Optimal Tuning of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Multivariate Distribution Loading
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Encoding and Loading Classical Information in Quantum Registers: Overcoming the Challenges of the NISQ Era
2.1. Techniques for Exact Data Loading and Their Limitations
2.2. Approximate Data Loading with qGANs
3. From GANs to qGANs
3.1. The Generative Interpretation of qGANs
3.2. The Data-Compression Interpretation of qGANs
4. Results
4.1. Design of the Generative Quantum Circuit Network
4.2. Design of the Classical Discriminative Deep Neural Network
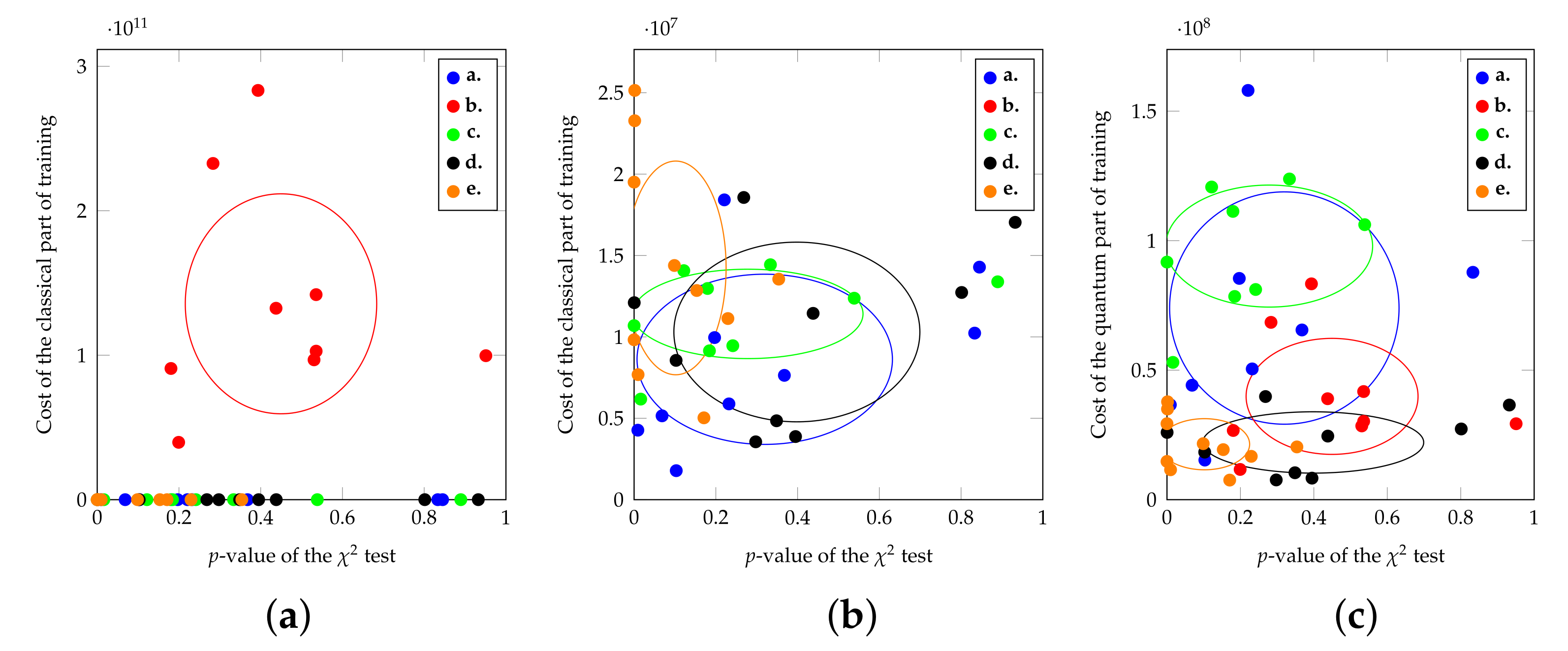
4.3. Optimization of the qGAN Accuracy and Comparison with Benchmarks
4.4. Trade-Off between Accuracy and Training Time: The Effect of the Optimizer and of Other Hyper-Parameters
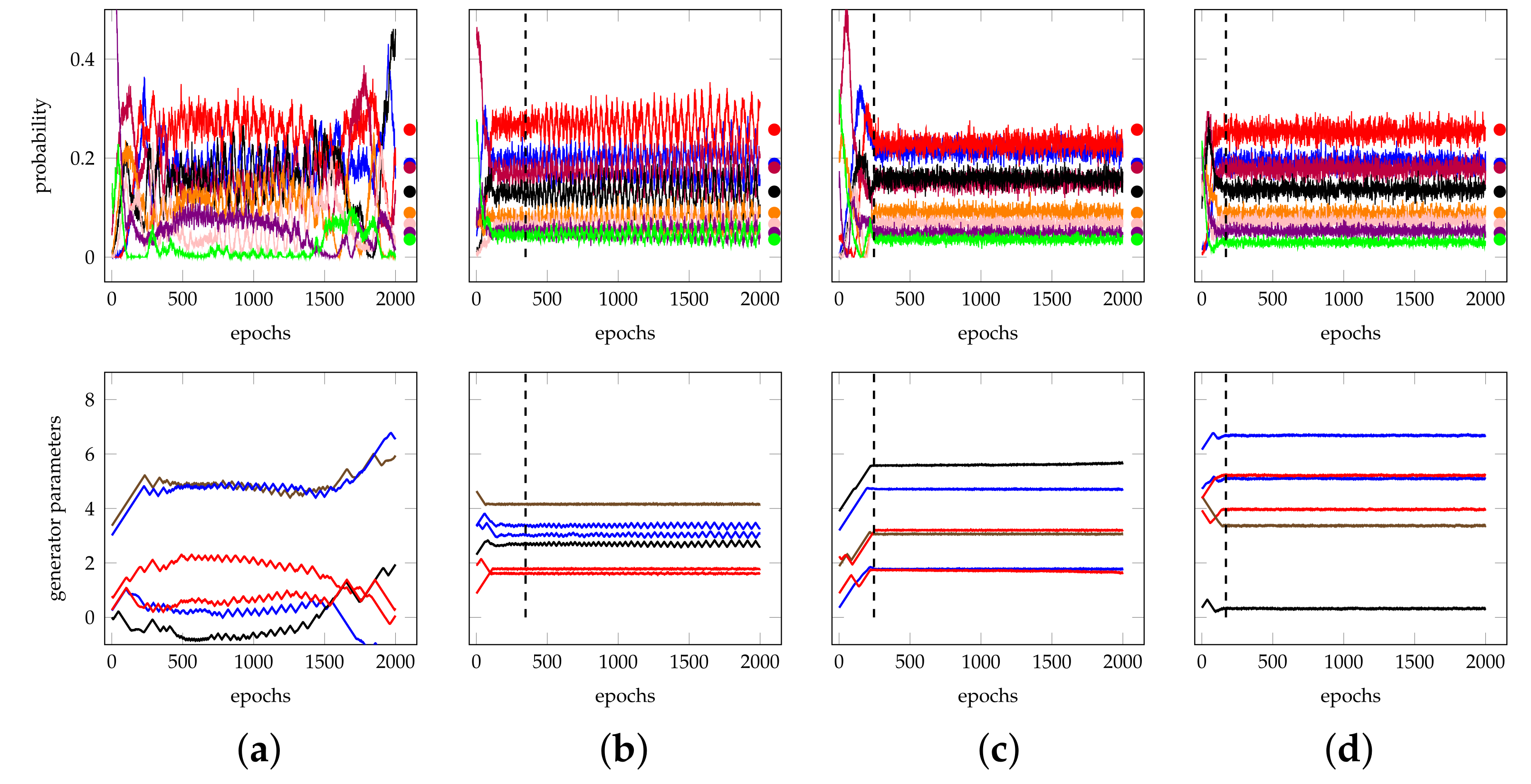
4.5. Isolation of the Best Runs
5. Methods
5.1. Testing Conditions
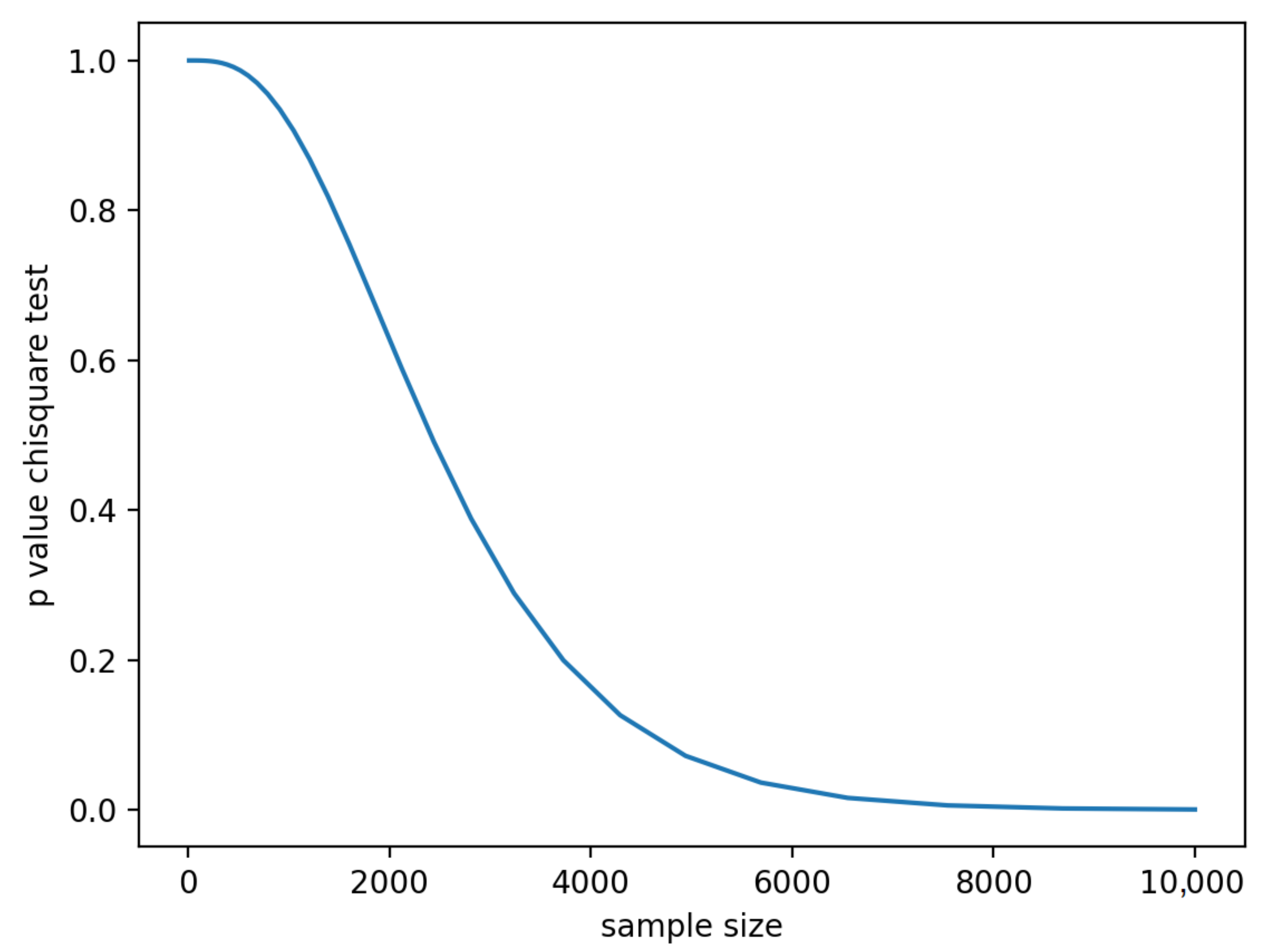
5.2. Run Evaluation
5.3. Objective Function and Optimizers
5.4. Estimating Complexity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Tuning a qGAN
Appendix A.1. Summary of Choices and Tunable Degrees of Freedom
Appendix A.2. The Testing Campaign
| Test Set | n | k | Generator Optimizer | Discriminator Optimizer | Max Epochs | Shots | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3 | 1 | 8 | 16 | Adam, lr = *, = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = *, = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | 2000 |
| B | 3 | 1 | * | * | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | 2000 |
| C | 3 | 1 | * | * | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | 2000 |
| D | 3 | 1 | * | * | Adam, lr = , = 0.9, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.9, = 0.99 | 2000 | 2000 |
| E | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | * |
| F | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | SPSA, lr = *, perturb = * | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 10000 | 2000 |
| G | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | SPSA, lr = , perturb = | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 10,000 | * |
| H | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | SPSA, lr = *, perturb = * | 10,000 | 2000 |
