Optical Characterization of a Sensitive Lophine Layer for the Detection of Hydrogen Ions (H+)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Liquid Phase
2.3. Solid Phase (Film)
2.4. Manufacturing of Fiber Optic Sensor
3. Results
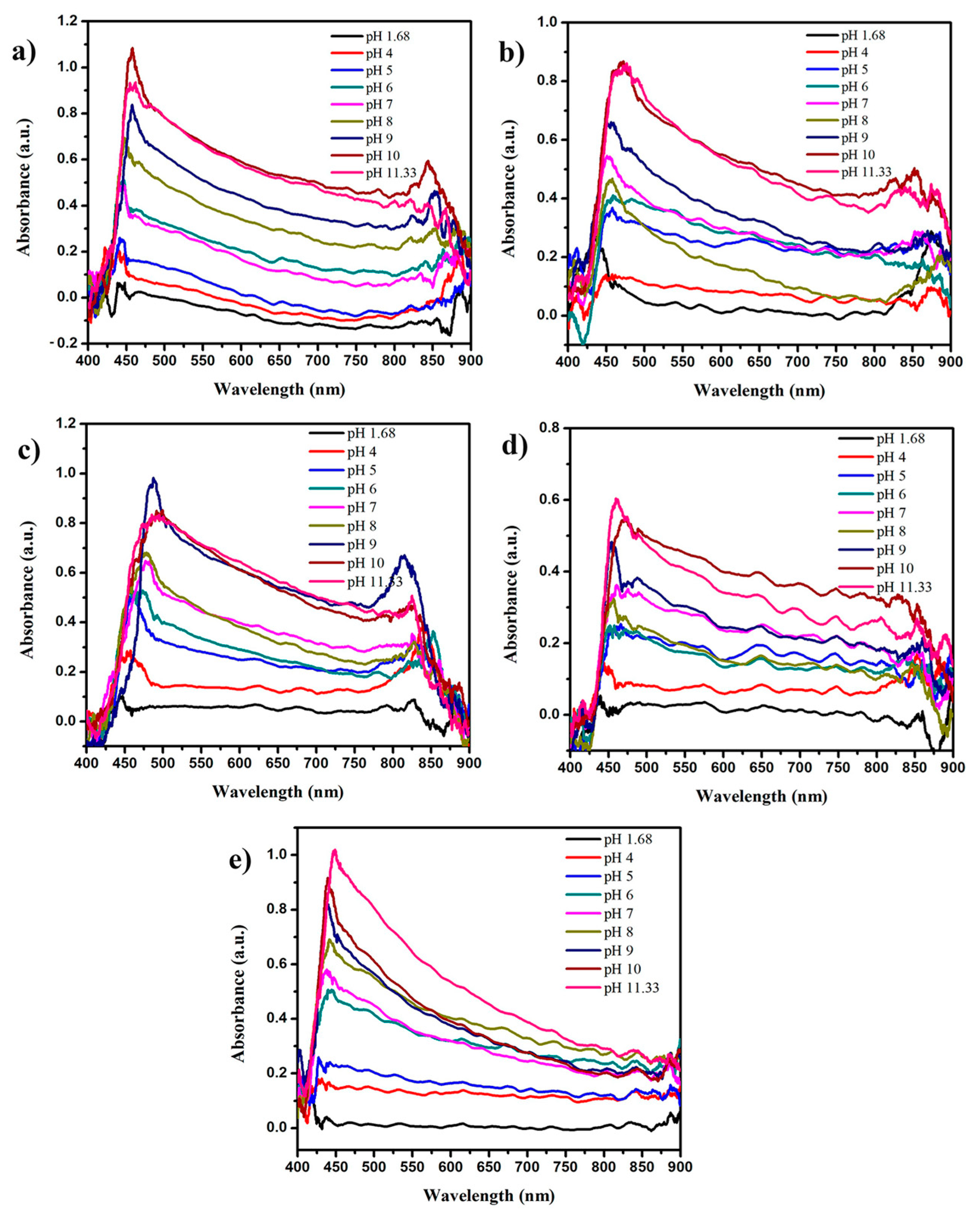
3.1. Spectroscopic Characterization Results
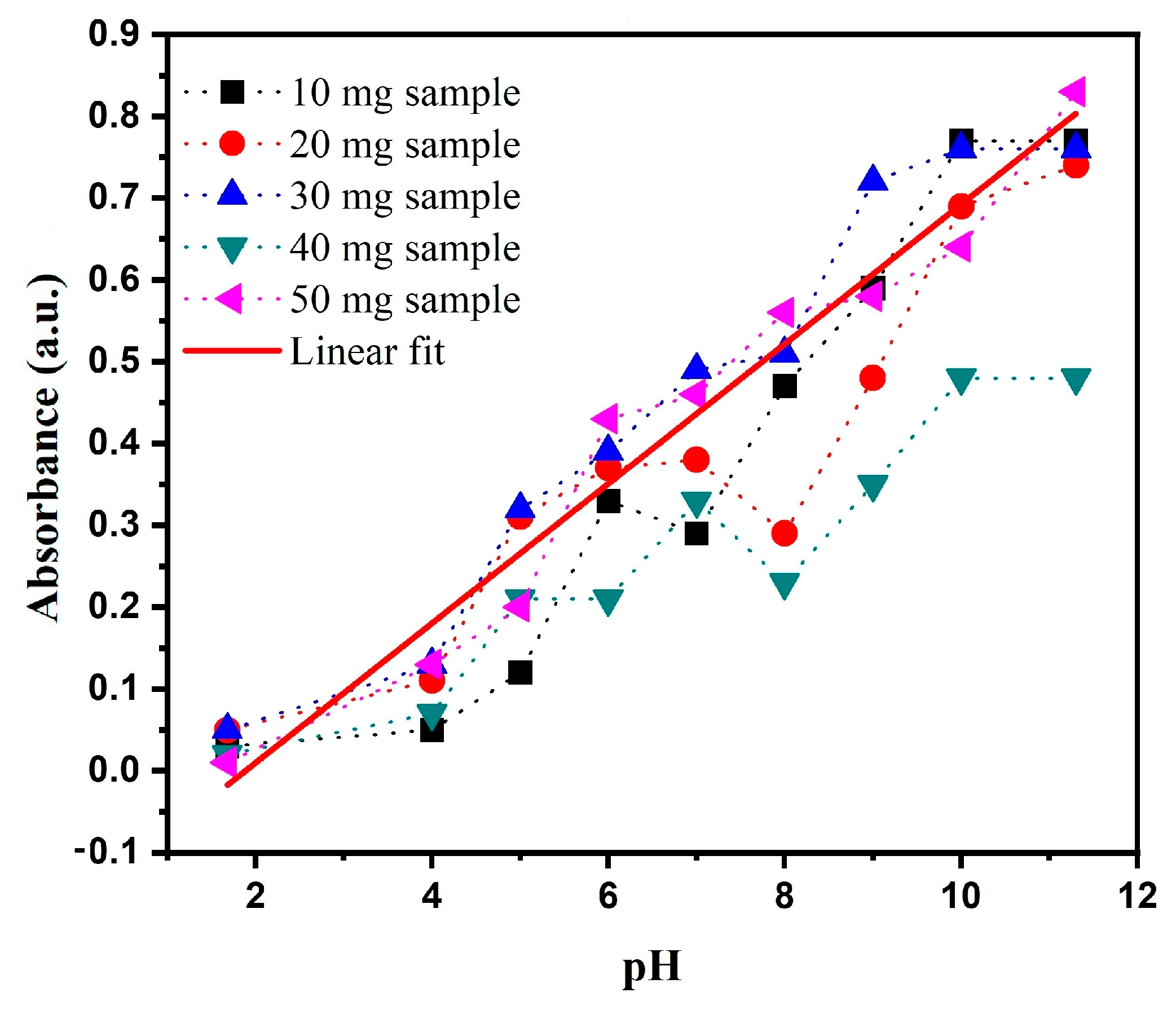
3.2. Characterization of the Material on Optical Fiber
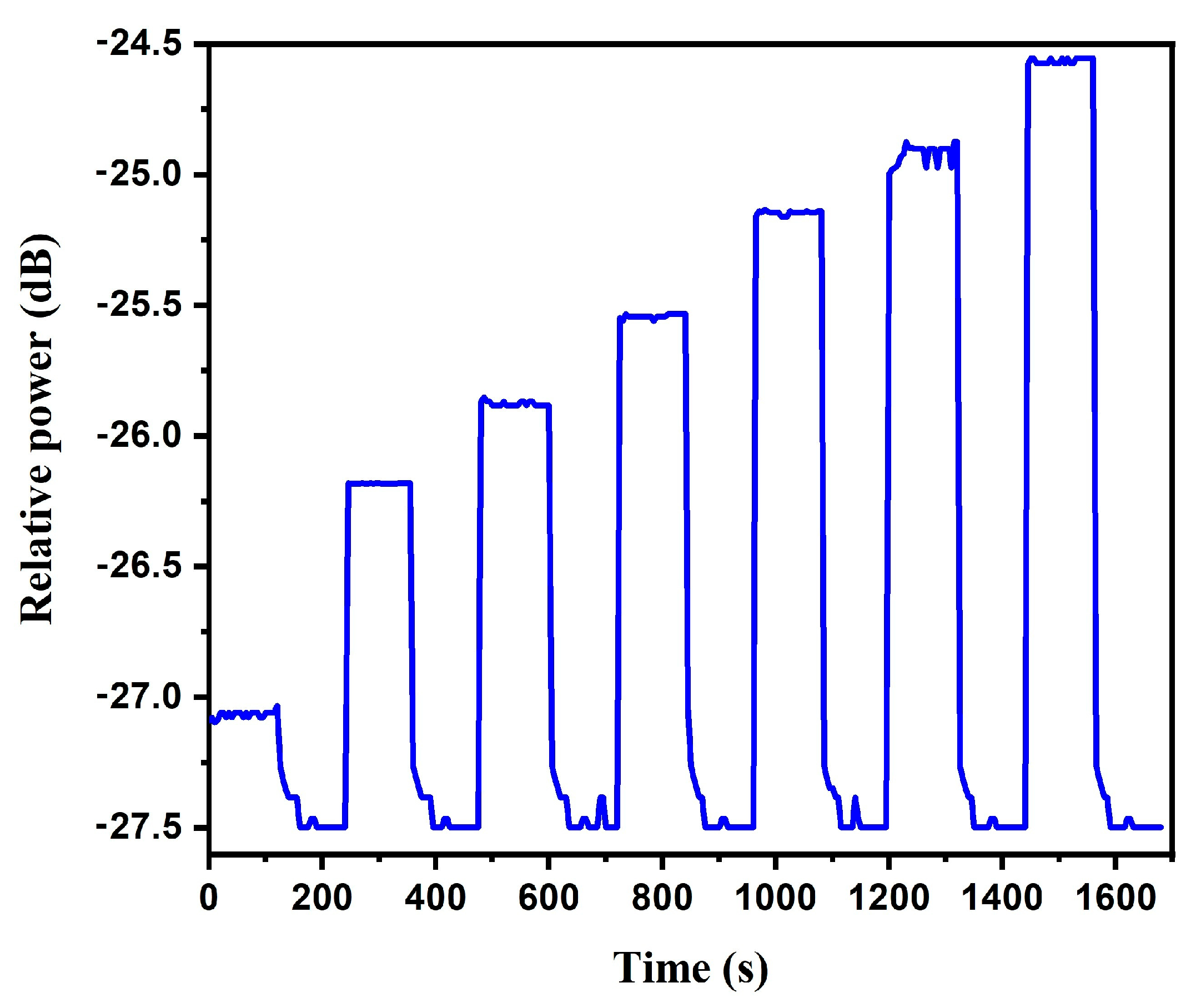
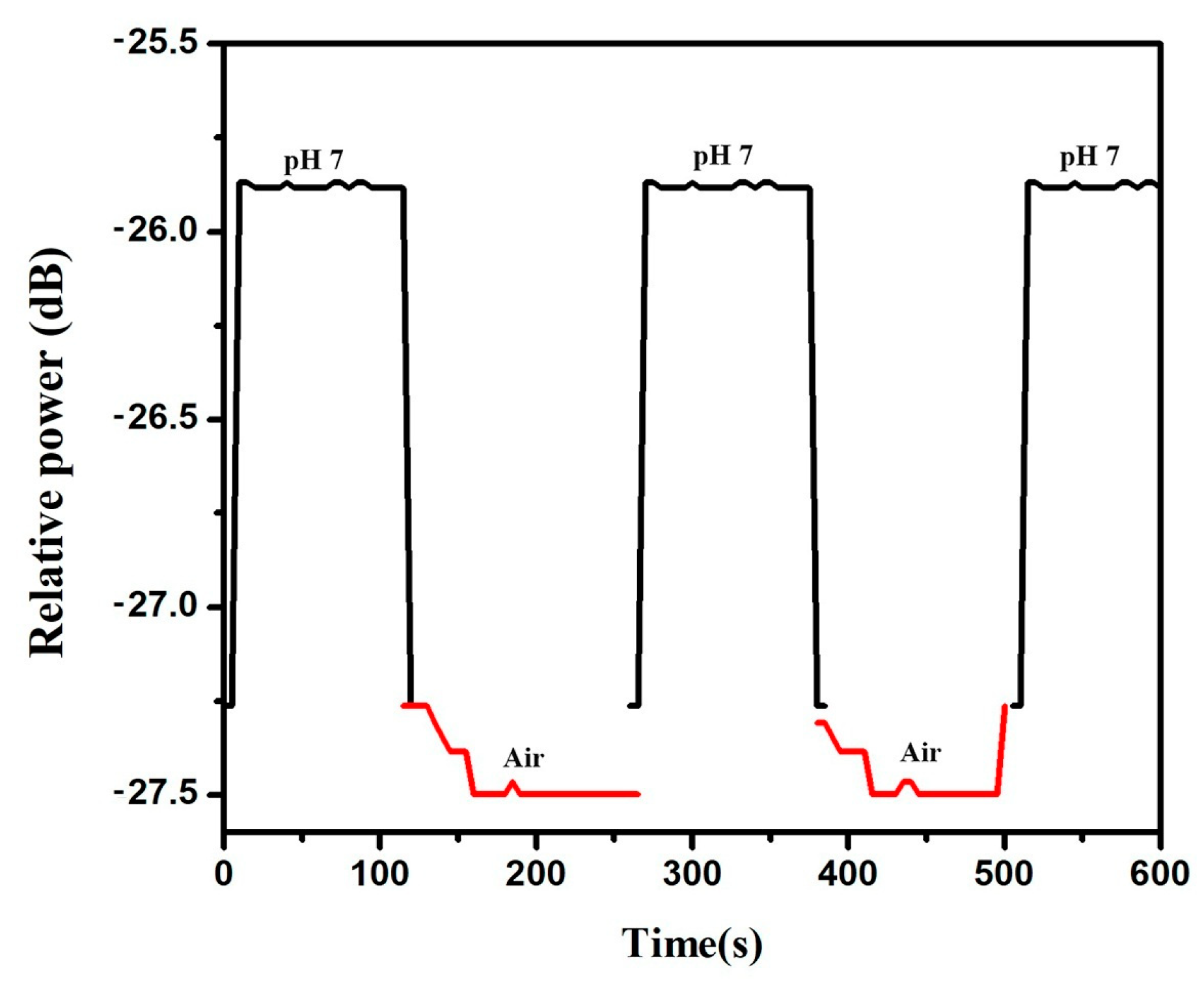
3.3. Power Characterization as a Function of pH
3.4. Fiber Optic Sensor Sensitivity and Repeatability
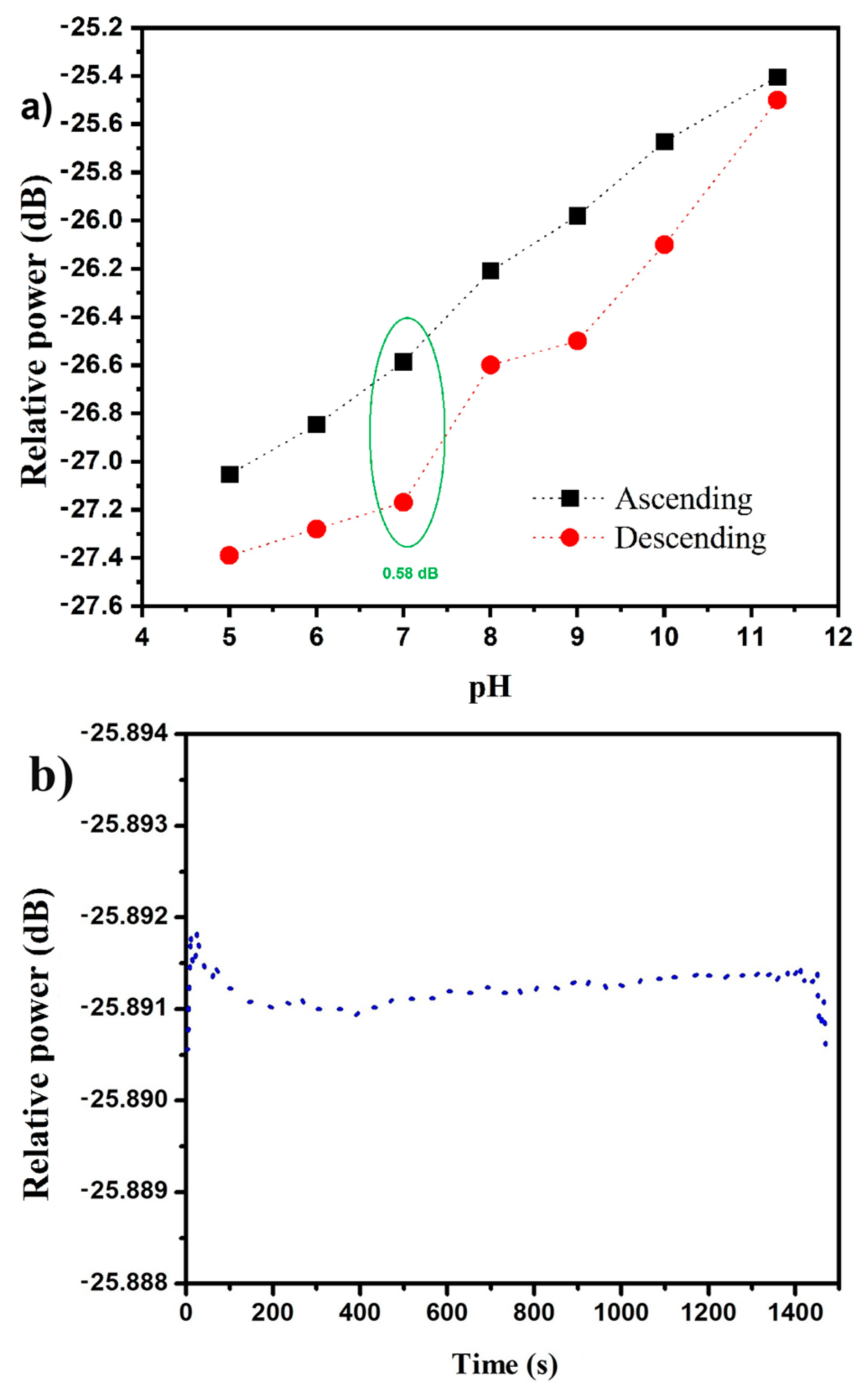
3.5. Sensor Hysteresis and Stability
3.6. Sensor Response and Recovery Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernal, W.; Anandhan, K.; Percino, M.J.; Barbosa-García, O.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, E.; Cerón, M.; Maldonado, J.L.; Rivadeneyra, M.S.; Thamotharan, S. Optoelectronic properties of (Z)-3-(4-(4,5-diphenyl-1H-imidazole-2-yl)phenyl)-2-phenylacrylonitrile films under acid and thermal environments for tuning OLED emission. Dye. Pigments 2021, 187, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srujana, P.; Radhakrishnan, T.P. Extensively reversible thermal transformations of a bistable, fluorescence-switchable molecular solid: Entry into functional molecular phase-change materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7270–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Das, S. Role of molecular packing in determining solid-state optical properties of π-conjugated materials. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P.; Cerón, M.