Parametric Dependence of Thermal Field in Laser-Assisted Turning of GH 4169
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
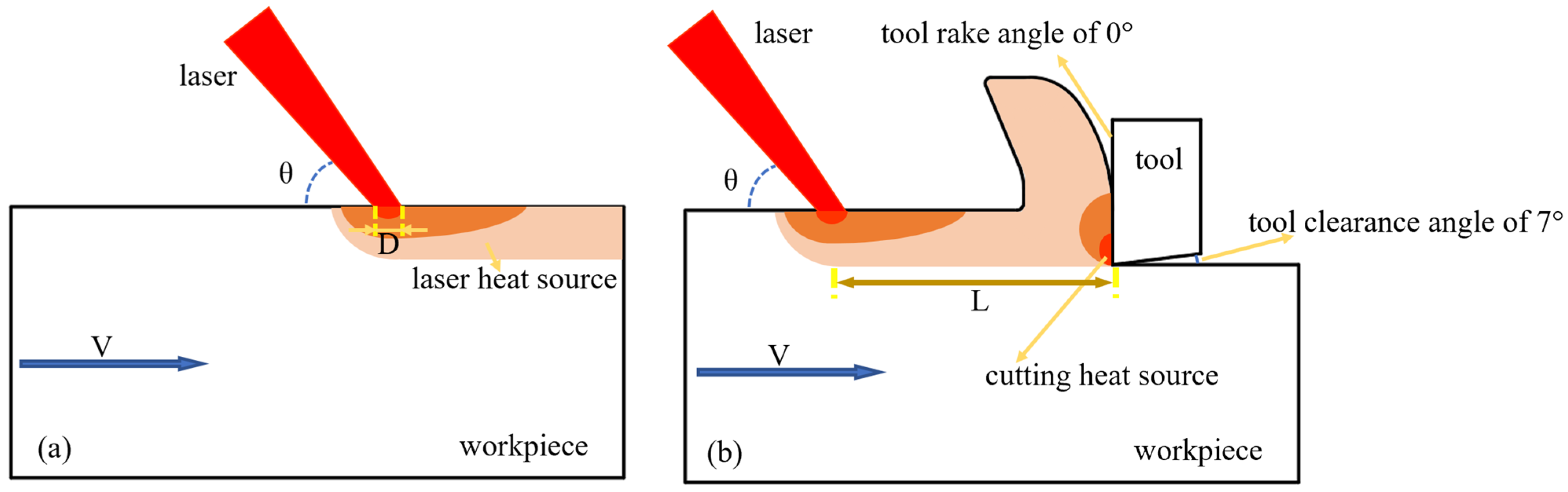
2.1. Experimental Setup of LAT of GH 4169
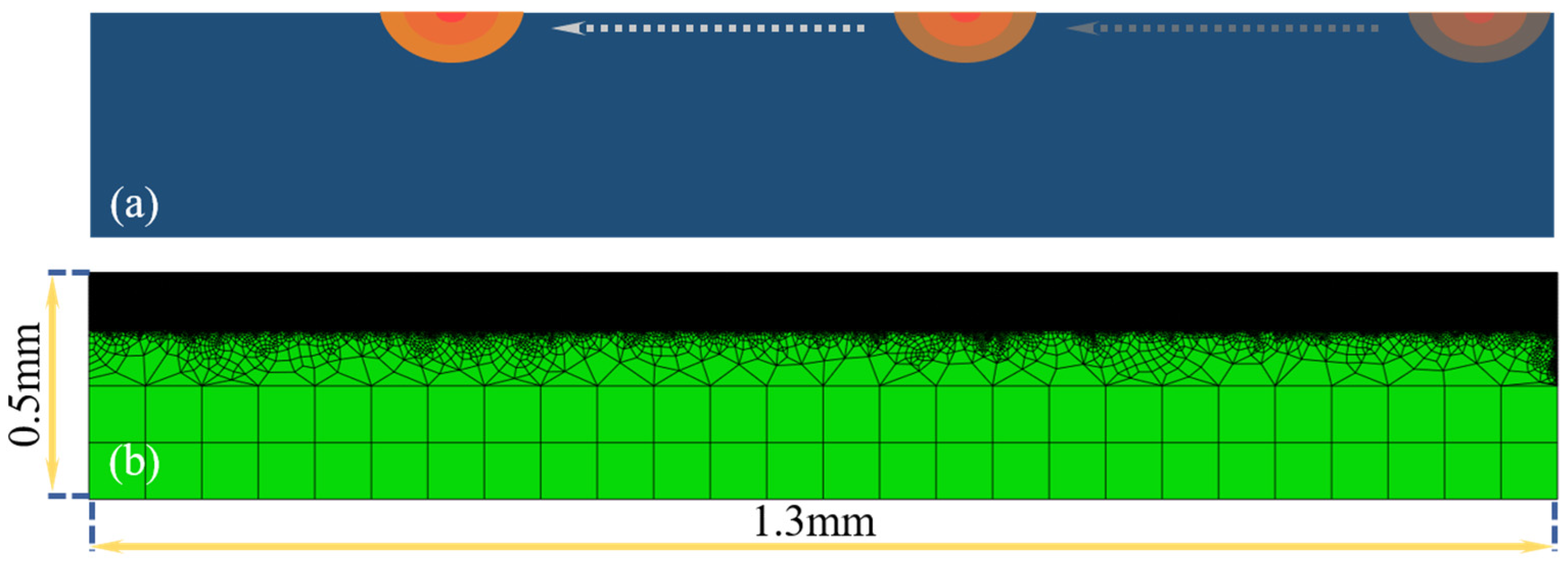
2.2. FE Model of LAT of GH 4169
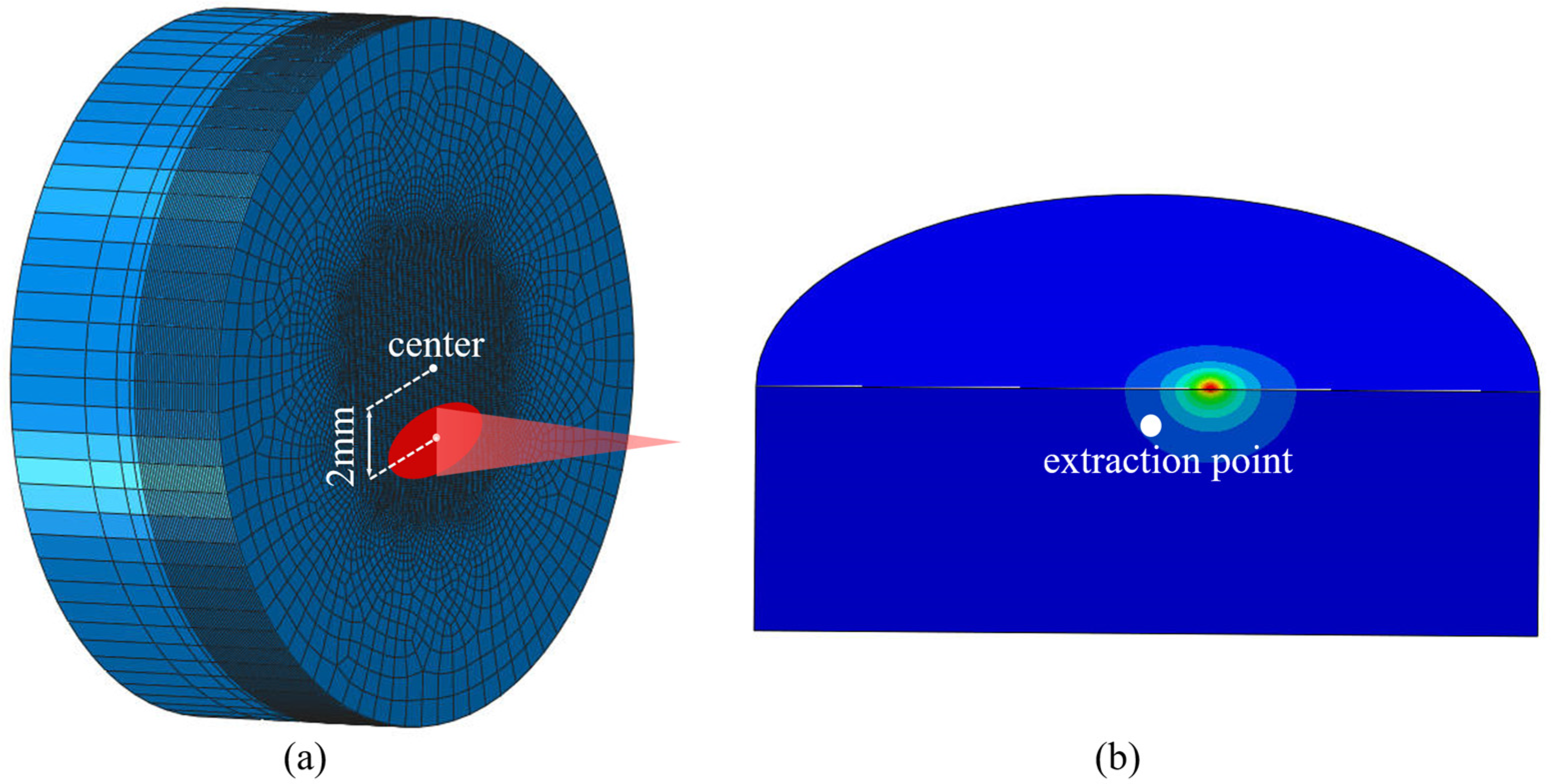
2.3. Calibration Setup of Absorption Coefficient for GH 4169
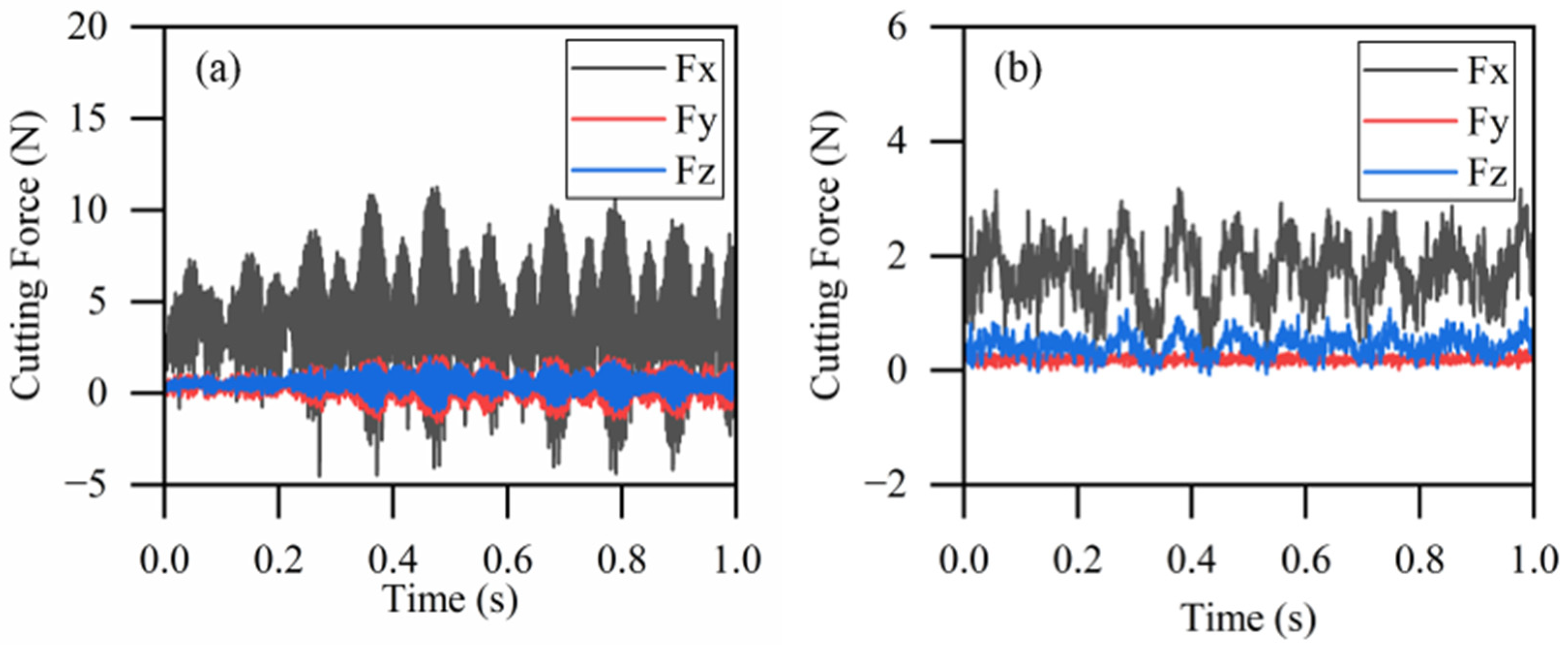
3. Results and Discussion
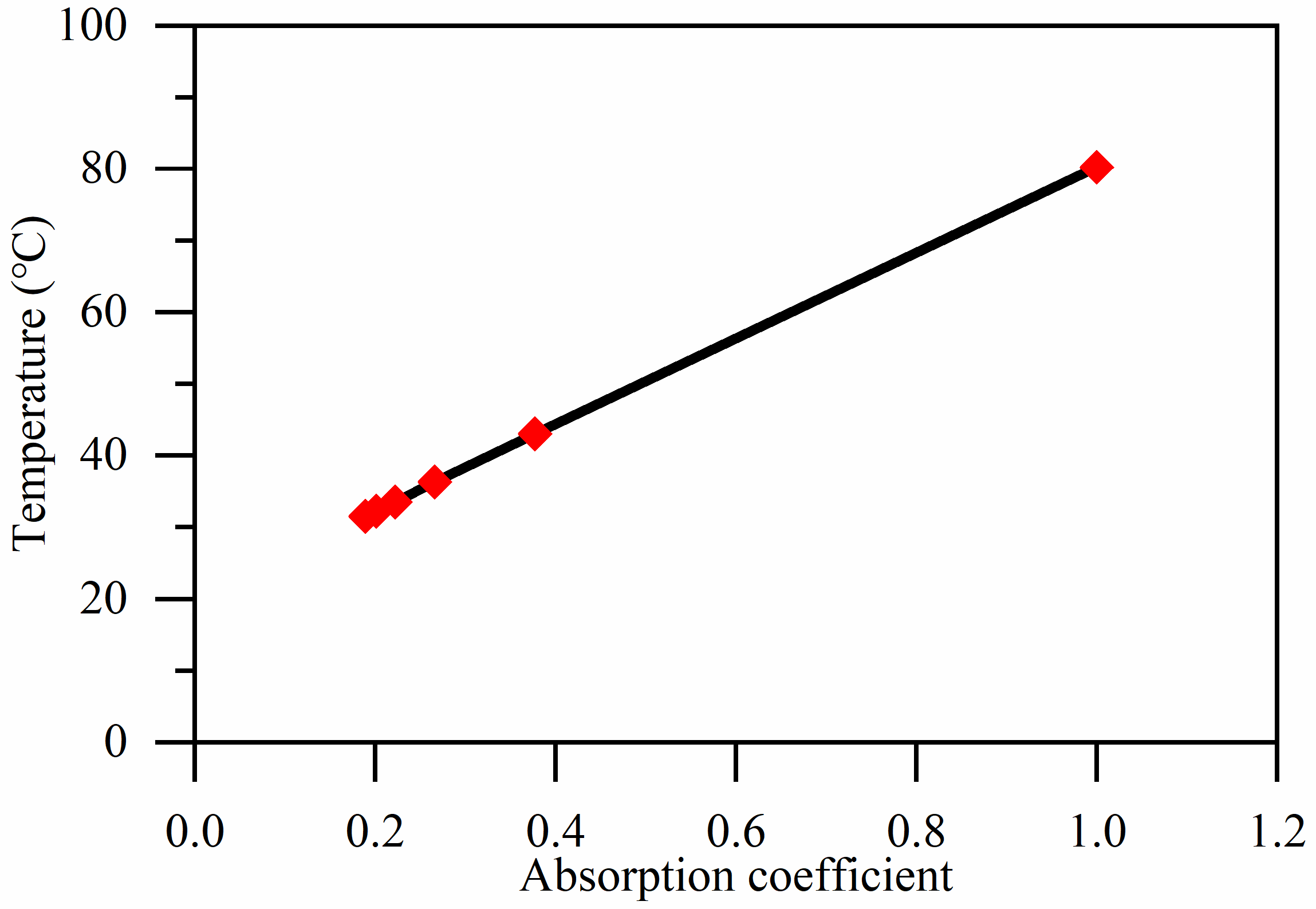
3.1. Calibration of Laser Absorption Coefficients for GH 4169
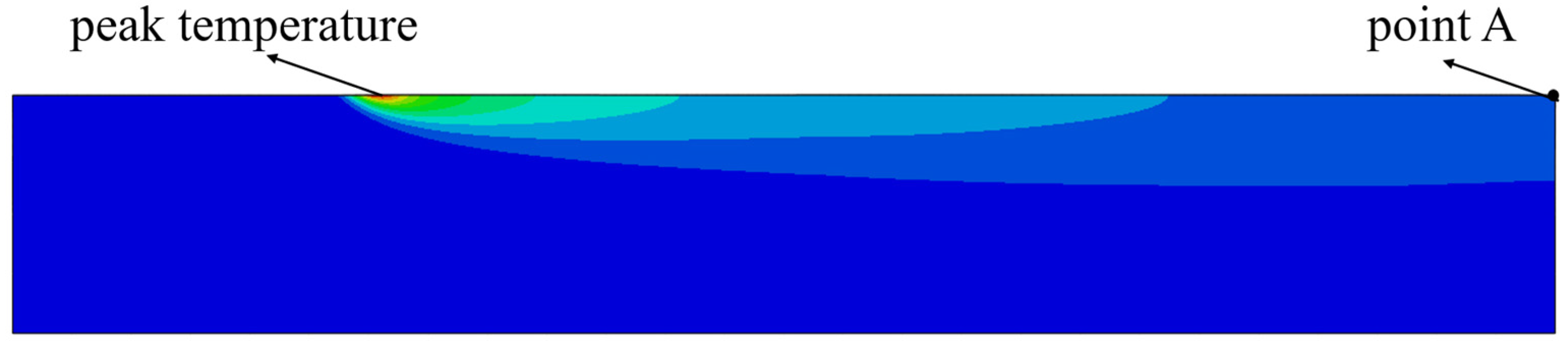
3.2. Influence of Laser Processing Parameters on Peak and Final Preheating Temperatures
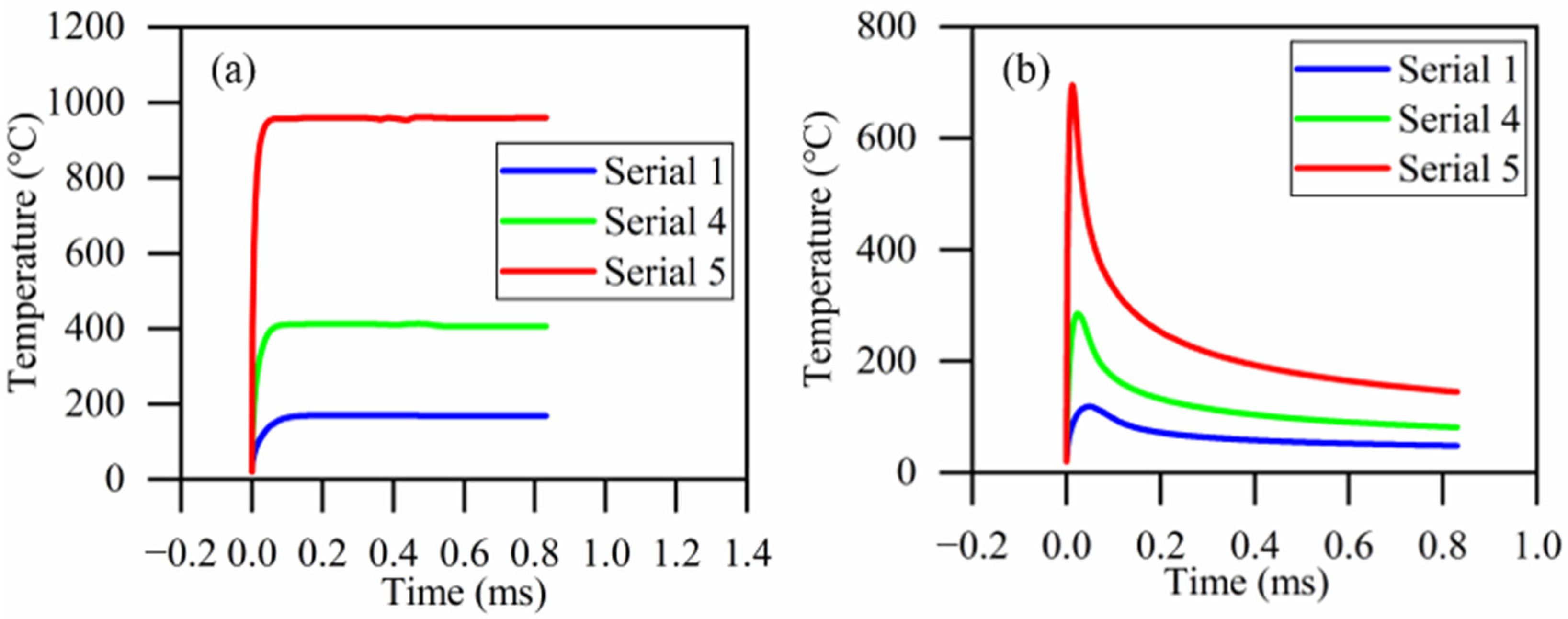
3.2.1. Laser Power
3.2.2. Laser Spot Diameter
3.2.3. Laser Spot Movement Speed
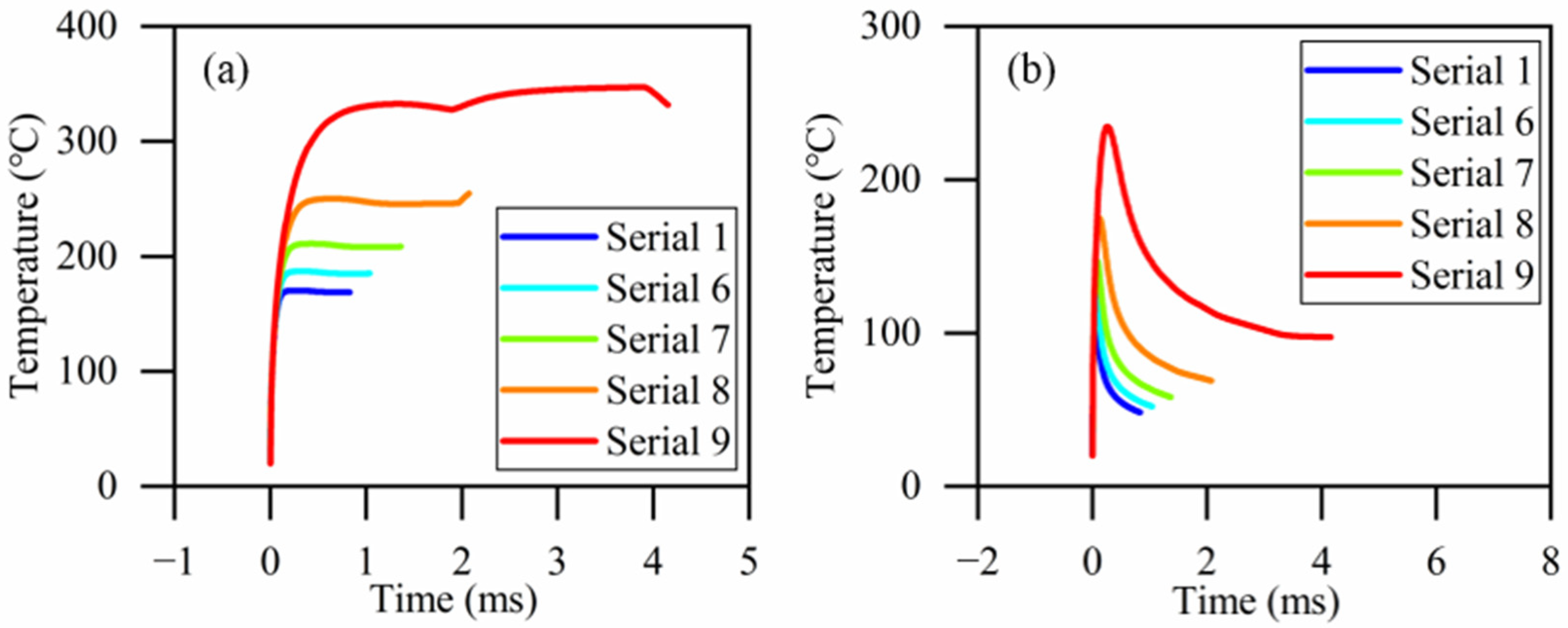
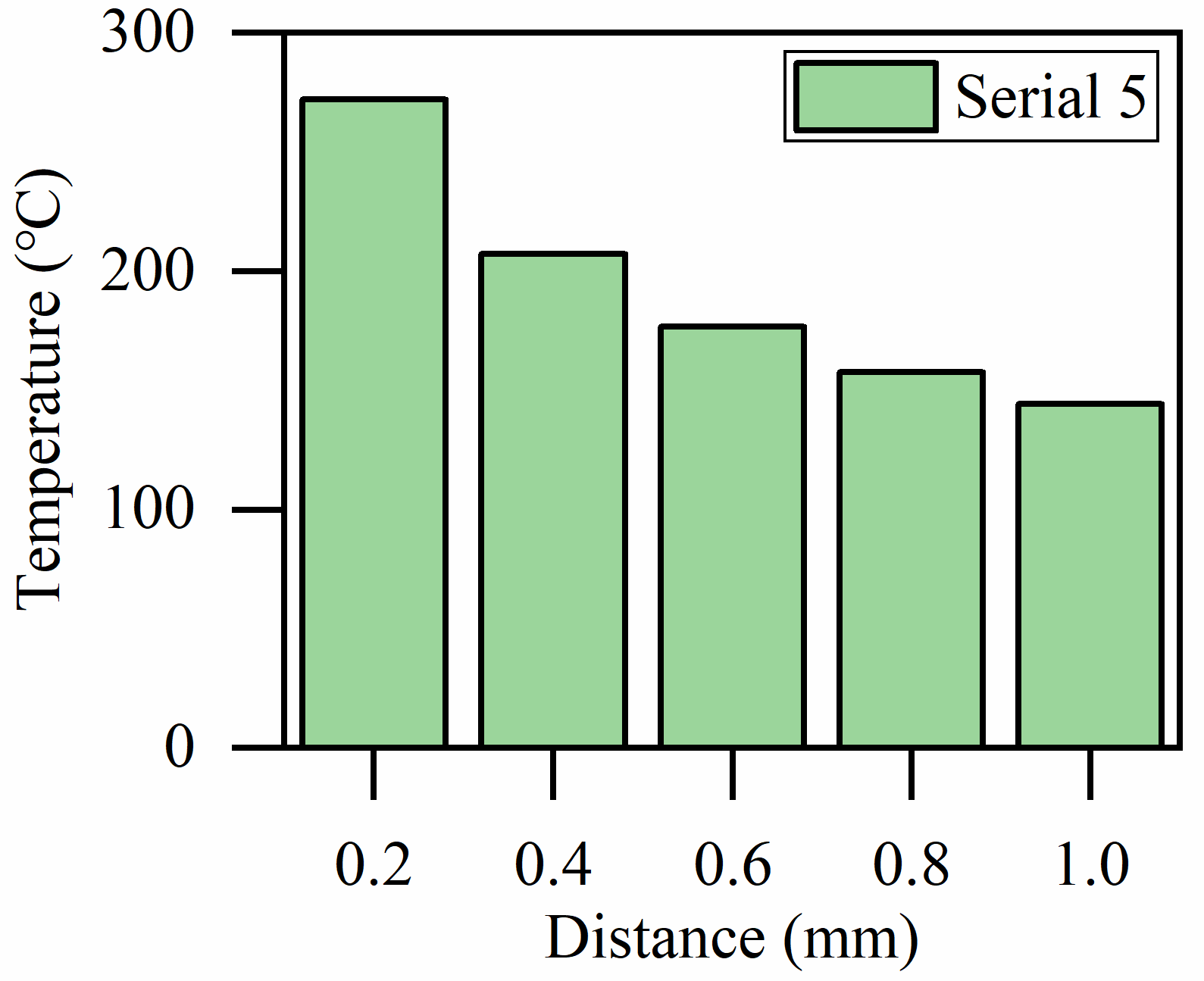
3.2.4. Laser Spot–Tool Edge Distance
3.3. Temperature Regulation for GH 4169
3.3.1. Temperature Regression Equation for GH 4169
3.3.2. Parameter Optimization for LAT of GH 4169
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LAT | Laser-assisted turning |
| FE | Finite element |
| CT | Conventional turning |
| LAM | Laser-assisted machining |
| PCD | Polycrystalline diamond |
| P | Laser power |
| D | Laser spot diameter |
| L | Laser spot–tool edge distance |
| V | Laser spot movement speed |
| F | Feed rate |
