Abstract
(1) Background: Cleft lip and palate is the most common congenital malformation of the head and neck. After surgical closure, velopharyngeal dysfunction can arise, which has implications for phonation, sucking, swallowing, middle ear function, and interpersonal well-being. This case series aimed to present an adaptation of the conventional pharyngeal obturator design in order to allow its use with fixed orthodontic appliances. (2) Methods: A new custom-made pharyngeal obturator device was built in order to enable a correct function of the velopharyngeal valve. The fabrication of the plate was made by altering the conventional Hawley retainer, replacing the Adams hooks with 0.9 mm spherical hooks and removing the buccal arch. (3) Results: The new pharyngeal obturator design was used in six cleft patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. The appliance was well tolerated and there was a slight improvement in auditory-perceptive evaluations. (4) Conclusions: The new pharyngeal bulb design proved to have good retention during fixed orthodontic treatment. Moreover, despite the short-term follow-up, it also showed a reduction in the severity of the hypernasality sentences.
1. Introduction
Cleft lip and palate (CLP) is the most common congenital malformation of the head and neck, with an international overall incidence of 14:10,000 [1]. CLP is responsible for an array of anomalies involving the lip, dental arch, and palate. These morphological issues are not only associated with occlusal dysfunction but also speech and breathing problems [2,3].
The CLP treatment begins shortly after birth and continues into adulthood. Orthodontic treatment timing and sequencing are usually set into four different stages of development: from birth to 2 years, 2 to 6 years, 7 to 12 years, and 13 years to adulthood. During neonatal care of CLP patients, the closure of the lip and/or palate is of utmost importance, and this process can be preceded by presurgical maxillary orthopedics to readjust the maxillary segments and separate the tongue from the cleft [2,3]. Primary lip repair performed after the use of the nasoalveolar molding appliance is deemed effective. This means that the continuity of the mucosa is reestablished on both the skin and the underlying mucosa. Lip closure is generally completed when the child is 3 to 6 months of age, while the closure of the palate occurs between 12 months to 2 years of age [4]. Primary lip and palate surgeries can result in different types of malocclusion since these surgeries may restrict maxillary growth in the anteroposterior and transverse plane despite re-establishing aesthetics and function [5]. Consequently, orthopedic treatment is usually needed, and the application of a facemask with or without maxillary expansion is the most frequently used treatment. During the mixed dentition stage, CLP patients may require additional secondary bone grafting surgery. After bone grafting, if craniofacial development is favorable, fixed orthodontic appliances should be used to successfully continue to correct facial esthetics and proper function [6]. Nonetheless, skeletal discrepancies can develop and as such, the orthodontist should consider combining orthodontic treatment with orthognathic surgery [7].
After these interventions, the healing process of the palate may not allow the complete closure of the velopharyngeal valve, creating a condition known as velopharyngeal dysfunction (VPD). This condition can be triggered by various factors, namely, the low regeneration capacity of the soft palate muscles (in association with a reduced number of satellite cells and their low differentiation rate), tissue fibrosis related to TGF-β1 (responsible for the production of collagen and extracellular matrix), and the presence of myostatin (responsible for inhibiting satellite cells, myoblast proliferation, and consequently, muscle regeneration) [8]. The prevalence of VPD in patients with CLP after primary repair of the palate ranges from 30% to 50% [8,9,10].
The velopharyngeal valve consists of the soft palate and the lateral and posterior walls surrounding the pharynx. The purpose of this valve is to close the communication between the nasal and oral cavities. VPD has implications for individuals in terms of phonation, sucking, middle ear function, intraoral air pressure, as well as social and interpersonal well-being [9,11,12,13]. VPD is frequently detected in speech with signs such as hypernasality, low intraoral air pressure, nasal air emission, and compensatory articulation (use of atypical articulation points in speech) [9,12].