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, E.; Castillo, A.E.; Thamotharan, S.; Robles, F.; Siegler, M.A.; Percino, M.J. Experimental and theoretical insights into the optical properties and intermolecular interactions in push-pull bromide salts. ChemistryOpen 2019, 8, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, S.P. Organic solid-state fluorescence: Strategies for generating switchable and tunable fluorescent materials. ChemPlusChem 2012, 77, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhan, K.; Cerón, M.; Ceballos, P.; Ramos-Hernández, R.; Perumal, V.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, E.; Sosa-Rivadeneyra, M.; Thamotharan, S.; Percino, M.J. 1H-NMR, photophysical, and pH studies of 4-(4,5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)benzaldehyde through experimental and DFT theoretical analysis. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, R.M. Colour Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; Khalili, B.; Haghayegh, A.S. A novel chromone based colorimetric sensor for highly selective detection of copper ions: Synthesis, optical properties and DFT calculations. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; Sekar, N. Synthesis, spectroscopic characteristics, dyeing performance and TD-DFT study of quinolone based red emitting acid azo dyes. Dye. Pigments 2019, 168, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairunisa, W.; Imawan, C. The effect of pH on the characteristics of the methyl red solution as a gamma-ray dosimeter. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1321, 022015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, T.; Le, T.; Voegtle, M.J.; Doyle, B.; Rimby, J.; Isovitsch, R. Synthesis, photophysical and computational studies of two lophine derivatives with electron-rich substituents in the 2-position. