Extended Cleavage Specificity of two Hematopoietic Serine Proteases from a Ray-Finned Fish, the Spotted Gar (Lepisosteus oculatus)
Abstract
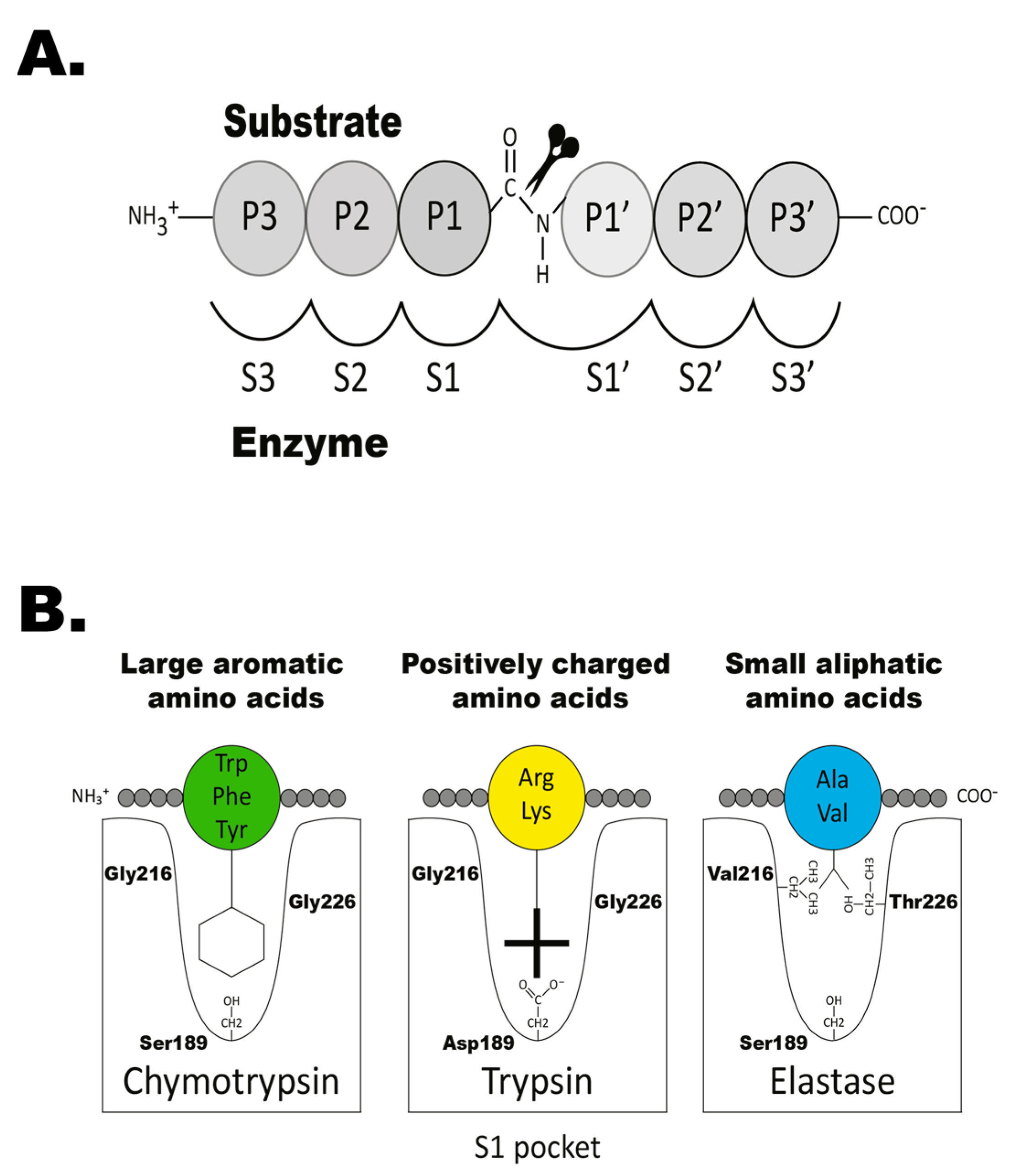
1. Introduction
2. Results
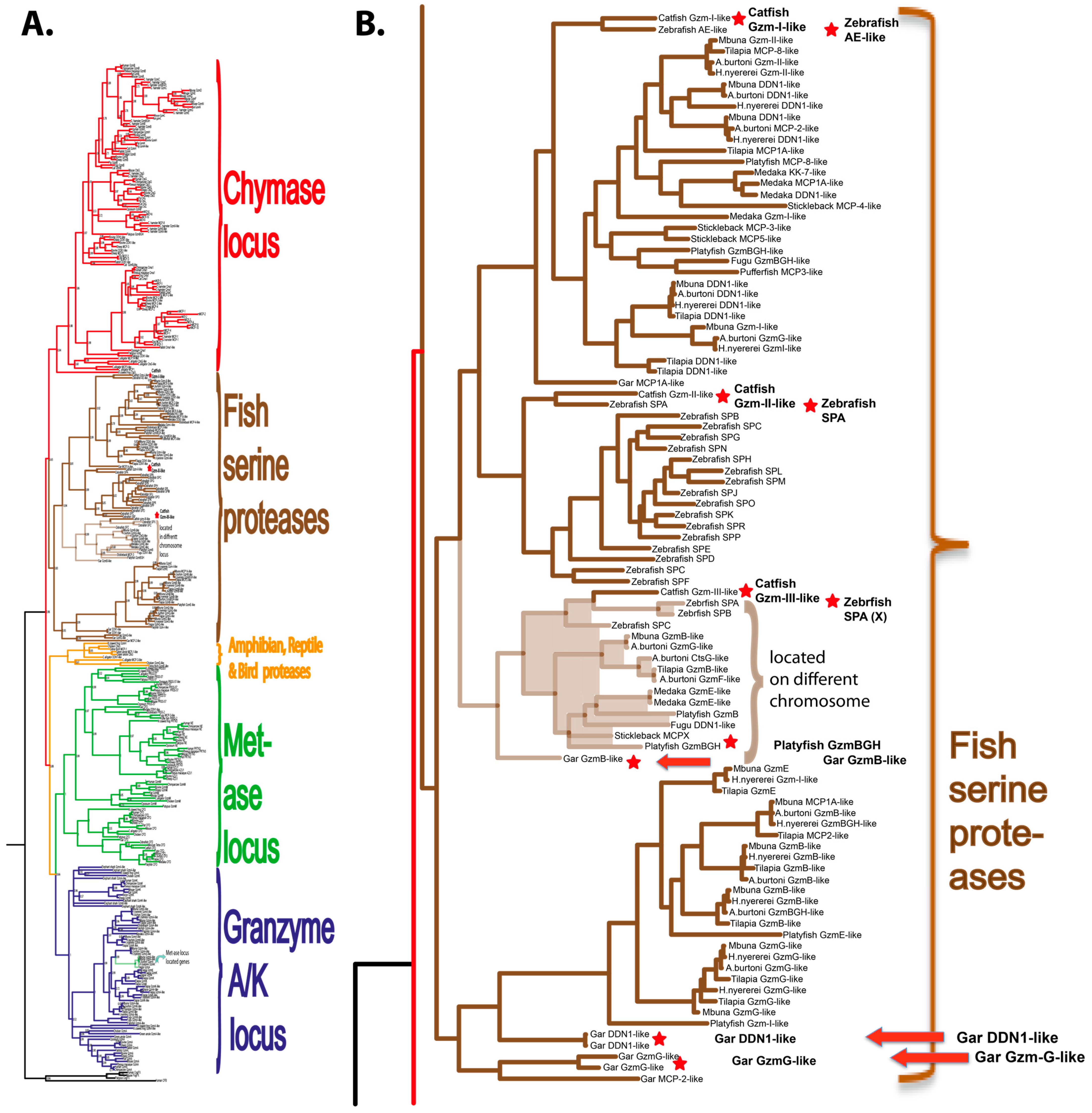
2.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
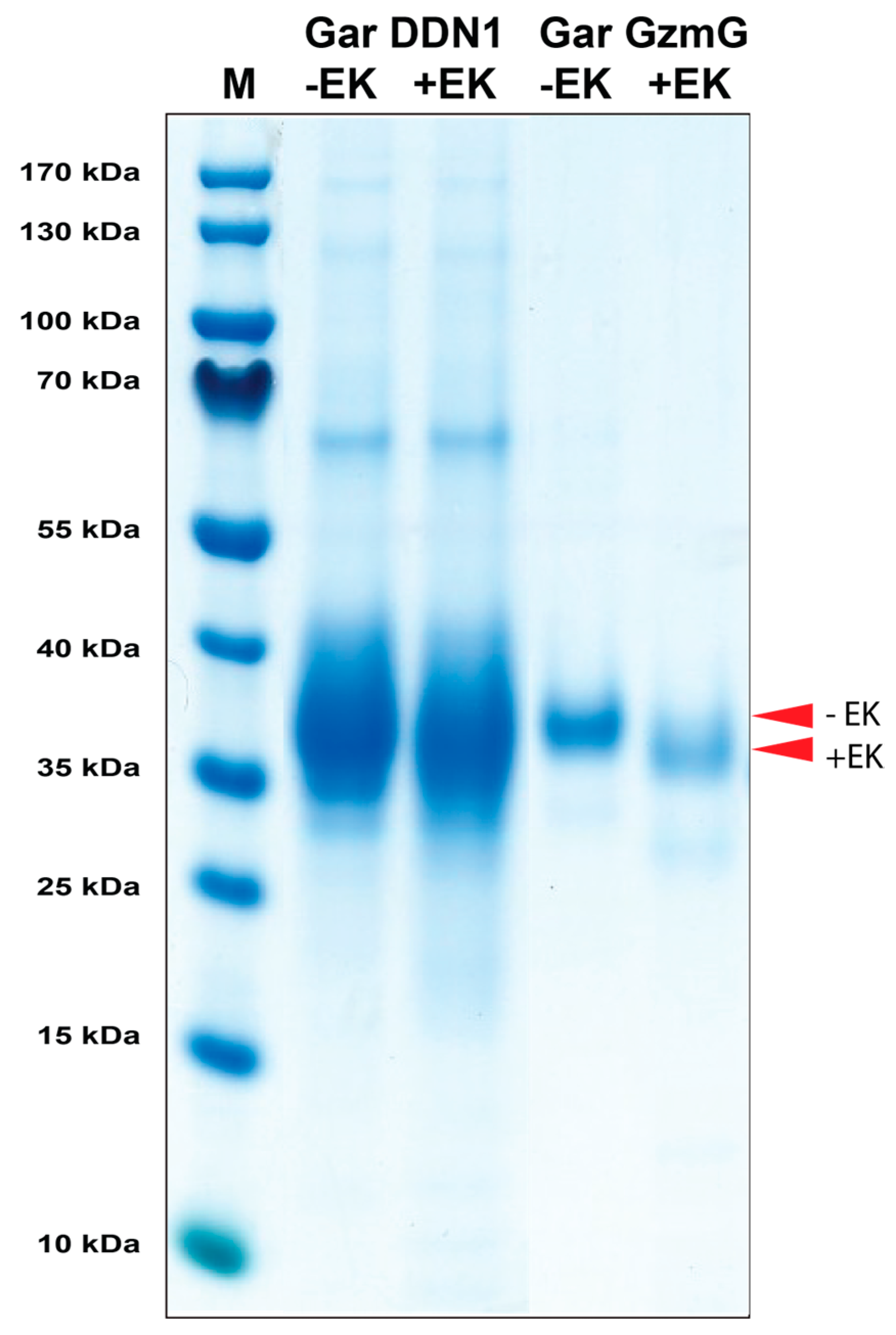
2.2. Production, Purification, and Activation of Gar Granzyme G and Gar Duodenase 1
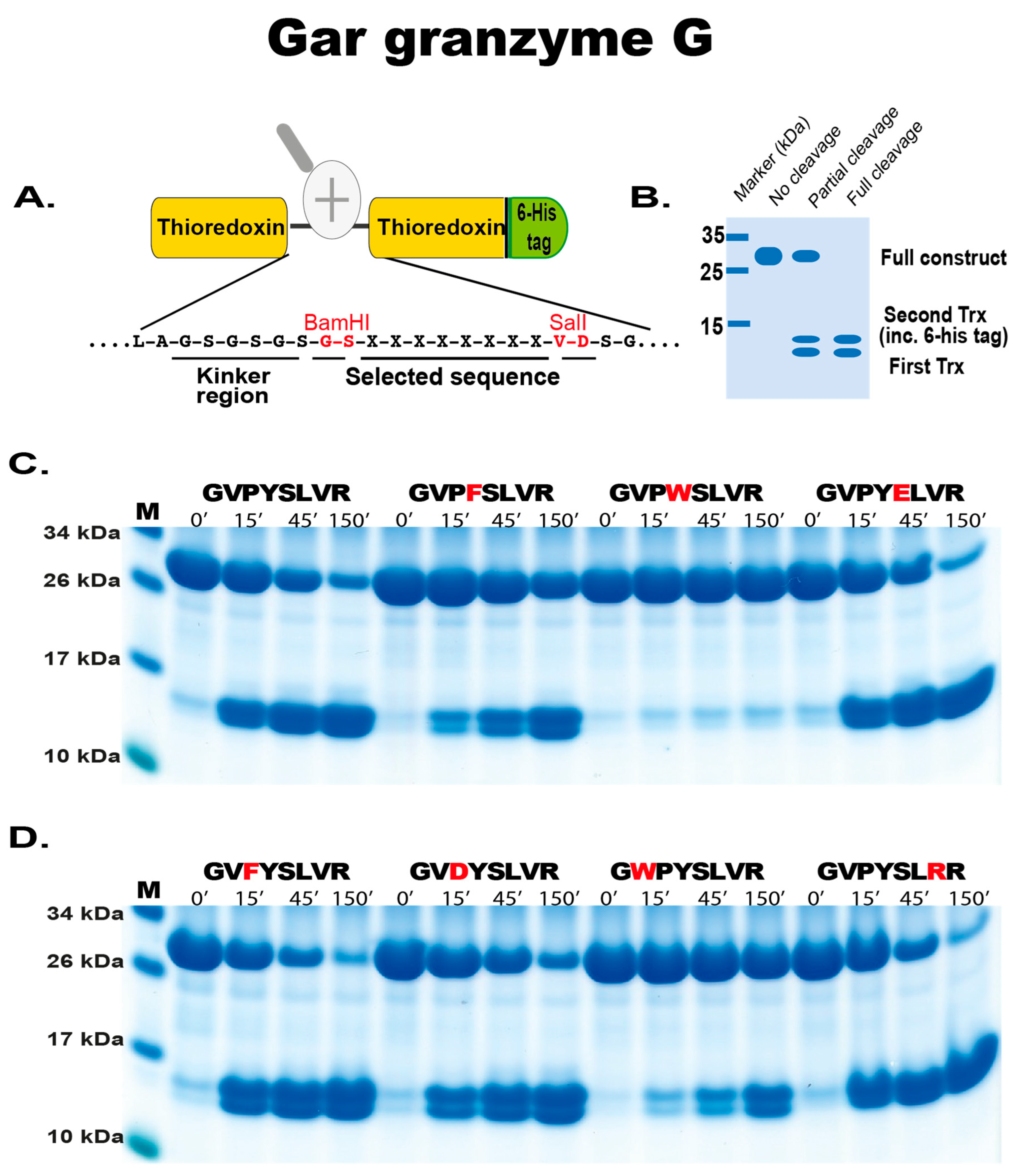
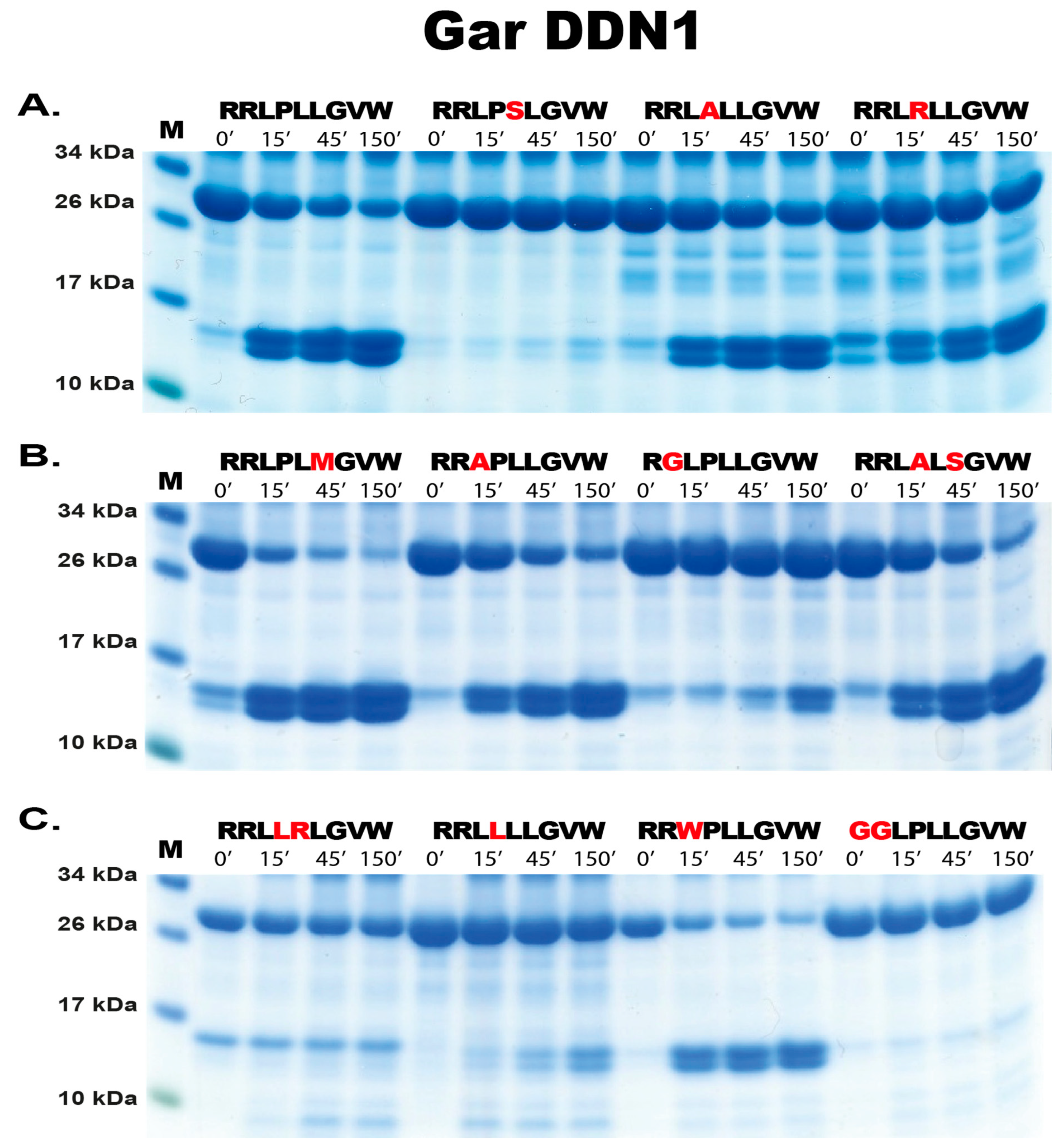
2.3. Substrate Phage Display
2.4. Phage Display Sequence Verification Using Recombinant Substrates
2.5. Screening for Potential In Vivo Substrates
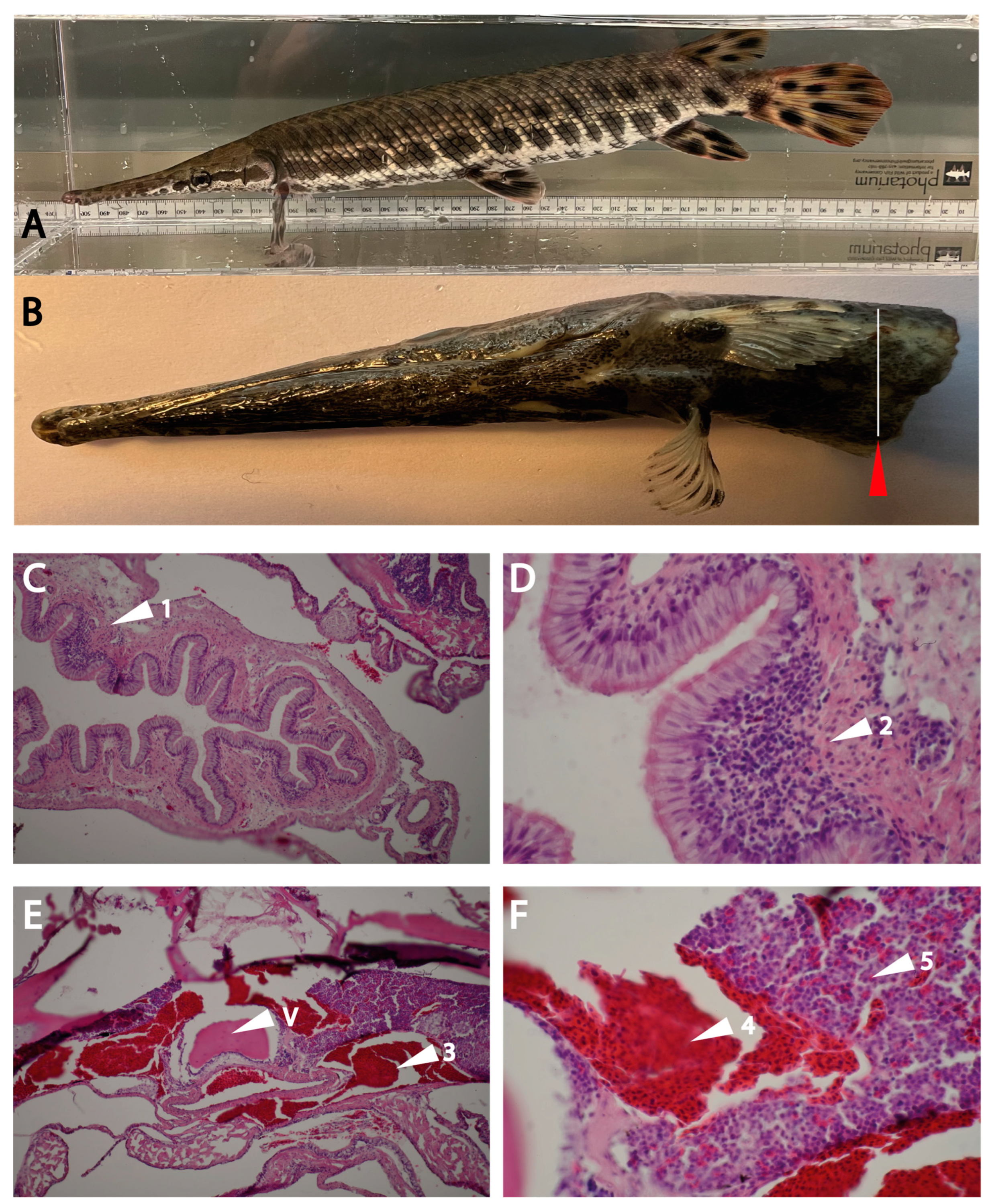
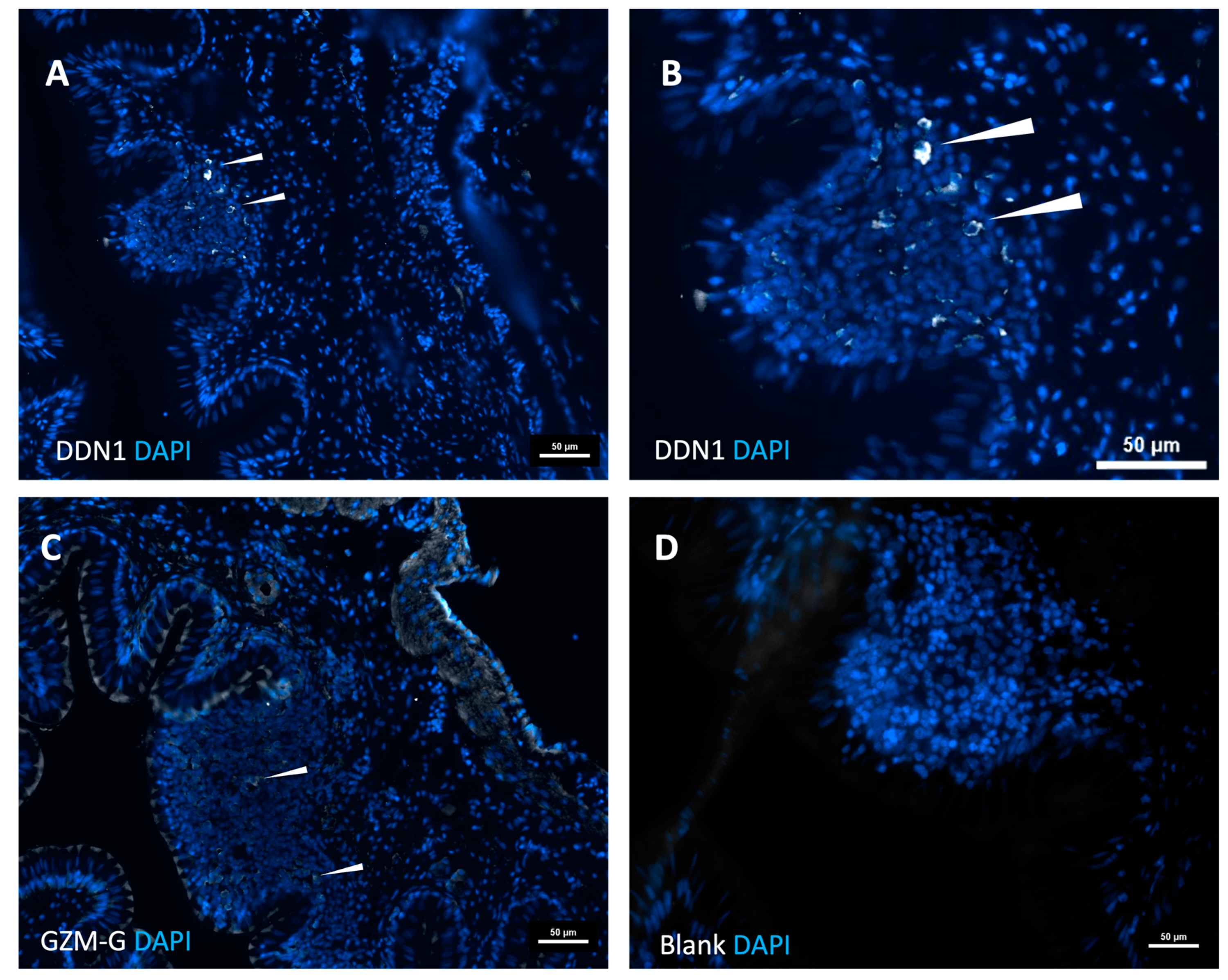
2.6. Analyzing Gar Tissue for Sites of Expression for the Two Gar Enzymes
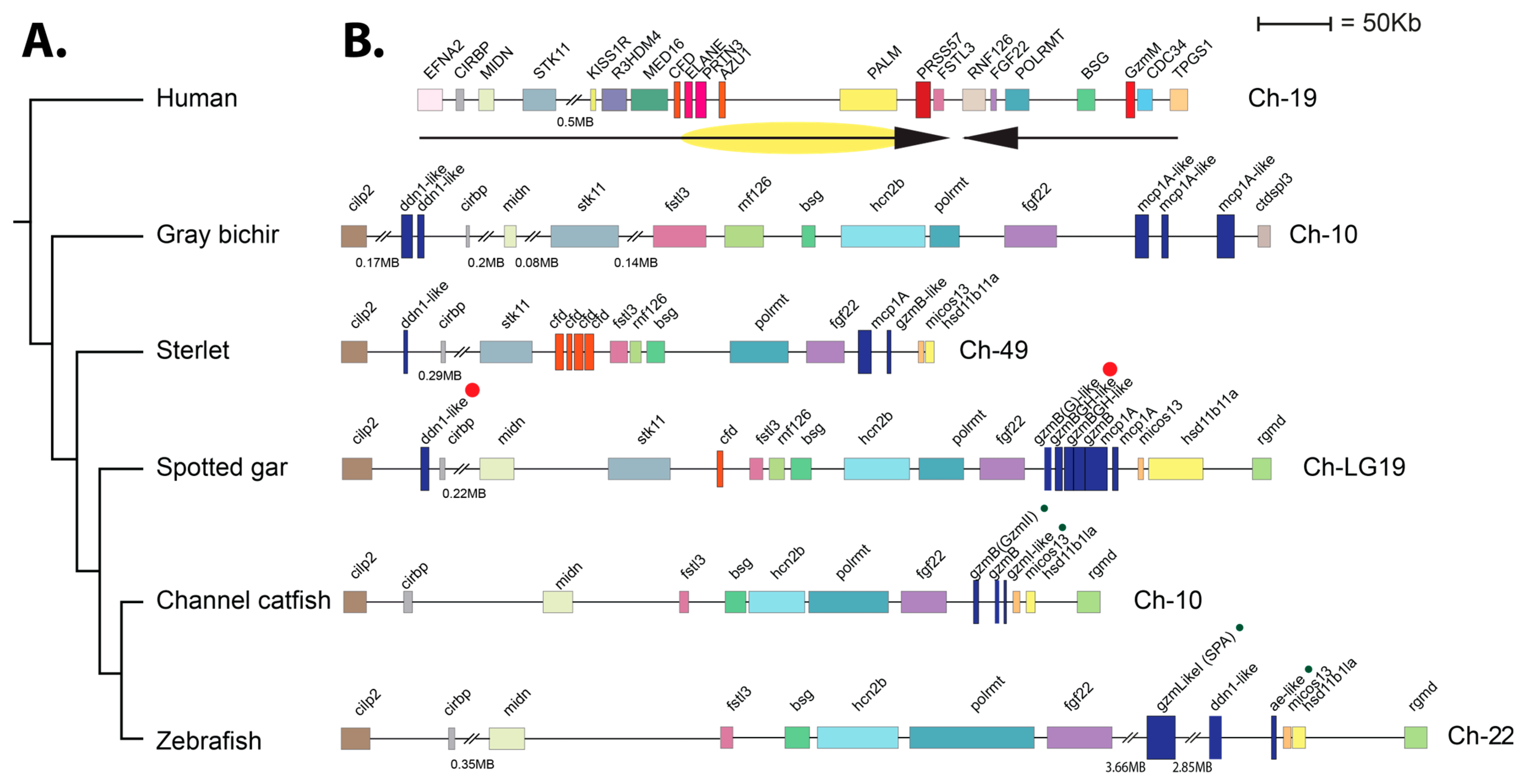
2.7. Gene Loci for Gar Hematopoietic Serine Proteases
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
4.2. Production and Purification of Recombinant Gar Gzm-G and Gar DDN1
4.3. Activation of Recombinant Gar Granzymes
4.4. Substrate Phage Display
4.5. Phage Display Sequence Verification Using a Two-Thioredoxin (trx) Approach
4.6. Screening for Potential In Vivo Substrates
4.7. Spotted Gar Husbandry and Tissue Sampling
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hellman, L.; Thorpe, M. Granule proteases of hematopoietic cells, a family of versatile inflammatory mediators—An update on their cleavage specificity, in vivo substrates, and evolution. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 15–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, S.; Thorpe, M.; Boinapally, V.; Hellman, L. Granule Associated Serine Proteases of Hematopoietic Cells—An Analysis of Their Appearance and Diversification during Vertebrate Evolution. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Akula, S.; Chahal, G.