| I | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | SPSA, lr = , perturb = | 10,000 | * |
| J | 4 | 1 | * | * | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | 2000 |
| K | 4 | 1 | 32 | 16 | Adam, lr = *, = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = *, = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | 2000 |
| L | 4 | 1 | 32 | 16 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 | * |
| Case | Originating Test Set |
|---|---|
| a. Baseline | B with |
| b. Big discriminator size | B with |
| c. Low generator learning rate | C with |
| d. Many shots | E with shots = 8000 |
| e. SPSA in generator | F with lr = and ratio = |
| Run | Originating Test Set |
|---|---|
| (a) Divergent | B with |
| (b) Oscillatory | B with |
| (c) Poor solution quality | B with |
| (d) Good solution quality | B with |

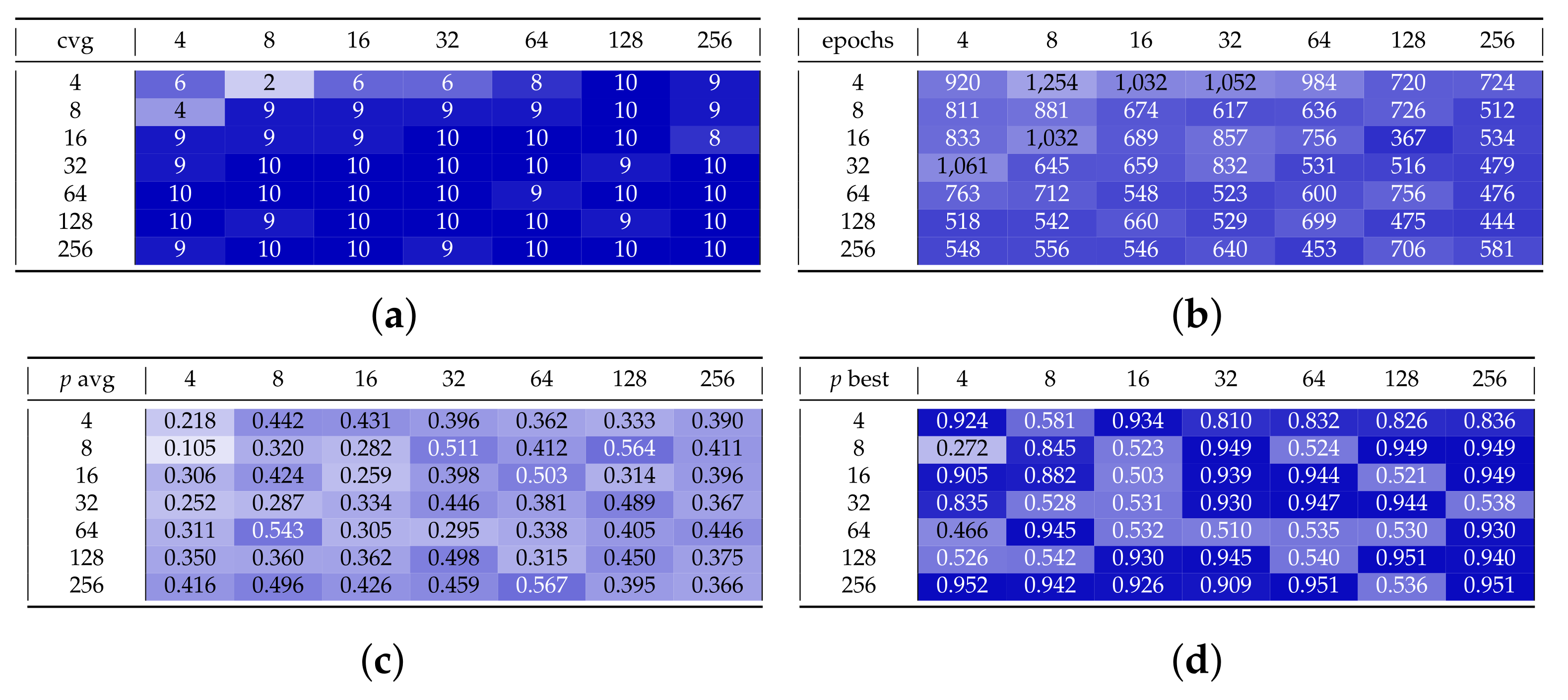

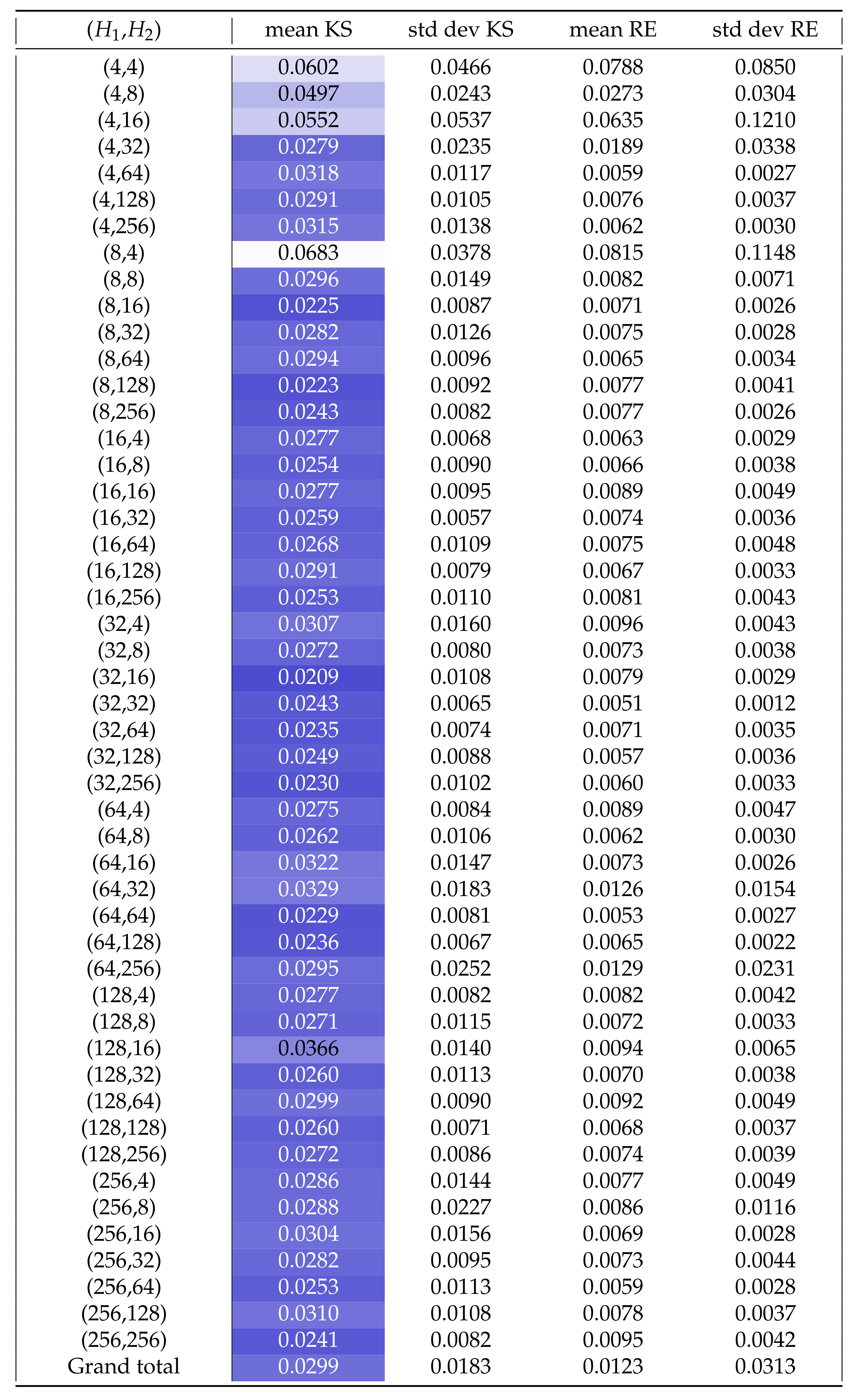
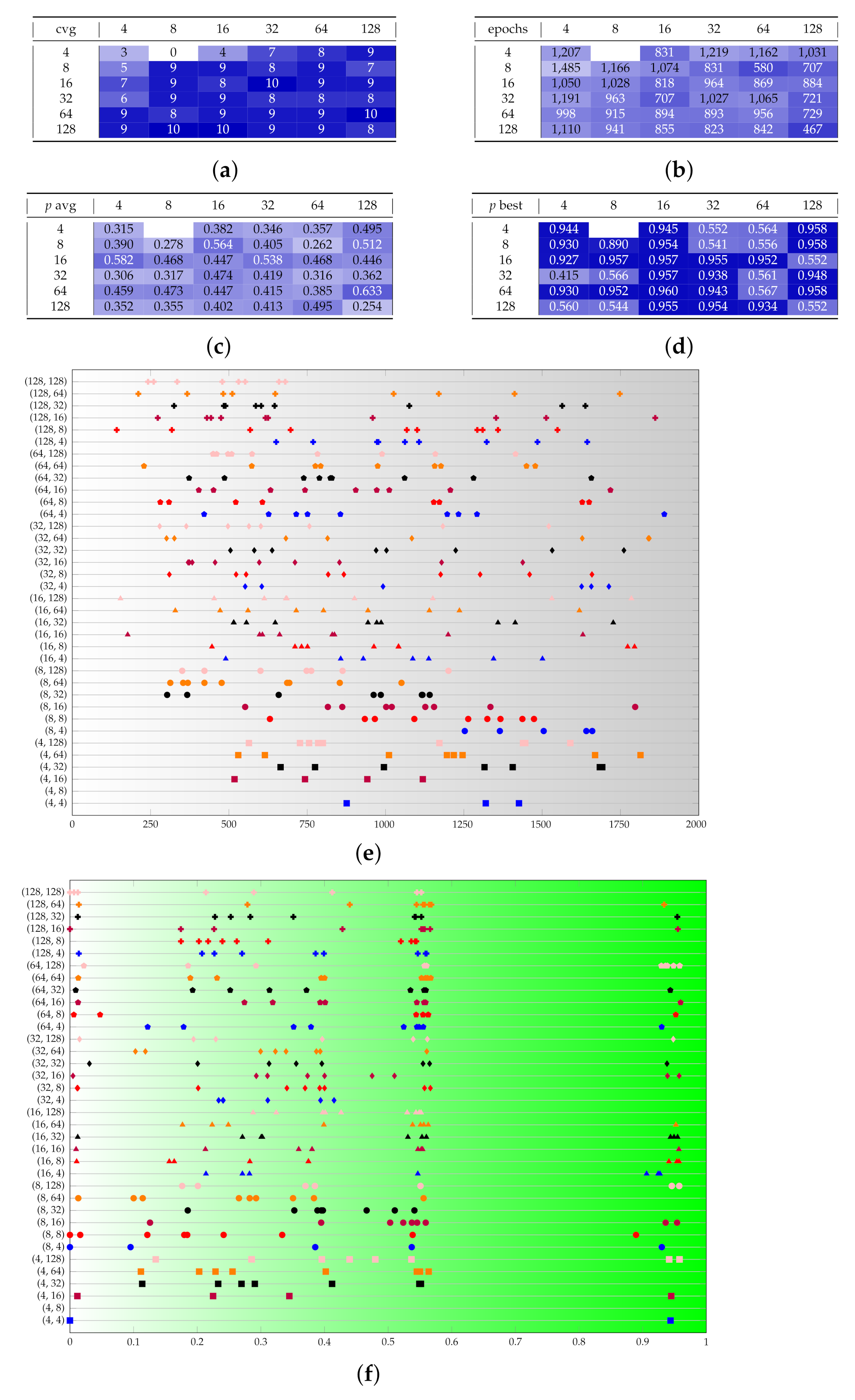
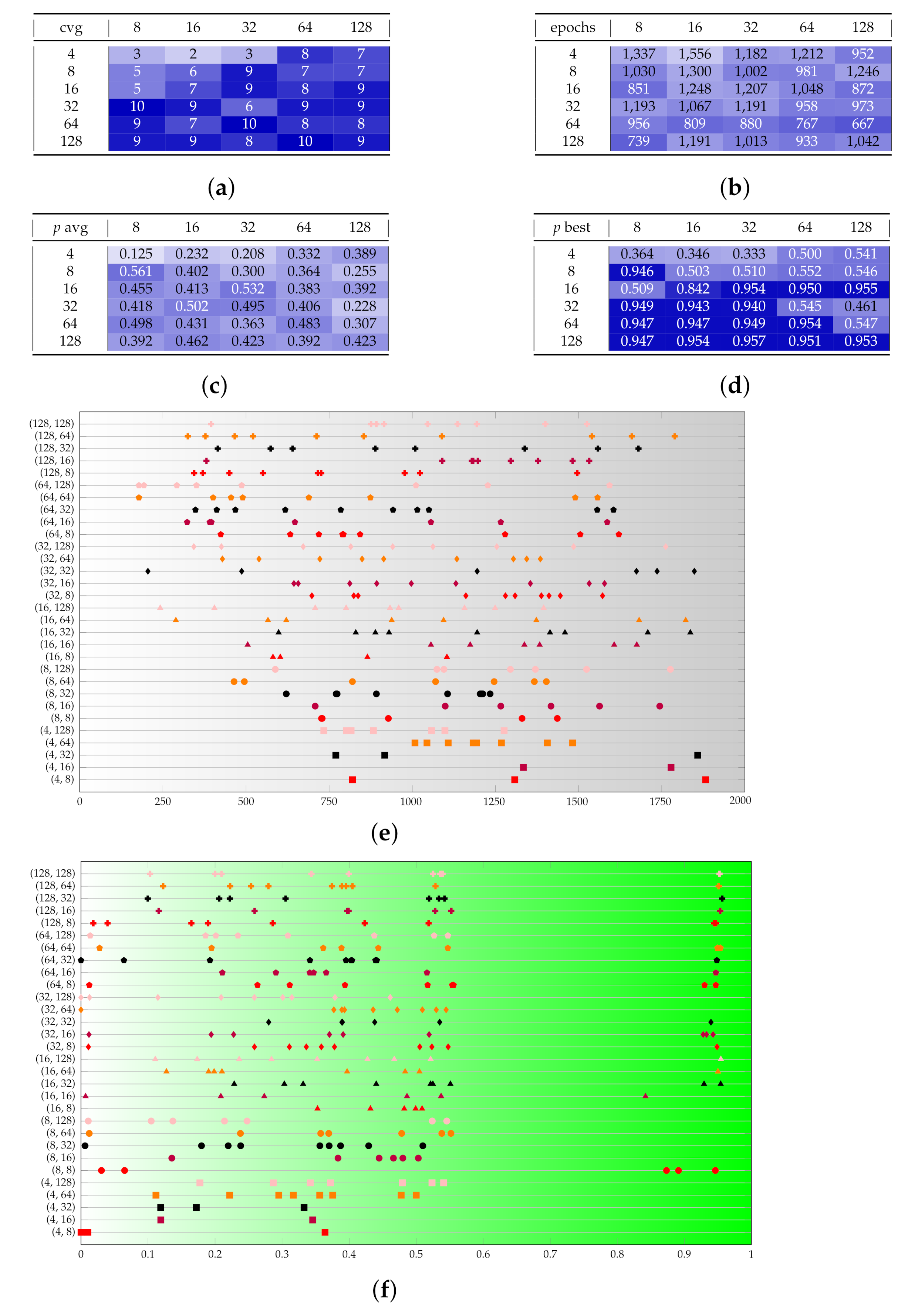
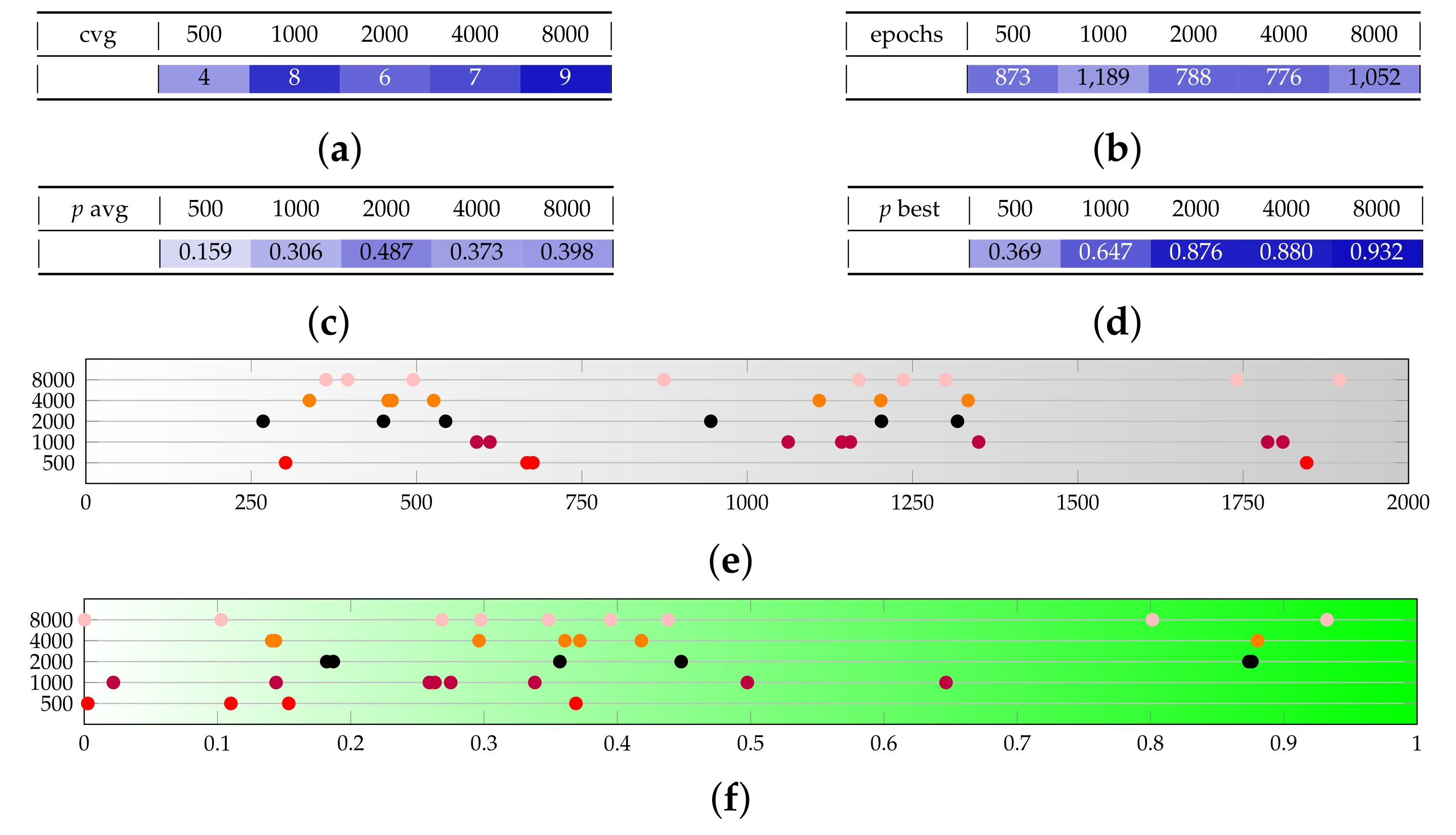
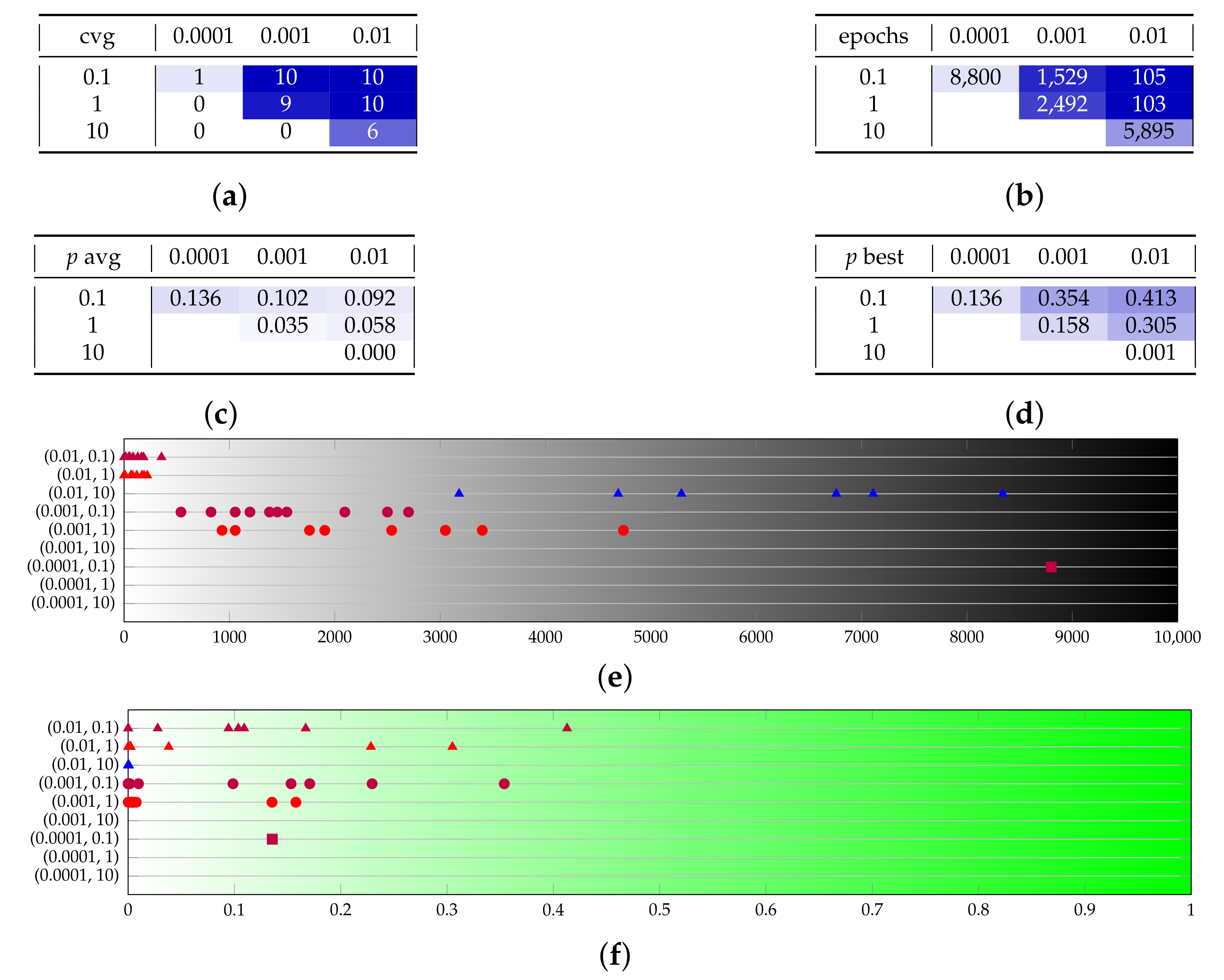

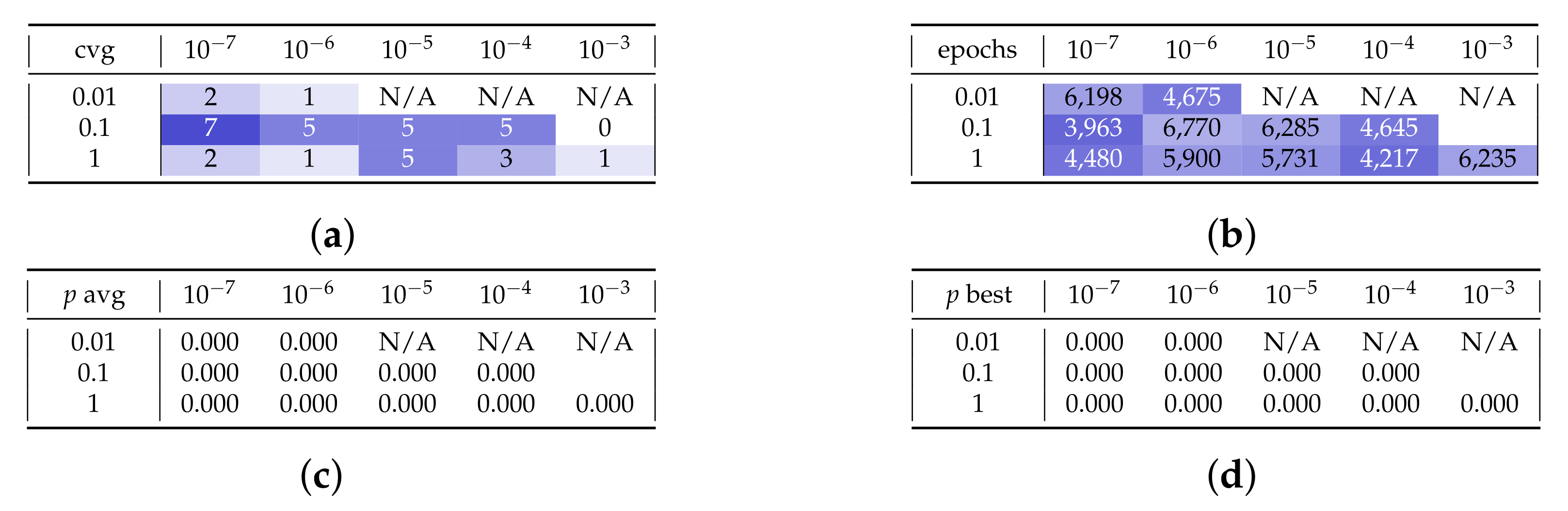

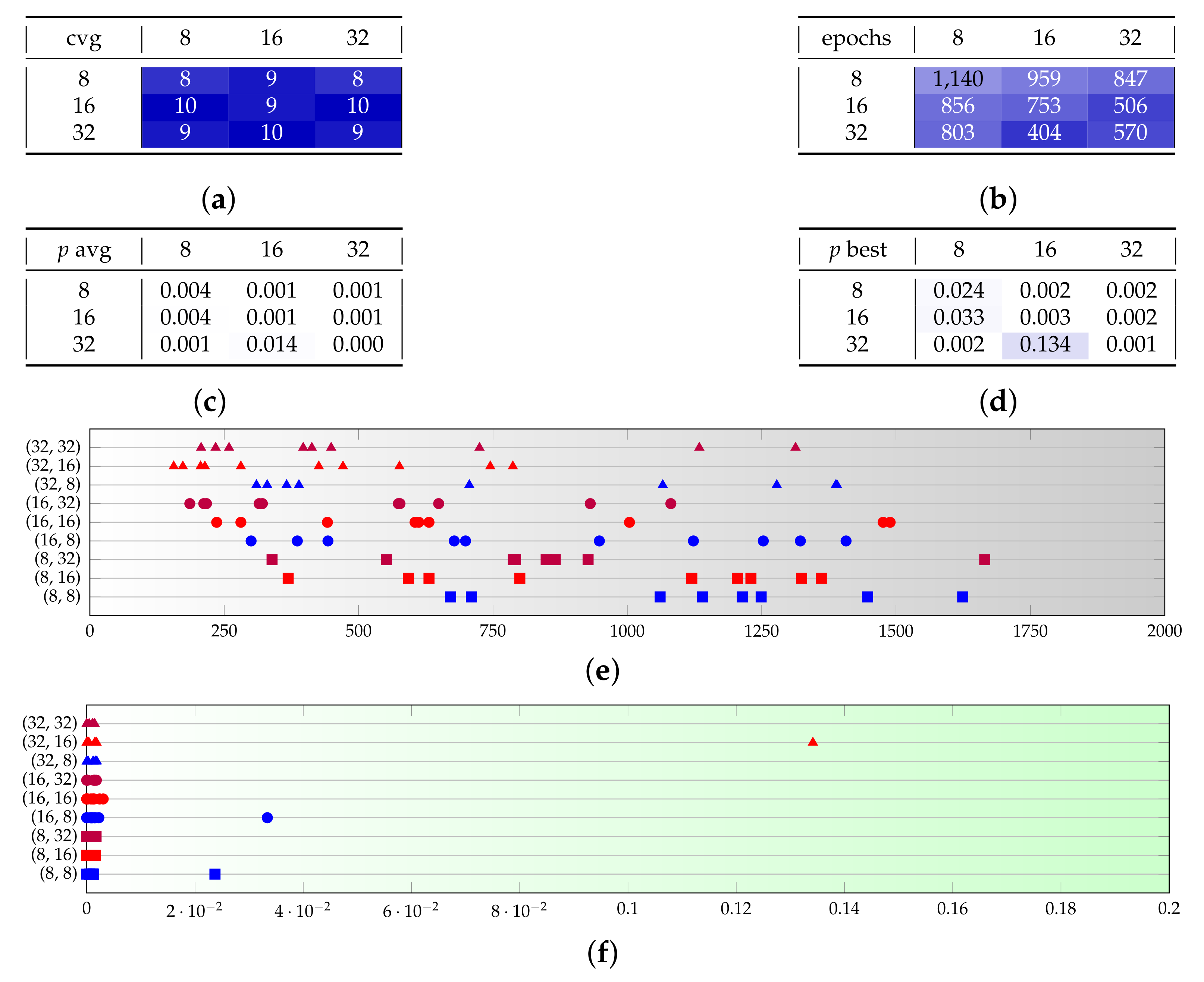
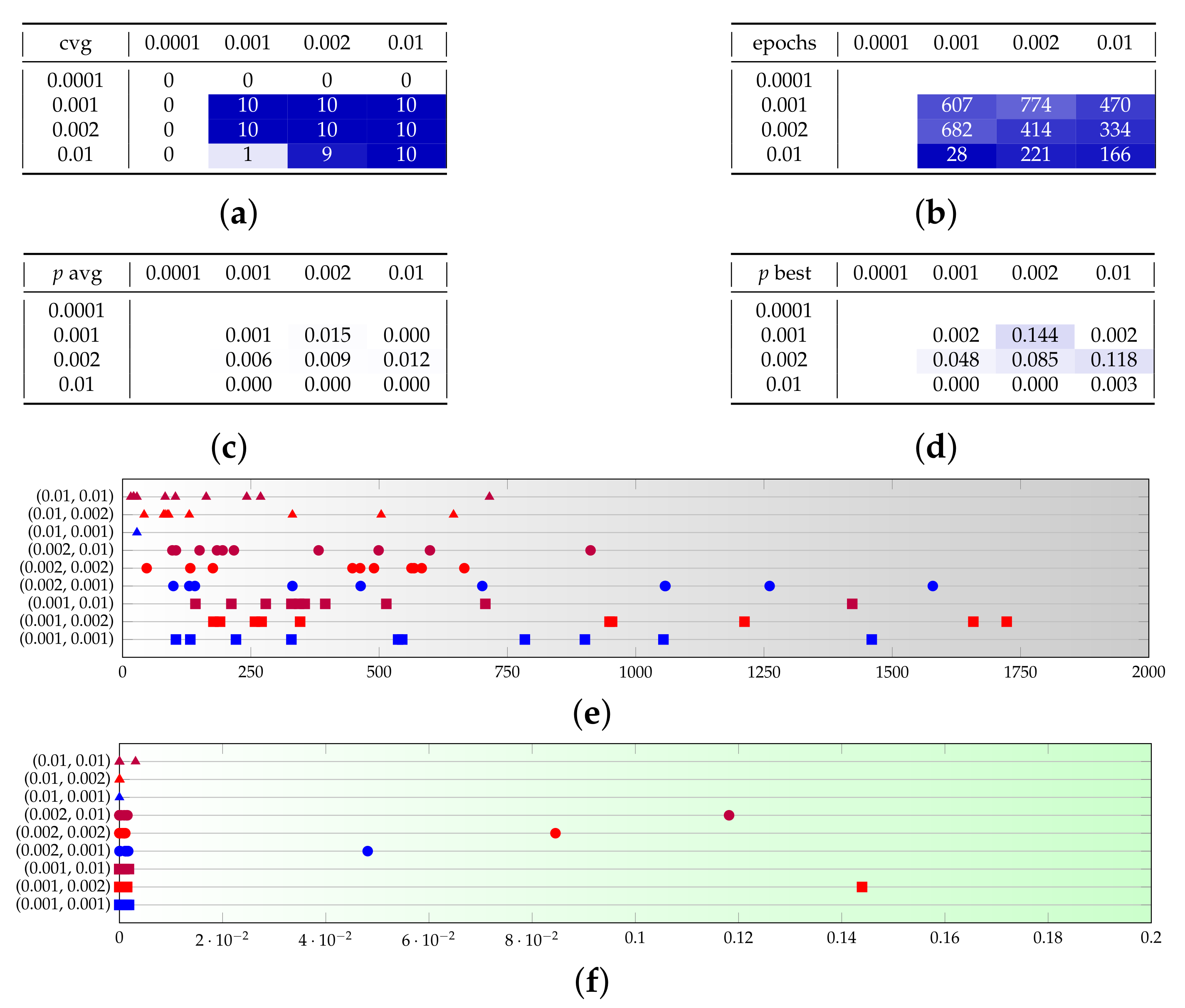
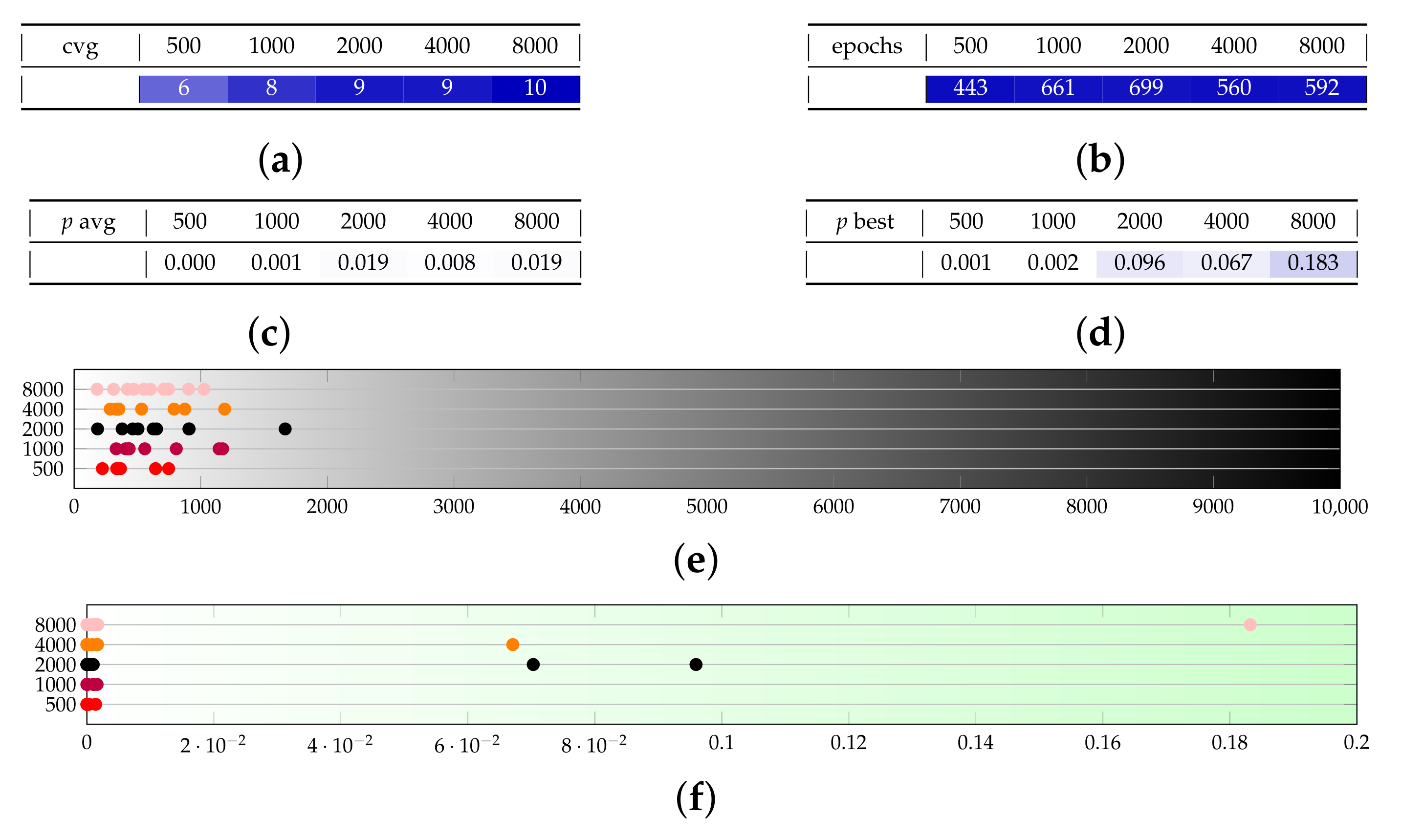
Appendix B. Additional Remarks on the Isolation of the Best Run

References
- Grover, L.K. Synthesis of Quantum Superpositions by Quantum Computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, L.; Rudolph, T. Creating superpositions that correspond to efficiently integrable probability distributions. arXiv 2002, arXiv:quant-ph/0208112. [Google Scholar]
- Mitarai, K.; Kitagawa, M.; Fujii, K. Quantum Analog-Digital Conversion. Phys. Rev. 2019, 99, 012301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, Y.R.; Low, G.H.; Scherer, A.; Berry, D.W. Black-box quantum state preparation without arithmetic. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 020502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aaronson, S. Read the fine print. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, V.; Lloyd, S.; Maccone, L. Architectures for a quantum random access memory. Phys. Rev. 2008, 78, 052310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, P.Q.; Dong, F.; Hirota, K. A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression, and processing operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 2011, 10, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoufal, C.; Lucchi, A.; Woerner, S. Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Learning and Loading Random Distributions. Npj Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakaji, K.; Uno, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Raymond, R.; Onodera, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tezuka, H.; Mitsuda, N.; Yamamoto, N. Approximate amplitude encoding in shallow parameterized quantum circuits and its application to financial market indicator. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.13211. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, M.Y.; Zlokapa, A.; Broughton, M.; Boixo, S.; Mohseni, M.; Smelyanskyi, V.; Neven, H. Entangling Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.00080. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Sun, Z.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Ye, J. A Review on Generative Adversarial Networks: Algorithms, Theory, and Applications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.06937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatopoulos, N.; Egger, D.J.; Sun, Y.; Zoufal, C.; Iten, R.; Shen, N.; Woerner, S. Option Pricing using Quantum Computers. Quantum 2020, 4, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agliardi, G.; Grossi, M.; Pellen, M.; Prati, E. Quantum integration of elementary particle processes. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.01547. [Google Scholar]
- Havlíček, V.; Córcoles, A.D.; Temme, K.; Harrow, A.W.; Kandala, A.; Chow, J.M.; Gambetta, J.M. Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 2019, 567, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrontegui, E.; García-Ripoll, J.J. Unitary quantum perceptron as efficient universal approximator. Epl. Europhys. Lett. 2019, 125, 30004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maronese, M.; Prati, E. A continuous rosenblatt quantum perceptron. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 2021, 98, 2140002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maronese, M.; Destri, C.; Prati, E. Quantum activation functions for quantum neural networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.03700. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, K.H.; Dahlsten, O.; Kristjánsson, H.; Gardner, R.; Kim, M.S. Quantum generalisation of feedforward neural networks. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2017, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, C. A quantum model of feed-forward neural networks with unitary learning algorithms. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Nakajima, K. Quantum Reservoir Computing: A Reservoir Approach Toward Quantum Machine Learning on Near-Term Quantum Devices. In Reservoir Computing; Nakajima, K., Fischer, I., Eds.; Natural Computing Series; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 423–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, M.; Galli, D.E.; Prati, E. Multi-class quantum classifiers with tensor network circuits for quantum phase recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.08386. [Google Scholar]
- Rocutto, L.; Destri, C.; Prati, E. Quantum Semantic Learning by Reverse Annealing of an Adiabatic Quantum Computer. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2021, 4, 2000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocutto, L.; Prati, E. A complete restricted Boltzmann machine on an adiabatic quantum computer. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 2021, 19, 2141003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaire-Demers, P.L.; Killoran, N. Quantum generative adversarial networks. Phys. Rev. 2018, 98, 012324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.L.; Du, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Liang, F.; Lin, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Experimental Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Image Generation. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 16, 024051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.A.; Baheri, B.; Chen, D.; Mao, Y.; Guan, Q.; Li, A.; Fang, B.; Xu, S. QuGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network Through Quantum States. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.09036. [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro, A. Quantum speedup of Monte Carlo methods. Proceedings. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.; Uno, S.; Raymond, R.; Tanaka, T.; Onodera, T.; Yamamoto, N. Amplitude estimation without phase estimation. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grinko, D.; Gacon, J.; Zoufal, C.; Woerner, S. Iterative Quantum Amplitude Estimation. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, D.J.; Gutiérrez, R.G.; Mestre, J.C.; Woerner, S. Credit risk analysis using quantum computers. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2021, 70, 2136–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, A.W.; Hassidim, A.; Lloyd, S. Quantum Algorithm for Linear Systems of Equations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 150502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebentrost, P.; Gupt, B.; Bromley, T.R. Quantum computational finance: Monte Carlo pricing of financial derivatives. Phys. Rev. 2018, 98, 022321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Salinas, A.; Cervera-Lierta, A.; Gil-Fuster, E.; Latorre, J.I. Data re-uploading for a universal quantum classifier. Quantum 2020, 4, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preskill, J. Quantum Computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boixo, S.; Isakov, S.V.; Smelyanskiy, V.N.; Babbush, R.; Ding, N.; Jiang, Z.; Bremner, M.J.; Martinis, J.M.; Neven, H. Characterizing Quantum Supremacy in Near-Term Devices. Version: 3. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaronson, S.; Chen, L. Complexity-Theoretic Foundations of Quantum Supremacy Experiments. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.05903. [Google Scholar]
- Pednault, E.; Gunnels, J.A.; Nannicini, G.; Horesh, L.; Magerlein, T.; Solomonik, E.; Draeger, E.W.; Holland, E.T.; Wisnieff, R. Pareto-Efficient Quantum Circuit Simulation Using Tensor Contraction Deferral. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1710.05867. [Google Scholar]