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1130, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabharathi, J.; Thanikachalam, V.; Srinivasan, N.; Perumal, M.V. Fluorescence spectral studies of some imidazole derivatives. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 90, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabharathi, J.; Thanikachalam, V.; Srinivasan, N.; Perumal, M.V.; Jayamoorthy, K. Physicochemical studies of molecular hyperpolarizability of imidazole derivatives. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourmohammadian, F.; Davoodzadeh, M.; Alizadeh, A.-A. New cyclopentadiene derivatives as novel pH indicators. Dye. Pigments 2007, 74, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Cho, S.; Kim, H.J. An anthracene appended guanidine derivative as water soluble fluorescence sensor for high pH values and water content measurements. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 383, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Karthikeyan, S.; Sagara, Y.; Moon, D.; Anthony, S.P. Unusual fluorescent photoswitching of imidazole derivatives: The role of molecular conformation and twist angle controlled organic solid state fluorescence. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 27385–27393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiethaus, G.; Toldo, J.M.; da Silveira Santos, F.; da Costa Duarte, R.; Gonçalves, P.F.B.; Rodembusch, F.S. Experimental and theoretical investigation of long-wavelength fluorescence emission in push–pull benzazoles: Intra-molecular proton transfer or charge transfer in the excited state? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 4408–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottman, E.W.; Moffett, R.B.; Moffett, S.M. The preparation and properties of chemiluminescent compounds of the lophine type. Proc. Indiana Acad. Sci. 1937, 47, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T.; Maeda, K. Mechanism of chemiluminescence of 2,4,5-triphenylimidazole. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1962, 35, 2057–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharasubramanian, A.; Ravichandran, Y.D. Synthesis and studies of electrochemical properties of lophine derivatives. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 54740–54746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, P.; et al. Highly efficient near ultraviolet organic light-emitting diode based on a meta-linked donor–acceptor molecule. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhan, K.; Cerón, M.; Perumal, V.; Ceballos, P.; Gordillo-Guerra, P.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, E.; Castillo, A.E.; Thamotharan, S.; Percino, M.J. Solvatochromism and pH effect on the emission of a triphenylimidazole-phenylacrylonitrile derivative: Experimental and DFT studies. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12085–12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhánek, J.; Bureš, F. Imidazole as a parent π-conjugated backbone in charge-transfer chromophores. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.H.; Harding, M.J.C. The chemiluminescence of lophine and its derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 5686–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, D.F.; Ingle, J.D. Determination of chromium(VI) in water by lophine chemiluminescence. Anal. Chem. 1981, 53, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.M.; Sonnenberg, J. Oxidation of triarylimidazoles. Structures of the photochromic and piezochromic dimers of triarylimidazyl radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camas-Anzueto, J.L.; Gómez-Valdéz, J.A.; Meza-Gordillo, R.; Pérez-Patricio, M.; Hernández de León, H.R.; León-Orozco, V. Sensitive layer based on lophine and calcium hydroxide for detection of dissolved oxygen in water. Measurement 2015, 68, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Zhu, Y.; Han, M.; Huang, H. Simultaneous load and temperature measurement using lophine-coated fiber Bragg gratings. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 115019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Valdivielso, C.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature using a fiber Bragg grating and a thermochromic material. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2002, 101, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camas-Anzueto, J.L.; Aguilar-Castillejos, A.E.; Castañón-González, J.H.; Lujpán-Hidalgo, M.C.; Hernández de León, H.R.; Mota Grajales, R. Fiber sensor based on lophine sensitive layer for nitrate detection in drinking water. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 60, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Bhoraniya, R.; Koladiya, M.; Bhopekar, V.; Patel, C.; Mori, T.; Modha, S. Solvatochromism and Halochromism in Nitro Lophine Derivatives: Photophysical Study, Computational Calculations and Applications as pH Sensing Material. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2024, 441, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Bolom, P.M.; Ruiz-Pérez, V.I.; Pérez-Patricio, M.; Hernández-Gutiérrez, C.A.; Camas-Anzueto, J.L. Enhancement of the dynamic range of the measurement of pH using a sensitive layer of methyl red-lophine. Opt. Contin. 2025, 4, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hou, L.; Jia, D.; Yao, K.; Meng, Q.; Qu, J.; Yan, B.; Luan, Q.; Liu, T. Highly sensitive fiber-optic chemical pH sensor based on surface modification of optical fiber with ZnCdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1294, 342281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.; Singh, V.K. PANI-ZnO clad modified multimode optical fiber pH sensor based on EWA. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2023, 50, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanikar, T.; Singh, V.K. PANI-PVA composite film coated optical fiber probe as a stable and highly sensitive pH sensor. Opt. Mater. 2019, 88, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wright, R.; Lu, P.; Cvetic, P.C.; Ohodnicki, P.R. Distributed fiber optic pH sensors using sol-gel silica based sensitive materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 340, 129853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sensitive Material | Fiber Type | Sensitivity | Work Range | Responsive Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxyl ZnCdSe/ZnS quantum dots | Tapered optical fiber | 0.139/pH | 6.0–9.01 | 40 s | [33] |
| PANI-ZnO | Evanescent wave | 2.46 µW/pH | 2.0–10.0 | [34] | |
