Abstract
Despite routine supplementation of dairy cattle with vitamins with antioxidant functions, such as α-tocopherol, the high energy demand of the transition period creates a pro-oxidant state that can overcome antioxidant defenses and damage macromolecules. Known as oxidative stress, this condition impairs host immune defenses, predisposing cattle to disease and causing dysfunctional inflammation through a dysregulated production of lipid inflammatory mediators known as oxylipids. Non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E have functions in other species that limit oxidative stress and dysfunctional inflammation but have largely remained unstudied in cattle. As non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E have functions similar to α-tocopherol yet are more rapidly metabolized, they may provide further antioxidative functions with a reduced risk for adverse effects. Indeed, in vitro and in vivo evidence in cattle show a strong safety profile of most non-α-tocopherol analogs, and by several measures, non-α-tocopherol analogs present equally or more potent antioxidative activities than α-tocopherol alone. Further, vitamin E analogs are shown to compete with certain fatty acids for enzymatic metabolism, which may impact proinflammatory mediator production. Given that non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E reduce the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and act as potent antioxidants, their safety and efficacy for these purposes should be further evaluated in cattle.
Keywords:
dairy cattle; oxidative stress; antioxidant; nutrition; tocopherol; tocotrienol; cytochrome P450 1. Introduction
The intense physiological and physical changes of the transition period in dairy cattle can disturb the animal’s oxidative balance and lead to increased macromolecule damage, known as oxidative stress, in animals lacking adequate antioxidant defenses to manage an increased oxidant load. Oxidative stress can disrupt normal cellular functions, including the coordination of an appropriate inflammatory response to pathogen challenge. Disruptions in certain cellular functions lead to aberrant inflammatory responses during the transition period, a hallmark of animals unable to properly cope with the physiological shifts around calving [1]. Such improper and dysregulated inflammatory responses can ultimately lead to disease predisposition and potentially increased severity of disease due to excessive or unresolving inflammation. It is because of this potential for disease predisposition and increased severity that oxidative stress remains a focus of research to reduce the prevalence and impact of transition disease [2]. Although not all transition cows will undergo oxidative stress severe enough to disrupt normal cellular functions, managing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), which are the causative agents of macromolecule damage, has become an important consideration of dairy cattle nutrition.
The supplementation of cattle with vitamins that have antioxidant functions has reduced the prevalence of antioxidant deficiencies that lead to clinical disease over the last three decades [3,4]. Unfortunately, due in part to a significant drop in feed intake during the transition period, fat-soluble vitamins such as α-tocopherol are significantly lower in blood and liver tissue at calving and into early lactation compared to other stages of the lactation cycle [5,6]. It is for this reason that several groups have studied the efficacy of parenteral administration of α-tocopherol rather than relying solely on dietary supplementation [7,8,9]. Vitamin E has been a focus of the dairy industry and human medicine for its antioxidant function in breaking lipid peroxidation chain reactions, which can otherwise ultimately lead to cell death [10]. Although supplementation of vitamin E to dairy cattle has increased robustly over the past few decades [5,11], some cattle still undergo increased oxidative stress during the transition period [12].
In cattle, α-tocopherol, an analog of vitamin E, has been considered one of the least toxic vitamins according to the United States National Research Council (NRC) despite few studies focusing on its safety when supplemented to cattle [3]. In the human medical literature, debate persists on whether chronic high-dose supplementation of vitamin E can be detrimental to health [13]. Despite being regarded as safe for cattle, feeding α-tocopherol at only three-times the NRC recommended concentrations, which is still well below the stated toxicity concentration of 75 IU/kg of body weight, raised concerns over further increases in its supplementation when fed for 60 days [3,14,15]. At this higher supplementation plane, Bouwstra et al. found increased ROS production in a subgroup of dairy cattle with a high vitamin E regeneration system and low initial blood α-tocopherol concentrations in addition to increased transition cow disease in studied animals overall [14,15]. Despite speculation, these counterintuitive findings may be due to the antioxidant phenomenon of “inversion of activity,” when antioxidants conversely act as pro-oxidants under certain conditions [16]. Specific to vitamin E, the inversion of activity can experimentally occur either when vitamin E is found at a considerably high concentration or when there is inadequate ascorbic acid to regenerate reduced vitamin E [16]. Others, however, have not found similar results when supplementing greater amounts than recommended.
