Effectiveness of Various Cleaning Protocols in Enhancing Resin–Zirconia Bond Strength After Saliva Contamination
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Objective
- (1)
- To determine the effect of these decontamination procedures on μSBS using a universal testing machine
- (2)
- To evaluate failure modes of all experimental groups after bond testing with light microscopy
- (3)
- To analyse the surface topography of zirconia before and after contamination, and after each cleaning protocol, using field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM)
- (4)
- To identify the chemical state and decontamination efficiency of zirconia through X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) and Fourier–transform infrared spectroscope (FTIR)
- (5)
- To evaluate the surface wettability of zirconia before and after cleaning by measuring the contact angle, to assess its impact on bond strength to resin cement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Description
2.2. Saliva Contamination
2.3. Cleansing Protocols
- Control group: specimens were not contaminated and did not undergo any cleaning.
- Distilled Water: contaminated specimens were rinsed with distilled water for 30 s and air-dried for 10 s.
- Sodium Hypochlorite (5.25%): After air-drying, contaminated specimens were treated with 5.25% NaOCl (Promida, Istanbul, Turkey) for 30 s using gentle agitation, then rinsed with tap water and air-dried [16].
- Phosphoric Acid (37%) + Ethanol (96%): Contaminated surfaces were cleaned with 37% phosphoric acid (Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein) for 30 s, rinsed thoroughly, air-dried, then immersed in 96% ethanol (Aljoud, Baghdad, Iraq) for 2 min, before final air-drying.
