An Analytical Solution for Short Thin-Walled Beams with Monosymmetric Open Sections Subjected to Eccentric Axial Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
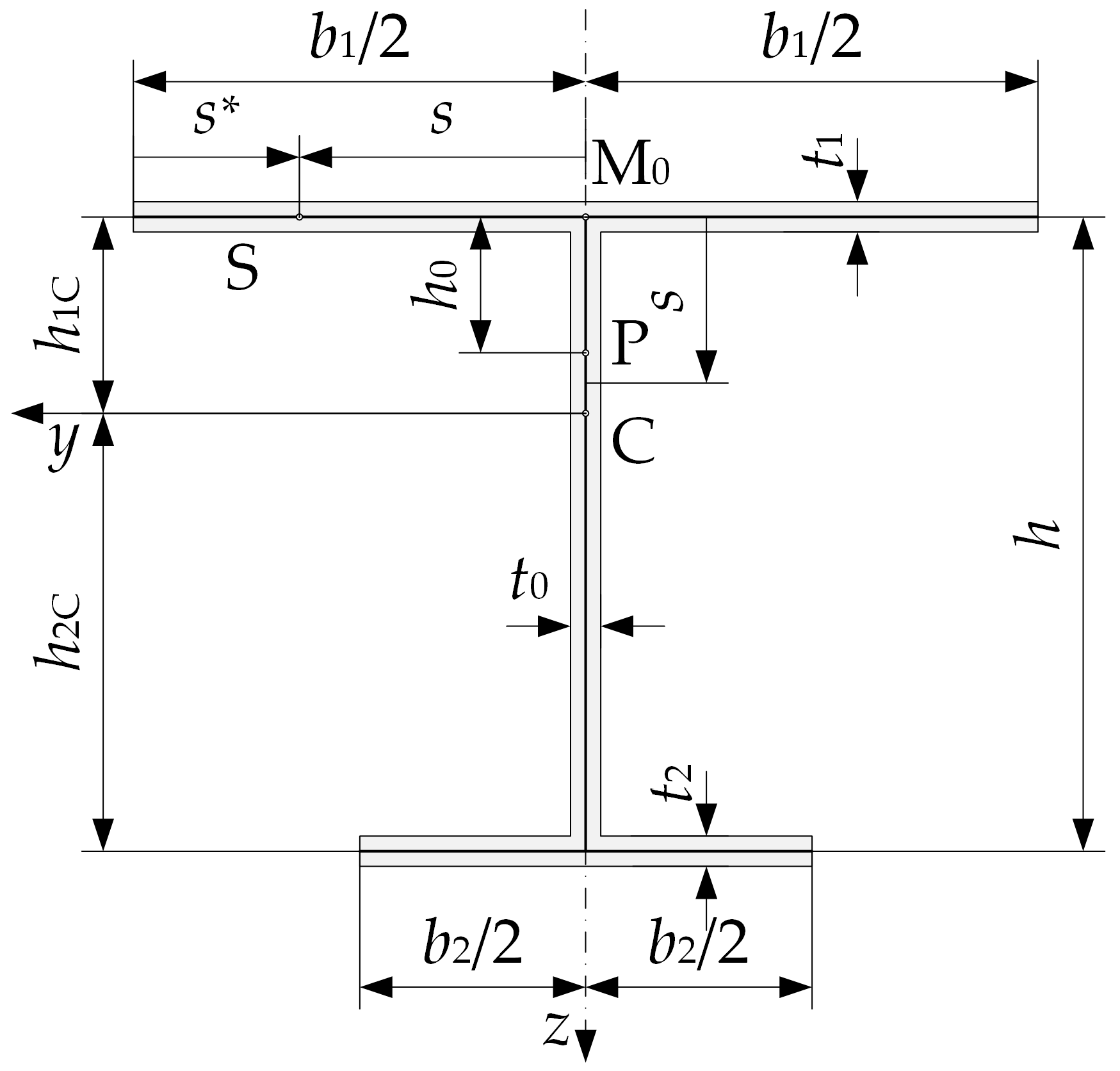
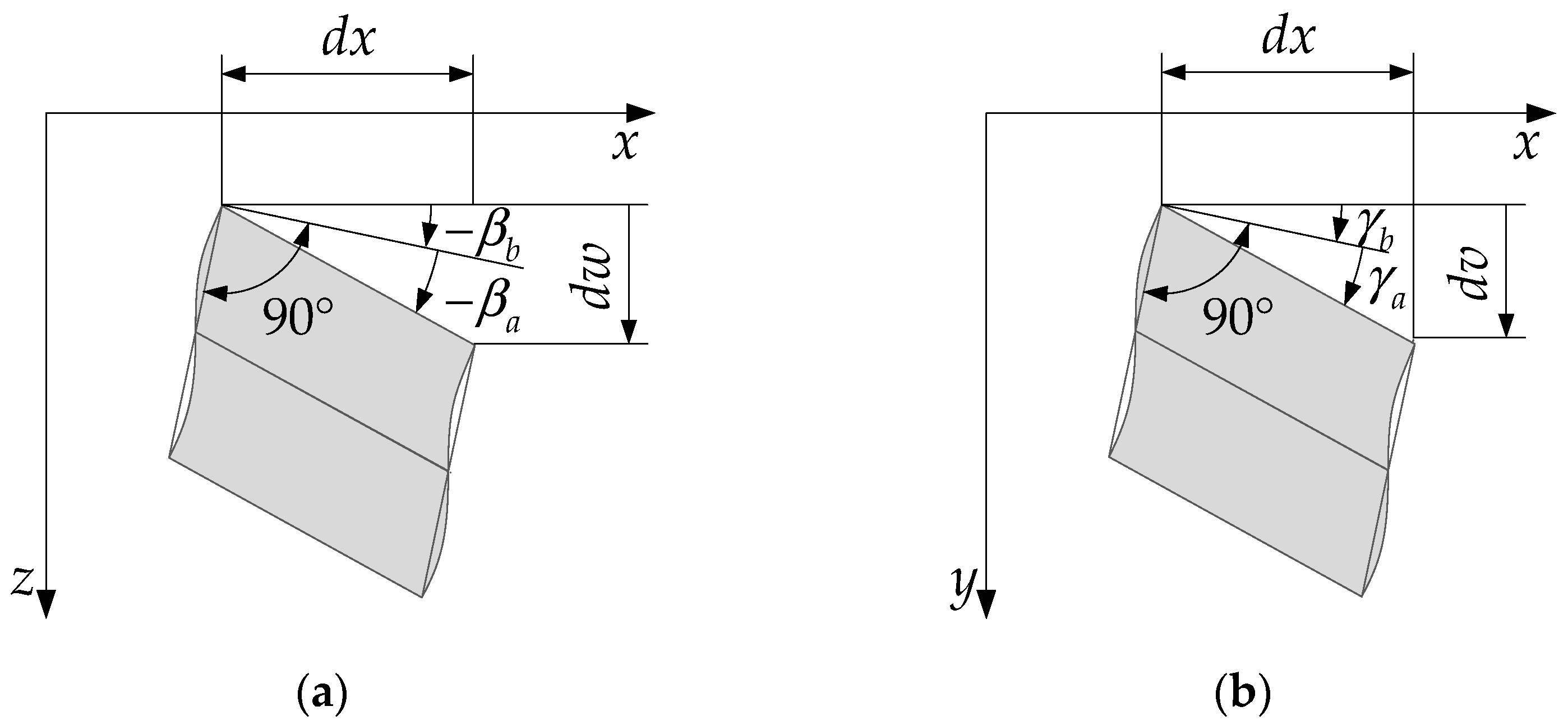
2. Analytic Solutions for Stresses and Displacements of Beams Subjected to Compression/Tension, Bending, and Torsion with Influence of Shear
2.1. Assumptions and Constraints
- The material is linear isotropic/orthotropic elastic;
- The shape of the cross-section is preserved during the beam deformations;
- Normal stresses in the beam walls are negligible, except for longitudinal normal stresses, which are uniformly distributed across the cross-section thickness;
- Shear stresses are negligible, except those acting tangentially along the midline of the cross-section. It is assumed that these stresses are also uniformly distributed across the cross-section thickness.
- The beam is a thin-walled structure with the following ratios: d/t ≥ 40, l/d ≤ 5, where t is the wall thickness, d is the length of the cross-section part (between rigid joints or between joint and free edge), and l is the beam length;
- The cross-section of the beam must be reinforced with appropriate diaphragms to prevent the distortion of the section;
- The applied load is below the critical buckling load.
2.2. Stresses and Internal Force Components of Axially Loaded Beams
2.3. The Method of Initial Parameters
Clamped-Hinged Beam Under Eccentric Axial Load
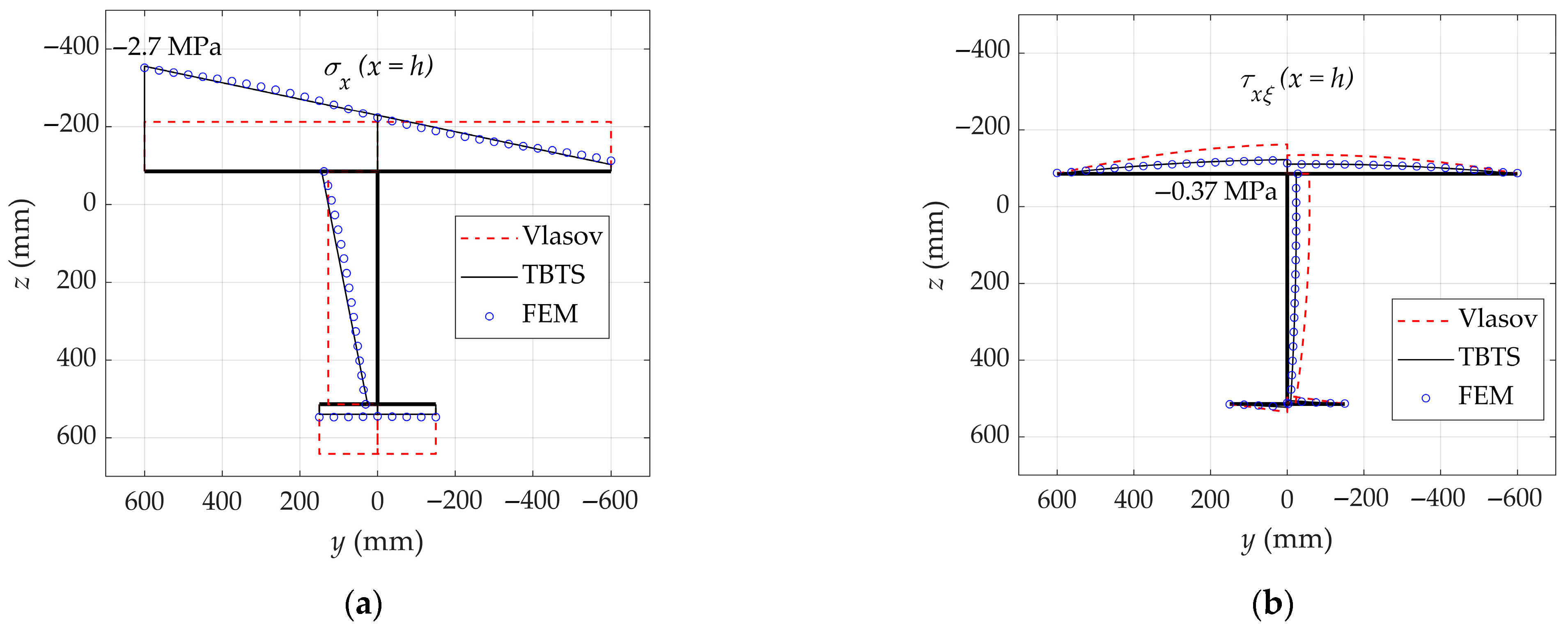
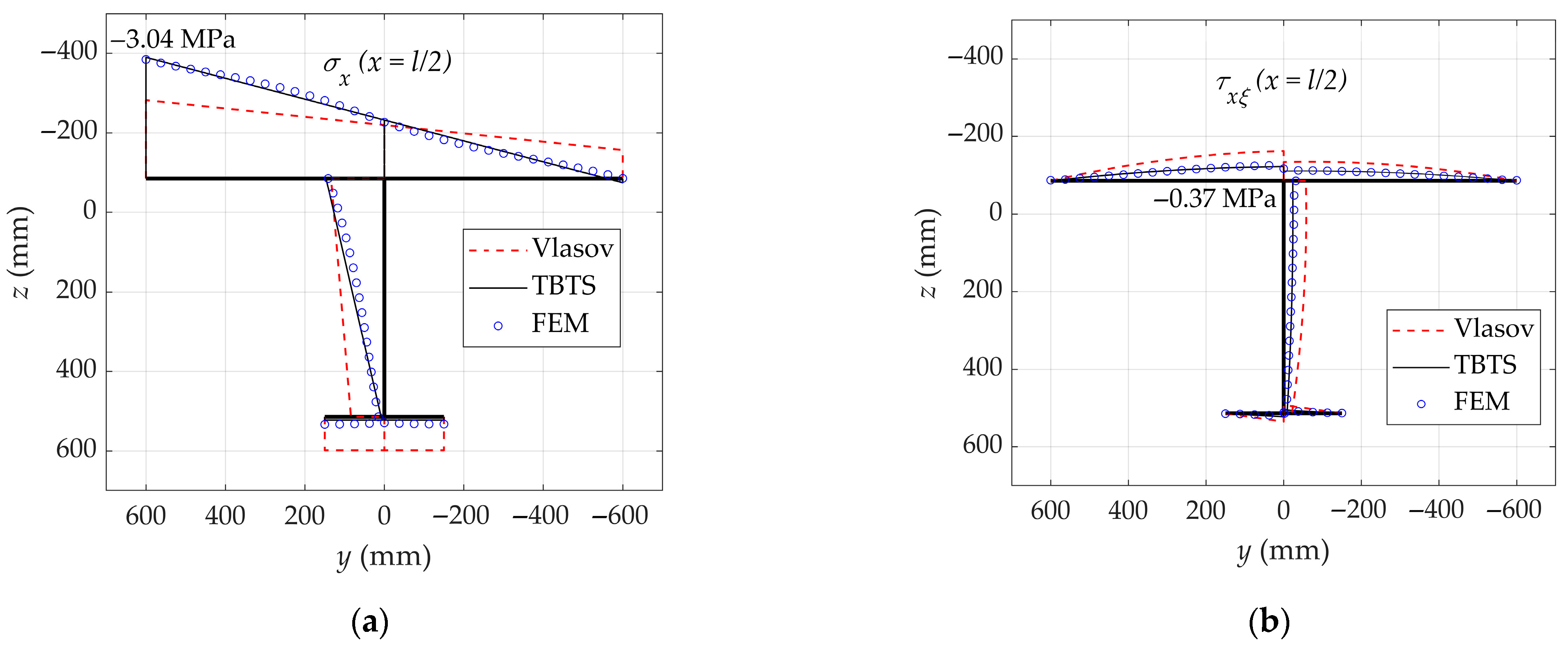
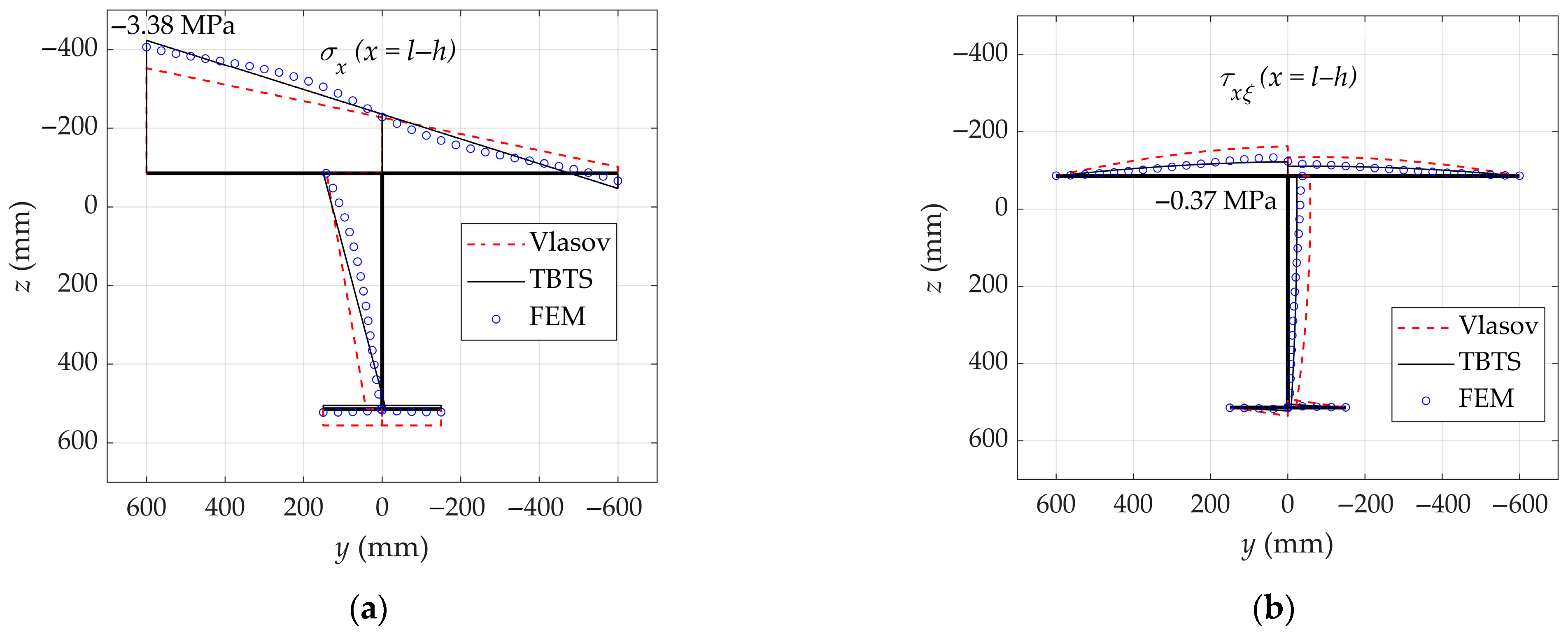
