A Quality Study on Patients’ Perceptions After Digitally Driven Smile Creation Including Aligners and Minimally Invasive Prosthetic Restorations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
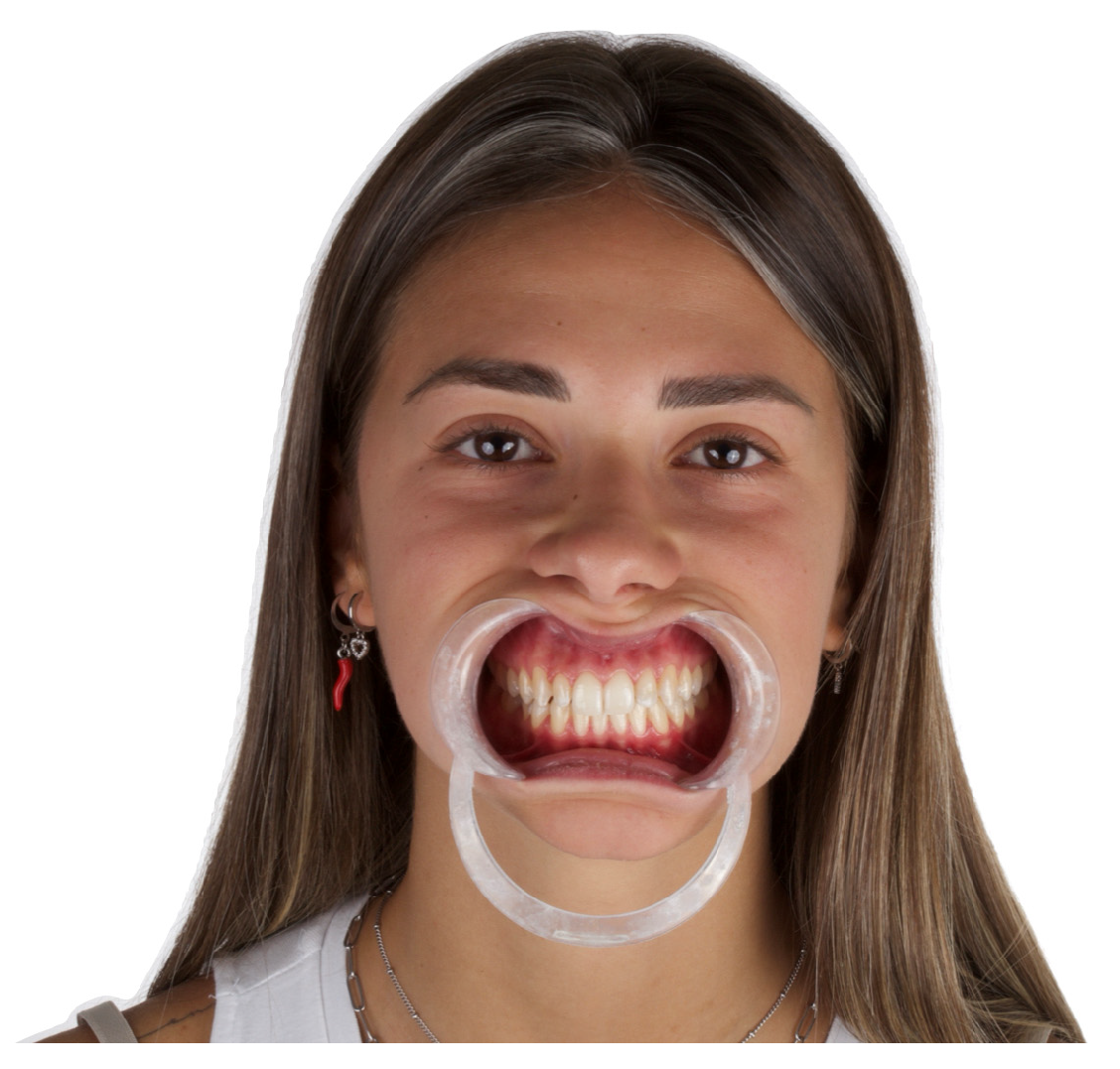
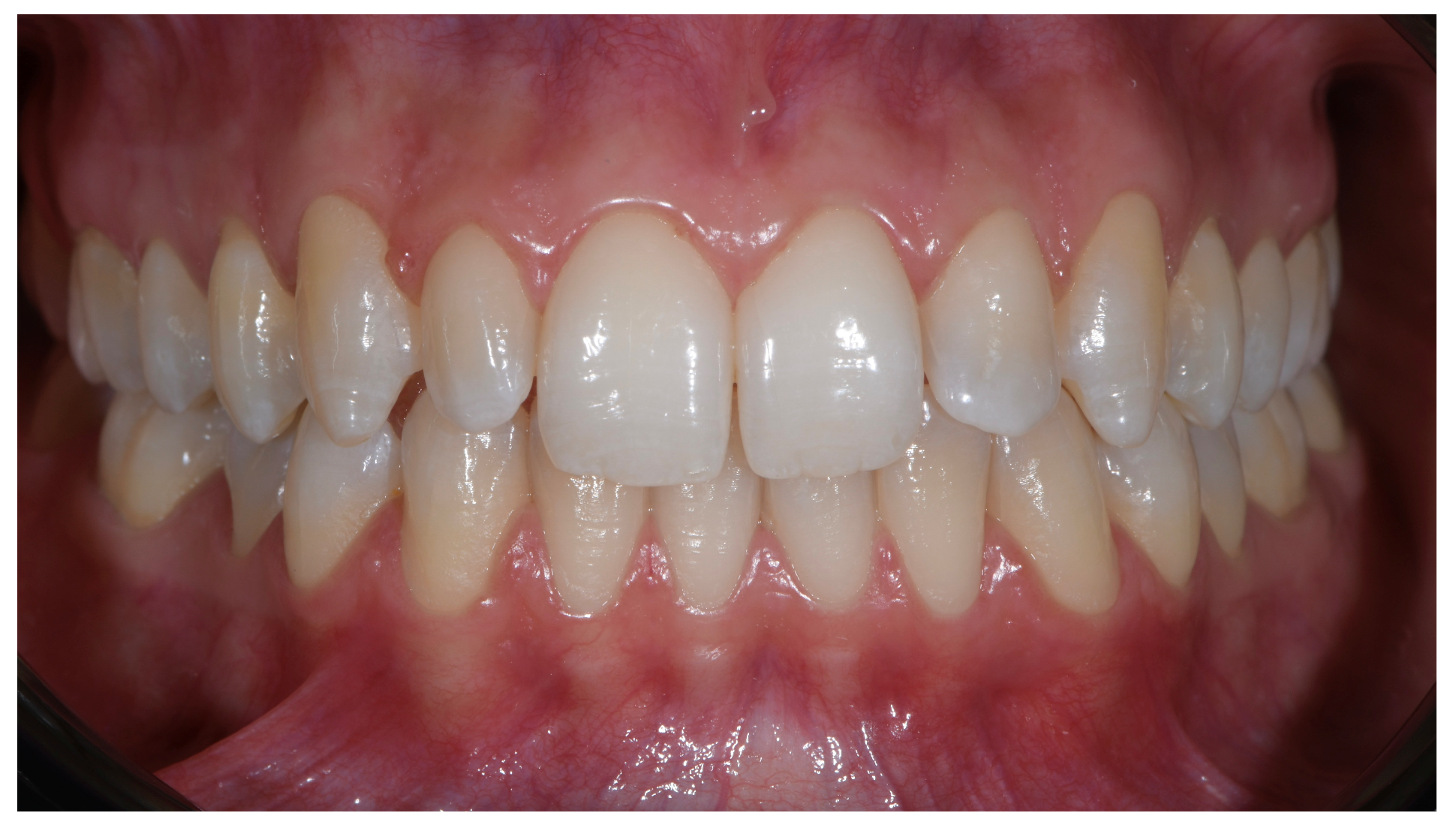