The most effective way to diagnose VPD is through an oral examination. This is performed by observation and/or an auditory-perceptive evaluation of the velopharyngeal function during phonation [14,15]. Currently, the auditory-perceptive evaluation is the gold-standard technique for speech assessment [16].
VPD therapy can involve the use of prosthetic devices, speech therapy, surgery, or a combination of any of these approaches. A recent umbrella review showed that the most common treatment for velopharyngeal insufficiency includes speech therapy and surgical intervention, but no surgical technique was considered to be the gold standard [17]. However, invasive procedures have also been associated with an increased risk of developing otitis media with effusion and obstructive sleep apnea [18,19]. When surgery is contraindicated due to anatomic, functional, or systemic limitations or when patients refuse the surgical procedure, the pharyngeal bulb may be the treatment option. When it comes to prosthetic treatments, palatal elevators are generally used when there is a functional deficit of the muscles associated with the velopharyngeal valve (velopharyngeal incompetence), and pharyngeal obturators when there is a structural deficiency (velopharyngeal insufficiency) [10,20]. The pharyngeal obturator partially fills the nasopharyngeal airspace. In this case, when a patient performs adduction of the lateral pharyngeal walls, there is contact with the obturator, which allows for the closure of the velopharyngeal valve. These devices are less invasive and expensive than a surgical approach as well as easily adjustable to the anatomical and functional needs of the patient. Bispo et al. reported that pharyngeal obturators allow for a significant reduction in hypernasality and, consequently, an improvement in speech intelligibility, especially at earlier ages [12]. However, how the bulb contributes to increasing the movement of the pharyngeal walls remains unclear. Some authors suggested that the bulb works as a sensorimotor stimulator that helps muscle function, especially when associated with speech therapy [21,22]. This appliance also controls nasal emission during speech and prevents nasal regurgitation of food and fluids during swallowing [23].
The manufacturing process of this device for children with VPD is challenging as they are going through a period of facial growth with changes in dentition as a result of orthodontic treatment and/or alveolar bone graft surgery [24,25,26]. Despite the known evidence on the use of the pharyngeal bulb to reduce hypernasality and improve speech intelligibility, the current design of these devices does not allow its application in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. The pharyngeal obturator prosthesis designs vary according to the nature and location of the velopharyngeal insufficiency. Typically, the pharyngeal prosthesis is composed of three parts: the anterior region, similar to an acrylic plate retained by Adams hooks; the intermediate region that connects the anterior part to the bulb; and the individualized pharyngeal bulb to promote the functional competence of the VPM. Other retention mechanisms have been suggested such as a removable partial denture, complete denture, or overdenture [27,28]. However, in partial or total edentulous patients, the weight and length of the bulb portion can produce a rotation around the fulcrum line due to gravitational forces or the inability to obtain a border seal [29,30]. Additionally, the majority of CLP patients require orthodontic treatment that begins shortly after birth and may continue into adulthood, and it also can produce changes in speech and velopharyngeal function. A recent randomized clinical trial showed that the perception of speech was changed, regardless of the orthodontic appliances used [31]. Moreover, none of the reported designs allow the adjustment of retention methods to the constant tooth movement caused by orthodontic treatment, which causes the detachment of the obturator. Therefore, it is crucial to adapt the conventional pharyngeal bulb to be used concurrently with fixed appliances, in order to reduce hypernasality and improve speech intelligibility.
The aim of this case series is to describe an adaptation of the conventional pharyngeal obturator design that allows its application during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra (CE-146/2020 on 25 November 2020) and conducted according to the Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. All patients gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
A pharyngeal obturator was manufactured in order to improve velopharyngeal dysfunction. This device consisted of an anterior or palatal portion, the acrylic plate, an intermediate portion, and a posterior portion that included the obturator or pharyngeal bulb. The fabrication of the plate was possible by altering the conventional Hawley retainer, replacing the Adams hooks with 0.9 mm spherical hooks and removing the buccal arch (Figure 1).
