Modular Stems in Revision Hip Arthroplasty: A Three-Step Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Surgical Technique
1.2. Postoperative Management
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berry, D.J. Epidemiology: Hip and knee. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 30, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, H.; Malchau, H.; Herberts, P.; Garellick, G. Periprosthetic femoral fractures: Classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- W-Dahl, A.; Kärrholm, J.; Rogmark, C.; Nåtman, J. The Swedish Arthroplasty Register Annual Report 2023; Ola Rolfson: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, J.N.; Evans, J.T.; Relton, S.; Whitehouse, M.R.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Pandit, H. The incidence of postoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture following total hip replacement: An analysis of UK National Joint Registry and Hospital Episodes statistics data. PLoS Med. 2024, 21, e1004462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr. Course Lect. 1995, 44, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoffel, K.; Horn, T.; Zagra, L.; Mueller, M.; Perka, C.; Eckardt, H. Periprosthetic fractures of the proximal femur: Beyond the Vancouver classification. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.; Grossmann, A.; Singer, J. Hip revision arthroplasty in periprosthetic fractures of Vancouver type B2 and B3. J. Orthop. Trauma 2012, 26, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.; Fuerst, M.; Singer, J. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur associated with hip arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2005, 125, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H. A revision prosthesis for the hip joint. Der Orthop. 1989, 18, 438–453. [Google Scholar]
- Ovesen, O.; Emmeluth, C.; Hofbauer, C.; Overgaard, S. Revision total hip arthroplasty using a modular tapered stem with distal fixation: Good short-term results in 125 revisions. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, C.; Mashadi, M.; Parvizi, J.; Austin, M.S.; Hozack, W.J. Modular femoral stems for revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beals, R.K.; Tower, S.S. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur: An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 327, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barghi, A.; Hanna, P.; Merchan, N.; Lechtig, A.; Haggerty, C.; Weaver, M.J.; von Keudell, A.; Wixted, J.; Appleton, P.; Rodriguez, E. Outcomes after operative fixation of Vancouver B2 and B3 type periprosthetic fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 36, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapienza, M.; Di Via, D.; Vaccalluzzo, M.S.; Costarella, L.; Pavone, V.; Testa, G. Comparative Analysis of Cemented and Cementless Straight-Stem Prostheses in Hip Replacement Surgery for Elderly Patients: A Mid-Term Follow-up Study. Prosthesis 2024, 6, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perticarini, L.; Rossi, S.M.P.; Fioruzzi, A.; Jannelli, E.; Mosconi, M.; Benazzo, F. Modular tapered conical revision stem in hip revision surgery: Mid-term results. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.-X.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z.-J.; Li, Y.-K.; Ban, Z.-N. Revision total hip arthroplasty using a fluted, tapered, modular stem follow-up method for a mean of three years: A preliminary study. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 873584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, J.; Alijanipour, P.; Heller, S.; Dove, M.; Parvizi, J. Increased risk of heterotopic ossification following revision hip arthroplasty for periprosthetic joint infection. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 6, 486. [Google Scholar]
- Hug, K.T.; Alton, T.B.; Gee, A.O. In Brief: Classifications in Brief: Brooker Classification of Heterotopic Ossification After Total Hip Arthroplasty; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sukopp, M.; Taylor, D.; Forst, R.; Seehaus, F. Femoral stem fracture in hip revision arthroplasty: A systematic literature review of the real-world evidence. Z. Für Orthopädie Und Unfallchirurgie 2022, 160, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, A.J.; Steidle, C.; Schmidutz, F.; Gonser, C.; Hemmann, P.; Stöckle, U.; Ochs, G. Hip revision arthroplasty of Periprosthetic Fractures Vancouver B2 and B3 with a modular revision stem: Short-term results and review of literature. Z. Für Orthopädie Und Unfallchirurgie 2022, 160, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.Y.; Gong, Y.J.; Safir, O.A.; Gross, A.E.; Kuzyk, P.R. Fixation options following greater trochanteric osteotomies and fractures in total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. JBJS Rev. 2018, 6, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bakoury, A.; Hosny, H.; Williams, M.; Keenan, J.; Yarlagadda, R. Management of vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures by Distal locking femoral stem (Cannulok) in patients 75 Years and older. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B.; Oremek, D. Hip revision arthroplasty for failed osteosynthesis in periprosthetic Vancouver type B1 fractures using a cementless, modular, tapered revision stem. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutalos, A.A.; Varitimidis, S.; Malizos, K.N.; Karachalios, T. Clinical, functional and radiographic outcomes after revision total hip arthroplasty with tapered fluted modular or non-modular stems: A systematic review. Hip Int. 2022, 32, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Schleck, C.; Harmsen, S.; Lewallen, D. Clinically important improvement thresholds for Harris Hip Score and its ability to predict revision risk after primary total hip arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, H.; Gu, J.; Tang, H.; Tang, Q. What is the difference between modular and nonmodular tapered fluted titanium stems in revision total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 3108–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.N.; Huddleston, J.I.; Hwang, K.; Imrie, S.; Goodman, S.B. Early outcome of a modular femoral component in revision total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, C.; Mulliez, A.; Verdonk, R.; Audenaert, E. Revision hip arthroplasty using a cementless modular tapered stem. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottino, U.; Pirato, F.; Battaglia, D.L.; Dettoni, F.; Bruzzone, M.; Rossi, R. Indications, complications and outcomes of modular stems in total hip revision arthroplasty: A systematic review of the literature. Minerva 2024, 75, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
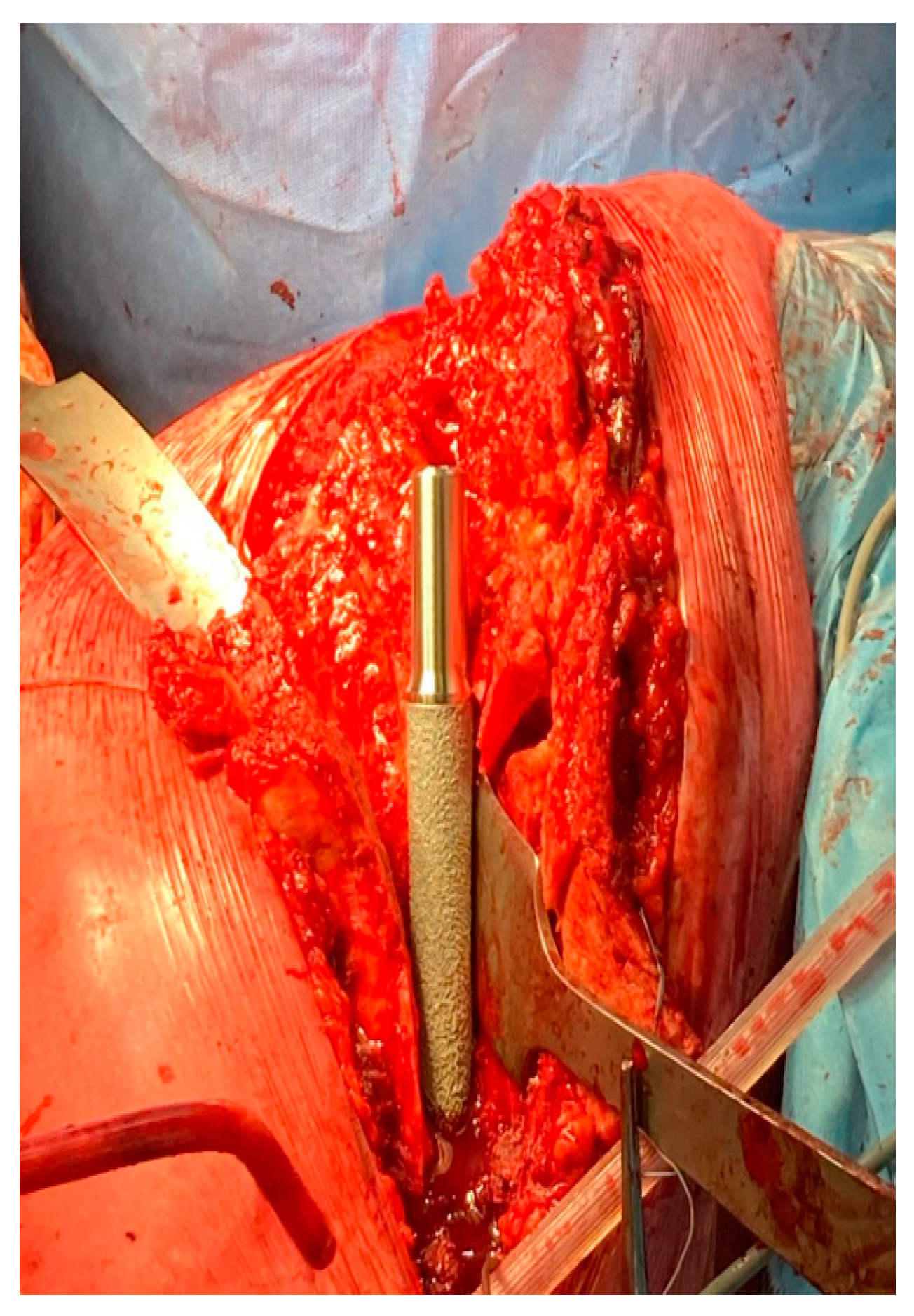


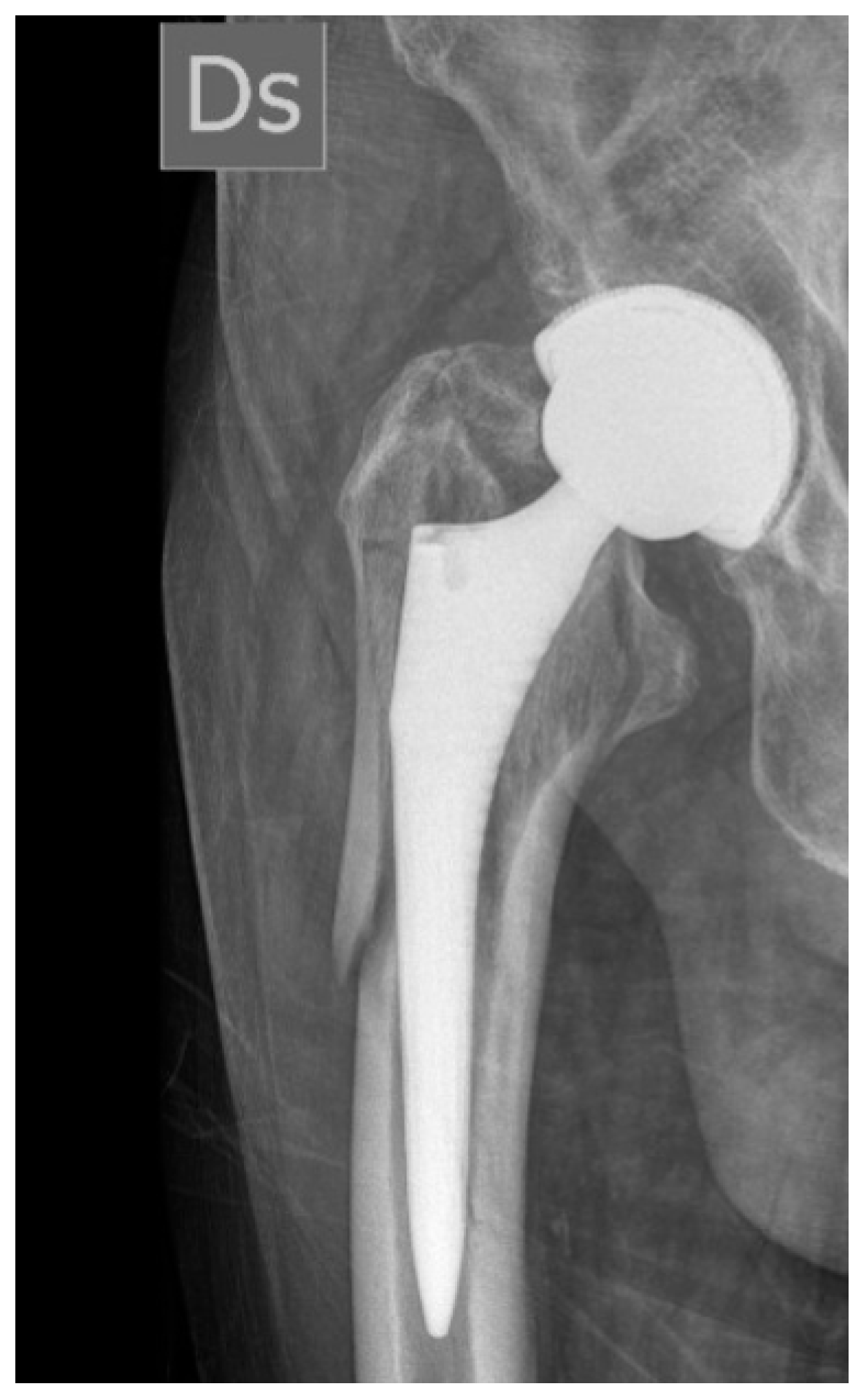

| Step | Goal | Key |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Distal primary stability | Diaphyseal preparation to obtain distal stem stability to build on. |
| 2 | Leg length restoration | Trail proximal body selection and insertion to avoid leg length discrepancies. |
| 3 | Anteversion and offset fixation | Fixing the neck anteversion and offset selection to obtain a stable hip. |
| 3A | Reduction and fixation | Metaphyseal trochanteric bone should be reduced and fixed after stem implantation with another stability evaluation to avoid impingements. |
| Reason for Revision: | |
|---|---|
| Aseptic loosening | 2/10 (20%) |
| Periprosthetic fractures | 7/10 (70%) |
| Nail failure | 1/10 (10%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirato, F.; Vittori, J.; Dettoni, F.; Bruzzone, M.; Rossi, R.; Cottino, U. Modular Stems in Revision Hip Arthroplasty: A Three-Step Technique. Prosthesis 2024, 6, 1553-1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6060111
Pirato F, Vittori J, Dettoni F, Bruzzone M, Rossi R, Cottino U. Modular Stems in Revision Hip Arthroplasty: A Three-Step Technique. Prosthesis. 2024; 6(6):1553-1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6060111
Chicago/Turabian StylePirato, Francesco, Jacopo Vittori, Federico Dettoni, Matteo Bruzzone, Roberto Rossi, and Umberto Cottino. 2024. "Modular Stems in Revision Hip Arthroplasty: A Three-Step Technique" Prosthesis 6, no. 6: 1553-1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6060111
APA StylePirato, F., Vittori, J., Dettoni, F., Bruzzone, M., Rossi, R., & Cottino, U. (2024). Modular Stems in Revision Hip Arthroplasty: A Three-Step Technique. Prosthesis, 6(6), 1553-1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6060111