2.2. Standardized Protocol for Patient Photo Recording
2.3. Standardized Protocol for Patient Video Recording
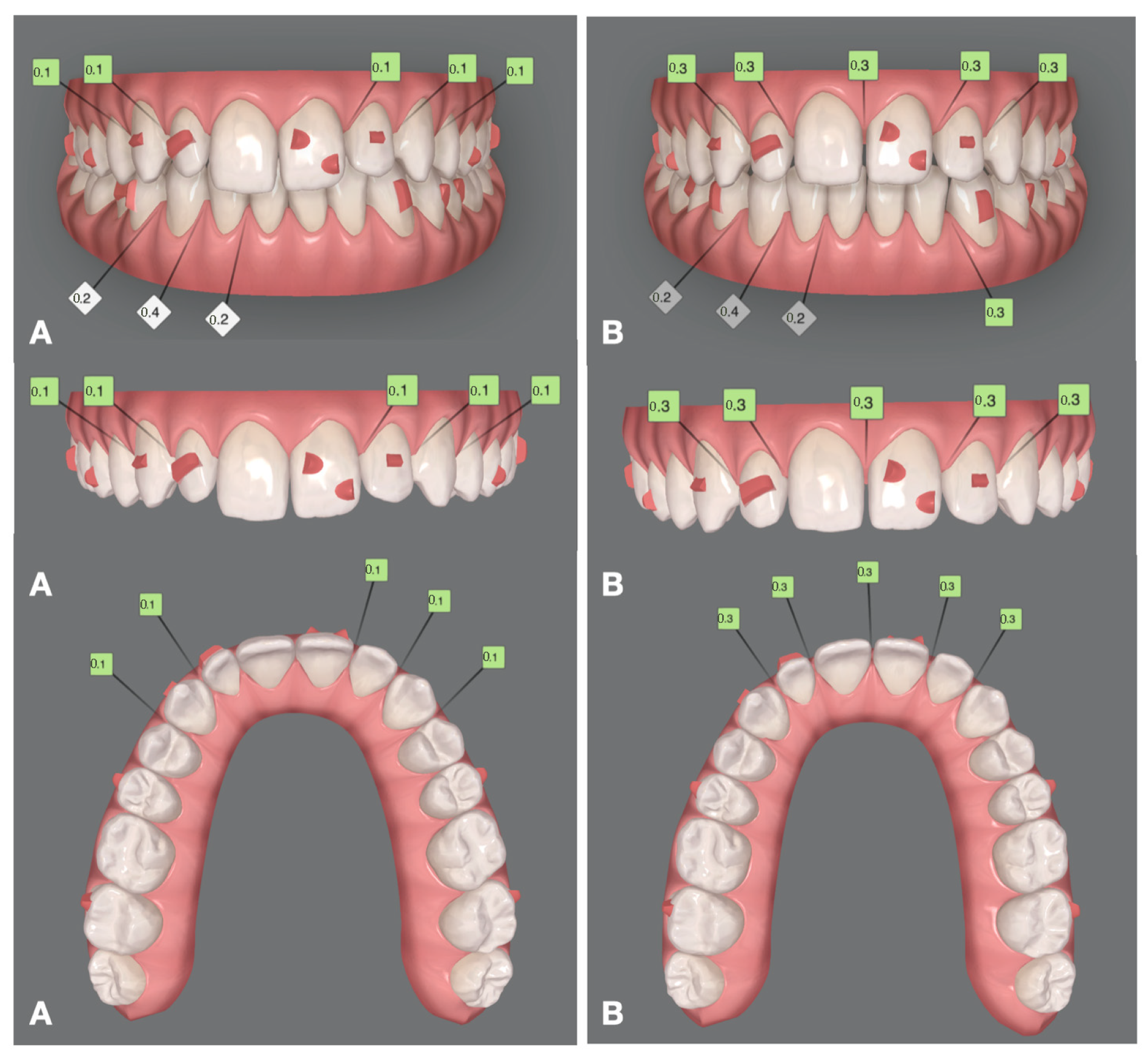
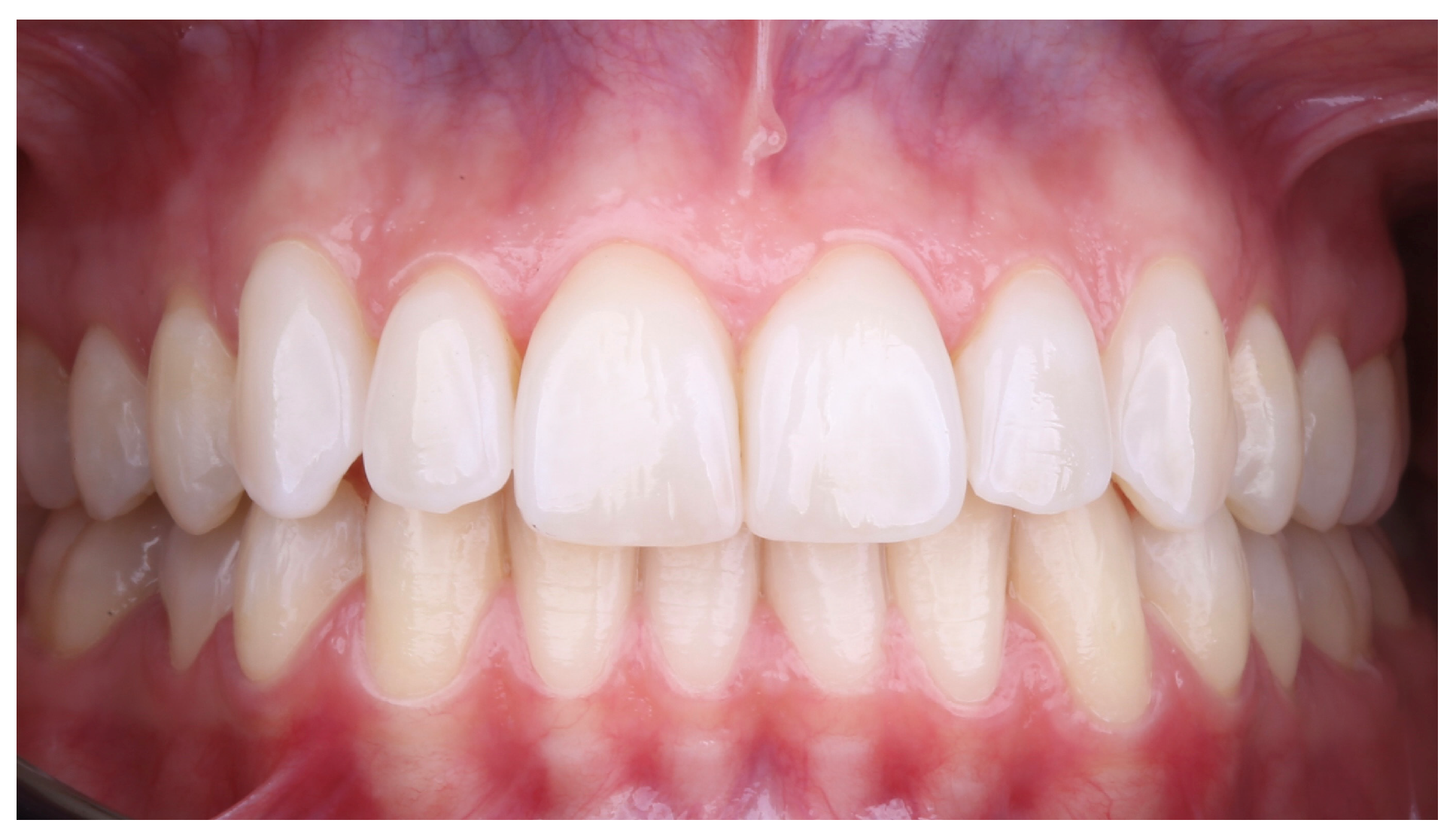
2.4. Digital Mock-Up and Orthodontic Treatment
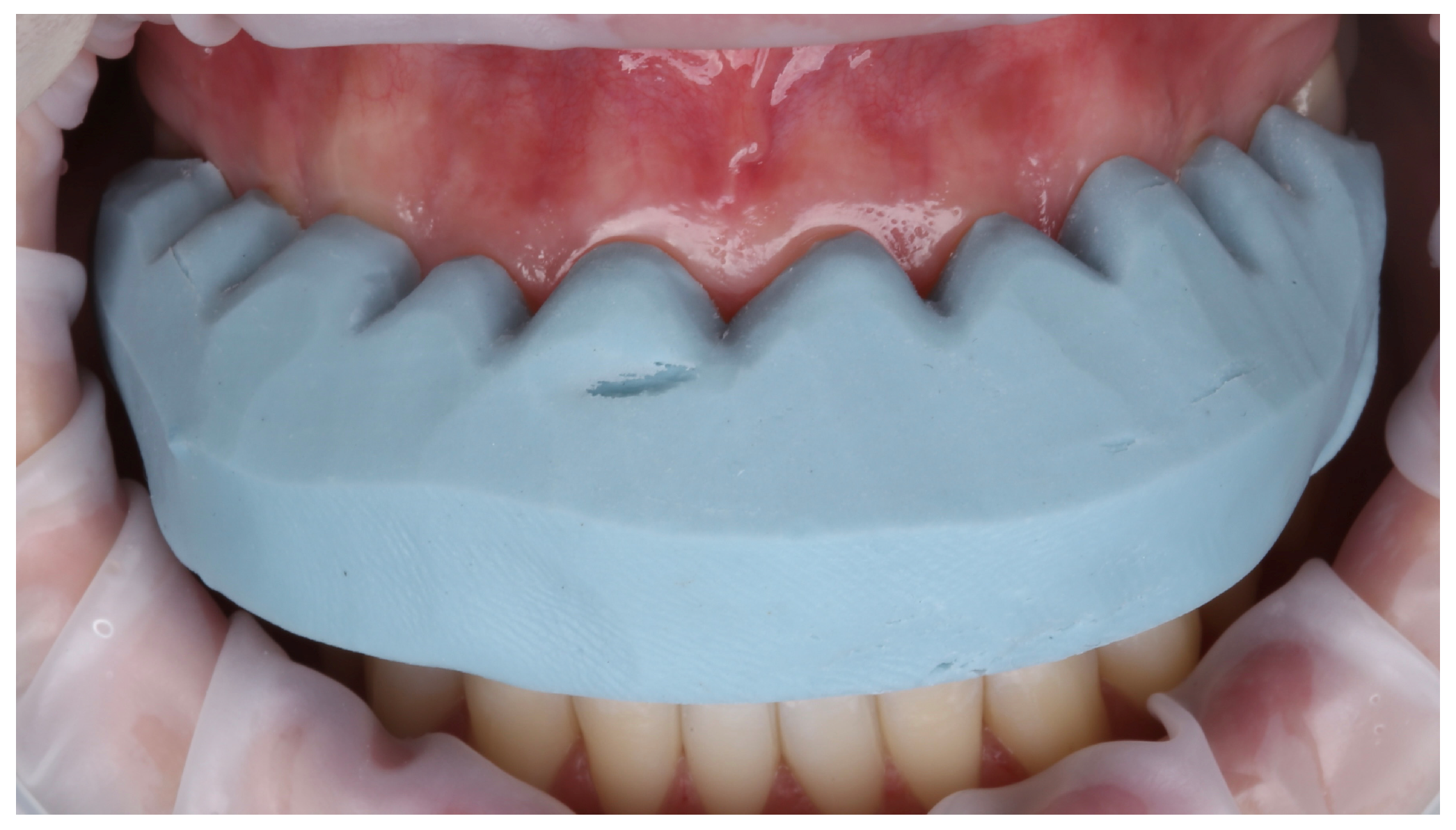
