Tomographic Universality of the Discrete Wigner Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Generalized Pauli Group and Displacement Operators
3. Phase Space Construction and the Wigner Map
4. Tomographic Universality of the Discrete Wigner Function
4.1. Tomographic Property for a Given DPS Partition
4.2. Odd Local Dimensions
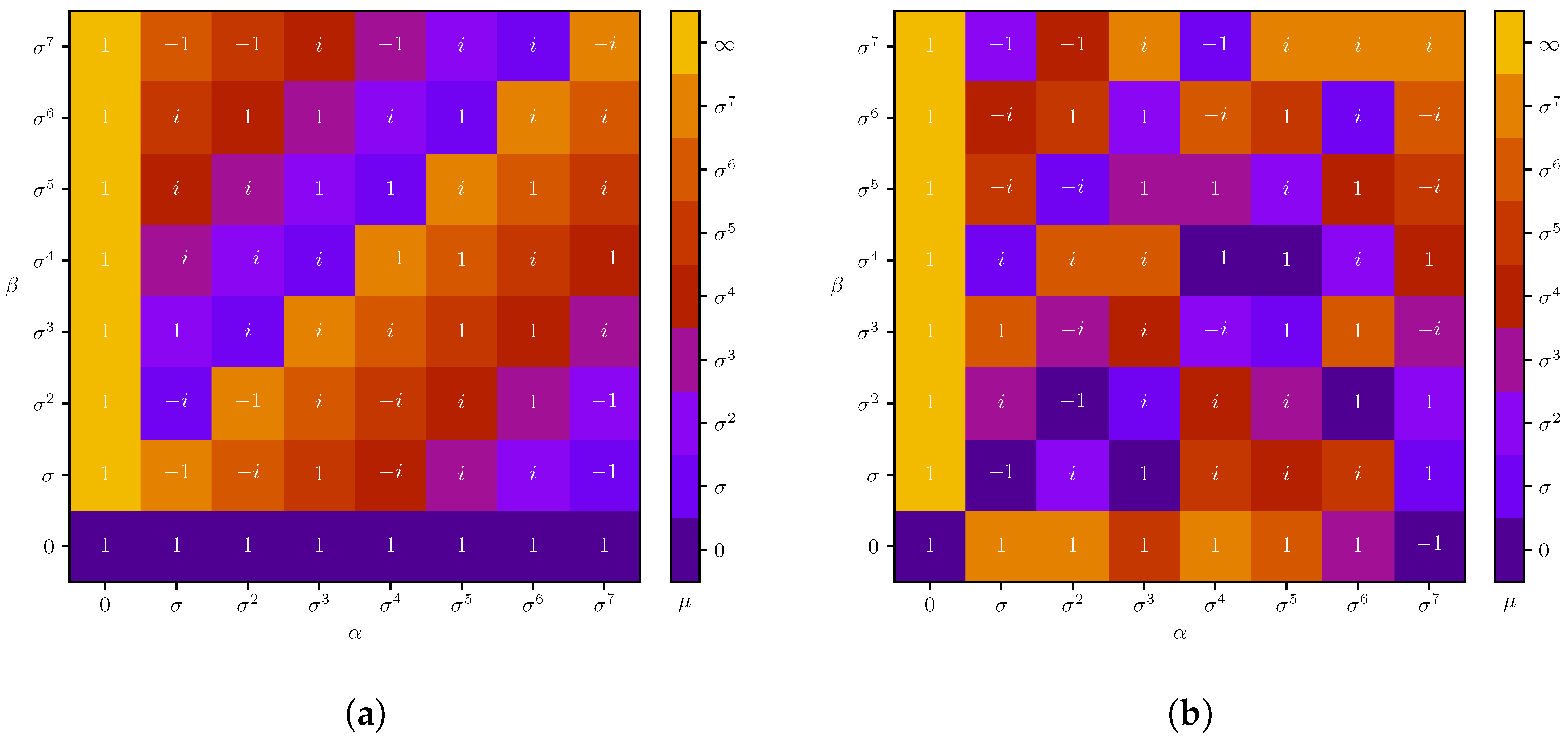
4.3. Even Local Dimensions
- 1.
- If , then ;
- 2.
- If , then ;
- 3.
