Electroless Nickel Plating of Magnesium Particles for Hydrogen Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
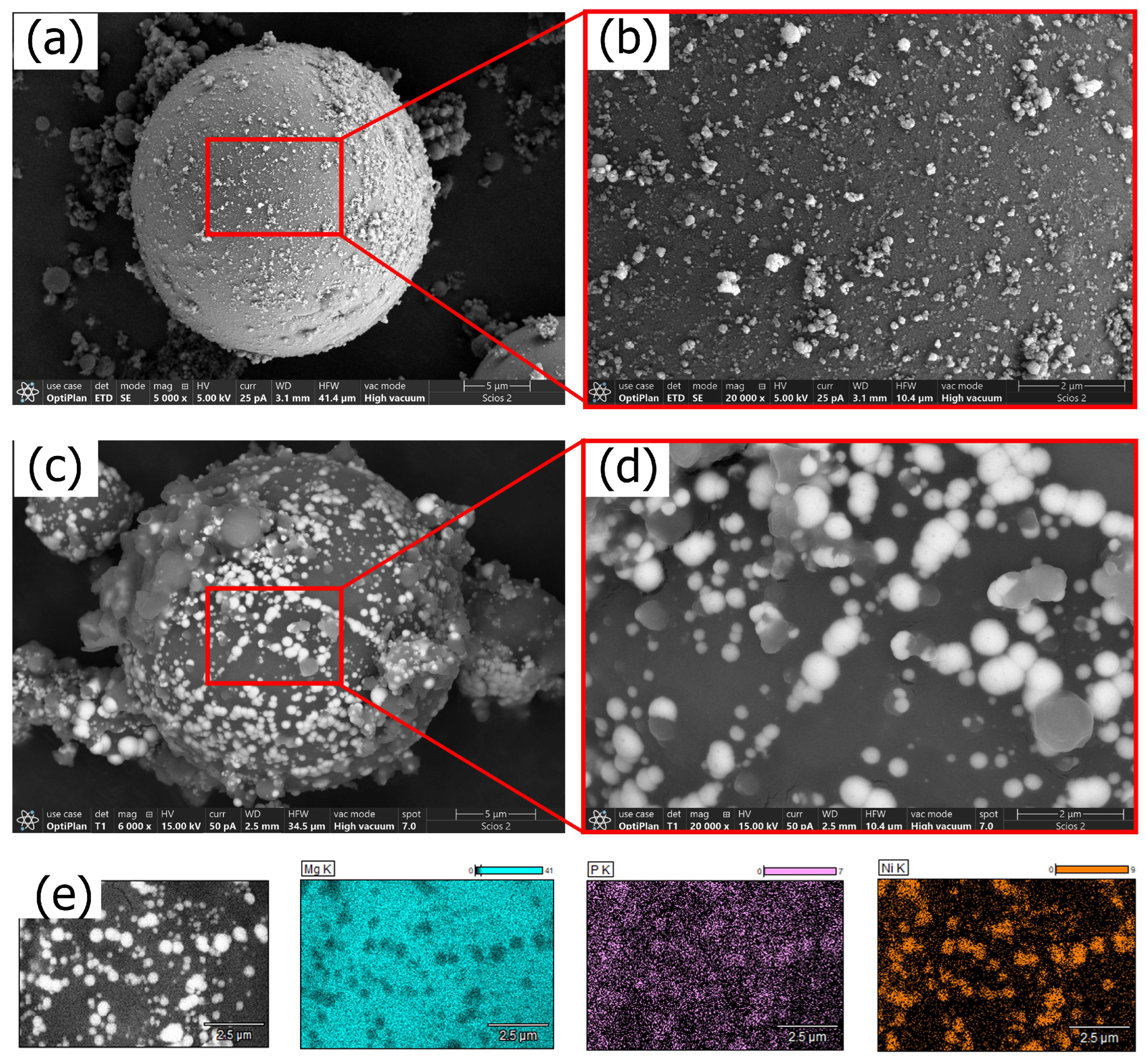
3.1. Aqueous Ni–P Electroless Bath
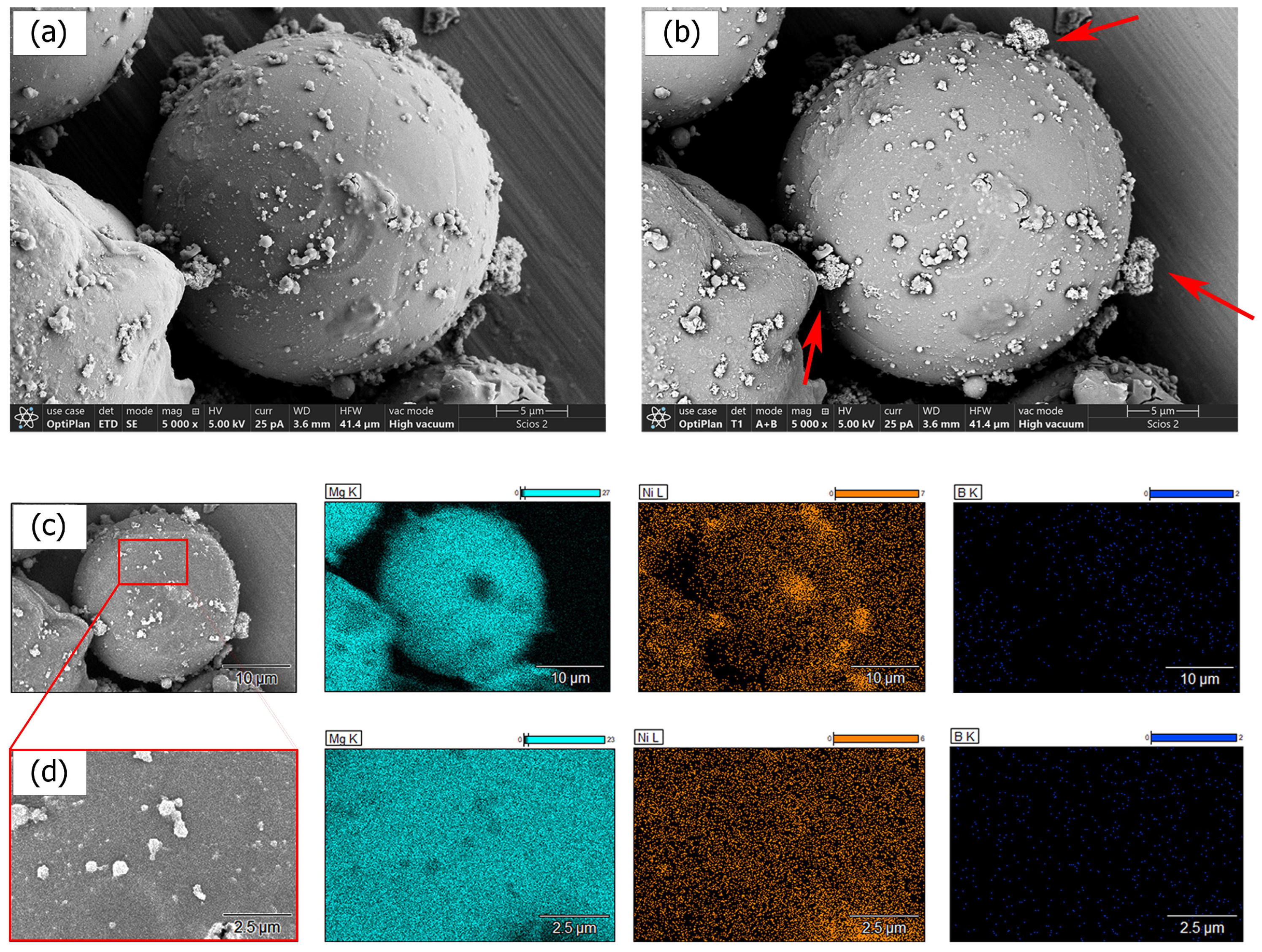
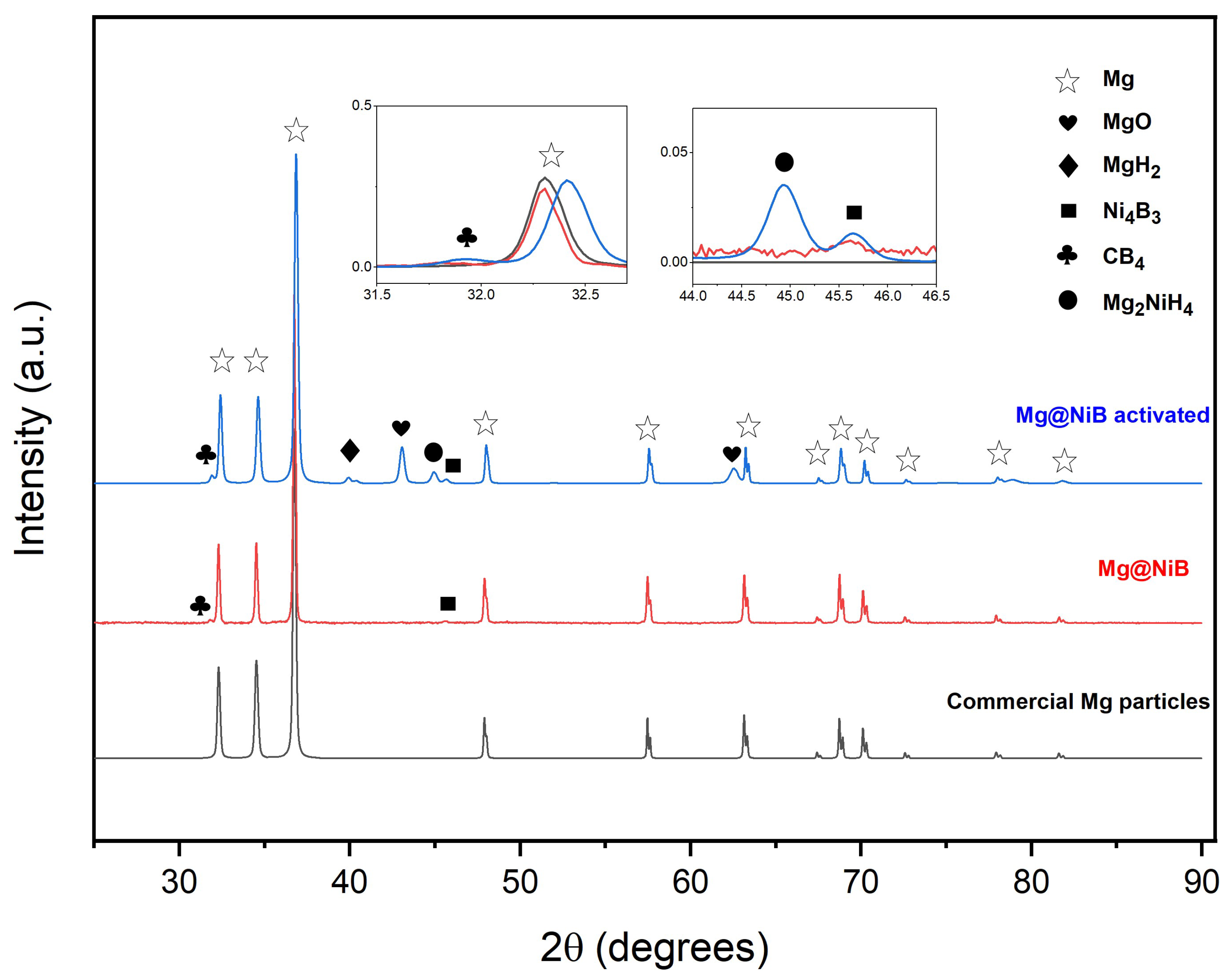
3.2. Anhydrous Ni–B Electroless Bath
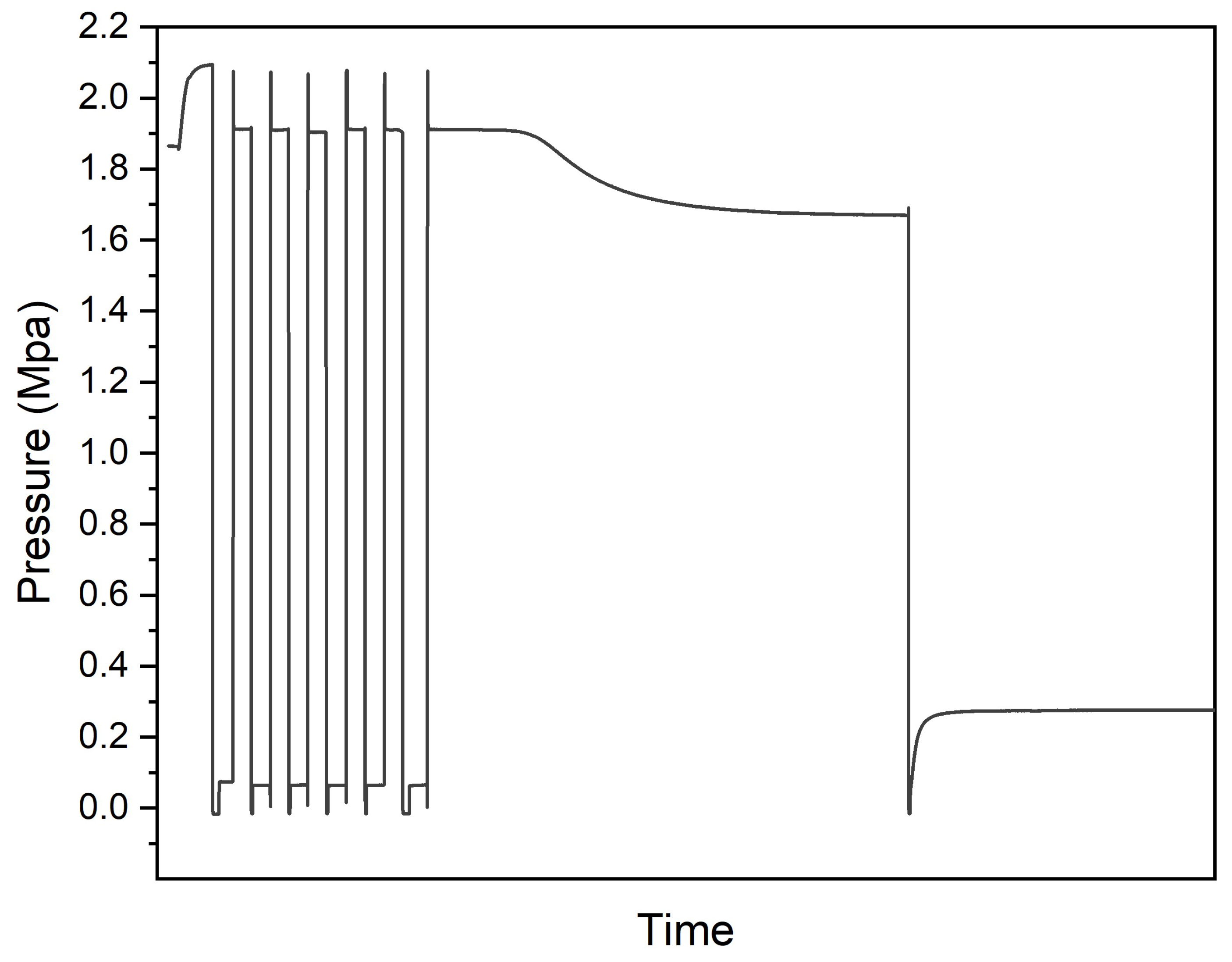
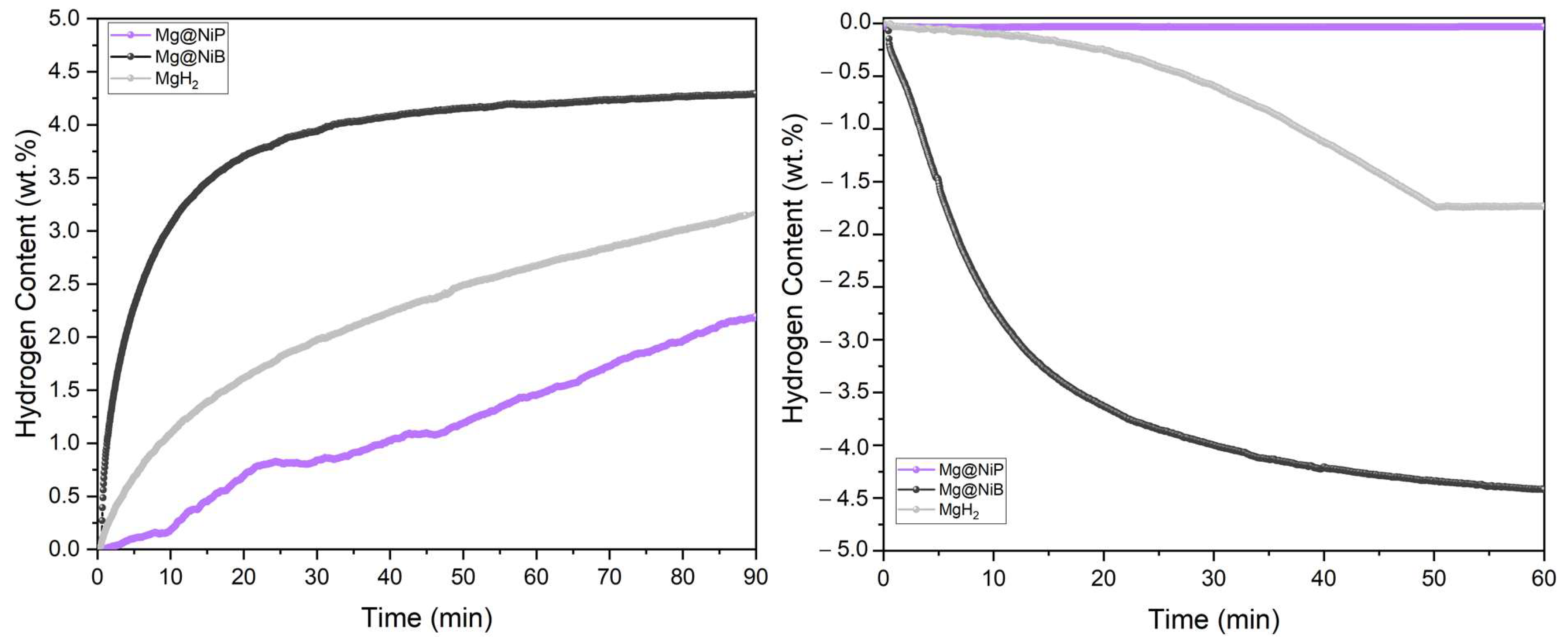
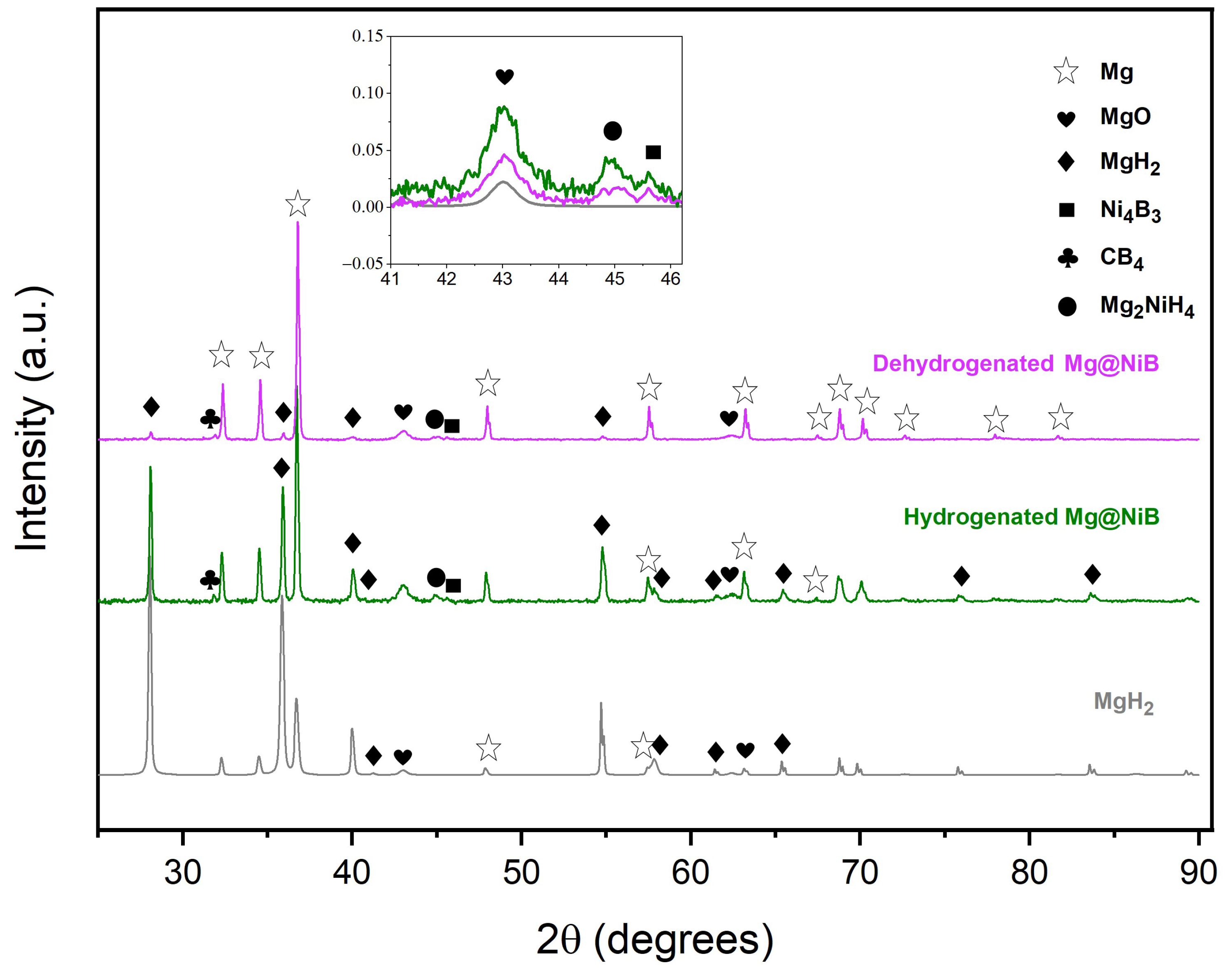
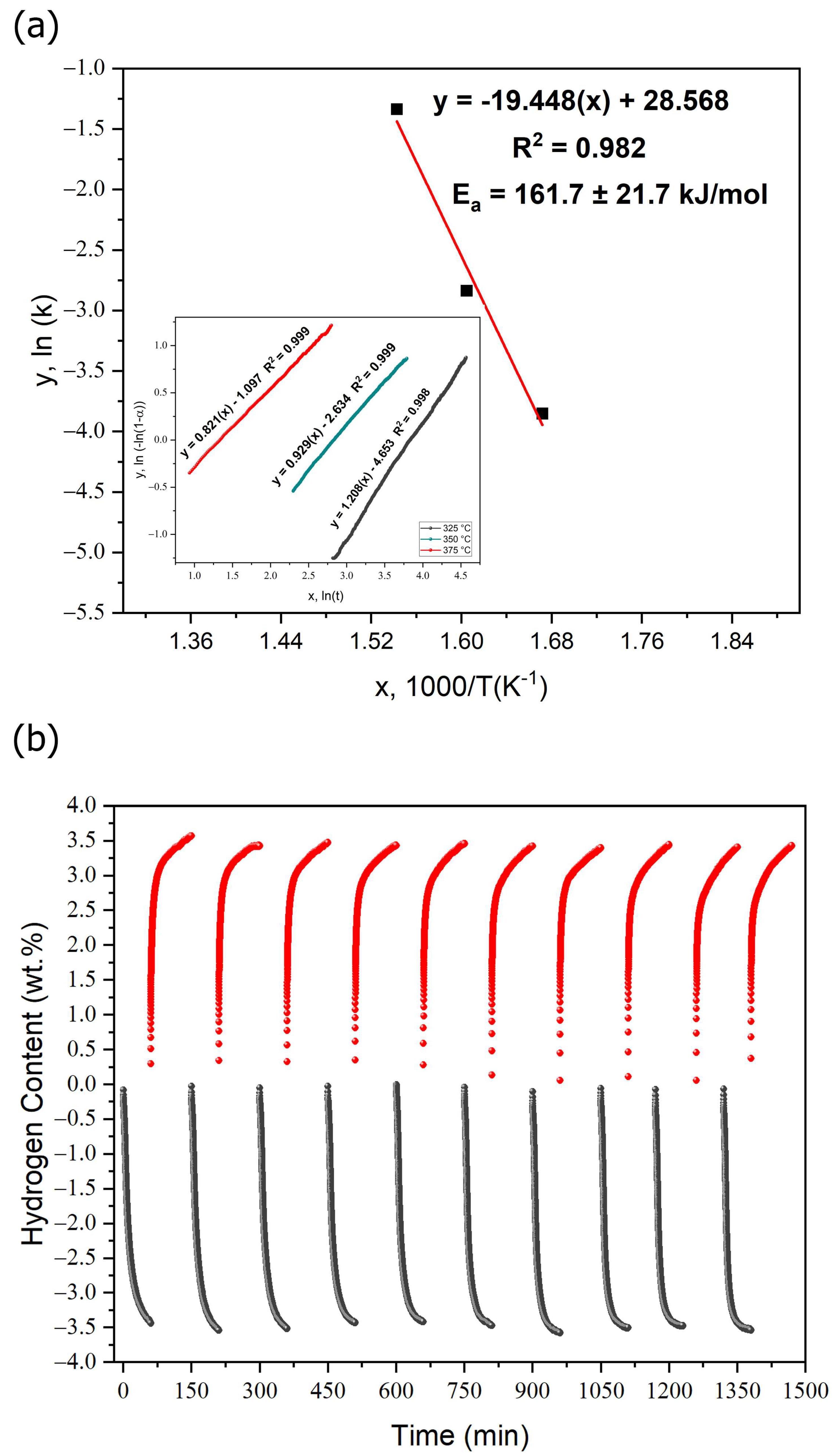
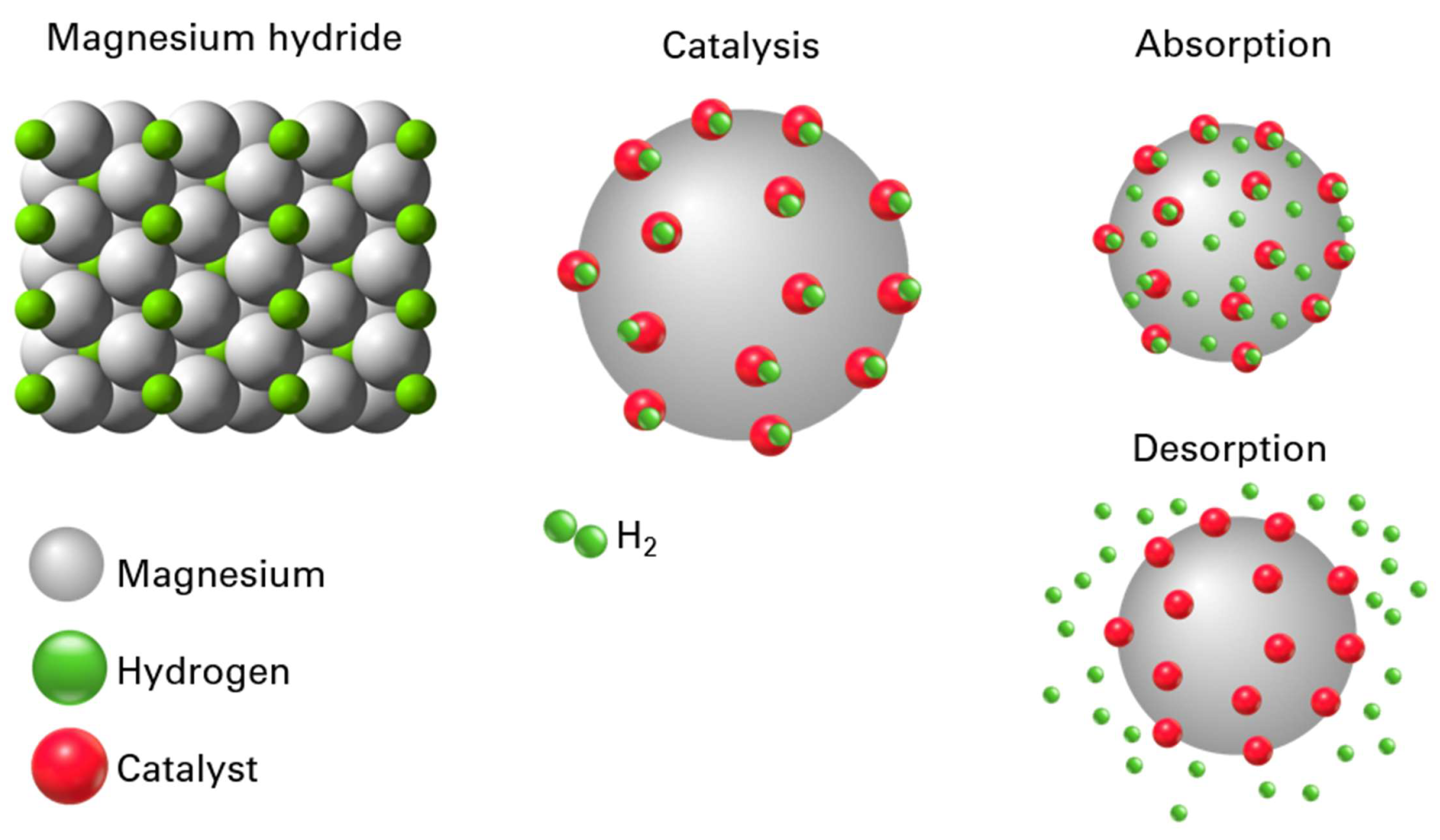
3.3. Thermal and Hydrogen Storage Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, Y.; Pistidda, C.; Gizer, G.; Klassen, T.; Dornheim, M. Mg-Based Materials for Hydrogen Storage. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1837–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Pan, H. Enhanced Hydrogen Storage Performance of MgH2 by the Catalysis of a Novel Intersected Y2O3/NiO Hybrid. Processes 2021, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zou, J.; Shi, X.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Synthesis and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Core–Shell Structured Binary Mg@Ti and Ternary Mg@Ti@Ni Composites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, R.; Groth, K.M. Hydrogen Storage and Delivery: Review of the State of the Art Technologies and Risk and Reliability Analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 12254–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, L.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, L. State of the Art Multi-Strategy Improvement of Mg-Based Hydrides for Hydrogen Storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 796–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Bolarin, J.A.; Lei, G.; Li, Z.; He, T.; Cao, H.; Chen, P. Potassium Hydride Reduced Black TiO2−x for Boosting the Hydrogenation of Magnesium at Room Temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 897, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtuckmeyster, D.; Bereznitsky, M.; Shelly, L.; Maman, N.; Hanuka, E.; Moskovich, N.; Shneck, R.Z.; Jacob, I. First Hydrogenation Kinetics and Properties of Mechanically Treated Pure Mg. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, 8, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yartys, V.A.