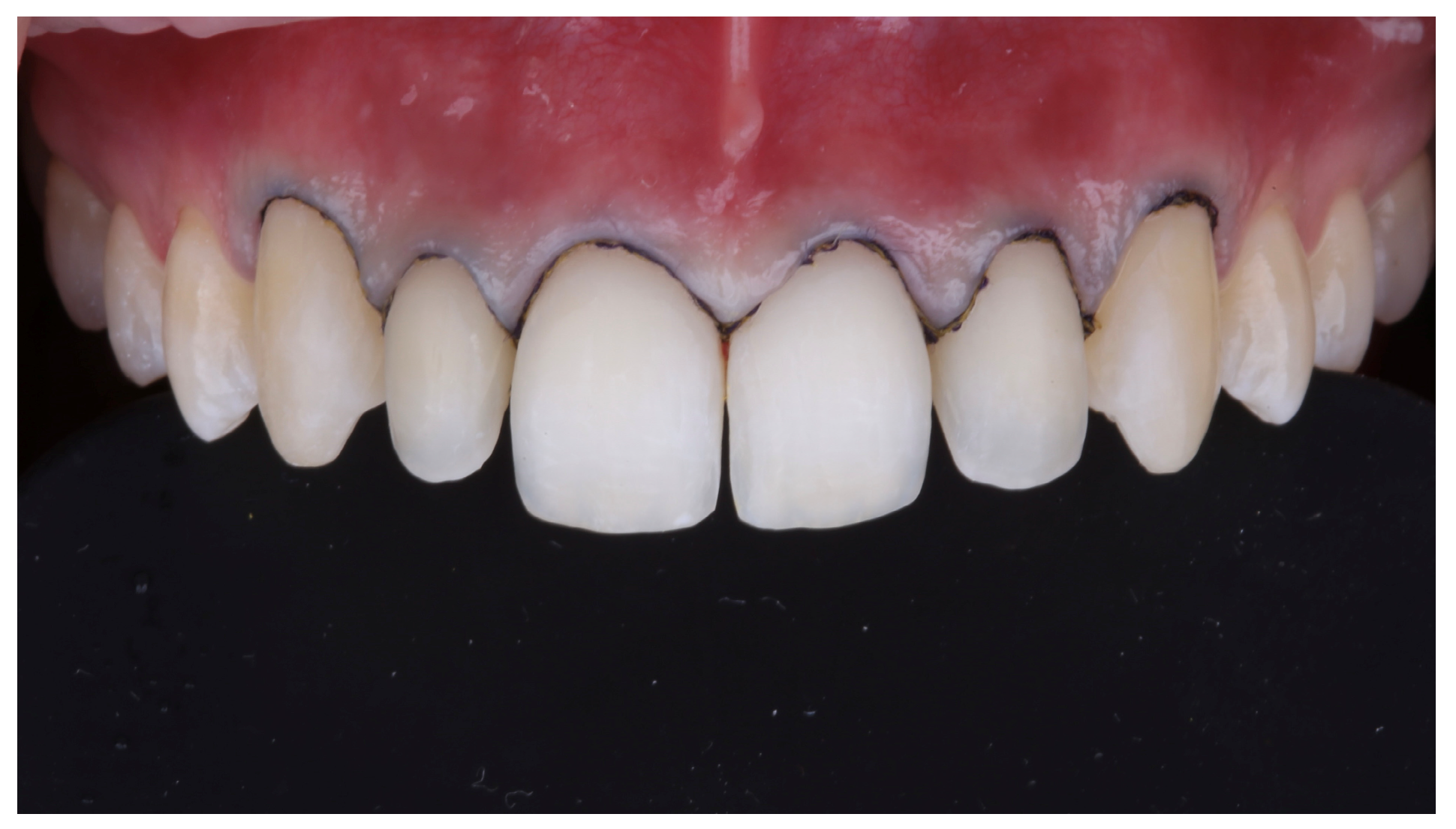
2.5. Prosthetic Treatment
2.6. Primary Outcome
Patient Questionnaire: Evaluation of Digital Smile Design and Treatment Outcomes
- What were your main reasons for seeking treatment? (Select all that apply):
- 2.
