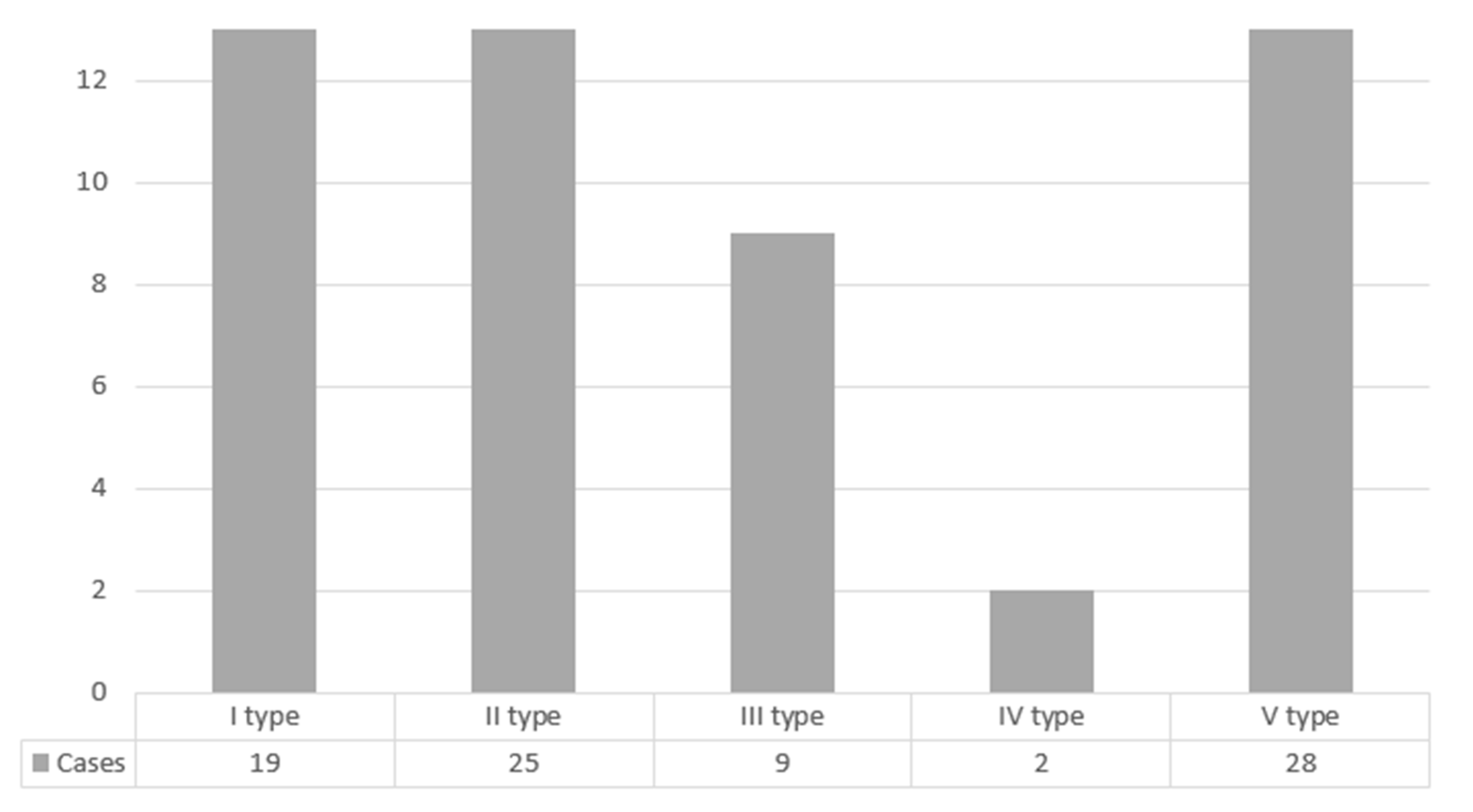
In 53.01% of cases, the maxillary posterior teeth and the sinus floor were separated by a bone. The detailed distribution of cases according to the anatomical relationship between the floor of maxillary sinus and causative teeth roots by Kwak classification is shown in Figure 2.
