Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability of the Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Black Sea Inner Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data
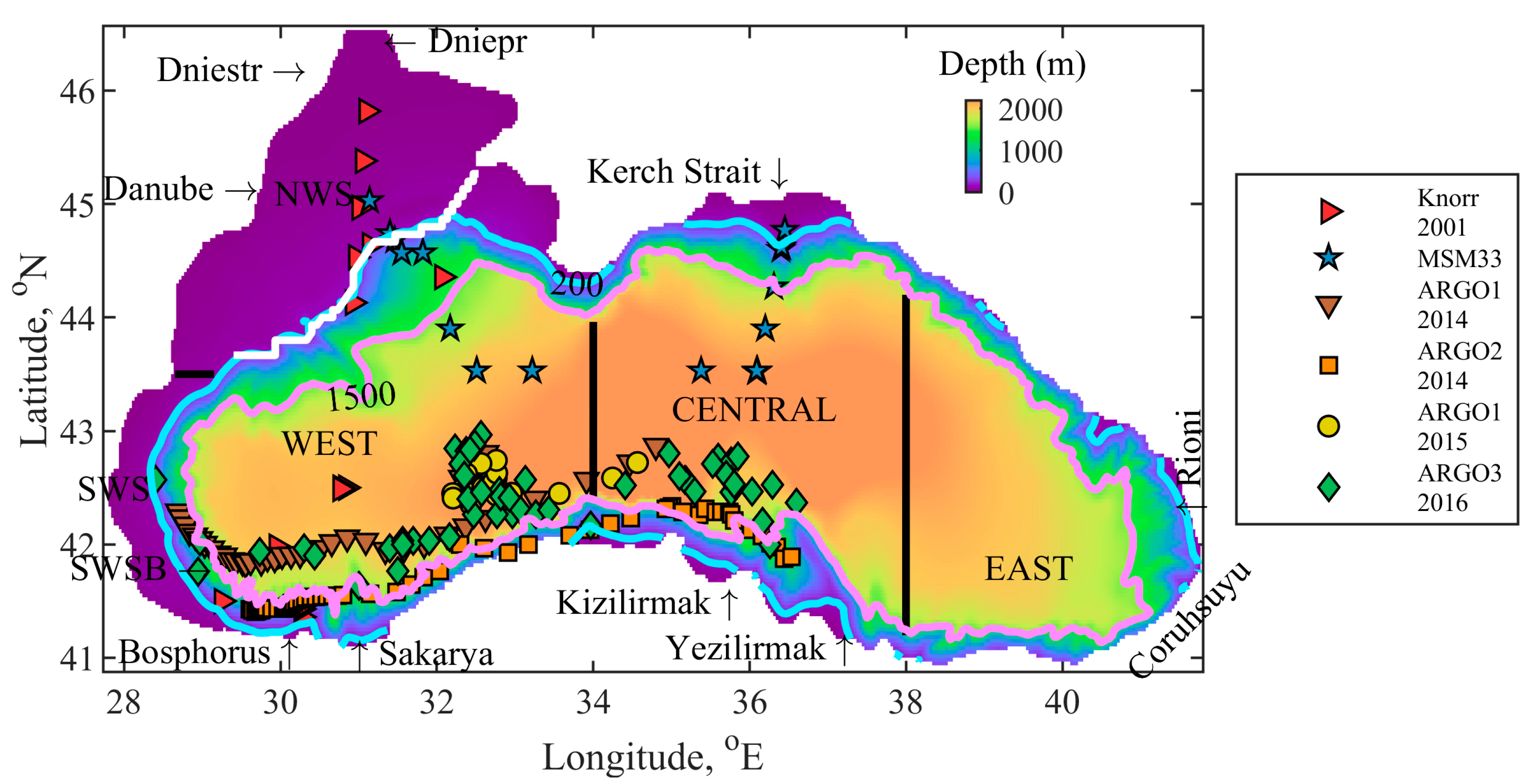
2.1. Geographical Area of Interest
2.2. Hydrodynamic Model
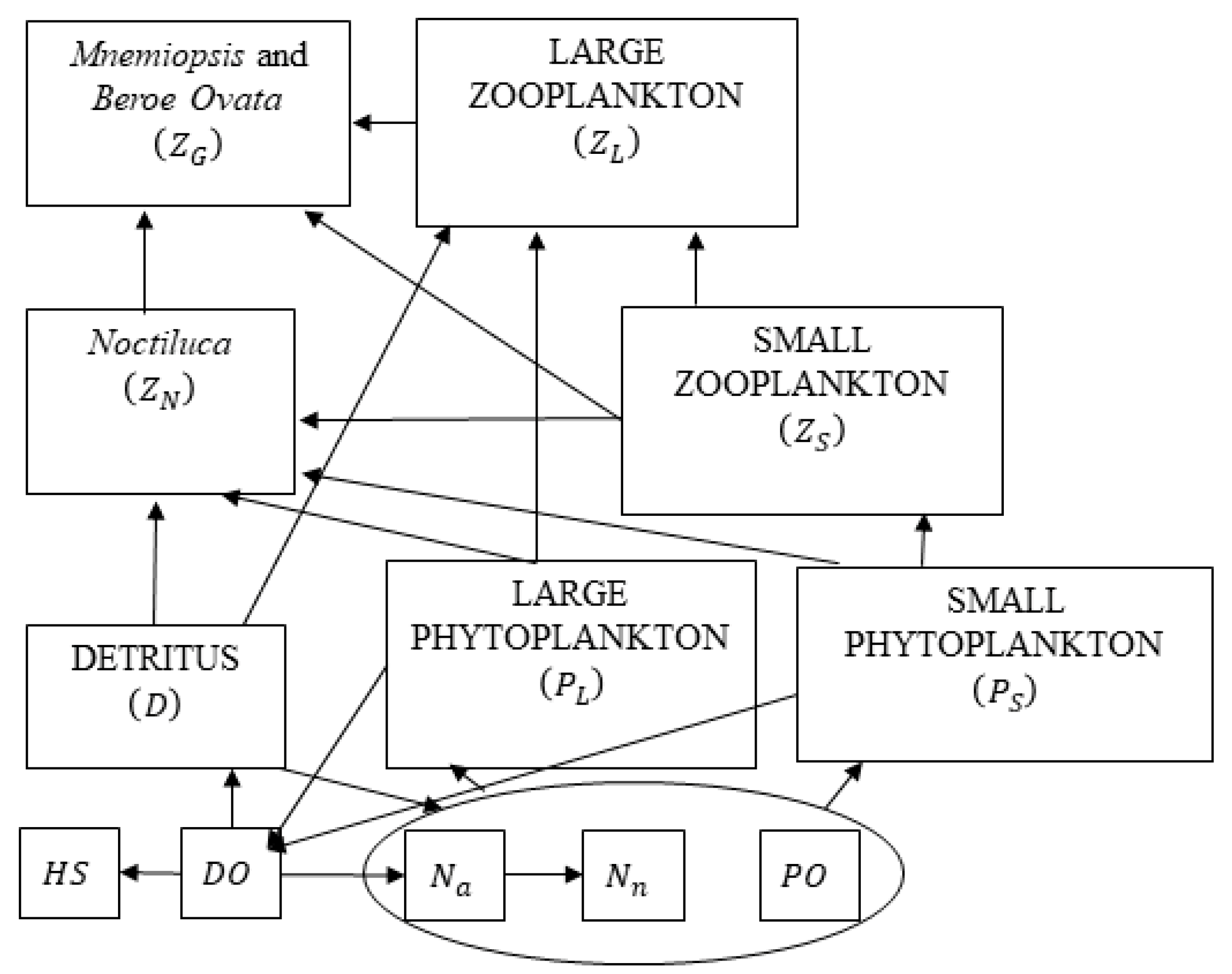
2.3. Lower Trophic Level Model
2.4. Model Validation Statistics
2.5. Validation Data
3. Validation of the Phytoplankton Distribution Model
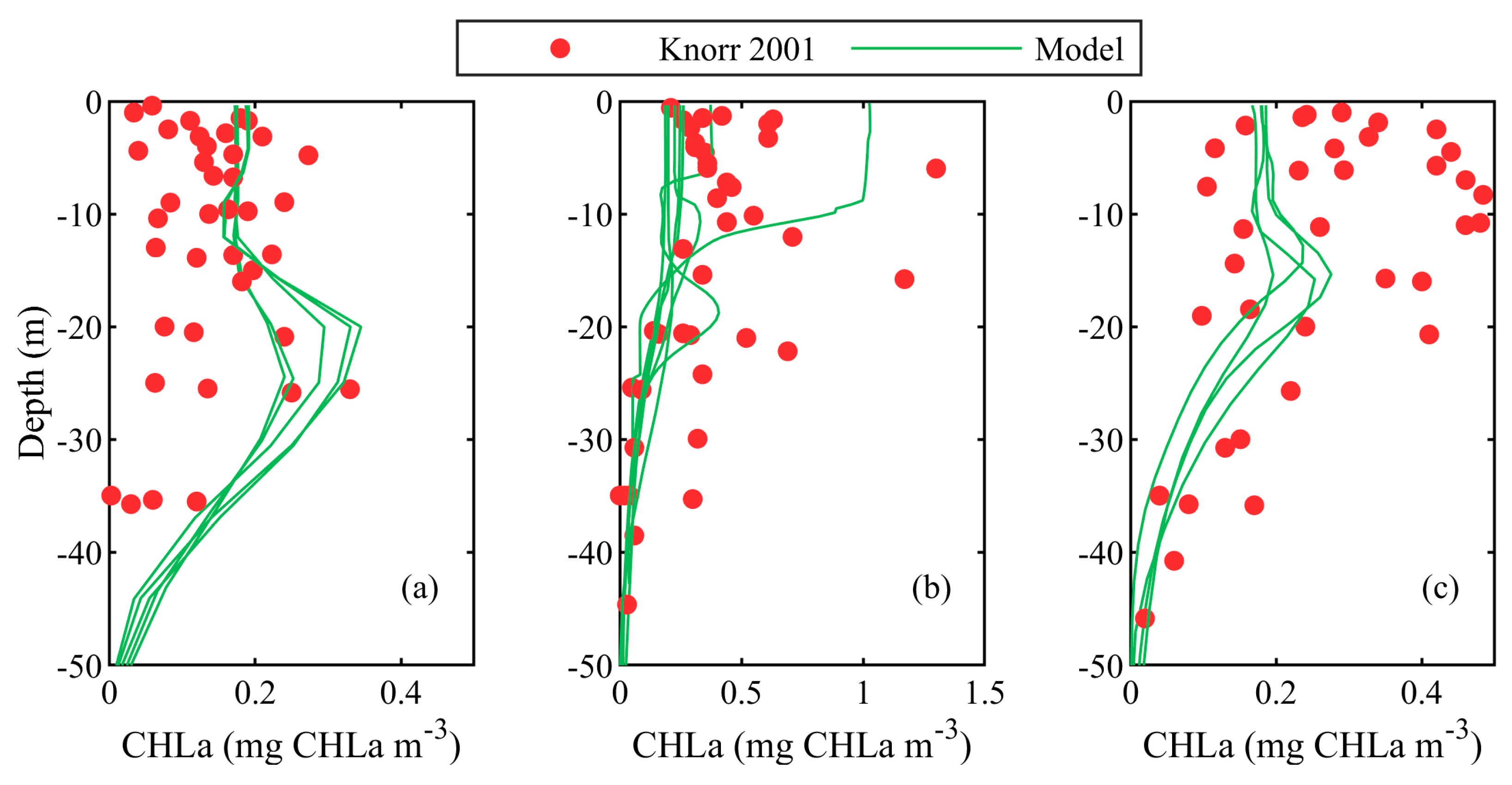
3.1. Validation against In-Situ Vertical Profile Data
3.2. Validation against Remote Sensing Data
3.3. Model Validation against Argo Floats Empirical Data
4. Results
4.1. Seasonal Variability of PHY
4.2. Inter-Annual Variability of Plankton Blooms
4.3. The Role of CIL
4.4. Mechanism behind Autumn Blooms in the Black Sea
4.5. Mass and Volume Transport across the NWS Break
5. Discussions and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smayda, T.J. What is a bloom? A commentary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedernikov, V.I.; Demidov, A.B. Vertical Distribution of Primary Production and Chlorophyll during Different Seasons in Deep Regions of the Black Sea. Oceanology 1997, 37, 376–384. [Google Scholar]
- Nezlin, N.P. Seasonal and interannual variability of remotely sensed chlorophyll. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Kostianoy, G., Kosarev, A.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 333–349. [Google Scholar]
- Finenko, Z.Z.; Suslin, V.V.; Kovaleva, I.V. Seasonal and long-term dynamics of the chlorophyll concentration in the Black Sea according to satellite observations. Oceanology 2014, 54, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Cokacar, T.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Ducklow, H.W. Climatic warming and accompanying changes in the ecological regime of the Black Sea during 1990s. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Dippner, J.W.; Kaymaz, Z. Climatic regulation of the Black Sea hydro-meteorological and ecological properties at interannual-to-decadal time scales. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 60, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T. Long-Term Impacts of Anthropogenic Forcing on the Black Sea Ecosystem. Oceanography 2005, 18, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McQuatters-Gollop, A.; Mee, L.D.; Raitsos, D.E.; Shapiro, G.I. Non-linearities, regime shifts and recovery: The recent influence of climate on Black Sea chlorophyll. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Chasovnikov, V.K.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Stanichny, S.V. Phenology and drivers of the winter–spring phytoplankton bloom in the open Black Sea: The application of Sverdrup’s hypothesis and its refinements. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Ediger, D. Comparision of in situ and satellite-derived chlorophyll pigment concentrations, and impact of phytoplankton bloom on the suboxic layer structure in the western Black Sea during May-June 2001. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2006, 53, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BSC2008 State of Environment of the Black Sea (2001–2006/7). Available online: http://www.blacksea-commission.org/_publ-SOE2009.asp (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Stanichny, S.V.; Zatsepin, A.G.; Kremenetskiy, V.V. Long-term variations of the Black Sea dynamics and their impact on the marine ecosystem. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 163, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Ducklow, H.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Tugrul, S.; Nezlin, N.P.; Unluata, U. Simulation of annual plankton productivity cycle in the Black Sea by a one-dimensional physical-biological model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1996, 101, 16585–16599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, M. Modeling the nitrogen cycling and plankton productivity in the Black Sea using a three-dimensional interdisciplinary model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109, C05007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Salihoglu, B. Simulation of eddy-driven phytoplankton production in the Black Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiaras, K.P.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Davidov, A.; Staneva, J. A three-dimensional coupled model of the Western Black Sea plankton dynamics: Seasonal variability and comparison to Sea WiFS data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, A.G. Observations of Black Sea mesoscale eddies and associated horizontal mixing. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.A.; Bagaev, A.V.; Stanichny, S.V.; Belokopytov, V.N. Thermohaline structure, transport and evolution of the Black Sea eddies from hydrological and satellite data. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, S.K.; Murray, J.W. Variations in the chemistry of the Black Sea on a time scale of decades (1960–1995). J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 31, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Velikova, V. Abrupt transition of the northwestern Black Sea shelf ecosystem from a eutrophic to an alternative pristine state. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kideys, A.E. ECOLOGY: Enhanced: Fall and Rise of the Black Sea Ecosystem. Science (80-) 2002, 297, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Fach, B.; Salihoglu, B. Invasion dynamics of the alien ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi and its impact on anchovy collapse in the Black Sea. J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Macias Moy, D. Black Sea thermohaline properties: Long-term trends and variations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 5624–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ærtebjerg, G.; Carstensen, J. Indicator Fact Sheet: (WEU4) Nutrients in Coastal Waters. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/nutrients-in-coastal-waters-1/ (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Tugrul, S.; Basturk, O.; Saydam, C.; Yilmaz, A. Changes in the hydrochemistry of the Black Sea inferred from water density profiles. Nature 1992, 359, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilova, T.; Suslin, V.; Krivenko, O.; Efimova, T.; Moiseeva, N.; Mukhanov, V.; Smirnova, L. Light absorption by phytoplankton in the upper mixed layer of the Black Sea: Seasonality and parametrization. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.J.; Yilmaz, A.; Coban-Yildiz, Y.; Nevins, J.L. Nitrogen cycling in the offshore waters of the Black Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunev, O.A.; Carstensen, J.; Moncheva, S.; Khaliulin, A.; Aertebjerg, G.; Nixon, S. Nutrient and phytoplankton trends on the western Black Sea shelf in response to cultural eutrophication and