PVA-Based Electrospun Materials—A Promising Route to Designing Nanofiber Mats with Desired Morphological Shape—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
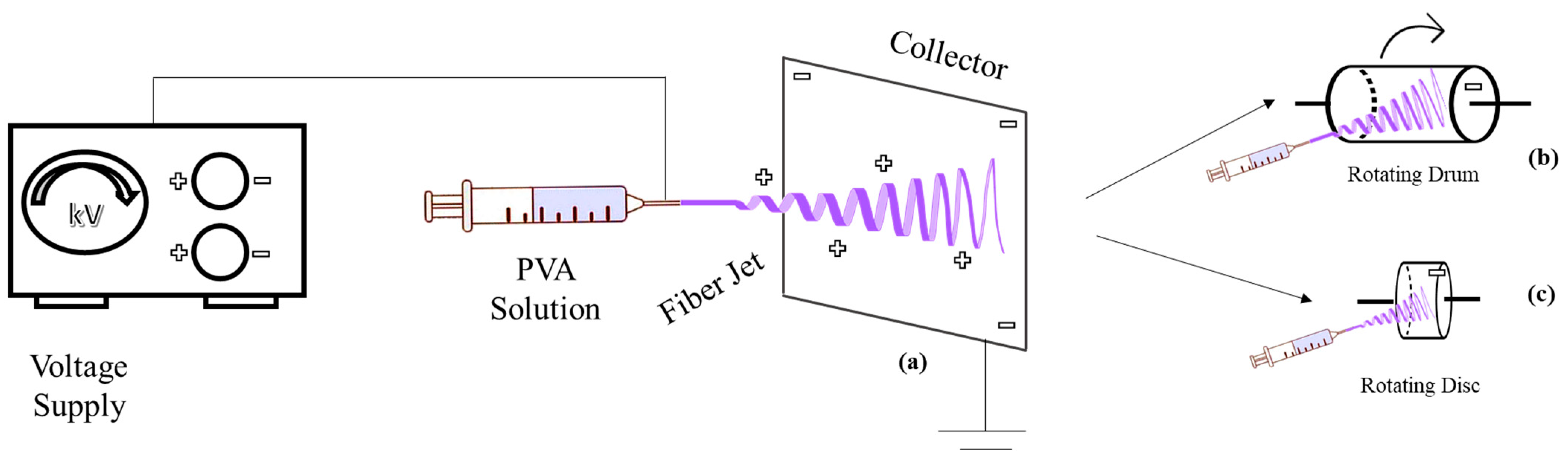
2. Electrospinning of PVA-Based Membrane
2.1. Influence of Operating Parameters on Electrospinning PVA Nanofibers
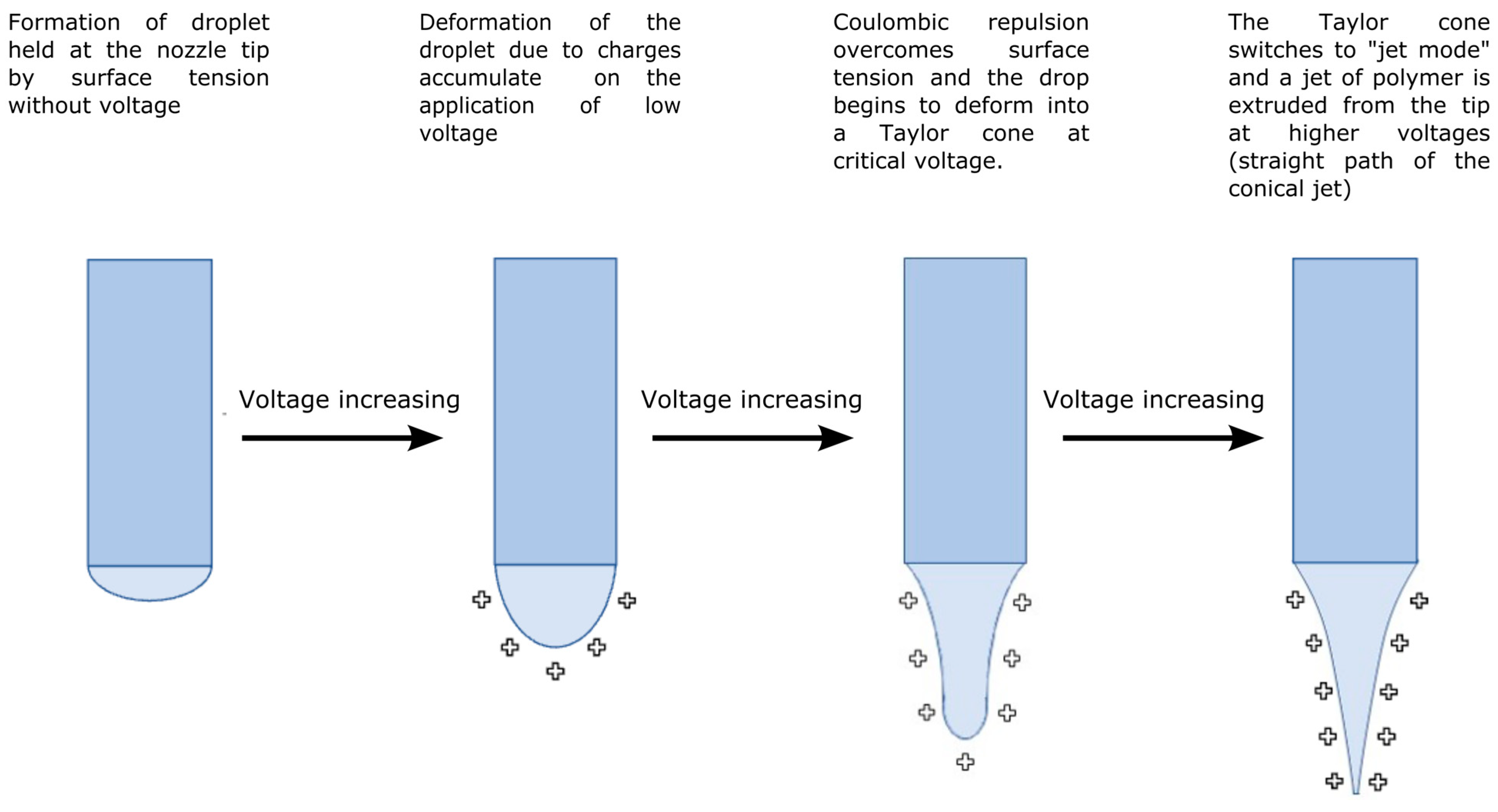
2.1.1. Voltage
2.1.2. Feed Rate
2.1.3. Tip-to-Collector Working Distance (TCD)
2.1.4. Collector Design
2.2. Influence of Formulation Parameters on Electrospinning PVA Nanofibers
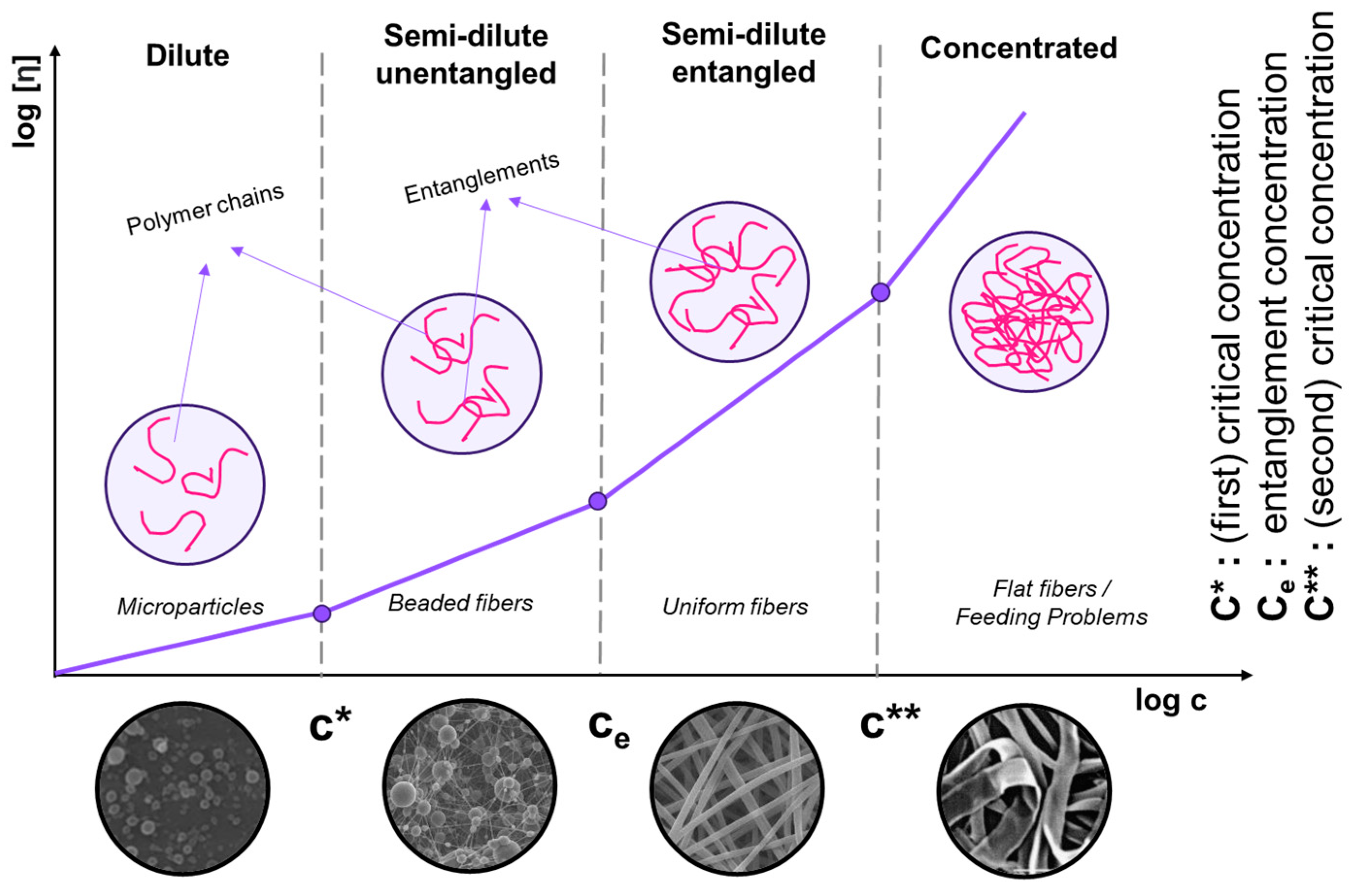
2.2.1. Polymer Concentration, Viscosity, and Surface Tension
2.2.2. Conductivity
2.2.3. Solvent
2.3. Influence of Relative Humidity on Electrospinning PVA Nanofibers
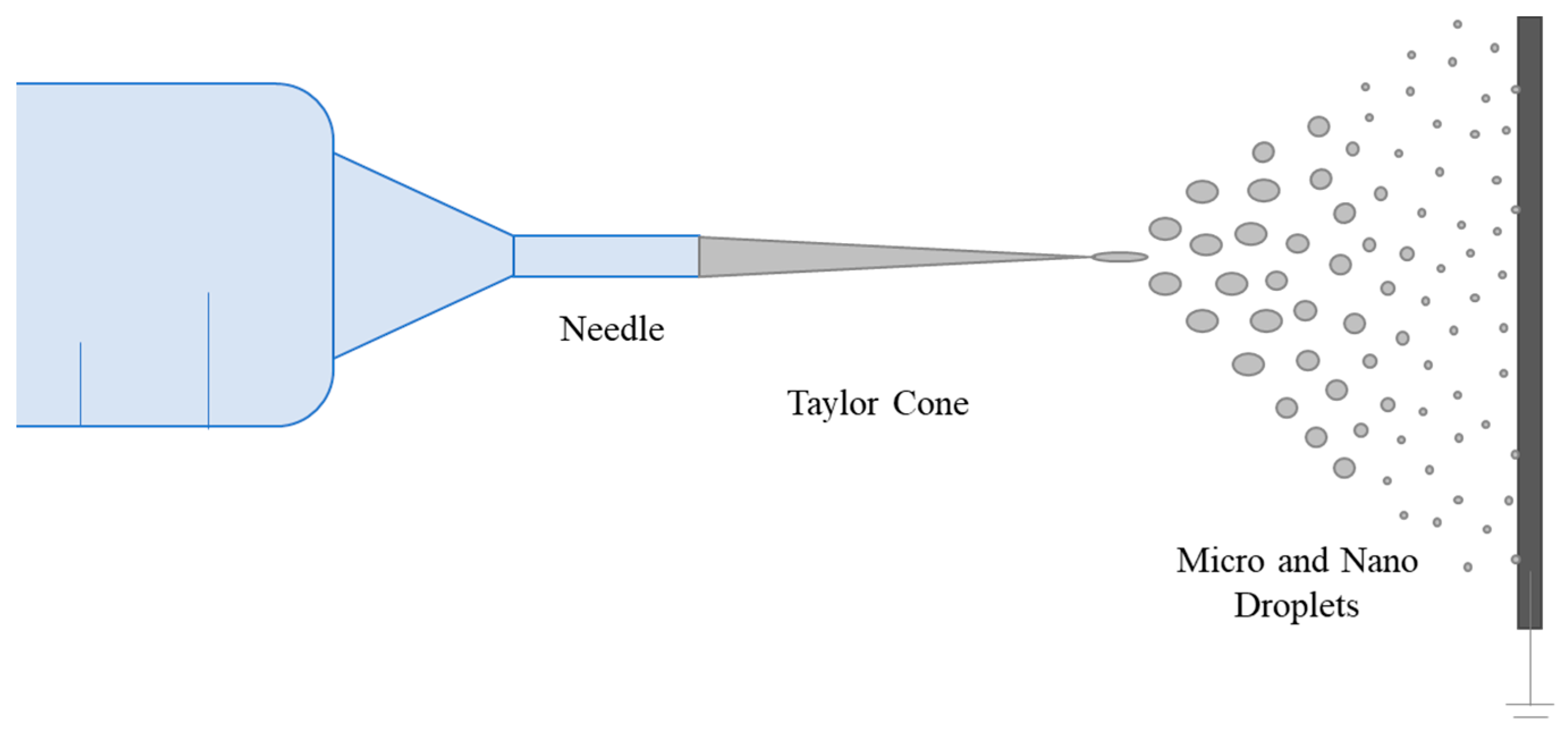
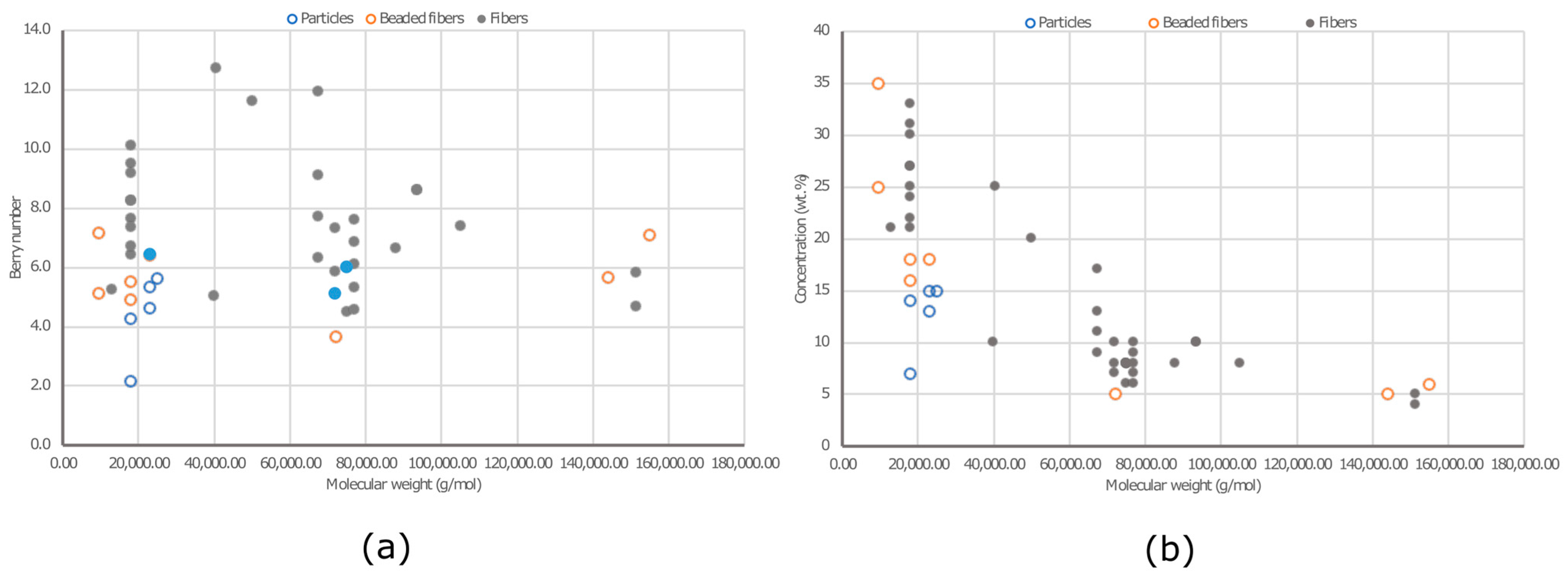
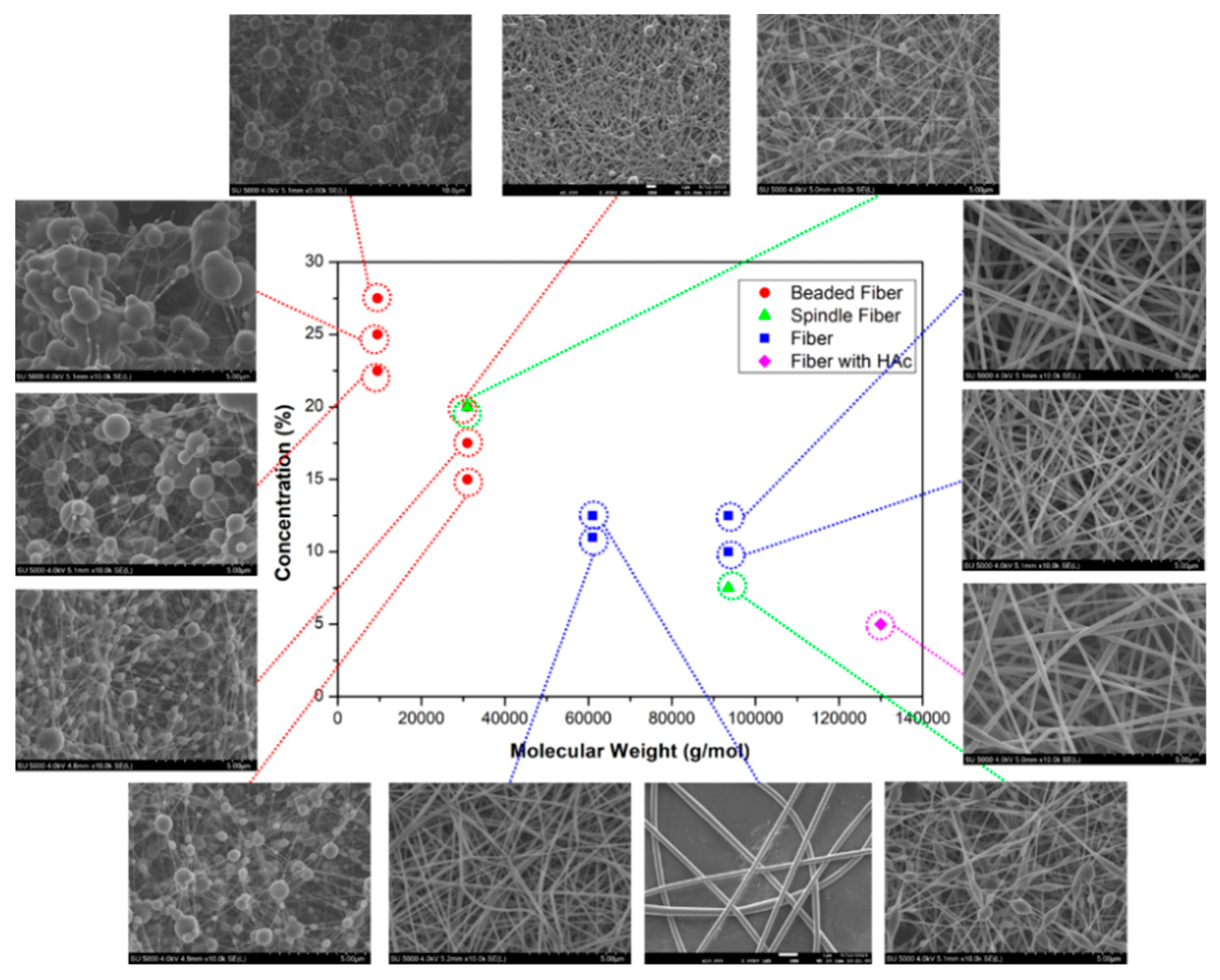
3. Morphology of Electrosprayed/Electrospun PVA Materials
4. Applications of PVA Nanofibers
4.1. Filtration
4.2. Gas Sensor
4.3. Biosensors
4.4. Tissue Engineering
4.5. Wound Dressing
4.6. Drug Delivery
4.7. Cancer Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| TCD | Tip to Collector Distance |
| C* | Critical concentration |
| Ce | Entanglement concentration |
| C** | Second critical concentration |
| Mw | Molecular Weight |
| DH | Degree of Hydrolysis |
| SDBS | Sodium DodecylBenzene Sulfonate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| EG | Ethylene Glycol |
| NMP | N-methyl pyrrolidone |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| CUR | Curcumin |
| ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
| CS | Chitosan |
| GO | Graphene Oxide |
| Ag | Silver |
| EPS | Extracellular Polymeric Substances |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| HAC | Acetic acid |
| Be | Berry number |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| PPE | Personal Protective Equipment |
| Hal-NH2 | Amino group grafted halloysite nanotubes |
| Cd(II) | Divalent cadmium |
| Pb(II) | Divalent lead |
| GA | Glutaraldehyde |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| DOX | Doxorubicin Hydrochloride |
| MoS2 | 2D Molybdenum Disulfide |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| AuCl4 | Tetrachloroaurate ion |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PLGA | Poly(lactid-co-glycolic acid) |
| Cip | Ciprofloxacin |
| CipHCl | Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride |
References
- Herrmann, W.O.; Haehnel, W. Process for the Preparation of Polymerized Vinyl Alcohol and Its Derivatives. U.S. Patent 1,672,156, 5 June 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Lyoo, W.; Lee, H. Synthesis of high-molecular-weight poly(vinyl alcohol) with high yield by novel one-batch suspension polymerization of vinyl acetate and saponification. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moad, G.; Solomon, D.H. The Chemistry of Radical Polymerization, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Murahashi, S.; Yuki, H.; Sano, T.; Tadokoro, H.; Yonemura, U.; Chatani, Y. Isotactic Polyvinyl Alcohol. J. Polym. Sci. 1962, 62, S77–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogah, D.Y.; Webster, O.W. Sequential silyl aldol condensation in controlled synthesis of living poly(vinyl alcohol) precursors. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jung, J.; Park, S.-I.; Seo, J. Preparation and characterization of LDPE/PVA blend films filled with glycerin-plasticized polyvinyl alcohol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.I.; Walsh, S.P.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. A review of polyvinyl alcohol and its uses in cartilage and orthopedic applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.I.; Chafer, M.; Chiralt, A.; Gonzalez-Martinez, C. Physical and microstructural properties of biodegradable films based on pea starch and PVA. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasselkus, A.; Weiskircher-Hildebrandt, E.; Schornick, E.; Bauer, F.; Zheng, M. What’s Old Is New: The Rebirth of Polyvinyl Alcohol for Enhanced Solubility and Sustained Release Formulations. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2019. Available online: https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com/Featured-Articles/357906-What-s-Old-Is-New-The-Rebirth-of-Polyvinyl-Alcohol-for-Enhanced-Solubility-and-Sustained-Release-Formulations/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Chiellini, E.; Corti, A.; D’Antone, S.; Solaro, R. Biodegradation of poly (vinyl alcohol) based materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 963–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, Y.; Muro, C.; Illescas, J.; Riera, F. Polymer nanoparticles for the release of complex molecules. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering; Holban, A.-M., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 135–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, L.; Warkar, S.G.; Ahmad, S.I.; Kant, R.; Jain, M. A review on carboxylic acid cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol: Properties and applications. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 62, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supaphol, P.; Chuangchote, S. On the electrospinning of poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofiber mats: A revisit. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-M.; Simon, P.; Kim, J.-S. Electrospun PVA/HAp nanocomposite nanofibers: Biomimetics of mineralized hard tissues at a lower level of complexity. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2008, 3, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asran, A.S.; Henning, S.; Michler, G.H. Polyvinyl alcohol–collagen–hydroxyapatite biocomposite nanofibrous scaffold: Mimicking the key features of natural bone at the nanoscale level. Polymer 2010, 51, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wei, S.; Wang, Z.; Karki, A.B.; Li, Y.; Bernazzani, P.; Young, D.P.; Gomes, J.A.; Cocke, D.L.; et al. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on polyvinyl alcohol: Interfacial layer and bulk nanocomposites thin film. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 12, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumova, L.L.; Veretennikova, A.A.; Zaikov, G.Y.; Vol’f, L.A. Degradation of polyvinyl alcohol surgical thread. Polymer Sci. U.S.S.R. 1983, 25, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, N.; Ma, Y.; Minus, M.L.; Benson, K.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Ling, X.; Zhu, H. Superstrong and Tough Hydrogel through Physical Cross-Linking and Molecular Alignment. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 4476–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, M.; Ogura, Y.; Honda, Y.; Hyon, S.H.; Cha, W.; Ikada, Y. Evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel as a soft contact lens material. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1990, 228, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyon, S.H.; Cha, W.I.; Ikada, Y.; Kita, M.; Ogura, Y.; Honda, Y. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels as soft contact lens material. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1994, 5, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Loutfy, S.A.; Hussein, Y.; Kenawy, E.S. Recent advances in PVA-polysaccharide based hydrogels and electrospun nanofibers in biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Wang, X. Dialysis/adsorption bifunctional thin-film nanofibrous composite membrane for creatinine clearance in portable artificial kidney. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, D.K. Plasticizer effect on the melting and crystallization behavior of polyvinyl alcohol. Polymer 2003, 44, 8139–8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aty, M.; Othman, H.; Hassabo, A. A Critique on Synthetic Thickeners in Textile Printing. J. Text. Color. Polym. Sci. 2022, 19, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, H.; Hernandez-Parra, H.; Bernal-Chavez, S.A.; Prado-Audelo, M.L.D.; Caballero-Floran, I.H.; Borbolla-Jimenez, F.V.; Gonzalez-Torres, M.; Magana, J.J.; Leyva-Gomez, G. Non-Ionic Surfactants for Stabilization of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Biomedical Uses. Materials 2021, 14, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaisheng, C.; Yiping, Q.; Chuyang, Z.; Hwang, Y.-J.; McCord, M. Effect of Atmospheric Plasma Treatment on Desizing of PVA on Cotton. Text. Res. J. 2016, 73, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, W. Influences of PVA modification on performance of microencapsulated reversible thermochromic phase change materials for energy storage application. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 222, 110938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Xu, X.Q.; Li, W.P.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhu, L.-Q. Shell Material’s Performance of the Microcapsule for Electrolytic Co-Deposition. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2012, 24, 3124–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikkumaran, M.; Agrawal, A.K.; Jassal, M. Water-proof Breathable Coatings Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) for Cellulosic Fabric. J. Ind. Text. 2008, 38, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, P.; Ge, M. The experimental study of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) textile material degradation by ozone oxidation process. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 112, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, N.; Xiang, Y.; Qin, M. Crack Resistance and Mechanical Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol Fiber-Reinforced Cement-Stabilized Macadam Base. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6564076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Han, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, J.; Hui, D. Effect of PVA fiber on mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2021, 60, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Yutong, Y.; Shiping, Y. Thermal and moisture performance parameters of high toughness engineered cementitious Composite(ECC) with PVA fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.H.A.; Cerize, N.N.P.; de Oliveira, A.M. Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning Technology: Overview and Application in Cosmetics. In Nanocosmetics and Nanomedicines; Beck, R., Guterres, S., Pohlmann, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 311–332. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, T.F.; Quinaz, T.; Fertuzinhos, A.; Quyen, N.T.; de Moura, M.; Martins, M.; Zille, A.; Dourado, N. Thermal, Mechanical and Chemical Analysis of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Multifilament and Braided Yarns. Polymers 2021, 13, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, A.; El Nahrawy, A. Comfort Properties of Woven Fabrics Produced From Twist-Less Weft Using PVA Yarns. Mansoura Eng. J. 2020, 40, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor Turkmen, B.; Celik, P.; Sehit, H.; Bedez Ute, T. The effects of hollow yarn and fabric structure on permeability and moisture management properties of woven fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Park, K.H.; Tao, X.M.; Chen, W.; Cheng, X.Y. Electrically conductive yarns based on PVA/carbon nanotubes. Compos. Struct. 2007, 78, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Ding, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Tian, M.; Tao, G. Superabsorbent Fibers for Comfortable Disposable Medical Protective Clothing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2020, 2, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cayla, A.; Devaux, E.; Otazaghine, B.; Salaun, F. Simultaneous surface modification and mechanical enhancement of micro/nanofiber fabrics achieved by Janus particles. Express Polym. Lett. 2021, 15, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cayla, A.; Devaux, E.; Otazaghine, B.; Salaün, F. Polypropylene/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Blends Compatibilized with Kaolinite Janus Hybrid Particles and Their Transformation into Fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 10931–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cayla, A.; Devaux, E.; Salaun, F. Microstructure Evolution of Immiscible PP-PVA Blends Tuned by Polymer Ratio and Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Cayla, A.; Salaün, F.; Devaux, E.; Liu, P.; Huang, T. A green method to fabricate porous polypropylene fibers: Development toward textile products and mechanical evaluation. Text. Res. J. 2020, 90, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cayla, A.; Salaün, F.; Devaux, E.; Liu, P.; Mao, J.; Huang, T. Porous fibers surface decorated with nanofillers: From melt-spun PP/PVA blend fibers with silica nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, T.; Ibrahim, S.; El said, A. Spinning Techniques of Poly (vinyl Alcohol) Fibers for Various Textile Applications. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 67, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Polymer nanofibers assembled by electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ryan, A.J. Introduction to electrospinning. In Electrospinning for Tissue Regeneration; Bosworth, L.A., Downes, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nauman, S.; Lubineau, G.; Alharbi, H.F. Post Processing Strategies for the Enhancement of Mechanical Properties of ENMs (Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes): A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrostat. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Taylor cone and jetting from liquid droplets in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N.C. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabur, A.R.; Abbas, L.K.; Muhi Aldain, S.M. Effects of Ambient Temperature and Needle to Collector Distance on PVA Nanofibers Diameter Obtained From Electrospinning Technique. Eng. Technol. J. 2017, 35, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A.; Amorim, M.T.P.; Felgueiras, H.P. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Nanofibrous Electrospun Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2019, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adon, S.; Abd Razak, S.I.; Ismail, A.E.; Fakhruddin, K. Drug-Loaded Poly-Vinyl Alcohol Electrospun Nanofibers for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Review on Factors Affecting the Drug Release. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fawal, G.F.; Hassan, H.S.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Elkady, M.F. Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofibers Containing Titanium Dioxide for Gas Sensor Applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 44, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, J.; Pastene-Navarrete, E.; Acevedo, F. Electrospun Fibers Loaded with Natural Bioactive Compounds as a Biomedical System for Skin Burn Treatment. A Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Duan, G. A review of smart electrospun fibers toward textiles. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, R.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Diao, G.; Chen, M. Tube-in-tube composite nanofibers with high electrochemistry performance in energy storage applications. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 19, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.; Mazinani, S.; Gharehaghaji, A.A. A review on emerging developments in thermal and moisture management by membrane-based clothing systems towards personal comfort. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Markova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun non-woven nanofibrous hybrid mats based on chitosan and PLA for wound-dressing applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, B.A.; Krishnaswamy, M.; Xu, H.; Hoque, M.E. Electrospinning of Biomedical Nanofibers/Nanomembranes: Effects of Process Parameters. Polymers 2022, 14, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman Mohammadi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Yousefi, M. Application of electrospinning technique in development of intelligent food packaging: A short review of recent trends. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4656–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino Vidal, C.; Lopez de Dicastillo, C.; Rodriguez-Mercado, F.; Guarda, A.; Galotto, M.J.; Munoz-Shuguli, C. Electrospinning and cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: An emerging technological combination for developing novel active food packaging materials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5495–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, V.V.; Wang, L.; Padhye, R. Electrospun nanofibre materials to filter air pollutants—A review. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 47, 2253–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Bubakir, M.M.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y. Water filtration properties of novel composite membranes combining solution electrospinning and needleless melt electrospinning methods. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozior, T.; Mamun, A.; Trabelsi, M.; Wortmann, M.; Lilia, S.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning on 3D Printed Polymers for Mechanically Stabilized Filter Composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, K.A.; Birch, N.P.; Schiffman, J.D. Designing electrospun nanofiber mats to promote wound healing—A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4531–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrigo, M.; McArthur, S.L.; Kingshott, P. Electrospun nanofibers as dressings for chronic wound care: Advances, challenges, and future prospects. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, K.; Gupta, A.; Rath, G.; Mathur, R.B.; Dhakate, S.R. In vivo wound healing performance of drug loaded electrospun composite nanofibers transdermal patch. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.M.D.; Siqueira, N.M.; Prabhakaram, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning and electrospray of bio-based and natural polymers for biomaterials development. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 92, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, B.; Taylor, R.M.; Reifsnider, K. Mechanical and Dielectric Properties of Aligned Electrospun Fibers. Fibers 2021, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, A.; Ventre, M.; Chiappini, C.; Onesto, V.; Coluccio, M.L.; Netti, P.; Gentile, F. Nanoscaffolds for neural regenerative medicine. In Neural Regenerative Nanomedicine; Razavi, M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 47–88. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S.; Becker, A.; Glasmacher, B. Impact of Apparatus Orientation and Gravity in Electrospinning-A Review of Empirical Evidence. Polymers 2020, 12, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
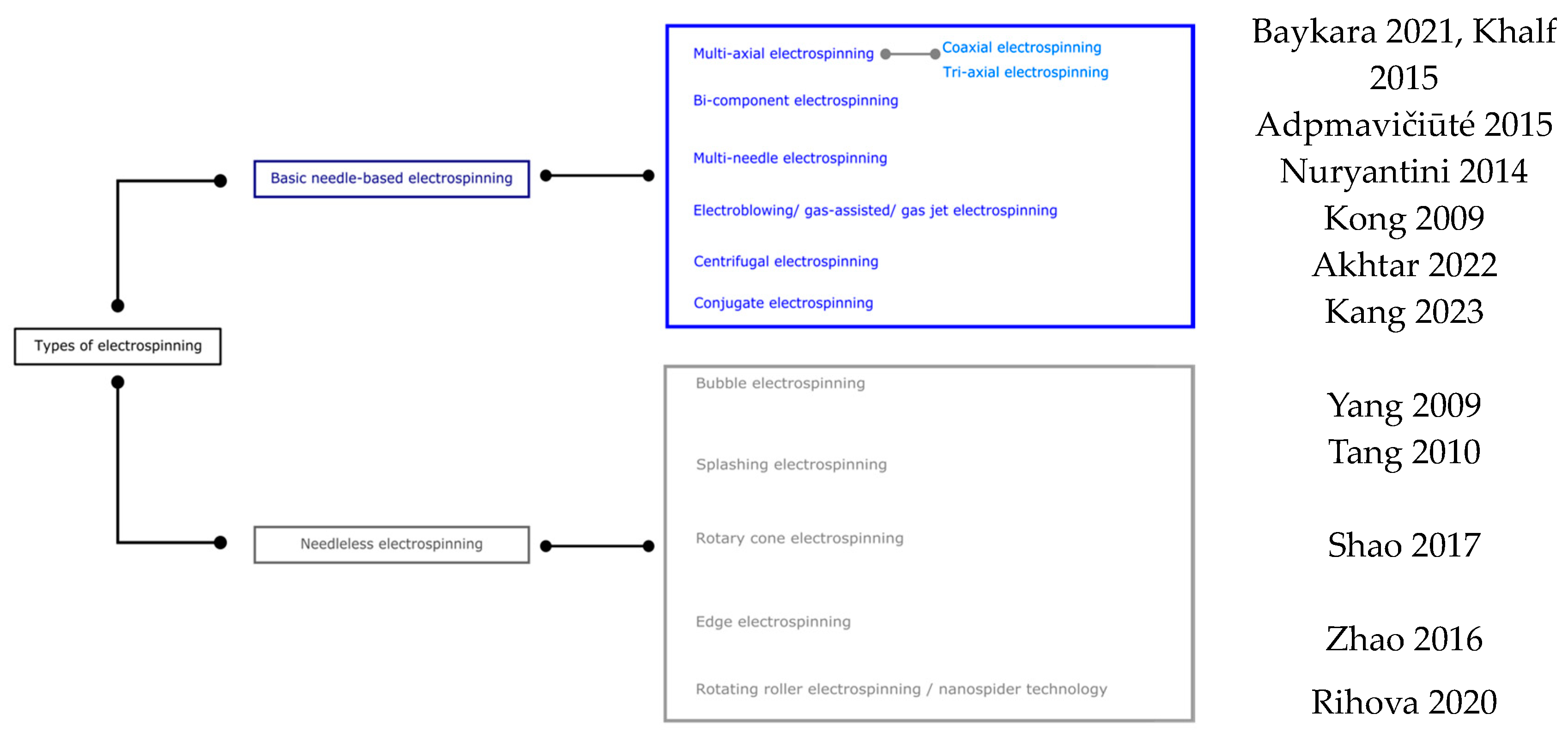
