Design of ZnO-Drug Nanocarriers against the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): An In Silico Assay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Binding and Adsorption Energies
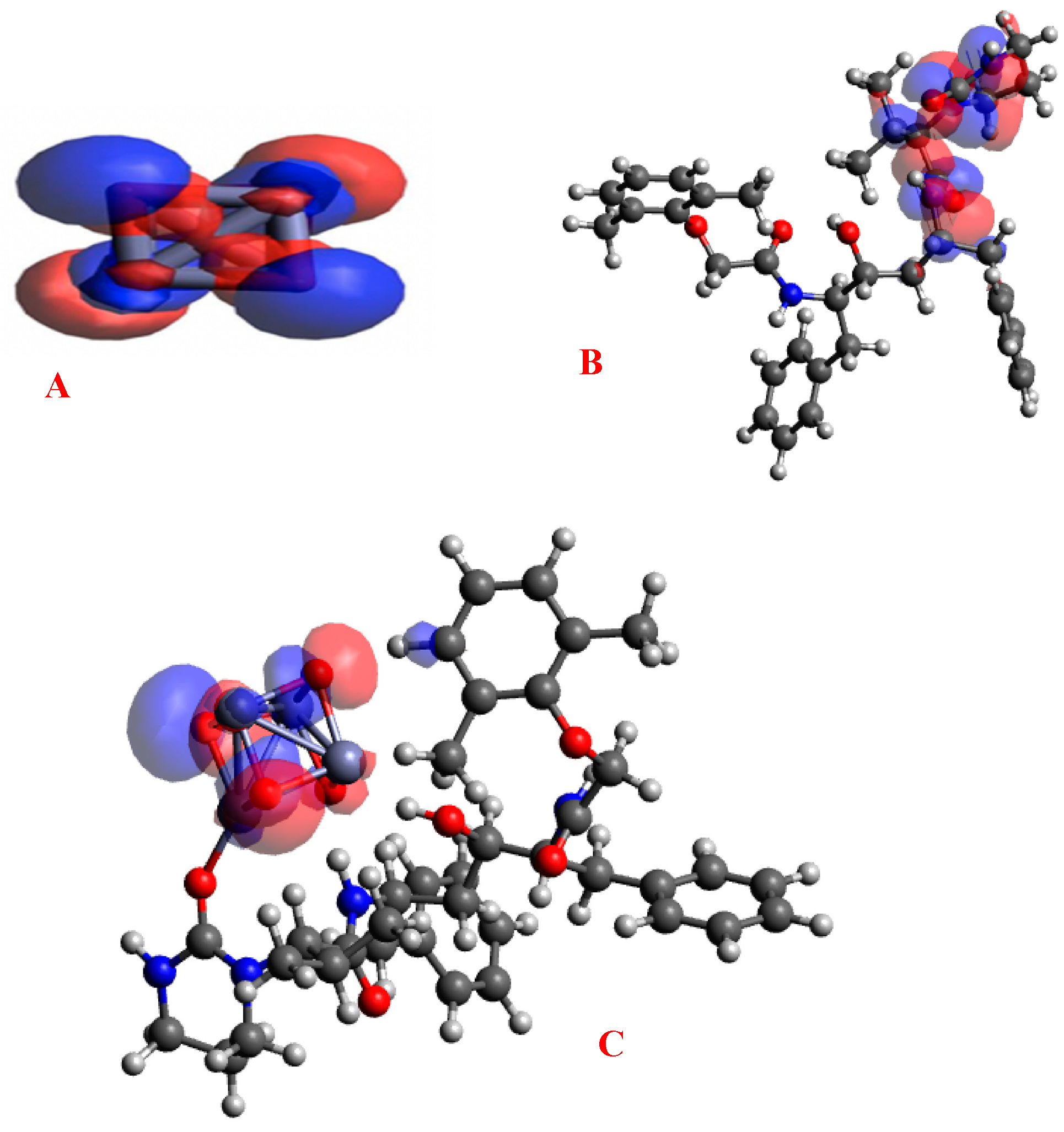
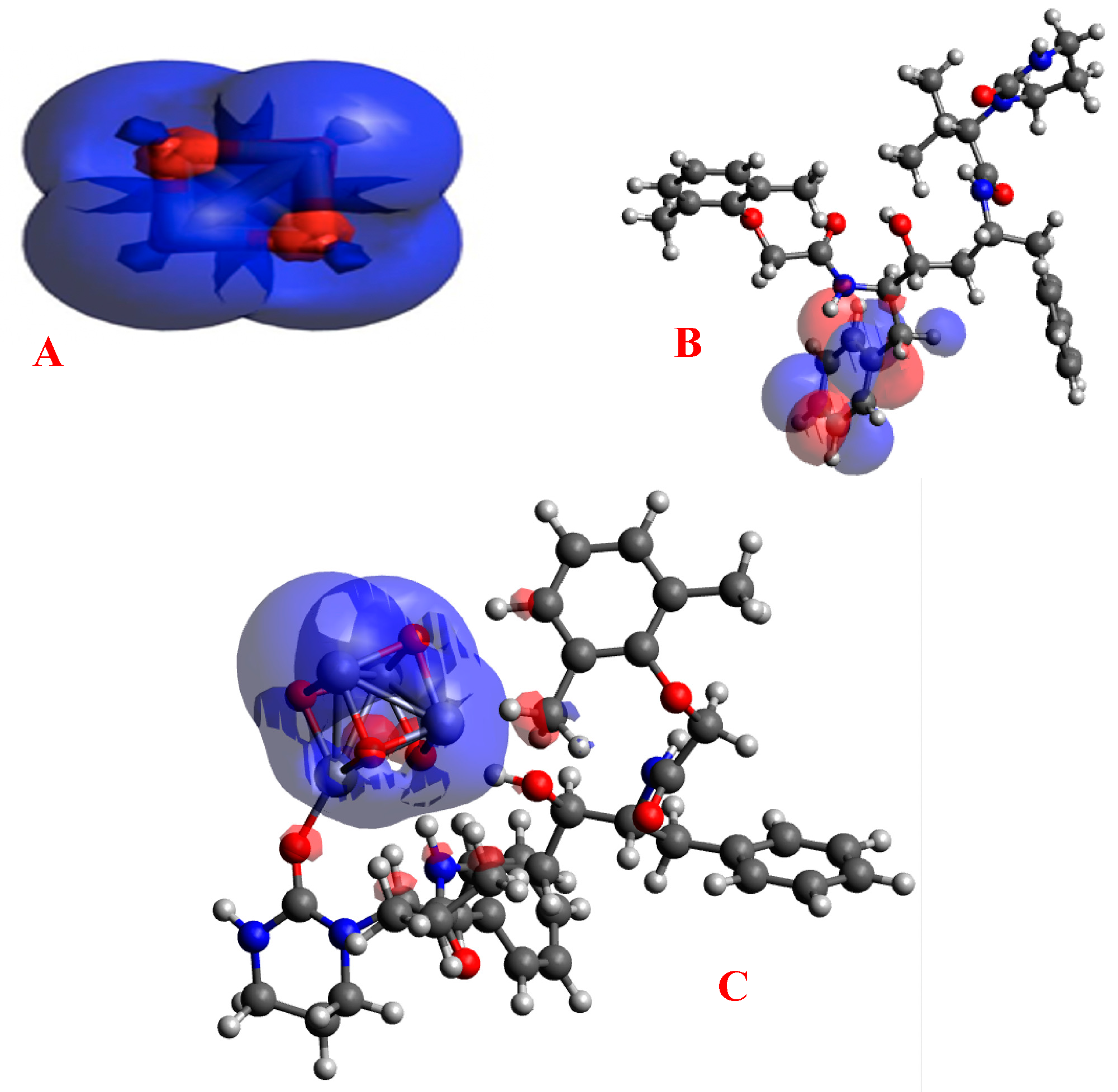
3.2. Gap Energies and Molecular Orbital Analysis
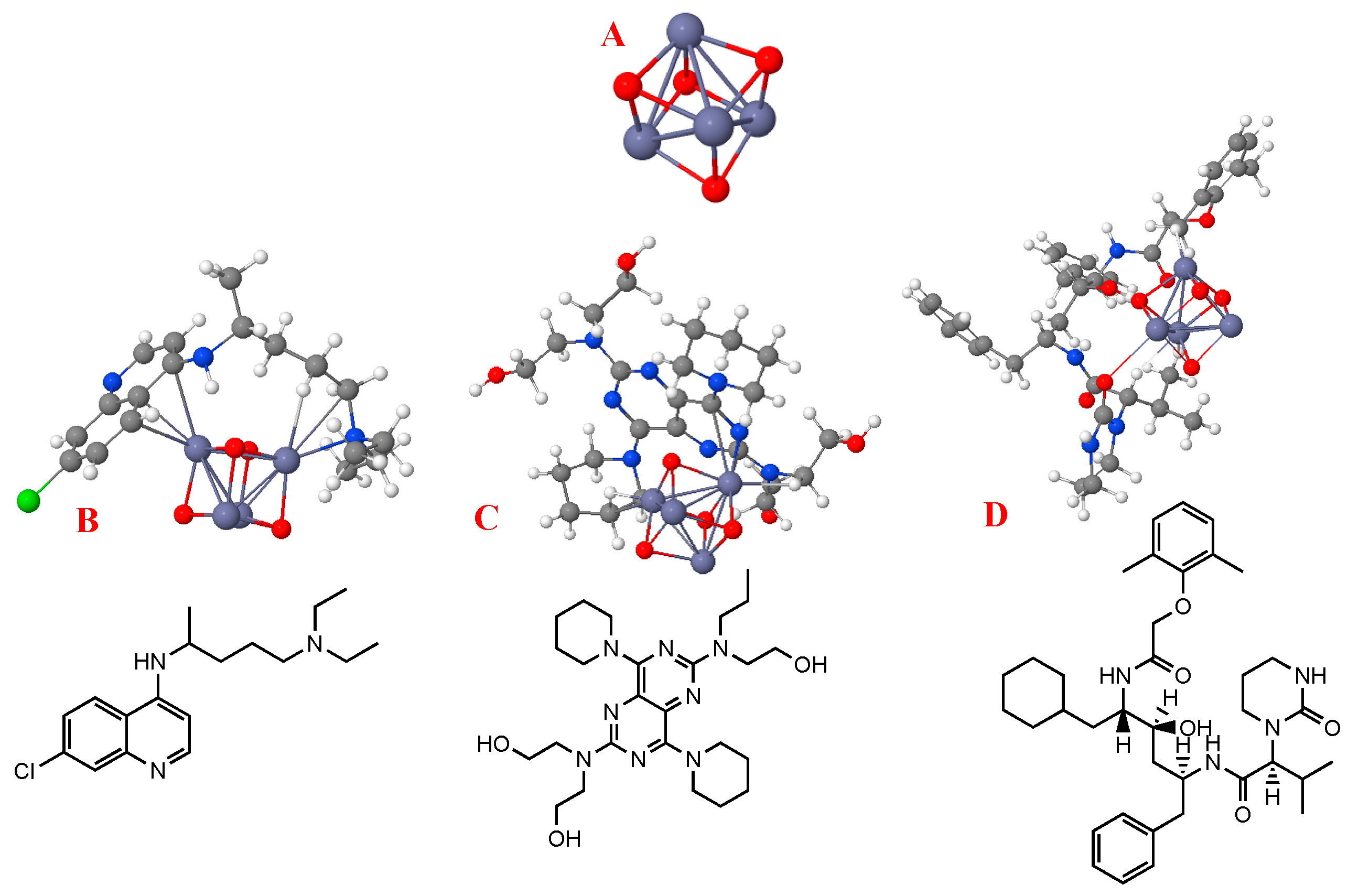
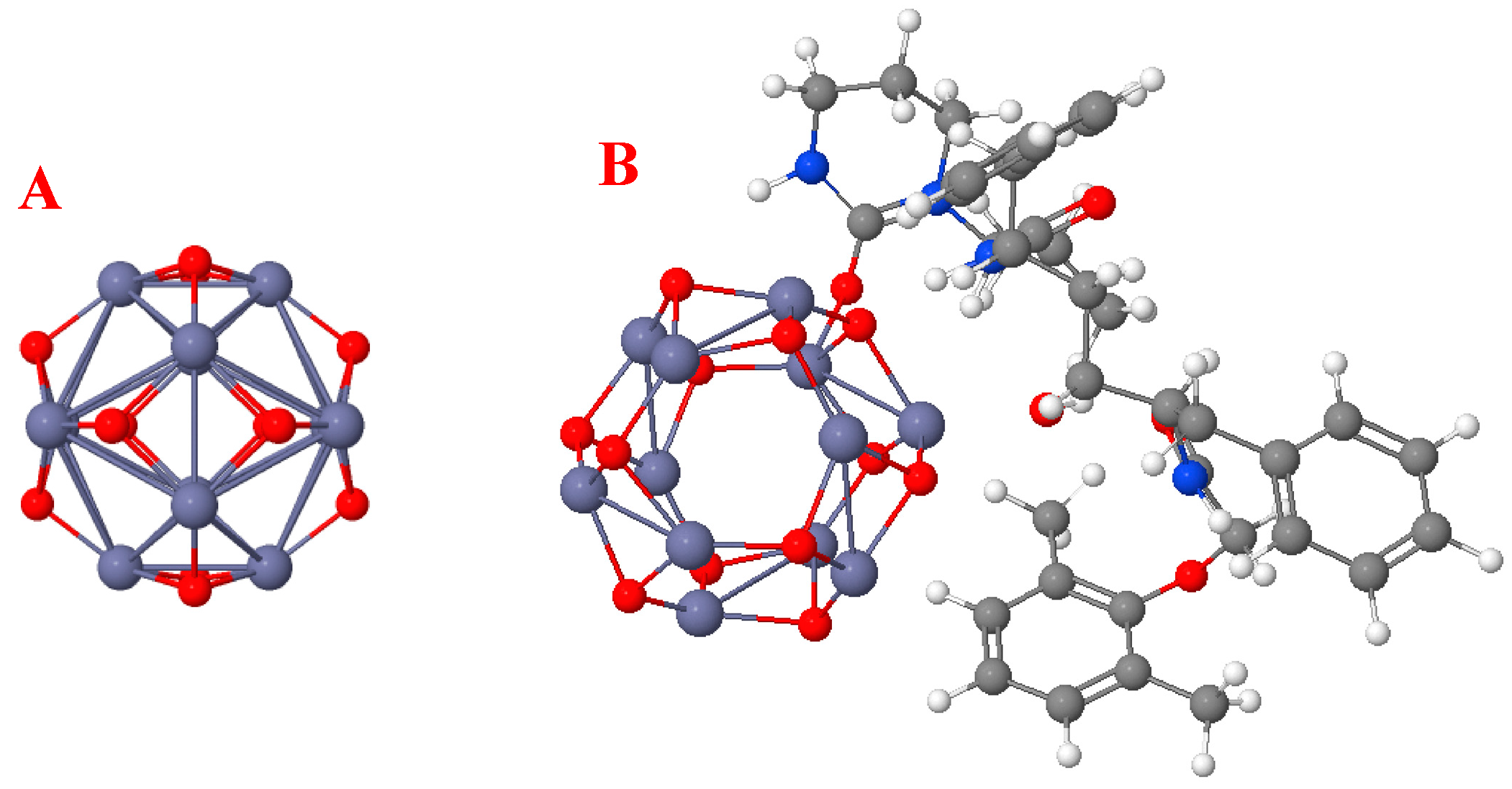
3.3. Effect of ZnO-NP (Geometric) Structure on Adsorption
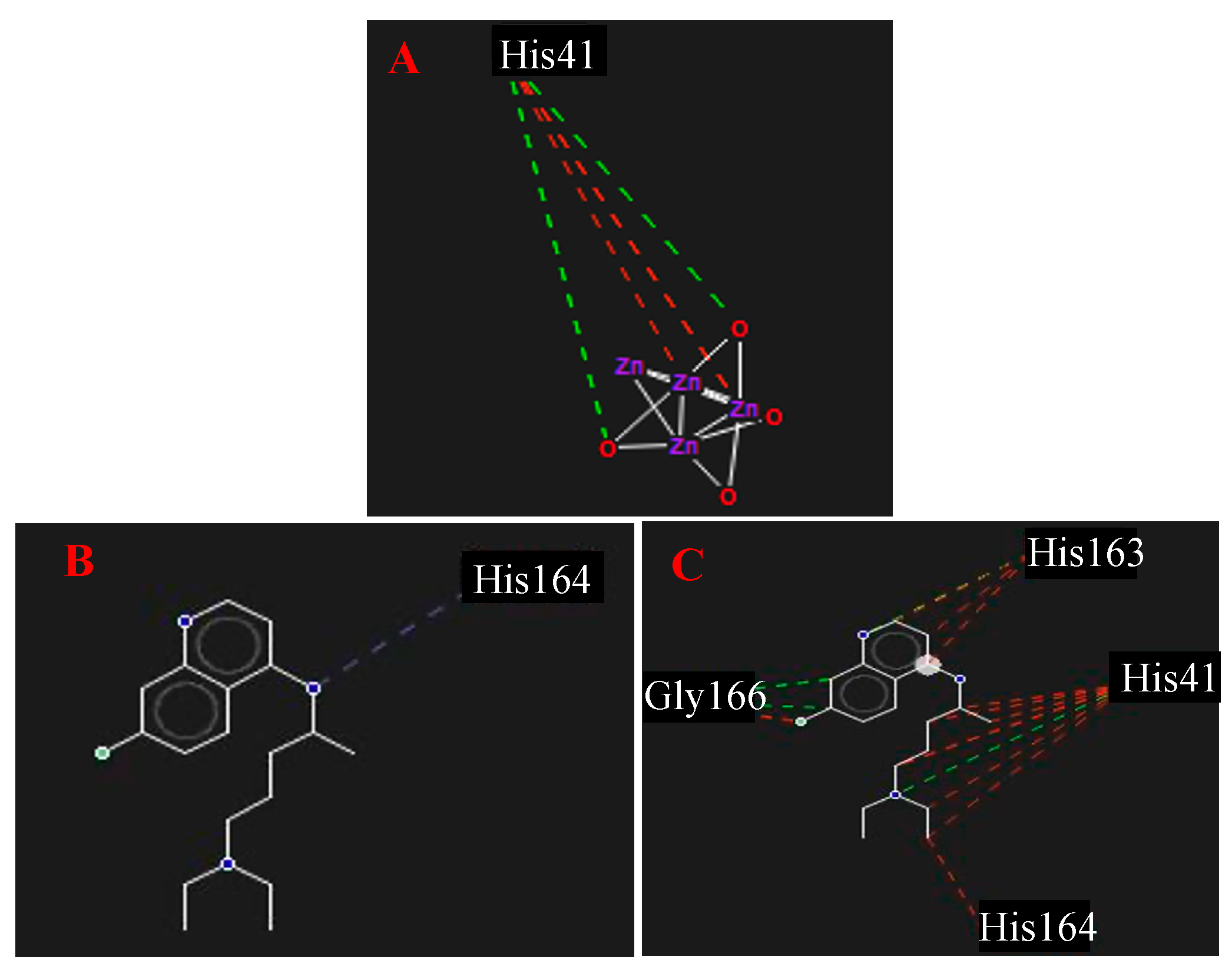
3.4. Molecular Docking Assay
4. Discussion
4.1. Binding and Adsorption Energies
4.2. Gap Energies and Molecular Orbital Analysis
4.3. Effect of ZnO-NP (Geometric) Structure on Adsorption
4.4. Molecular Docking Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Hernigou, J.; Valcarenghi, J.; Safar, A.; Ferchichi, M.A.; Chahidi, E.; Jennart, H.; Hernigou, P. Post-COVID-19 return to elective orthopaedic surgery—is rescheduling just a reboot process? Which timing for tests? Is chest CT scan still useful? Safety of the first hundred elective cases? How to explain the “new normality health organization” to patien. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, P.; Hajj, A.; Badro, D.A.; Acouselwan, C.; Aoun, R.; Sacre, H. Mental Health Outcomes of the COVID-19 Pandemic and a Collapsing Economy: Perspectives from a Developing Country. Psichiatr. Res. 2020, 294, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-García, C.J.; Chacón-García, L.; Mejía-Benavides, J.E.; Díaz-Cervantes, E. Tackling