Abstract
The dairy industry faces challenges from mastitis, which affects milk quality. Somatic Cell Counts (SCCs) are key indicators of udder health, subclinical mastitis presence, and legal thresholds. However, limited research has explored geographic disparities and temporal patterns in SCCs across the USA, despite their critical role in informing targeted herd management strategies, optimizing policy interventions, and ensuring consistent milk quality standards. This study aimed to examine temporal trends and geographic disparities in median weighted SCCs (mwSCCs) across USA states. This study analyzes SCC data using records from the Dairy Herd Improvement Association across 42–45 states between 2011 and 2023. State-level differences in mwSCCs were examined, with temporal changes assessed using percent differences between 2011 and 2023. Moran’s I and Local Indicators of Spatial Association (LISA) were used to identify spatial clusters of states with high and low mwSCCs. The mwSCCs decreased by 24.8%, from 234,000 cells/mL in 2011 to 176,000 cells/mL in 2023, with significant reductions in Virginia and Georgia, while Tennessee and South Carolina had minimal declines. However, Texas, California, and Colorado saw increases, with Colorado rising by 147.9%. Spatial clustering revealed high mwSCCs in the southeast and low levels in the northeast, highlighting the need for region-specific strategies.
1. Introduction
One of the major issues plaguing the dairy industry by drastically decreasing milk quality and yield is mastitis, the inflammation of the mammary gland. Mastitis is the most economically detrimental disease in the industry, due to not only the loss of quality and quantity of milk, but also the elevated number of prematurely culled animals [1,2]. The world’s population has an upward trend, increasing exponentially along with the increased demand for food supply. The human population has always relied heavily on milk and dairy product consumption, contributing to over 70% of required dietary calcium in the food supply today [3]. Milk consumption has been associated with additional nutritional benefits—including probiotics, protein, vitamins, and minerals—which may contribute to health advantages such as a reduced risk of diseases like diabetes and certain cancers [4]. Thus, the importance of quality, not just quantity, of milk. Lack of focus on improving milk quality may lead to subsequently produced dairy products exhibiting a decreased shelf life [5,6,7].
Nevertheless, the international dairy industry continues pursuing the goal of increasing milk production per cow by introducing practices that include optimizing environmental conditions, genetics, animal health, and successful breeding. The overarching theme is to obtain the highest milk yield per cow, enhancing efficiency of individual cows and the overall industry while still supplying high quality milk, to ensure the production of high-quality dairy products. Tests evaluating somatic cell counts (SCCs) remain the customary method for monitoring healthy and mastitic cows, providing the basis for developing indices used to determine milk quality and pricing. Unweighted individual cow SCCs as well as weighted individual cow SCCs are aggregated into total bulk tank somatic cell counts (BTSCCs). Calculating the percentage of weight by volume for each animal, and how it influences the overall BTSCC based on their individual SCCs, provides a more precise snapshot of the BTSCCs and allows for statistics to reflect actual SCCs, indicated by weighted individual cow SCCs.
Internationally, the original cutoff for a “healthy quarter” was 500,000 cells/mL of milk, so deemed by the International Dairy Federation in 1971 [8]. Other initial literature further defines SCCs of greater than 283,000 cells/mL of milk as the threshold for subclinical mastitis prevalence in a quarter [9]. Recent studies have found that a SCC threshold of less than 100,000 cells/mL is more appropriate for identifying a ‘healthy quarter’ [10,11]. Cows with SCCs above this level are likely to experience milk loss in the affected quarter, which is an indicator of subclinical mastitis and subsequent decrease in milk yield, fat, and protein [10,11]. Thresholds are also used for legal limits in the international dairy industry, for example, in the United States of America (USA), the legal SCC limit is 750,000 cells/mL, followed by far lower limits in Canada (500,000 cells/mL) and Europe (400,000 cells/mL) [12]. A BTSCC above the regulatory limits will result in milk not being picked up and transported to processing plants, with further costs falling on farmers for disposal. Additionally, various thresholds exist in different states and regions in the USA, offering increased premiums for higher quality milk. For instance, in Wisconsin, if BTSCCs are ≤350,000 cells/mL, each 25,000 cells/mL reduction results in an added milk premium of $0.10 per 45 kg of milk [13]. Economic losses from unmet milk production potentials due to clinical and subclinical mastitis resulting in decreased milk yield and quality have an unmatched detrimental effect in the industry.