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Akiba, E.; Albert, R.; Antonov, V.E.; Ares, J.R.; Baricco, M.; Bourgeois, N.; Buckley, C.E.; Bellosta von Colbe, J.M.; et al. Magnesium Based Materials for Hydrogen Based Energy Storage: Past, Present and Future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7809–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouki, M.; Ghodbane, O.; Abdellaoui, M. Study of Hydrogen Absorption Kinetics of Mg2Ni-Based Powders Produced by High-Injected Shock Power Mechanical Alloying and Subsequent Annealing. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2013, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivello, J.C.; Dam, B.; Denys, R.V.; Dornheim, M.; Grant, D.M.; Huot, J.; Jensen, T.R.; de Jongh, P.; Latroche, M.; Milanese, C.; et al. Review of Magnesium Hydride-Based Materials: Development and Optimisation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 2016, 122, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Ye, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, W.; Fang, F.; Sun, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Xia, G. Light-Enabled Reversible Hydrogen Storage of Borohydrides Activated by Photogenerated Vacancies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 2786–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Y.; Xia, G.; Yu, X.; Sun, D.; Fang, F. In Situ Construction of Interface with Photothermal and Mutual Catalytic Effect for Efficient Solar-Driven Reversible Hydrogen Storage of MgH2. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2400274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ju, S.; Ye, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, W.; Yao, L.; Xia, G.; Fang, F.; Sun, D.; et al. Solar-Driven Reversible Hydrogen Storage. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2206946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ju, S.; Li, C.; Hao, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; He, L.; Xia, G.; et al. Atomic Reconstruction for Realizing Stable Solar-Driven Reversible Hydrogen Storage of Magnesium Hydride. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Xia, G.; Sun, D.; Yu, X. Heterostructures Built in Metal Hydrides for Advanced Hydrogen Storage Reversibility. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2202647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogen Desorption Kinetics of Magnesium Hydride Co-Doped with Titanium Trifluoride and Nickelocene. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czujko, T.; Varin, R.A.; Wronski, Z.; Zaranski, Z.; Durejko, T. Synthesis and Hydrogen Desorption Properties of Nanocomposite Magnesium Hydride with Sodium Borohydride (MgH2 + NaBH4). J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zou, J.; Zeng, X.; Wu, X.; Li, D.; Ding, W. Hydrogen Storage Properties of a Mg-Ni Nanocomposite Coprecipitated from Solution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 18401–18411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Czujko, T.; Wasmund, E.B.; Wronski, Z.S. Hydrogen Desorption Properties of MgH2 Nanocomposites with Nano-Oxides and Inco Micrometric- and Nanometric-Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446–447, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houari, A.; Matar, S.F.; Eyert, V. Electronic Structure and Magnetic Ordering of NiN and Ni2N from First Principles. Electron. Struct. 2019, 1, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraj, K.S.; Assadi, M.H.N. Detrimental 2p-3d Hybridisation in Ni Nanosheets Supported on Strontium Dioxide for Catalytic H2 Production, Necessitating Thickness Optimisation. Energy Transit. Towar. Carbon Neutrality 2024, 44, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Jin, C.; Jiang, K.; Bao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chu, J. Applications of Nickel-Based Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2022, 3, 2100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S.; Al-Nasrallah, E.; Banyan, M.; Al-Ajmi, F. Bulk Nanocomposite MgH2/10 Wt% (8 Nb2O5/2 Ni) Solid-Hydrogen Storage System for Fuel Cell Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 23382–23396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.J.; Theodore, A.; Wu, C.Y.; Cai, M. Hydrogen Absorption/Desorption Kinetics of Magnesium Nano-Nickel Composites Synthesized by Dry Particle Coating Technique. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Chen, L.; Li, H. Recent Advances of Magnesium Hydride as an Energy Storage Material. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 149, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, B.P.; Arbuzov, A.A.; Mozhzhuhin, S.A.; Volodin, A.A.; Fursikov, P.V.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Yartys, V.A. Hydrogen Storage Behavior of Magnesium Catalyzed by Nickel-Graphene Nanocomposites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29212–29223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S.; Al-Ajmi, F.; Banyan, M. Mechanically-Induced Catalyzation of MgH2 Powders with Zr2Ni-Ball Milling Media. Catalysts 2019, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loto, C.A. Electroless Nickel Plating–A Review. Silicon 2016, 8, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, C.; Lai, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, D.W.