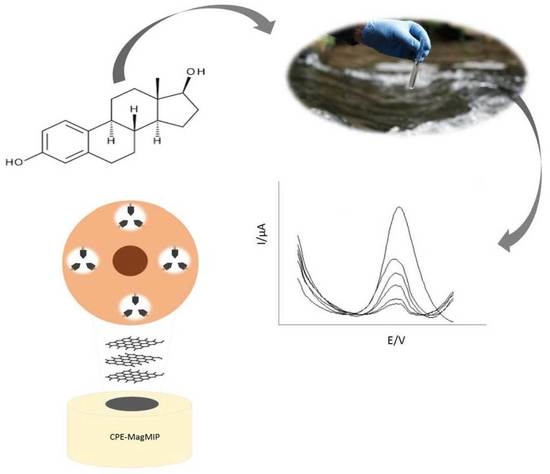
Development of a Chemically Modified Electrode with Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MagMIP) for 17-β-Estradiol Determination in Water Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. MagMIP Synthesis
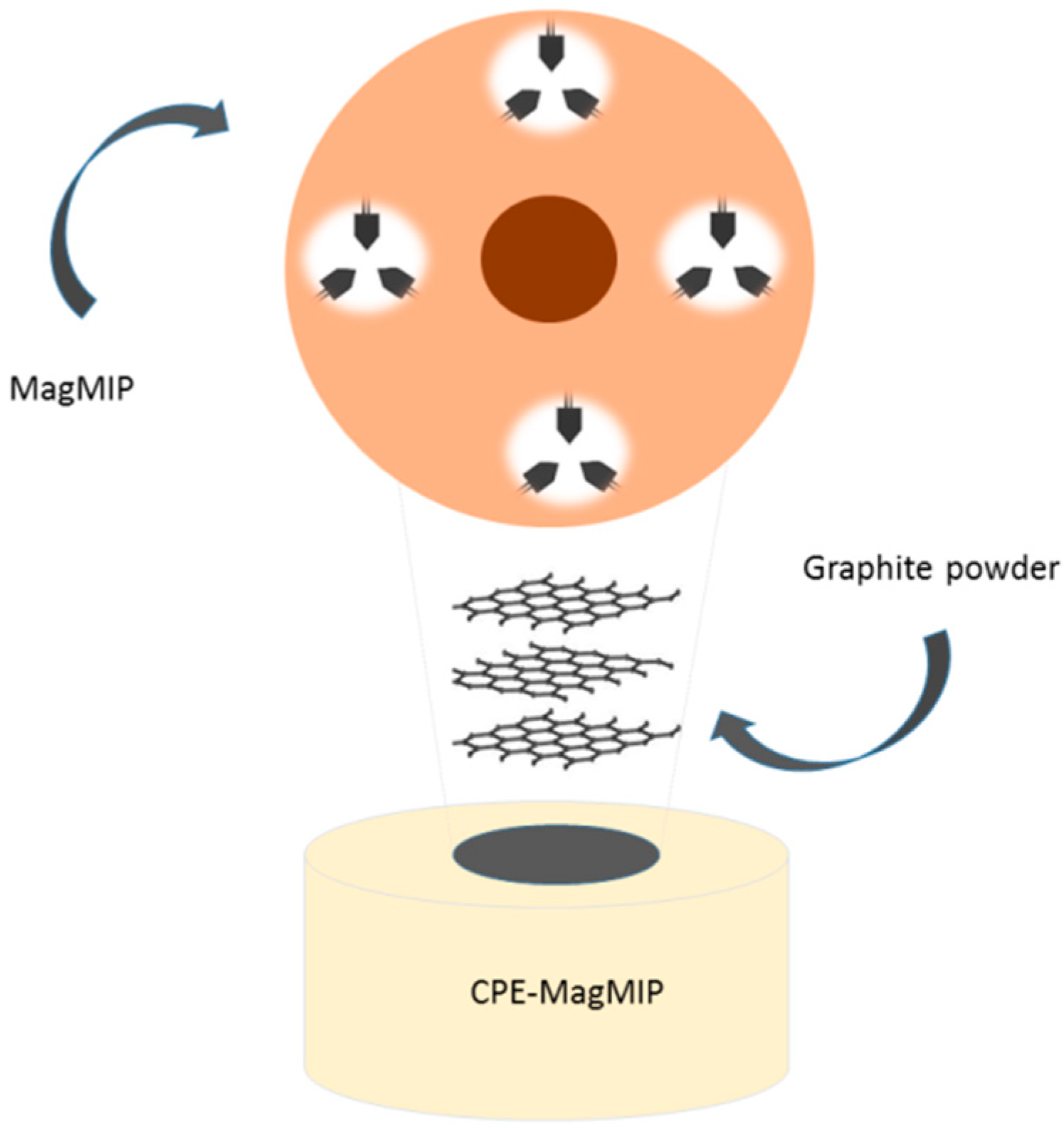
2.3. Preparation of CPE-MagMIP
2.4. Apparatus
2.5. Experimental Parameters Optimization
2.6. Application in Water Samples
3. Results
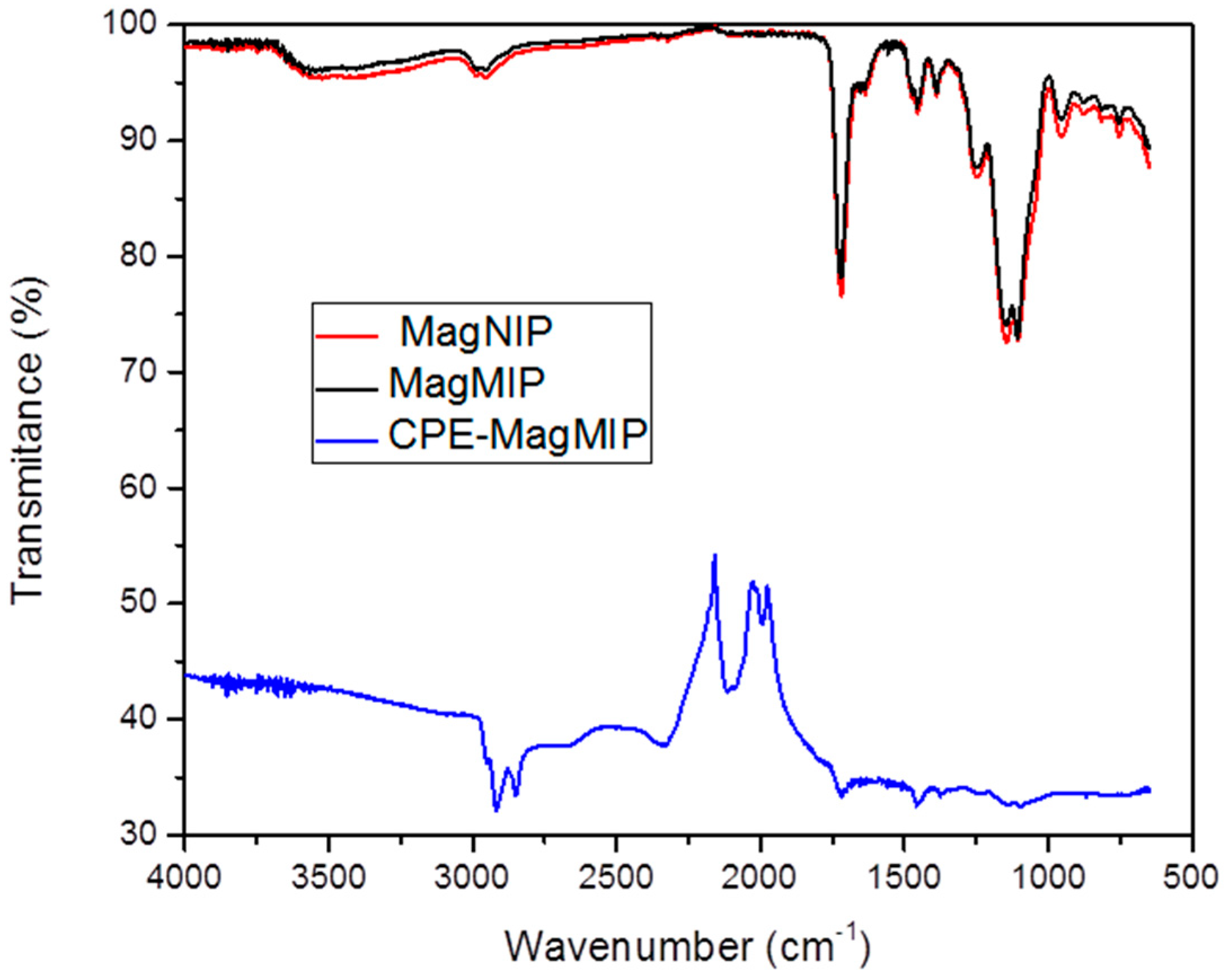
3.1. FT-IR Characterization
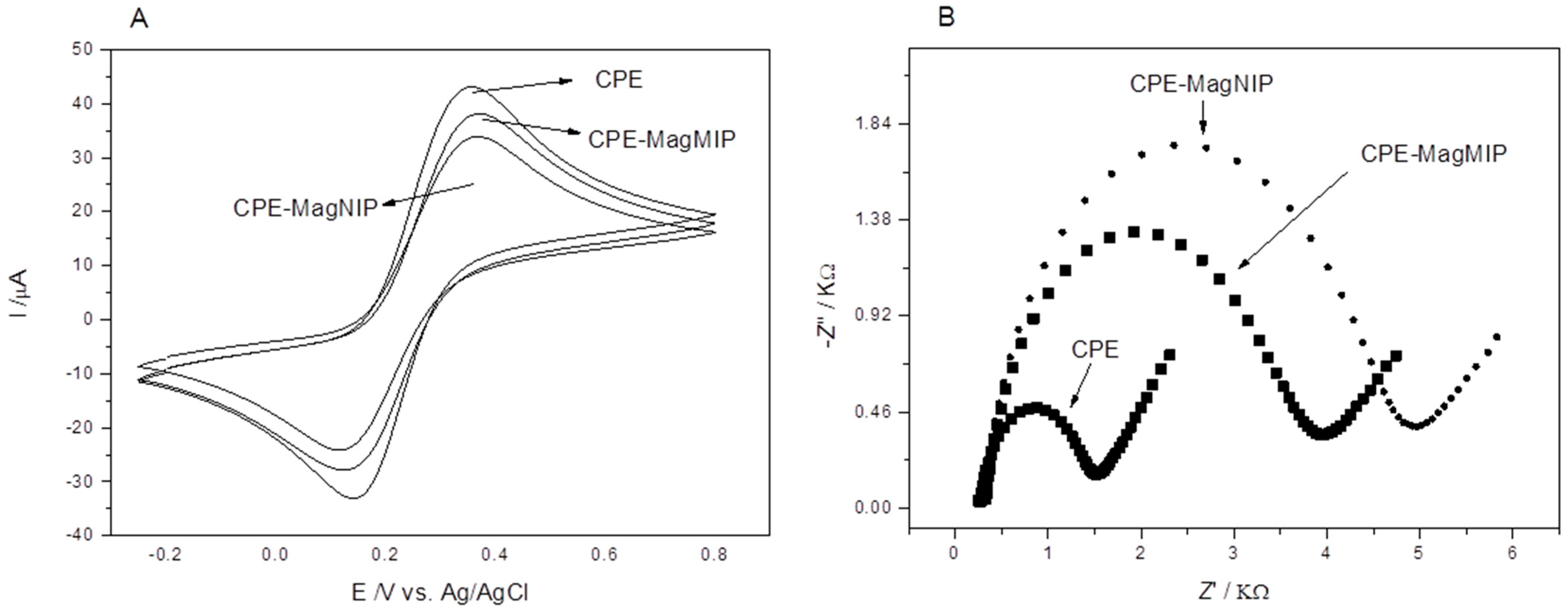
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
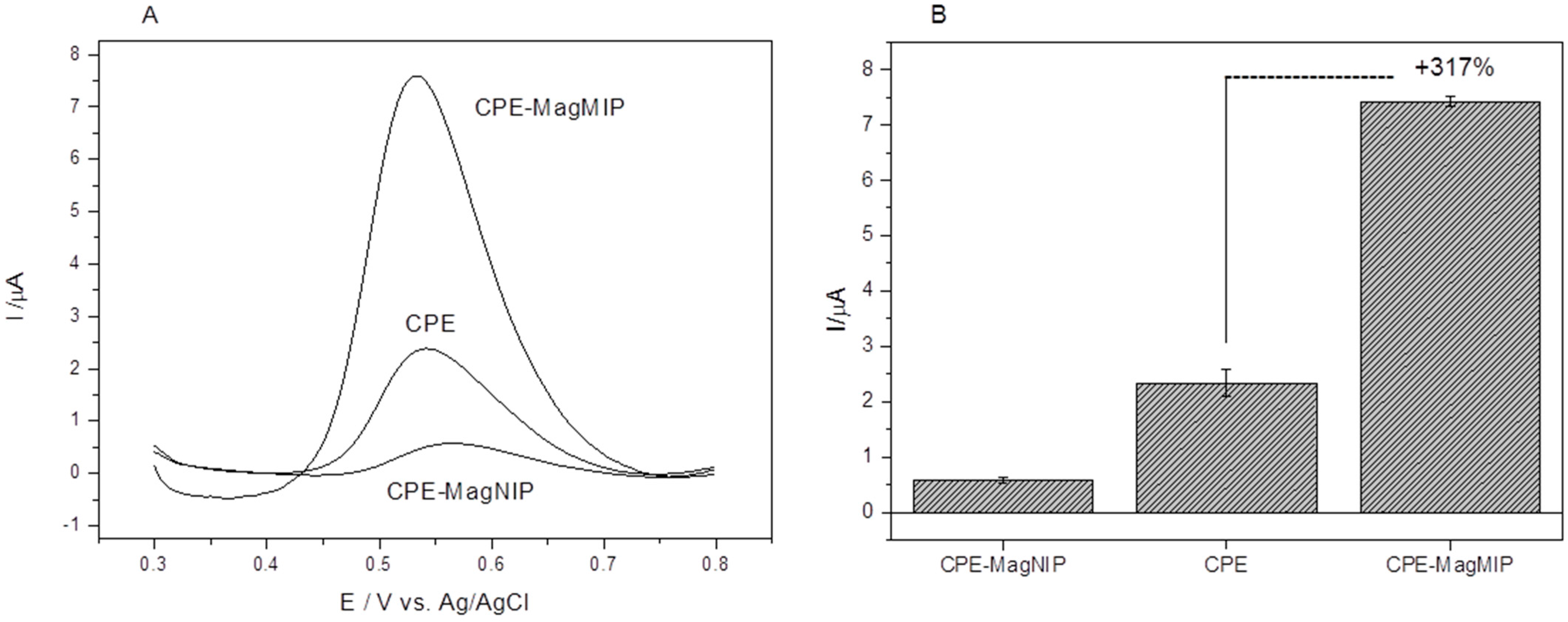
3.3. Modification Influence (MagMIP)
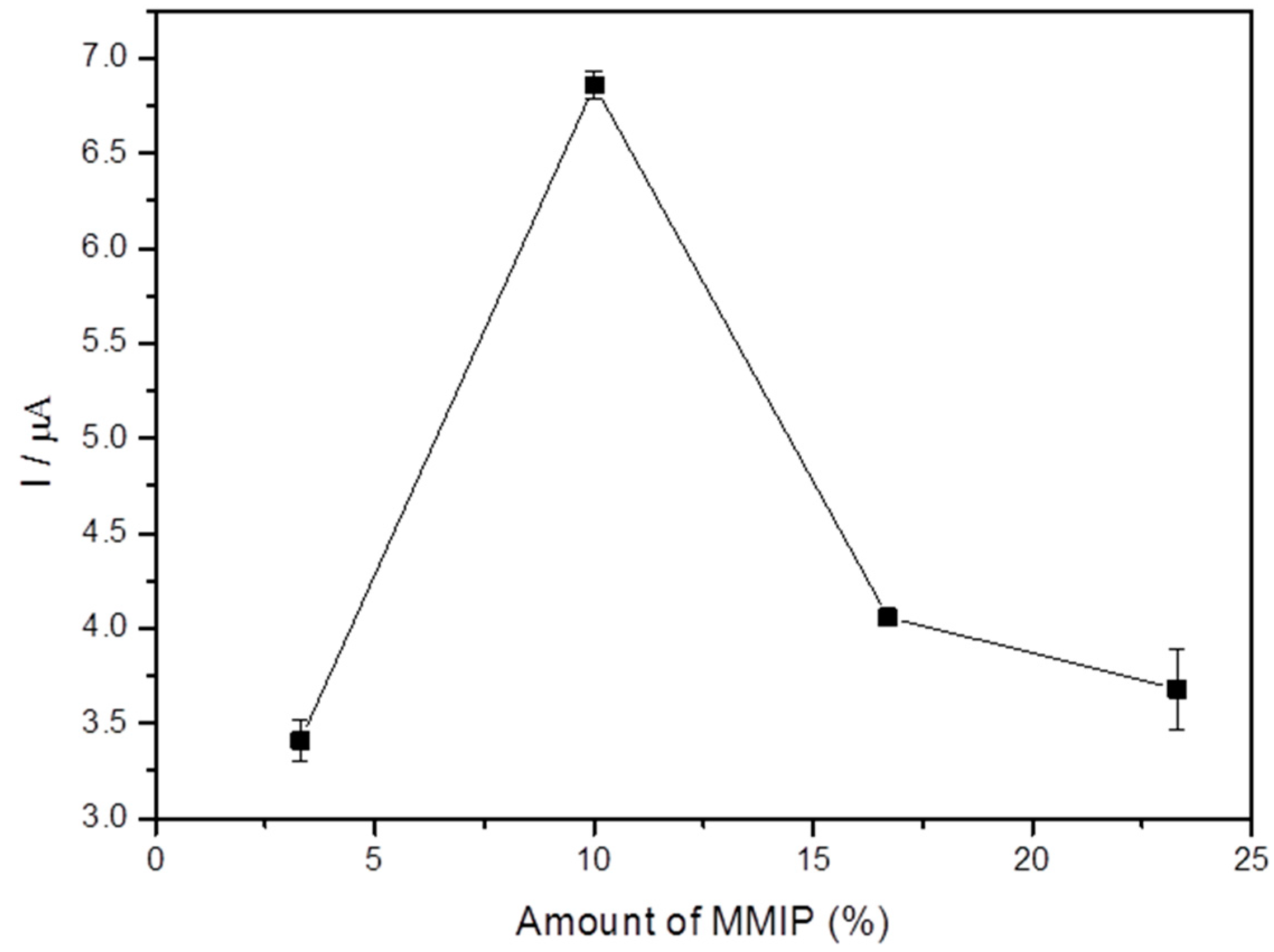
3.4. Influence of the Amount of MagMIP
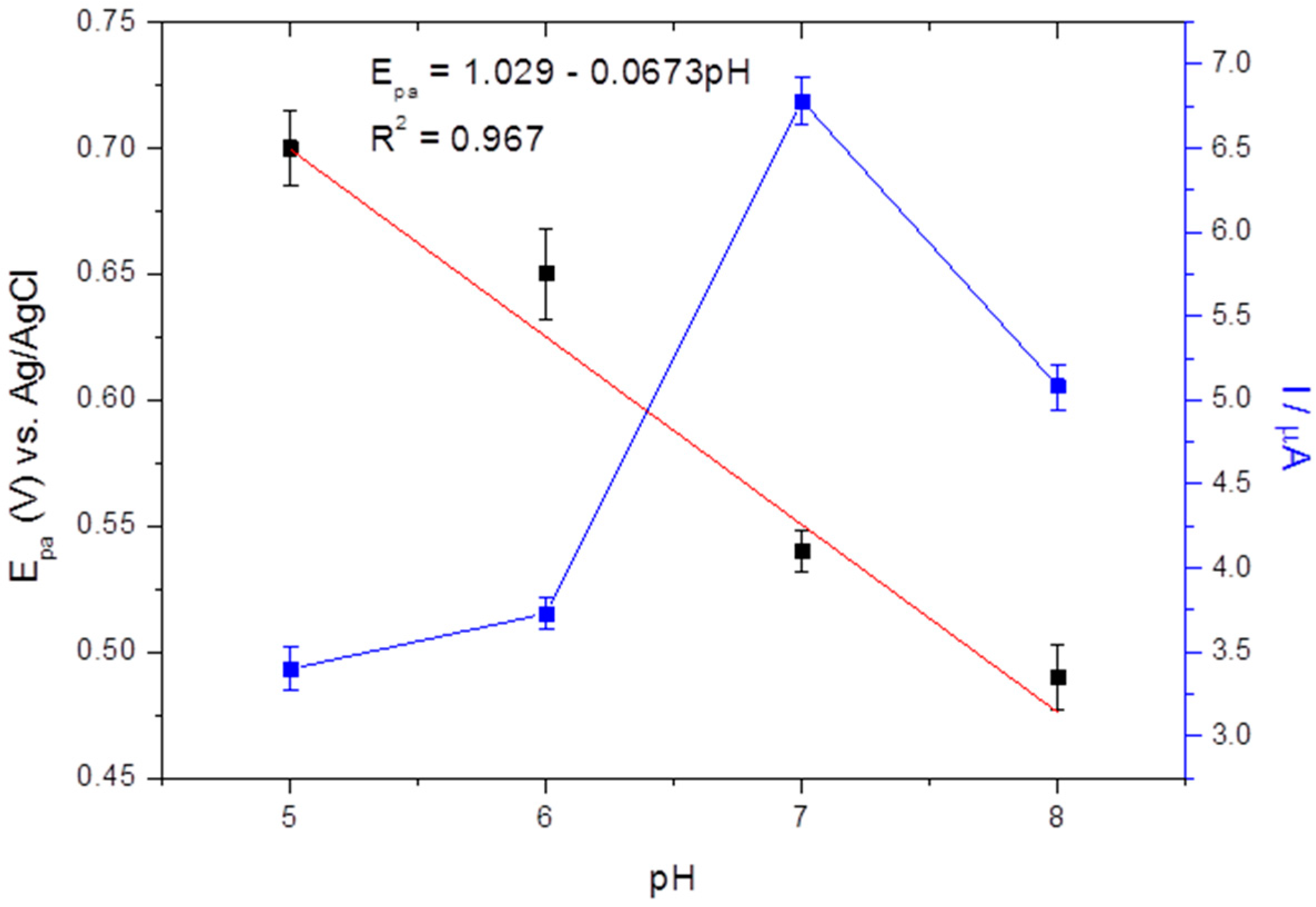
3.5. Influence of pH
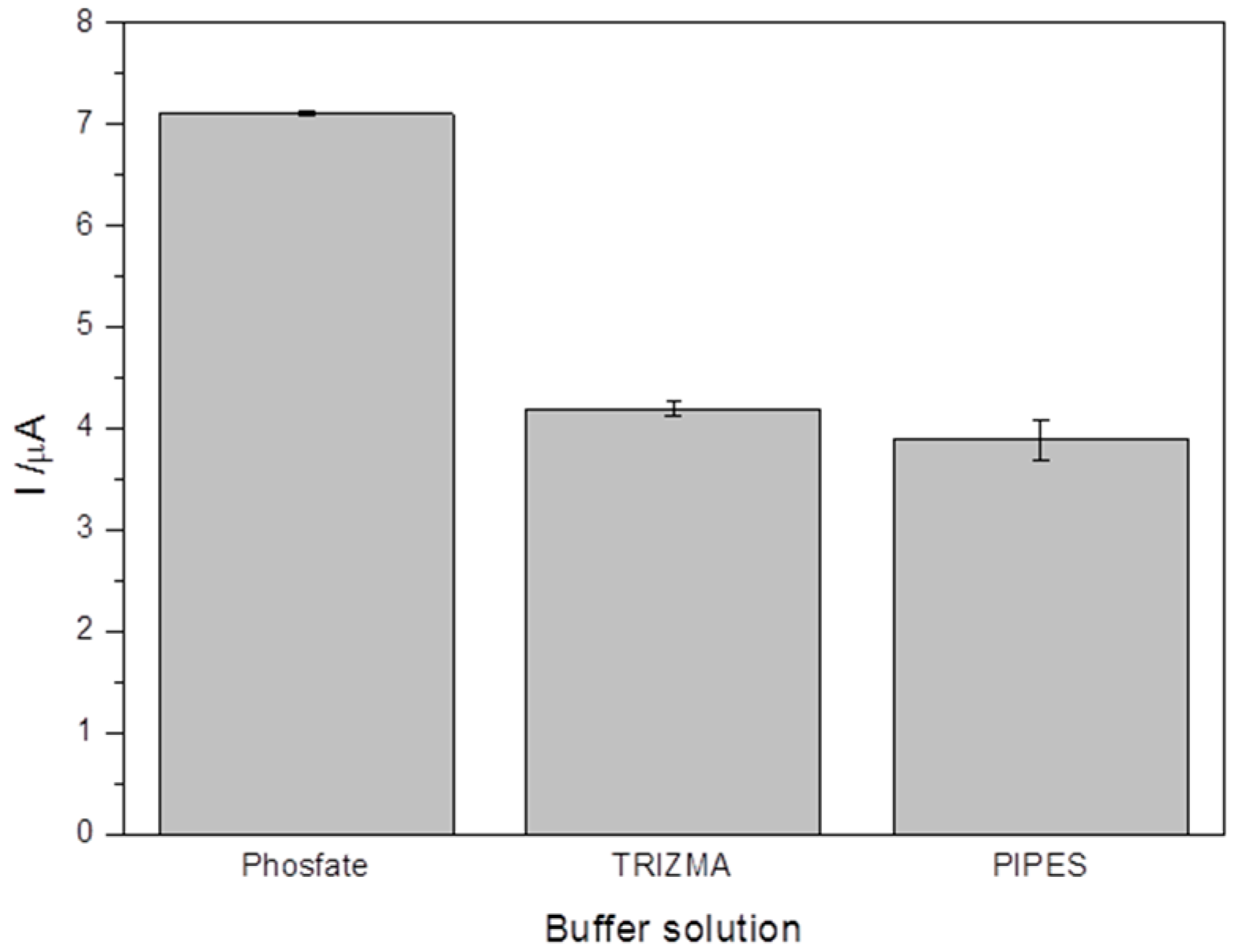
3.6. Influence of Buffer Solution
3.7. The Effects of Interferences
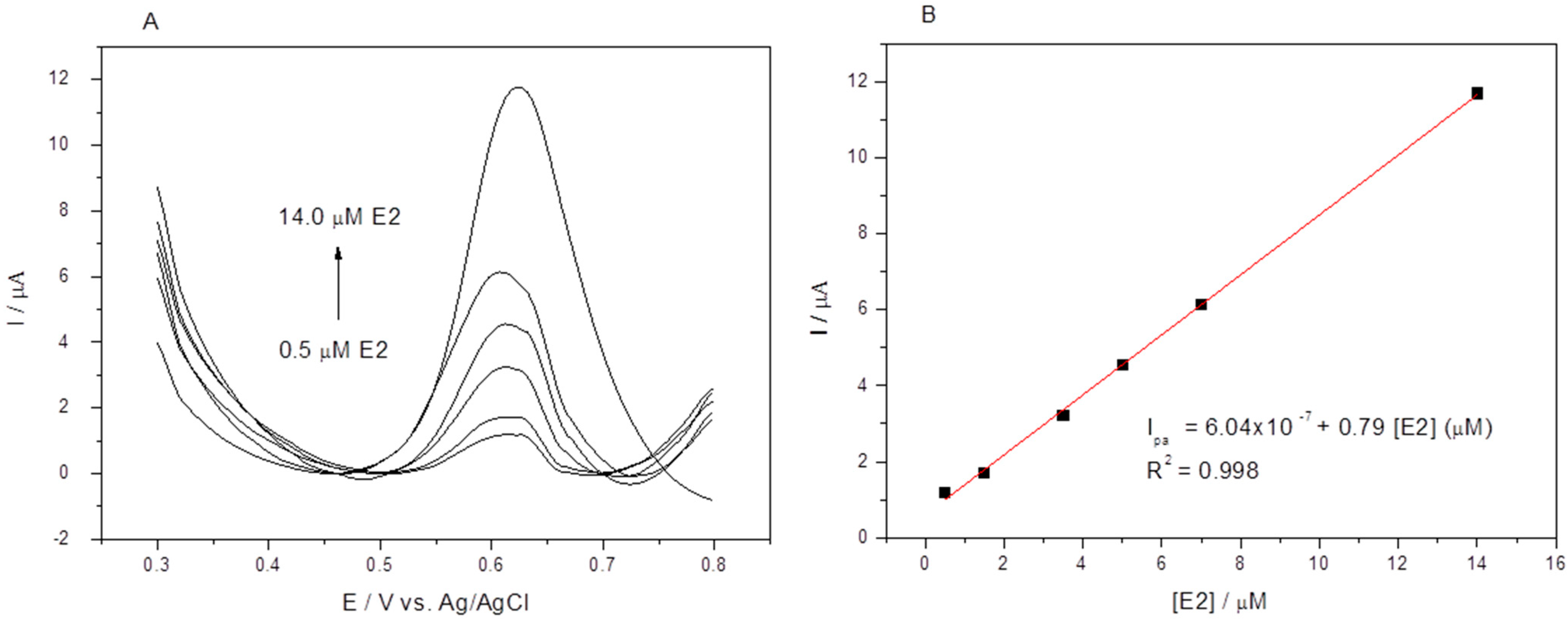
3.8. Analytical Curve
| Technique/Electrode | Linear Range (μM) | LOD (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSV/CDs-PANI/GCE a | 1.0–100 | 0.043 | [39] |
| SWV/GCE/MWCNTs-Pt b | 0.5–15 | 0.18 | [44] |
| DPV/BPIDS/GCE c | 0.1–10 | 0.05 | [45] |
| DPV/Pt/Pol/HRP/GCE d | 0.1–200 | 0.105 | [46] |
| DPV/CdMoO4/CNS/SPCE e | 0.05–24 | 0.003 | [47] |
| DPAdSV/CPE-MagMIP | 0.5–14.0 | 0.13 | This work |
3.9. Determination of E2 in Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gandhi, A.; Matta, M.K.; Stewart, S.; Chockalingam, A.; Knapton, A.; Rouse, R.; Wu, W.; Patel, V. Quantitative analysis of underivatized 17 β-estradiol using a high-throughput LC–MS/MS assay—Application to support a pharmacokinetic study in ovariectomized guinea pigs. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smajdor, J.; Piech, R.; Ławrywianiec, M.; Paczosa-Bator, B. Glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon black for sensitive estradiol determination by means of voltammetry and flow injection analysis with amperometric detection. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 544, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, B.; Kadioglu, Y. Determination of 17 β-estradiol in pharmaceutical preparation by UV spectrophotometry and high performance liquid chromatography methods. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1422–S1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Baleg, A.A.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E.; Amine, A. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of nanostructured magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for 17-β-Estradiol determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Hemmati, S. Analytical methodology for the electro-catalytic determination of estradiol and progesterone based on graphene quantum dots and poly(sulfosalicylic acid) co-modified electrode. Talanta 2017, 174, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.; Fukushima, K.; Miwa, A. Combined use of surfactant-induced coagulation of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) with peroxidase-mediated degradation for the rapid removal of estrogens and phenolic compounds from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, Q.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Qian, L.; Shao, S.; Gao, S. The promotion effect of phenolic acid compound on the photo-removal of estrogen from water under simulated sunlight irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 123999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-W.; Yeh, F.-L.; Shieh, B.-S.; Chen, C.-M.; Lai, H.-T.; Wang, S.-Y.; Huang, D.-J. Development and assays estradiol equivalent concentration from prawn (p-EEQ) in river prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense, in Taiwan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeury, K.; Munoz, G.; Duy, S.V.; Prévost, M.; Sauvé, S. Occurrence and seasonal distribution of steroid hormones and bisphenol A in surface waters and suspended sediments of Quebec, Canada. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, G.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Fanali, S.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Determination of estrogenic compounds in milk and yogurt samples by hollow-fibre liquid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7447–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Ling, J.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Y. Rapid detection of 17β-estradiol based on shaddock peel derived fluorescent aptasensor for forensic examination. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 331, 111153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, P.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. A fluorescence aptasensor based on carbon quantum dots and magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of 17β-estradiol. Food Chem. 2022, 373 Pt B, 131591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Yan, B. Design of a ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on metal organic frameworks and Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica composites for 17β-Estradiol detection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 583, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, D.; Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Deng, P.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Qian, D.; Xie, H. Facile synthesis of Pd/N-doped reduced graphene oxide via a moderate wet-chemical route for non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of estradiol. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 769, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Gomes, N.O.; Machado, S.A.S.; Oliveira, O.N. Simultaneous, ultrasensitive detection of hydroquinone, paracetamol and estradiol for quality control of tap water with a simple electrochemical method. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, M.; Luo, M.; Yu, N.; Xiong, H.; Peng, H. A nanowell-based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of 17β-estradiol in food samples. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Ding, Y.; Li, L.; Duan, D.; Mei, Q.; Zhuang, Q.; Cui, S.; He, X. A novel electrochemical enzyme biosensor for detection of 17β-estradiol by mediated electron-transfer system. Talanta 2018, 192, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, F.; Zhe, T.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical structure engineering of AuNPs/Co(OH)2 nanocomposite on carbon cloth: An advanced and efficient electrode for highly sensitive and specific determination of nitrite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 342, 130061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xia, D.; Xu, J.; Ye, C.; Zhang, D.; Deng, D.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G. Sequential injection-square wave voltammetric sensor for phosphate detection in freshwater using silanized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, A.; Frontana, C. Evaluation of a Carbon Ink Chemically Modified Electrode Incorporating a Copper-Neocuproine Complex for the Quantification of Antioxidants. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 313, 128070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.V.; Mello, L.S.; Dockal, E.R.; de Oliveira, M.F. Electrochemical determination of ethanol on carbon paste electrode chemically modified with [N,N′-cis-1,2-cyclohexylene bis (salicylideneaminate)] nickel(II) Schiff base complex. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wong, A.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Electrochemical sensors based on biomimetic magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective quantification of methyl green in environmental samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymers for electrochemical detection and analysis: Progress and perspectives. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12568–12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarley, C.R.T.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Kubota, L.T. Polímeros biomiméticos em química analítica. Parte 1: Preparo e aplicações de MIP (“Molecularly Imprinted Polymers”) em técnicas de extração e separação. Quím. Nova 2005, 28, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, D.; Shao, J.; Sun, X. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles based electrochemical sensor for the measurement of Gram-negative bacterial quorum signaling molecules (N-acyl-homoserine-lactones). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical sensors based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, Z.; Mohadesi, A.; Karimi, M.A.; Fathirad, F. A highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer magnetic nanocomposite for patulin determination. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, D.N.; de Oliveira, H.L.; Borges, K.B.; Pereira, A.C. Sensitive determination of 17β-estradiol using a Magneto Sensor Based on Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, C.J.; Botelho, M.J.C.; Sato, M.I.Z. (Eds.) Guia Nacional de Coleta e Preservação de Amostras: Água, Sedimento, Comunidades Aquáticas e Efluentes Líquidos; Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil; Agência Nacional de Águas: Brasília, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.C.F.; de Araújo, O.R.P.; Moura, F.A.; Khan, S.; Tanaka, A.A.; Santana, A.E.G.; Pividori, M.I.; Sotomayor, M.P.T.; Goulart, M.O.F. Development of magnetic nanoparticles modified with new molecularly imprinted polymer (MIPs) for selective analysis of glutathione. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadali, A.; Leili, M.; Afkhami, A.; Bahrami, A.; Karami, M. Synthesize and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (mag-MIPs) to extract 1-Aminopyrene from the human urine sample. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, H.L.; Pires, B.C.; Teixeira, L.S.; Dinali, L.A.F.; Simões, N.S.; de Souza, W.B.; Borges, K.B. Novel restricted access material combined to molecularly imprinted polymer for selective magnetic solid-phase extraction of estrogens from human urine. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, J.P.; Borges, K.B.; Tarley, C.R.T.; Ribeiro, E.S.; Pereira, A.C. Development and application of an electrochemical biosensor based on carbon paste and silica modified with niobium oxide, alumina and DNA (SiO2/Al2O3/Nb2O5/DNA) for amitriptyline determination. J. Electroanal. Chem 2013, 704, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Highly sensitive Fe3O4 nanobeads/graphene-based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for 17β-estradiol in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 884, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharif, H.F.; Patel, S.; Ndunda, E.N.; Reddy, S.M. Electrochemical detection of dioctyl phthalate using molecularly imprinted polymer modified screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1196, 339547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Santos, A.M.; Fava, E.L.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Voltammetric determination of 17β-estradiol in different matrices using a screen-printed sensor modified with CuPc, Printex 6L carbon and Nafion film. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, G.B.; Oliveira, A.E.F.; Pereira, A.C. Total Determination of Estrogenic Phenolic Compounds in River Water Using a Sensor Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide and Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Niu, L.; Li, G. Poly(3,6-diamino-9-ethylcarbazole) based molecularly imprinted polymer sensor for ultra-sensitive and selective detection of 17-β-estradiol in biological fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 104, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supchocksoonthorn, P.; Alvior Sinoy, M.C.