- Ivoclean: Contaminated specimens were treated with Ivoclean (Ivoclar Vivadent, Liechtenstein) for 20 s, rinsed with tap water, and air-dried.
2.4. Surface Analysis
- Field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM)
- 2.
- X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
- 3.
- Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
- 4.
- Contact angle
2.5. Bonding Procedure
2.6. Thermal Ageing Technique
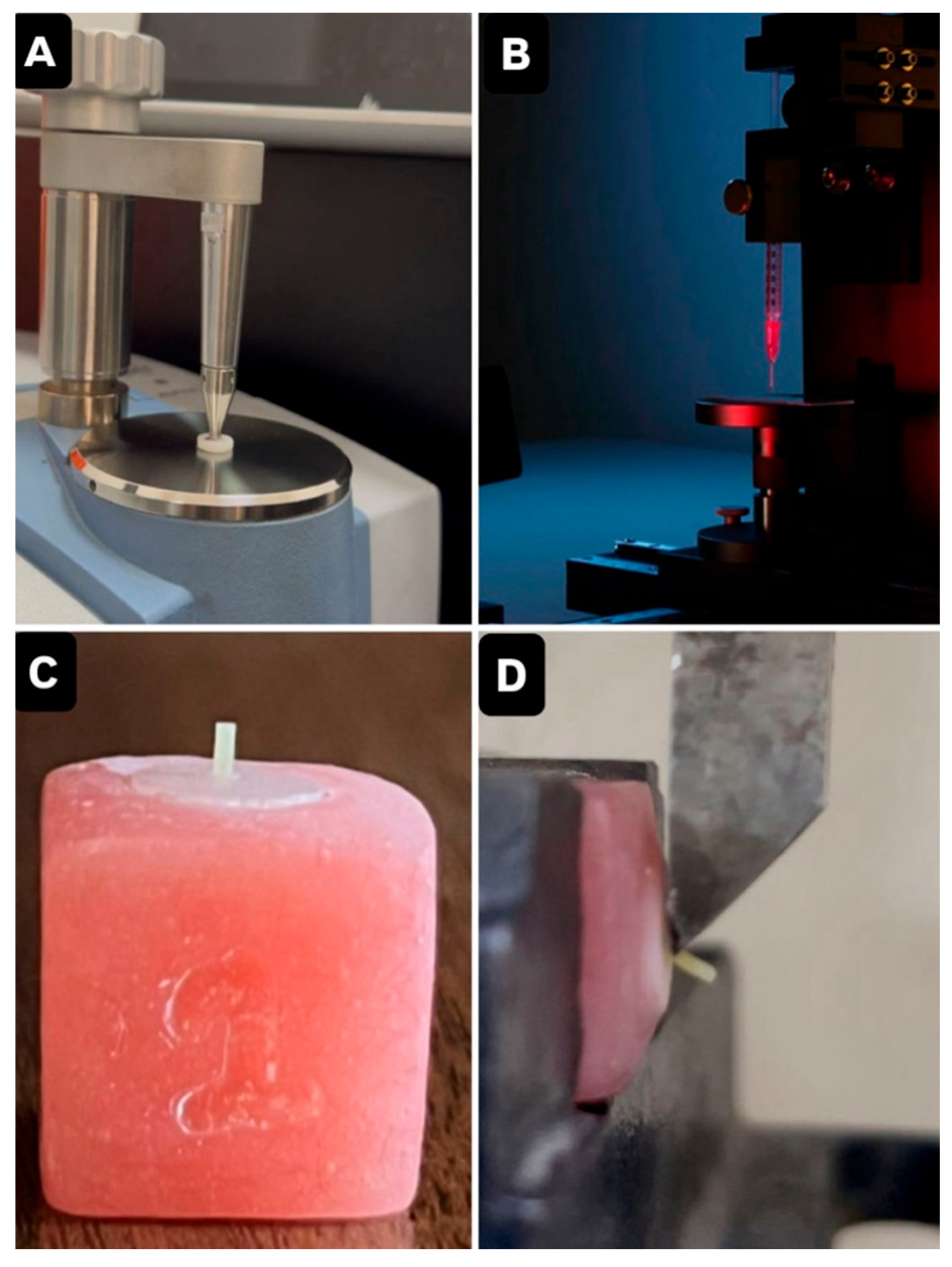