In the USA, overall milk quality is monitored autonomously on farms or by farmers enrolling in programs such as the Dairy Herd Improvement Association (DHIA). The DHIA program provides timely monitoring and reporting of unweighted individual cow SCCs, weighted individual cow SCCs, and BTSCCs, with somatic cell counts determined by flow cytometry and results typically available within 24–48 h of sample collection [14,15]. Field technicians typically visit participating farms approximately 10–12 times annually to collect both milk weights and milk samples. DHIA provides farmers with both individual and weighted SCCs to enable more informed decision-making within herds. Beyond herd-level management, broader geographic factors—such as regional climate— may also contribute to differences in SCC levels. Overall, a study published over a decade ago showed the US has seen a steady decrease in SCCs [16]. Despite the importance of SCCs in monitoring milk quality, recent geographic and temporal patterns in the USA remain underexplored, yet understanding these patterns is essential for identifying states with consistent SCC levels and implementing targeted interventions to improve milk quality and regional dairy management. The objectives of the study were to investigate (a) temporal patterns in median weighted SCCs (mwSCCs) between 2011 and 2023 and (b) state-level geographic disparities in mwSCCs across USA states.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
The study used data provided by the DHIA (Dairy Records Management Systems in Raleigh, NC, USA). The DHIA obtained monthly information, including weighted SCCs, from selected dairy farms across the USA that subscribe to their service. The data contained herd-level monthly weighted SCC data from January 2011 to December 2023 across 45 US states. Across the 13-year study period, the number of DHIA test-days per year ranged from roughly 73,000 to 135,000. DHIA reports herd-level results on a monthly basis, so a single herd can contribute multiple records—up to roughly 12 observations per year—while herds remain anonymous and individual cows are not identified. To protect farm privacy, DHIA includes a state–month–year record in the analysis only when at least three individual herds with more than 1000 cows per herd are present for that period. The dataset includes records from multiple dairy breeds—Ayrshire, Brown Swiss, Guernsey, Holstein, Jersey, Milking Shorthorn, and herds containing more than one breed rather than formal crossbreds. Annual state-level mwSCC values were calculated for the study duration. Monthly herd-level records were first aggregated by state and year, and the annual median weighted SCCs were then calculated from these state–year aggregates. The mwSCC values were analyzed in their original scale; no transformation of the data distribution was required for this descriptive analysis. The mwSCC data and subsequent calculations were performed using the statistical software RStudio (2023.06.0+421 “Mountain Hydrangea”; Boston, MA, USA) using the R packages dplyr (Version 1.1.4) and tidyr (Version 1.3.1) [17,18,19].
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.1. Temporal Analysis
Descriptive statistics (count, mwSCCs) were used to summarize data yearly. Yearly temporal analysis was performed at both the state and national levels.
At the state level, counts and median mwSCC values were calculated for each year. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test was conducted to evaluate changes in state-level mwSCCs over time, specifically comparing values from 2011 vs. 2023 using the R package broom [20,21]. To control for multiple comparisons, Benjamini and Hochberg (BH) adjustments were applied to the resulting p-values [22].
At the national level, the national mwSCCs (nmwSCCs) were computed using a weighted approach, where the number of observations per state served as weights. National mwSCCs were analyzed as a continuous variable; no additional categorical thresholds were applied. Annual percentage changes in nmwSCCs were calculated for each year, and the overall percentage change between 2011 and 2023 was determined. To quantify trends over time, a linear regression model was fitted to estimate the annual rate of change in nmwSCCs from 2011 to 2023. The nmwSCCs and their fitted regression line were visualized using the R package ggplot2 [23].
2.2.2. Calculation of Measures of Spatial Clustering
All spatial analyses were conducted at the state level, using inverse distance weighting to define spatial relationships between states. This weighting approach assumes that closer states have stronger spatial interactions than more distant ones.
To assess spatial autocorrelation in median weighted SCCs (mwSCCs), Global Moran’s I was first employed to evaluate overall clustering patterns. Next, Local Indicators of Spatial Association (LISA) were used to identify specific high- and low-value clusters and spatial outliers, offering deeper insight into localized geographic disparities. For the LISA maps, state-level mwSCC values were compared with the overall national mean. This comparison allowed each state to be classified into one of the standard categories: high–high (a state with a high mwSCC surrounded by other high-mwSCC states), low–low (low mwSCC surrounded by other low-mwSCC states), high–low (a high-mwSCC state surrounded by low-mwSCC states), or low–high (a low-mwSCC state surrounded by high-mwSCC states).
Statistical significance was assessed using 99,999 Monte Carlo permutations. All spatial analyses were conducted using GeoDa (Version 1.8.10) [24].
2.3. Cartographic Displays
All cartographic manipulations and displays were conducted using ArcGIS Pro (Version 3.2.2; Redlands, CA, USA) [25]. State-level cartographic boundary files were obtained from the USA Census Bureau website [26] for use in all cartographic displays. The Jenks optimization classification scheme was employed to determine critical intervals for mapping the mwSCCs in the choropleth maps. To facilitate comparisons of the distribution of the mwSCC across years, subsequent class intervals of mwSCCs were adjusted to match those of the mwSCCs in the 2011 map. Only statistically significant percent differences (p < 0.05, BH-adjusted) in mwSCCs between 2011 and 2023 computed for each state (n = 43) were mapped using ArcGIS [25]. Moran scatterplots and Moran significance maps were utilized to assess the presence of local clustering of mwSCCs.