climate changes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Latun, V.S.; Latif, M.A.; Vladimirov, V.V.; Sur, H.I.; Markov, A.A.; Özsoy, E.; Kotovshchikov, B.B.; Eremeev, V.V.; Ünlüata, Ü. Circulation in the surface and intermediate layers of the Black Sea. Deep. Res. Part I 1993, 40, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotaev, G.; Oguz, T.; Nikiforov, A.; Koblinsky, C. Seasonal, interannual, and mesoscale variability of the Black Sea upper layer circulation derived from altimeter data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GETM, 3D General Estuarine Transport Model. Available online: http://www.getm.eu/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- ECMWF, European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecast. Available online: http://www.ecmwf.int (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- GRDC, Global Runoff Data Centre. Available online: http://www.bafg.de/GRDC (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- MEDAR/MEDATLAS II Project. Available online: http://www.ifremer.fr/medar (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Macias Moy, D. Formation and changes of the Black Sea cold intermediate layer. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Macias Moy, D. Modelling Toolbox 2: The Black Sea Ecosystem Model; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, T.; Ducklow, H.W.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Murray, J.W.; Shushkina, E.A.; Vedernikov, V.I.; Unluata, U. A physical-biochemical model of plankton productivity and nitrogen cycling in the Black Sea. Deep Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T. Modeling aggregate dynamics of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and their interactions with a pelagic food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 582, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Merico, A. Factors controlling the summer Emiliania huxleyi bloom in the Black Sea: A modeling study. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 59, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinova, S.; Adolf, S.; Diego, M.M.; Elisa, G.G. Revised Black Sea Ecosystem Model; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, W.; Dumont, E.; Meybeck, M.; Heussner, S. River discharges of water and nutrients to the Mediterranean and Black Sea: Major drivers for ecosystem changes during past and future decades? Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 80, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuǧrul, S.; Murray, J.W.; Friederich, G.E.; Salihoǧlu, I. Spatial and temporal variability in the chemical properties of the oxic and suboxic layers of the black sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 135, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codispoti, L.A.; Friederich, G.E.; Murray, J.W.; Sakamoto, C.M. Chemical variability in the Black Sea: Implications of continuous vertical profiles that penetrated the oxic/anoxic interface. Deep Res. Part A 1991, 38, S691–S710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baştürk, Ö.; Tuğrul, S.; Konovalov, S.; Salihoğlu, İ. Variations in the Vertical Structure of Water Chemistry within the Three Hydrodynamically Different Regions of the Black Sea. In Sensitivity to Change: Black Sea, Baltic Sea and North Sea; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Koçak, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Tutsak, E.; Violaki, K.; Theodosi, C.; Zarmpas, P.; Kalegeri, P. Atmospheric deposition of macronutrients (dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorous) onto the Black Sea and implications on marine productivity. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubilay, N.; Yemenicioglu, S.; Saydam, A.C. Airborne material collections and their chemical composition over the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 30, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, J.; Klais, R.; Cloern, J.E. Phytoplankton blooms in estuarine and coastal waters: Seasonal patterns and key species. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 162, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finenko, Z.Z.; Hoepffner, N.; Williams, R.; Piontkovski, S.A. Phytoplankton carbon to chlorophyll a ratio: Response to light, temperature and nutrient limitation. Mar. Ecol. J. 2003, II, 40–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E.; Grenz, C.; Vidergar-Lucas, L. An empirical model of the phytoplankton chlorophyll: Carbon ratio-the conversion factor between productivity and growth rate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, D.M.; Knauer, G.A. Microbial