2.7. Micro-Shear Bond Strength (uSBS)
2.8. Failure Mode
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
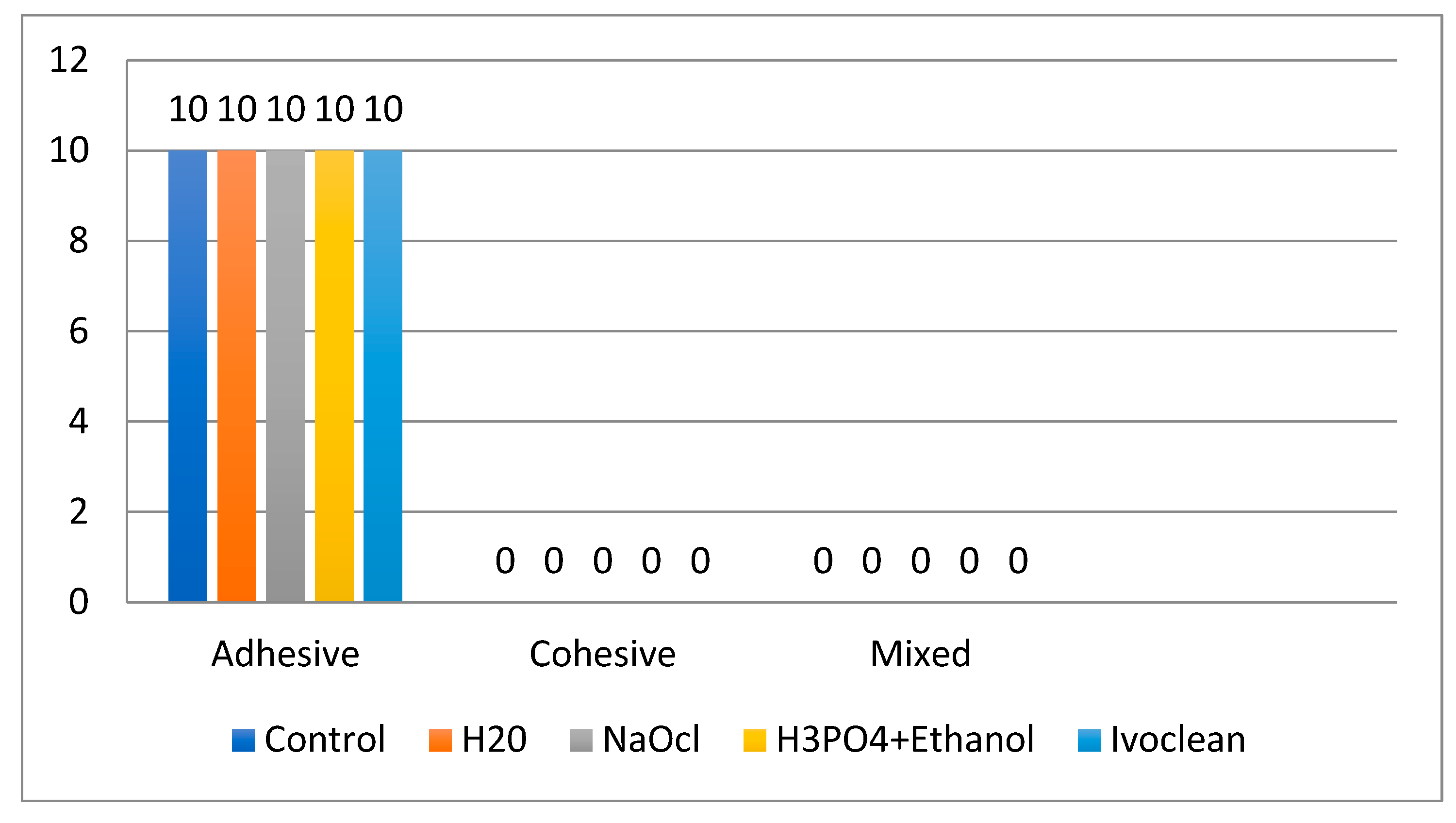
3.2. Failure Mode Analysis
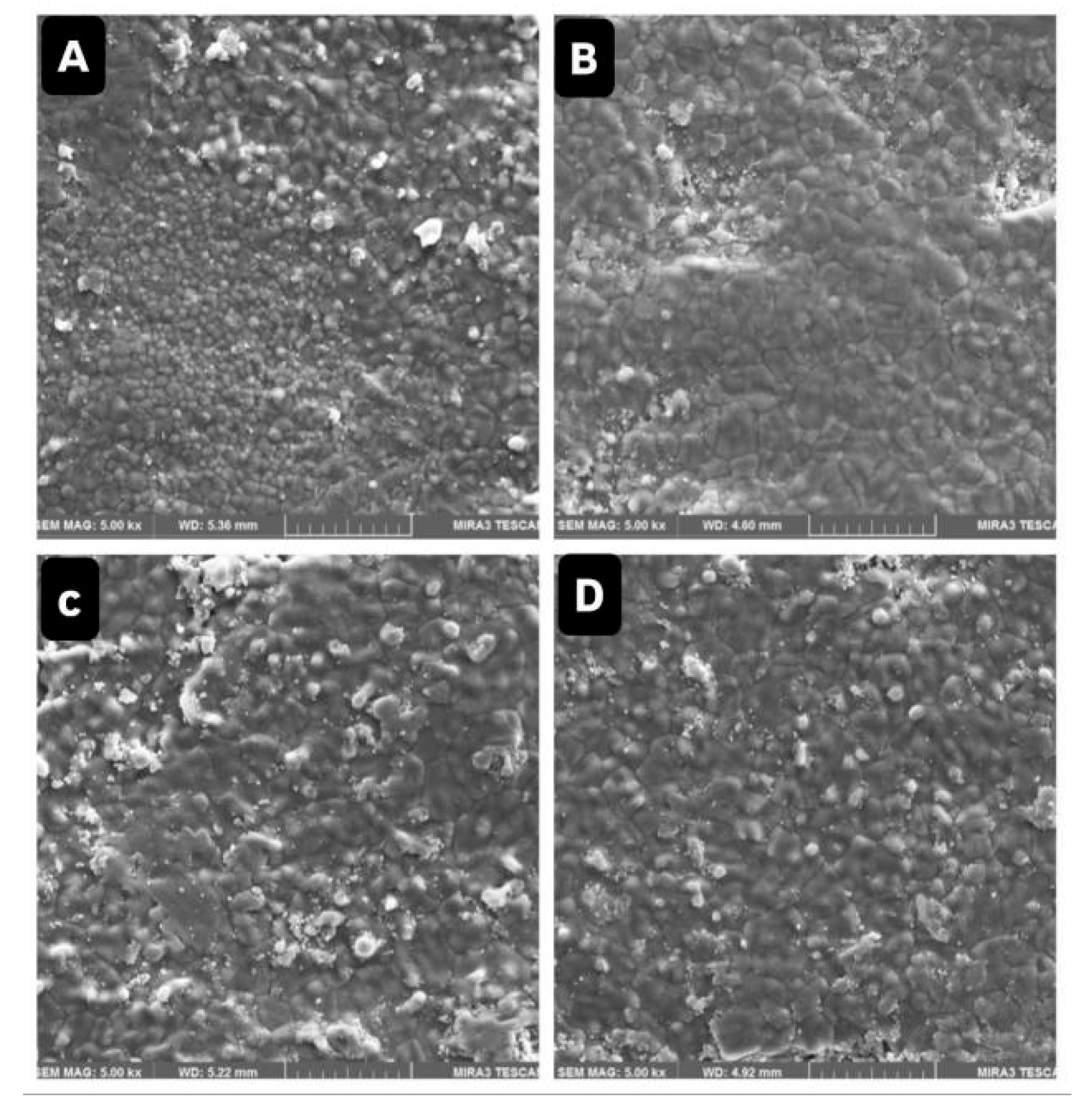
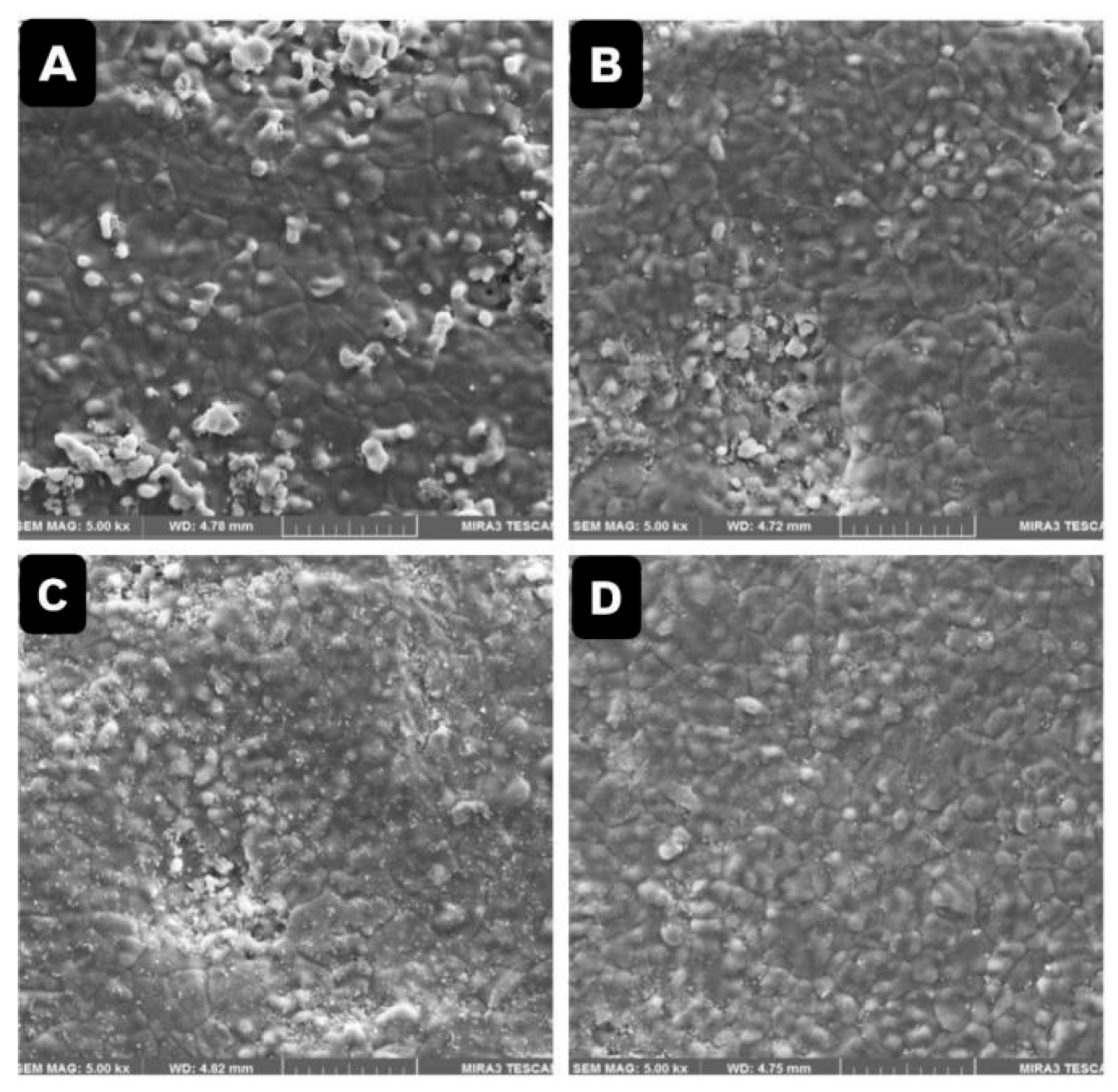
3.3. Surface Morphology by FESEM
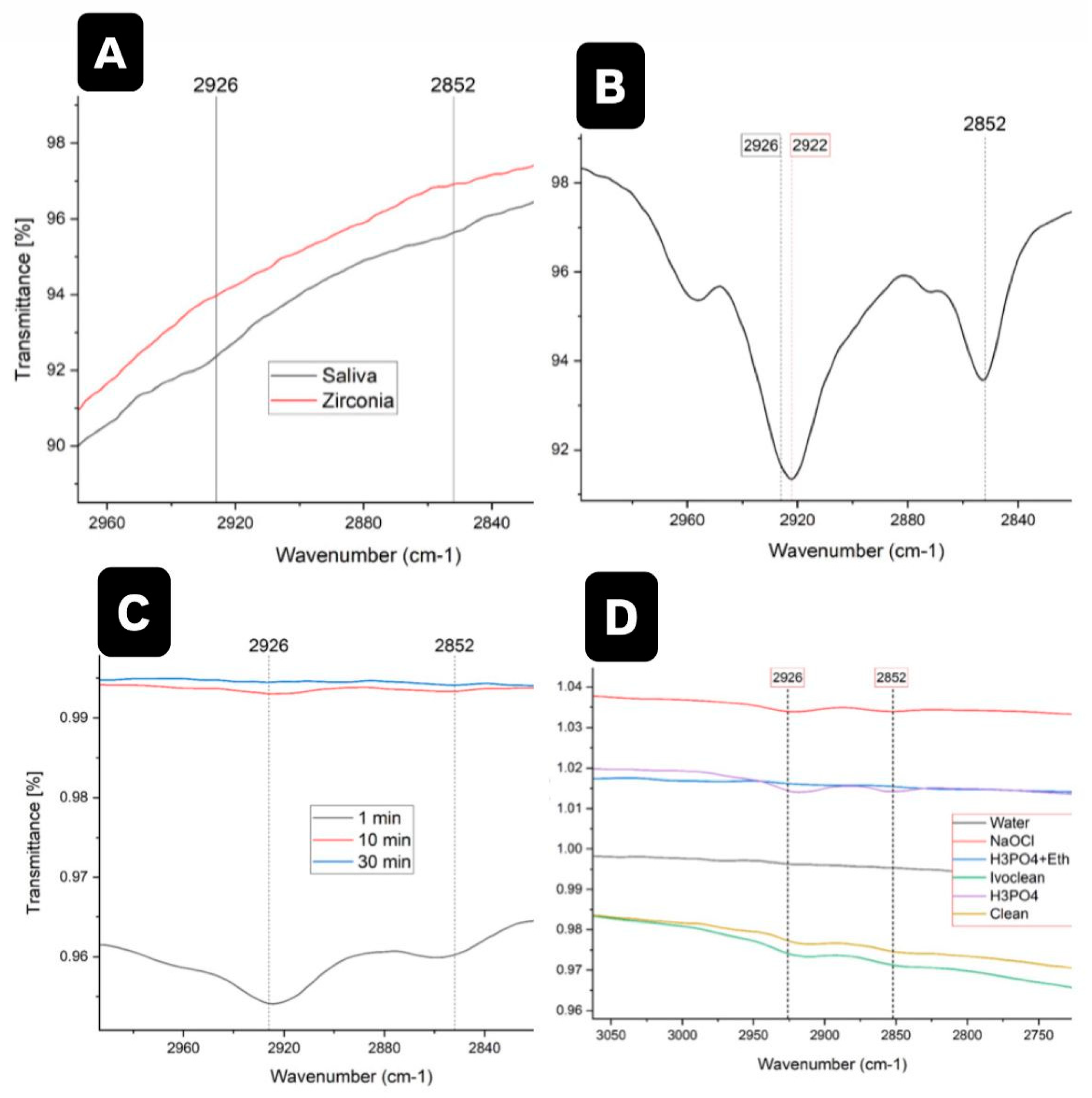
3.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.5. XPS
3.6. Contact Angle Measurement
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
- Saliva was the only contaminant used, excluding clinical sources such as blood or silicone.