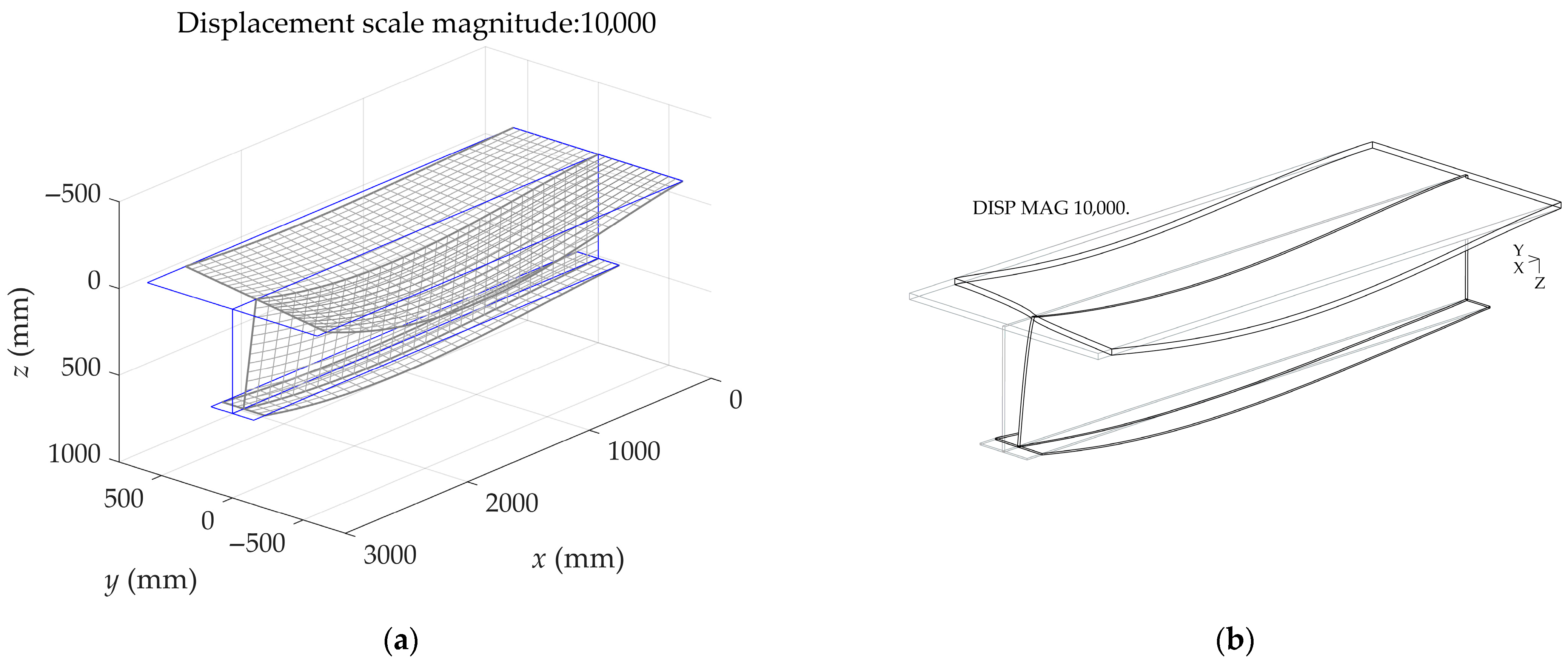
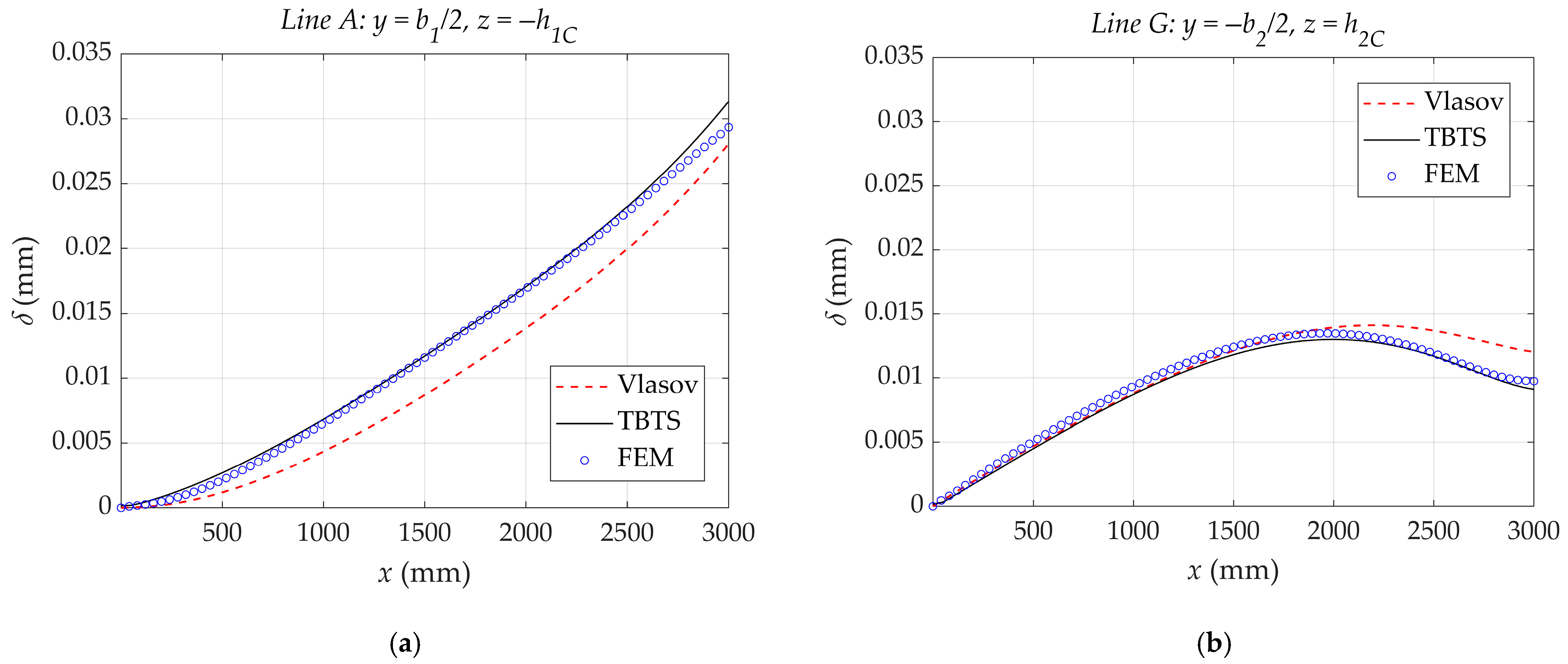
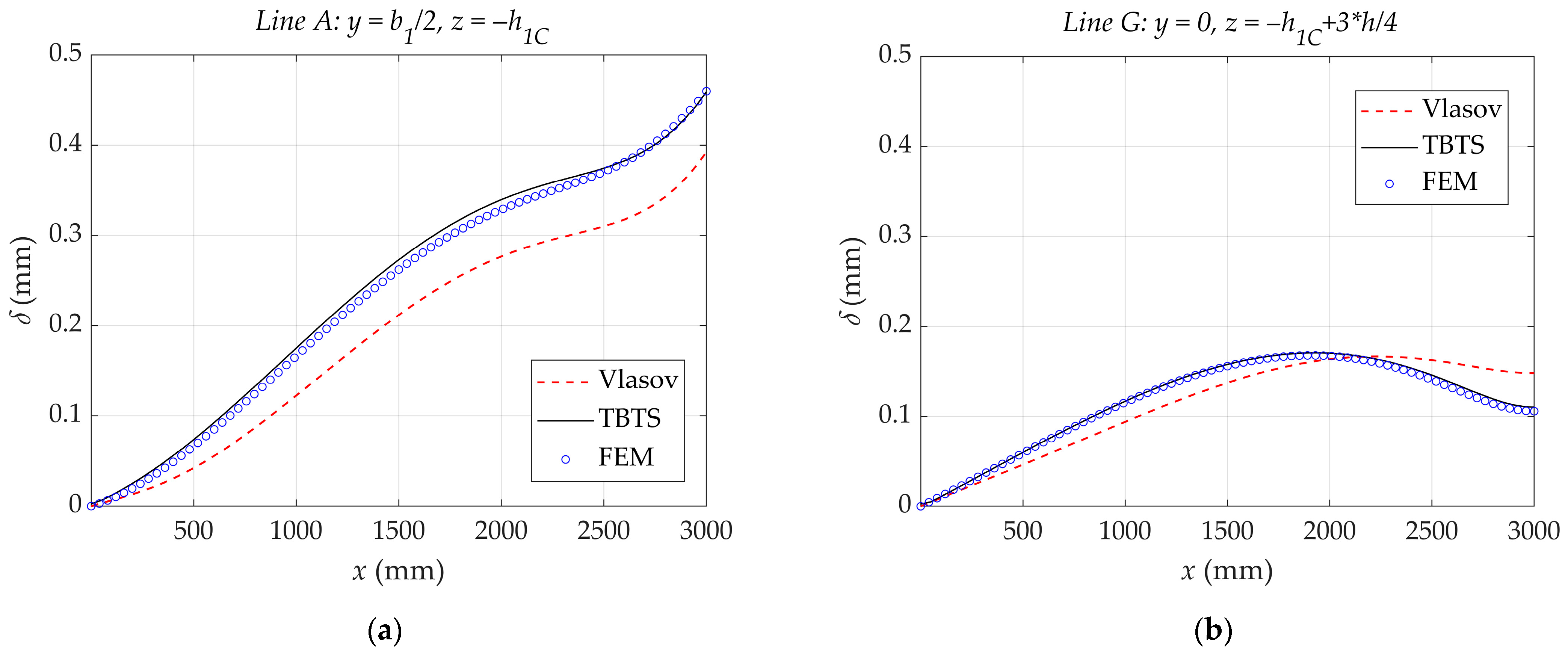
3. Illustrative Examples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FEM | Finite element method |
| TBTS | Theory of bending and torsion with the influence of shear |
| VL | General Vlasov’s theory |
Appendix A
Monosymmetric I Section—Cross-Section Properties
References
- Kim, Y.Y.; Jang, G.W.; Choi, S. Analysis of Thin-Walled Beams; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaglia, C.; Camotim, D. Generalized Beam Theory: Moving from Isolated Members to Structural Systems—A state-of-the-art review on GBT applications in thin-walled steel structures. In Proceedings of the Annual Stability Conference Structural Stability Research Council (SSRC 2021), Louisville, KY, USA, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 87–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-H.; Kang, T.H.-K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kang, K. Strain compatibility method for the design of short rectangular concrete-filled tube columns under eccentric axial loads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakouri Mahmoudabadi, N.; Bahrami, A.; Saghir, S.; Ahmad, A.; Iqbal, M.; Elchalakani, M.; Özkılıç, Y.O. Effects of eccentric loading on performance of concrete columns reinforced with glass fiber-reinforced polymer bars. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parunov, J.; Garbatov, Y. Ship Structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patuelli, C.; Cestino, E.; Frulla, G. A Beam Finite Element for Static and Dynamic Analysis of Composite and Stiffened Structures with Bending-Torsion Coupling. Aerospace 2023, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, V.Z. Thin-Walled Elastic Beams; Israel Program for Scientific Translation Ltd.: Jerusalem, Israel, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- El Fatmi, R. Non-uniform warping including the effects of torsion and shear forces. part I: A general beam theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 5912–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-I.; Kim, M.-Y. Exact dynamic/static stiffness matrices of non-symmetric thin-walled beams considering coupled shear deformation effects. Thin-Walled Struct. 2005, 43, 701–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipiras, V.J.; Sapountzakis, E.J. Bars under nonuniform torsion—Application to steel bars, assessment of EC3 Guidelines. Eng. Struct. 2014, 60, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavazza, R. Torsion of thin-walled beams of open cross-section with influence of shear. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2005, 47, 1099–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavazza, R.; Matoković, A.; Vukasović, M. A theory of torsion of thin-walled beams of arbitrary open sections with influence of shear. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2020, 50, 206–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavazza, R.; Matoković, A. Bending of thin-walled beams of open section with influence of shear, part I: Theory. Thin-Walled Struct. 