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F. Tailoring Magnesium Based Materials for Hydrogen Storage through Synthesis: Current State of the Art. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 10, 168–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, E.; Zuleta, A.A.; Guerra, L.; Castaño, J.G.; Echeverría, F.; Baron-Wiecheć, A.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E. Formation of Electroless Ni-B on Bifluoride-Activated Magnesium and AZ91D Alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D327–D336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, D.F.; Bermudez, A.; Gómez, M.A.; Zuleta, A.A.; Castaño, J.G.; Mischler, S. Fretting-Corrosion Behavior of Electroless Ni-P/Ni-P-TiO2 Coatings Obtained on AZ91D Magnesium Alloy by a Chromium-Free Process. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.D.; Romankiw, L.T. Electroless Ni-Fe Deposition Process. U.S. Patent US3382079A, 7 May 1968. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3382079A/en1964 (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Cheng, A.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; You, J.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Hou, K.H.; Ger, M. Der Evaluation of Electroless Plating on Magnesium Alloy Micro-Arc Oxidation Layer with Different Electroless Ni-P Plating Baths. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1011, 178398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Sheu, H.H.; Jian, J.S.; Chang, S.Y.; Yen, C.H.; Lin, H.E. Supercritical-CO2 Electroless Nickel Plating Enhanced Anti-Corrosion Properties of Micro-Arc Oxidized AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Hu, C.; Li, L.; Hu, B.; Song, Z.; Yan, D.; Yu, G. Electroless Deposition and Characterization of a Double-Layered Ni-B/Ni-P Coating on AZ91D Mg Alloy from Eco-Friendly Fluoride-Free Baths. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 342, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Zhan, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, F.; Wang, C. Deposition Mechanism of Electroless Nickel Plating of Composite Coatings on Magnesium Alloy. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Gharde, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Electroless Nickel Fabrication on Surface Modified Magnesium Substrates. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, G.L.; Kruger, J. Corrosion of Magnesium. Int. Mater. Rev. 1993, 38, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.L.; Lemmon, E.W.; Bell, I.H.; McLinden, M.O. The NIST REFPROP Database for Highly Accurate Properties of Industrially Important Fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 15449–15472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, M.; Mu, D.; Gao, Y.; He, L.; Ma, L. Synergistic Combination of Ni Nanoparticles and Ti3C2 MXene Nanosheets with MgH2 Particles for Hydrogen Storage. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 21521–21531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hou, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J. Improvement of the Hydrogen Storage Characteristics of MgH2 with a Flake Ni Nano-Catalyst Composite. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Shi, X.; Ding, X.; Dao, V.D.; Li, Y. Size-Dependent Activity Modulation of Supported Ni Nanocatalysts for Efficient Solid-State Hydrogen Storage in Magnesium. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Peng, C.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, D. Facilitated Hydrogen Storage Properties of MgH2 by Ni Nanoparticles Anchored on Mo2C@C Nanosheets. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 85, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Qiu, S.; Xia, Y.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.; Chu, H. Ni-Based Catalyst Assisted by MnO to Boost the Hydrogen Storage Performance of Magnesium Hydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 55, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Ong, W.J. Tailoring Hydrogen Storage Materials Kinetics and Thermodynamics Through Nanostructuring, and Nanoconfinement With In-Situ Catalysis. Interdiscip. Mater. 2025, 4, 249–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Alcántara, K.; Flores-Jacobo, N.I.; del Pilar Osorio-García, M.; Cabañas-Moreno, J.G. Fast Hydrogen Sorption Kinetics in Mg-VCl3 Produced by Cryogenic Ball-Milling. Materials 2023, 16, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Crystallite Growth Characteristics of Mg during Hydrogen Desorption of MgH2. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Zou, J.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, N.A.; Saud, S.; Panda, S. The Adaptable Effect of Ru on Hydrogen Sorption Characteristics of the MgH2 System. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 301, 127583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyahuma, F.M.; Zhang, L.; Song, M.; Lu, X.; Xiao, B.