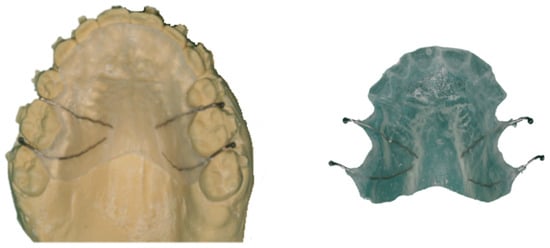
Figure 1.
Pharyngeal obturator–anterior or palatal portion.
The intermediate portion was produced in-mouth using Dentaurum® 0.90 mm diameter stainless steel (Remanium, Ispringen, Germany) and pink wax (Kemdent®, Swindon, UK) (Figure 2). To make the connector, a handle was molded to help retain the material needed for the pharyngeal bulb. After determining adequate tutor length, any loose ends were fixed in the center of the distal part of the palatal plate using self-curing acrylic resin. After this, the tutor was coated with malleable pink wax (previously warmed in a container with 60 °C water) to mold the pharyngeal obturator. The patient was asked to say some words like “papá” (daddy), “batata” (potato), and “taco” (taco) in order to promote the contact of the pharyngeal walls with the bulb.
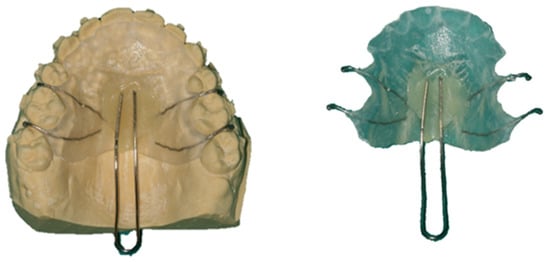
Figure 2.
Pharyngeal obturator–intermediate portion.
The patient was also asked to move their head down, back and to the sides, so as to refine the impression of the pharyngeal musculature. This molding process was repeated until an adequate conformation was achieved, which was manifested in decreased hypernasality and nasal air emission. Lastly, this portion was acrylized with a self-curing resin and polished (ProBase Cold, Ivoclar Vivadent®, Zurich, Switzerland) (Figure 3). During placement, areas that caused discomfort to the patient during the function were eliminated, and if necessary, the obturator impression was refined (Figure 4).
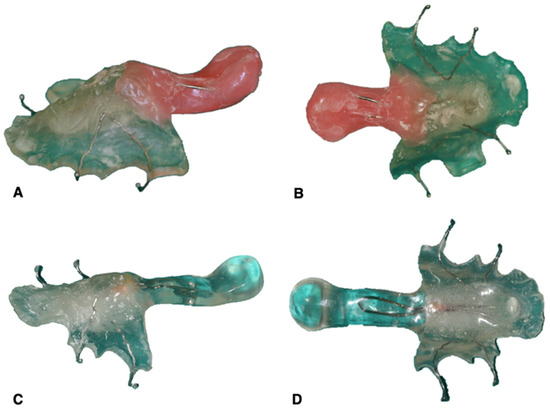
Figure 3.
Pharyngeal obturator–posterior portion: (A,B) pharyngeal bulb molding with pink wax and (C,D) finished pharyngeal obturator.
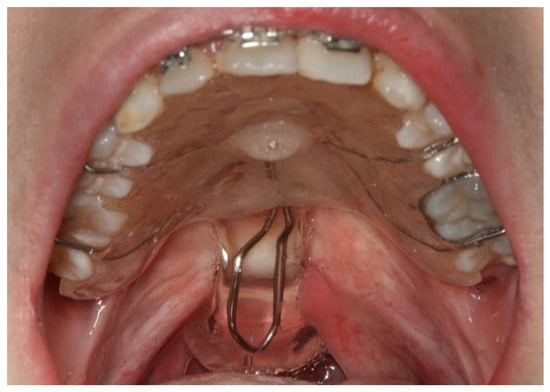
Figure 4.
Placement of the pharyngeal obturator.
