Influence of Lubricant Properties on Elastohydrodynamic Oil Film Thickness in Angular Contact Ball Bearings: A Numerical Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
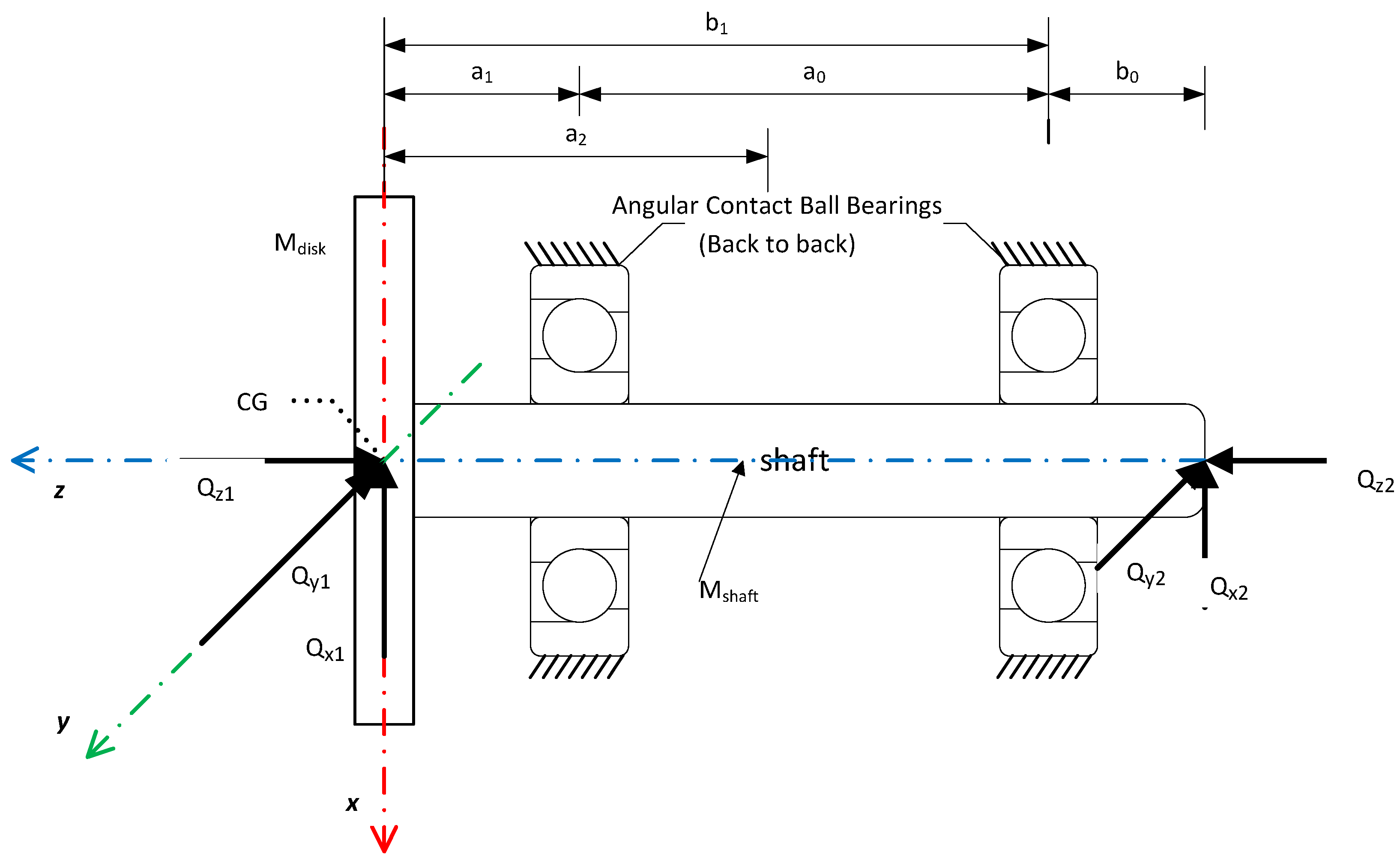
2. Model of Overhung Disc–Shaft–Ball Bearing System
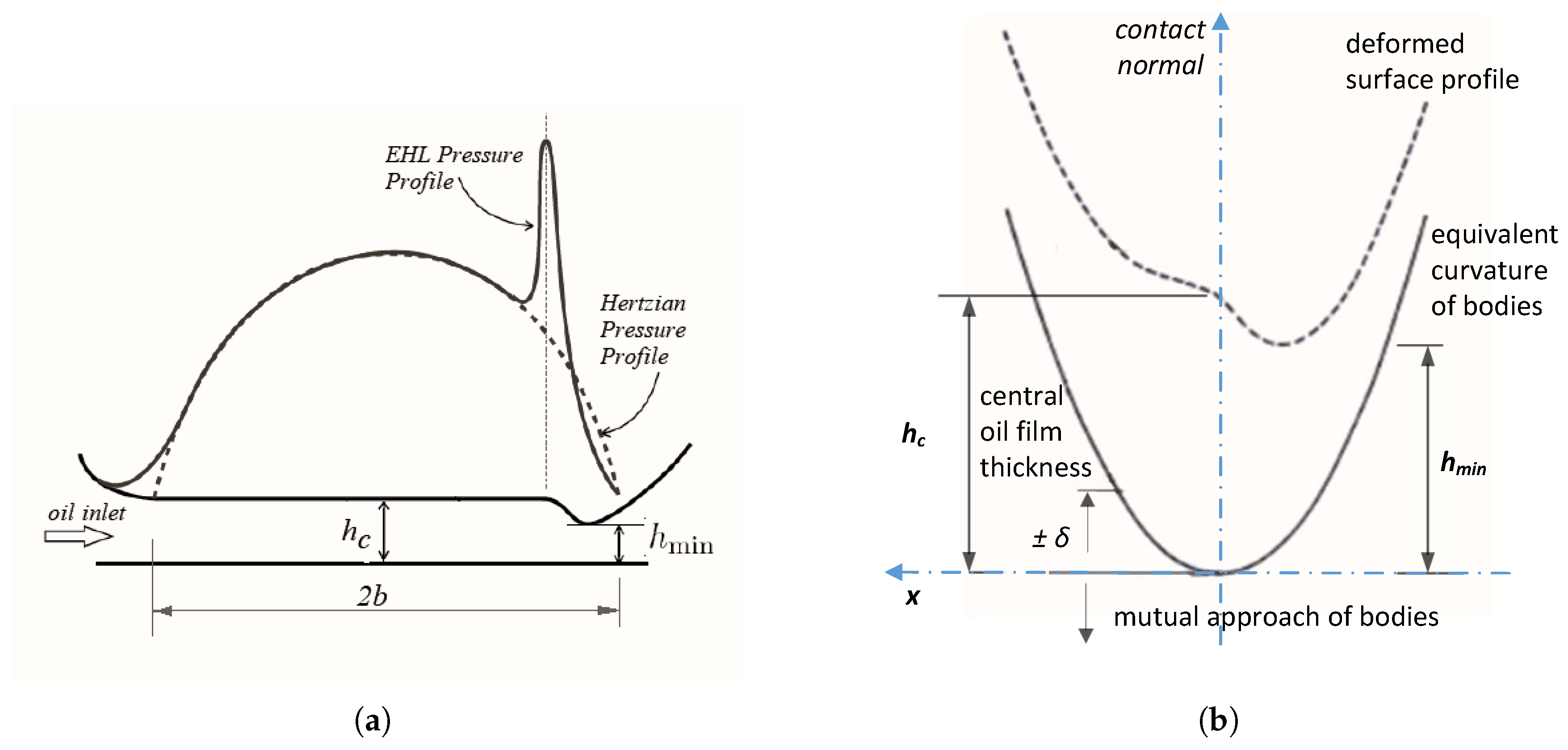
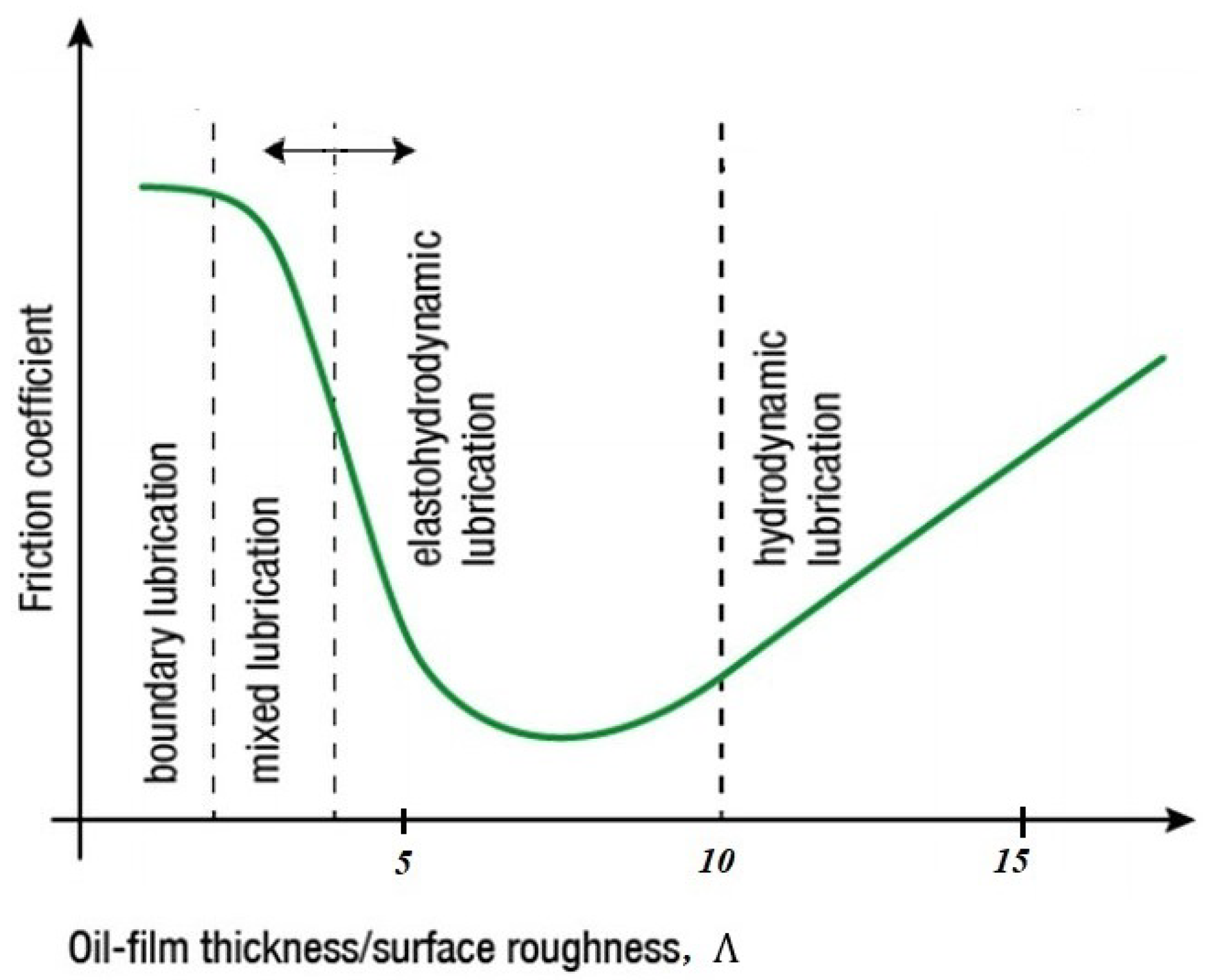
3. Results of Numerical Analyses and Discussion