Nonetheless, a new approach to antioxidant supplementation is necessary to address oxidative stress that remains a problem for certain dairy cattle. One such approach may be the use of non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E. This review will discuss the merits and potential pitfalls to the use of non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E in dairy cattle and their prospective application for the prevention or treatment of transition cow disease.
2. Vitamin E Analogs
Although nearly all vitamin E research in cattle has focused on α-tocopherol, a burgeoning field in other mammals has begun to uncover beneficial effects of non-α-tocopherol analogs [10,17,18]. These eight analogs are split into two sub-groups: the tocopherols with a saturated phytyl tail and tocotrienols with unsaturated phytyl tails (Figure 1). Each of these sub-groups is comprised of an α, β, γ, and δ analog based upon methylation of the chromanol ring. In addition, each of these analogs is broken down into a cascade of water-soluble metabolites by cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated ω-hydroxylation and subsequent steps of β-oxidation prior to excretion. Despite α-tocopherol receiving the greatest attention from research, γ-tocopherol is the major form of vitamin E found in North American human diets [19]. This focus on α-tocopherol is due to its greater retention and bioavailability in the body compared to non-α-tocopherol analogs in both humans and other mammals [13].
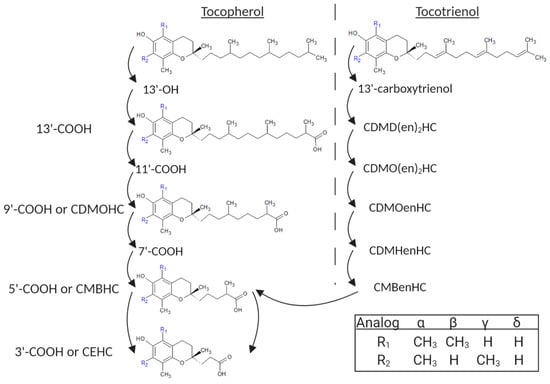
Figure 1.
Metabolic cascade of vitamin E tocopherol and tocotrienol compounds. Metabolites with significant bioactivity and referenced within the body of this review are represented structurally, whereas those not referenced are listed stepwise as their generally accepted abbreviation. Carboxychromanol (COOH); hydroxychromanol (OH); carboxymethyloctylhydroxychromanol (CDMOHC); carboxymethylbutylhydroxychromanol (CMBHC); carboxyethylhydroxychromanol (CEHC); carboxydimethyldecadienylhydroxychromanol (CDMD(en)2HC); carbodimethyloctdienylhydroxychromanol (CDMO(en)2HC); carbodimethyloctenylhydroxychromanol (CDMOenHC); carboxymethylhexenylhydroxychromanol (CDMHenHC); carboxymethylbutadienylhydroxychromanol (CMBenHC). Created with Biorender.com and ChemSketch from ACD Labs.
Although the mechanisms are not fully understood, two primary and independent processes play a role in preserving hepatic concentrations of α-tocopherol over other analogs. First, the rate-limiting and initial step in vitamin E metabolism, undertaken by cytochrome P450 family 4 sub-family F member 2 (CYP4F2), preferentially metabolizes non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E over α-tocopherol in microsomal reaction studies [20]. Secondly, the α-tocopherol transport protein (αTTP), which is imperative for the transport of vitamin E out of the liver and its protection from metabolism, is considered to have 100% affinity for α-tocopherol but only 38% affinity for β-tocopherol and 12% or fewer for all other analogs [21].
In the basal diet of cattle, analogs of vitamin E can be found primarily in forages or concentrated in oils [3,22,23]. Supplementation of vitamin E almost exclusively comes from synthetic mixes of α-tocopherol added to total mixed rations (TMR).
Interestingly, such exclusive supplementation of α-tocopherol in TMR may actively increase the ratio of α-tocopherol to non-α-tocopherol analogs by a third mechanism. Increased concentrations of α-tocopherol in CYP450 microsomal reaction systems increase the metabolism of non-α-tocopherol analogs through heterotropic cooperativity [20]. Thus, supplementing α-tocopherol alone may not only increase the intake of α-tocopherol but additionally increase the breakdown of non-α-tocopherol analogs found basally in the diet. This mechanism may further contribute to the 10- to 1000-times greater concentration of α-tocopherol compared to non-α-tocopherol analogs found in serum and liver of cattle [6].