Finally, the acrylic surrounding the upper teeth was selectively removed, accordingly to the orthodontic movements that were planned to be carried out (Figure 5). These adjustments were carried out on a monthly basis.
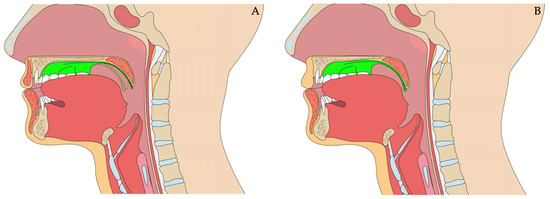
Figure 5.
Placement of the pharyngeal obturator: (A) passive appliance and (B) pharyngeal bulb activated, which allows the palatopharyngeal sphincter to close but also restores defects in the soft palate. Image created with biorender.com (accessed on 13 October 2023).
3. Results
Six patients (4 male and 2 female) with cleft lip and palate and subsequent velopharyngeal insufficiency who underwent orthodontic treatment were rehabilitated with a new design for the pharyngeal obturator. Table 1 presents the demographic data of the study participants, as well as the type of cleft according to the Spina Classification [32], dates of surgery, and the current phase of orthodontic treatment for the patients.

Table 1.
Sample characterization.
The patients did not have any physical and/or psychological pathologies associated.
An auditory-perceptive evaluation developed in 2008 by Henningsson et al. [14] was performed on both individuals in two periods: T0—before the placement of the pharyngeal obturator and T1—after the pharyngeal obturator placement with a follow-up of at least a month. According to this protocol, CLP patients’ phonation is appraised using four parameters: hypernasality, audible nasal air emission or nasal turbulence, compensatory articulation, and vocal changes.
Table 2 presents the result of the auditory-perceptual assessment prior and after to the placement of the obturator. At T0, it was verified that the worst results were observed in the parameters of hypernasality and audible emission. The T1 evaluation was performed between 30 and 55 days (42 days average) after device placement. Similar to what was observed in Table 1, the worst results were related to hypernasality and audible air emission. Case 3 presented better results in terms of resonance of the sentences 2 and 3.

Table 2.
Results of the auditory-perceptive evaluation in T0 and T1.
All patients showed good adaptation to the device after 1 week of use, and it was also verified that the extension of the obturator had static contact with soft tissues, not affecting the stability of the obturator. Additionally, the tooth movement promoted by the fixed appliance did not affect the stability of the obturator.
4. Discussion
The pharyngeal obturators should be used in cases of refusal of the surgical approach, surgical failure, or when surgery is unadvisable due to systemic, anatomical, or functional limitations such as cardiac anomalies, blood dyscrasia, and insufficient tissue for the anatomical and functional closure of the velopharyngeal mechanism [10,28].
The pharyngeal obturator treatment approach requires a long and continuous follow-up, which can lead to a decrease in collaboration and consequently to a less effective treatment. Moreover, this device is used concomitantly with changes in facial growth and dental development, which can lead to rapid loss of adaptation to the oral cavity [28]. Previous studies report the use of this device in primary, mixed and permanent dentitions. However, none of these studies report the use of the obturator concomitantly with orthodontic appliances [28,33]. During the deciduous and mixed dentition stage, CLP patients may require orthopedic treatment to correct the anteroposterior and transverse plane of the maxillary [5]. The orthodontic appliances most used at this stage are fixed or removable expanders [34], which makes it impossible to concomitantly use a pharyngeal obturator due to the volume and adjustment of both appliances. The application of the pharyngeal obturator with fixed appliances after the leveling and alignment phase allows the clinician to better predict orthodontic movement, which allows small adjustments to be made to the obturator, preventing loss of retention. In this study, it was verified that the tooth movement promoted by the fixed appliance did not affect the stability of the obturator.