| n | Spindle speed |
| ap | Depth of cut |
| Tmax | Peak temperature of laser preheating |
| TA | Final preheating temperature of point A |
References
- Bartolomeis, A.D.; Newman, S.T.; Jawahir, I.; Biermann, D.; Shokrani, A. Future research directions in the machining of Inconel 718. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 297, 117260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, Z.; Fan, W.; Gasser, A.; Huang, W. The influence of Laves phases on the room temperature tensile properties of Inconel 718 fabricated by powder feeding laser additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2019, 164, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Popovich, V.A. A review of mechanical properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Du, J.; Deng, Q.; Zhuang, J. Stress rupture properties of GH4169 superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.L.; Zhang, B.; Chu, C.L.; Zhou, L.; Chu, P.K. Evolution of microstructures and properties of the GH4169 superalloy during short-term and high-temperature processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 744, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Hou, N.; Zhao, M. Surface integrity of laser-assisted turning of the GH4169 alloy. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Ahsana, N.; Zhao, L. Wear characteristics of GH4169 superalloy at elevated temperatures. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2025, 25, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B. State-of-the-art of surface integrity induced by tool wear effects in machining process of titanium and nickel alloys: A review. Measurement 2019, 132, 150–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Monaca, L.A.; Murray, J.; Speidel, A.; Ushmaev, D.; Clare, A.; Axinte, D.; M’Saoubi, R. Surface integrity in metal machining—Part I: Fundamentals of surface characteristics and formation mechanisms. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 162, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıkaya, M.; Gupta, M.K.; Tomaz, I.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Kuntoğlu, M.; Khanna, N.; Yıldırım, Ç.V.; Krolczyk, G.M. A state-of-the-art review on tool wear and surface integrity characteristics in machining of superalloys. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 624–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhang, M.; Xin, W.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Lu, J. An Experiment Study on Surface Topography of GH4169 Assisted by Ultrasonic Elliptical Vibration Ultra-Precision Turning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Huang, T.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Ye, C. Improving surface integrity of GH4169 alloy through magnetic-assisted cutting. Manuf. Lett. 2024, 41, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cui, E.; Zheng, G.