The Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithms on Near-Term Devices: A Practical Guide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
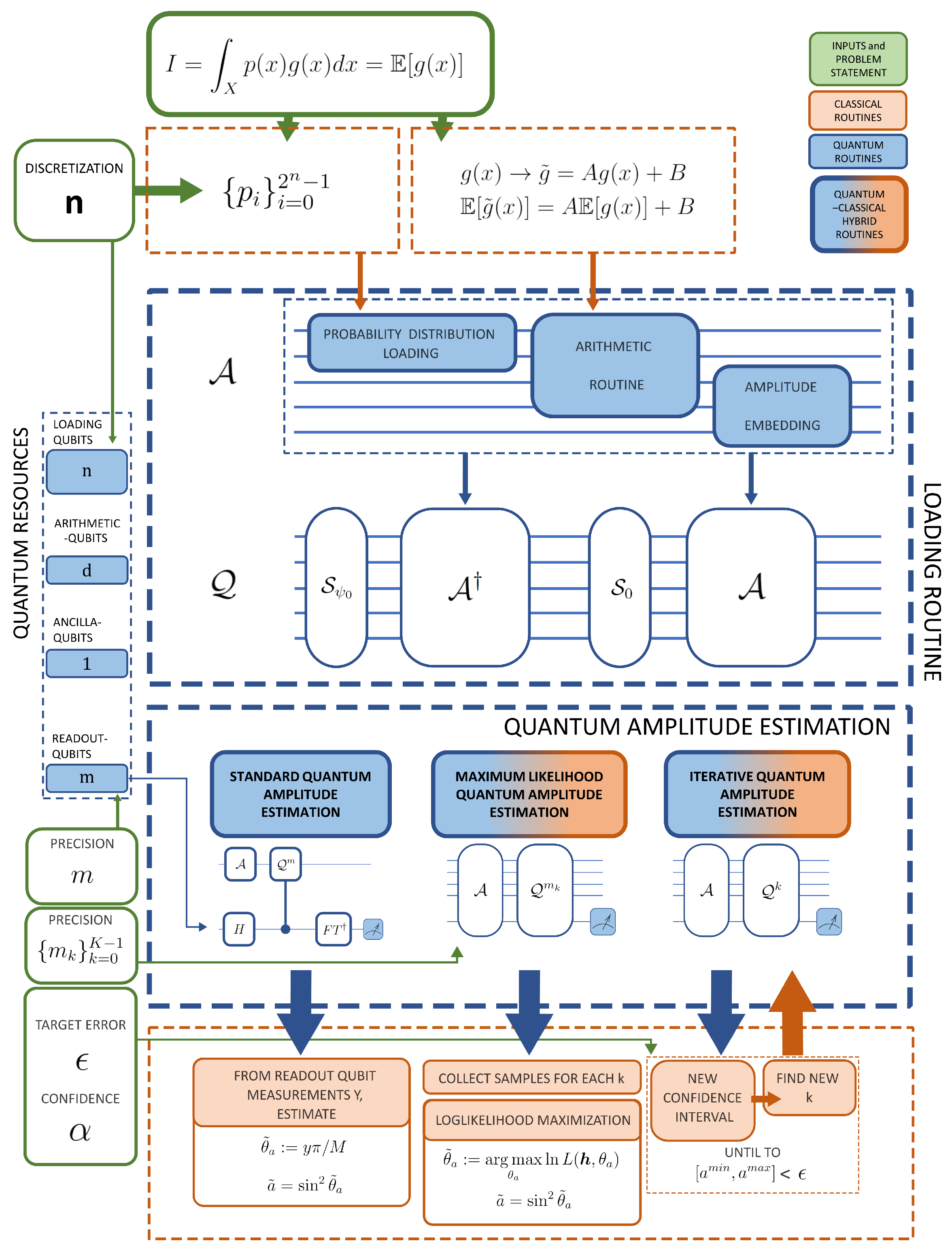
2. Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithms
2.1. Original Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithm
2.2. Alternative Quantum Amplitude Estimation Methods
2.2.1. MLAE Approach
2.2.2. Iterative Approach
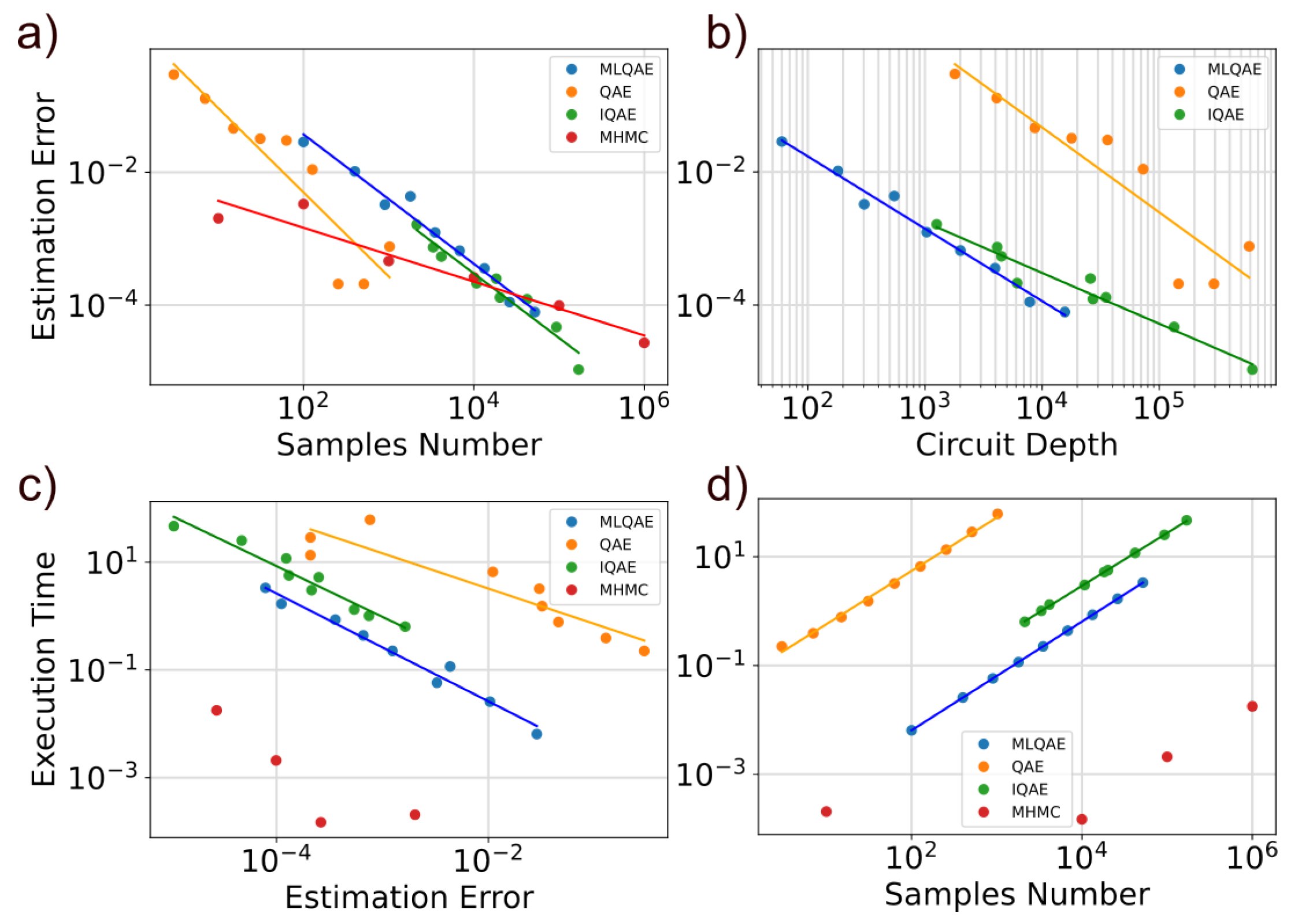
3. Comparison of the Algorithms by Statistical Analysis
Benchmarking the Methods of Quantum Amplitude Estimation
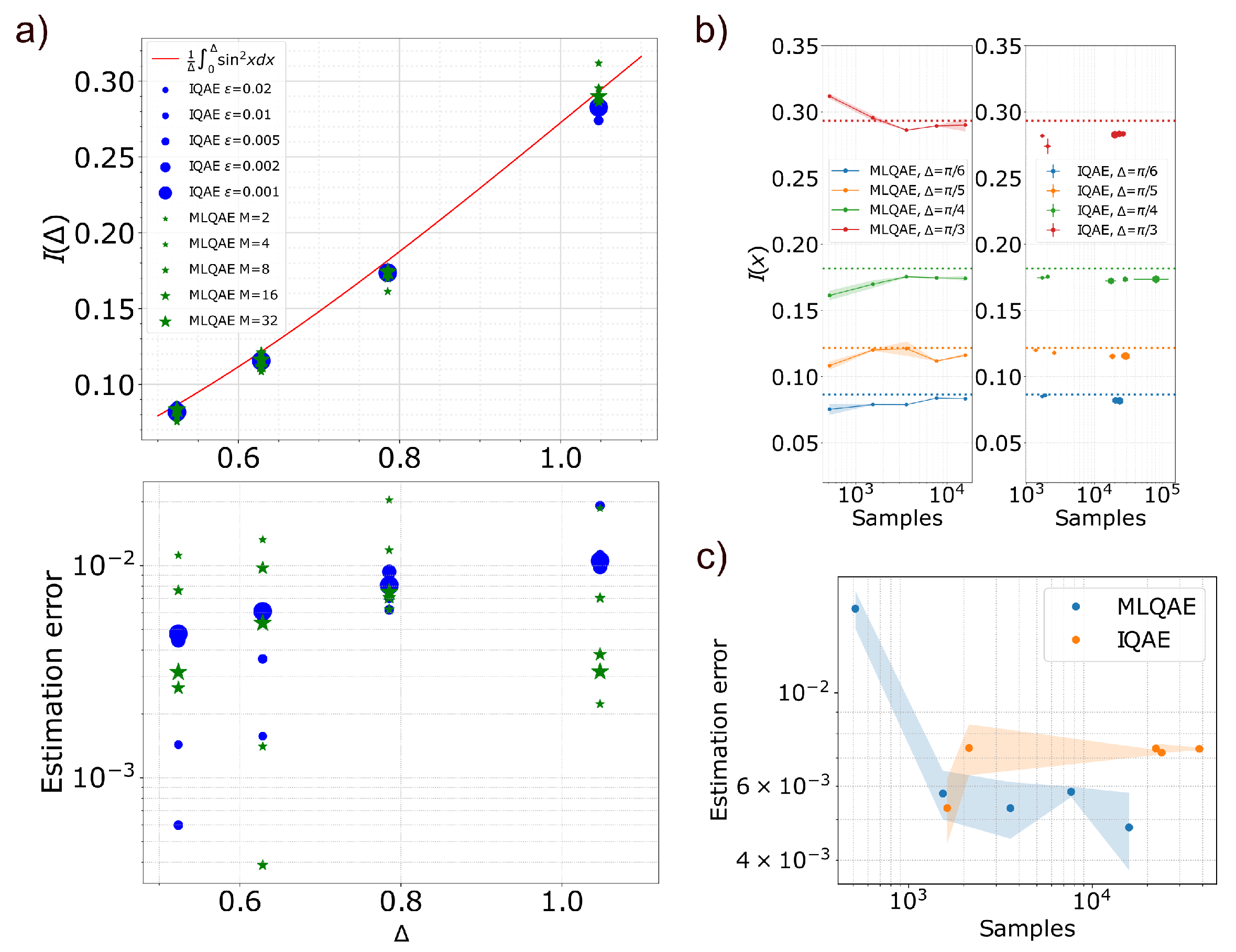
4. Experimental Test on a Trapped-Ion Quantum Computer
4.1. Trapped-Ion Quantum Computer Used for the Experimental Test
4.2. Assessing the Performances on a Trapped-Ion Device
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fishman, G. Monte Carlo: Concepts, Algorithms, and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Glasserman, P. Monte Carlo Methods in Financial Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, M.; Kaur, K.; Usman, M.; Buyya, R. Quantum computing: A taxonomy, systematic review and future directions. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2022, 52, 66–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriet, L.; Beguin, L.; Signoles, A.; Lahaye, T.; Browaeys, A.; Reymond, G.O.; Jurczak, C. Quantum computing with neutral atoms. Quantum 2020, 4, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Wu, D.; Fan, D.; Zhu, X. Superconducting quantum computing: A review. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 180501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzewicz, C.D.; Chiaverini, J.; McConnell, R.; Sage, J.M. Trapped-ion quantum computing: Progress and challenges. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 021314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzalini, A. Topological photonics for optical communications and quantum computing. Quantum Rep. 2019, 2, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, E.; Prati, E. Is all-electrical silicon quantum computing feasible in the long term? Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Michielis, M.; Ferraro, E.; Prati, E.; Hutin, L.; Bertrand, B.; Charbon, E.; Ibberson, D.J.; Gonzalez-Zalba, F. Silicon spin qubits from laboratory to industry. J. Phys. D 2023, 56, 363001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, G.; Hoyer, P.; Mosca, M.; Tapp, A. Quantum amplitude amplification and estimation. Contemp. Math. 2002, 305, 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Rebentrost, P.; Gupt, B.; Bromley, T.R. Quantum computational finance: Monte Carlo pricing of financial derivatives. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 022321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, A. Quantum speed-up of Monte Carlo methods. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150301. [Google Scholar]
- Agliardi, G.; Grossi, M.; Pellen, M.; Prati, E. Quantum integration of elementary particle processes. Phys. Lett. B 2022, 832, 137228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, J.; Zhang, S. Quantum machine learning. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maronese, M.; Destri, C.; Prati, E. Quantum activation functions for quantum neural networks. Quantum Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, M.; Galli, D.E.; Prati, E. Multi-class quantum classifiers with tensor network circuits for quantum phase recognition. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 434, 128056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, R.; Destri, C.; Prati, E. Optimization of the memory reset rate of a quantum echo-state network for time sequential tasks. Phys. Lett. A 2023, 465, 128713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agliardi, G.; Prati, E. Optimal tuning of quantum generative adversarial networks for multivariate distribution loading. Quantum Rep. 2022, 