The Stress Distribution and Deformation of Maxillary Bilateral Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures with U-Shaped Palatal Major Connectors Fabricated from Different Materials: A Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pre-Processing Phase
2.1.1. Model Simulation
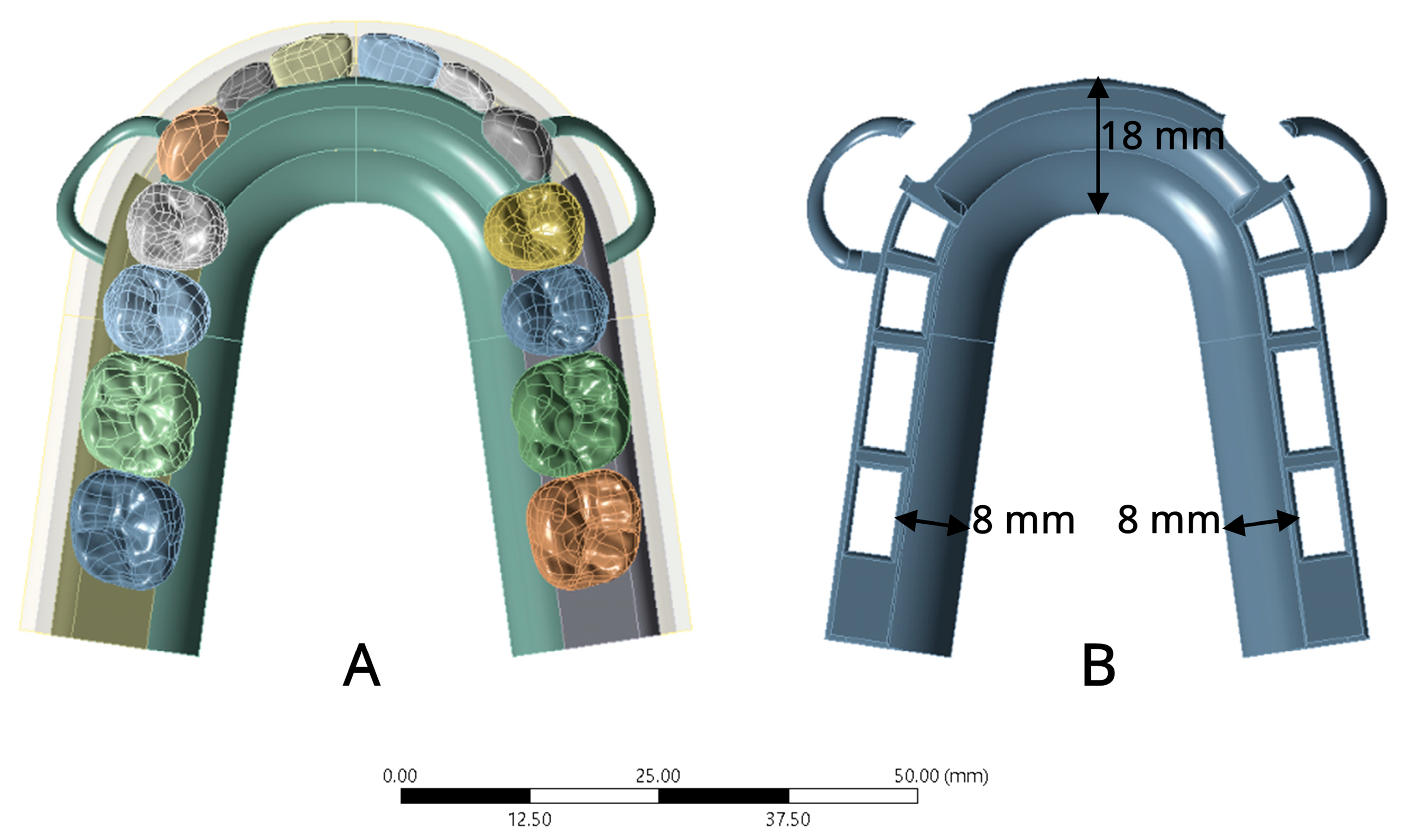
2.1.2. Meshing Model
2.1.3. Material Mechanical Properties for FEA
