The Mechanics of Synchronization: From Phase Modulation to Elliptical Gears with Quasi-Relativistic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Order Reduction in Driven Self Sustained Oscillations: The Phase Oscillator Model
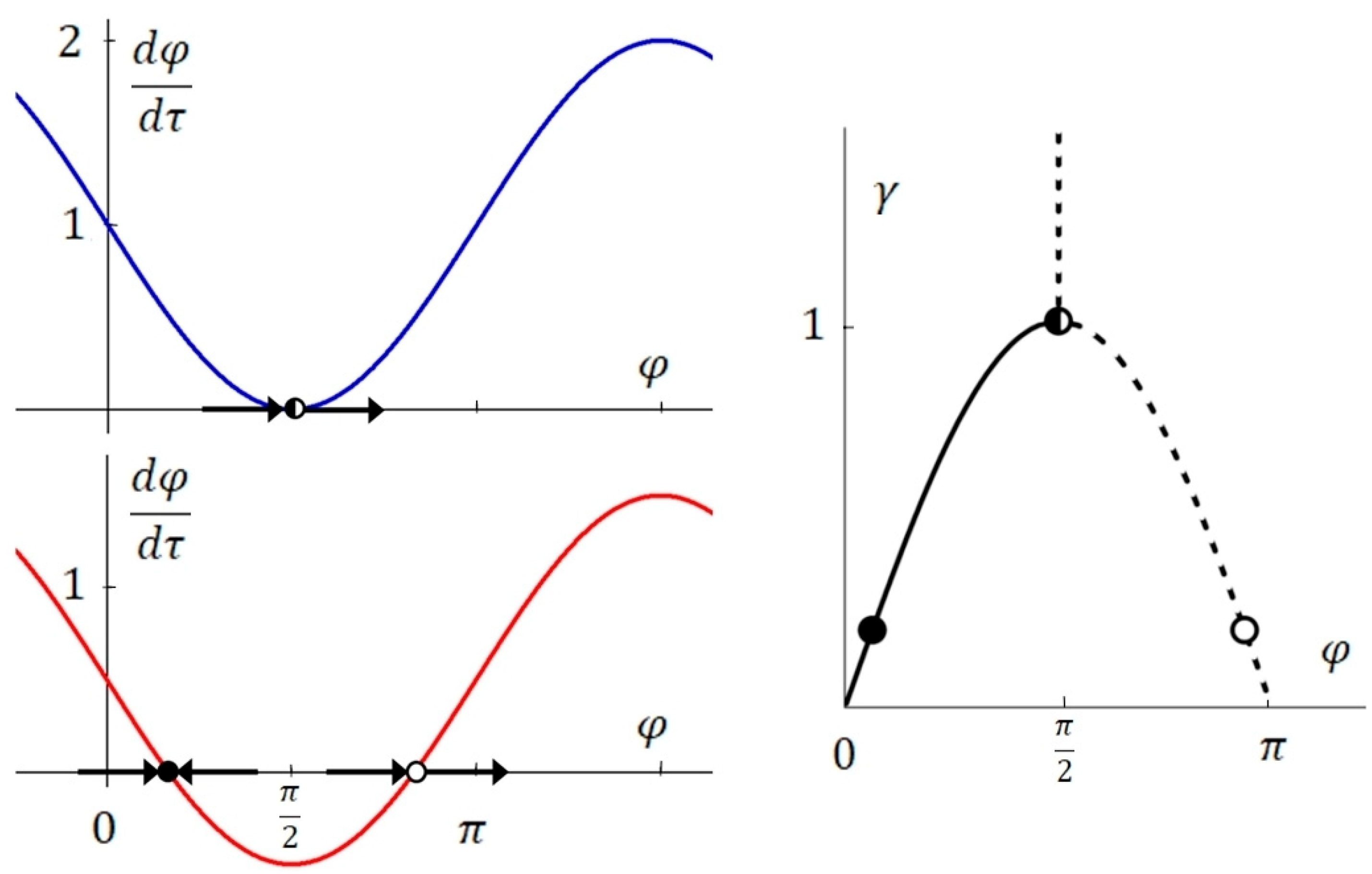
3. Adler-Type Equations: Analytical Solutions
3.1. Integral of the Adler Equation in the Original Form
3.2. Integral of the Adler Equation in the Cos Form
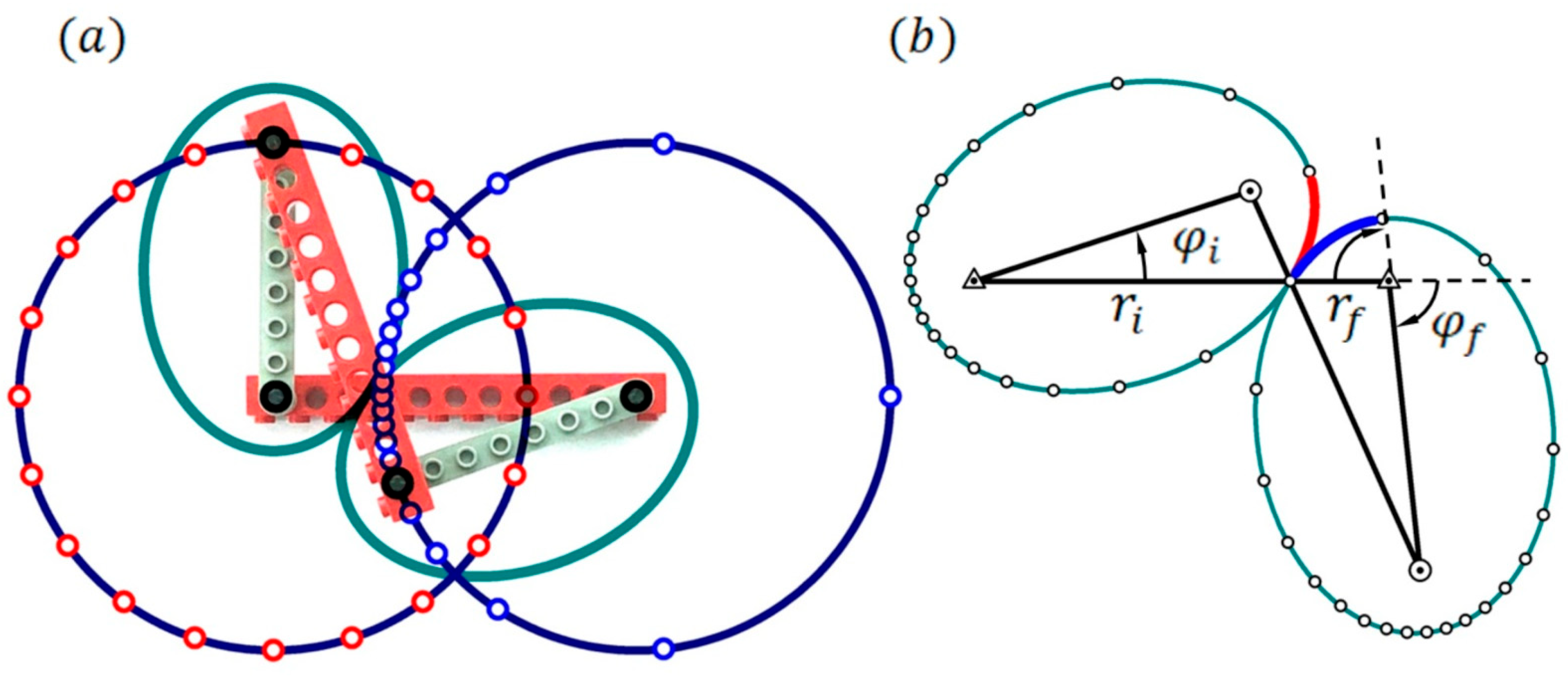
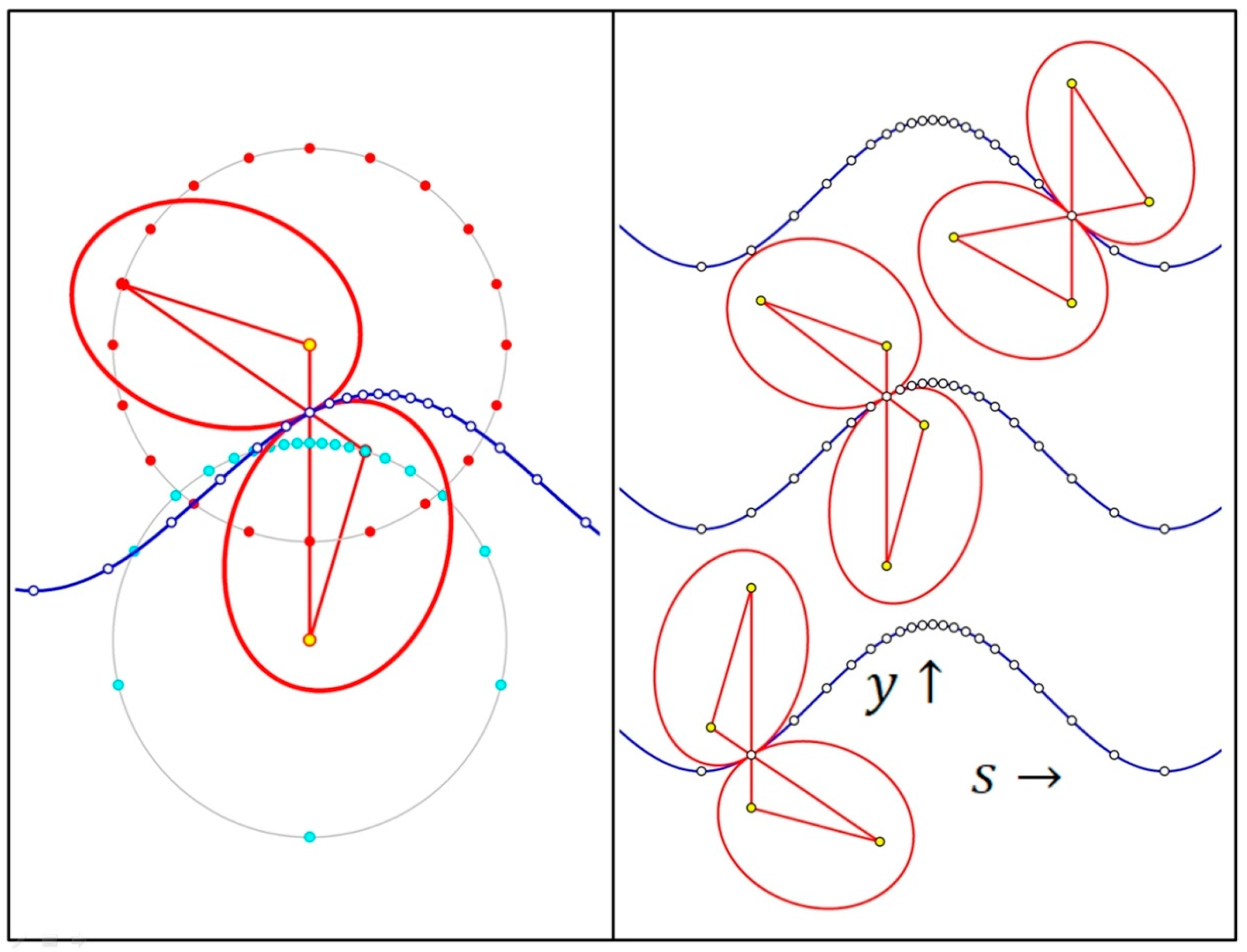
4. Phase Modulation and Elliptical Gear Kinematics: The Common Theoretical Core
4.1. Identifying an Adler-Type Differential Equation in Elliptical Gear Kinematics
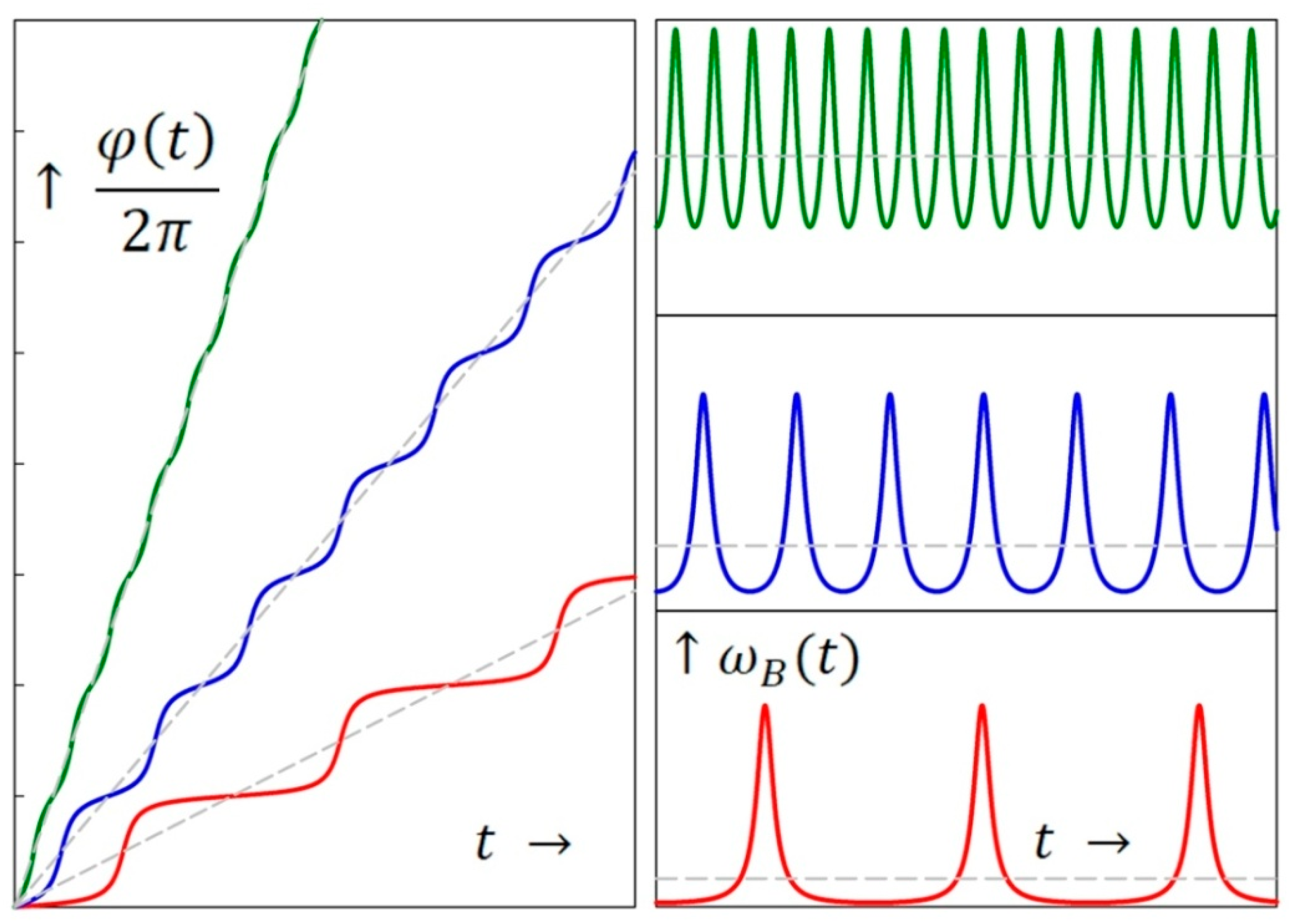
4.2. Gear Kinematics, Phase Modulation and Comb Spectra
5. Gear Kinematics: Nonuniform Rack Motion from Phase Modulation
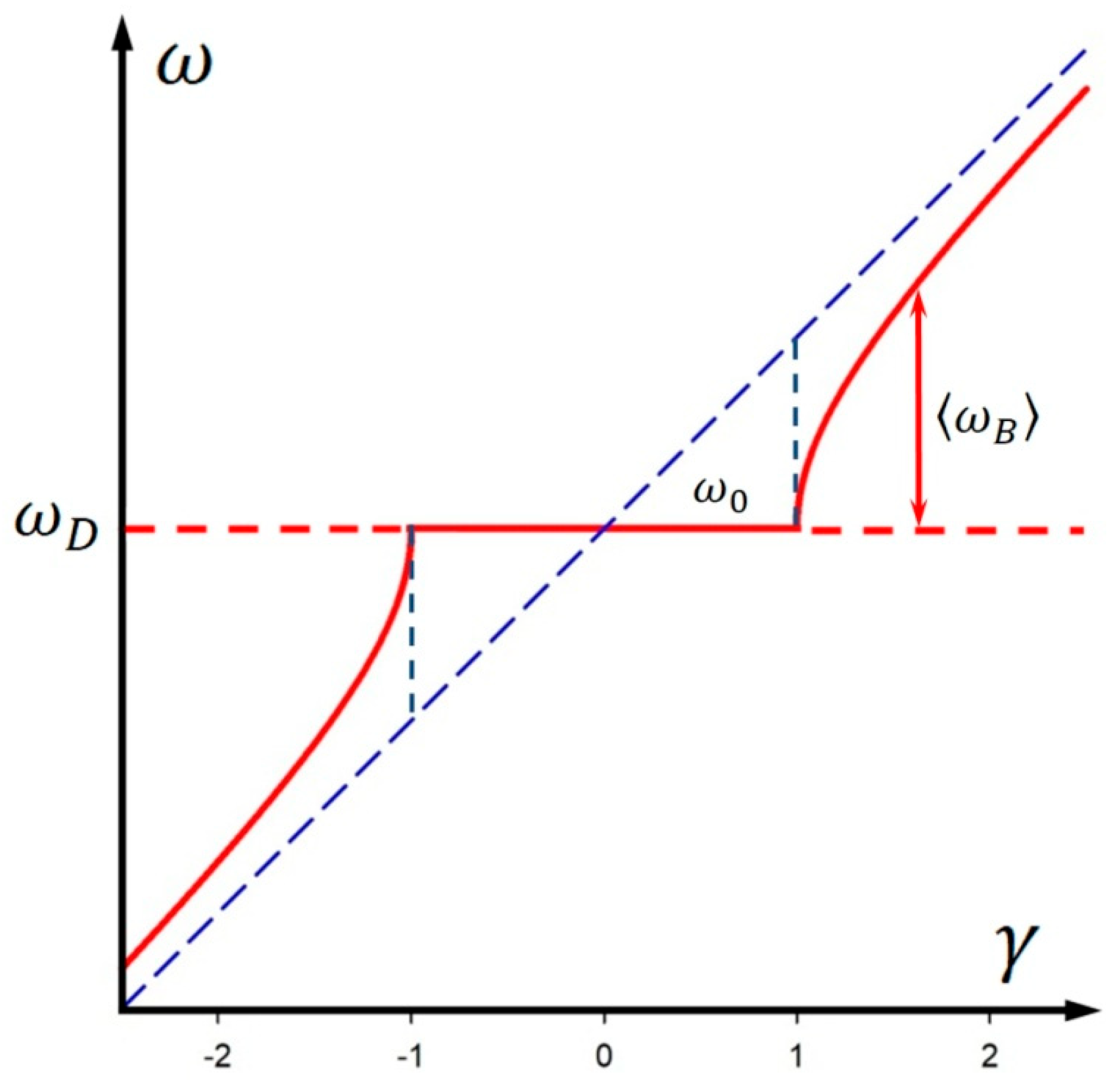
6. Beyond Classical Mechanics: Quasi-Relativistic Properties of Phase Modulation and Elliptical Gear Kinematics
6.1. Summary of Relevant Relativistic and Quantum Correspondences
6.2. Quasi-Relativistic Properties of Rack Propagation in the Gear Model
6.3. Conformity with Quantum Uncertainty
7. Conclusions and Outlook: The Heuristic Role of Mechanical Models Between Intuition and Abstraction
