The Effects of Surfactant and Metal Ions on the Stability and Rheological Properties of Nanoemulsions Loaded with Gardenia Yellow Pigment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of the Emulsions
2.2.2. Selection of HLB Values
2.2.3. Optimization of the Preparation Conditions
2.2.4. Optimization of the Formulas
2.2.5. Determination of the Droplet Size and PDI
2.2.6. Rheological Analysis
2.2.7. Long-Term Stability
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
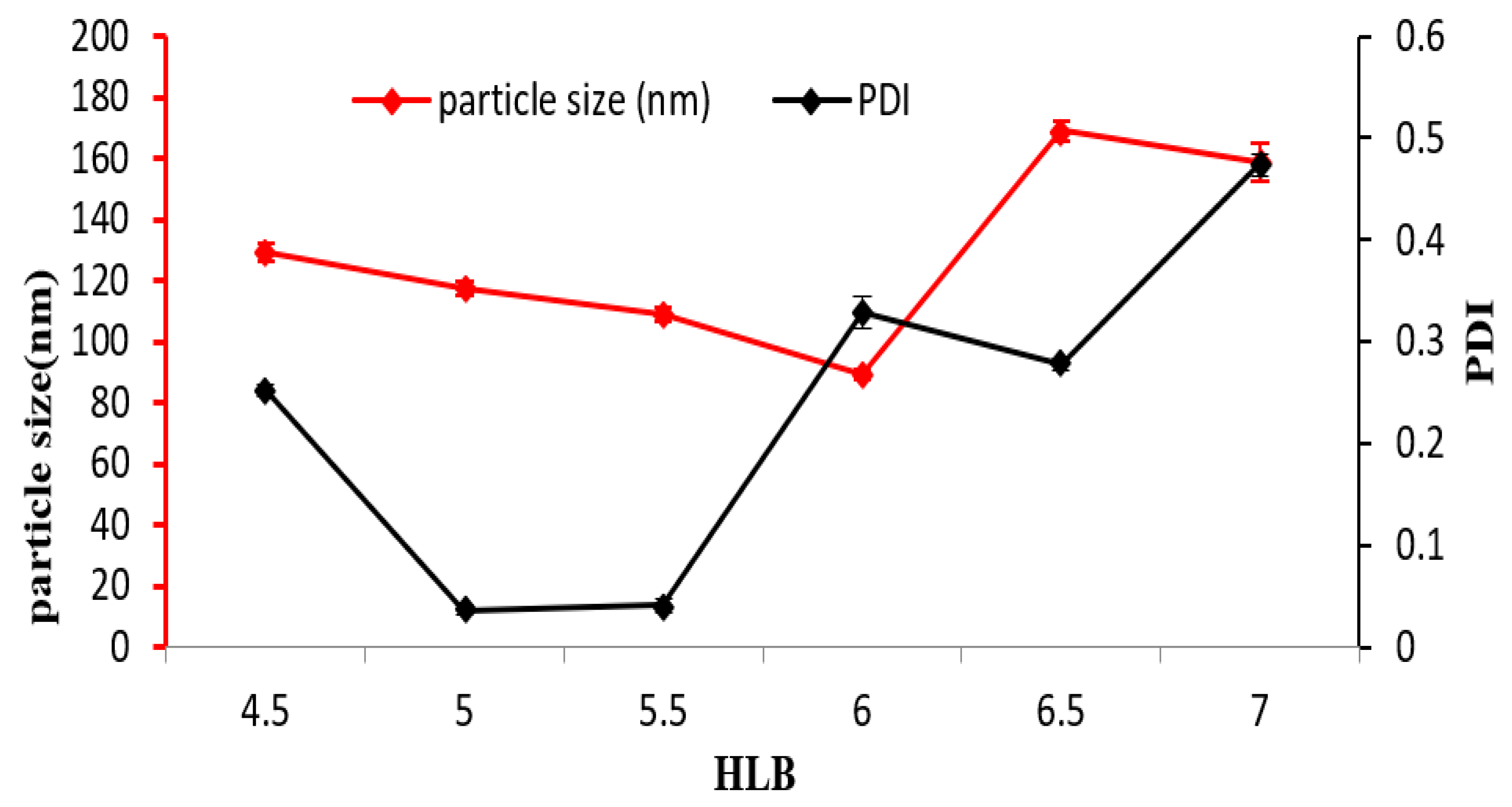
3.1. Influence of the HLB Value
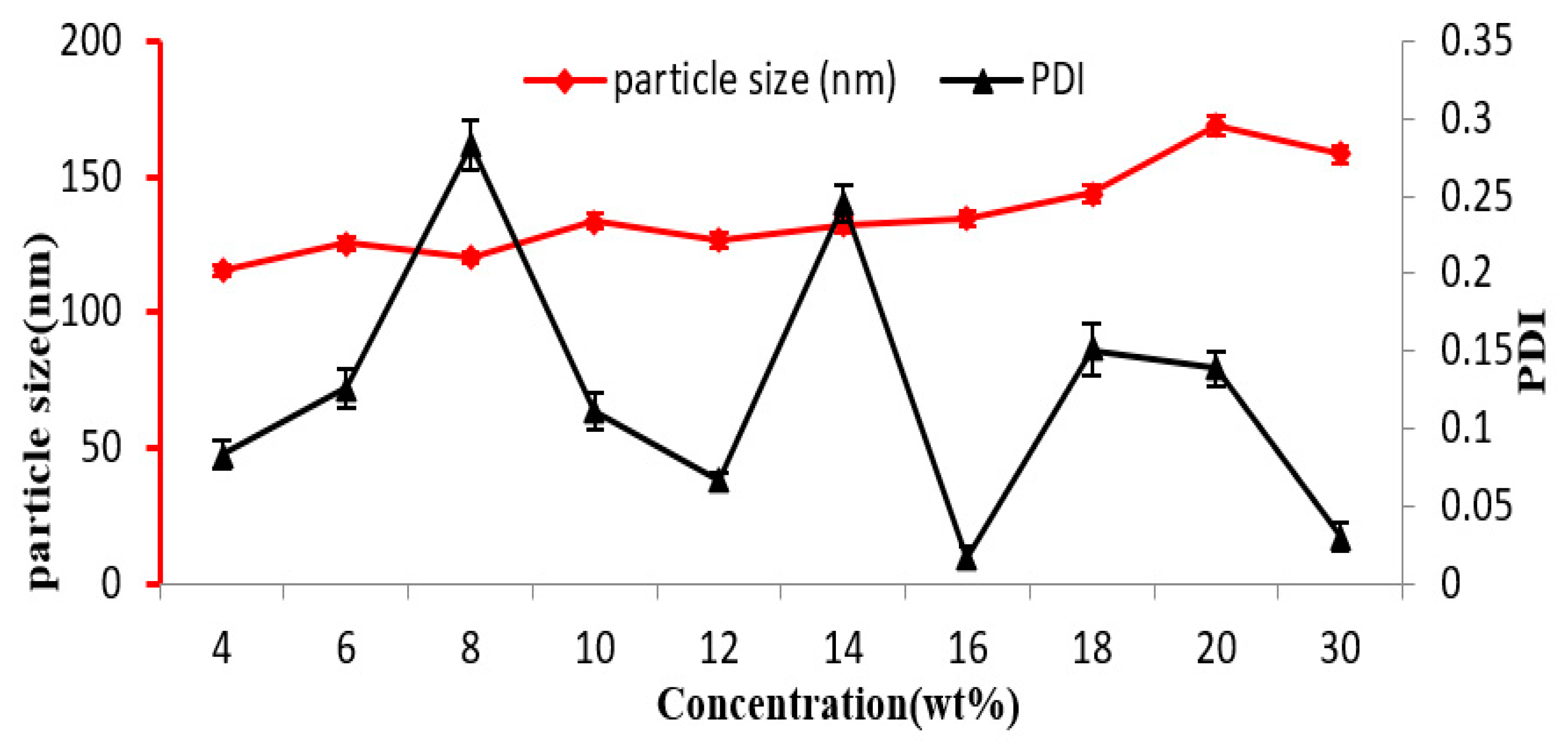
3.2. Influence of EC
3.3. Influence of the Oil–Water Ratio (OWR)
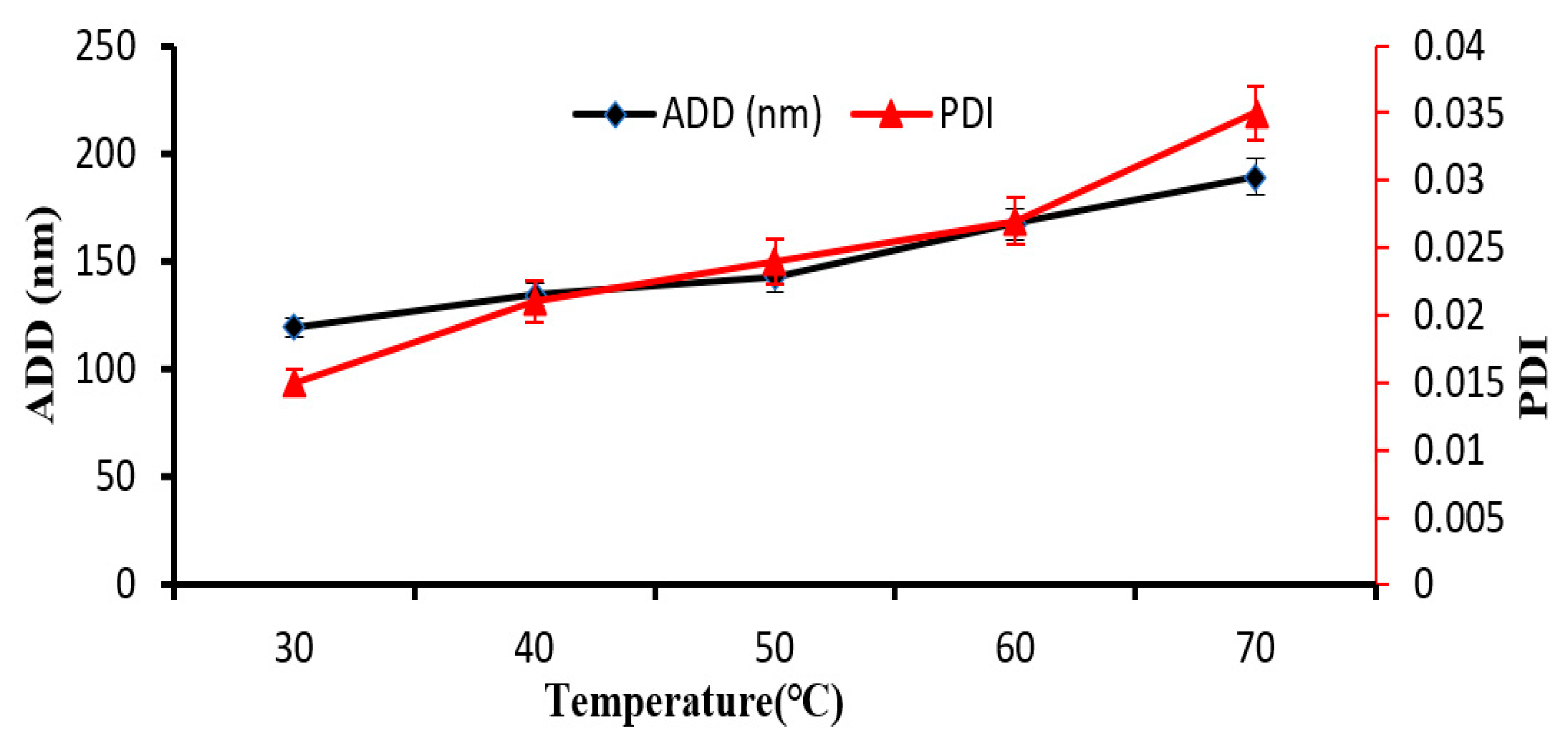
3.4. Influence of T
3.5. Orthogonal Experiments Design
3.6. Rheology
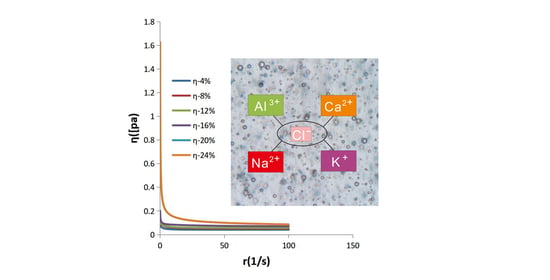
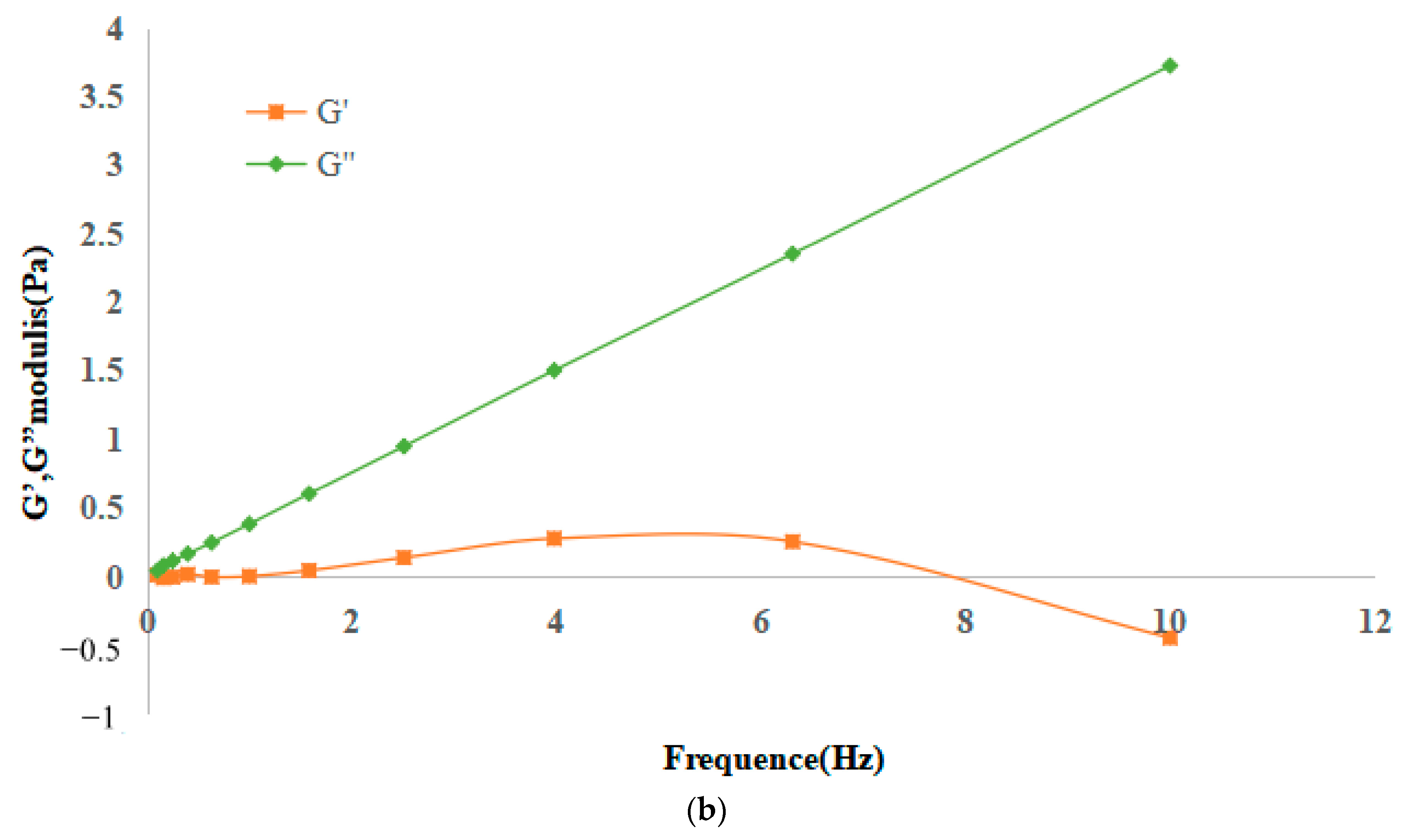
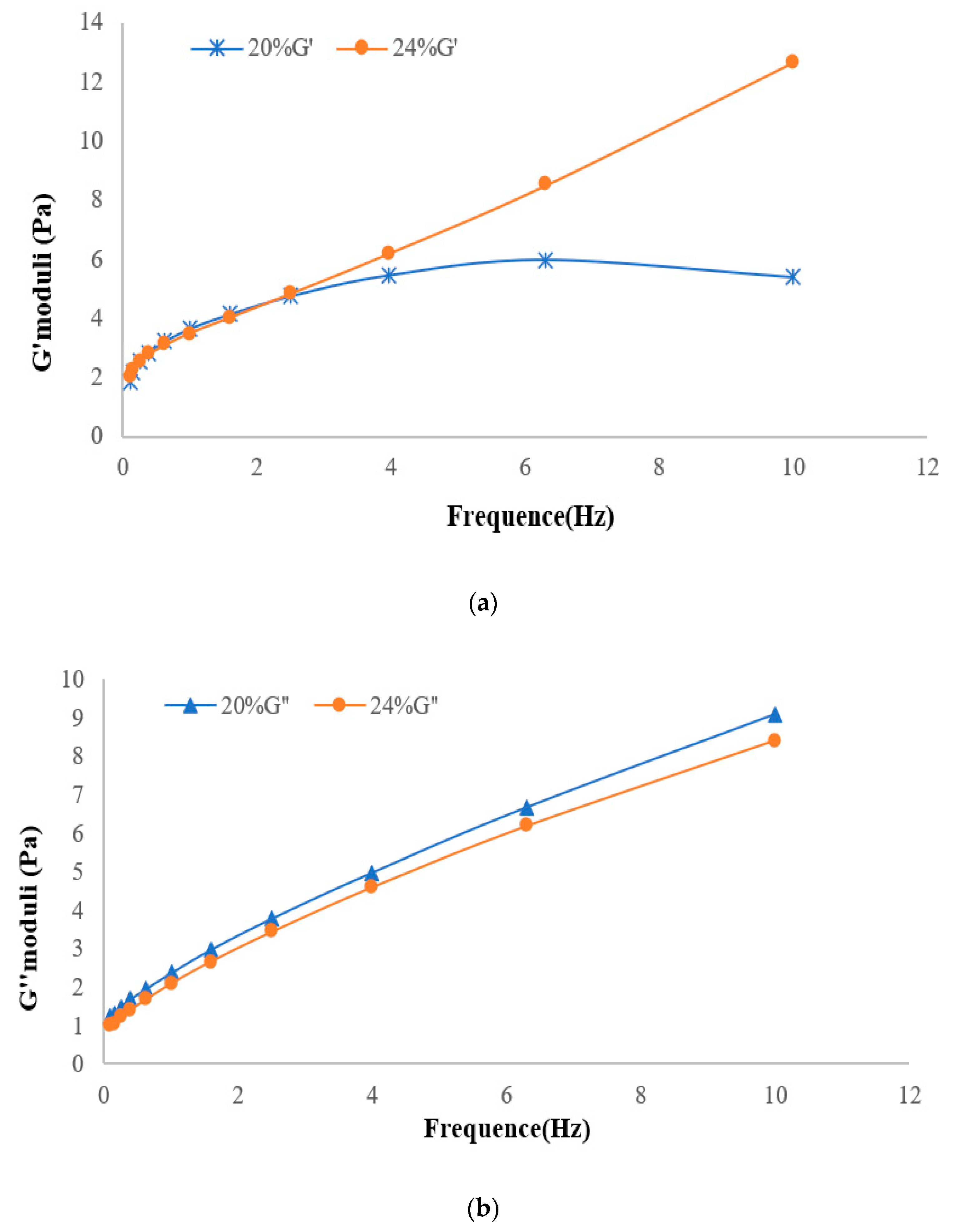
3.6.1. Shear Flow Tests
3.6.2. Oscillation Strain Sweep
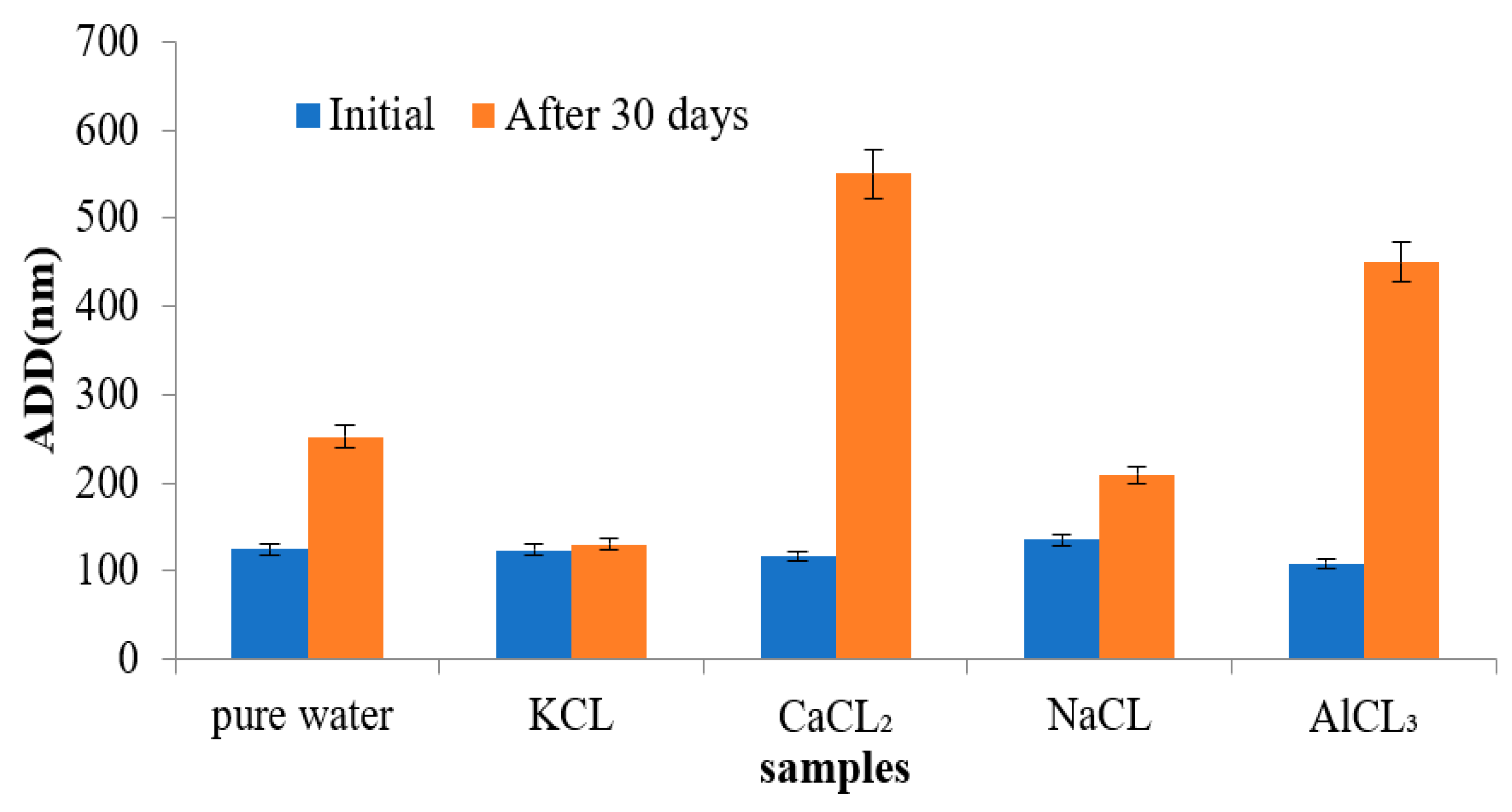
3.7. Stability Evaluation of the Emulsions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADD | average droplet diameter |
| EC | emulsifier concentration |
| HLB | hydrophilic–lipophilic balance |
| O/W | oil-in-water |
| OWR | oil–water ratio |
| PDI | polydispersity index |
| PT | preparation T |
| SD | standard deviation |
| T | temperature |
| W/O | water-in-oil |
References
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Extraction optimization by using response surface methodology and purification of yellow pigment from Gardenia jasminoides var. radicans Makikno. Food Sci. Nutitionr. 