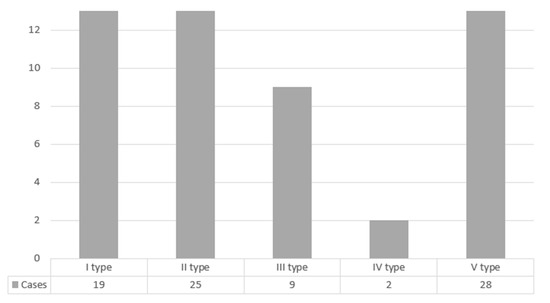
Figure 2.
Distribution of cases according to the anatomical relationship between the floor of maxillary sinus and causative teeth roots by Kwak classification.
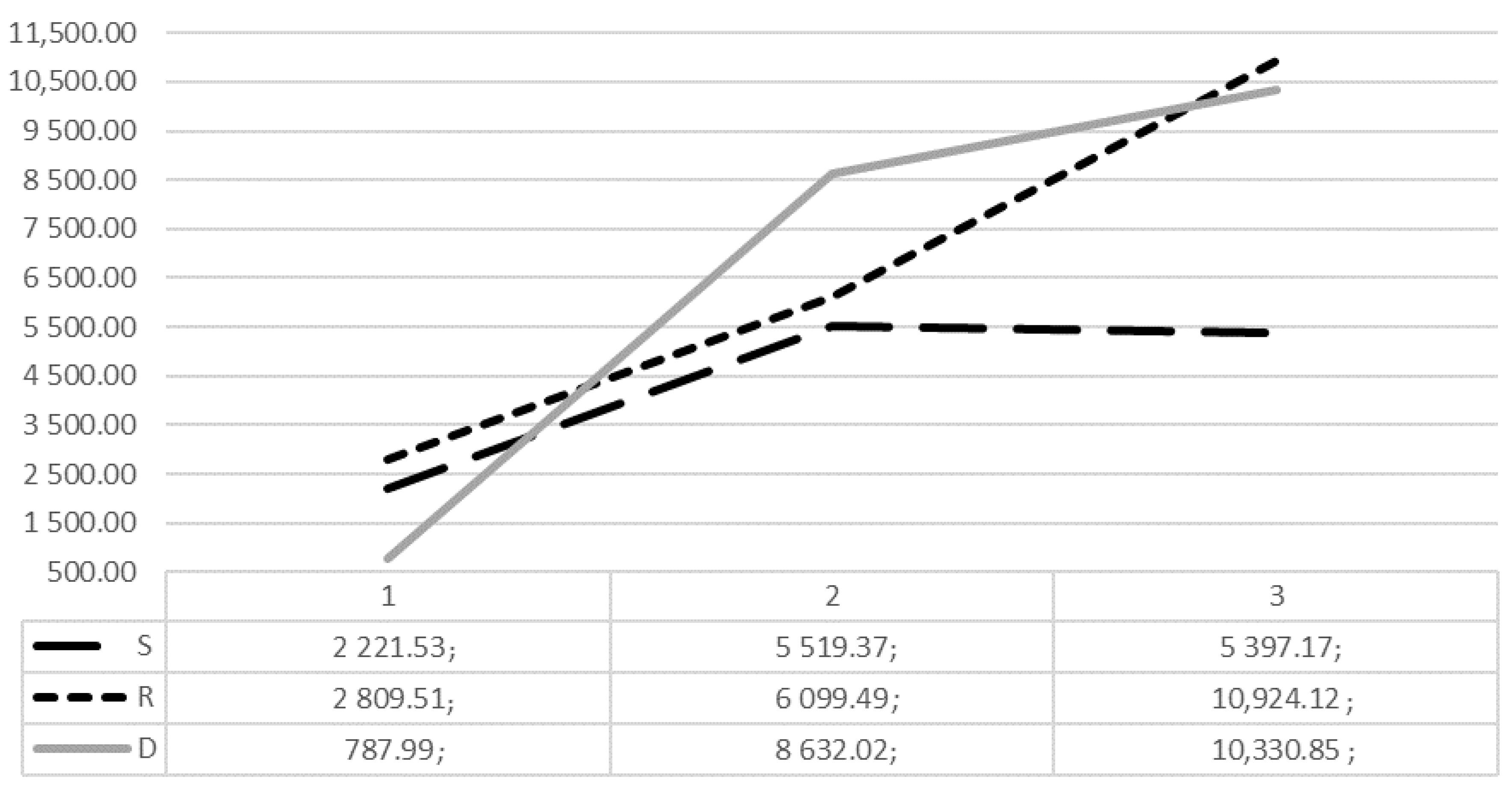
When analysing MMV in separate COPI groups, the smallest mucosal volume was found in the D1 group (787.99 mm3), while the largest was found in the R3 (10,924.12 mm3) and D3 (10,330.85 mm3), independently of other factors. The detailed analysis of maxillary sinus mucosal thickening in mm3 according to COPI index is shown in Figure 3.