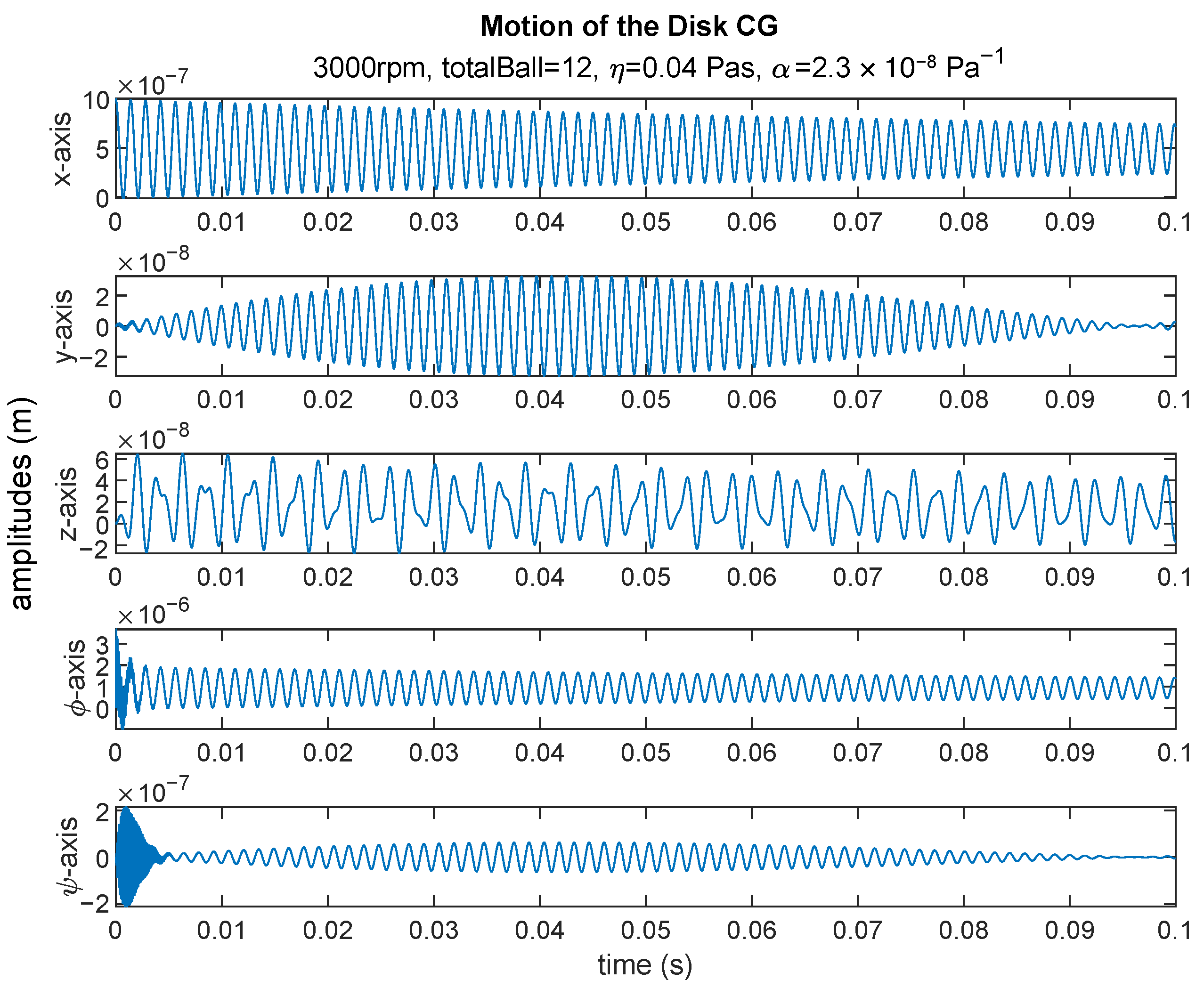
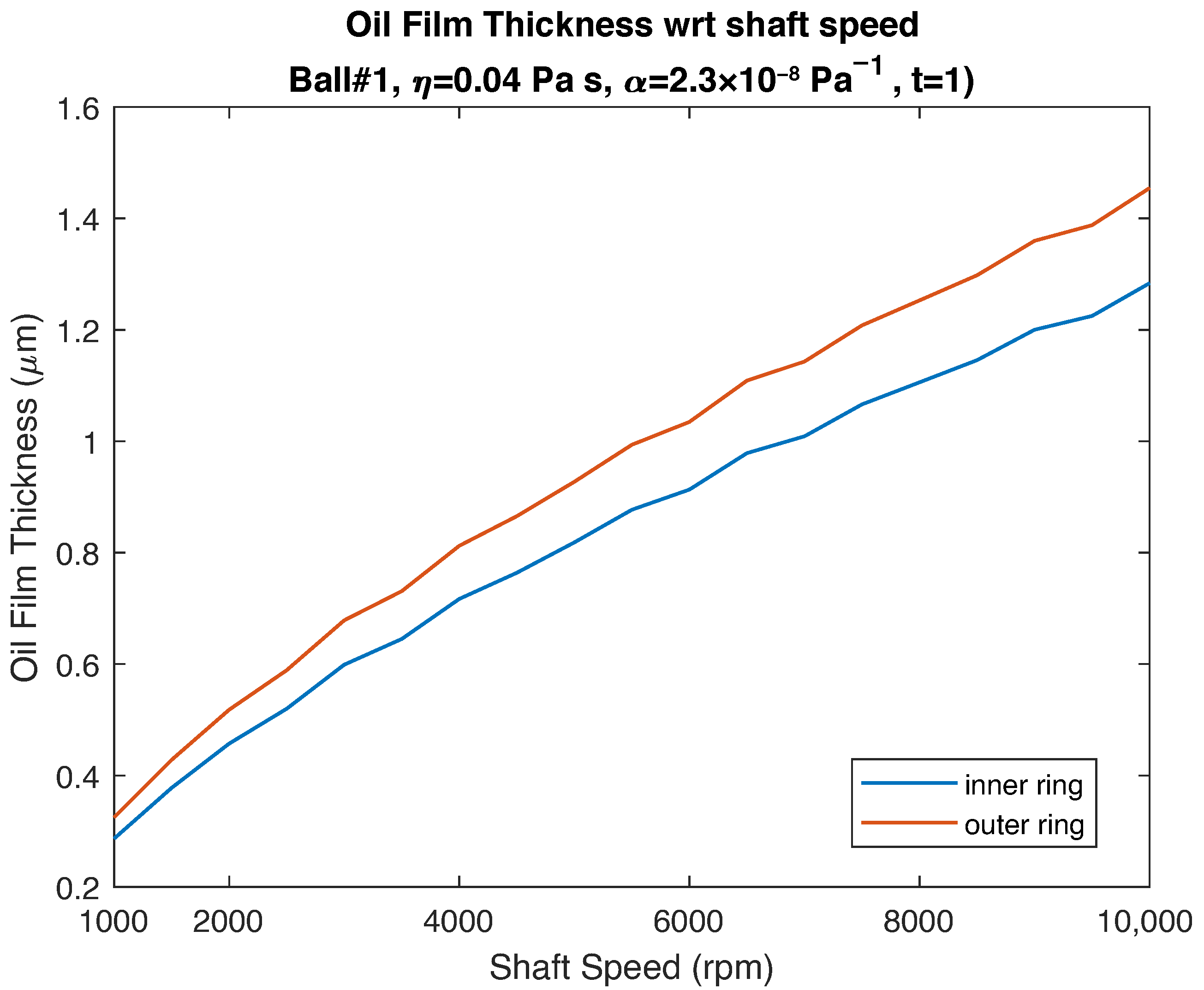
3.1. Effect of the Speed on Oil Film Thickness
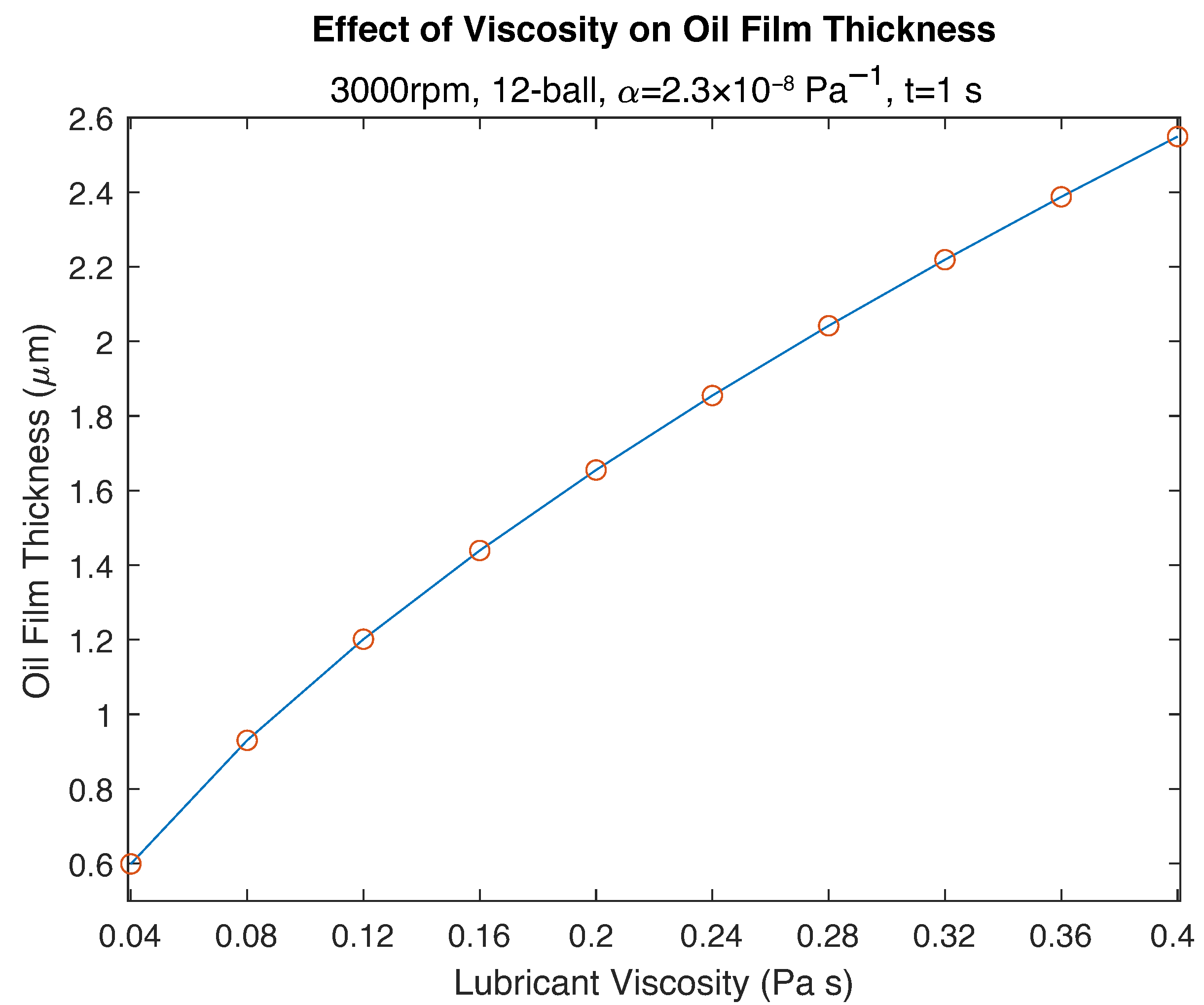