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificity of human neutrophil elastase, human proteinase 3 and their distant orthologue clawed frog PR3-three elastases with similar primary but different extended specificities and stability. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Alemayehu, R.; Roy, A.; Kervinen, J.; de Garavilla, L.; Abrink, M.; Hellman, L. Highly Selective Cleavage of Cytokines and Chemokines by the Human Mast Cell Chymase and Neutrophil Cathepsin G. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, S.; Fu, Z.; Wernersson, S.; Hellman, L. The Evolutionary History of the Chymase Locus -a Locus Encoding Several of the Major Hematopoietic Serine Proteases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, J.M.; Samollow, P.B.; Hellman, L. High degree of conservation of the multigene tryptase locus over the past 150-200 million years of mammalian evolution. Immunogenetics 2010, 62, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.K.; Enoksson, M.; Gallwitz, M.; Hellman, L. The extended substrate specificity of the human mast cell chymase reveals a serine protease with well-defined substrate recognition profile. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.K.; Karlson, U.; Hellman, L. The extended cleavage specificity of the rodent beta-chymases rMCP-1 and mMCP-4 reveal major functional similarities to the human mast cell chymase. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.K.; Pemberton, A.D.; Miller, H.R.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificity of mMCP-1, the major mucosal mast cell protease in mouse-High specificity indicates high substrate selectivity. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2548–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, J.M.; Enoksson, M.; Samollow, P.B.; Hellman, L. Extended substrate specificity of opossum chymase-Implications for the origin of mast cell chymases. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Qiao, C.; Ryu, J.; Chahal, G.; de Garavilla, L.; Kervinen, J.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Duodenases are a small subfamily of ruminant intestinal serine proteases that have undergone a remarkable diversification in cleavage specificity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Thorpe, M.; Chahal, G.; de Garavilla, L.; Kervinen, J.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificity of sheep mast cell protease-2: A classical chymase with preference to aromatic P1 substrate residues. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 92, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificities of two mast cell chymase-related proteases and one granzyme B-like protease from the platypus, a monotreme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Akula, S.; Hellman, L. Asp-ase Activity of the Opossum Granzyme B Supports the Role of Granzyme B as Part of Anti-Viral Immunity Already during Early Mammalian Evolution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. rMCP-2, the Major Rat Mucosal Mast Cell Protease, an Analysis of Its Extended Cleavage Specificity and Its Potential Role in Regulating Intestinal Permeability by the Cleavage of Cell Adhesion and Junction Proteins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernersson, S.; Reimer, J.M.; Poorafshar, M.; Karlson, U.; Wermenstam, N.; Bengten, E.; Wilson, M.; Pilstrom, L.; Hellman, L. Granzyme-like sequences in bony fish shed light on the emergence of hematopoietic serine proteases during vertebrate evolution. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, M.; Akula, S.; Hellman, L. Channel catfish granzyme-like I is a highly specific serine protease with metase activity that is expressed by fish NK-like cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 63, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Olsson, A.K.; Hellman, L. Chicken cathepsin G-like-A highly specific serine protease with a peculiar tryptase specificity expressed by chicken thrombocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 129, 104337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Olsson, A.K.