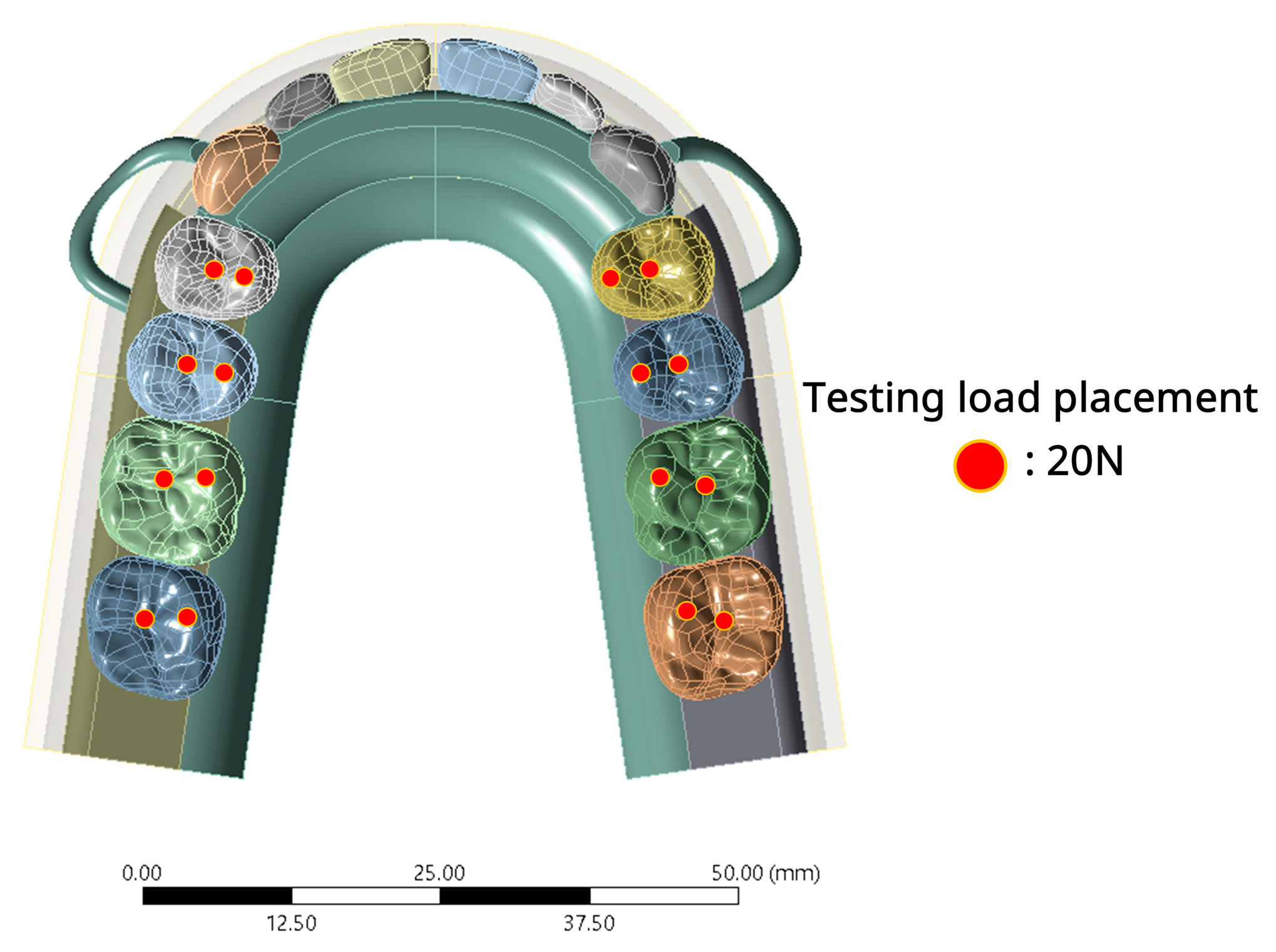
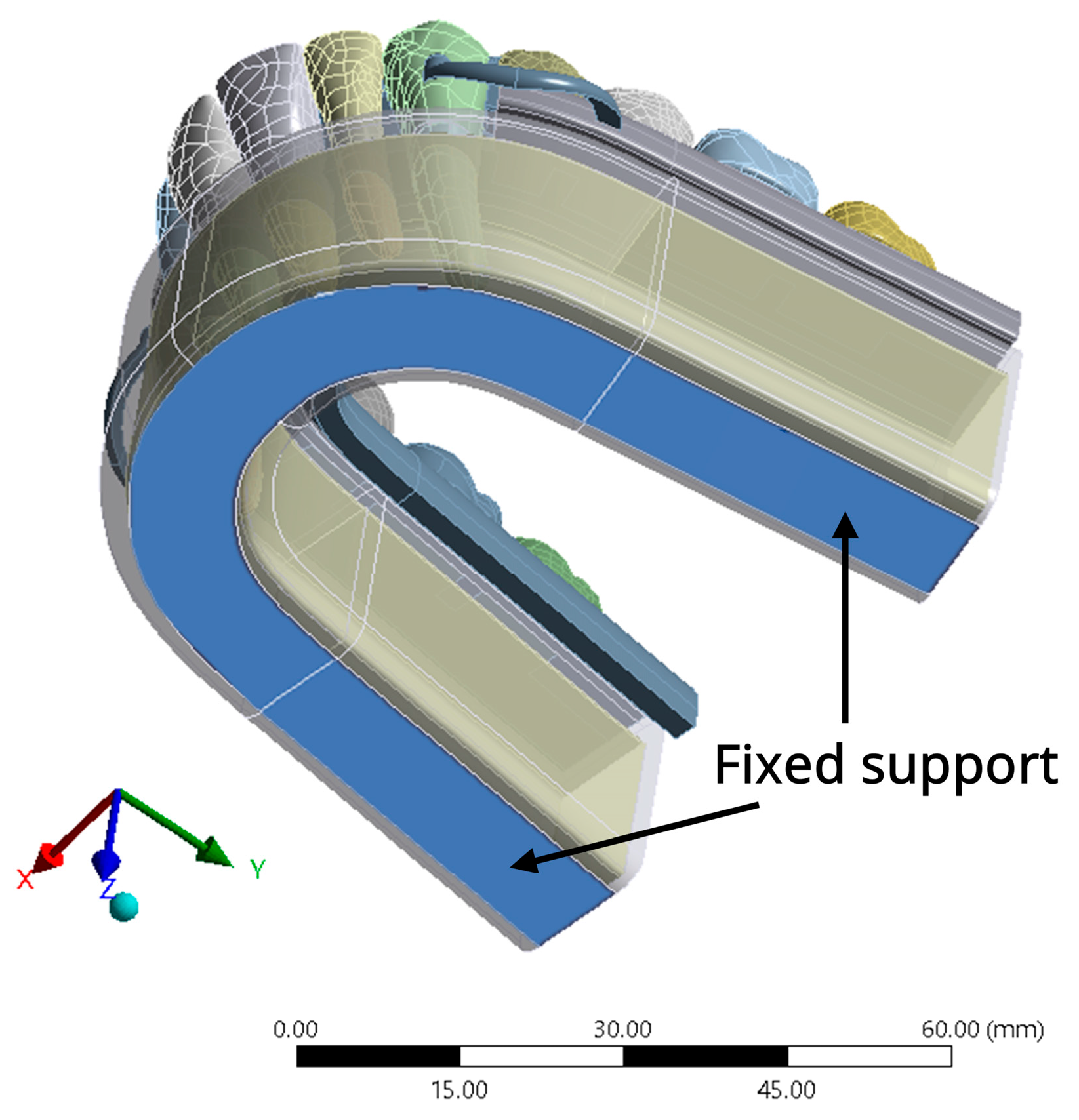
2.1.4. Boundary Condition and Loading
2.2. Solution Phase and Post-Processing Phase
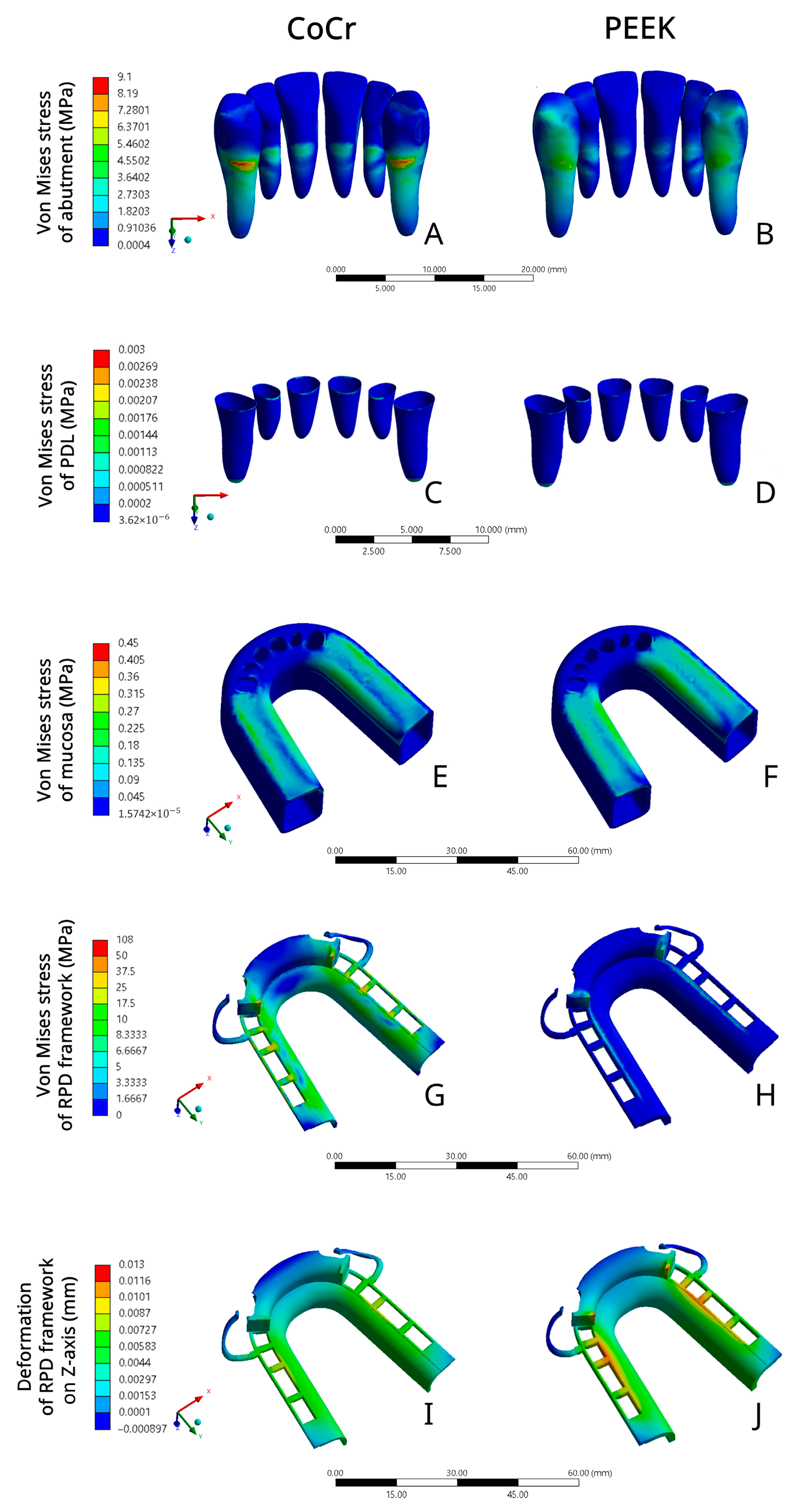
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- CoCr RPD exerted higher stress on the abutment in comparison to PEEK RPD, which suggested that PEEK RPD might have a better protective effect on the abutment.