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H. Investigation of the effects of GnP-ZrO2 hybrid nanofluids minimum quantity lubrication (NMQL) on the machinability of GH4169. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 5841–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Ming, Z.; Cui, B.; Wang, J. Research Progress on Laser-Assisted Precision Machining Technology. Micromachines 2025, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Yan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Peng, F. Analytical modeling of the heat-affected zone in laser-assisted milling of AerMet100 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatir, F.A.; Sadeghi, M.H.; Akar, S. Investigation of surface roughness in laser-assisted hard turning of AISI 4340. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Tak, M.; Rao, N.; Vallleti, K.; Bathe, R. Investigations on laser-assisted turning of IN625 alloy with hot hardness approach using uncoated and CrAlSiN coated WC tools. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2024; online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, C.; Dong, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, C. Experimental Investigation on Process Parameters during Laser-Assisted Turning of SiC Ceramics Based on Orthogonal Method and Response Surface Methodology. Materials 2022, 15, 4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, J. Mechanism of surface quality formation in laser-assisted turning of Si3N4 ceramics. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenmann, R.; Langhorst, M.; Zaeh, M.F. Computerized Optimization of the Process Parameters in Laser-Assisted Milling. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12 Pt A, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Sun, G.; Xu, J.; Zhao, B. Numerical simulation of temperature field in C/SiC laser-assisted machining. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Xi’an, China, 2–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrizubieta, J.I.; Klocke, F.; Gräfe, S.; Arntz, K.; Lamikiz, A. Thermal Simulation of Laser-assisted Turning. Procedia Eng. 2015, 132, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hung, T.-P.; Lu, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-F.; Hsu, F.-C.; Lin, C.-F.; Lu, Y.-C.; Liang, S.Y. Flank tool wear prediction of laser-assisted milling. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 43 Pt A, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Zhai, C.; Zhou, F.; Li, J. Study on chip formation and surface integrity of nickel-based superalloy Inconel 718 by laser assisted micro-cutting. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 113, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, J. The temperature process analysis and control on laser-assisted milling of nickel-based superalloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Zeng, F.; Liang, S.Y. Modeling of laser-assisted micro-milling Inconel718. Precis. Eng. 2024, 88, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Hou, N.; Wang, M. Evolution mechanism of residual stress under the influence of thermomechanical coupling in laser-assisted machining of superalloy GH4169. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 138, 4005–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X. Building of Laser-assisted Micromachining Temperature Field. In Proceedings of the 2015 CSIC International Conference on Computer Science and Intelligent Communication, Zhengzhou, China, 18–19 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Hu, W.; Sun, T.; Zhang, J. Investigation of Laser-Assisted Micro-Milling Process of Inconel 718. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Lob, S.P. Machining characteristics of Inconel 718 using ultrasonic and high temperature-aided cutting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 198, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, Y. The prediction of surface roughness of PCBN turning GH4169 based on adaptive genetic algorithm. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2017, 180, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wu, Z.R.; Fang, L.; Song, Y.D. Investigation of surface damage and roughness for nickel-based superalloy GH4169 under hard turning processing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 234, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





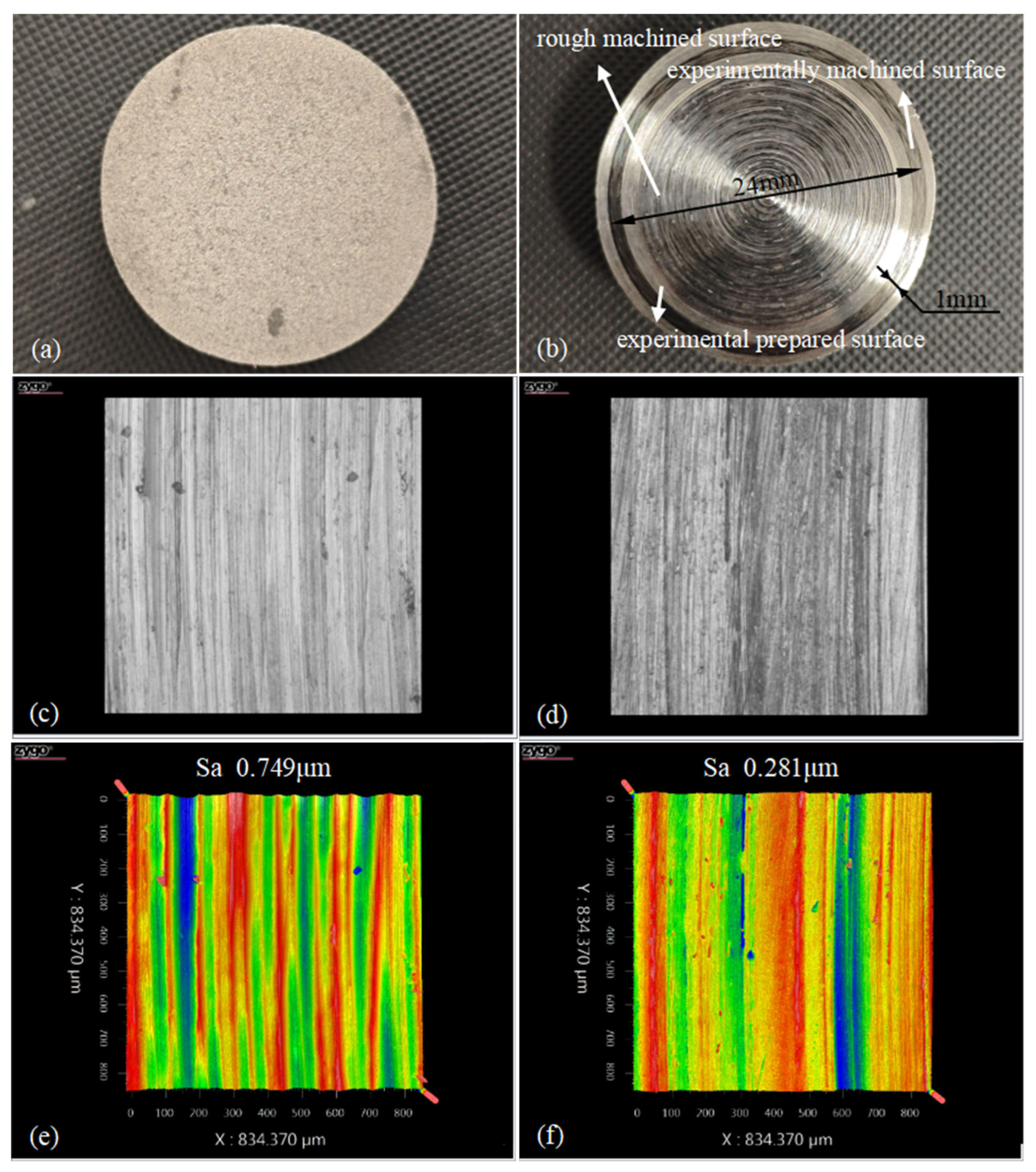
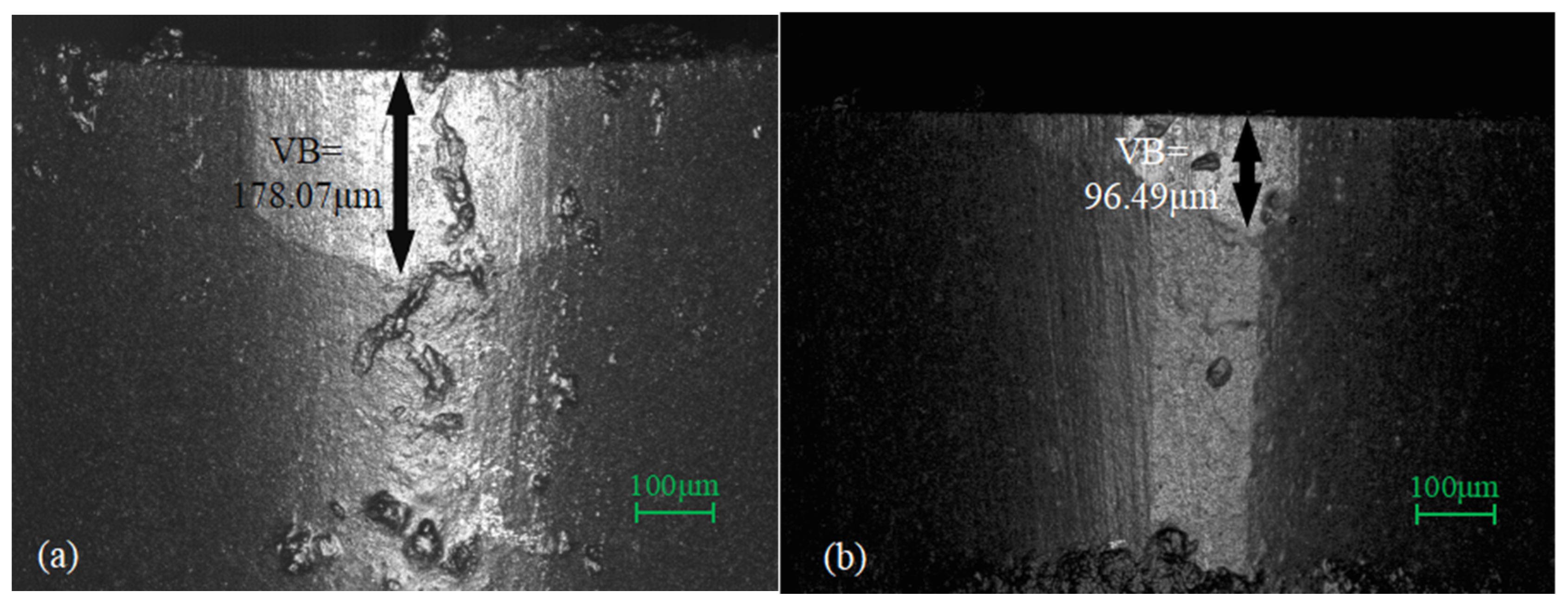
| Manufacturer | Model Number | Power Output Range W | Power Stability | Wavelength nm | Operating Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPG, New York, NY, USA | YLM-100-AC | 0–100 | ±1% | 1064 | Continuous |
| Temp °C | Conductivity mW/(mm × °C) | Density ×10−9 Toone/mm3 | Young’s Modulus MPa | Poisson’s Ratio | Expansion ×10−5/°C | Specific Heat ×108 mJ/(Ton × °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 13.4 | 8.24 | 2.10 | 0.3 | 1.18 | 4.51 |
| 200 | 15.9 | 1.92 | 1.30 | 4.82 | ||
| 300 | 17.8 | 1.35 | 4.87 | |||
| 400 | 18.3 | 1.85 | 1.41 | 4.92 | ||
| 500 | 19.6 | 1.44 | 5.14 | |||
| 600 | 21.2 | 1.73 | 1.48 | 5.39 | ||
| 700 | 22.8 | 1.54 | 5.73 | |||
| 800 | 23.6 | 1.54 | 1.70 | 6.15 | ||
| 900 | 27.6 | 1.84 | 6.57 |
| Serial | P W | D mm | θ ° | t s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 60 | 5 |
| 2 | 20 | |||
| 3 | 30 |
| Serial | Measurement Results °C |
|---|---|
| 1 | 30.3 |
| 2 | 40.7 |
| 3 | 50.9 |
| Serial | Absorption Coefficient |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.189 |