- SalehHudin, H.S.; Mohamad, E.N.; Mahadi, W.N.L.; Muhammad Afifi, A. Multiple-jet electrospinning methods for nanofiber processing: A review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, A.; Wei, L.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. Mass production of high-quality nanofibers via constructing pre-Taylor cones with high curvature on needleless electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, T.; Taylan, G. Coaxial electrospinning of PVA/Nigella seed oil nanofibers: Processing and morphological characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Adv. 2021, 265, 115012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalf, A.; Singarapu, K.; Madihally, S.V. Influence of solvent characteristics in triaxial electrospun fiber formation. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 90, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavičiūtė, E.; Stanys, S.; Žilius, M.; Briedis, V. Formation and Analysis of Electrospun Nonwoven Mats from Bicomponent PVA/Aqueous Propolis Nano-Microfibres. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2015, 23, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuryantini, A.Y.; Munir, M.M.; Ekaputra, M.P.; Suciati, T.; Khairurrijal, K. Electrospinning of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Chitosan via Multi-Nozzle Spinneret and Drum Collector. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 896, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.S.; Yoo, W.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, H.S. Nanofiber deposition by electroblowing of PVA (polyvinyl alcohol). J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Ahmed, S.; Hussain, R.; Wadood, A.; Roy, I.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Boccaccini, A.R. Centrifugal spinning of polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate-di -aldehyde-gelatin based antibacterial nanofibers intended for skin tissue engineering. Mater. Lett. 2022, 323, 132530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; An, G. PTFE/PVA-PVDF Conjugated Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Triboelectric Effect Used in Face Mask. Fiber. Polym. 2023, 24, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Bubble-electrospinning for fabricating nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X. Splashing needleless electrospinning of nanofibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, M. High-Throughput Fabrication of Quality Nanofibers Using a Modified Free Surface Electrospinning. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Y.; Pan, Z. Adhesion and protective properties of electrospun PVA/ES composites obtained by using spiral disk spinnerets. Text. Res. J. 2016, 87, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihova, M.; Ince, A.E.; Cicmancova, V.; Hromadko, L.; Castkova, K.; Pavlinak, D.; Vojtova, L.; Macak, J.M. Water-born 3D nanofiber mats using cost-effective centrifugal spinning: Comparison with electrospinning process: A complex study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 49975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulupi, M.; Haryadi, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Electrospinning PVA Nanofiber-Crosslinked by Glutaraldehyde. Mater. Today-Proc. 2019, 13, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, A.; Yim, K.; Shivkumar, S. Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Choi, K.H.; Do Ghim, H.; Kim, S.S.; Chun, D.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lyoo, W.S. Role of molecular weight of atactic poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) in the structure and properties of PVA nanofabric prepared by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeev, U.S.; Anand, K.A.; Menon, D.; Nair, S. Control of nanostructures in PVA, PVA/chitosan blends and PCL through electrospinning. B. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodoplu, D.; Mutlu, M. Effects of Electrospinning Setup and Process Parameters on Nanofiber Morphology Intended for the Modification of Quartz Crystal Microbalance Surfaces. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradzadegan, A.; Ranaei-Siadat, S.-O.; Ebrahim-Habibi, A.; Barshan-Tashnizi, M.; Jalili, R.; Torabi, S.-F.; Khajeh, K. Immobilization of acetylcholinesterase in nanofibrous PVA/BSA membranes by electrospinning. Eng. Life Sci. 2010, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahian, R.; Mirjalili, M.; Khajavi, R.; Rahimi, M.K.; Nasirizadeh, N. Fabrication of antibacterial and hemostatic electrospun PVA nanofibers for wound healing. Sn Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Electrospinning, mechanical properties, and cell behavior study of chitosan/PVA nanofibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sengupta, P.; Higaki, Y.; Takahara, A.; Badiger, M.V. Electrospinning of non-ionic cellulose ethers/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers: Characterization and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aphale, A.N.; Mahakalkar, K.; Macwan, I.G.; Mukerji, I.; Cox, P.J.; Mahapatra, M.; Singh, P.; Ajayan, P.M.; Patra, P.K. Fabrication and Experimental Analysis of Axially Oriented Nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanumantharao, S.N.; Rao, S. Multi-Functional Electrospun Nanofibers from Polymer Blends for Scaffold Tissue Engineering. Fibers 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkasaby, M.; Hegab, H.A.; Mohany, A.; Rizvi, G.M. Modeling and optimization of electrospinning of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Adv. Polym. Technol. 2017, 37, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phachamud, T.; Phiriyawirut, M. Physical properties of polyvinyl alcohol electrospun fiber mat. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays and Layer-by-Layer Stacked Films. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachley, V.; Wen, X. Effect of electrospinning parameters on the nanofiber diameter and length. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2009, 29, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wei, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Rutman, D.; Guo, Z. Manipulated Electrospun PVA Nanofibers with Inexpensive Salts. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-aziz, A.M.; El-Maghraby, A.; Taha, N.A. Comparison between polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber/hydroxyapatite (HA) for removal of Zn 2+ ions from wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental investigation of the governing parameters in the electrospinning of polymer solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.; Al-Ashwal, R.H.; Sani, M.H.; Saidin, S. Effects of Electrospinning Voltage and Flow Rate on Morphology of Poly-vinyl Alcohol Nanofibers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1372, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Shao, C.L.; Lee, D.R.; Park, S.J.; Kwag, G.B.; Choi, K.J. Preparation and characterization of a nanoscale poly(vinyl alcohol) fiber aggregate produced by an electrospinning method. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2002, 40, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelca, Z.; Krumme, A.; Kukle, S.; Viirsalu, M.; Vilcena, L. Effect of Electrode Type on Electrospun Membrane Morphology Using Low-Concentration PVA Solutions. Membranes 2022, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuangchote, S.; Supaphol, P. Fabrication of aligned poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2006, 6, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.B.; Yeum, J.H. Morphological Comparison of Aligned Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanofibers Fabricated by Modified Electrospinning and Centrifugal Jet Spinning Techniques. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2017, 17, 9056–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncheurn, K.; Infahsaeng, Y. Electric field effect on electrospun fiber alignment using a parallel electrode plate. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1719, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, Y.; Ula, N.M.; Jahidah, K.; Kusumasari, E.M.; Triyana, K.; Sosiati, H.; Harsojo. Study of parallel oriented electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers using modified electrospinning method. Aip Conf. Proc. 2016, 1725, 020104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, G.R.; Ranjit, G.S.; Karthikeyan, K.K.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Biji, P. A facile route for controlled alignment of carbon nanotube-reinforced, electrospun nanofibers using slotted collector plates. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, B.S.; So, H.-M.; Won, K.; Lee, J.-O.; Kong, K.-J.; Chang, H. Detection of Tumor Markers Using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2006, 6, 3499–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markatos, D.; Sarakinis, A.; Mavrilas, D. Tuning Fiber Alignment to Achieve Mechanical Anisotropy on Polymeric Electrospun Scaffolds for Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, L.; Hu, L.; Cui, X. Continuous aligned polymer fibers produced by a modified electrospinning method. Polymer 2006, 47, 4901–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bolger, B.; Cahill, P.A.; McGuinness, G.B. Assembly of aligned polyvinyl alcohol–styrylpyridinium pendent group nanofibres for vascular tissue engineering applicationsg. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. N J. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2016, 223, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.-J.; Supaphol, P. Rotating-disk electrospinning: Needleless electrospinning of poly(caprolactone), poly(lactic acid) and poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofiber mats with controlled morphology. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chvojka, J.; Hinestroza, J.; Lukas, D. Production of Poly (vinylalcohol) Nanoyarns Using a Special Saw-like Collector. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2013, 21, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzerara, R.; Achour, S.; Tabet, N.; Zerkout, S. Synthesis and characterisation of ZnO/PVA composite nanofibres by electrospinning. Int. J. Nanoparticles 2011, 4, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Teber, O.O.; Mehrabi, M.; Koyuncu, I. Polyvinyl alcohol-based separation membranes: A comprehensive review on fabrication techniques, applications and future prospective. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 28, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, R.H.; Fetters, L.J.; Funk, W.G.; Graessley, W.W. Effects of concentration and thermodynamic interaction on the viscoelastic properties of polymer solutions. Macromolecules 2002, 24, 3873–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Song, X.; Ye, G.; Xu, J. Preparation of PVA/paraffin thermal regulating fiber by in situ microencapsulation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Venkatraman, S.S. Importance of viscosity parameters in electrospinning: Of monolithic and core–shell fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Elkins, C.; Long, T.E.; Wilkes, G.L. Electrospinning of linear homopolymers of poly(methyl methacrylate): Exploring relationships between fiber formation, viscosity, molecular weight and concentration in a good solvent. Polymer 2005, 46, 4799–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi, A.K.; Akbari, M. Trends in electrospinning of natural nanofibers. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 2007, 204, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, F.L. Vinyl Alcohol Polymers. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-C.; Ito, T.; Kim, K.-O.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, B.-S.; Khil, M.-S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, I.-S. Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers: Effects of degree of hydrolysis and enhanced water stability. Polym. J. 2010, 42, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, S.P.; Huang, C.C. Electrospinning PVA solution-rheology and morphology analyses. Fiber. Polym. 2012, 13, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Qin, X.-H. The effect of different surfactants on the electrospinning poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) nanofibers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 112, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwiiri, F.K.; Daniels, R. Influence of PVA Molecular Weight and Concentration on Electrospinnability of Birch Bark Extract-Loaded Nanofibrous Scaffolds Intended for Enhanced Wound Healing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewaldz, E.; Randrup, J.; Brettmann, B. Solvent Effects on the Elasticity of Electrospinnable Polymer Solutions. ACS Polym. Au 2022, 2, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, Z.; Shao, Z.; Xu, L. Effect of surface-active agent on morphology and properties of electrospun PVA nanofibres. Fiber. Polym. 2016, 17, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, G.K.; Khan, S.; Heiden, P.A. Comparison of the Effects of an Ionic Liquid and Other Salts on the Properties of Electrospun Fibers, 2–Poly(vinyl alcohol). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2009, 294, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Li, Y.; Chan, K.H.K.; Kotaki, M. Morphology and mechanical properties of PVA nanofibers spun by free surface electrospinning. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 2761–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadajji, V.G.; Betageri, G.V. Water Soluble Polymers for Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1972–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. The electrospinning behavior of poly(vinyl alcohol) in DMSO–water binary solvent mixtures. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102947–102955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Kanaya, T.; Nishida, K.; Kaji, K. Effects of cononsolvency on gelation of poly(vinyl alcohol) in mixed solvents of dimethyl sulfoxide and water. Polymer 2003, 44, 4075–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.M.; Perveen, A.; Matin, M.A.; Arafat, M.T. Effects of binary solvent mixtures on the electrospinning behavior of poly (vinyl alcohol). Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 115407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Sakai, S.; Taya, M. Enhanced productivity of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous mats using aqueous N,N-dimethylformamide solution and their application to lipase-immobilizing membrane-shaped catalysts. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Ito, E.N.; Gregorski, K.S.; Robertson, G.H.; Offeman, R.D.; Wood, D.F.; Orts, W.J.; Imam, S.H. Electrospun Nanofibers of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofibrils. J. Biobased Mater. Bio. 2008, 2, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Jankovic, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksa, A.; Numpaisal, P.-o.; Ruksakulpiwat, Y. The effect of humidity during electrospinning on morphology and mechanical properties of SF/PVA nanofibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3458–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peresin, M.S.; Habibi, Y.; Zoppe, J.O.; Pawlak, J.J.; Rojas, O.J. Nanofiber composites of polyvinyl alcohol and cellulose nanocrystals: Manufacture and characterization. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, I.; Medina, C.; Meruane, V.; Akbari-Fakhrabadi, A.; Flores, P.; Rodríguez-Llamazares, S. The effect of molecular weight and hydrolysis degree of poly(vinyl alcohol)(PVA) on the thermal and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/PVA blends. Polimeros. 2018, 28, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Campagne, C.; Salaün, F. Preparation of n-Alkane/Polycaprolactone Phase-Change Microcapsules via Single Nozzle Electro-Spraying: Characterization on Their Formation, Structures and Properties. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Campagne, C.; Salaun, F. Influence of a Coaxial Electrospraying System on the n-Hexadecane/Polycaprolactone Phase Change Microcapsules Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, P.; Chen, Y.; Campagne, C.; Salaün, F. Electrospraying poly(lactic acid) microcapsules loaded with n-hexadecane for thermal energy storage systems. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Salaün, F.; Liu, P.; Campagne, C. Coaxial two-capillary electrosprayed double-layered shells microcapsules used for in-situ thermally induced coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 172, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wan, J.; Zheng, C.; Du, Q.; Zhou, G.; Yang, X. Fabrication of Fe3O4@PVA microspheres by one-step electrospray for magnetic resonance imaging during transcatheter arterial embolization. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.-R.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Kaufman, S.L. Electrospraying of conducting liquids for monodisperse aerosol generation in the 4 nm to 1.8 μm diameter range. J. Aerosol Sci. 1995, 26, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.J.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Martens, P.J. Combining submerged electrospray and UV photopolymerization for production of synthetic hydrogel microspheres for cell encapsulation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Shivkumar, S. Molecular weight dependent structural regimes during the electrospinning of PVA. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2325–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, B.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Zamani, M.; Rodríguez, A.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrosprayed poly(vinyl alcohol) particles: Preparation and evaluation of their drug release profile. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konta, A.A.; Garcia-Pina, M.; Serrano, D.R. Personalised 3D Printed Medicines: Which Techniques and Polymers Are More Successful? Bioengineering 2017, 4, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türkoğlu, G.C.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Salaün, F. Investigation of the PVA Solutions Properties on The Electrospinning Mat. In Proceedings of the XVIth IITAS-International Izmir Textile and Apparel Symposium, Izmir, Turkey, 25–27 October 2023; pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Silva, C.J.; Buttel, Z.; Guimaraes, R.; Pereira, S.B.; Tamagnini, P.; Zille, A. Preparation and characterization of polysaccharides/PVA blend nanofibrous membranes by electrospinning method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. A review: Electrospinning of biopolymer nanofibers and their applications. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 317–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonino, C.A.; Krebs, M.D.; Saquing, C.D.; Jeong, S.I.; Shearer, K.L.; Alsberg, E.; Khan, S.A. Electrospinning alginate-based nanofibers: From blends to crosslinked low molecular weight alginate-only systems. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 85, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, M.; Ye, G.; Xu, J. A novel method to prepare poly(vinyl alcohol) water-soluble fiber with narrowly dissolving temperature range. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Fabrication and characterization of hydrophilic poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend cell scaffolds by melt-molding particulate-leaching method. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.H.; Wang, S.Y. Electrospun nanofibers from crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) and its filtration efficiency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.W.; Lin, M.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lai, M.F.; Shiu, B.C.; Lin, J.H. Preparation of Needleless Electrospinning Polyvinyl Alcohol/Water-Soluble Chitosan Nanofibrous Membranes: Antibacterial Property and Filter Efficiency. Polymers 2022, 14, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.; Cho, J.; Park, J. Facile and Novel Eco-Friendly Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofilters Using the Photocatalytic Property of Titanium Dioxide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5026–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.T.; Chathuranga, K.