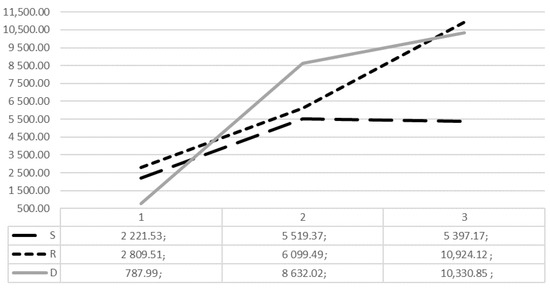
Figure 3.
Distribution of mean mucosal thickening volume (mm3) according to COPI index S, R, D groups.
3.4. Risk Factors of Maxillary Sinus Mucosa Thickening Volume
According to univariate multiple regression analysis of all independent variables on dependent maxillary sinus volume (mm3) changes, the mean mucosal volume of 18 years old male patient in case of S1R1D1 AR1 configuration is 9294 mm3. Sex was a statistically significant risk factor in determining mucosal volume, where men had larger mucosal volume by 3302 mm3. The 2nd molar was associated with increased mucosa volume by 2580 mm3. When the periapical lesion is in a relationship with anatomically significant structures, such as the floor of maxillary sinus or, in case of cortical bone destruction (D), mean mucosal thickening, volume is higher by 5768 and 6286 mm3, accordingly. By decreasing distance by 1 mm from periapical bone destruction to maxillary sinus mucosa, thickening increased by 728 mm3. Moreover, apical protrusions of the buccal and palatal root apices over the inferior wall of the sinus (type V) increased mucosal volume by 4490 mm3. The multiple regression model statistically significantly predicted maxillary sinus mucosa thickening volume (mm3), F (3, 79) = 20.19, p < 0.0001, R2 = 41.25%.
Periapical bone destruction volume (mm3) was the most detailed variable to determine volumetric mucosal thickening changes and increased MMV by 9.255 mm3, but it was not statistically significant (p = 0.134). The same tendency was observed with periapical bone destruction diameter (2D measure) and periapical bone destruction size (S1-S2-S3 configurations), and the relationship between the root and the lesion (R1-R2-R3), (p > 0.05).