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F. Significantly Improved Hydrogen Storage Behaviors in MgH2 with Nb Nanocatalyst. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galey, B.; Auroux, A.; Sabo-Etienne, S.; Dhaher, S.; Grellier, M.; Postole, G. Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of Mg/MgH2 Thanks to the Addition of Nickel Hydride Complex Precursors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28848–28862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, G. Effect of Porous Nanosheet NiO on Hydrogen Storage Performance of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 135, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, J. A Note on the Johnson–Mehl–Avrami–Kolmogorov Kinetic Model: An Attempt Aiming to Introduce Time Non-Locality. Eng 2025, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, O.; Shang, Y.; Huang, X.; Szabó, D.V.; Le, T.T.; Wagner, S.; Klassen, T.; Kübel, C.; Pistidda, C.; Pundt, A. Transformation Kinetics of LiBH4–MgH2 for Hydrogen Storage. Molecules 2022, 27, 7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooij, L.; Dam, B. Nucleation and Growth Mechanisms of Nano Magnesium Hydride from the Hydrogen Sorption Kinetics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11501–11510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Dixit, V.; Jain, A.; Srivastava, O.N.; Huot, J. Effect of Magnesium Fluoride on Hydrogenation Properties of Magnesium Hydride. Energies 2015, 8, 12546–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.J.; Gao, M.X.; Pan, H.G. Empowering Hydrogen Storage Performance of MgH2 by Nanoengineering and Nanocatalysis. Mater. Today Nano 2020, 9, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ma, C. Enhanced Hydrogen Storage Property of MgH2 Caused by a BaCrO4 Nanocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 23930–23942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazaz, S.; Billeter, E.; Longo, F.; Borgschulte, A.; Łodziana, Z. Why Hydrogen Dissociation Catalysts Do Not Work for Hydrogenation of Magnesium. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2304603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S.; Shaban, E.; Ali, N.; Aldakheel, F.; Alkandary, A. In-Situ Catalyzation Approach for Enhancing the Hydrogenation/Dehydrogenation Kinetics of MgH2 Powders with Ni Particles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Qi, L.; Mishra, R.K.; Zeng, X.; Minor, A.M. Size-Dependent Mechanical Properties of Mg