- Peruzzo, A.; McClean, J.; Shadbolt, P.; Yung, M.H.; Zhou, X.Q.; Love, P.J.; Aspuru-Guzik, A.; O’Brien, J.L. A variational eigenvalue solver on a photonic quantum processor. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClean, J.R.; Romero, J.; Babbush, R.; Aspuru-Guzik, A. The theory of variational hybrid quantum-classical algorithms. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 023023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, J.A.; Braje, T.M. Loading Classical Data into a Quantum Computer. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01958. [Google Scholar]
- Shende, V.V.; Bullock, S.S.; Markov, I.L. Synthesis of Quantum Logic Circuits. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2006, 25, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerenidis, I.; Prakash, A. Quantum Recommendation Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08675. [Google Scholar]
- Hann, C.T.; Zou, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Schoelkopf, R.J.; Girvin, S.; Jiang, L. Hardware-Efficient Quantum Random Access Memory with Hybrid Quantum Acoustic Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 250501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, S.; Weedbrook, C. Quantum Generative Adversarial Learning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bharti, K.; Cervera-Lierta, A.; Kyaw, T.H.; Haug, T.; Alperin-Lea, S.; Anand, A.; Degroote, M.; Heimonen, H.; Kottmann, J.S.; Menke, T.; et al. Noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) algorithms. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.08448. [Google Scholar]
- Schuld, M.; Sinayskiy, I.; Petruccione, F. The quest for a Quantum Neural Network. Quantum Inf. Process. 2014, 13, 2567–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biamonte, J.; Wittek, P.; Pancotti, N.; Rebentrost, P.; Wiebe, N.; Lloyd, S. Quantum Machine Learning. Nature 2017, 549, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, B.; Henderson, M.; Le, J.C.J.; Kumar, N.; Paini, M.; Kashefi, E. Quantum versus Classical Generative Modelling in Finance. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo, M.; Arrasmith, A.; Babbush, R.; Benjamin, S.C.; Endo, S.; Fujii, K.; McClean, J.R.; Mitarai, K.; Yuan, X.; Cincio, L.; et al. Variational Quantum Algorithms. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.09265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, L. Information Perspective to Probabilistic Modeling: Boltzmann Machines versus Born Machines. Entropy 2018, 20, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, H.; Akhalwaya, I.Y.; Aleksandrowicz, G.; Alexander, T.; Alexandrowics, G.; Arbel, E.; Asfaw, A.; Azaustre, C.; AzizNgoueya, P.B.; Barron, G. Qiskit: An open-source framework for quantum computing. Zenodo 2019, 2562111. [Google Scholar]
- SciPy User Guide–SciPy v1.7.1 Manual. Available online: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/ (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Benedetti, M.; Lloyd, E.; Sack, S.; Fiorentini, M. Parameterized quantum circuits as machine learning models. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gacon, J.; Zoufal, C.; Carleo, G.; Woerner, S. Simultaneous Perturbation Stochastic Approximation of the Quantum Fisher Information. Quantum 2021, 5, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, J.R.; Boixo, S.; Smelyanskiy, V.N.; Babbush, R.; Neven, H. Barren plateaus in quantum neural network training landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerezo, M.; Sone, A.; Volkoff, T.; Cincio, L.; Coles, P.J. Cost function dependent barren plateaus in shallow parametrized quantum circuits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fontana, E.; Cerezo, M.; Sharma, K.; Sone, A.; Cincio, L.; Coles, P.J. Noise-Induced Barren Plateaus in Variational Quantum Algorithms. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2007.14384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Sutter, D.; Zoufal, C.; Lucchi, A.; Figalli, A.; Woerner, S. The power of quantum neural networks. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2021, 1, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrasmith, A.; Cerezo, M.; Czarnik, P.; Cincio, L.; Coles, P.J. Effect of barren plateaus on gradient-free optimization. Quantum 2021, 5, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- torch.optim—PyTorch 1.8.1 Documentation. Available online: https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html(accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Nagarajan, V.; Raffel, C.; Goodfellow, I.J. Theoretical Insights into Memorization in GANs; Neural Information Processing Systems Workshop: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