Despite being used clinically in humans for the treatment of inflammatory conditions, such as asthma and nicotine replacement therapy [17,24], and the first studies of mixed tocopherol supplementation in cattle dating back to the 1940s [25], few studies since have supplemented mixed tocopherols or specific non-α-tocopherol analogs in cattle—and none to the author’s knowledge have purposefully supplemented tocotrienols.
In one study feeding a tocopherol mix (α: 9%, β: 1%, δ: 24%, γ: 62%) to mid-lactation dairy cattle for nine days, concentrations of α-tocopherol were reduced in hepatic tissue as concentrations of γ-tocopherol increased in liver, muscle, and mammary tissues [26]. Reduced liver accumulation of α-tocopherol may be due to the αTTP being expressed almost solely in the liver. Since αTTP has affinity, however low, for γ-tocopherol, there is potential that increased concentrations of γ-tocopherol may displace some α-tocopherol and allow for proportionally increased α-tocopherol metabolism. Interestingly, both α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol were increased in the blood, with peak concentrations after only five days of feeding, although after reaching a peak, γ-tocopherol decreased as α-tocopherol plateaued [26]. A 2021 study in Holstein calves fed varying amounts of an 8% α-tocopherol:89% γ/δ-tocopherol mix for 56 days, however, did not see a dose-related change in liver or intestinal α-tocopherol stores despite increases in tissue γ- and δ-tocopherol [27].
Subsequently, Qu et al. fed mid-lactation, multiparous dairy cattle a mixture of tocopherols and measured a variety of health parameters [28]. This study concluded that feeding such a vitamin mix would not negatively affect either circulating concentrations of leukocytes or impair their ability to mount an inflammatory response to challenge. This was further supported by Quigley et al. (2021) in a 56 day calf study [27]. They showed that calves fed over 20 mg/kg body weight of an 89% γ/δ tocopherol mix had no greater number of medical days (days when a calf was treated with an antibiotic or anti-inflammatory medication) nor a different fecal score, which is an observational assessment of fecal consistency, than those fed a control diet [27]. Further, calves fed greater amounts of non-α-tocopherols were found to have a wider hip width and increased daily gain, which the authors suggest may be due to increased health allowing the body to prioritize energy for growth rather than an immune response.
3. Antioxidant Capacity
3.1. Analog Antioxidant Functions
Primarily known for its antioxidative capacity, α-tocopherol and all other vitamin E analogs directly scavenge reactive metabolites by donating a hydrogen atom from the phenolic group of their chromanol ring. The advantage of this antioxidant function is its inclination to break the chain reaction of lipid peroxidation in cellular membranes, limiting reactive metabolite damage to macromolecules (Figure 2A) [23]. Although all analogs of vitamin E have antioxidant functions, the extent of these functions varies.
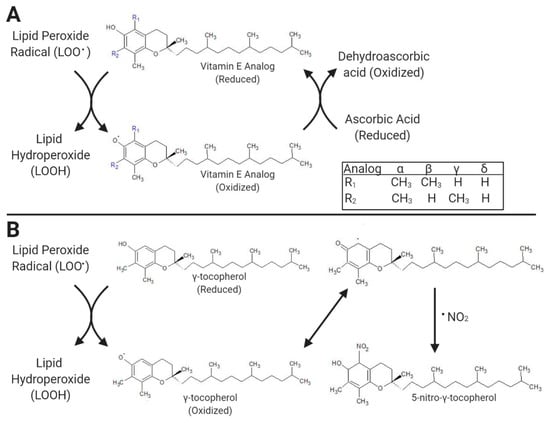
Figure 2.
As antioxidants, the primary known function of vitamin E analogs (represented by a tocopherol structure in (A)) is to break lipid peroxidation chain reactions by reducing lipid peroxides to lipid hydroperoxides (A) by forming an analog radical. Vitamin E analog radicals are then reduced by ascorbic acid to dehydroascorbic acid, regenerating reduced vitamin E analogs. Dehydroascorbic acid is subsequently reduced to ascorbic acid by reduced glutathione. Vitamin E analogs with an unsubstituted 5’ position of the chromanol ring, as designated by R1 in (A) and represented by γ-tocopherol in (B), can further reduce reactive nitrogen species, for example, nitrogen dioxide (•NO2), to form 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol, a marker of redox balance. Created with Biorender.com and ChemSketch from ACD Labs.