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificity of a Chinese alligator granzyme B homologue, a strict Glu-ase in contrast to the mammalian Asp-ases. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 128, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, K.; Evans, D.L.; Jaso-Friedmann, L. Evidence for the existence of granzyme-like serine proteases in teleost cytotoxic cells. J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 58, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, K.; Leary, J.H., 3rd; Evans, D.L.; Jaso-Friedmann, L. Molecular characterization and expression of a granzyme of an ectothermic vertebrate with chymase-like activity expressed in the cytotoxic cells of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, K.; Leary, J.H., 3rd; Evans, D.L.; Jaso-Friedmann, L. Nonspecific cytotoxic cells of teleosts are armed with multiple granzymes and other components of the granule exocytosis pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Pozo, E.; Valero, Y.; Lozano, M.T.; Rodriguez-Cerezo, P.; Miao, L.; Campo, V.; Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A. Fish Granzyme A Shows a Greater Role Than Granzyme B in Fish Innate Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, I.; Gehrke, A.R.; Smith, J.J.; Kawasaki, K.; Manousaki, T.; Pasquier, J.; Amores, A.; Desvignes, T.; Batzel, P.; Catchen, J.; et al. The spotted gar genome illuminates vertebrate evolution and facilitates human-teleost comparisons. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Ren, Y.; Uesaka, M.; Beavan, A.J.S.; Muffato, M.