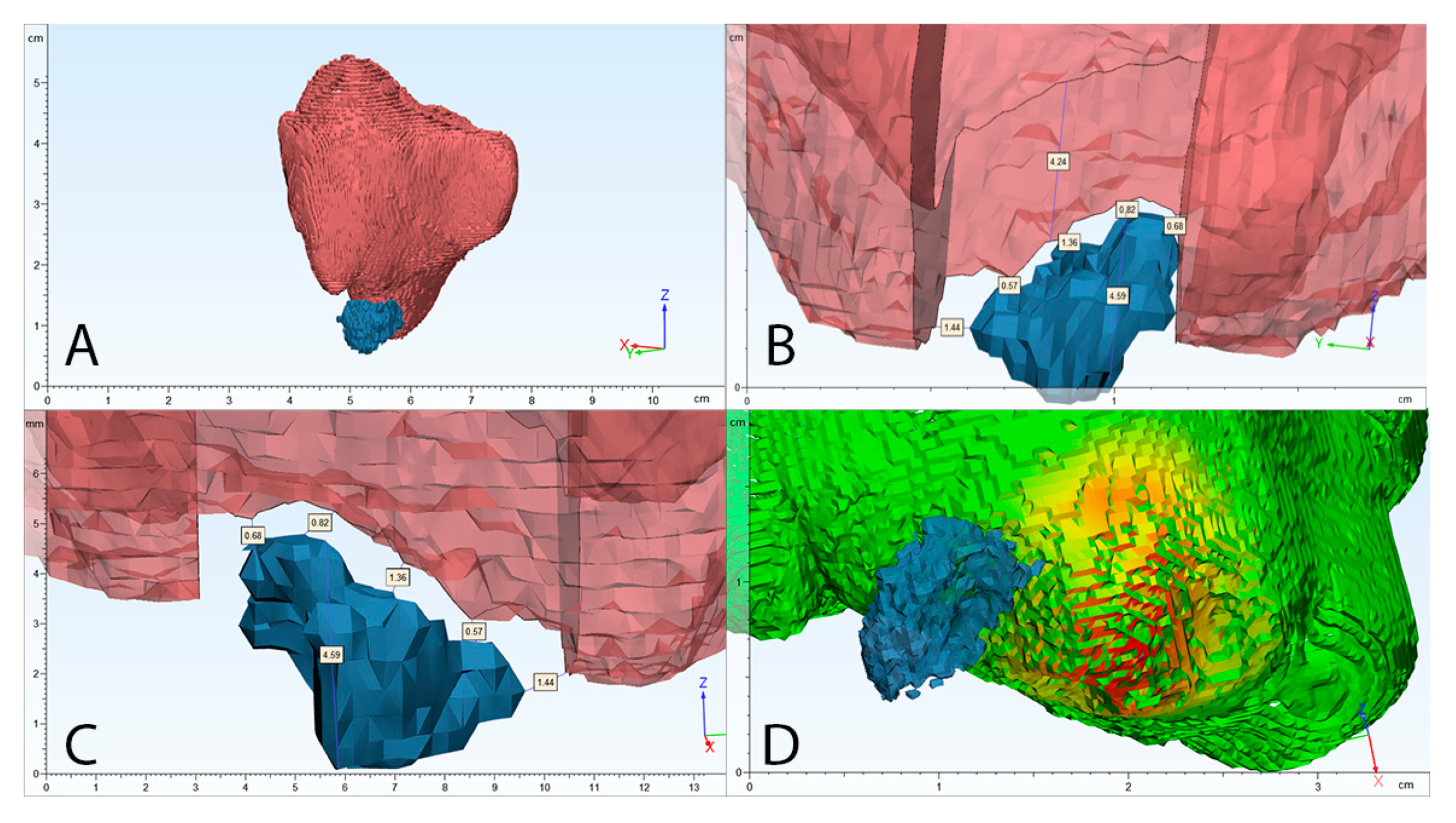
The detailed univariate multiple regression analysis of all independent variables on dependent maxillary sinus volume (mm3) changes can be seen in Table 4. An example of volumetric/2D analysis of maxillary sinus mucosa and periapical bone destruction is shown in Figure 4. Clinical case examples can be seen in Figure 5.

Table 4.
Univariate multiple regression analysis model to determine risk factors of maxillary sinus mucosa thickening volume in mm3.
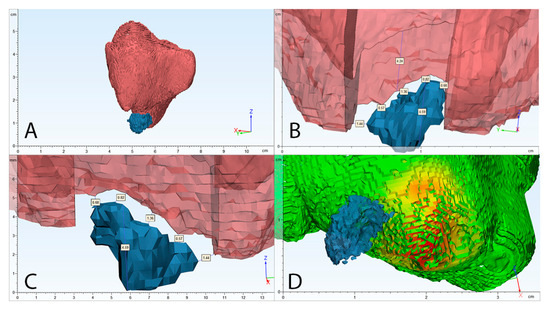
Figure 4.