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Distribution
The state-level distribution of mwSCCs varied annually from 2011 to 2023, although certain USA regions, such as the northeast and Midwest, consistently maintained relatively low mwSCC values across the study period (Figure 1). The southeastern region of the USA consistently exhibited higher mwSCCs compared to other regions. In contrast, the northeastern and midwestern regions had lower mwSCCs consistently across the study period.
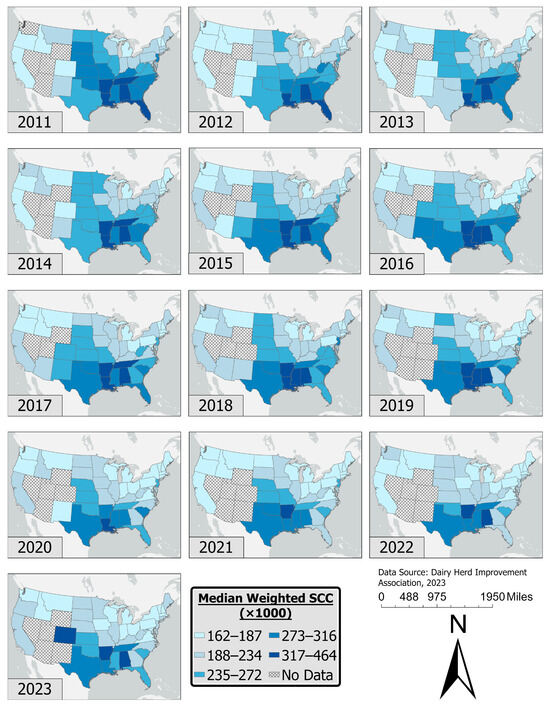
Figure 1.
Distribution of median weighted SCCs in the United States from January 2011 to December 2023.
Many of the states experienced significant reductions in mwSCCs, particularly in the Midwest and eastern regions of the country (Figure 2). The most significant reductions in mwSCCs were observed in Virginia (−36.6%) and Georgia (−34.5%). However, three states experienced an overall significant increase in mwSCC, Texas (10.1%), California (22.1%), and Colorado (147.9%).
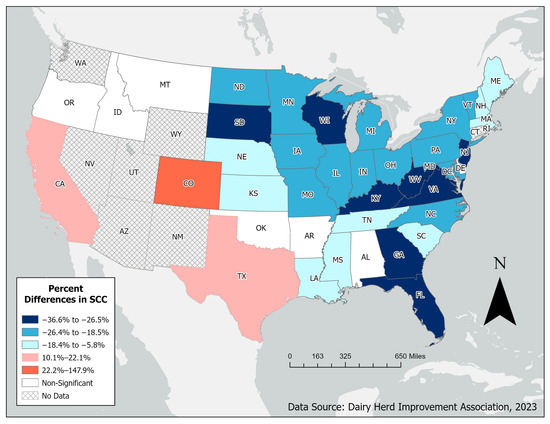
Figure 2.
Distribution of percent changes in median weighted SCCs in the United States between 2011 and 2023.
There was an overall decrease in nmwSCCs from 224,000 in 2011 to 168,000 in 2023. The nmwSCC decreased significantly in most years, with notable decreases from 2011 to 2012 (−7.14%) and from 2018 to 2019 (−7.94%). However, there was a notable increase from 2020 to 2021 (3.03%), followed by a smaller increase from 2021 to 2022 (1.18%) (Table 1). Over the study period, nmwSCCs declined by a total of 25.0%, corresponding to an average annual reduction of 2.3%.

Table 1.
The percent changes in national median weighted SCC values from 2011 to 2023.
The slope of the regression line, which is approximately −4.15 (p < 0.0001), indicates that the nmwSCCs decreased by about 4.15 units per year on average over the period from 2011 to 2023 (Figure 3).
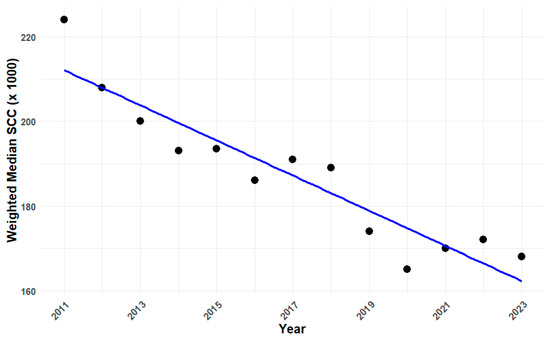
Figure 3.
Changes in national median SCC values (cells/ mL) from 2011 to 2023.
3.2. Spatial Clustering of mwSCCs
There was a significant spatial autocorrelation based on global Moran’s I test of spatial autocorrelations (Moran’s I = 0.382; p = 0.0004). Some states showed evidence of local clustering of mean weighted SCCs (Figure 4).