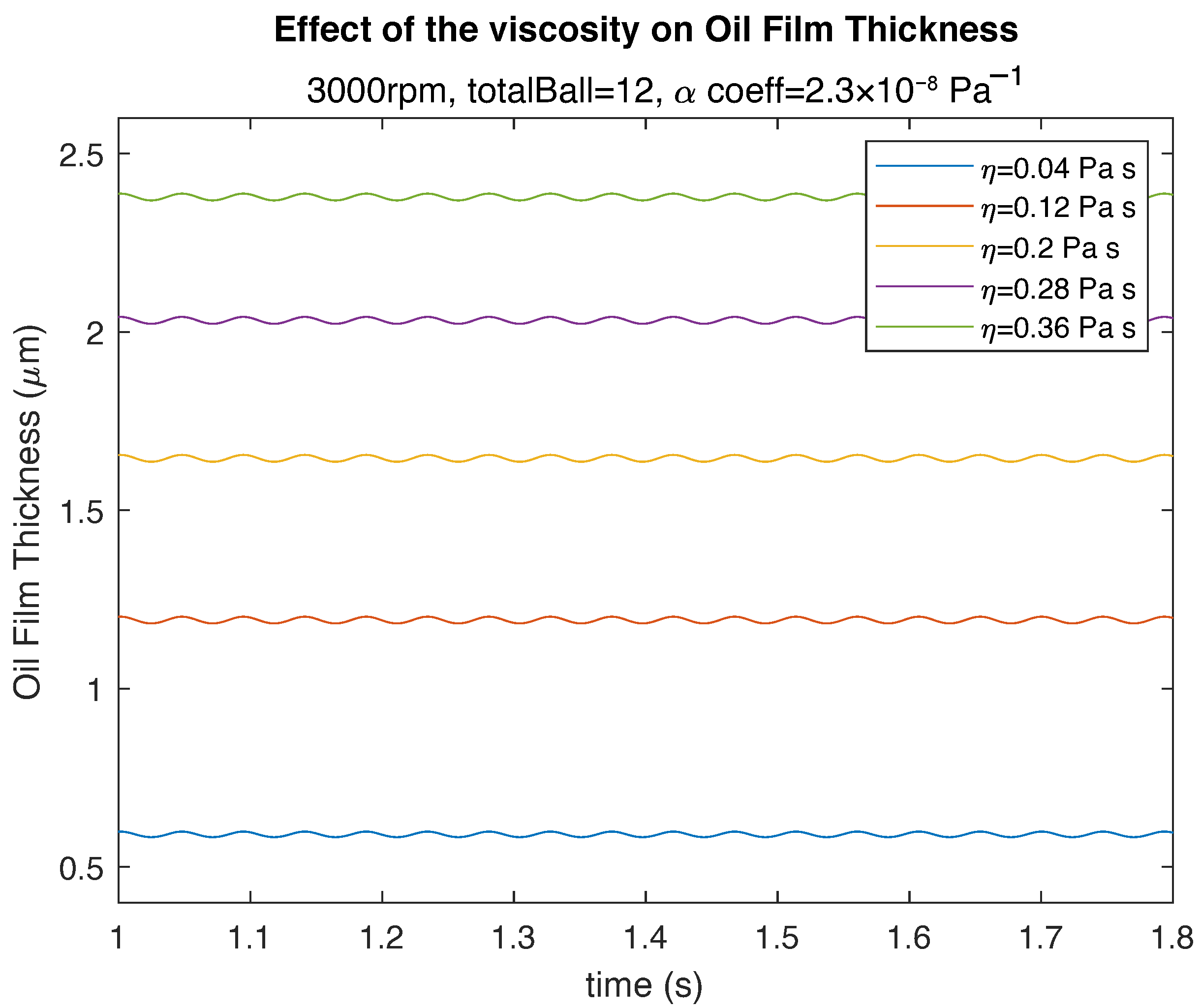
3.2. Effect of Viscosity
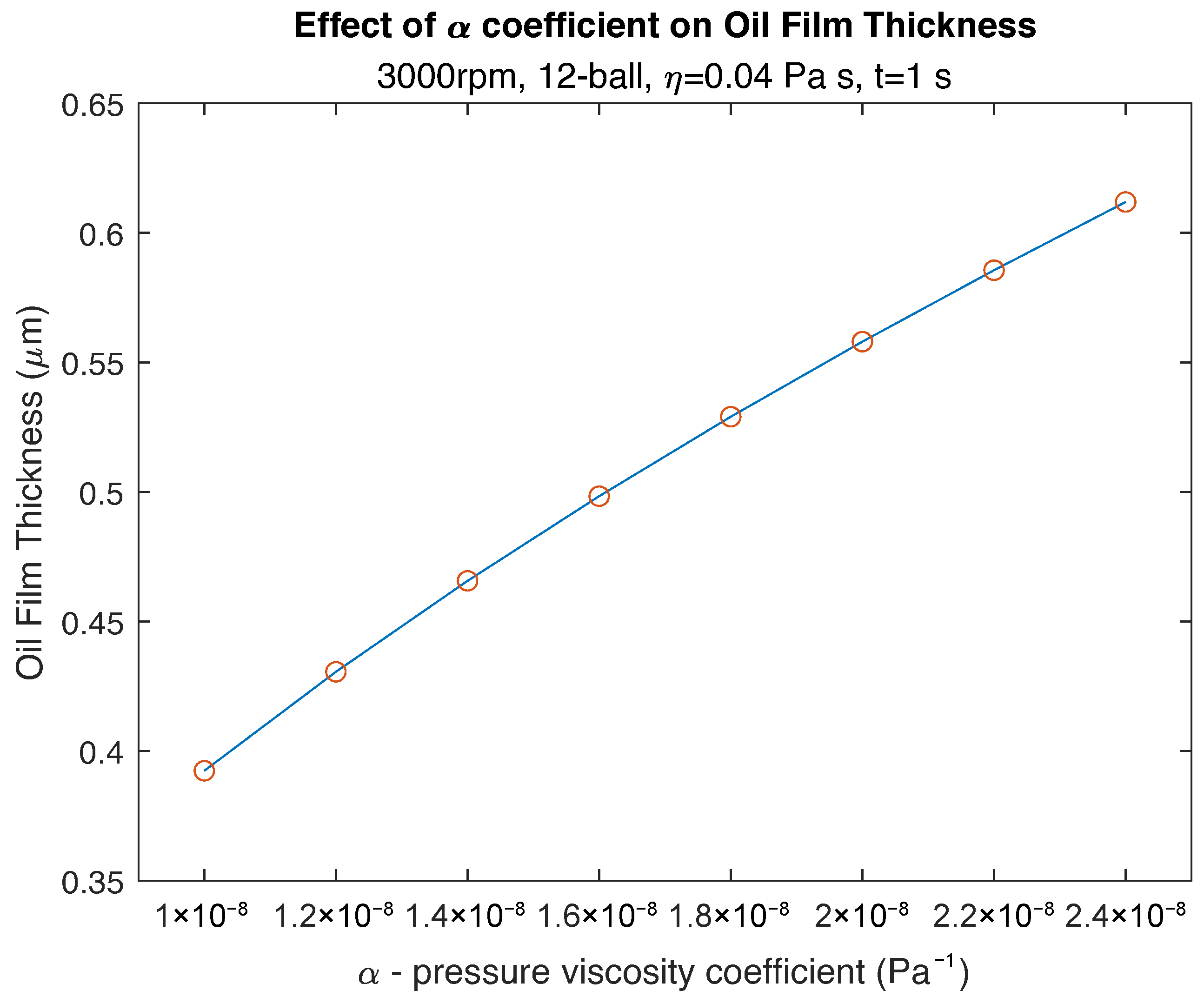
3.3. Effect of Pressure-Viscosity Coefficient
4. Conclusions
- Oil film continuously altering at the ball–raceway contact during the rotation of shaft,
- A twofold increase in shaft speed leads to an approximate 57% increase in oil film thickness,
- Oil film in the outer raceway is approximately 13% thicker than that in the inner raceway,
- The effect of viscosity on lubricant film thickness is nonlinear; a twofold increase in viscosity induce nearly 54% increase in oil film thickness.