This device has numerous advantages over invasive procedures as it stimulates the muscles that form the velopharyngeal valve while avoiding complications from surgical interventions, such as snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, airway obstruction, and hyponasality [9,28]. Furthermore, when compared to the surgical approach, this protocol is less invasive, less expensive, easily adjustable to the patient’s functional and anatomical needs, and its temporary use can help improve the prognosis of a future surgery [9,12,20]. It also can be used as a diagnostic tool method when the patient has an unclear surgical prognosis [28].
Despite clinical improvements in hypernasality, the perceptual auditory evaluation did not show any significant changes between T0 and T1. A possible explanation for this can be the short time period for the follow-up evaluation. According to Ogata et al., the pharyngeal obturator is used, on average, for a period longer than a year in order to obtain an adequate activation of the velopharyngeal muscles and a significant reduction in hypernasality [35]. However, papers with shorter follow-up periods, specifically between 1 and 5 days, showed a significant improvement when the use of this device was paired with an intensive speech therapy program [20].
Case 2 showed greater improvement in two nasality parameters, which may be associated with better compliance. The main complaint expressed by both patients was the discomfort caused by the obturator in the first few days, which compromised full-time use. It should be noted that CLP patients are generally less compliant; as such, communication between doctor, child, and legal guardian is essential so as to convey the notion that treatment success is highly dependent on device use [9]. Both patients placed the obturator after the secondary bone graft, which may have contributed to the adaptation of this device. Rieger et al. reported that patients with soft and/or hard palate resections presented more discomfort while using the obturator [36].
Meier et al. suggested that obturator devices should not be used during the mixed dentition period nor during orthodontic treatment due to constant changes in occlusion. These changes could lead to a lack of retention, which would subsequently limit obturator use in the pediatric population [37]. Nonetheless, in patients with psychological issues due to altered phonetics, the new obturator design suggested in this study can be considered as an option throughout the entire duration of orthodontic fixed appliance treatment. On the other hand, some studies suggested that if the pharyngeal obturator was temporarily effective, the patient was a candidate for VPM surgical treatment with a good speech prognosis [38].
This study presents some limitations since the speech outcome may be affected by some factors, namely, persistent compensatory articulation, failure to close the velopharyngeal gap completely with the bulb, and individual anatomic and functional characteristics that compromise the fabrication of the device.
Future studies should include longer follow-ups, specifically not less than a year, in order to allow for a progressive adaptation to this device, therefore, establishing realistic milestones regarding speech improvement, which would ultimately promote patient motivation and compliance [39]. Improving VPM and phonation with this new design obturator offers a therapeutic option with economic advantages and contributes to the promotion of self-esteem and well-being of patients. Finally, the application of this device with orthodontic appliances in primary and mixed dentition should be investigated.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the use of pharyngeal obturators stimulates the muscles that form the velopharyngeal valve while avoiding complications from surgical interventions at the same time.
This study introduces a new method for fabricating these pharyngeal obturators, which allows for their use during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. The obturator described was well tolerated by the patients and showed good retention, which allowed its use with fixed appliances and consequent improvement in the auditory-perceptual assessment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.V.; methodology, F.V. and I.F.; formal analysis, M.R. and F.M.; investigation, J.R., C.N. and R.T.; resources, A.P.; data curation, C.M.M., A.B.P. and I.F.; writing—original draft preparation, J.R. and C.N.; writing—review and editing—C.M.M., F.V., I.F. and A.B.P.; visualization—A.P., F.M., M.R. and R.T.; supervision, F.