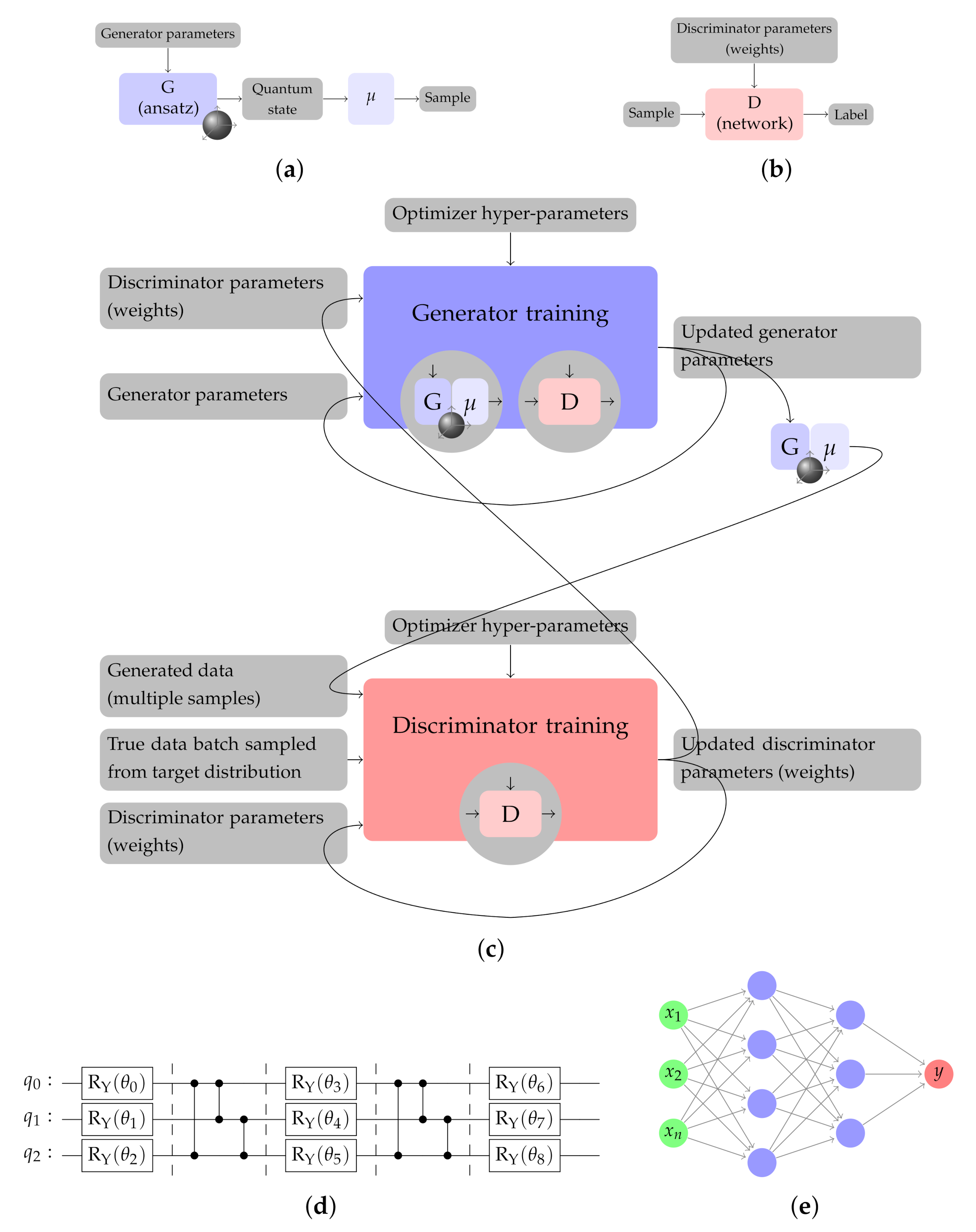
| Encoding | Form | Number of Qubits | Data Type of Each Item | Algorithms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-register | Any binary string of length m (including integer, fixed point, and floating point numbers). In literature, a common choice for numbers is fixed point. | Quantum arithmetic (adder, multiplier, max,…) | ||
| Digital | Any binary string of length m (including integer, fixed point, and floating point numbers). In literature, a common choice for numbers is fixed point. | Grover | ||
| Analog | n | Complex numbers satisfying the constraint . | Quantum Fourier Transform (QFT), HHL |
| Case | n | k | Generator | Discriminator | Shots | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a. Baseline | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 |
| b. Big discriminator size | 3 | 1 | 128 | 128 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 |
| c. Low generator learning rate | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 |
| d. Many shots | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 8000 |
| e. SPSA in generator | 3 | 1 | 8 | 8 | SPSA, lr = , perturbation = | Adam, lr = , = 0.7, = 0.99 | 2000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agliardi, G.; Prati, E. Optimal Tuning of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Multivariate Distribution Loading. Quantum Rep. 2022, 4, 75-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum4010006
Agliardi G, Prati E. Optimal Tuning of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Multivariate Distribution Loading. Quantum Reports. 2022; 4(1):75-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum4010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgliardi, Gabriele, and Enrico Prati. 2022. "Optimal Tuning of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Multivariate Distribution Loading" Quantum Reports 4, no. 1: 75-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum4010006
APA StyleAgliardi, G., & Prati, E. (2022). Optimal Tuning of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Multivariate Distribution Loading. Quantum Reports, 4(1), 75-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/quantum4010006