| PANI/PVA | Cladding modification | 2.79 µW/pH | 2.0–9.0 | 8–12 s for 2–4 pH value 18–22 s for 4–9 pH value | [35] |
| Au-SiO2 | Evanescent wave with No core fiber | 19.9 T %/pH | 8.0–12.0 | 10 s | [36] |
| Lophine | Evanescent wave | 63.84 µW/pH | 5.0–11.3 | 5 s | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velasco-Bolom, P.M.; Camas-Anzueto, J.L.; Meza-Gordillo, R.; Pérez-Patricio, M.; Ramírez-Morales, M.; Anzueto-Sánchez, G.; Grajales-Coutiño, R.; Hoyo-Montaño, J.A. Optical Characterization of a Sensitive Lophine Layer for the Detection of Hydrogen Ions (H+). Optics 2025, 6, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040058
Velasco-Bolom PM, Camas-Anzueto JL, Meza-Gordillo R, Pérez-Patricio M, Ramírez-Morales M, Anzueto-Sánchez G, Grajales-Coutiño R, Hoyo-Montaño JA. Optical Characterization of a Sensitive Lophine Layer for the Detection of Hydrogen Ions (H+). Optics. 2025; 6(4):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelasco-Bolom, Pedro Marcos, Jorge Luis Camas-Anzueto, Rocío Meza-Gordillo, Madaín Pérez-Patricio, Marcoantonio Ramírez-Morales, Gilberto Anzueto-Sánchez, Rubén Grajales-Coutiño, and José Antonio Hoyo-Montaño. 2025. "Optical Characterization of a Sensitive Lophine Layer for the Detection of Hydrogen Ions (H+)" Optics 6, no. 4: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040058
APA StyleVelasco-Bolom, P. M., Camas-Anzueto, J. L., Meza-Gordillo, R., Pérez-Patricio, M., Ramírez-Morales, M., Anzueto-Sánchez, G., Grajales-Coutiño, R., & Hoyo-Montaño, J. A. (2025). Optical Characterization of a Sensitive Lophine Layer for the Detection of Hydrogen Ions (H+). Optics, 6(4), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6040058