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra (CE-146/2020 on 25 November 2020) and conducted according to the Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. All patients gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the subject involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Institutional Review Board Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Vieira, A.R.; Orioli, I.M. Birth order and oral clefts: A meta analysis. Teratology 2002, 66, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNEIL, C.K. Orthodontic procedures in the treatment of congenital cleft palate. Dent. Rec. 1950, 70, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. The orthodontist, an essential partner in CLP treatment. B-ENT 2006, 2 (Suppl. S4), 57–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vig, K.W.L.; Mercado, M.A. The orthodontist’s role in a cleft palate-craniofacial team. In Orthodontics Current Principles & Techniques, 4th ed.; Orthodontic Practice US: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2005; pp. 1097–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Semb, G. A study of facial growth in patients with bilateral cleft lip and palate treated by the Oslo CLP Team. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 1991, 28, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.J.; Smith, I.; Nugent, M.; Richards, C.; Anderson, P.J. From birth to maturity: A group of patients who have completed their protocol management. Part III. Bilateral cleft lip-cleft palate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollet, P.J.P.M.; Katsaros, C.; Huyskens, R.W.F.; Borstlap, W.A.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Cephalometric evaluation of long-term craniofacial development in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients treated with delayed hard palate closure. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal Monroy, P.L.; Grefte, S.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Wagener, F.A.D.T.G.; Von den Hoff, J.W. Strategies to Improve Regeneration of the Soft Palate Muscles After Cleft Palate Repair. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2012, 18, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-J.; Ko, S.-O. Successful and Rapid Response of Speech Bulb Reduction Program Combined with Speech Therapy in Velopharyngeal Dysfunction: A Case Report. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 37, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboloyoun, A.I.; Ghorab, S.; Farooq, M.U. Palatal Lifting Prosthesis and Velopharyngeal Insufficiency: Preliminary Report. Acta Medica Acad. 2013, 42, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, A. Types and Causes of Velopharyngeal Dysfunction. Semin. Speech Lang. 2011, 32, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, N.H.M.; Whitaker, M.E.; Aferri, H.C.; Neves, J.D.A.; Dutka, J.C.R.; Pegoraro-Krook, M.I. Speech Therapy for Compensatory Articulations and Velopharyngeal Function: A Case Report. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2011, 19, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, A. Velopharyngeal Dysfunction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2013, 26, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henningsson, G.; Kuehn, D.P.; Sell, D.; Sweeney, T.; Trost-Cardamone, J.E.; Whitehill, T.L. Universal Parameters for Reporting Speech Outcomes in Individuals with Cleft Palate. Cleft. Palate Craniofac. J. 2008, 45, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Shi, B.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q. Velopharyngeal Function Assessment in Patients with Cleft Palate: Perceptual Speech Assessment versus Nasopharyngoscopy. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmander, A.; Hagberg, E.; Persson, C.; Willadsen, E.; Lundeborg, I.; Davies, J.; Havstam, C.; Boers, M.; Kisling-Møller, M.; Alaluusua, S.; et al. Validity of Auditory Perceptual Assessment of Velopharyngeal Function and Dysfunction—The VPC-Sum and the VPC-Rate. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2017, 31, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, F.; Paula, A.B.; Travassos, R.; Nunes, C.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Marques, F.; Pereira, F.; Carrilho, E.; Marto, C.M.; Francisco, I. Velopharyngeal Insufficiency Treatment in Cleft Palate Patients: Umbrella Review. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téblick, S.; Ruymaekers, M.; van de Casteele, E.; Nadjmi, N. Effect of Cleft Palate Closure Technique on Speech and Middle Ear Outcome: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 77, 405.e1–405.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnik, N.M.; Weidler, E.M.; Lien, K.M.; Cordero, K.N.; Williams, J.L.; Temkit, M.H.; Beals, S.P.; Singh, D.J.; Sitzman, T.J. The Effectiveness of Palate Re-Repair for Treating Velopharyngeal Insufficiency: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cleft. Palate Craniofac. J. 2020, 57, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.Z.; Bressmann, T.; Dutka, J.C.R.; Whitaker, M.E.; Boer, G.; Marino, V.C.C.; Pegoraro-Krook, M.I. Analysis of Oral-Nasal Balance after Intensive Speech Therapy Combined with Speech Bulb in Speakers with Cleft Palate and Hypernasality. J. Commun. Disord. 