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Sato, I.; Wan, W.; Clark, J.W.; et al. Hagfish genome elucidates vertebrate whole-genome duplication events and their evolutionary consequences. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parey, E.; Louis, A.; Montfort, J.; Guiguen, Y.; Roest Crollius, H.; Berthelot, C. An atlas of fish genome evolution reveals delayed rediploidization following the teleost whole-genome duplication. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Stock, M.; Kneitz, S.; Klopp, C.; Woltering, J.M.; Adolfi, M.C.; Feron, R.; Prokopov, D.; Makunin, A.; Kichigin, I.; et al. The sterlet sturgeon genome sequence and the mechanisms of segmental rediploidization. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Venkatesh, B. The Divergent Genomes of Teleosts. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2018, 6, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, H. The versatility of proteolytic enzymes. J. Cell. Biochem. 1986, 32, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, J.J.; Craik, C.S. Structural basis of substrate specificity in the serine proteases. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 1995, 4, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, I.; Berger, A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1967, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, M.; Akula, S.; Fu, Z.; Hellman, L. The Extended Cleavage Specificity of Channel Catfish Granzyme-like II, A Highly Specific Elastase, Expressed by Natural Killer-like Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernersson, M.; Ledin, A.; Johansson, J.; Hellman, L. Generation of therapeutic antibody responses against IgE through vaccination. Faseb J. 2002, 16, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aybay, E.; Elkhalifa, M.; Akula, S.; Wernersson, S.; Hellman, L. Two granzyme A/K homologs in Zebra mbuna have different specificities, one classical tryptase and one with chymase activity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 148, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongwei, Y.; Akula, S.; Fu, Z.; de Garavilla, L.; Kervinen, J.