Clinical case volumetric and two-dimensional analysis example. (A) segmented 3D view of maxillary sinus mucosa (red) and periapical bone lesion (blue); (B) cross-section of maxillary sinus mucosa, maximum thickening area; (C) 3D location of periapical bone destruction according to maxillary sinus mucosa with evaluation of highest diameter of periapical bone destruction and shortest distance between these structures; (D) automatic algorithm analysis of maxillary sinus mucosa thickening in mm (results are shown in coloured histogram: green—the lowest, red—the highest mucosal thickening).
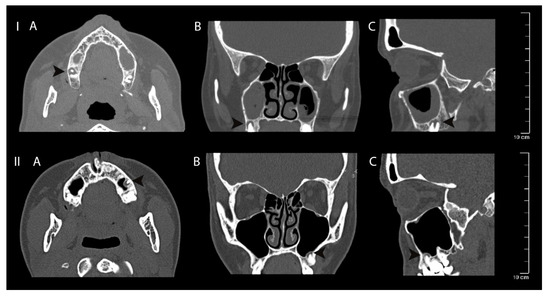
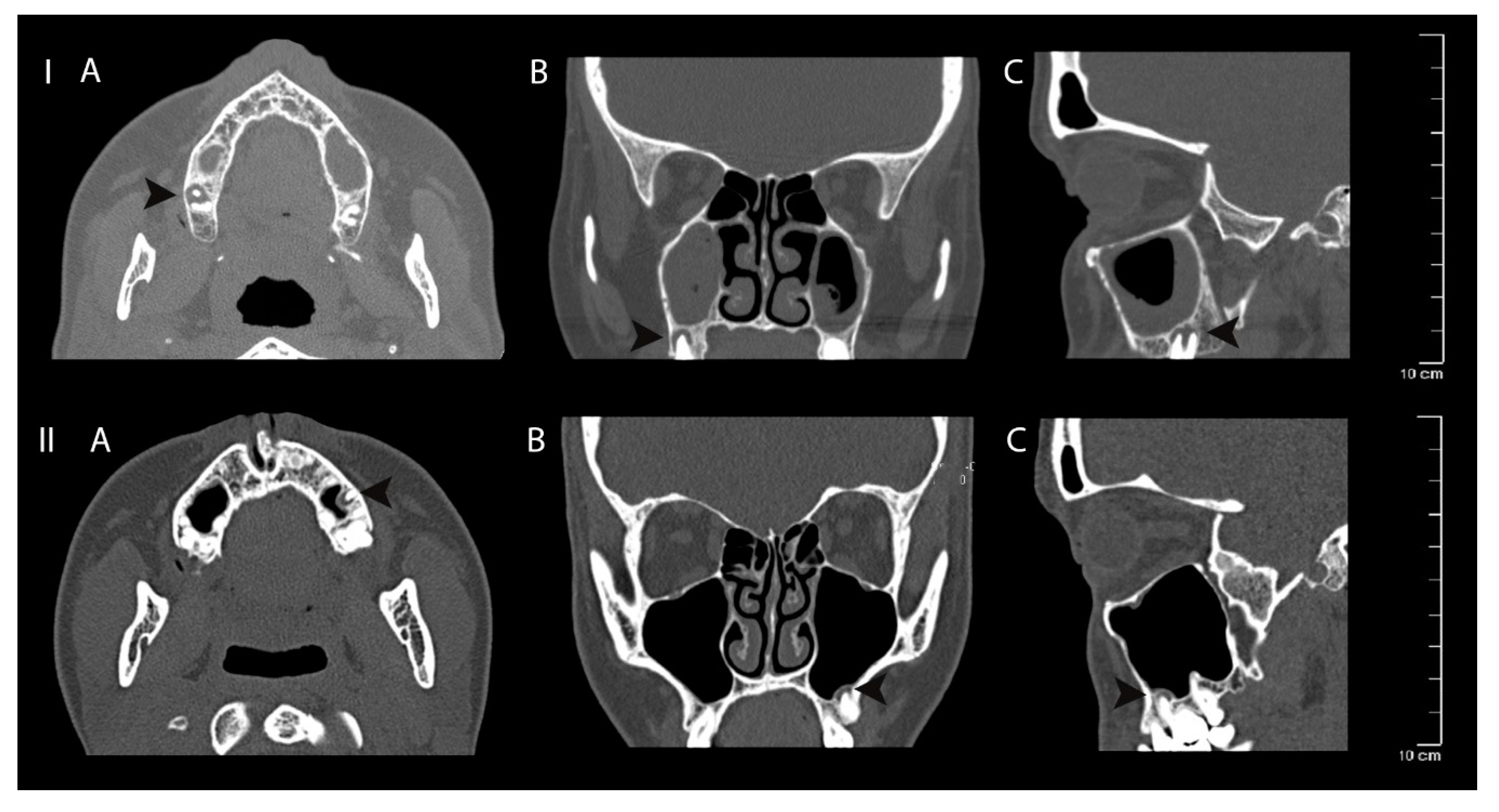
Figure 5.