- CoCr RPD and PEEK RPD applied similar stress on the mucosa and PDL, whose stress values were all within the tissue’s physiological limitation. Both PEEK RPD and CoCr RPD were unlikely to cause severe mechanical damage to the mucosa and PDL.
- The RPD framework rigidity was related to the stress distribution and deformation within the framework. The rigid CoCr RPD exerted greater stress on the RPD framework and less deformation compared to PEEK, which was more flexible. Therefore, the thickness of the PEEK framework should be considered.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phoenix, R.D.; Cagna, D.R.; Defreest, C.F. Stewart’s Clinical Removable Partial Prosthodontics, 4th ed.; Quintessence Pub Co.: Hanover Park, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rungsiyakull, C.; Rungsiyakull, P.; Suttiat, K.; Duangrattanaprathip, N. Stress Distribution Pattern in Mini Dental Implant-Assisted RPD with Different Clasp Designs: 3D Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 2416888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVere, A.M.; Krol, A.J. Selection of a Major Connector for the Extension-Base Removable Partial Denture. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 94, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ur, Z.; Matalon, S.; Aviv, I.; Cardash, H.S. Rigidity of Major Connectors When Subjected to Bending and Torsion Forces. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 62, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ur, Z.; Mijiritsky, E.; Gorfil, C.; Brosh, T. Stiffness of Different Designs and Cross-Sections of Maxillary and Mandibular Major Connectors of Removable Partial Dentures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mm, G. Removable Partial Denture Designing: Variation of Hard and Soft Tissue Anatomy and Maxillary Major Connector Selection. Int. J. Dent. Oral Sci. 2017, 4, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, M.; Wakabayashi, N.; Ohyama, T. Finite Element Analysis of Deflections in Major Connectors for Maxillary RPDs. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2002, 15, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akl, M.A.; Stendahl, C.G. Removable Partial Denture Frameworks in the Age of Digital Dentistry: A Review of the Literature. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizoglu, S.; Duymus, Z.Y. Evaluation of Cobalt, Chromium, and Nickel Concentrations in Plasma and Blood of Patients with Removable Partial Dentures. Dent. Mater. J. 2006, 25, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoki, M.; Nishigaw, K. Dental Metal Allergy. In Contact Dermatitis; Ro, Y.S., Ed.; InTech: San Jose, CA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-577-8. [Google Scholar]
- Skirbutis, G.; Dzingutė, A.; Masiliūnaitė, V.; Šulcaitė, G.; Žilinskas, J. A Review of PEEK Polymer’s Properties and Its Use in Prosthodontics. Stomatologija 2017, 19, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Kamposiora, P.; Papavasiliou, G.; Ferrari, M. The Use of PEEK in Digital Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S.; Cangül, S.; Adıgüzel, Ö.; Değer, Y. Areas for Use of PEEK Material in Dentistry. Int. Dent. Res. 2018, 8, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.A.; Abdullah, J.Y.; Jamayet, N.B.; El-Anwar, M.I.; Ganji, K.K.; Alam, M.K.; Husein, A. Biomechanics in Removable Partial Dentures: A Literature Review of FEA-Based Studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5699962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopade, S.; Madhav, V.; Palaskar, J. Finite Element Analysis: New Dimension in Prosthodontic Research. J. Dent. Allied Sci. 2014, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Advancements in Finite Element Analysis for Prosthodontics. Prog. Med. Devices 2024, 2, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, F.; Steiner, M.; Shahin, R.; Kern, M. Retentive Forces and Fatigue Resistance of Thermoplastic Resin Clasps. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayinger, F.; Micovic, D.; Schleich, A.; Roos, M.; Eichberger, M.; Stawarczyk, B. Retention Force of Polyetheretherketone and Cobalt-Chrome-Molybdenum Removable Dental Prosthesis Clasps after Artificial Aging. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribst, J.P.M.; Dal Piva, A.M.D.O.; Borges, A.L.S.; Araújo, R.M.; Da Silva, J.M.F.; Bottino, M.A.