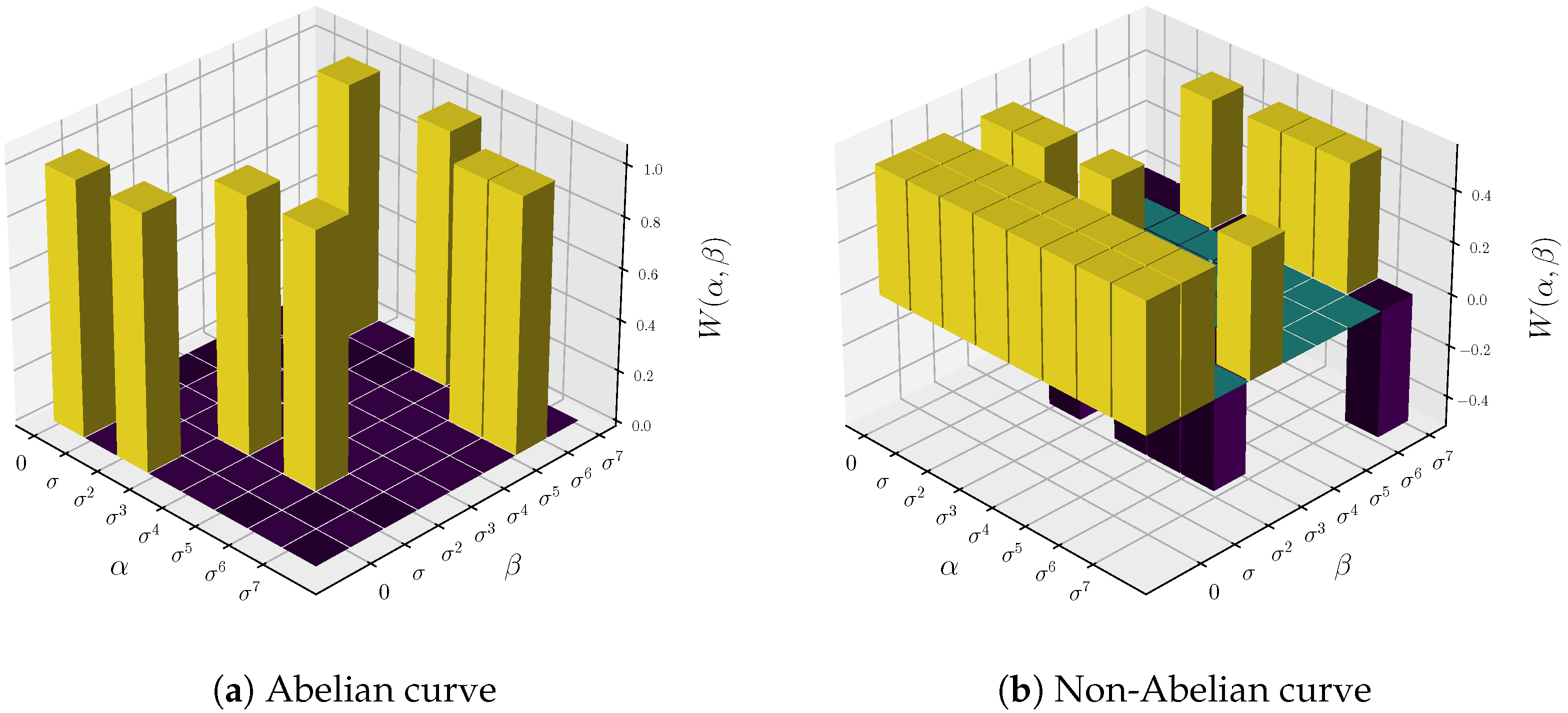
- If , there are no values producing Abelian curves, as can be observed in the example in Figure 1b, where the only Abelian curve is the ray .
- 1.
- If , then ;
- 2.
- If , then ;
- 3.
- If , .
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
- (a)
- Regular curves
- (b)
- Exceptional curves
Appendix C
References
- Wigner, E. On the quantum correction for thermodynamic equilibrium. Phys. Rev. A 1932, 40, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, F. Zur Theorie des Austauschproblems und der Remanenzerscheinung der Ferromagnetika. Z. für Phys. 1932, 74, 295–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewold, H.J. On the principles of elementary quantum mechanics. Physica 1949, 12, 405–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyal, J.E. Quantum mechanics as a statistical theory. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1947, 45, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, L.; Wolf, E. Coherence Properties of Optical Fields. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1965, 37, 231–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.R.; Murray, S. A quasi-classical formulation of the Wigner function approach to quantum ballistic transport. Phys. Lett. A 1983, 93, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chiu, L.C. Quantum theory of electron transport in the Wigner formalism. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.V. Semi-classical mechanics in phase space: A study of Wigner’s function. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1977, 287, 237–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, R.F.; Wigner, E.P. Manifestations of Bose and Fermi statistics on the quantum distribution functionfor systems of spin-0 and spin-1/2 particles. Phys. Rev. A 1984, 30, 2613–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.; Scully, M.O. Joint Wigner distribution for spin-1/2 particles. Foud. Phys. 1986, 16, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootters, W.K. A Wigner-function formulation of finite-state quantum mechanics. Ann. Phys. 1987, 176, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, K.S.; Hoffman, M.J.; Wootters, W.K. Discrete phase space based on finite fields. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, D. The Heisenberg representation of quantum computers. In Group 22: International Colloquium on Group Theoretical Methods in Physics, Proceedings of 22nd International Colloquium, Group22, ICGTMP’98, Hobart, Australia, 13–17 July 1998; Corney, S.P., Delbourgo, R., Jarvis, P.D., Eds.; International Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Galvão, E.F. Discrete Wigner functions and quantum computational speedup. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 71, 042302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormick, C.; Galvão, E.F.; Gottesman, D.; Paz, J.P.; Pittenger, A.O. Classicality in discrete Wigner functions. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 012301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D. Hudson’s theorem for finite-dimensional quantum systems. J. Math. Phys. A 2006, 47, 122107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, V.C.; Ferrie, C.; Gross, D.; Emerson, J. Negative quasi-probability as a resource for quantum computation. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raussendorf, R.; Browne, D.E.; Delfosse, N.; Okay, C.; Bermejo-Vega, J. Contextuality and Wigner-function negativity in qubit quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Du, H.; Shelby, J.H.; Pusey, M.F. Uniqueness of Noncontextual Models for Stabilizer Subtheories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 120403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raussendorf, R.; Okay, C.; Zurel, M.; Feldmann, P. The role of cohomology in quantum computation with magic states. Quantum 2023, 7, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniga, M.; Planat, M.; Rosu, H. Mutually unbiased bases and finite projective planes. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 2004, 6, L19–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovic, I.D. Geometrical description of quantal state determination. J. Phys. A 1984, 14, 3241–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootters, W.K.; Fields, B.D. Optimal State-Determination by Mutually Unbiased Measurements. Ann. Phys. 1989, 191, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klappenecker, A.; Rötteler, M. Constructions of mutually unbiased bases. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science Vol. 2948: Finite Fields and Applications, Procceedings of 7th International Conference, Fq7, Toulouse, France, 5–9 May 2003; Mullen, G., Poli, A., Stichtenoth, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Boykin, P.O.; Roychowdhury, V.; Vatan, F. A new proof for the existence of mutually unbiased bases. Algorithmica 2002, 34, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimov, A.B.; Romero, J.L.; Björk, G.; Sánchez-Soto, L.L. Discrete phase-space structure of n-qubit mutually unbiased bases. Ann. Phys. 2009, 324, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimov, A.B.; Romero, J.L.; Björk, G.; Sánchez-Soto, L.L. Geometrical approach to mutually unbiased bases. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2007, 40, 9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, A.O.; Rubin, M.H. Wigner functions and separability for finite systems. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2005, 38, 6005–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfosse, N.; Guerin, P.A.; Bian, J.; Raussendorf, R. Wigner Function Negativity and Contextuality in Quantum Computation on Rebits. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.; Wallman, J.; Vietch, V.; Emerson, J. Contextuality supplies the ‘magic’ for quantum computation. Nature 2014, 510, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfosse, N.; Okay, C.; Bermejo-Vega, J.; Browne, D.E.; Raussendorf, R. Equivalence between contextuality and negativity of the Wigner function for qudits. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 123024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.; Klimov, A.B.; Sanchez-Soto, L.L. Discrete phase-space structures and Wigner functions for N qubits. Quantum Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidl, R.; Niederreiter, H. Introduction to Finite Fields and Their Applications, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; ISBN 978-052-146-094-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schwinger, J. Unitary Operator Bases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1960, 46, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwinger, J. Unitary Transformations and the Action Principle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1960, 46, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Brukner, Č.; Zeilinger, A. Mutually unbiased binary observable sets on N qubits. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 65, 032320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.L.; Björk, G.; Klimov, A.B.; Sánchez-Soto, L.L. Structure of the sets of mutually unbiased bases for N qubits. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 062310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durt, T. About Weyl and Wigner tomography in finite-dimensional Hilbert spaces. Open Sys. Inf. Dyn. 2006, 13, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourdas, A. Quantum systems with finite Hilbert space. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2004, 67, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourdas, A. Factorization in finite quantum systems. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2003, 36, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, J.P.; Roncaglia, A.J.; Saraceno, M. Qubits in phase space: Wigner-function approach to quantum-error correction and the mean-king problem. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 012309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjork, G.; Klimov, A.B.; Sanchez-Soto, L.L. The discrete Wigner function. In Progress in Optics, 1st ed.; Wolf, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 51, pp. 469–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimov, A.B.; Muñoz, C.; Romero, J.L. Geometrical approach to the discrete Wigner function in prime power dimensions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2006, 39, 14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sainz, I.; Camacho, E.; García, A.; Klimov, A.B. Tomographic Universality of the Discrete Wigner Function. Quantum Rep. 2024, 6, 58-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010005
Sainz I, Camacho E, García A, Klimov AB. Tomographic Universality of the Discrete Wigner Function. Quantum Reports. 2024; 6(1):58-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSainz, Isabel, Ernesto Camacho, Andrés García, and Andrei B. Klimov. 2024. "Tomographic Universality of the Discrete Wigner Function" Quantum Reports 6, no. 1: 58-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010005
APA StyleSainz, I., Camacho, E., García, A., & Klimov, A. B. (2024). Tomographic Universality of the Discrete Wigner Function. Quantum Reports, 6(1), 58-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010005