- Similarly, a twofold increase in the pressure–viscosity coefficient causes a 42% increase in oil film thickness.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EHL | ElastoHydrodynamicLubrication |
| EHD | ElastoHydroDynamic |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| FDM | Finite Difference Method |
| EOM | Equations of Motion |
| CG | Center of Gravity |
| DoF | Degree of Freedom |
| LHS | Left Hand Side |
| RHS | Right Hand Side |
References
- Hamrock, B.J.; Schmid, S.R.; Jacobson, B.O. Fundamentals of Fluid Film Lubrication, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Dowson, D. Ball Bearing Lubrication: The eLastohydrodynamics of Elliptical Contacts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Khonsari, M.M.; Booser, E.R. Applied Tribology: Bearing Design and Lubrication; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A.G.W. The Principles of Lubrication; Longman: London, UK, 1966; ISBN 9780582528804. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrock, B.; Dowson, D. Isothermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Point Contacts I—Theoretical Formulation. NASA TN D-8049; 1975; p. 33. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19750022492 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Hamrock, B.; Dowson, D. Isothermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Point Contacts III—Fully Flooded Results. NASA TN D-8317; 1976; p. 33. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19770004457 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Roelands, C.J.A. Correlational Aspects of the viscOsity-Temperature-Pressure Relationship of Lubricating Oils. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Khonsari, M.M.; Booser, E.R. Proper film thickness key to bearing survival. Mach. Des. 2006, 78, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, T.A.; Kotzalas, M.N. Advanced Concepts of Bearing Technology: Rolling Bearing Analysis, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2270; Standard Practice for Calculating Viscosity Index from Kinematic Viscosity at 40 and 100 °C. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Qing, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, S. The effect of lubricant temperature on dynamic behavior in angular contact ball bearings. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 149, 103832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarey, M.J.; Gonçalves, D.E.; Liñeira Del Río, J.M.; Comuñas, M.J.; Fernández, J.; Seabra, J.H. Lubricant properties of trimethylolpropane trioleate biodegradable oil: High pressure density and viscosity, film thickness, Stribeck curves and influence of nanoadditives. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Fan, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Z. Experimental investigation of the film behavior in a model rolling bearing. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, P.; Li, X.; Jin, X.; Tian, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Yan, X. Effects of Oil and Solid Body Temperatures on Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Film Formation. Lubricants 2024, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLaren, A.; Kadiric, A. Elastohydrodynamic Traction and Film Thickness at High Speeds. Tribol. Lett. 2024, 72, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnejat, H.; Gohar, R. The Vibrations of Radial Ball Bearings. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1985, 199, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofi, A. Oil Film Thickness and Pressure Distribution in Elastohydrodynamic Elliptical Contacts. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering Imperial College of Science and Technology University of London, London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hirani, H.; Rao, T.; Athre, K.; Biswas, S. Rapid performance evaluation of journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 1997, 30, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hashimoto, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Kaneta, M. Pure rolling elastohydrodynamic lubrication of short stroke reciprocating motion. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnant, Y.H.; Wensing, J.A.; Nijen, G.C. The influence of lubrication on the dynamic behaviour of ball bearings. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 222, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, P.; Nijen, J.; van Nijen, G.C. Rolling bearing damping for dynamic analysis of multi-body systems—Experimental and theoretical results. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2000, 214, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Glovnea, R. An experimental investigation of grease lubricated EHD contact subjected to normal sinusoidally variable loading. Tribol. Int. 2020, 147, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Deng, Y. Effects of oil film thickness and viscosity on the performance of misaligned journal bearings with couple stress lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, P.; Meijer, R.J.; Osara, J.A.; Pasaribu, R.; Lugt, P.M. Vibrations and film thickness in grease-lubricated deep groove ball bearings. Tribol. Int. 2024, 193, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.C.; Doranga, S.; Li, Y.; Khanal, M. System Identification and Dynamic Analysis of the Propulsion Shaft Systems Using Response Surface Optimization Technique. Appl. Mech. 2024, 5, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.; Jian, Y.; Li, W. A method for the dynamic characteristic analysis of a rotor-rolling bearing system influenced by elastohydrodynamic lubrication. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 608, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkovich, A.; Perfilyev, V.; Gorni, D.; Lapsker, I.; Rapoport, L. The effect of Cu grain size on transition from EHL to BL regime (Stribeck curve). Wear 2011, 271, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chang, L. Some insights into asperity temperatures in mixed-film lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2001, 34, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Khonsari, M.M. On the lift-off speed in journal bearings. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 20, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.z.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.z.; Wang, H. Effect of surface roughness parameters on mixed lubrication characteristics. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Marian, M.; Tremmel, S.; Wartzack, S. Numerical Modeling of Wear in a Thrust Roller Bearing under Mixed Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. Lubricants 2020, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; He, T.; Gu, L.