Clinical case I—mucosal thickening—advanced, periapical bone destruction size S3; Clinical case II—mucosal thickening up to 2 mm, periapical bone destruction size S3. Computed tomography axial (A), coronal (B) and sagittal (C) views of apical periodontitis around the roots of the teeth and maxillary sinus mucosa thickening. The lesions are indicated with black arrows.
4. Discussion
Dental infection pathways into maxillary sinus was first observed by the Bauer in the mid-20th century [7]. It spreads from periapical lesion via bone marrow, blood vessels and lymphatics, and therefore can cause maxillary sinusitis even without perforation of cortical bone [8,9,10].
While the exact incidence of odontogenic sinusitis is still unknown and is being given in 10–41% of all rhinosinusitis cases, apical and marginal periodontitis are the most common causes of odontogenic sinusitis and constitute up to 83% of dental cases [11].
In the present study, the causative teeth were the first (48.2%) and second (21.7%) molars. The average diameter of the periapical lesion was 5.94 (1.27 to 15.32) mm, with an average volume of 200.3 (11.23 to 878.45) mm3. In similar research by Arasu et al., the average diameter and volume values were 4.11 (3.64 to 5.49) mm and 130 (0 to 6113) mm3, accordingly [12].
Yu Lu et al., allocated periapical lesions according to the periapical index scoring system [11]. The most common lesion was minimal periodontal violation and well-defined apical periodontitis. In this research, we used a standardized COPI index which provides a more objective analysis [5].
The most common periapical lesion configuration was S3R1D1, S2R1D1 and S3R3D3, which shows that the spreading of the large lesion (S2, S3) into anatomical structures is limited. There was no statistically important difference in lesion diameter between S1 and S2, R2 and R3 groups and in all D groups, while the volume differed in all R groups, and also between D2 and D3 groups.
These differences can be explained by the fact that every periapical lesion is different in shape and only a 2D diameter cannot accurately determine the true extent of the disease. Thus, it shows the inaccuracy of two-dimensional measuring compared to three-dimensional.
The average diameter of maxillary mucosa was (8.81 ± 12.59 mm) and cases with >2mm thickening made up to 49.4%, which is similar to other studies [11,13,14,15,16]. Type 2 (up to 2 mm) was the most common mucosal thickening type. Men had statistically larger mucosa thickening than women by 3302 mm3. These results support other studies in which sex has a significant impact on sinus mucosal thickening. One of the causes of this difference can be the patient selection, with females being predominant in our study (65%) vs. men (35%). Other reasons why mucosal thickening may be male-predominant can be associated with risk factors, such as smoking. As this study was intended to objectively analyse standardized variables’ influence on MT in 3D, other factors still need completed data in the future studies [2,14,15].
The mild mucosal thickening group had a higher average diameter and volume (2.66 mm and 862.73 mm3) than the no-mucosa thickening group (1.16 mm and 1198.79 mm3). However, while the range of mean mucosa thickening in mm is still clearly higher in the mild mucosa thickening group (0.34–1.94 vs. 2.04–3.73), the range of volume measurements is higher in the no-mucosa (0–2 mm) group, exceeding the maximum value of the mild mucosa group by two times (99.34–7254.59 vs. 84.37–3675.36). This again shows the drawbacks of two-dimensional measuring, when a larger process got into the lower diameter group.