2020, 85, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maghraby, R.M.; El-Didi, L.M.; Al-Shimy, A.M.; Abdel Razek, M.M. The Speech Outcome of Definitive Obturators Constructed Using Two Different Impression Techniques. Egypt J. Otolaryngol. 2016, 32, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, N.; Sun, G. Application of Obturator to Treat Velopharyngeal Incompetence. Chin. Med. J. 2002, 115, 842–845. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, H.; Coskun, M.E.; Akin, E.G.; Ozdemir, A.K. Multidisciplinary approach for esthetic, functional, and quality-of-life outcome in soft palate cleft patient. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2012, 49, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Filho, O.G.; Boiani, E.; de Oliveira Cavassan, A.; Santamaria, M. Rapid Maxillary Expansion after Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Patients with Alveolar Cleft. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2009, 46, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, I.; Paula, A.B.; Oliveiros, B.; Fernandes, M.H.; Carrilho, E.; Marto, C.M.; Vale, F. Regenerative Strategies in Cleft Palate: An Umbrella Review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, W.R.; Di Francesco, R.C. Variation of Patterns of Malocclusion by Site of Pharyngeal Obstruction in Children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuna, S.H.; Pekkan, G.; Gumus, H.O.; Aktas, A. Prosthetic Rehabilitation of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency: Pharyngeal Obturator Prostheses with Different Retention Mechanisms. Eur. J. Dent. 2010, 4, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegoraro-Krook, M.I.; Rosa, R.R.; Aferri, H.C.; Andrade, L.K.F.D.; Dutka, J.D.C. Pharyngeal Bulb Prosthesis and Speech Outcome in Patients with Cleft Palate. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 88, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.W. Dental Implants to Rehabilitate a Patient with an Unrepaired Complete Cleft of the Hard and Soft Palate: A Clinical Report. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1992, 29, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumer, J.; Curtis, T.A.; Marunick, M.T. Speech, Velopharyngeal Function, and Restoration of Soft Palate Defects. In Maxillofacial Rehabilitation: Prosthodontic and Surgical Considerations; Ishiyaku EuroAmerica, Inc.: St. Louis, MI, USA, 1996; pp. 285–324. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, P.E.D.; Bocato, J.R.; Conti, A.C.C.F.; Souza, K.R.S.; Fernandes, T.M.F.; Almeida, M.R.; Oltramati, P.V.P. Effects of orthodontic treatment with aligners and fixed appliances on speech. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, V. A proposed modification for the classification of cleft lip and cleft palate. Cleft Palate J. 1973, 10, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.H.N.; Dalben, G.S.; Pegoraro-Krook, M.I. Speech intelligibility of patients with cleft lip and palate after placement of speech prosthesis. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2007, 44, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allareddy, V.; Bruun, R.; MacLaine, J.; Markiewicz, M.R.; Ruiz, R.; Miller, M.A. Orthodontic Preparation for Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Patients with Complete Cleft Lip and Palate. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, Y.; Matsuzaki, S.; Sasaguri, M.; Kubota, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Nakamura, S.; Shirasuna, K.; Nakamua, N. Effects of Bulb Type Palatal Lift Prosthesis Therapy on Nasality and Velopharyngeal Function of Patients Following Palatoplasty. Oral Sci. Int. 2009, 6, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, J.M.; Wolfaardt, J.F.; Jha, N.; Seikaly, H. Maxillary Obturators: The Relationship between Patient Satisfaction and Speech Outcome. Head Neck 2003, 25, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.D.; Muntz, H.R. Velopharyngeal Dysfunction Evaluation and Treatment. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 24, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, D.; Mars, M.; Worrell, E. Process and Outcome Study of Multidisciplinary Prosthetic Treatment for Velopharyngeal Dysfunction. Int. J. Lang Commun. Disord. 2006, 41, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillo Dutka, J.C.; Uemeoka, É.; Aferri, H.C.; Pegoraro-Krook, M.I.; De Castro Marino, V.C. Total Obturation of Velopharynx for Treatment of Velopharyngeal Hypodynamism: Case Report. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2012, 49, 488–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).