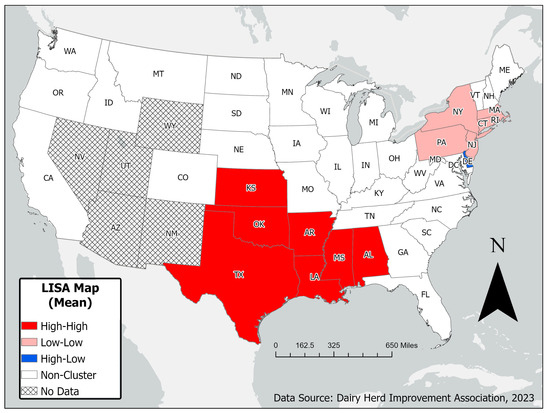
Figure 4.
Univariate Moran’s I LISA map showing spatial clustering of median weighted SCCs (mwSCCs) by state using mean inverse distance spatial weights.
Based on the univariate Moran’s I using mean spatial inverse distance weights, significant spatial clustering of mwSCCs was observed. Clusters of states with high mwSCC values surrounded by other states with similarly high values were identified in the southern United States, including Mississippi, Oklahoma, Louisiana, Texas, Alabama, Kansas, and Arkansas (Figure 4). In contrast, clusters of low mwSCC values surrounded by other low-value states were found in the northeastern United States, including Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
4. Discussion
This study provides valuable insights into the state-level temporal and spatial patterns of weighted SCCs in the USA dairy industry from 2011 to 2023. The findings align with previous research [27] but also reveal novel aspects of SCC distribution, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to enhance milk quality. For simplicity, moving forward, mwSCC will be referred to as SCC. The observed 24.8% reduction in median SCCs—from 234,000 cells/mL in 2011 to 176,000 cells/mL in 2023 mirrors global trends documented in studies such as Ruegg (2017), who reported similar declines across several countries [27]. These improvements have often been attributed to advancements in mastitis management, enhanced disease control, and better dairy technology [28,29]. For example, a review by Kour et al. (2022) highlighted that advancements in diagnostic tools and treatment protocols have significantly contributed to the reduction in SCC levels globally [30]. Our findings support these conclusions, suggesting that widespread improvements in hygiene standards, veterinary care, and participation in programs like the DHIA has collectively contributed to this downward trend.
Notably, Table 1 shows a steady decline in the number of annual DHIA test-days over the study period. This decline parallels the broader contraction of the USA dairy sector: according to the USA Census of Agriculture, the number of licensed dairy farms fell from 54,599 in 2017 to 36,024 in 2022, while the national dairy-cow inventory decreased only slightly, from 9.54 million to 9.31 million cows [31,32]. These figures indicate that U.S. milk production has become increasingly concentrated in fewer, typically larger herds. This structural change likely contributes to the reduced number of DHIA test-days over time and provides important context for interpreting national SCC trends.
Farms participating in programs such as DHIA are more likely to have better management practices as well. This aligns with Hadrich et al. (2018), who showed that farms implementing comprehensive mastitis control measures not only reduced SCCs but also improved milk yield and quality, illustrating the interconnected benefits of effective SCC management [11]. However, farms that do not participate in programs such as DHIA have been shown to record higher SCCs [33]. Given that we observed areas of disparity in SCCs at the state level, even among DHIA participants, it suggests that these problems could be more pronounced among individual farms within these regions. However, since our analysis is based on state-level data, caution is warranted when extrapolating these findings to individual farms due to potential ecological fallacy.
Despite the overall decline, our analysis identified periods of slight increases, notably in 2019 (1.05%) and 2022 (1.17%), which can likely be attributed to external factors such as extreme weather and economic pressures. Seasonal heat stress, particularly during summer, is a well-documented factor contributing to elevated SCC levels, as highlighted by Becker et al. (2020) [34]. Similarly, Guinn et al. (2019) observed higher SCC levels during warmer months, attributing them to environmental stress on cows [35]. These patterns were particularly evident in southern states, where relatively high temperatures and humidity exacerbate mastitis risk in comparison to the northern states. The slight increase in 2022 might also reflect broader economic disruptions, such as those experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic, which affected farm operations and management practices [36]. Although the pandemic began in 2020, many of its economic impacts, including supply chain interruptions, labor shortages, increased input costs, and changes in market demand—persisted well beyond the initial outbreak. These ongoing challenges likely strained farm resources and delayed investments in herd health and mastitis control measures. Consequently, the cumulative effects of these disruptions may have manifested as a rise in somatic cell counts only by 2022, reflecting a lag between the onset of disruptions and their impact on milk quality indicators. While these factors likely play a significant role, a detailed exploration of their specific impacts falls outside the current study’s scope and warrants further investigation.