production and particle flux in the upper 350 m of the Black Sea. Deep. Res. Part A 1991, 38, S921–S942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelevich, O.V.; Sheberstov, S.V.; Yunev, O.; Basturk, O.; Finenko, Z.Z.; Nikonov, S.; Vedernikov, V.I. Surface chlorophyll in the Black Sea over 1978–1986 derived from satellite and in situ data. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 36, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorr 2001, NATO 2001 Black Sea Expedition. Available online: https://www.ocean.washington.edu/cruises/Knorr2001/ (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Kaiser, D.; Konovalov, S.; Schulz-Bull, D.E.; Waniek, J.J. Organic matter along longitudinal and vertical gradients in the Black Sea. Deep Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 129, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CMEMS, Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service. Available online: https://marine.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Kubryakov, A.A.; Silkin, V.A.; Pautova, L.A.; Chasovnikov, V.K. Regional climate and patterns of phytoplankton annual succession in the open waters of the Black Sea. Deep Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2018, 142, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, D.M. Water Circulation and Structure of the Black Sea; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Mikaelyan, A.S.; Zatsepin, A.G.; Chasovnikov, V.K. Long-term changes in nutrient supply of phytoplankton growth in the Black Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 117–118, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunev, O.A.; Vedernikov, V.I.; Basturk, O.; Yilmaz, A.; Kideys, A.E.; Moncheva, S.; Konovalov, S.K. Long-term variations of surface chlorophyll a and primary production in the open Black Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 230, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkin, V.A.; Pautova, L.A.; Giordano, M.; Chasovnikov, V.K.; Vostokov, S.V.; Podymov, O.I.; Pakhomova, S.V.; Moskalenko, L.V. Drivers of phytoplankton blooms in the northeastern Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Ocean Color. Available online: http://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Macias