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Extended Cleavage Specificities of Rabbit and Guinea Pig Mast Cell Chymases: Two Highly Specific Leu-Ases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, L.; Pan, H.; Jiang, H.; Wei, Q.; Fang, M.; Yu, H.; Zhu, C.; Cai, Y.; et al. Tracing the genetic footprints of vertebrate landing in non-teleost ray-finned fishes. Cell 2021, 184, 1377–1391.e1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousalova, I.; Krepela, E. Granzyme B-induced apoptosis in cancer cells and its regulation (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1361–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Ewen, C.L.; Kane, K.P.; Bleackley, R.C. A quarter century of granzymes. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, G.H.; Raymond, W.W.; Wolters, P.J. Angiotensin II generation by mast cell alpha- and beta-chymases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1480, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, P.; Akula, S.; Fu, Z.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Extended Cleavage Specificity of the Rat Vascular Chymase, a Potential Blood Pressure Regulating Enzyme Expressed by Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Jin, D.; Yamada, M.; Kirimura, K.; Miyazaki, M. Different angiotensin II-forming pathways in human and rat vascular tissues. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 305, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Highly Selective Cleavage of TH2-Promoting Cytokines by the Human and the Mouse Mast Cell Tryptases, Indicating a Potent Negative Feedback Loop on TH2 Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Olsson, A.K.; Kervinen, J.; Hellman, L. Mast Cells and Basophils in the Defense against Ectoparasites: Efficient Degradation of Parasite Anticoagulants by the Connective Tissue Mast Cell Chymases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.; Piliponsky, A.M.; Chen, C.C.; Lammel, V.; Abrink, M.; Pejler, G.; Tsai, M.