Nanoparticles Used for Hydrogen Storage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 261903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinthamani, S.; Kannan, G.; George, G.D.; Sreedharan, C.E.; Rajagopal, K.S. Effect of Nano B4C on the Tribological Behaviour of Magnesium Alloy Prepared Through Powder Metallurgy. Mater. Sci. 2020, 26, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztop, H.F.; Gürgenç, E.; Gür, M. Thermophysical Properties and Enhancement Behavior of Novel B4C-Nanoadditive RT35HC Nanocomposite Phase Change Materials: Structural, Morphological, Thermal Energy Storage and Thermal Stability. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2024, 272, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, K.; Ye, F.; Wang, X.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y. Facile Synthesis of Small MgH2 Nanoparticles Confined in Different Carbon Materials for Hydrogen Storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 825, 153953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Li, L. Facile Synthesis of Carbon Supported Nano-Ni Particles with Superior Catalytic Effect on Hydrogen Storage Kinetics of MgH2. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, B.; Prvulović, M.; Filipović, N.; Mravik, Ž.; Sekulić, Z.; Govedarović, S.M.; Milanović, I. Hydrogen Storage Properties of MgH2–Tm: Ni-Catalysis vs. Mechanical Milling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 54, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourabdoli, M.; Raygan, S.; Abdizadeh, H.; Uner, D. Determination of Kinetic Parameters and Hydrogen Desorption Characteristics of MgH2-10 Wt% (9Ni–2Mg–Y) Nano-Composite. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 11910–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czujko, T.; Oleszek, E.E.; Szot, M. New Aspects of MgH2 Morphological and Structural Changes during High-Energy Ball Milling. Materials 2020, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Cao, G.; Li, S.; Yan, M. Improved Hy-drogen Storage Properties of MgH2 by Ball Milling with AlH3: Prepara-tions, de/Rehydriding Properties, and Reaction Mechanisms. J Mater Chem A Mater 2013, 1, 12527–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, R.A.; Arias-Velandia, J.; Lenis, J.A.; Zuleta Gil, A.A.; Bello, S.; Correa, E.; Arrieta, C.; Bolívar, F.J.; Echeverría, F.E. Catalytic Effect of Commercial Carbon-Coated Nickel Nanoparticles on the Hydrogen Storage Performance of Magnesium Hydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 129, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Long, S.