The most widely studied of the three other tocopherol analogs, γ-tocopherol shows a proclivity for scavenging of RNS due to its unsubstituted group at the five position of the chromanol ring, a characteristic also found in δ-tocopherol, γ-tocotrienol, and δ-tocotrienol (Figure 2B) [18]. Indeed, when Kuhn et al. (2021) challenged primary bovine mammary endothelial cells (BMEC) with DETA-NONOate (DetaNO), a spontaneous nitric oxide donor and driver of ROS production, γ-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol measurably reduced ROS accumulation at lower supplemented concentrations than α-tocopherol, showing a more potent antioxidative effect in these cells [29].
The cellular benefits from γ-tocopherol supplementation in BMEC were further proven as cell cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and cellular lipid peroxidation were all significantly reduced in cells supplemented with vitamin E analogs compared to challenge alone of either DetaNO or hydrogen peroxide but generally to a greater extent in those supplemented with γ-tocopherol than α-tocopherol [29]. Interestingly, it was shown that a mixture of 10 μM each (30 μM total) of α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, and γ-tocotrienol reduced cell cytotoxicity when challenged with DetaNO to a significantly greater extent than 30 μM of α-tocopherol alone, suggesting that, indeed, a mixture of vitamin E in the presence of an ROS/RNS generator offers cellular benefits over α-tocopherol alone [29].
One of the few studies focused on vitamin E analogs in cattle used the characteristic of γ- and δ-tocopherol to reduce RNS as a major outcome variable for their study [30]. Elsasser et al. fed a diet to beef calves (211 ± 6 kg body weight) supplemented with γ-tocopherol and δ-tocopherol [30]. Protein damage due to nitrosative stress created by intravenous lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration was then measured. Calves supplemented with either α-tocopherol or a γ-tocopherol/δ-tocopherol mix had reduced cellular protein damage as measured by tyrosine nitration compared to the control calves [30]. An important consideration for this study is that the supplementation of the γ-tocopherol/δ-tocopherol mix (3850 mg/calf) was greater than that of α-tocopherol (1250 mg/calf) to compensate for the relatively faster metabolism of non-α-tocopherol analogs. The outcomes of this study are promising for the use of non-α-tocopherol analogs to reduce cellular damage due to the accumulation of RNS, which are generally cytotoxic and disrupt many cell signaling pathways [31]. Although RNS have beneficial roles in the initiation of inflammation and phagocyte microbial killing, excessive or chronic accumulation has been linked to many human health disorders and likely contributes to the excessive tissue damage of metabolically stressed animals undergoing disease [31,32].
Aside from cattle, a reduction in reactive metabolite-mediated cellular damage from tocopherol supplementation has also been shown in other ruminants. In sheep, those fed either α-tocopherol (500 mg or ~7.7 mg/kg) or γ-tocopherol (1000 mg or ~15.4 mg/kg) in late gestation had reduced serum concentrations of 8-isoprostane, a biomarker of oxidative stress, compared to control ewes starting seven days after supplementation until the final sample collection point two weeks prior to lambing [33]. Akin to results noted by Elsasser et al., who saw reduced cellular protein damage due to nitrosative stress in animals fed a non-α-tocopherol mix [30], those ewes fed the γ-tocopherol supplement had significantly less 8-isoprostane concentrations than those fed α-tocopherol, while both ewes fed either tocopherol had significantly lesser 8-isoprostane than control cows [33]. A greater ability of γ-tocopherol to reduce 8-isoprostane compared to α-tocopherol has also been noted in rats supplemented for merely three days [34]. Similarly, mice fed either γ-tocopherol or γ-tocotrienol had reductions in serum 8-isoprostane [35].
Interestingly, a human study conducted by Wiser et al. with a supplement equivalent to the tocopherol mixture used by Qu et al. in dairy cattle showed a significant reduction the accumulation of 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol, a byproduct of the reaction of γ-tocopherol and RNS (Figure 2B) [18,28]. Reductions in 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol should only occur if either supplementation of γ-tocopherol is reduced, supplementation of α-tocopherol is increased, or there is a reduction of RNS with which γ-tocopherol can react. In studies that supplement γ-tocopherol, reduction in 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol indirectly quantifies the presence of RNS. Similar reductions in 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol have also been noted in γ-tocopherol-supplemented rats [36]. As part of the same study assessing 5-nitro-γ-tocopherol, Wiser et al. conducted a safety assessment in humans when supplementing a tocopherol mixture and found no changes in complete blood counts or liver enzymes and reported no adverse health events in patients [18]. This safety profile is similar to that seen in ruminant studies. Unfortunately, assessing redox balance or oxidative stress was not an aim of the feeding trial by Qu et al. (2018) [28].