Regional nuances in temporal trends also emerged, underscoring the importance of localized strategies. De Vries and Cole (2009) found that SCC trends in the southern USA are more variable due to inconsistent mastitis management and higher environmental stress compared to northern states [37]. Our findings align with this observation, highlighting that while national trends show overall improvement, some regions exhibit volatility. This variability underscores the need for region-specific interventions to address unique challenges and ensure sustainable improvements in milk quality. For instance, the southeastern USA consistently exhibited higher SCC levels compared to the northeastern and midwestern regions [38,39]. This aligns with Tančin et al. (2018), who demonstrated that warm, humid climates—prevalent in the southern USA—foster pathogen growth, increasing mastitis risk [40]. A study performed in Canada by Sargeant et al. in 1998 found herds to experience a SCC increase in up to 71% of herds with higher temperature and humidity with each influx of the summer season [41]. Conversely, cooler climates in the northeastern states, such as Pennsylvania, New York, and New Jersey, create less favorable conditions for mastitis-causing bacteria, contributing to lower SCC levels [41]. The clustering of high SCC levels in states such as Texas, Louisiana, and Mississippi potentially highlights the significant impact of environmental stressors, such as temperature and humidity, resulting in heat stress [42,43,44,45]. Elevated temperatures and humidity impair cows’ immune systems, increasing their susceptibility to infections [42,43,44]. Rakib et al. (2020) also demonstrated a strong correlation between heat stress and elevated SCC levels, reinforcing the need for effective heat stress management strategies, such as improved ventilation and cooling systems [46].
These regional disparities are not unique to the USA. Similar patterns have been observed internationally; studies in South America and southeastern Asia report higher SCC levels in regions with warm climates and limited access to advanced mastitis management resources [37,47,48]. Our findings contribute to this broader understanding, emphasizing the need for region-specific interventions to address environmental stressors. Comparative analyses of intervention strategies across different climatic regions could further inform best practices for SCC management and enhance global dairy production standards.
Management practices also play a pivotal role in SCC variability. Our study found that states with rigorous mastitis control programs, such as those in the northeastern USA, consistently reported lower SCC levels. This observation aligns with DeLong et al. (2017), who noted that northern states are more proactive in implementing comprehensive mastitis management strategies, including regular veterinary consultations, stringent hygiene protocols, and advanced milking technologies [39,49]. Conversely, southern states often adopt a reactive approach, addressing SCC issues only when levels surpass critical thresholds [50,51]. This reactive approach may contribute to higher SCC rates, as seen in our results and reflected in findings by Ruegg (2012), who emphasized the importance of early intervention and continuous monitoring [52]. Enhanced education and training programs for dairy farmers in high-SCC regions could improve adherence to best practices, thereby reducing SCC levels [52]. Additionally, variations in access to veterinary services and mastitis control resources further influence regional differences in herd health and milk quality [52,53]. Effective antimicrobial-resistance (AMR) management has been shown to improve udder health and indirectly reduce SCCs [54,55,56]. For example, national surveillance programs in the USA report that herds implementing judicious antimicrobial use and robust mastitis-prevention protocols show lower prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant bacterial strains, which in turn supports better mastitis control and helps maintain lower somatic cell counts [57,58]. Although antimicrobial resistance is a critical global concern in dairy production, detailed assessment of resistance management strategies was beyond the scope of this study. It is important to note; however, that participation in DHIA and the associated emphasis on preventive mastitis control typically aligns with broader efforts to use antimicrobials judiciously and to monitor resistance trends, which are addressed by separate national surveillance and regulatory programs such as the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS). While our study identifies broad trends, future research focusing on farm-level factors is needed to provide a more nuanced understanding of these dynamics.
The role of regulatory standards and economic incentives is equally critical. The legal SCC limit for “Grade A” milk in the USA (750,000 cells/mL) is higher than those in Canada (500,000 cells/mL), and Europe (400,000 cells/mL) [12,59,60]. Southern states with higher SCC levels, such as the patterns seen in this study, may face restricted market opportunities internationally, limiting their competitiveness. Lombard et al. (2011) found that stricter regulatory thresholds in the European Union incentivize farmers to adopt more robust quality control measures, suggesting that aligning USA standards with global benchmarks could drive further improvements in milk quality [60]. Economic incentives also influence SCC management practices [61,62,63,64]. In the northeastern USA, higher premiums for milk with lower SCC levels motivate farmers to adopt stringent quality controls [65,66]. This economic motivation potentially contributes to the consistent declines observed in these states, as corroborated by De Vries and Cole (2009), who demonstrated that financial incentives are crucial in encouraging best practices [37]. This study was designed as an exploratory, descriptive analysis of temporal and geographic patterns in mwSCCs. Identifying the specific climate, herd-level or management, and state-level factors that drive these patterns is beyond the scope of the present work and should be addressed in future research. Such future studies could also examine the impact of regional pricing structures and subsidy programs on long-term SCC trends to inform policy development strategies aimed at improving milk quality nationwide.