4, 75–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatopoulos, N.; Egger, D.J.; Sun, Y.; Zoufal, C.; Iten, R.; Shen, N.; Woerner, S. Option pricing using quantum computers. Quantum 2020, 4, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Krishnakumar, R.; Mazzola, G.; Stamatopoulos, N.; Woerner, S.; Zeng, W.J. A threshold for quantum advantage in derivative pricing. Quantum 2021, 5, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, F.; Vuppala, R.K.; Kara, K.; Gaitan, F. Solving Burgers’ equation with quantum computing. Quantum Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskill, J. Fault-tolerant quantum computation. In Introduction to Quantum Computation and Information; World Scientific: Singapore, 1998; pp. 213–269. [Google Scholar]
- Prati, E.; Rotta, D.; Sebastiano, F.; Charbon, E. From the Quantum Moore’s Law toward Silicon Based Universal Quantum Computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Rebooting Computing (ICRC), Washington, DC, USA, 8–9 November 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, I.; Levine, H.; Keesling, A.; Bluvstein, D.; Wang, S.T.; Lukin, M.D. Hardware-efficient, fault-tolerant quantum computation with rydberg atoms. Phys. Rev. X 2022, 12, 021049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberland, C.; Noh, K.; Arrangoiz-Arriola, P.; Campbell, E.T.; Hann, C.T.; Iverson, J.; Putterman, H.; Bohdanowicz, T.C.; Flammia, S.T.; Keller, A.; et al. Building a fault-tolerant quantum computer using concatenated cat codes. PRX Quantum 2022, 3, 010329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Jang, K.; Seo, H. Improved Low-Depth SHA3 Quantum Circuit for Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computers. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejpasand, M.T.; Sasani Ghamsari, M. Research Trends in Quantum Computers by Focusing on Qubits as Their Building Blocks. Quantum Rep. 2023, 5, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Liu, C.; Lv, X.; Pei, C. Implementation of Fault-Tolerant Encoding Circuit Based on Stabilizer Implementation and “Flag” Bits in Steane Code. Entropy 2022, 24, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskill, J. Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerner, S.; Egger, D.J. Quantum risk analysis. npj Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maronese, M.; Moro, L.; Rocutto, L.; Prati, E. Quantum compiling. In Quantum Computing Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 39–74. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.; Uno, S.; Raymond, R.; Tanaka, T.; Onodera, T.; Yamamoto, N. Amplitude estimation without phase estimation. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinko, D.; Gacon, J.; Zoufal, C.; Woerner, S. Iterative quantum amplitude estimation. npj Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Beck, K.M.; Debnath, S.; Amini, J.; Nam, Y.; Grzesiak, N.; Chen, J.S.; Pisenti, N.; Chmielewski, M.; Collins, C.; et al. Benchmarking an 11-qubit quantum computer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; Chen, J.S.; Pisenti, N.C.; Wright, K.; Delaney, C.; Maslov, D.; Brown, K.R.; Allen, S.; Amini, J.M.; Apisdorf, J.; et al. Ground-state energy estimation of the water molecule on a trapped-ion quantum computer. npj Quantum Inf. 2020, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanov, K.; Rosenkranz, M.; Fiorentini, M.; Lubasch, M. Variational quantum amplitude estimation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.03687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgica-Tiron, T.; Kerenidis, I.; Labib, F.; Prakash, A.; Zeng, W. Low depth algorithms for quantum amplitude estimation. Quantum 2022, 6, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaronson, S.; Rall, P. Quantum approximate counting, simplified. In Symposium on Simplicity in Algorithms; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, R.J. Mathematical Statistics: An Introduction to Likelihood