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells can enhance resistance to snake and honeybee venoms. Science 2006, 313, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahoshi, M.; Song, C.H.; Piliponsky, A.M.; Metz, M.; Guzzetta, A.; Abrink, M.; Schlenner, S.M.; Feyerabend, T.B.; Rodewald, H.R.; Pejler, G.; et al. Mast cell chymase reduces the toxicity of Gila monster venom, scorpion venom, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4180–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Metz, M.; Starkl, P.; Marichal, T.; Tsai, M. Mast cells and IgE in defense against lethality of venoms: Possible “benefit” of allergy. Allergo J. Int. 2020, 29, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkl, P.; Gaudenzio, N.; Marichal, T.; Reber, L.L.; Sibilano, R.; Watzenboeck, M.L.; Fontaine, F.; Mueller, A.C.; Tsai, M.; Knapp, S.; et al. IgE antibodies increase honeybee venom responsiveness and detoxification efficiency of mast cells. Allergy 2022, 77, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.; Stavenhagen, K.; Kolarich, D.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Maurer, M.; Metz, M. Human Mast Cell Tryptase Is a Potential Treatment for Snakebite Envenoming Across Multiple Snake Species. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aybay, E.; Ryu, J.; Fu, Z.; Akula, S.; Enriquez, E.M.; Hallgren, J.; Wernersson, S.; Olsson, A.K.; Hellman, L. Extended cleavage specificities of human granzymes A and K, two closely related enzymes with conserved but still poorly defined functions in T and NK cell-mediated immunity. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1211295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J. Granzyme A activates another way to die. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 235, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, S.S.; Menaa, C.; Pardo, J.; Wang, B.; Wallich, R.; Freudenberg, M.; Kim, S.; Raja, S.M.; Shi, L.; Simon, M.M.; et al. Human and mouse granzyme A induce a proinflammatory cytokine response. Immunity 2008, 29, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhoff, V.; Arold, N.; Taube, D.; Ehrhardt, W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis 1988, 9, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valentini, P.; Akula, S.; Alvarado-Vazquez, A.; Hallgren, J.; Fu, Z.; Racicot, B.; Braasch, I.; Thorpe, M.; Hellman, L. Extended Cleavage Specificity of two Hematopoietic Serine Proteases from a Ray-Finned Fish, the Spotted Gar (Lepisosteus oculatus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031669
Valentini P, Akula S, Alvarado-Vazquez A, Hallgren J, Fu Z, Racicot B, Braasch I, Thorpe M, Hellman L. Extended Cleavage Specificity of two Hematopoietic Serine Proteases from a Ray-Finned Fish, the Spotted Gar (Lepisosteus oculatus). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031669
Chicago/Turabian StyleValentini, Paolo, Srinivas Akula, Abigail Alvarado-Vazquez, Jenny Hallgren, Zhirong Fu, Brett Racicot, Ingo Braasch, Michael Thorpe, and Lars Hellman. 2024. "Extended Cleavage Specificity of two Hematopoietic Serine Proteases from a Ray-Finned Fish, the Spotted Gar (Lepisosteus oculatus)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031669
APA StyleValentini, P., Akula, S., Alvarado-Vazquez, A., Hallgren, J., Fu, Z., Racicot, B., Braasch, I., Thorpe, M., & Hellman, L. (2024). Extended Cleavage Specificity of two Hematopoietic Serine Proteases from a Ray-Finned Fish, the Spotted Gar (Lepisosteus oculatus). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031669