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; De Jager, N. Effect of Different Materials and Undercut on the Removal Force and Stress Distribution in Circumferential Clasps during Direct Retainer Action in Removable Partial Dentures. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, L.; Yu, H. A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Mechanical Function for 4 Removable Partial Denture Designs with 3 Framework Materials: CoCr, Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and PEEK. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, I.E.; Abdel-Khalek, E.A.; Hegazy, S.A. CAD/CAM Constructed Poly(Etheretherketone) (PEEK) Framework of Kennedy Class I Removable Partial Denture: A Clinical Report. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e595–e598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemnithikul, N.; Angkasith, P.; Chaijareenont, P. Removable Partial Denture Polyetheretherketone Framework: A Case Report. Chiang Mai Dent. J. 2021, 42, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Zoidis, P.; Papathanasiou, I.; Polyzois, G. The Use of a Modified Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (PEEK) as an Alternative Framework Material for Removable Dental Prostheses. A Clinical Report. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kanbara, R.; Ochiai, K.T.; Tanaka, Y. A Finite Element Evaluation of Mechanical Function for 3 Distal Extension Partial Dental Prosthesis Designs with a 3-Dimensional Nonlinear Method for Modeling Soft Tissue. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, N.R.; Senthil Kumar, K.; Nagachandran, K.; Hashir, Y. Apical Stress Distribution on Maxillary Central Incisor during Various Orthodontic Tooth Movements by Varying Cemental and Two Different Periodontal Ligament Thicknesses: A FEM Study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2012, 23, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.J.E.; Zwirner, J.; Ramani, R.S.; Ma, S.; Hussaini, H.M.; Waddell, J.N.; Hammer, N. Mechanical Properties of Human Oral Mucosa Tissues Are Site Dependent: A Combined Biomechanical, Histological and Ultrastructural Approach. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2020, 6, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, K.; Morita, M.; Matsuka, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Watanabe, T. Rehabilitation of Biting Abilities in Patients with Different Types of Dental Prostheses. J. Oral Rehabil. 2000, 27, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viecilli, R.F.; Katona, T.R.; Chen, J.; Hartsfield, J.K.; Roberts, W.E. Three-Dimensional Mechanical Environment of Orthodontic Tooth Movement and Root Resorption. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, e11–e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, A.H.; Taha, A.R.; Khorazaty, N.S. Evaluation of Periodontal Health of The Abutment Teeth in Partial Dentures Made of Injection Molded PEEK Framework Versus Cobalt Chromium Framework in Mandibular Kennedy Class I Free End Saddle Edentulous Cases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Adv. Dent. J. 2024, 6, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogimoto, T.; Ogawa, T.; Sumiyoshi, K.; Matsuka, Y.; Koyano, K. Pressure–Pain Threshold Determination in the Oral Mucosa: Validity and Reliability. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, H.; Sakurai, K. Changes of Blood Flow in the Mucosa Underlying a Mandibular Denture Following Pressure Assumed as a Result of Light Clenching. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruoka, M.; Ishizaki, K.; Sakurai, K.; Matsuzaka, K.; Inoue, T. Morphological and Molecular Changes in Denture-supporting Tissues under Persistent Mechanical Stress in Rats. J. Oral Rehabil. 2008, 35, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szentpétery, A.G.; John, M.T.; Slade, G.D.; Setz, J.M. Problems Reported by Patients before and after Prosthodontic Treatment. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2005, 18, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ogimoto, T.; Okushi, N.; Koyano, K.; Takeuchi, K. Mapping, Profiling and Clustering of Pressure Pain Threshold (PPT) in Edentulous Oral Mucosa. J. Dent. 2004, 32, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Koli, D.K.; Jain, V.; Nanda, A. Stress Distribution and Patient Satisfaction in Flexible and Cast Metal Removable Partial Dentures: Finite Element Analysis and Randomized Pilot Study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 11, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, P.; Madan, R.; Ritwal, P.; Yadav, B.; Girotra, M.; Singh, D. Comparative Evaluation of the Stresses on the Terminal Abutment and Edentulous Ridge in Unilateral Distal Extension Condition When Restored with Different Prosthetic Options: An FEA Analysis. Int. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2023, 13, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Russo, L.; Chochlidakis, K.; Caradonna, G.; Molinelli, F.; Guida, L.; Ercoli, C. Removable Partial Dentures with Polyetheretherketone Framework: The Influence on Residual Ridge Stability. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, A.; Tosun, B. Effect of Different Surface Roughening Treatment on Polyether Ether Ketone and Acrylic Resin Bonding: A Pilot Study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2024, 61, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurahashi, K.; Matsuda, T.; Ishida, Y.; Ichikawa, T. Effect of Surface Treatments on Shear Bond Strength of Polyetheretherketone to Autopolymerizing Resin. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Machado, P.; Cadore Rodrigues, A.C.; Chaves, E.T.; Susin, A.H.; Valandro, L.F.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Rippe, M.P. Surface Treatments and Adhesives Used to Increase the Bond Strength Between Polyetheretherketone and Resin-Based Dental Materials: A Scoping Review. J. Adhes. Dent. 2022, 24, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Darvell, B.W. Determination of the Flexural Modulus of Elasticity of Orthodontic Archwires. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Structure | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Enamel [24] | 41.1 | 0.35 |
| Dentin [24] | 18.6 | 0.35 |
| Cementum [25] | 15.4 | 0.31 |
| Periodontal ligament [24] | 0.0004 | 0.49 |
| Residual ridge mucosa [26] | 0.03736 | 0.49 |
| Cortical bone [24] | 11.76 | 0.25 |
| Cancellous bone [24] | 1.47 | 0.3 |
| Resin acrylic and artificial teeth [24] | 2.45 | 0.3 |
| Cobalt–chromium alloy (CoCr) [20] | 235 | 0.33 |
| Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) [20] | 4.1 | 0.4 |
| Components | CoCr RPD Model VMS (MPa) | PEEK RPD Model VMS (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Abutment | 9.098 | 7.515 |
| Periodontal ligament | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| Residual ridge mucosa | 0.353 | 0.442 |
| RPD framework | 107.99 | 11.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weerayutsil, P.; Sae-Lee, D.; Suriyawanakul, J.; Rungsiyakull, P.; Poovarodom, P. The Stress Distribution and Deformation of Maxillary Bilateral Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures with U-Shaped Palatal Major Connectors Fabricated from Different Materials: A Finite Element Analysis. Prosthesis 2025, 7, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060150
Weerayutsil P, Sae-Lee D, Suriyawanakul J, Rungsiyakull P, Poovarodom P. The Stress Distribution and Deformation of Maxillary Bilateral Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures with U-Shaped Palatal Major Connectors Fabricated from Different Materials: A Finite Element Analysis. Prosthesis. 2025; 7(6):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060150
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeerayutsil, Peerada, Daraporn Sae-Lee, Jarupol Suriyawanakul, Pimduen Rungsiyakull, and Pongsakorn Poovarodom. 2025. "The Stress Distribution and Deformation of Maxillary Bilateral Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures with U-Shaped Palatal Major Connectors Fabricated from Different Materials: A Finite Element Analysis" Prosthesis 7, no. 6: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060150
APA StyleWeerayutsil, P., Sae-Lee, D., Suriyawanakul, J., Rungsiyakull, P., & Poovarodom, P. (2025). The Stress Distribution and Deformation of Maxillary Bilateral Distal-Extension Removable Partial Dentures with U-Shaped Palatal Major Connectors Fabricated from Different Materials: A Finite Element Analysis. Prosthesis, 7(6), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7060150