| 2 | 0.175 |
| 3 | 0.171 |
| Serial | P W | L mm | D mm | V mm/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 0.2 | 1204.28 |
| 2 | 20 | 0.2 | 1204.28 | |
| 3 | 30 | 0.2 | 1204.28 | |
| 4 | 10 | 0.1 | 1204.28 | |
| 5 | 10 | 0.05 | 1204.28 | |
| 6 | 10 | 0.2 | 963.40 | |
| 7 | 10 | 0.2 | 722.57 | |
| 8 | 10 | 0.2 | 481.71 | |
| 9 | 10 | 0.2 | 240.86 |
| Serial | P W | D mm | L mm | F μm/r | n rpm | ap μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | - | - | - | 0.83 | 600 | 1 |
| LAT | 13 | 0.08 | 0.4 | 0.83 | 600 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Parametric Dependence of Thermal Field in Laser-Assisted Turning of GH 4169. Optics 2025, 6, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6030044
Zhou S, Xu J, Zhao L, Yang Y, Li Z, Zhang J. Parametric Dependence of Thermal Field in Laser-Assisted Turning of GH 4169. Optics. 2025; 6(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shuai, Jiwen Xu, Liang Zhao, Yuqi Yang, Zengqiang Li, and Junjie Zhang. 2025. "Parametric Dependence of Thermal Field in Laser-Assisted Turning of GH 4169" Optics 6, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6030044
APA StyleZhou, S., Xu, J., Zhao, L., Yang, Y., Li, Z., & Zhang, J. (2025). Parametric Dependence of Thermal Field in Laser-Assisted Turning of GH 4169. Optics, 6(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/opt6030044