When analysing risk factors to determine the maxillary sinus mucosa thickening, there was no statistically important relationship between S1-S2-S3 or R1-R2-R3 and maxillary sinus mucosa volume (mm3), (p < 0.05). From these results, we can see that the size of apical lesion and the relationship between the root and radiolucent lesion has no significant impact on sinus mucosal volume alone. On the other hand, the important factor was the distance of apical lesion from the sinus floor. The size of mucosal volume differed more than 10 times between D1 and D2 groups—787.99 mm3 and 8632.02 mm3, accordingly. The closer the lesion is to the maxillary sinus floor, the larger volume of sinus mucosa we can expect (every 1 mm increases the volume by 728.35 mm3). When periapical lesion is in relationship with anatomically significant structures, such as the floor of maxillary sinus or in case of cortical bone destruction (D index), mean mucosal volume is higher by 5768 and 6286 mm3, respectively. This can be explained by porous alveolar bone marrow, numerous vascular anastomosis and lymphatics through which bacteria and toxins can infect the maxillary sinus mucosa. The closer the apical lesion is to the sinus floor, the shorter and easier the path by which infection invades the maxillary sinus. In the study by Lu et al., the size of periapical lesion was the most important factor causing the mucosal thickening, while the anatomical relationship had no impact on it. However, those results were not statistically different. In our study, periapical bone destruction volume in mm3 was considered to be the most detailed factor to determine maxillary sinus mucosa-thickening volume (every increase in 1 mm3 of periapical bone destruction increases maxillary sinus mucosa volume by 9.255 mm3), however, this factor was not shown to be statistically significant (p = 0.134). Periapical bone destruction diameter in mm was shown to increase maxillary sinus mucosa volume by 496.674 mm3, however, this was also not statistically significantly (p = 0.304). Some other studies confirm the relationship between apical lesions and sinus floor as being the most important factor in the occurrence of MT [16,17,18,19,20].
According to the results of the present study, sex, causative tooth number and anatomical relationship Type V could be precise factors determining the volume of MT (mm3). Women were significantly associated with lower maxillary sinus mucosa thickening than men by 3302 mm3, while the 2nd molar was associated with increased mucosa volume by 2580 mm3. In most cases, the roots of maxillary lateral teeth were not in contact with cortical bone of the floor of maxillary sinus (I type), was in contact (II type) and protruded into the maxillary sinus (V type). Only with the latter was the sinus mucosa thickening associated with increased mucosal volume by 4490 mm3 (p < 0.05). These results confirm the fact that distance between periapical lesion and sinus floor is an important factor in determining MT. According to the literature, the roots of 2nd molar are the shortest distance (mean 1.97 mm) from the sinus floor, while in AR type V there is no bone separating these structures. Shorter distance facilitates the access of bacteria into the maxillary sinus, which causes a larger inflammatory reaction.
In this study, the volumetric CT analysis was used for the first time in order to evaluate the connection between sinus MT and apical periodontitis bony lesions. Three-dimensional analysis of these structures helped to explore this connection further and showed the drawbacks of two-dimensional views, which were mostly used for this purpose to date. The detailed statistical analysis and selection of standardized and adopted for 3D CT views criteria are the strong points of this study. However, more research with volumetric CT analysis of such a type and larger samples in different countries should be performed in order to confirm these results. Moreover, future studies should select standardized criteria according to the newest classifications in order to facilitate comparison of data from different research.