- On a scale from 0 to 10, how would you rate the aesthetics of your current smile?
- 3.
- On a scale from 0 to 10, how would you rate the functionality of your current smile (e.g., chewing, speaking)?
- 4.
- Would you be willing to undergo orthodontic treatment with aligners to improve aesthetics and/or function?
- 5.
- Regarding tooth shape and appearance, which do you prefer?
- 6.
- Do you prefer:
- 7.
- On a scale from 0 to 10, how would you rate the 2D digital aesthetic preview of your smile?
- 8.
- On a scale from 0 to 10, how would you rate the 3D digital aesthetic preview of your smile?
- 9.
- Based on the previews, how satisfied are you with the proposed aesthetic outcome so far?
- 10.
- After reviewing the mock-up, how well did the tooth shape meet your expectations? (0 = not at all, 10 = perfectly)
- 11.
- How well did the tooth color match your expectations? (0 = not at all, 10 = perfectly)
- 12.
- Do you feel that the use of digital software improved communication between you and your dentist?
- 13.
- On a scale from 0 to 10, how satisfied are you with the final aesthetic result?
- 14.
- On a scale from 0 to 10, how satisfied are you with the final functional result?
- 15.
- To what extent did the final results meet your expectations?
- 16.
- Overall, how much do you like your smile now? (0 = not at all, 10 = completely)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kokich, V.O.; Kiyak, H.A.; Shapiro, P.A. Comparing the perception of dentists and lay people to altered dental esthetics. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 1999, 11, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihali, S.G.; Lolos, D.; Popa, G.; Tudor, A.; Bratu, D.C. Retrospective long-term clinical outcome of feldspathic ceramic veneers. Materials 2022, 15, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, S.; Albanesi, R.B.; Sesma, N.; Agra, C.M.; Braga, M.M. Main clinical outcomes of feldspathic porcelain and glass-ceramic laminate veneers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of survival and complication rates. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venezia, P.; Ronsivalle, V.; Isola, G.; Ruiz, F.; Casiello, E.; Leonardi, R.; Lo Giudice, A. Prosthetically guided orthodontics (PGO): A personalized clinical approach for aesthetic solutions using digital technology. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkut, B.; Unal, T.; Murat, N.; Özcan, M. Effect of prerestorative short-term clear aligner therapy in restorative treatment planning. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025, 133, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, M.B.; Ackerman, J.L. Smile analysis and design in the digital era. J. Clin. Orthod. 2002, 36, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coachman, C.; Paravina, R.D. Digitally enhanced esthetic dentistry—From treatment planning to quality control. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2016, 28, S3–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.F.; Culp, L.; Luedin, N. A digital approach to improved overdentures for the adolescent oligodontia patient. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2016, 28, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervino, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Arzukanyan, A.V.; Spagnuolo, G.; Cicciù, M. Dental restorative digital workflow: Digital smile design from aesthetic to function. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, P.P.; da Costa, R.G.; Calgaro, M.; Ritter, A.V.; Correr, G.M.; da Cunha, L.F.; Gonzaga, C.C. Digital smile design and mock-up technique for esthetic treatment planning with porcelain laminate veneers. J. Conserv. Dent. 2018, 21, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshiddi, I.F.; BinSaleh, S.M.; Alhawas, Y. Patient’s perception on the esthetic outcome of anterior fixed prosthetic treatment. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2015, 16, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Gallucci, G.O. The virtual patient in dental medicine. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, F.; Gandolfi, A.; Luongo, G.; Logozzo, S. Intraoral scanners in dentistry: A review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, P.; Spitznagel, F.A.; Zembic, A.; Prott, L.S.; Pieralli, S.; Bongaerts, B.; Metzendorf, M.I.; Langner, R.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C. Survival and Complication Rates of Feldspathic, Leucite-Reinforced, Lithium Disilicate and Zirconia Ceramic Laminate Veneers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2025, 37, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarone, F.; Russo, S.; Sorrentino, R.; Ferrari, M.; Morgano, S.M. Minimally invasive approaches for anterior teeth restoration: Clinical guidelines. Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 2021, 16, 408–422. [Google Scholar]
- Zotti, F.; Pappalardo, D.; Capocasale, G.; Sboarina, A.; Bertossi, D.; Albanese, M. Aesthetic Dentistry, How You Say and How You See: A 500-People Survey on Digital Preview and Color Perception. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2020, 12, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buduru, S.; Cofar, F.; Mesaroș, A; Tăut, M.; Negucioiu, M.; Almășan, O. Perceptions in Digital Smile Design: Assessing Laypeople and Dental Professionals’ Preferences Using an Artificial-Intelligence-Based Application. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Question | Result |
|---|---|
| Mean age | 26.6 years |
| Reason for treatment | All for aesthetic reasons |
| Pre-treatment smile aesthetics (0–10) | 4.8 (range: 4–6) |
| Pre-treatment function (0–10) | 6.6 (range: 5–8) |
| Accepted aligner therapy | All accepted |
| Smile style preference | All preferred natural-looking smile |
| Tooth color preference | 4 natural, 1 super white |
| 2D preview rating (0–10) | 7.8 |
| 3D preview rating (0–10) | 9.2 |
| Satisfaction with proposed outcome | All very satisfied |
| Tooth shape expectation match (0–10) | 9.4 |
| Tooth color expectation match (0–10) | 9.2 |
| Post-treatment smile aesthetics (0–10) | 9.8 (range: 9–10) |
| Post-treatment function (0–10) | 9.4 (range: 8–10) |
| Expectation fulfillment | Most completely met |
| Overall smile satisfaction (0–10) | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tallarico, M.; Lumbau, A.I.; Sorrenti, M.; Lione, R.; Cacciò, C.; Annucci, M.; Meloni, S.M.; Pisano, M. A Quality Study on Patients’ Perceptions After Digitally Driven Smile Creation Including Aligners and Minimally Invasive Prosthetic Restorations. Prosthesis 2025, 7, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7040068
Tallarico M, Lumbau AI, Sorrenti M, Lione R, Cacciò C, Annucci M, Meloni SM, Pisano M. A Quality Study on Patients’ Perceptions After Digitally Driven Smile Creation Including Aligners and Minimally Invasive Prosthetic Restorations. Prosthesis. 2025; 7(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleTallarico, Marco, Aurea Immacolata Lumbau, Mariapia Sorrenti, Roberta Lione, Carlotta Cacciò, Marco Annucci, Silvio Mario Meloni, and Milena Pisano. 2025. "A Quality Study on Patients’ Perceptions After Digitally Driven Smile Creation Including Aligners and Minimally Invasive Prosthetic Restorations" Prosthesis 7, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7040068
APA StyleTallarico, M., Lumbau, A. I., Sorrenti, M., Lione, R., Cacciò, C., Annucci, M., Meloni, S. M., & Pisano, M. (2025). A Quality Study on Patients’ Perceptions After Digitally Driven Smile Creation Including Aligners and Minimally Invasive Prosthetic Restorations. Prosthesis, 7(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7040068