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.W.; Park, W.H. Tannic-Acid-Enriched Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanofibrous Membrane as a UV-Shie lding and Antibacterial Face Mask Filter Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 20435–20443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshabanah, L.A.; Hagar, M.; Al-Mutabagani, L.A.; Abozaid, G.M.; Abdallah, S.M.; Shehata, N.; Ahmed, H.; Hassanin, A.H. Hybrid Nanofibrous Membranes as a Promising Functional Layer for Personal Protection Equipment: Manufacturing and Antiviral/Antibacterial Assessments. Polymers 2021, 13, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, G.; Zane, D.; Foglia, S.; Dragone, R. Application of Electrospun Water-Soluble Synthetic Polymers for Multifunctional Air Filters and Face Masks. Molecules 2022, 27, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wei, J.; Shi, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Multi-Unit Needleless Electrospinning for One-Step Construction of 3D Waterproof MF-PVA Nanofibrous Membranes as High-Performance Air Filters. Small 2023, 19, e2206403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, W.A.; Shaheen, B.S.; Ghanem, L.G.; Badawy, I.M.; Abodouh, M.M.; Abdou, S.M.; Zada, S.; Allam, N.K. Cost-Effective Face Mask Filter Based on Hybrid Composite Nanofibrous Layers with High Filtration Efficiency. Langmuir 2021, 37, 7492–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Fan, Y.; Cen, X.; Wang, Y.; Shiu, B.C.; Ren, H.T.; Peng, H.K.; Jiang, Q.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Polypropylene/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Metal-Organic Framework-Based Melt-Blown Electrospun Composite Membranes for Highly Efficient Filtration of PM(2.5). Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmtshirazi, R.; Mohammadi, T.; Asadi, A.A. Incorporation of amine-grafted halloysite nanotube to electrospun nanofibrous membranes of chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) for Cd (II) and Pb(II) removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 220, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Kang, L.; Gao, X.; Zhao, K. Antibacterial, efficient and sustainable CS/PVA/GA electrospun nanofiber membrane for air filtration. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 125002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Salles, V.; Kaneti, Y.V.; Liu, M.; Maillard, M.; Journet, C.; Jiang, X.; Brioude, A. Fabrication of highly sensitive gas sensor based on Au functionalized WO3 composite nanofibers by electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, S.; Misra, M. Electrospun polymeric nanofibers: New horizons in drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lin, X.; Ee, L.Y.; Li, S.F.Y.; Huang, M. A Review on Electrospinning as Versatile Supports for Diverse Nanofibers and Their Applications in Environmental Sensing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2023, 5, 429–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-X.; Yu, G.-F.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. Conductive polymer ultrafine fibers via electrospinning: Preparation, physical properties and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, K.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, J.; Mao, S.; Jiang, T.; Ma, Z. Electrospun Ribbon-Like Microfiber Films of a Novel Guanidine-Based ABA Triblock Copolymer: Fabrication, Antibacterial Activity, and Cytotoxicity. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ma, H.; Xiao, S.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Cao, X.; Shi, X. Facile immobilization of gold nanoparticles into electrospun polyethyleneimine/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers for catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4493–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Y.; Cai, S.; Du, M.; Zhu, H.; Bao, S.; Xie, Q. Facile Fabrication of Palladium Nanoparticles Immobilized on the Water-Stable Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyehyleneimine Nanofibers ViaIn-SituReduction and Their High Electrochemical Activity. Soft Mater. 2014, 12, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iitani, K.; Nakaya, M.; Tomono, T.; Toma, K.; Arakawa, T.; Tsuchido, Y.; Mitsubayashi, K.; Takeda, N. Enzyme-embedded electrospun fiber sensor of hydrophilic polymer for fluorometric ethanol gas imaging in vapor phase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R. The principles of rehabilitation science on the field of regenerative medicine. Rev. De. Atenção À Saúde 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.R.; Navarro, J.; Coburn, J.C.; Mahadik, B.; Molnar, J.; Holmes, J.H.t.; Nam, A.J.; Fisher, J.P. Current and Future Perspectives on Skin Tissue Engineering: Key Features of Biomedical Research, Translational Assessment, and Clinical Application. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 8, e1801471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatialis, D.F.; Papenburg, B.J.; Gironés, M.; Saiful, S.; Bettahalli, S.N.M.; Schmitmeier, S.; Wessling, M. Medical applications of membranes: Drug delivery, artificial organs and tissue engineering. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atala, A. Tissue engineering of human bladder. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 97, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Atala, A. Engineering blood vessels and vascularized tissues: Technology trends and potential clinical applications. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1115–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.L.; Liau, L.L.; Ng, M.H.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Law, J.X. Current Progress in Tendon and Ligament Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, A.; Yang, Y. Decellularization Strategies for Regenerative Medicine: From Processing Techniques to Applications. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9831534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoka, T.; Miyachi, H. Current Status of Tissue Engineering Heart Valve. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2016, 7, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngadiman, N.H.A.; Yusof, N.M.; Idris, A.; Fallahiarezoudar, E.; Kurniawan, D. Novel Processing Technique to Produce Three Dimensional Polyvinyl Alcohol/Maghemite Nanofiber Scaffold Suitable for Hard Tissues. Polymers 2018, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei, S.; Omidi, M.; Nasehi, F.; Golzar, H.; Mohammadrezaei, D.; Rezai Rad, M.; Khojasteh, A. Egg shell-derived calcium phosphate/carbon dot nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Fabrication and characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 100, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lu, T.; Yang, L.; Luo, S.; Wang, Z.; Ye, C. In situ cell electrospun using a portable handheld electrospinning apparatus for the repair of wound healing in rats. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q. A novel bioactive membrane by cell electrospinning. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 338, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.O.; Yoon, I.