Moy, D.; Garcia-Gorriz, E. Pathways and mixing of the north western river waters in the Black Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 236, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Shapiro, G.; Wobus, F. Cross-shelf exchange in the northwestern Black Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 2143–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Aubrey, D. Wind and thermohaline circulation of the Black Sea driven by yearly mean climatological forcing. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmakh, L.V.; Gorbunova, T.I. Carbon-to-chlorophyll-a ratio in the phytoplankton of the Black Sea surface layer: Variability and regulatory factors. Ecol. Montenegrina 2018, 17, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, E.D.; Martiny, A.C. A simple nutrient-dependence mechanism for predicting the stoichiometry of marine ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8199–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, D.; Huertas, I.E.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Stips, A. Non-Redfieldian dynamics driven by phytoplankton phosphate frugality explain nutrient and chlorophyll patterns in model simulations for the Mediterranean Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 173, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
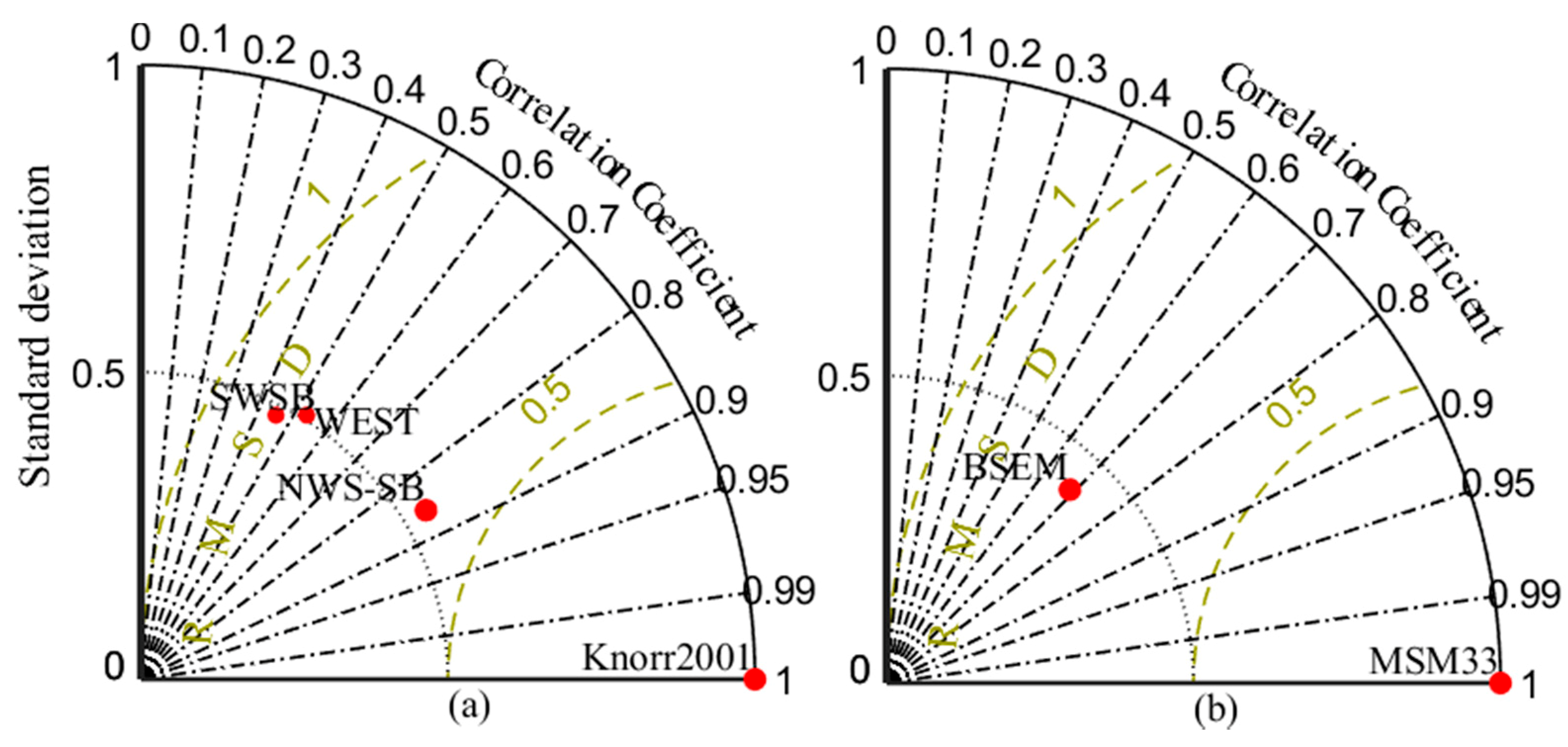
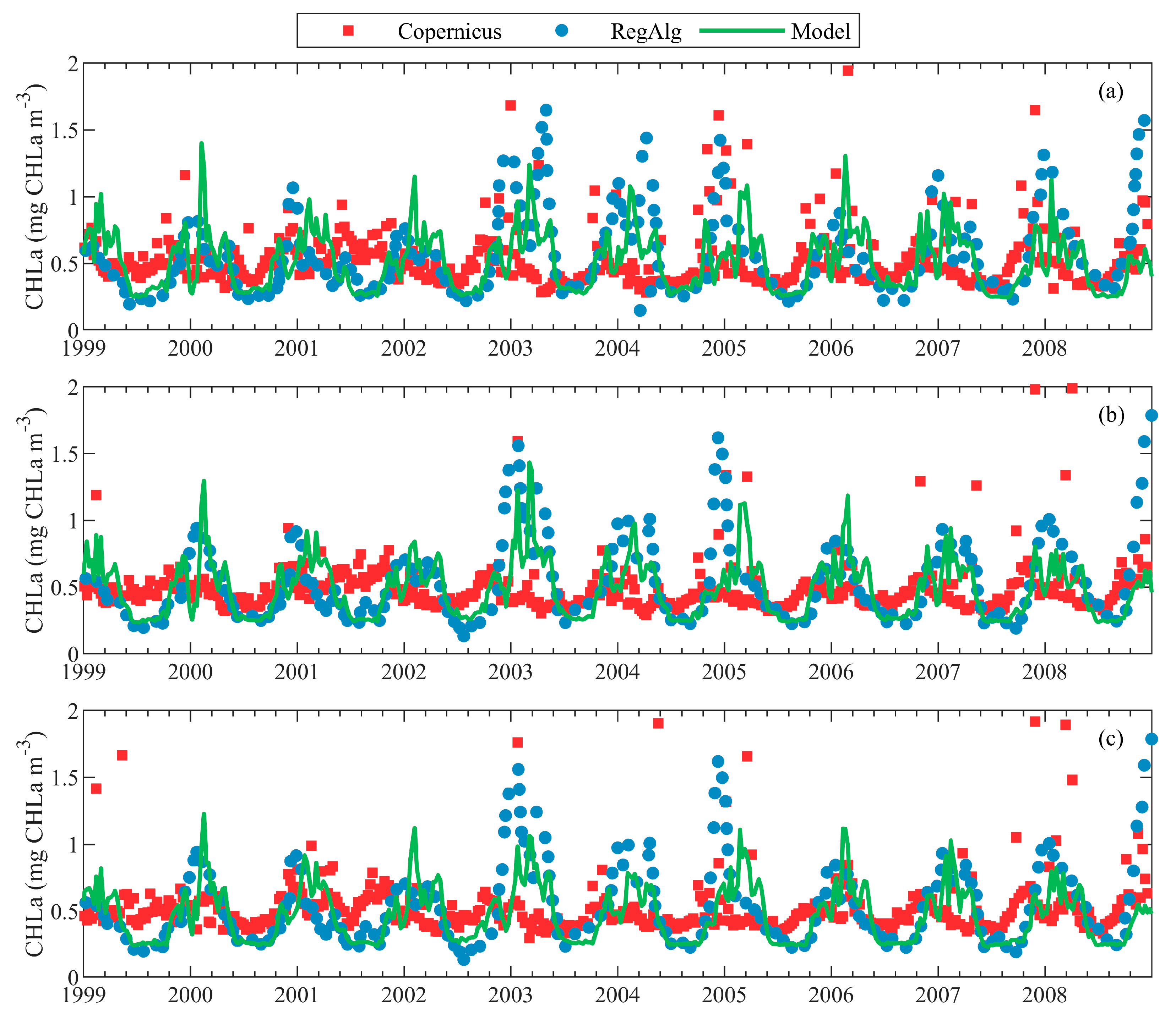

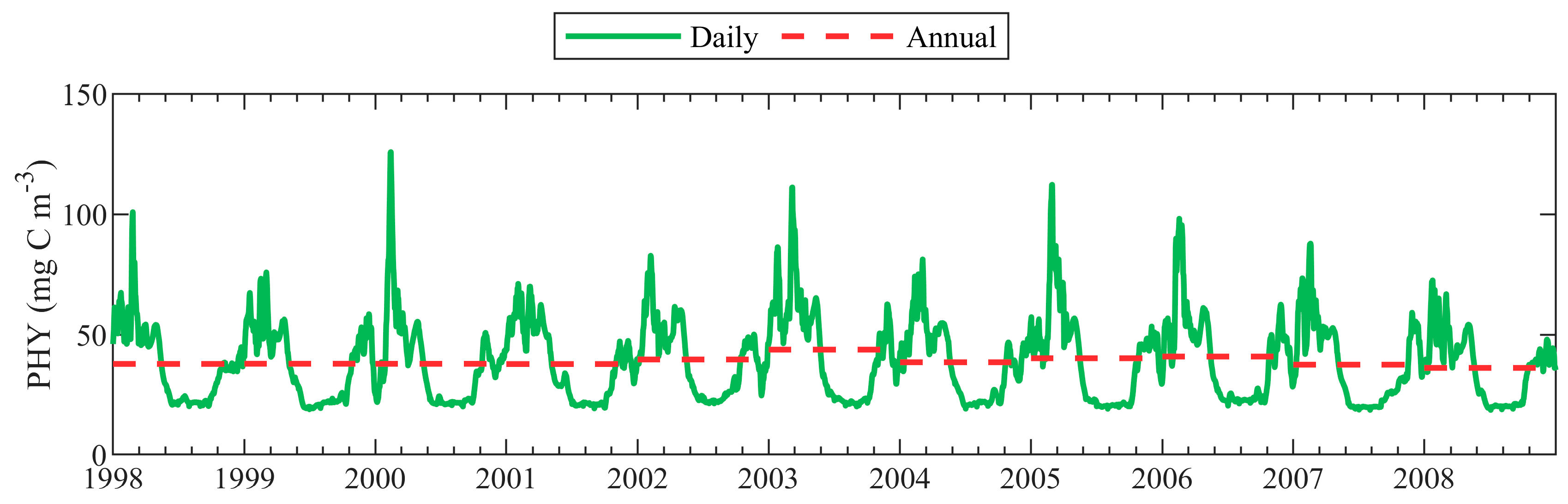
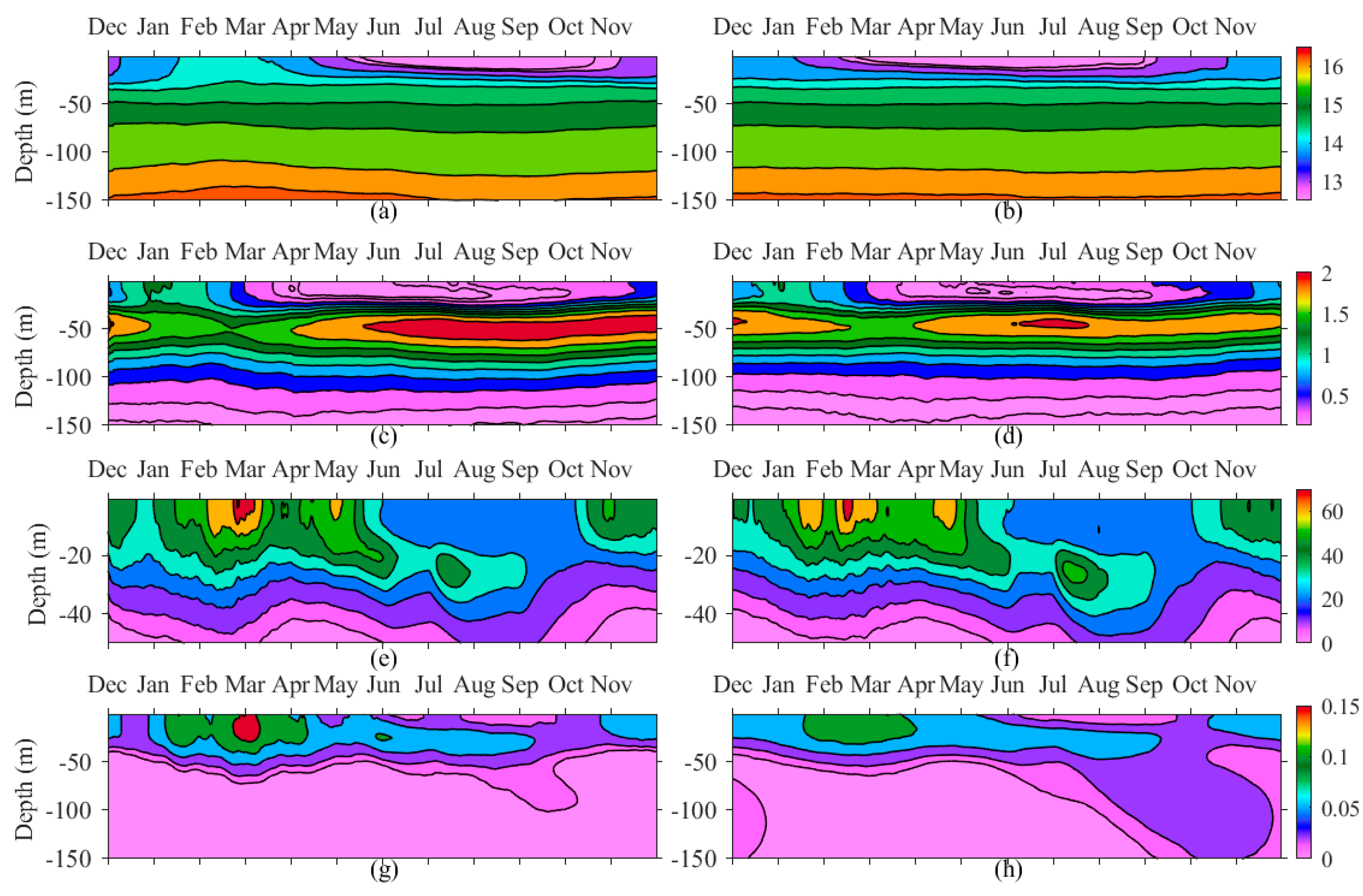



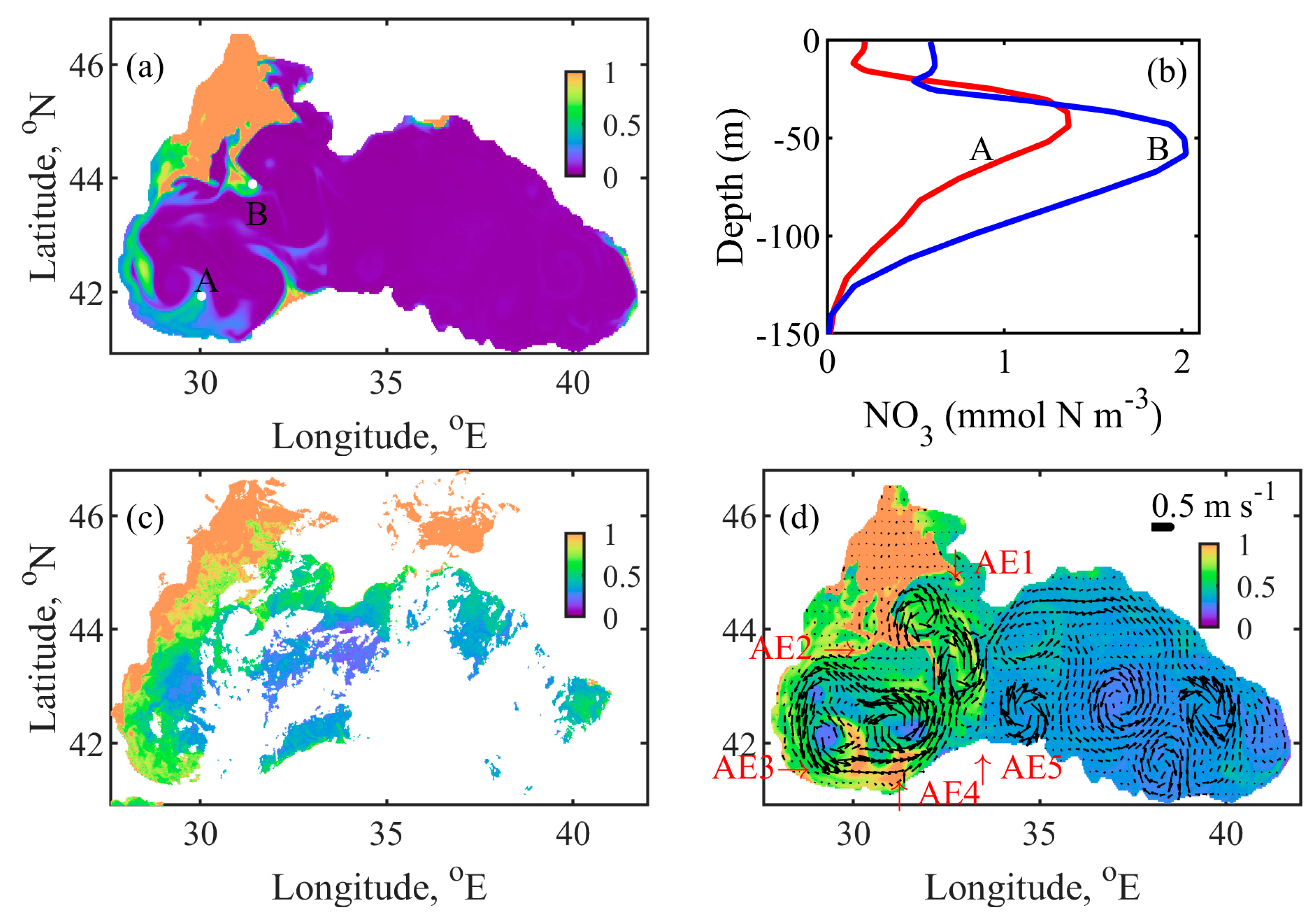
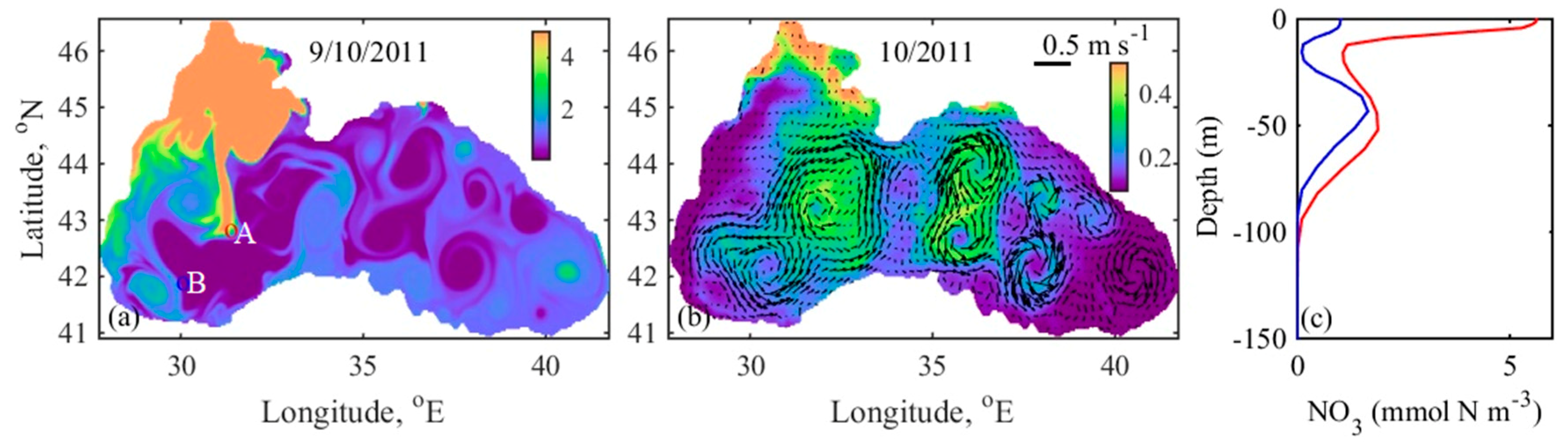

| Short Name | Type of Dataset | Resolution | Coverage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copernicus | Satellite (Copernicus OCTAC) | 1 × 1 km, 1-day average | 1998–2017, Surface of the entire basin (a lot of missing data in December and January) | [54] |
| RegAlg | Satellite (SeaWiFS) | 4 × 4 km, daily | 1999–2008, Mean surface data for several particular regions | [4] |
| Knorr 2001 | In-situ | Stations | 23 May to 10 June 2001 Vertical profiles in WEST, SWSB (south-western shelf-break areas) and NWS | [52] |
| MSM33 | In-situ | Stations | 11 November to 2 December 2013 | [53] |
| ARGO1 | In-situ | Profiling float | 2014, Vertical profiles in WEST and CENTRAL 2015, in WEST | [54] |