- Only four of the numerous possible cleaning regimens were tested, without other promising strategies.
- Fixed protocol times were used; variable times could change efficacy.
- Only one resin cement (Panavia V5) was tested alone, limiting generalisability.
- Thermocycling was limited to 5000 cycles, which may not be representative of long-term ageing.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ban, S.; Yasuoka, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Matsuura, Y. Translucent and highly toughened zirconia suitable for dental restorations. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavriqi, L.; Traini, T. Mechanical properties of translucent zirconia: An in vitro study. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szawioła-Kirejczyk, M.; Chmura, K.; Gronkiewicz, K.; Gala, A.; Loster, J.E.; Ryniewicz, W. Adhesive cementation of zirconia based ceramics-surface modification methods literature review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Hickel, R.; Ilie, N. Adverse effects of salivary contamination for adhesives in restorative dentistry: A literature review. Am. J. Dent. 2017, 30, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alajrash, M.; Kassim, M.; Gholam, M. Effect of different resin luting materials on the marginal fit of lithium disilicate CAD/CAM crowns (a comparative study). Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2020, 14, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Ebeid, K.; Wille, S.; Salah, T.; Wahsh, M.; Zohdy, M.; Kern, M. Evaluation of the effect of different surface treatments on the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramic. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kui, A.; Manziuc, M.; Petruțiu, A.; Buduru, S.; Labuneț, A.; Negucioiu, M.; Chisnoiu, A. Translucent Zirconia in Fixed Prosthodontics—An Integrative Overview. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammajaruk, P.; Guazzato, M.; Naorungroj, S. Cleaning methods of contaminated zirconia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dent. Mater. 2023, 39, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Kondas, V.V.; Dhanasekaran, S.V.; Elavarasu, P.K. Comparative evaluation of shear bond strength of zirconia restorations cleansed with various cleansing protocols bonded with two different resin cements: An in vitro study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2017, 28, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, N.R.; de Araújo, G.M.; Vila-Nova, T.E.L.; Bezerra, M.G.P.G.; dos Santos Calderon, P.; Özcan, M.; de Assunção e Souza, R.O. Which zirconia surface-cleaning strategy improves adhesion of resin composite cement after saliva contamination? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Adhes. Dent. 2022, 24, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, H.; Yanikoglu, N.; Sagsöz, N. Effect of MDP-based silane and different surface conditioner methods on bonding of resin cements to zirconium framework. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noori, S.T.; Gholam, M.K. Evaluation of the marginal discrepancy of cobalt chromium metal copings fabricated with additive and subtractive techniques. J. Int. Oral Health 2021, 13, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaraghuli, A.M.; Gholam, M. The influence of different types of surface treatment on the surface roughness and bond strength of zirconia (an in vitro study). Front. Biomed. Technol. 2025, 37, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.H.; Gholam, M.K. The influence of cement spacer thickness on retentive strength of monolithic zirconia crowns cemented with different luting agents (a comparative in-vitro study). Indian J. Forensic Med. Toxicol. 2021, 15, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Feitosa, S.A.; Patel, D.; Borges, A.L.S.; Özcan, M. Effect of cleansing methods on saliva-contaminated zirconia: An XPS and shear bond strength analysis. J. Adhes. Dent. 2014, 16, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Phark, J.; Duarte, S.; Blatz, M. Effect of saliva contamination on bond strength of self-adhesive cements to zirconia. Oper. Dent. 2009, 34, 703–710. [Google Scholar]