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Preparation and Hydrogen Sorption Properties of a Ni Decorated Mg Based Mg@Ni Nano-Composite. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadonougbo, J.O.; Kim, H.J.; Suh, B.C.; Suh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Shim, J.H.; Yim, C.D.; Cho, Y.W. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of near Eutectic Mg-Mg2Ni Composites Produced by Casting Process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 29009–29022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Chemical Composition | |
| Component | Composition (g/L) |
| C4H6O6 | 2.5 |
| NiCl2 | 11.3 |
| NaOH | 9.3 |
| NaBH4 | 1.7 |
| Mixing conditions | |
| Stirring speed | >600 RPM |
| Temperature (°C) | 70 ± 5 |
| Time (minutes) | 25 |
| Plating conditions | |
| Load bath | 4 mg/mL |
| Stirring speed | >600 RPM |
| Temperature (°C) | 60 ± 1 |
| Time (minutes) | 5 |
| Centrifugation-assisted washing conditions (≥6000 RPM) | |
| Centrifugal separation time (minutes) | 45 |
| Centrifugal wash acetone time (minutes) | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bello, S.; Aguirre Ocampo, R.; Arias Velandia, J.; Zuleta Gil, A.; Correa, E.; Silva, W.; Lenis Rodas, J.A.; Arrieta, C.; Bolívar, F.; Nieto, C.; et al. Electroless Nickel Plating of Magnesium Particles for Hydrogen Storage. Appl. Nano 2025, 6, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6030016
Bello S, Aguirre Ocampo R, Arias Velandia J, Zuleta Gil A, Correa E, Silva W, Lenis Rodas JA, Arrieta C, Bolívar F, Nieto C, et al. Electroless Nickel Plating of Magnesium Particles for Hydrogen Storage. Applied Nano. 2025; 6(3):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleBello, Sindy, Robinson Aguirre Ocampo, Julián Arias Velandia, Alejandro Zuleta Gil, Esteban Correa, Wilber Silva, Julián Andrés Lenis Rodas, Carlos Arrieta, Francisco Bolívar, Cesar Nieto, and et al. 2025. "Electroless Nickel Plating of Magnesium Particles for Hydrogen Storage" Applied Nano 6, no. 3: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6030016
APA StyleBello, S., Aguirre Ocampo, R., Arias Velandia, J., Zuleta Gil, A., Correa, E., Silva, W., Lenis Rodas, J. A., Arrieta, C., Bolívar, F., Nieto, C., & Echeverria, F. (2025). Electroless Nickel Plating of Magnesium Particles for Hydrogen Storage. Applied Nano, 6(3), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano6030016