5. Conclusions
Volumetric CT analysis is a circumstantial method to evaluate the association between maxillary posterior teeth apical periodontitis and MSM thickening. This relationship is not related to the size of the apical lesion, but depends on their anatomical position and the distance to the maxillary sinus mucosa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S., P.T., S.V.; methodology, R.S., P.T.; validation, R.S., M.L.; software, P.T., M.L.; investigation, R.S., M.L., P.T.; formal analysis, P.T., data curation, P.T., N.Š.; resources, R.K.; supervision, S.V., R.K.; writing—original draft, R.S., P.T., M.L.; writing—review and editing, R.K., N.Š., S.V.; visualization, P.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AP | Apical periodontitis |
| AR | Anatomical relationship |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| COPI | Complex periapical index |
| D | Location of bone destruction |
| MMV | Mean mucosal volume |
| MS | Maxillary sinus |
| MSM | Maxillary sinus mucosal thickening |
| MT | Mucosa thickening |
| OMC | Ostiomeatal complex |
| PESS | Periapical and endodontic status scale |
| R | Relationship between the root and radiolucent lesion |
| S | Size of the radiolucent lesion |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Graunaite, I.; Lodiene, G.; Maciulskiene, V. Pathogenesis of apical periodontitis: A literature review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2012, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Y. Significance of maxillary sinus mucosal thickening in patients with periodontal disease. Int. Dent. J. 2015, 65, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.J.; O Gamba, T.; Bertinato, J.V.J.; Freitas, D.Q. Comparison of panoramic radiography and CBCT to identify maxillary posterior roots invading the maxillary sinus. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2016, 45, 20160043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.M.; Qian, L.; Xin, X.Z.; Wei, B.; Gong, Y. An analysis of the proximity of maxillary posterior teeth to the maxillary sinus using cone-beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venskutonis, T.; Plotino, G.; Tocci, L.; Gambarini, G.; Maminskas, J.; Juodzbalys, G. Periapical and endodontic status scale based on periapical bone lesions and endodontic treatment quality evaluation using cone-beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.; Park, H.; Yoon, H.; Kang, M.; Koh, K.S.; Kim, H.J. Topographic anatomy of the inferior wall of the maxillary sinus in Koreans. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, H. Maxillary sinusitis of dental origin. Am. J. Orthod. Oral Surg. 1943, 29, B133–B151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschieri, S.; Torretta, S.; Corbella, S.; Del Fabbro, M.; Francetti, L.; Lolato, A.; Capaccio, P. Pathophysiology of sinusitis of odontogenic origin. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2015, 8, e12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, A.D.; Granquist, E.J.; Adappa, N.D. Odontogenic sinusitis. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, D.P.; Kretzschmar, C.J.L. Rhinosinusitis: review from a dental perspective. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2003, 96, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Q.; Duan, X.; Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Huang, D.M. Associations between maxillary sinus mucosal thickening and apical periodontitis using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: A retrospective study. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, E. Evaluation of Volumetric Change of Periapical Lesions After Apicoectomy as a Measure of Postsurgical Healing Utilizing Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikhi, M.; Jafaripozve, N.; Khorrami, L. Using cone beam computed tomography to detect the relationship between the periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. Dent. Res. J. 2014, 11, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Shanbhag, S.; Karnik, P.; Shirke, P.; Shanbhag, V. Association between periapical lesions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic study. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, S.; Zamiri, B.; Panahi, R. Evaluation of the association of sinus mucosal thickening with dental and periodontal status using cone beam computed tomographic imaging. J. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. Pathol. Surg. 2016, 5, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phothikhun, S.; Suphanantachat, S.; Chuenchompoonut, V.; Nisapakultorn, K. Cone-beam computed tomographic evidence of the association between periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauman, C.H.J.; Chandler, N.P.; Tong, D.C. Endodontic implications of the maxillary sinus: A review. Int. Endod. J. 2002, 35, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallo, J.; Suominen-Taipale, L.; Huumonen, S.; Soikkonen, K.; Norblad, A. Prevalence of mucosal abnormalities of the maxillary sinus and their relationship to dental disease in panoramic radiography: Results from the Health 2000 Health Examination Survey. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2010, 109, e80–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onișor-Gligor, F.; Lung, T.; Pintea, B.; Mureşan, O.; Pop, P.B.; Juncar, M. Maxillary odontogenic sinusitis, complicated with cerebral abscess—Case report. Chirurgia 2012, 107, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehra, P.; Jeong, D. Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009, 9, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).