- Sadid-Zadeh, R.; Strazzella, A.; Li, R.; Makwoka, S. Effect of zirconia etching solution on the shear bond strength between zirconia and resin cement. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lange-Jansen, H.C.; Scharnberg, M.; Wolfart, S.; Ludwig, K.; Adelung, R.; Kern, M. Influence of saliva contamination on zirconia ceramic bonding. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K. Influence of cleaning methods on resin bonding to saliva-contaminated zirconia. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2018, 30, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, S.A.; Patel, D.; Borges, A.L.S.; Alshehri, A.; Bottino, M.A.; Özcan, M. Effect of cleansing methods on salivary contamination and bonding to zirconia. Oper. Dent. 2015, 40, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Raja, K.K.; Anniyappan, B.; Soosairaj, C.D.R.; Jayaseelan, J.D.; Srinivasan, M.K. Comparing the effects of different cleansing agents on the shear bond strength of resin cements on surface-contaminated zirconia: An in vitro study. Cureus 2025, 17, e78795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Isshi, K.; Kakura, K.; Ikeda, H.; Shimizu, H.; Kido, H.; Kawaguchi, T. Effects of ytterbium laser surface treatment on the bonding of two resin cements to zirconia. Dent. Mater. J. 2022, 41, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangione, E.; Özcan, M. Adhesion of resin cements to contaminated zirconia resin cements on zirconia: Effect saliva-contamination and surface conditioning. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.S.T.; Ozkurt-Kayahan, Z.; Kazazoglu, E. In vitro evaluation of shear bond strength of three primer/resin cement systems to monolithic zirconia. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 32, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaiwan, W.; Chaijareenont, P. The effect of cleaning saliva-contaminated zirconia with various sodium hypochlorite concentrations on shear bond strength. J. Int. Dent. Med. Res. 2024, 17, 3038–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-H.; Son, J.-S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, T.-Y. Efficacy of various cleaning solutions on saliva contaminated zirconia for improved resin bonding. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Takagaki, T.; Wada, T.; Uo, M.; Nikaido, T.; Tagami, J. The effect of different cleaning agents on saliva contamination for bonding performance of zirconia ceramics. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, M.D.S.; Fronza, B.M.; André, C.B.; de Castro, E.F.; Soto-Montero, J.; Price, R.B.; Giannini, M. Effect of zirconia decontamination protocols on bond strength and surface wettability. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornatitanakul, V.; Klaisiri, A.; Sriamporn, T.; Swasdison, S.; Thamrongananskul, N. The Influence of Tooth Primer and Zirconia Cleaners on the Shear Bond Strength of Saliva-Contaminated Zirconia Bonded with Self-Adhesive Resin Cement. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, N.; Genc, O.; Akkese, I.B.; Malkoc, M.A.; Ozcan, M. Bonding effectiveness of saliva-contaminated monolithic zirconia ceramics using different decontamination protocols. Biomed. Res. Int. 2024, 2024, 6670159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukcheep, C.; Thammajaruk, P.; Guazzato, M. Investigating the impact of different cleaning techniques on bond strength between resin cement and zirconia and the resulting physical and chemical surface alterations. J. Prosthodont. Off. J. Am. Coll. Prosthodont. 2024; Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Reddy, S.M.; Alva, H.; Shetty, J. Influence of cleaning solutions on shear bond strength of resin cement to saliva contaminated zirconia: An in-vitro study. RGUHS J. Med. Sci. 2022, 12, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, T.A.; Altak, A.; Abdulmajeed, A.; Rodgers, B.; Lawson, N. Cleaning zirconia surface prior to bonding: A comparative study of different methods and solutions. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Kocjan, A.; Lehmann, F.; Kosmac, T.; Kern, M. Influence of contamination on resin bonding to zirconia. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, R.; Tsujimoto, A.; Takamizawa, T.; Tsubota, K.; Suzuki, T.; Shimamura, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Influence of surface treatment of contaminated zirconia on surface free energy and resin cement bonding. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lümkemann, N.; Schönhoff, L.M.; Buser, R.; Stawarczyk, B. Effect of Cleaning Protocol on Bond Strength between Resin Composite Cement and Three Different CAD/CAM Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf Shirazi, A.; Majidinia, S.; Parhizkar, T. Effect of Different Cleaning Methods on Bond Strength of Resin to Saliva-Contaminated Zirconia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of in Vitro Studies. Ann. Stomatol. 