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Paoprasert, P. Facile fabrication of 17β-estradiol electrochemical sensor using polyaniline/carbon dot-coated glassy carbon electrode with synergistically enhanced electrochemical stability. Talanta 2021, 235, 122782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoski, C.G. Handbook of Electrochemistry, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, A.; Topçuoğulları, D. Voltammetric determination of 17-β-estradiol by cysteamine self-assembled gold nanoparticle modified fumed silica decorated graphene nanoribbon nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 250, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Expert Working Group. ICH-harmonised Tripartite Guideline, validation of analytical procedures: Methodology, technical requirements for the registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization, Geneva, Switzerland, 30 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, N.H.; de Oliveira, G.S.S.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Eguiluz, K.I.B.; Salazar-Banda, G.R. Environmental aspects of hormones estriol, 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol: Electrochemical processes as next-generation technologies for their removal in water matrices. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, Y. A sensitive determination of estrogens with a Pt nano-clusters/multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Tu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, G.; Li, C. A novel electrochemical sensor for estradiol based on nanoporous polymeric film bearing poly{1-butyl-3-[3-(N-pyrrole)propyl]imidazole dodecyl sulfonate} moiety. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychalska, K.; Zając, D.; Cabaj, J. Electrochemical biosensor for detection of 17β-estradiol using semi-conducting polymer and horseradish peroxidase. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9079–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, R.; Alagumalai, K.; Chen, S.-M.; Ganesan, T. Electrochemical evaluation of organic pollutant estradiol in industrial effluents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Added Concentration (μM) | Detected Concentration (μM) ± RSD a | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ND b | - |
| 1.5 | 1.47 ± 0.08 | 98.3 |
| 5.0 | 4.84 ± 0.28 | 96.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, D.N.; Pereira, A.C. Development of a Chemically Modified Electrode with Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MagMIP) for 17-β-Estradiol Determination in Water Samples. Electrochem 2022, 3, 809-819. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem3040053
da Silva DN, Pereira AC. Development of a Chemically Modified Electrode with Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MagMIP) for 17-β-Estradiol Determination in Water Samples. Electrochem. 2022; 3(4):809-819. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem3040053
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Daniela Nunes, and Arnaldo César Pereira. 2022. "Development of a Chemically Modified Electrode with Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MagMIP) for 17-β-Estradiol Determination in Water Samples" Electrochem 3, no. 4: 809-819. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem3040053
APA Styleda Silva, D. N., & Pereira, A. C. (2022). Development of a Chemically Modified Electrode with Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MagMIP) for 17-β-Estradiol Determination in Water Samples. Electrochem, 3(4), 809-819. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem3040053