the SARS-CoV-2 main protease using hybrid derivatives of 1,5-disubstituted tetrazole-1,2,3-triazoles: An in silico assay. PeerJ 2020, 2, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ramírez, V.; Suarez-Castro, A.; Villa-Lopez, M.; Díaz-Cervantes, E.; Chacón-García, L.; Cortes-García, C. Synthesis of Novel Acylhydrazone-Oxazole Hybrids and Docking Studies of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Chem. Proc. 2021, 3, 8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathaneni, V.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Drug repurposing: A promising tool to accelerate the drug discovery process. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Modi, P.; Sagar, S.R. In silico Studies on Therapeutic Agents for COVID-19: Drug Repurposing Approach. Life Sci. 2020, 252, 117652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeel, M.; Al-Nazawi, M. Virtual screening and repurposing of FDA approved drugs against COVID-19 main protease. Life Sci. 2020, 251, 117627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, P.R.; Saha, A.; Palermo, G. Molecular dynamics simulations revealed a promising immune target on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, proposing novel strategies for vaccine development. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpiana, P.T.; Tshibangu, D.S.; Kilembe, J.T.; Gbolo, B.Z.; Mwanangombo, D.T.; Inkoto, C.L.; Lengbiye, E.M.; Mbadiko, C.M.; Matondo, A.; Bongo, G.N.; et al. Identification of potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease from Aloe vera compounds: A molecular docking study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 754, 137751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, M.; Chen, C.Z.; Guo, H.; Shen, M.; Hu, X.; Shinn, P.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Michael, S.G.; Zheng, W. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease Inhibitors by a Quantitative High-Throughput Screening. ACS Pharmacol. Trasnl. Sci. 2020, 3, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, A.-T.; Gentile, F.; Hsing, M.; Ban, F.; Cherkasov, A. Rapid Identification of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Deep Docking of 1.3 Billion Compounds. Mol. Inf. 2020, 39, 2000028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; et al. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 2020, 582, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Z. Potential covalent drugs targeting the main protease of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3295–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong-Thuy, B.T.; Ai-My, T.T.; Thanh-Hai, N.T.; Trung-Hieu, L.; Thai-Hoa, T.; Phuong-Loan, H.T.; Thanh-Triet, N.; Van-Anh, T.T.; Tu-Quy, P.; Van-Tat, P.; et al. Investigation into SARS-CoV-2 Resistance of Compounds in Garlic Essential Oil. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8312–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaraz-Girón, M.; Calderón-Jaimes, E.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; Díaz-Cervantes, E.; Castañón-Alonso, E.; Islas-Jácome, A.; Domínguez-Ortiz, A.; Castañón-Alonso, S. Search for Non-Protein Protease Inhibitors Constituted with an Indole and Acetylene Core. Molecules 2021, 26, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hu, J.; Bian, C.; Zhu, C.; Chen, C.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Agyekum, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, X. pH-Responsive and Biodegradable ZnO-Capped Mesoporous Silica Composite Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Materials 2020, 13, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayevska, N.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Florczak, P.; Jarek, M.; Janiszewska, E.; Woźniak, A.; Jurgaa, S. ZnO:Tb3+ hierarchical structures as carriers for drug delivery application. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 822, 153623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Joyce, E.; Beddow, J.; Mason, T. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of zno nanoparticles coated sonochemically onto textile fabrics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2012, 2021, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffari, H.; Tavakoli, A.; Moradi, A.; Tabarraei, A.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Zahmatkeshan, M.; Farahmand, M.; Javanmard, D.; Kiani, S.; Esghaei, M.; et al. Inhibition of H1N1 influenza virus infection by zinc oxide nanoparticles: Another emerging application of nanomedicine. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, A.; Ataei-Pirkooh, A.; MM Sadeghi, G.; Bokharaei-Salim, F.; Sahrapour, P.; Kiani, S.; Moghoofei, M.; Farahmand, M.; Javanmard, D.; Monavari, S. Polyethylene glycol-coated zinc oxide nanoparticle: An efficient nanoweapon to fight against herpes simplex virus type 1. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 2675–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y. A DFT investigation on ZnO clusters and nanostructures. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 894, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.; Curtis, D.; Lonie, D.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J Cheminformatics 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Wallingford CT. 2009. Available online: https://gaussian.com/ (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other function. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2006, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Schultz, N.E.; Truhlar, D.G. Design of density functionals by combining the method of constraint satisfaction with parametrization for thermochemistry, ther-mochemical kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Pople, J.A.; Binkley, J.S. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods 25. Supplementary functions for Gaussian basis sets. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, T., Jr.; Hay, P.J. Modern Theoretical Chemistry; Schaefer, H., III, Ed.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, J.M.; Artacho, E.; Gale, J.D.; García, A.; Junquera, J.; Ordejón, P.; Sánchez-Portal, D. The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J. Phys. Cond. Matt. 2002, 14, 2745–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Chen, C. Gemdock: A generic evolutionary method for molecular docking. Proteins 2004, 55, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Molecule | Eads | Eb | Eb/atom * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clq | - | 217.182 | 4.525 |
| Lop | - | 442.528 | 4.708 |
| Dip | - | 337.413 | 4.440 |
| (ZnO)4 | - | 20.691 | 2.586 |
| (ZnO)4-Clq | 1.531 | 239.405 | 4.275 |
| (ZnO)4-Lop | 2.084 | 465.304 | 4.562 |
| (ZnO)4-Dip | 0.582 | 358.686 | 4.270 |
| Molecule | GapHOMO-LUMO |
|---|---|
| Clq | 3.230 |
| Lop | 4.099 |
| Dip | 2.498 |
| (ZnO)4-NP | 2.531 |
| (ZnO)4-Clq | 2.638 |
| (ZnO)4-Lop | 2.497 |
| (ZnO)4-Dip | 2.206 |
| Molecule | E | LE | H-Bond | VdW | Electro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ZnO)4 | −2.121 | −0.265 | 0.000 | −0.317 | −0.038 |
| Clq | −5.787 | −0.263 | −0.001 | −1.711 | 0.012 |
| Lop | −8.199 | −0.178 | −0.182 | −1.447 | −0.004 |
| Dip | −8.306 | −0.231 | −0.337 | 0.866 | −0.047 |
| (ZnO)4-Clq | −6.635 | −0.221 | −0.067 | −1.481 | 0.052 |