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y. Investigation on the angular contact ball bearings under low speed and heavy load with coupled mixed lubrication and quasi-dynamic analysis. Lubr. Sci. 2020, 32, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, M.; Diab, Y.; Cavoret, J.; Majdoub, F.; Changenet, C.; Ville, F. An Experimental Study on the Impact of Roughness Orientation on the Friction Coefficient in EHL Contact. Lubricants 2025, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, J.; El Hajj, A.; Vergne, P.; Habchi, W. Machine Learning for Film Thickness Prediction in Elastohydrodynamic Lubricated Elliptical Contacts. Lubricants 2023, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Bhushan, B. Role of fractal geometry in roughness characterization and contact mechanics of surfaces. J. Tribol. 1990, 112, 205–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.A. Oil flow in plain steadily loaded journal bearings: Realistic predictions using rapid techniques. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 1998, 212, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzakkir, S.M.; Hirani, H.; Thakre, G.D.; Tyagi, M.R. Tribological failure analysis of journal bearings used in sugar mills. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H.; Akturk, N. Vibration modeling of wind turbine shaft as rigid shaft supported by EHL contact ball bearings with overhung disc system. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacay, T.; Akturk, N. Vibrations of a grinding spindle supported by angular contact ball bearings. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2008, 222, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofi, A.; Gohar, R. Oil Film Thickness and Pressure Distribution in Elastohydrodynamic Point Contacts. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1982, 24, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Liu, M.; Song, C. Oil film stiffness and damping in an elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact-vibration. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 3031–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrecht, A. The Numerical Solution of the Elastohydrodynamically Lubricated Line- and Point Contact Problem, Using Multigrid Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Koninklijke Bibliotheek, Den Haag, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, T.A. An Analytical Method to Predict Skidding in Thrust-Loaded, Angular-Contact Ball Bearings. J. Lubr. Technol. 1971, 93, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, J.F.; Visa, C.; Sauvey, C. Approximate Analytical Model for Hertzian Elliptical Contact Problems. J. Tribol. 2006, 128, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H.; Ateş, K.; Karaçay, T.; Aktürk, N. Effect of Preload on the Vibrations of EHL Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Theoretical and Experimental Results. Lubricants 2022, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiu, G.D.; Gafitanu, M.D. Dynamic characteristics of high speed angular contact ball bearings. Wear 1997, 211, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H. Rüzgâr Türbinlerinde Kullanılan ElastoHidrodinamik Yağlamalı Rulmanların Dinamik Davranışının İncelenmesi. (Investigation of Dynamic Behaviour of Elasto-Hydrodynamic Lubricated Rolling Bearing Using in Wind Turbines). Ph.D. Thesis, The Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, D.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, C. Design and optimization of a temperature controller with low overshoot, fast respond and high COP based on water-source thermoelectric heat pump. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 242, 122473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Noda, N.A.; Takaki, R.; Sano, Y. Intensity of singular stress fields (ISSFs) in micro-bond test in comparison with ISSFs in pull-out test. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 183, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Step | Operation |
|---|---|
| step 1 | Start |
| step 2 | Input system data, operating conditions, time span, material properties, and initial conditions (as listed in Table 2 and Table 3). |
| step 3 | Perform initial calculations for the parameters in the equations of motion (EoM), including contact characteristics based on the initial conditions. |
| step 4 | Solve the EoM (Equation (4)) using the Runge–Kutta method with a constant time step. |
| step 5 | Calculate the oil film thickness along the contact normal direction, mutual approach, elastic deformation, and contact force for each ball at every time step, considering shaft rotation and position of each ball by solving Equations (1)–(3) using a quasi-static approach. Apply convergence tolerance as for Newton–Raphson method. [Subroutine] |
| step 6 | Compute the 5-DoF positions and velocities of the disc’s center of gravity (CG). |
| step 7 | If the time vector is complete, finalize the EoM calculations; otherwise, return to Step 4. |
| step 8 | Save the results. |
| step 9 | End |
| Disc | Shaft | 12 Ball–Angular Contact Ball Bearing (1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Value | Parameter | Value |
| Diameter | 0.1 m | 0.04 m | Outer Raceway Diameter | 0.061933 m |
| Length | – | 0.55 m | Outer Ring Diameter | 0.068 m |
| Mass | 5.5 kg | 0 | Inner Ring Diameter | 0.04 m |
| Configuration Geometry | = 0.05 m | = 0.275 m | Inner Raceway Diameter | 0.046038 m |
| = 0.55m | = 0.6 m | |||
| Ball Diameter | 0.0079375 m | |||
| Case Study | Simulation | Shaft Speed (RPM) | Preload (N) | Viskozite (Pa s) | Presure-Viskozite Coeff. (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–19 | 1 | [1000:500:10,000] | 100 | 0.04 | |
| 20–30 | 2 | 3000 | 100 | [0.04:0.04:0.4] | |
| 31–38 | 3 | 3000 | 100 | 0.04 | :: |
| Shaft Speed (rpm) | 1500 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 | 6000 | 8000 | 10,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Ring (m) | 0.3778 | 0.4572 | 0.5988 | 0.7169 | 0.8183 | 0.9132 | 1.1057 | 1.2838 |
| Outer Ring (m) | 0.4280 | 0.5180 | 0.6785 | 0.8122 | 0.9272 | 1.0347 | 1.2528 | 1.4545 |
| Lubricant Viscosity (Pa s) | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.2 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.4 |
| Lubricant Viscosity * (cSt) | 47.1 | 94.1 | 141.2 | 235.3 | 288.4 | 376.5 | 470.6 |
| Oil Film Thickness (m) | 0.5988 | 0.9302 | 1.2014 | 1.6551 | 1.8547 | 2.219 | 2.5492 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bal, H. Influence of Lubricant Properties on Elastohydrodynamic Oil Film Thickness in Angular Contact Ball Bearings: A Numerical Investigation. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030064
Bal H. Influence of Lubricant Properties on Elastohydrodynamic Oil Film Thickness in Angular Contact Ball Bearings: A Numerical Investigation. Applied Mechanics. 2025; 6(3):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleBal, Hikmet. 2025. "Influence of Lubricant Properties on Elastohydrodynamic Oil Film Thickness in Angular Contact Ball Bearings: A Numerical Investigation" Applied Mechanics 6, no. 3: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030064
APA StyleBal, H. (2025). Influence of Lubricant Properties on Elastohydrodynamic Oil Film Thickness in Angular Contact Ball Bearings: A Numerical Investigation. Applied Mechanics, 6(3), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6030064