2017, 116, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavazza, R.; Matoković, A.; Vukasović, M. Bending of thin-walled beams of open section with influence of shear—Part II: Application. Thin-Walled Struct. 2017, 116, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papangelis, J. On the Stresses in Thin-Walled Channels Under Torsion. Buildings 2024, 14, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.A.; Reyes-Rodríguez, A.M.; Sánchez-González, E.; Ríos, J.D. Experimental and Numerical Flexural–Torsional Performance of Thin-Walled Open-Ended Steel Vertical Pile Foundations Subjected to Lateral Loads. Buildings 2023, 13, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczak, I.; Snela, M.; Rozylo, P. Investigation of an Effective Anchoring Length of CFRP Tapes Used to Strengthen Steel Thin-Walled Beams with a Rectangular Cross-Section Subjected to Four-Point Bending. Materials 2023, 16, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z. Research on the Shear Performance of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled Steel-Glued Laminated Wood Composite Beams. Buildings 2023, 13, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Cheng, S.; Diao, B. Computational analysis of shear deformation effects on open thin-walled beams. Structures 2022, 36, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.W.A.; Alsheikh, A.M.S. Theory of Flexural Shear, Bending and Torsion for a Thin-Walled Beam of Open Section. World J. Mech. 2024, 14, 23–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshenko, S.P.; Gere, J.G. Theory of Elastic Stability, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Trahair, N.S. Flexural–Torsional Buckling of Structures; E&FN SPON: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Szychowski, A.; Brzezińska, K. Local Buckling and Resistance of Continuous Steel Beams with Thin-Walled I-Shaped Cross-Sections. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.-E. Flexural–torsional buckling of thin-walled I-section composites. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.P.; Lee, J. Flexural–torsional buckling of thin-walled composite box beams. Thin-Walled Struct. 2007, 45, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asadi, A.; Sheikh, A.H.; Thomsen, O.T. Buckling behaviour of thin-walled laminated composite beams having open and closed sections subjected to axial and end moment loading. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 141, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Asgarian, B. Lateral-Torsional Stability of Axially Functionally Graded Beams with Open Sections. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2020, 56, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolghasemian, R.; Soltani, M.; Ghasemi, A.R. Evaluation of the Influence of Axial Loading on the Lateral Buckling Resistance of Tapered Laminated Composite I-Section Beam-Column. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2024, 48, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubina, D.; Ungureanu, V. Local/Distortional and overall interactive buckling of thin-walled cold-formed steel columns with open cross-section. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 182, 110172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, H.S.; Ozkan, I.; Erkmen, R.E. Buckling analysis of thin-walled I-beams with web deformations. J. Struct. 2024, 69, 107498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, W.; Shi, T.; Qu, J. Local and Distortional Interaction Buckling of Cold-Formed Thin-Walled High Strength Lipped Channel Columns. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2021, 21, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraei, A.; Pezeshky, P.; Sasibut, S.; Rong, F.; Mohareb, M. Finite element formulation for the dynamic analysis of shear deformable thin-walled beams. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 173, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Fan, X.; Lv, X. Flexural–torsional vibration of thin-walled beams with open cross sections considering the additional torsional moment. Acta Mech. 2023, 234, 6341–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Islam, M.F.A.; Jamil, S.N.S.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, A.; Alam, M.J. Analytical solution of vibration of simply supported beam under eccentric axial compressive loading. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2825, 010001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, H.; Zheng, B.; Tian, D.; He, L. Integrated Dynamic Analysis of Thin-Walled Beams: Coupled Bidirectional Bending, Torsion, and Axial Vibrations Under Axial Loads. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czechowski, L.; Kotełko, M.; Jankowski, J.; Ungureanu, V.; Sanduly, A. Strength analysis of eccentrically loaded thin-walled steel lipped C-profile columns. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2023, 69, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, D.B.; Hussein, A.B. Numerical Investigation of the Axial Load Capacity of Cold-Formed Steel Channel Sections: Effects of Eccentricity, Section Thickness, and Column Length. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezgy-Nazargah, M.; Vidal, P.; Polit, O. A quasi-3d finite element model for the analysis of thin-walled beams under axial–flexural–torsional loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 164, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkey, W.D. Analysis and Design of Elastic Beams: Computational Methods; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E.; Giunta, G.; Petrolo, M. Beam Structures, Classical and Advanced Theories; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavazza, R.; Vlak, F.; Vukasović, M. Short steel thin-walled columns subjected to eccentric axial loads. Procedia Eng. 2016, 161, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavazza, R.; Vlak, F.; Vukasović, M.; Primorac, B.B. Eccentric compressive load on short pultruded wide flange beam. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech 2023), Split–Bol, Croatia, 20–23 June 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F. Influence of the boundary constraint condition on torsional effects of thin-walled beams. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 035126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADINA 23.00.01 Theory and Modeling Guide; Bentley Systems Inc.: Exton, PA, USA, 2024.
- MATLAB, R2022b; MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022.