3.2. Analog Concentratiosn in Cattle
Oxidative stress around the time of calving may be exasperated by a significant drop in dry matter intake (DMI), including supplemented vitamins such as α-tocopherol. Such a reduction in vitamin intake contributes to reduced serum and liver α-tocopherol concentrations [11]. In addition, reduced liver function after calving may limit vitamin E exportation. Although liver samples for tocopherol quantification are the most accurate assessment of vitamin E status, serum concentrations are nonetheless consistently reported as a representation of total body status and may help to put changes in liver status into perspective. To account for changes in liver function around the time of calving, concentrations of vitamin E are commonly reported as a ratio with serum cholesterol to account for changes in liver function. Unfortunately, no ratios for non-α-tocopherols of vitamin E in plasma or serum have yet been reported in cattle.
Interestingly, not all vitamin E analogs fluctuate similarly across the transition period and into lactation. In serum, α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, and β-tocotrienol follow a similar pattern, increasing from a lesser amount at days −21 to 1 relative to calving to a greater plateau from 21 to 70 days in milk (DIM) [6]. Alternatively, α-tocotrienol, γ-tocotrienol, and δ-tocotrienol remain unchanged across this time period. These differences in concentration fluctuations may reflect the preference of αTTP in the liver and its capacity to export greater amounts of tocopherols as transcription of the protein increases in the liver as lactation progresses. Although assessed for a limited time frame, periparturient cows indeed have a significant increase in hepatic αTTP mRNA abundance from zero DIM to one DIM that generally plateaus through the first week of lactation but increases at a statistically significant level over the course of the first 105 DIM [6,11]. Alternatively, as diets may change by lactation stage, changes in diet ingredients may alter the relative availability of individual dietary analogs. Given the proven benefits of non-α-tocopherol analogs in other species for reducing oxidative stress, further studies should evaluate their potential for causing adverse effects and include in study outcomes their potential to reduce oxidative stress during periods when blood and liver α-tocopherol concentrations are reduced [6,16].
Parenteral injections of α-tocopherol were studied previously as an intervention to overcome the reduction in DMI and liver function of the transition period [7,8,37]. The parenteral administration of α-tocopherol has been shown to have a lesser ability to reduce disease incidence in cattle that are already adequately supplemented with α-tocopherol in the dry period; however, on farms with lower dietary supplementation, even a single parenteral injection of α-tocopherol can have significant health benefits [7,8]. Given the potential benefits of non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E, parenteral administration is an unstudied but intriguing intervention approach. The increased labor of administering injections is an obvious limitation to the use of parenteral vitamins compared to dietary supplementation; however, the ability to precisely control timing and dose of injectable vitamins lends parenteral use to more targeted supplementation. For this reason, parenteral administration may be suitable for effective applications of mixed tocopherols, such as a therapeutic for animals with an overly robust or chronic inflammatory condition or who are harmfully oxidatively stressed.
4. Inflammatory Regulation
4.1. Pro-Inflammatory Signaling
Inflammation is a carefully orchestrated balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators that must meet pathogen challenge with an adequate response to contain infection yet sufficiently controlled to prevent excessive tissue damage [1]. During the transition period, inflammation in dairy cattle can become aberrant in some animals and result in excessive inflammation or inflammation that fails to resolve in an appropriate amount of time [1]. In either case, the excessive or delayed resolution of inflammation can result in tissue damage due to increased exposure to pro-oxidants. Although inflammation should not be hindered in carrying out normal and necessary inflammatory responses, anti-inflammatory interventions can play an important part in limiting excessive damage to tissues from inflammation that has become dysregulated and damaging.
An essential control point for inflammatory responses is the vascular endothelium. Regulated leukocyte recruitment and migration to sites of infection is crucial for fighting infection, and this movement relies on a well-regulated endothelial barrier for appropriate migration. Excessive or prolonged leukocyte infiltration in response to infection due to either disproportionate leukocyte recruitment signaling or endothelial barrier breakdown, however, can result in exacerbated tissue damage beyond that of infection alone.