2020, 9, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Fan, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, L. Stability assessment of crocetin and crocetin derivatives in Gardenia yellow pigment and Gardenia fruit pomace in presence of different cooking methods. Food Chem. 2019, 312, 126031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z. Comparative study of chemical compositions and antioxidant activities of Zhizi fruit extracts from different regions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Torii, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Jiang, X.; Ikeda, S.; Yotsukura, E.; Koh, S.; Kurihara, T.; Nishida, K.; Tsubota, K. The Effffect of Dietary Supplementation of Crocetin for Myopia Control in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umigaia, N.; Takedab, R.; Moric, A. Effffect of crocetin on quality of sleep: A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, crossover study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 41, 4–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Tao, W.; Wang, P.; Tian, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological and industrial applications of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Tanada, C.; Nishikawa, H.; Matsuda, S.; Tada, A.; Ito, Y.; Min, J.Z.; Todoroki, K.; Sugimoto, N.; Toyo’oka, T.; et al. Evaluation of gardenia yellow using crocetin from alkaline hydrolysis based on ultra high performance liquid chromatography and high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3619–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Bera, A. Surfactant Stabilized nanoemulsion: Characterization and Application in Enhanced Oil Recovery. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 6, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, V.K.; Mishra, N.; Yadav, K.S.; Yadav, N.P. Nanoemulsion as Pharmaceutical Carrier for Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery: Formulation Development, Stability Issues, Basic Considerations and Applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Jain, K.; Gowthamarajan, K. Optimization of Curcumin nanoemulsion for Intranasal Delivery Using Design of Experiment and Its Toxicity Assessment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Kundu, A.; Sarkar, L.; Karmakar, S.; Jaisankar, P.; Pal, T.K. nanoemulsion Strategy for Olmesartan Medoxomil Improves Oral Absorption and Extended Antihypertensive Activity in Hypertensive Rats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 115, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, B.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, J. Nanoemulsion Improves the Oral Bioavailability of Baicalin in Rats: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3769–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solans, C.; Izquierdo, P.; Nolla, J.; Azemar, N.; Garciacelma, M.J. Nanoemulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.; Saharan, V.K. Ultrasonic assisted formation and stability of mustard oil in water nano–emulsion: Effect of process parameters and their optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Esfanjani, A.F.; Akhavan, S. Application of nanoencapsulated olive leaf extract in controlling the oxidative stability of soybean oil. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, F.; Crushell, E.; O’Driscoll, K.; Bourke, B. Liquid paraffin: A reappraisal of its role in the treatment of constipation. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 85, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.E.; Docherty, M.H. Constipation complication: Lung injury following inadvertent intravenous injection of liquid paraffin. Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015213685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urganci, N.; Akyildiz, B.; Polat, T.B. A comparative study: The effificacy of liquid paraffin and lactulose in management of chronic functional constipation. Pediatr. Int. 2005, 47, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermén, M.; Verallo, R.; Stephanie, S.; Katalbas, J.P. Pangasinan1. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chuberre, B.; Araviiskaia, E.; Bieber, T.; Barbaud, A. Mineral oils and waxes in cosmetics: An overview mainly based on the current European regulations and the safety profile of these compounds. JEADV 2019, 33, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.C. Calculation of HLB Values of Non-Ionic Surfactants. Am. Perfum. Essent. Oil Rev. 1955, 65, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Song, X.; Liang, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, F. Stability and Phase Behavior of Acrylamide-Based Emulsions before and after Polymerization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 9079–9084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Mei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Sun, D. Formation and Properties of Paraffin Wax Submicron Emulsions Prepared by the Emulsion Inversion Point Method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 356, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sun, D.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J. Formation and Stability of Paraffin Oil-in-Water nanoemulsions Prepared by the Emulsion Inversion Point Method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, T.S.H.; Wooster, T.J.; Kentish, S.E.; Ashokkumar, M. Minimising Oil Droplet Size Using Ultrasonic Emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati, H.; Coombes, A.G.A.; Adler, J.; Holland, J.; Davis, S.S. Protein-Loaded Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) Microparticles for Oral Administration: Formulation, Structural and Release Characteristics. J. Control. Release 1997, 43, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayoubi, A.; Abufayyad, A.; Rawasqalaji, M.M.; Sylvester, P.W.; Nazzal, S. Effect of lipid viscosity and high-pressure homogenization on the physical stability of “Vitamin E” enriched emulsion. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 20, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Patel, D.K.; Thakur, R.; Mishra, D.P.; Maiti, P.; Haldar, C. Anti-Cancer Evaluation of Quercetin Embedded PLA Nanoparticles Synthesized by Emulsified Nanoprecipitation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.J.; Liao, A.M.; Zhang, H.X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, S.T. Optimization of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Silkworm Pupal Oil Applying the Response Surface Methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4214–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Chen, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, Y. Orthogonal Design Preparation of Phenolic Fiber by Melt Electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, Z.; Jin, Y.; Ru, X.; Ding, D.; Li, J. Optimization and Investigation of the Governing Parameters in Electrospinning the Home-Made Poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone-diOH). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3600–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vild, A.; Teixeira, S.; Kühn, K.; Cuniberti, G.; Sencadas, V. Orthogonal Experimental Design of Titanium Dioxide—Poly(methyl methacrylate) Electrospun Nanocomposite Membranes for Photocatalytic Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3151–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.G.; Moghaddam, A.Z.; Omidkhah, M.R. The Influence of Process Parameters on Desulfurization of Mezino Coal by HNO3/HCl Leaching. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; Beheshti, P.; Assadpoor, E. Rheological behavior and stability of d-limonene emulsions made by a novel hydrocolloid (Angum gum) compared with Arabic gum. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Mu, R.-J.; Du, Y.; Wu, C.; Pang, J. The rheological and physicochemical properties of a novel thermosensitive hydrogel based on konjac glucomannan/gum tragacanth. LWT 2019, 100, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. The effects of emulsifier type, phase ratio, and homogenization methods on stability of the double emulsion. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, P. Rheological Changes in Emulsions on Aging: III. At Very Low Rates of Shear. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1967, 24, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. Fundamental Principles of Emulsion Rheology and Their Applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 91, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; Assadpoor, E.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Re-Coalescence of Emulsion Droplets during High-Energy Emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. Emulsion Formation, Stability, and Rheology. In Emulsion Formation and Stability; Tadros, T.F., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Scherze, I.; Knoth, A.; Muschiolik, G. Effect of Emulsification Method on the Properties of Lecithin-and PGPR-Stabilized Water-in-Oil-Emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2006, 27, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, A.L.; Medrano, A.; Panizzolo, L.A.; Wagner, J.R. Effect of Calcium Salts and Surfactant Concentration on the Stability of Water-in-Oil (W/O) Emulsions Prepared with Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Level | Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLB | EC (wt%) | OWR (w/w) | T (°C) | |
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1 | 5.0 | 10 | 2:1 | 40 |
| 2 | 5.5 | 12 | 3:1 | 50 |
| 3 | 6.0 | 16 | 4:1 | 60 |
| Run | HLB | EC (wt%) | OWR (w/w) | T (°C) | ADD (nm) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 120.432 | 0.032 | |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 141.105 | 0.172 | |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 189.306 | 0.148 | |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 130.423 | 0.152 | |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 117.406 | 0.082 | |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 141.323 | 0.011 | |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 99.207 | 0.225 | |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 94.104 | 0.573 | |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 104.413 | 0.204 | |
| ADD | k1 | 150.28 | 116.69 | 118.62 | 114.08 | ||
| k2 | 129.72 | 117.54 | 125.31 | 127.21 | |||
| k3 | 99.24 | 145.01 | 135.31 | 137.94 | |||
| R | 51.04 | 28.33 | 16.69 | 23.86 | |||
| order of importance A > B > D > C | |||||||
| optimal level A3B1D1C1 | |||||||