2024, 15, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charasseangpaisarn, T.; Wiwatwarrapan, C.; Siriwat, N.; Khochachan, P.; Mangkorn, P.; Yenthuam, P.; Thatphet, P. Different cleansing methods effect to bond strength of contaminated zirconia. J. Dent. Assoc. Thai. 2018, 68, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wahsh, M.; Taha, D.; Shaheen, O. Effect of surface contamination and cleansing methods on resin bond strength and failure modes of partially stabilized zirconia: An in vitro study. Int. J. Appl. Dent. Sci. 2024, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rus, F.; Rodríguez, C.; Salido, M.P.; Pradíes, G. Influence of different cleaning procedures on the shear bond strength of 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate-containing self-adhesive resin cement to saliva contaminated zirconia. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2021, 65, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekçe, N.; Tuncer, S.; Demirci, M.; Kara, D. The effect of surface treatments on bond strength of resin cement to contaminated zirconia. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2018, 10, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzaga, C.C.; Cesar, P.F.; Miranda, W.G.; Yoshimura, H.N. Bonding effectiveness of resin cements to contaminated and cleaned zirconia ceramic surfaces. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 687–694. [Google Scholar]
| Groups | N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | SD | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Group | 10 | 52.0 | 66.0 | 59.5 | 4.2 | 1.5 |
| H2O | 10 | 25.0 | 43.0 | 33.5 | 6.3 | 1.9 |
| NaOCl | 10 | 30.0 | 46.0 | 41.1 | 5.7 | 1.8 |
| H3PO4 + Ethanol | 10 | 40.0 | 51.0 | 46.8 | 4.7 | 1.5 |
| Ivoclean | 10 | 50.0 | 63.0 | 56.7 | 4.8 | 1.5 |
| Microshear | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | N | Mean | SD | Statistics | df | p-Value |
| Control | 10 | 59.5 | 4.2 | 42.4 | 4 | <0.009 |
| H2O | 10 | 33.5 | 6.3 | |||
| NaOCl | 10 | 41.1 | 5.7 | |||
| H3PO4 + Ethanol | 10 | 46.8 | 4.7 | |||
| Ivoclean | 10 | 56.7 | 4.8 | |||
| Post hoc Pairwise Differentiation (Tukey HSD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) Group | (J) Group | Mean Difference (I − J) | Std. Error | p-Value |
| Control | H2O | 26.0 | 4.3 | <0.001 |
| NaOCl | 18.4 | 4.3 | <0.001 | |
| H3PO4 + Ethanol | 13.3 | 4.3 | <0.001 | |
| Ivoclean | 3.2 | 4.3 | 0.5 | |
| H2O | NaOCl | −7.6 | 2.4 | 0.02 |
| H3PO4 + Ethanol | −13.3 | 4.0 | <0.001 | |
| Ivoclean | −23.2 | 4.0 | <0.001 | |
| NaOCl | H3PO4 + Ethanol | −5.7 | 4.0 | 0.1 |
| Ivoclean | −15.6 | 4.0 | <0.001 | |
| H3PO4 + Ethanol | Ivoclean | −9.9 | 4.0 | 0.002 |
| Sample | C1s | O1s | N1s | Zr3d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean sample without contamination (Control) | 65.81 | 21.92 | ------ | 6.31 |
| Sample Contaminated with saliva without cleaning | 71.83 | 26.53 | 7.39 | 4.34 |
| Water | 67.64 | 17.45 | 2.85 | 1.04 |
| Sodium hypochlorite | 53.77 | 24.45 | ------ | 5.32 |
| 37% Phosphoric acid + 96% ethanol | 42.16 | 36.67 | 5.3 | 10.59 |
| Ivoclean | 57.1 | 31.84 | 1.88 | 9.18 |
| Sample | Contact Angle |
|---|---|
| Clean sample without contamination (Control) | 27.27 |
| Sample Contaminated with saliva without cleaning | 36.00 |
| Water | 66.81 |
| Sodium hypochlorite | 81.37 |
| 37% Phosphoric acid + 96% ethanol | 77.73 |
| Ivoclean | 75.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsultani, R.Z.; Gholam, M.K. Effectiveness of Various Cleaning Protocols in Enhancing Resin–Zirconia Bond Strength After Saliva Contamination. Prosthesis 2025, 7, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060158
Alsultani RZ, Gholam MK. Effectiveness of Various Cleaning Protocols in Enhancing Resin–Zirconia Bond Strength After Saliva Contamination. Prosthesis. 2025; 7(6):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060158
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsultani, Reyam Zahir, and Mohammed Kassim Gholam. 2025. "Effectiveness of Various Cleaning Protocols in Enhancing Resin–Zirconia Bond Strength After Saliva Contamination" Prosthesis 7, no. 6: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060158
APA StyleAlsultani, R. Z., & Gholam, M. K. (2025). Effectiveness of Various Cleaning Protocols in Enhancing Resin–Zirconia Bond Strength After Saliva Contamination. Prosthesis, 7(6), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060158