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, D.D.; Lee, S.J.; Park, W.H.; Hudson, S.M. Chitosan-coated poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers for wound dressings. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Attar, A.A.; El-Wakil, H.B.; Hassanin, A.H.; Bakr, B.A.; Almutairi, T.M.; Hagar, M.; Elwakil, B.H.; Olama, Z.A. Silver/Snail Mucous PVA Nanofibers: Electrospun Synthesis and Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities. Membranes 2022, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Karthick, S.; Ragavi, T.K.; Naresh, K.; Rama Sreekanth, P.S. A study on collagen-PVA and chitosan-PVA nanofibrous matrix for wound dressing application. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 56, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Lee, W.H.; Gao, Z.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Gao, Y. Wound dressing from polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan electrospun fiber membrane loaded with OH-CATH30 nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilotra, S.; Chouhan, D.; Bhardwaj, N.; Nandi, S.K.; Mandal, B.B. Potential of silk sericin based nanofibrous mats for wound dressing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 90, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira, R.S.; Miguel, S.P.; Cabral, C.S.D.; Moreira, A.F.; Ferreira, P.; Correia, I.J. Development of a poly(vinyl alcohol)/lysine electrospun membrane-based drug delivery system for improved skin regeneration. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouro, C.; Gomes, A.P.; Ahonen, M.; Fangueiro, R.; Gouveia, I.C. Chelidoniummajus L. Incorporated Emulsion Electrospun PCL/PVA_PEC Nanofibrous Meshes for Antibacterial Wound Dressing Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-Rives, M.; Beltran-Osuna, A.A.; Gomez-Tejedor, J.A.; Gomez Ribelles, J.L. Electrospun PVA/Bentonite Nanocomposites Mats for Drug Delivery. Materials 2017, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannesari, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Morshed, M.; Zamani, M. Composite poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(vinyl acetate) electrospun nanofibrous mats as a novel wound dressing matrix for controlled release of drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Anwar Hamzah, M.S.; Abd Razak, S.I.; Abdul Sukor, J.; Nayan, N.; Mat Nayan, N.H. Study on Morphological Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Poly (lactic acid) Wound Dressing Membrane as Drug Delivery Carrier in Wound Healing Treatment. J. Adv. Ind. Technol. Appl. 2020, 1, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, S.; Asadi, H.; Ghalei, B. Zein nanoparticle-embedded electrospun PVA nanofibers as wound dressing for topical delivery of anti-inflammatory diclofenac. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Electrospun Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide Nanofibrous Membrane with Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Drug for Potential WoundDressing Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.X.; Zheng, Z.F.; Lin, L.Y.; Si, J.H.; Wang, Q.T.; Peng, X.F.; Chen, W.Z. Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Arya, D.K.; Pandey, P.; Anand, S.; Gautam, A.K.; Ranjan, S.; Saraf, S.A.; Mahalingam Rajamanickam, V.; Singh, S.; Chidambaram, K.; et al. ECM Mimicking Biodegradable Nanofibrous Scaffold Enriched with Curcumin/ZnO to Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing via Multifunctional Bioactivity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 6843–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, E.; Pourmadadi, M.; Zandi, N.; Rahdar, A.; Baino, F. pH-Responsive PVA-Based Nanofibers Containing GO Modified with Ag Nanoparticles: Physico-Chemical Characterization, Wound Dressing, and Drug Delivery. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamady Hussein, M.A.; Ulag, S.; Abo Dena, A.S.; Sahin, A.; Grinholc, M.; Gunduz, O.; El-Sherbiny, I.; Megahed, M. Chitosan/Gold Hybrid Nanoparticles Enriched Electrospun PVA Nanofibrous Mats for the Topical Delivery of Punica granatum L. Extract: Synthesis, Characterization, Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5133–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, B.S.; de Lima, G.G.; de Lima, T.A.M.; Seba, V.; Lemarquis, C.; Pereira, B.L.; Bandeira, M.; Cao, Z.; Nugent, M. Effect of thermal annealing on a bilayer polyvinyl alcohol/polyacrylic acid electrospun hydrogel nanofibres loaded with doxorubicin and clarithromycin for a synergism effect against osteosarcoma cells. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, T.; Lou, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Ran, H. Drug release from core-shell PVA/silk fibroin nanoparticles fabricated by one-step electrospraying. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X.; Pei, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Gold nanorods contained polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan nanofiber matrix for cell imaging and drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, D.; Li, Z. Photothermal transforming agent and chemotherapeutic co-loaded electrospun nanofibers for tumor treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3893–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Rashid, M.H.; Arbab, A.S.; Khan, M. Encapsulation of Anticancer Drugs (5-Fluorouracil and Paclitaxel) into Polycaprolactone (PCL) Nanofibers and In Vitro Testing for Sustained and Targeted Therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Türkoğlu, G.C.; Khomarloo, N.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Neznakomova, M.; Salaün, F. PVA-Based Electrospun Materials—A Promising Route to Designing Nanofiber Mats with Desired Morphological Shape—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031668
Türkoğlu GC, Khomarloo N, Mohsenzadeh E, Gospodinova DN, Neznakomova M, Salaün F. PVA-Based Electrospun Materials—A Promising Route to Designing Nanofiber Mats with Desired Morphological Shape—A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031668
Chicago/Turabian StyleTürkoğlu, Gizem Ceylan, Niloufar Khomarloo, Elham Mohsenzadeh, Dilyana Nikolaeva Gospodinova, Margarita Neznakomova, and Fabien Salaün. 2024. "PVA-Based Electrospun Materials—A Promising Route to Designing Nanofiber Mats with Desired Morphological Shape—A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031668
APA StyleTürkoğlu, G. C., Khomarloo, N., Mohsenzadeh, E., Gospodinova, D. N., Neznakomova, M., & Salaün, F. (2024). PVA-Based Electrospun Materials—A Promising Route to Designing Nanofiber Mats with Desired Morphological Shape—A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031668