Strengths and Limitations
This study possesses several notable strengths. First, it leverages a large, longitudinal dataset of mwSCCs from the DHIA, encompassing over a decade (2011–2023) and 45 USA states. Nationally, approximately 18,000 herds and about 4.3 million cows are enrolled in DHIA services, representing roughly 39% of licensed USA herds and 46% of the cows. Participation spans operations of all sizes and breeds—from herds of fewer than 99 cows (about 55% of DHIA herds, 12% of the cows) to herds with more than 2000 cows (about 2% of herds, nearly 29% of the cows) as of 2018 [31,32,67]. This broad and stable enrollment provides strong geographic and structural representation of the U.S. dairy industry and allows for detailed assessment of both long-term trends and regional disparities in milk quality. Second, the use of weighted SCCs rather than unweighted measures provides a more accurate reflection of milk quality and udder health at the herd level.
However, several limitations warrant consideration. First, the study includes only farms that participate in DHIA, potentially biasing the results toward herds with more intensive management and data reporting practices, and they may not fully represent the remaining licensed herds. Farms not enrolled in DHIA, which may have higher SCCs or differing management strategies, are not represented. While the breadth of DHIA coverage strengthens the analysis, the voluntary nature of enrollment should be kept in mind when interpreting the generalizability of the findings. Second, while spatial analyses account for geographic clustering, other unmeasured confounders, such as laboratory variability in SCC testing, herd management practices (e.g., hygiene protocols, milking routines, mastitis control strategies), breed composition, or pathogen profiles, could influence results. Notably, farm management is a critical driver of SCCs and likely accounts for a substantial portion of the regional and temporal variation observed. Finally, environmental factors such as temperature and humidity are hypothesized to contribute to SCC patterns but were not directly measured or modeled in this study. These limitations notwithstanding, the findings of this study offer practical insights for processors designing quality assurance programs and for policymakers developing strategies to support the dairy sector.
5. Conclusions
Overall, the study identified meaningful geographic differences and temporal changes in milk somatic cell counts across states in the United States from 2011 to 2023. Somatic cell counts declined nationally, reflecting improvements in milk quality and udder health, but several regions continued to show elevated values, pointing to the need for targeted interventions and improved herd management. The results align with prior research emphasizing the importance of proactive practices such as regular veterinary care and strong hygiene protocols. Economic incentives and regulatory standards also appear to influence outcomes, suggesting that closer alignment of national limits with international benchmarks may enhance milk quality and competitiveness. Although further investigation is needed to explore the causes of regional variation, these findings offer practical insights for processors designing quality assurance programs and for policymakers developing strategies to support the dairy sector.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.V. and C.C.O.; methodology, J.V., A.O., R.Z. and C.C.O.; software, J.V., A.O. and R.Z.; validation, J.V., A.O., R.Z. and C.C.O.; formal analysis, J.V., A.O. and R.Z.; investigation, J.V. and C.C.O.; resources, J.V., A.O. and C.C.O.; data curation, J.V. and R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.V. and C.C.O.; writing—review and editing, J.V., A.O., R.Z. and C.C.O.; visualization, J.V., A.O. and C.C.O.; supervision, C.C.O.; project administration, J.V. and C.C.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for open access to this research was provided by University of Tennessee’s Open Publishing Support Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to a nondisclosure agreement.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Dairy Herd Improvement Association (DHIA) and Dairy Records Management Systems for sharing the records evaluated in this study. Special appreciation goes to Katie England, John Clay, and Robert Fourdraine.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SCC | Somatic Cell Counts |
| BTSCC | Bulk Tank Somatic Cell Counts |
| mwSCC | Median weighted Somatic Cell Counts |
| nmwSCC | National median weighted Somatic Cell Counts |
| DHIA | Dairy Herd Improvement Association |
| LISA | Local Moran’s I |
References
- Heikkilä, A.-M.; Nousiainen, J.; Pyörälä, S. Costs of clinical mastitis with special reference to premature culling. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogeveen, H.; Huijps, K.; Lam, T. Economic aspects of mastitis: New developments. N. Z. Vet. J. 2011, 59, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, P.; DiRienzo, D.; Miller, G. Major scientific advances with dairy foods in nutrition and health. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunick, M.H.; Van Hekken, D.L. Dairy products and health: Recent insights. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9381–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbano, D.M.; Ma, Y.; Santos, M.V.d. Influence of raw milk quality on fluid milk shelf life. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, E15–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.; Woonton, B.; Smithers, G. Improving the sensory quality, shelf-life and functionality of milk. In Functional and Speciality Beverage Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 170–231. [Google Scholar]