| (ZnO)4-Lop | −8.242 | −0.153 | −0.153 | −0.143 | 0.054 |
| (ZnO)4-Dip | −8.751 | −0.199 | −0.231 | −2.592 | 0.050 |
| Co-crystal | −9.184 | −0.219 | −0.363 | −2.364 | −0.026 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Cervantes, E.; Zenteno-Zúñiga, C.; Rodríguez-González, V.; Aguilera-Granja, F. Design of ZnO-Drug Nanocarriers against the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): An In Silico Assay. Appl. Nano 2021, 2, 257-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano2030018
Díaz-Cervantes E, Zenteno-Zúñiga C, Rodríguez-González V, Aguilera-Granja F. Design of ZnO-Drug Nanocarriers against the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): An In Silico Assay. Applied Nano. 2021; 2(3):257-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano2030018
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Cervantes, Erik, Cristal Zenteno-Zúñiga, Vicente Rodríguez-González, and Faustino Aguilera-Granja. 2021. "Design of ZnO-Drug Nanocarriers against the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): An In Silico Assay" Applied Nano 2, no. 3: 257-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano2030018
APA StyleDíaz-Cervantes, E., Zenteno-Zúñiga, C., Rodríguez-González, V., & Aguilera-Granja, F. (2021). Design of ZnO-Drug Nanocarriers against the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): An In Silico Assay. Applied Nano, 2(3), 257-266. https://doi.org/10.3390/applnano2030018