| Isotropic | Orthotropic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1/b2 | l/h, Line | ||||
| 2 | 3, A | 1.194 | −24.927 | 1.705 | −38.143 |
| 3, B | −0.882 | −21.423 | −5.179 | −35.332 | |
| 3, C | −1.024 | −12.452 | 3.925 | −13.196 | |
| 3, D | −0.577 | 9.316 | 7.845 | 45.177 | |
| 3, E | 16.119 | 154.525 | 12.467 | −66.598 | |
| 5, A | −0.034 | −13.671 | −0.444 | −26.924 | |
| 5, B | 0.009 | −10.889 | −1.356 | −22.430 | |
| 5, C | −0.223 | −6.607 | 1.495 | −10.540 | |
| 5, D | −0.184 | 2.140 | 0.814 | 11.656 | |
| 5, E | 0.319 | 26.918 | −9.925 | 110.506 | |
| 4 | 3, A | 1.335 | −20.917 | 1.805 | −34.170 |
| 3, B | −0.814 | −16.553 | −5.091 | −30.378 | |
| 3, C | −1.193 | −6.132 | 3.870 | −5.099 | |
| 3, D | −0.426 | 19.391 | 8.061 | 63.097 | |
| 3, E | 15.876 | 172.870 | −3.056 | 20.109 | |
| 5, A | −0.013 | −10.899 | −0.347 | −22.980 | |
| 5, B | 0.018 | −7.593 | −1.292 | −17.530 | |
| 5, C | −0.276 | −2.613 | 1.305 | −3.953 | |
| 5, D | −0.136 | 7.360 | 0.897 | 22.117 | |
| 5, E | 0.437 | 33.118 | −8.191 | 130.485 | |
| Isotropic | Orthotropic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1/b2 | l/h, Line | ||||
| 2 | 3, A | −0.814 | −15.071 | −3.582 | −30.631 |
| 3, B | −0.521 | −13.433 | −3.595 | −27.628 | |
| 3, C | 0.120 | −10.380 | 1.494 | −17.693 | |
| 3, D | −1.869 | −6.531 | −7.227 | −9.498 | |
| 3, E | −6.006 | 14.985 | −51.015 | 59.820 | |
| 5, A | −0.022 | −6.300 | −1.263 | −16.083 | |
| 5, B | 0.099 | −5.636 | −1.069 | −14.468 | |
| 5, C | −0.144 | −4.909 | 0.171 | −10.761 | |
| 5, D | −0.699 | −3.376 | −2.336 | −7.052 | |
| 5, E | −1.190 | 3.976 | −9.132 | 13.187 | |
| 4 | 3, A | 0.372 | −7.298 | −3.245 | −28.305 |
| 3, B | 0.628 | −7.737 | −3.189 | −24.613 | |
| 3, C | −0.117 | −10.001 | 1.880 | −13.306 | |
| 3, D | −6.440 | −23.444 | −6.117 | −1.889 | |
| 3, E | 7.357 | 12.674 | −44.306 | 85.724 | |
| 5, A | 1.456 | −1.638 | −1.071 | −14.218 | |
| 5, B | 1.518 | −1.904 | −0.866 | −12.142 | |
| 5, C | −0.054 | −4.188 | 0.249 | −7.759 | |
| 5, D | −7.580 | −15.333 | −1.809 | −2.165 | |
| 5, E | 9.554 | 12.313 | −6.798 | 23.730 | |
| Isotropic | Orthotropic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1/b2 | l/h, Line | ||||
| 2 | 3, A | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.057 | 0.414 |
| 3, C | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.032 | 0.147 | |
| 3, E | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.208 | 0.118 | |
| 3, F | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.169 | |
| 3, G | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.067 | 0.145 | |
| 5, A | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.046 | 0.564 | |
| 5, C | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.058 | 0.327 | |
| 5, E | 0.023 | 0.011 | 0.405 | 0.154 | |
| 5, F | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.220 | |
| 5, G | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.046 | 0.277 | |
| 4 | 3, A | 0.004 | 0.020 | 0.052 | 0.373 |
| 3, C | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.030 | 0.106 | |
| 3, E | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.210 | 0.160 | |
| 3, F | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.026 | 0.189 | |
| 3, G | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.027 | 0.157 | |
| 5, A | 0.005 | 0.021 | 0.046 | 0.496 | |
| 5, C | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.055 | 0.235 | |
| 5, E | 0.023 | 0.016 | 0.400 | 0.195 | |
| 5, F | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.036 | 0.205 | |
| 5, G | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.037 | 0.180 | |
| Isotropic | Orthotropic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b1/b2 | l/h, Line | ||||
| 2 | 3, A | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.043 | 0.438 |
| 3, C | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.040 | 0.268 | |
| 3, E | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.087 | 0.191 | |
| 3, F | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.032 | 0.168 | |
| 3, G | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.040 | 0.139 | |
| 5, A | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.072 | 0.422 | |
| 5, C | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.060 | 0.402 | |
| 5, E | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.138 | 0.391 | |
| 5, F | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.042 | 0.170 | |
| 5, G | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.039 | 0.217 | |
| 4 | 3, A | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.041 | 0.418 |
| 3, C | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.042 | 0.243 | |
| 3, E | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.094 | 0.164 | |
| 3, F | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.046 | 0.176 | |
| 3, G | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.043 | 0.153 | |
| 5, A | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.067 | 0.409 | |
| 5, C | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.065 | 0.369 | |
| 5, E | 0.021 | 0.010 | 0.190 | 0.308 | |
| 5, F | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.065 | 0.150 | |
| 5, G | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.049 | 0.166 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bužančić Primorac, B.; Vukasović, M.; Pavazza, R.; Vlak, F. An Analytical Solution for Short Thin-Walled Beams with Monosymmetric Open Sections Subjected to Eccentric Axial Loading. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030068
Bužančić Primorac B, Vukasović M, Pavazza R, Vlak F. An Analytical Solution for Short Thin-Walled Beams with Monosymmetric Open Sections Subjected to Eccentric Axial Loading. Applied Mechanics. 2025; 6(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleBužančić Primorac, Branka, Marko Vukasović, Radoslav Pavazza, and Frane Vlak. 2025. "An Analytical Solution for Short Thin-Walled Beams with Monosymmetric Open Sections Subjected to Eccentric Axial Loading" Applied Mechanics 6, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030068
APA StyleBužančić Primorac, B., Vukasović, M., Pavazza, R., & Vlak, F. (2025). An Analytical Solution for Short Thin-Walled Beams with Monosymmetric Open Sections Subjected to Eccentric Axial Loading. Applied Mechanics, 6(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030068