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pikovsky, A.; Rosenblum, M.; Kurths, J. Synchronization: A Universal Concept in Nonlinear Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Balanov, A.; Janson, N.; Postnov, D.; Sosnovtseva, O. Synchronization: From Simple to Complex; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Strogatz, S. Sync: The Emerging Science of Spontaneous Order; Hyperion: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Winfree, A.T. The Geometry of Biological Time; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gros, C. Complex and Adaptive Dynamical Systems, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Strogatz, S.H. Sync: How Order Emerges from Chaos in the Universe, Nature, and Daily Life; Hachette: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, B. A study of injection locking and pulling in oscillators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, K. Injection locking of microwave solid-state oscillators. Proc. IEEE 1973, 61, 1386–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegman, A.E. Lasers; University Science Books: Herndon, VA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Paterno, G. Physics and Applications of the Josephson Effect; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Klinger, T.; Piel, A.; Seddighi, F.; Wilke, C. Van der Pol dynamics of ionization waves. Phys. Lett. A 1993, 182, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershkov, S.; Leshchenko, D. On the stability of Laplace resonance for Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede). An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2021, 93, e20201016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, S.; Nunnenkamp, A.; Bruder, C. Quantum synchronization of a driven self-sustained oscillator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 094102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.; Nunnenkamp, A.; Bruder, C. Quantum synchronization of two Van der Pol oscillators. Ann. Phys. 2015, 527, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, G.M.; Jäger, S.B.; Shankar, A. Quantum synchronization and dissipative quantum sensing. Phys. Rev. A 2025, 111, 012410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R. A study of locking phenomena in oscillators. Proc. IRE 1946, 34, 351–357, reprinted in Proc. IEEE 1973, 61, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramoto, Y. Self-entrainment of a population of coupled nonlinear oscillators. In International Symposium on Mathematical Problems in Theoretical Physics; Araki, H., Ed.; Lecture Notes Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; Volume 39, pp. 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Acebrón, J.A.; Spigler, R. The remote control and beyond: The legacy of Robert Adler. SIAM News 2007, 40, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, M. Universal synchronization: Acoustic experiments, the phase oscillator model and mechanical analogues. Eur. J. Phys. 2024, 45, 023003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, N.M.; Bogoliubov, N.N. Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Hänggi, P.; Riseborough, P. Dynamics of nonlinear dissipative oscillators. Am. J. Phys. 1983, 51, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.A. Saddle-node bifurcation. Scholarpedia 2006, 1, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liengme, B.V. Modeling Physics with Microsoft Excel; Morgan & Claypool: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Buonomo, A.; Schiavo, A.L. Remarks on the Adler’s equation. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (ECCTD), Trondheim, Norway, 24–26 August 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, R.; Giordano, A.; D’Acunto, I. Mechanical analog of an over-damped Josephson junction. Eur. J. Phys. 2015, 36, 055042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Litvin, F.L.; Fuentes-Aznar, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, I.; Hayasaka, K. Noncircular Gears: Design and Generation; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Jain, N.K.; Laubscher, R. Advanced Gear Manufacturing and Finishing: Classical and Modern Processes; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jameson, G.J.O. Inequalities for the perimeter of an ellipse. Math. Gaz. 2014, 98, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostol, T.M.; Mnatsakanian, M.A. Unwrapping curves from cylinders and cones. Am. Math. Mon. 2007, 114, 388–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindler, W. Relativity: Special, General, and Cosmological; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fraundorf, P. A one-map two-clock approach to teaching relativity in introductory physics. arXiv 1996, arXiv:9611. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, U. Relativistic rocket and space flight. Acta Astronaut. 2006, 59, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerschmitt, D.G. Relativistic timekeeping, motion, and gravity in distributed systems. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1511–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Broglie, L. Ondes et quanta. Comptes Rendus Acad. Sci. 1923, 177, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- de Broglie, L. Recherches sur la théorie des quanta. Ann. Phys. 1925, 3, 22–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoman, D.; Dragoman, M. Quantum-Classical Analogies; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D. Classical Dynamics and Its Quantum Analogues; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet, M.J.; Weinfurtner, S.; König, F. The next generation of analogue gravity experiments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.R.; Jacquet, M.J. Analogue gravity and the Hawking effect: Historical perspective and literature review. Eur. Phys. J. H 2023, 48, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, M. The mechanics of creative cognition: Orchestrating the productive interplay of procedural and conceptual knowledge in STEM education. Proc. Singap. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 15, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, O.M. From Electromagnetism to the electromagnetic field: The genesis of Maxwell’s equations [Historical Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2014, 56, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phase Modulation and Elliptical Gear Model | Relativistic Correspondence |
|---|---|
| relative detuning with as reference level | Lorentz factor |
| critical detuning | particle at rest with |
| average beat frequency | average momentum = |
| dispersion relation | dispersion relation |
| one timescale | two timescales: and |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Euler, M. The Mechanics of Synchronization: From Phase Modulation to Elliptical Gears with Quasi-Relativistic Properties. Appl. Mech. 2025, 6, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6020037
Euler M. The Mechanics of Synchronization: From Phase Modulation to Elliptical Gears with Quasi-Relativistic Properties. Applied Mechanics. 2025; 6(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleEuler, Manfred. 2025. "The Mechanics of Synchronization: From Phase Modulation to Elliptical Gears with Quasi-Relativistic Properties" Applied Mechanics 6, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6020037
APA StyleEuler, M. (2025). The Mechanics of Synchronization: From Phase Modulation to Elliptical Gears with Quasi-Relativistic Properties. Applied Mechanics, 6(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/applmech6020037