Based Inference; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaji, K. Faster amplitude estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.02417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certo, S.; Pham, A.D.; Beaulieu, D. Benchmarking Amplitude Estimation on a Superconducting Quantum Computer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.06987. [Google Scholar]
- Amazon. Technical Report; Amazon Braket; Amazon Web Service: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
| QAE Methods List | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | NISQ Readiness | Qubits | Depth | vs. | Speed-Up over MC | Ref. | Type |
| QAE | Low | ** | [10] | O | |||
| QAE NO-PE * | Medium | – | [32,41] | I | |||
| VarQAE * | High | – | [36] | I | |||
| Power-law QAE * | High | – | – | [37] | I | ||
| IQAE | Medium | Equation (12) | [33] | II | |||
| SQAE | Medium | – | – | – | [38] | II | |
| FAE | Medium | – | [40] | II | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maronese, M.; Incudini, M.; Asproni, L.; Prati, E. The Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithms on Near-Term Devices: A Practical Guide. Quantum Rep. 2024, 6, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010001
Maronese M, Incudini M, Asproni L, Prati E. The Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithms on Near-Term Devices: A Practical Guide. Quantum Reports. 2024; 6(1):1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaronese, Marco, Massimiliano Incudini, Luca Asproni, and Enrico Prati. 2024. "The Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithms on Near-Term Devices: A Practical Guide" Quantum Reports 6, no. 1: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010001
APA StyleMaronese, M., Incudini, M., Asproni, L., & Prati, E. (2024). The Quantum Amplitude Estimation Algorithms on Near-Term Devices: A Practical Guide. Quantum Reports, 6(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum6010001