In vitro, the electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) system can monitor cellular monolayers for perturbations in cellular junctions. When challenged with a potent dose of DetaNO in an ECIS system, BMEC lose their monolayer barrier integrity, most likely through ROS accumulation and damage, similar to what may occur in the elevated ROS environment of the mammary gland in an early-lactation cow [29]. Both α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol, to similar extents, rescued and maintained the cellular barrier integrity. Doing so shows a protective effect of these analogs against ROS-derived cellular damage and one mechanism through which multiple tocopherols may help to regulate barrier function and cellular migration. Overall, this protection can help to regulate the inflammatory response to infection.
Studies in non-ruminant species have provided a wide range of anti-inflammatory functions of vitamin E analogs as well [38,39,40]. In RAW 264.7 murine macrophages, supplementation with α-tocotrienol, γ-tocotrienol, or δ-tocotrienol reduced expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) after endotoxin stimulation [38]. Interestingly, this response was not elicited in α-tocopherol-supplemented cells. When repeated with BALB/c mice fed individual tocotrienol supplements, serum TNF-α was again reduced in supplemented animals after LPS challenge [38].
In human models of endotoxin-induced inflammation, vitamin E analogs have also shown a capacity to reduce the expression of adhesion molecules that would otherwise contribute to the recruitment of leukocytes to the underlying tissues. In human umbilical vein endothelial cells, supplementation with δ-tocotrienol and γ-tocotrienol significantly reduced expression of genes necessary for the adhesion of leukocytes to the endothelium, namely pro-recruitment genes ICAM1, VCAM1, and SELE [40]. The likely practical outcome of this is demonstrated in rats supplemented with γ-tocopherol. When challenged with nebulized LPS, γ-tocopherol-supplemented rats had both reduced expression of pro-recruitment genes such as MIP-2, CINC-1, and MCP-1 and reduced migration of neutrophils and total leukocytes [36,39].
These examples demonstrate anti-inflammatory functions of vitamin E analogs to reduce the recruitment of leukocytes in several species and to dampen the proinflammatory response in general. Although necessary for the initial responses to infection and instances of life-stage-dependent tissue remodeling, such as dry off in cattle, reducing leukocyte recruitment to resolve prolonged or excessive inflammation may be a potential use for analogs of vitamin E as a therapeutic intervention. Despite this, little research has been undertaken in ruminants to understand the inflammatory effects of tocopherols or tocotrienols, and their impact on inflammatory regulation may go well beyond vascular barrier integrity and leukocyte recruitment.
4.2. Lipid Mediator Aberration
A significant driver of inflammation, especially in the transition period, is the alteration of the production of a class of inflammatory lipid mediators known as oxylipids [1]. Although several polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) may act as a precursor for oxylipid production, arachidonic acid metabolites, known as eicosanoids, have been the most widely profiled of such oxylipids. These metabolites are produced both enzymatically through the cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), and CYP450 pathways and non-enzymatically through interaction with a reactive metabolite.
4.2.1. Lipoxygenase
Several studies have now presented evidence that non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E can reduce the activity of LOX enzymes and, subsequently, production of leukotrienes such as leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and leukotriene C4 after an inflammatory stimulus in vitro and in vivo when compared to α-tocopherol [34,41]. Predominately produced by neutrophils, leukotrienes are important chemotactic factors and increased significantly in cattle with acute and chronic mastitis [42,43]. Increased concentration of leukotrienes during inflammatory events underscores the importance of these oxylipids in orchestrating an effective inflammatory response to infection. Persistently increased concentrations of leukotrienes, however, may lead to delayed resolution of inflammation and subsequent tissue damage. In such cases, reducing the production of leukotrienes can contribute to the resolution of inflammation and allow for tissue to heal. In a rodent model of carrageenan-stimulated inflammation, Jiang and Ames reported significant reductions in the production of LTB4 in animals dietarily supplemented with γ-tocopherol but not those supplemented with α-tocopherol after subcutaneous inflammatory stimulation [34].
4.2.2. Cytochrome P450
In the CYP450 pathway, CYP4F2, the enzyme responsible for metabolizing tocopherols and tocotrienols, shares a metabolic capacity for arachidonic acid as well, producing the lipid mediator 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) from arachidonic acid substrate. 20-HETE is generally regarded as a pro-inflammatory lipid mediator in most situations, although exceptions exist [44]. In dairy cattle primary endothelial cells, it has been shown to break down the endothelial monolayer, making its excessive production a potentially contributing factor to the onset of disease such as mastitis [45].