| PDI | k1 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.11 | ||
| k2 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.14 | |||
| k3 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.29 | |||
| R | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.19 | |||
| order of importance A > D > B > C | |||||||
| optimal level A2D1B3C2 | |||||||
| Factor | HLB | EC (wt%) | OWR (w/w) | T (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| condition | 6 | 10 | 2:1 | 40 |
| times | once | second | third | mean |
| ADD (nm) | 73.17 | 65.91 | 65.83 | 45.15 |
| PDI | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.3 | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Li, B. The Effects of Surfactant and Metal Ions on the Stability and Rheological Properties of Nanoemulsions Loaded with Gardenia Yellow Pigment. Appl. Nano 2023, 4, 61-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano4020005
Gao L, Li B. The Effects of Surfactant and Metal Ions on the Stability and Rheological Properties of Nanoemulsions Loaded with Gardenia Yellow Pigment. Applied Nano. 2023; 4(2):61-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano4020005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Li, and Bin Li. 2023. "The Effects of Surfactant and Metal Ions on the Stability and Rheological Properties of Nanoemulsions Loaded with Gardenia Yellow Pigment" Applied Nano 4, no. 2: 61-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano4020005
APA StyleGao, L., & Li, B. (2023). The Effects of Surfactant and Metal Ions on the Stability and Rheological Properties of Nanoemulsions Loaded with Gardenia Yellow Pigment. Applied Nano, 4(2), 61-74. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano4020005