- Rysstad, G.; Kolstad, J. Extended shelf life milk—Advances in technology. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006, 59, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolle, A. A monograph on bovine mastitis. Ann. Bull. Int. Dairy Fed. Part 1971, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneau, J.K. Effective use of dairy herd improvement somatic cell counts in mastitis control. J. Dairy Sci. 1986, 69, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, K.; Godkin, A.; Kelton, D. Milk production and somatic cell counts: A cow-level analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrich, J.; Wolf, C.; Lombard, J.; Dolak, T. Estimating milk yield and value losses from increased somatic cell count on US dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3588–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, H.; Miller, R.; Wright, J.; Wiggans, G. Herd and state means for somatic cell count from dairy herd improvement. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.; Caraviello, D.; Ruegg, P. Management of Wisconsin dairy herds enrolled in milk quality teams. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, M.; Holm, C.; Blaabjerg, M.; Bro, M.N.; Schwarz, D. Differential somatic cell count—A novel method for routine mastitis screening in the frame of Dairy Herd Improvement testing programs. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4926–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Hogeveen, H.; Lam, T.J.; Van der Tol, R.; Koop, G. Performance of online somatic cell count estimation in automatic milking systems. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicconi-Hogan, K.; Gamroth, M.; Richert, R.; Ruegg, P.; Stiglbauer, K.; Schukken, Y. Associations of risk factors with somatic cell count in bulk tank milk on organic and conventional dairy farms in the United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 3689–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- tidyr: Tidy Messy Data. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidyr (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; Vaughan, D. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation, R Package Version 1.1.4. 2025. Available online: https://dplyr.tidyverse.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- broom: Convert Statistical Objects into Tidy Tibbles. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=broom (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Bogdan, M.; Ghosh, J.K.; Tokdar, S.T. A comparison of the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure with some Bayesian rules for multiple testing. In Beyond Parametrics in Interdisciplinary Research: Festschrift in Honor of Professor Pranab K. Sen; Institute of Mathematical Statistics: Beachwood, OH, USA, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 211–231. [Google Scholar]
- ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Kho, Y. GeoDa: An introduction to spatial data analysis. In Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis: Software Tools, Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, C.J. ArcView GIS Version 3.1. Bull. Med. Libr. Assoc. 1999, 87, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau, U.C. Cartographic Boundary Shapefiles-States. Available online: https://www.census.gov/geographies/mapping-files/time-series/geo/carto-boundary-file.html (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Ruegg, P.L. A 100-Year Review: Mastitis detection, management, and prevention. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10381–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.; Kamel, M. Bovine mastitis prevention and control in the post-antibiotic era. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Reps, N.; Sherman, G. NE1048: Mastitis Resistance to Enhance Dairy Food Safety; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Haxhiaj, K.; Wishart, D.S.; Ametaj, B.N. Mastitis: What it is, current diagnostics, and the potential of metabolomics to identify new predictive biomarkers. Dairy 2022, 3, 722–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture; National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS). Table 17. Milk cow herd size by inventory and sales: 2017. In 2017 Census of Agriculture; Publication AC-17-A-51; United States National Level Data: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 1, Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture; National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS). Table 17. Milk Cow Herd Size by Inventory and Sales: 2022. In 2022 Census of Agriculture; U.S. National Level Data: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Volume 1, Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Higginbotham, G.; Berry, S.; Lanka, K.; VerBoort, W.; Seldin, R.; Dei, C. Dairy producers value DHIA milk testing, but some deterred by cost. Calif. Agric. 1997, 51, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Collier, R.; Stone, A. Invited review: Physiological and behavioral effects of heat stress in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 6751–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinn, J.M.; Nolan, D.; Krawczel, P.; Petersson-Wolfe, C.; Pighetti, G.; Stone, A.; Ward, S.; Bewley, J.; Costa, J.H. Comparing dairy farm milk yield and components, somatic cell score, and reproductive performance among United States regions using summer to winter ratios. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11777–11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingbin, W.; Liu, C.-q.; Zhao, Y.-f.; Kitsos, A.; Cannella, M.; Wang, S.-K.; Lei, H. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the dairy industry: Lessons from China and the United States and policy implications. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2903–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, A.; Cole, J. Profitable dairy cow traits for hot climatic conditions. In Breeding for Robustness in Cattle; Wageningen Academic: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wenz, J.; Jensen, S.; Lombard, J.; Wagner, B.; Dinsmore, R. Herd management practices and their association with bulk tank somatic cell count on United States dairy operations. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 3652–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, K.L.; Lambert, D.M.; Schexnayder, S.; Krawczel, P.; Fly, M.; Garkovich, L.; Oliver, S. Farm business and operator variables associated with bulk tank somatic cell count from dairy herds in the southeastern United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9298–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tančin, V.; Mikláš, Š.; Mačuhová, L. Possible physiological and environmental factors affecting milk production and udder health of dairy cows: A review. Slovak J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 51, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sargeant, J.M.; Schukken, Y.H.; Leslie, K.E. Ontario bulk milk somatic cell count reduction program: Progress and outlook. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.W. Effects of heat-stress on production in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2131–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Amaral, B.; Connor, E.; Tao, S.; Hayen, M.; Bubolz, J.; Dahl, G. Heat stress abatement during the dry period influences metabolic gene expression and improves immune status in the transition period of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, H.; Bormann, J.; M’hamdi, N.; Montaldo, H.H.; Gengler, N. Evaluation of heat stress effects on production traits and somatic cell score of Holsteins in a temperate environment. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Bravo-Ureta, B.E.; De Vries, A. Dairy productivity and climatic conditions: Econometric evidence from South-eastern United States. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2013, 57, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.R.H.; Zhou, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Han, B.; Gao, J. Effect of heat stress on udder health of dairy cows. J. Dairy Res. 2020, 87, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jattawa, D.; Koonawootrittriron, S.; Elzo, M.; Suwanasopee, T. Somatic cells count and its genetic association with milk yield in dairy cattle raised under Thai tropical environmental conditions. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, R.; dos Santos Daltro, D.; Cobuci, J.A. Heat stress effects on somatic cell score of Holstein cattle in tropical environment. Livest. Sci. 2021, 247, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, G.; Baraitareanu, S. Approaches of Milking Biosecurity and Milking Parlour Hygiene in Dairy Farms; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Herndon, C. How the Southeast is different. Hoard’s Dairym. 2011, 20, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schewe, R.; Kayitsinga, J.; Contreras, G.; Odom, C.; Coats, W.; Durst, P.; Hovingh, E.; Martinez, R.; Mobley, R.; Moore, S. Herd management and social variables associated with bulk tank somatic cell count in dairy herds in the eastern United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7650–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegg, P.L. New perspectives in udder health management. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart-Getz, A.; Prokopy, L.S.; Floress, K. Why farmers adopt best management practice in the United States: A meta-analysis of the adoption literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 96, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, R.D.; Gillespie, B.E.; Ivey, S.; Pighetti, G.M.; Almeida, R.A.; Kerro Dego, O. Antimicrobial resistance of major bacterial pathogens from dairy cows with high somatic cell count and clinical mastitis. Animals 2021, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; McClure, J.T.; Scholl, D.; DeVries, T.; Barkema, H. Herd-level association between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in bovine mastitis Staphylococcus aureus isolates on Canadian dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Barkema, H.W.; Yang, J.; Kastelic, J.P.; Nobrega, D.B.; Li, X.; Tong, X.; Fan, Z.; Gao, J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Use on Chinese Dairy Farms: Awareness and Opinions Regarding Selective Treatments of Farm Managers. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, B.E.; Tate, H.; Plumblee, J.R.; Dessai, U.; Whichard, J.M.; Thacker, E.L.; Hale, K.R.; Wilson, W.; Friedman, C.R.; Griffin, P.M. National antimicrobial resistance monitoring system: Two decades of advancing public health through integrated surveillance of antimicrobial resistance. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Rokana, N.; Chandra, M.; Singh, B.P.; Gulhane, R.D.; Gill, J.P.S.; Ray, P.; Puniya, A.K.; Panwar, H. Antimicrobial resistance: Its surveillance, impact, and alternative management strategies in dairy animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 4, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.; Norman, H.; Wiggans, G.; Wright, J. National Survey of Herd Average Somatic Cell Counts on DHI Test Days; CDCC: Bowie, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, J.E.; Norman, H.D.; Kopral, C.A.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Wright, J.R. European Union bulk tank SCC standards and proposed US standards: Compliance based on data from four federal milk marketing orders. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Mastitis and Milk Quality, St. Louis, MO, USA, 22–24 September 2011; National Mastitis Council: Verona, WI, USA, 2011; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, S.L. Costs of herd-level production losses associated with subclinical mastitis in US dairy cows. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting—National Mastitis Council Incorporated, Arlington, VA, USA, 14–17 February 1999; National Mastitis Council Incorporated: New Prague, MN, USA, 1999; Volume 38, pp. 152–153. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.M.; Bailey, T.L. Understanding the Basics of Mastitis; Virginia Tech: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, E.; Bar, D.; Hertl, J.; Tauer, L.; Bennett, G.; González, R.; Schukken, Y.; Welcome, F.; Gröhn, Y. The cost and management of different types of clinical mastitis in dairy cows estimated by dynamic programming. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 4476–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Arnold, L.; Stowe, C.; Harmon, R.; Bewley, J. Estimating US dairy clinical disease costs with a stochastic simulation model. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1472–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. All Milk Prices Survey. 2023. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Surveys/Guide_to_NASS_Surveys/Milk/index.php (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Extension, P.S. Dairy Risk-Management Education: Understanding Your Milk Check. 2023. Available online: https://extension.psu.edu/dairy-risk-management-education-understanding-your-milk-check (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- DHI Participation as of January 1, 2018 DHI Report K-1. Available online: https://queries.uscdcb.com/publish/dhi/dhi18/partall.html (accessed on 1 May 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).