| ARGO2 | In-situ | Profiling float | 1 January to 18 October 2014 Vertical profiles in SS | [54] |
| ARGO3 | In-situ | Profiling float | 2016, Vertical profiles in WEST and CENTRAL | [54] |
| Region | WEST | CENTRAL | EAST | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data sources | AAE (±error) | R (interval) | AAE (±error) | R (interval) | AAE (±error) | R (interval) |
| RegAlg Copernicus | 0.275 ± 0.014 | 0.08 (0.05, 0.11) | 0.267 ± 0.019 | - | 0.259 ±0.032 | - |
| RegAlg BSEM | 0.197 ± 0.009 | 0.44 (0.42, 0.47) | 0.158 ± 0.008 | 0.58 (0.56, 0.60) | 0.151 ± 0.008 | 0.56 (0.54, 0.59) |
| Copernicus BSEM | 0.229 ± 0.013 | 0.08 (0.05, 0.11) | 0.220 ± 0.017 | - | 0.234 ± 0.031 | - |
| Winter PHY | Spring PHY | Summer PHY | Autumn PHY | Nitrate in the Storage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIL properties | R (interval) | ||||
| Temperature | −0.59 (−0.82, −0.20) | 0.75 (0.45, 0.89) | 0.67 (0.33, 0.86) | 0.65 (0.07, 0.77) | −0.76 (−0.9, −0.48) |
| Lower boundary | 0.64 (0.28, 0.84) | −0.65 (−0.85, −0.29) | −0.69 (−0.87, −0.35) | −0.51 (−0.78, −0.09) | 0.65 (0.3, 0.85) |
| Nitrate in the storage | 0.72 (0.41, 0.88) | - | −0.54 (−0.79, −0.12) | - | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Macias Moy, D.; Garcia-Gorriz, E. Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability of the Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Black Sea Inner Basin. Oceans 2020, 1, 251-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040018
Miladinova S, Stips A, Macias Moy D, Garcia-Gorriz E. Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability of the Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Black Sea Inner Basin. Oceans. 2020; 1(4):251-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiladinova, Svetla, Adolf Stips, Diego Macias Moy, and Elisa Garcia-Gorriz. 2020. "Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability of the Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Black Sea Inner Basin" Oceans 1, no. 4: 251-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040018
APA StyleMiladinova, S., Stips, A., Macias Moy, D., & Garcia-Gorriz, E. (2020). Seasonal and Inter-Annual Variability of the Phytoplankton Dynamics in the Black Sea Inner Basin. Oceans, 1(4), 251-273. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans1040018