When human recombinant CYP4F2 microsomes were driven to metabolize either arachidonic acid alone or an equal concentration of either α-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, or γ-tocotrienol, Kuhn et al. demonstrated that the addition of γ-tocopherol and γ-tocotrienol, but not α-tocopherol, to the microsomal reaction mixture significantly reduced production of 20-HETE through substate competition [46]. When bovine-kidney-derived microsomes were assessed in the same manner, similar results were noted for γ-tocopherol in reducing the production of 20-HETE, a surprising finding considering other 20-HETE producing CYP450 enzymes were also present in the cattle-derived microsomes, diluting any reduced production of 20-HETE from CYP4F2 [46]. These findings suggest that when found at appropriate concentrations (at least greater than 1:2.5 vitamin E to arachidonic acid), there is competition for the metabolic capacity of CYP4F2 between vitamin E and arachidonic acid and that the non-α-tocopherols appear to be more competitive. Further, a reduction in 20-HETE production through tocopherol competition presents one potential pathway that increases in non-α-tocopherol supplementation and could reduce proinflammatory signaling.
4.2.3. Cyclooxygenase
The COX pathway has also been implicated as being influenced by vitamin E [47]. Dependent on cell type and the vitamin E analog of focus, vitamin E analogs show evidence of acting as both positive and negative regulators of COX-derived oxylipid production. Many groups have shown reductions in the production of prostaglandins, typically pro-inflammatory oxylipids produced from COX1 and COX2 enzymes (PTGS1 and PTGS2) [34,48,49]. The mechanism by which the effects of vitamin E analogs influence COX-derived oxylipid production remains unclear, potentially being mediated by changes in gene expression, post-transcriptional regulation, alterations in PUFA availability, or direct competition between arachidonic acid and vitamin E analogs.
In RAW 264.7 murine macrophages, α-tocotrienol and δ-tocotrienol both showed an ability to reduce the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) after stimulation with LPS, whereas α-tocopherol significantly increased production of PGE2 [49]. These results were mirrored by LPS’s stimulation of PTGS2 transcription, which was ameliorated by α-tocotrienol, δ-tocotrienol, and γ-tocotrienol but not by α-tocopherol [49]. This suppression of PTGS2 induction was also noted in LPS-challenged primary murine macrophages supplemented with γ-tocotrienol [48].
Beyond the impact of changes in transcript expression on oxylipid production, γ-tocopherol and δ-tocopherol but not α-tocopherol reduced COX2 activity in a dose-dependent manner in human A549 lung epithelial cells, albeit through an unexpected mechanism. In this study, the breakdown of tocopherols and tocotrienols was first blocked with an inhibitor of CYP4F2, reducing the production of their downstream metabolites. When doing so, the authors found a reduced inhibitory activity of the vitamin E treatment on PGE2 production from COX compared to treatments without the inhibitor, which would have had increased concentrations of post-CYP4F2 vitamin E metabolites [50]. This suggests that post-CYP4F2 metabolites of vitamin E analogs have greater bioactivity to inhibit COX activity than their precursor molecules. As Jiang et al. employed an incomplete inhibitor of CYP4F2 (sesamin), had a complete inhibitor been assessed, COX inhibition may have been prevented altogether [50,51]. Jiang et al. showed that specifically 9′-COOH and 13′-COOH, early metabolites of analog metabolism, were responsible for inhibiting COX activity by directly competing with arachidonic acid for COX metabolism (Figure 1) [50].
Evidence of significant activity due to post-CYP4F2 vitamin E metabolites goes well beyond the production of PGE2, however. The initial breakdown product of δ-tocopherol, δ-13′-COOH, reduced the production of LTB4 in human HL-60 cells, an activity which was additionally validated for both δ-tocopherol and δ-13′-COOH in human primary neutrophils [41]. Specifically, this decrease in production was due to a reduction in the activity of the 5LOX enzyme.
The activities of downstream vitamin E analog metabolites will be necessary to consider if research aims to further investigate uses of CYP4F2 inhibitors, a potential necessity for the effectiveness of future mixed tocopherol supplementation. Supplementing a CYP4F2 inhibitor such as sesamin alongside an analog mix would help to reduce the amount of non-α-tocopherol analogs necessary to supplement to overcome their preferential metabolism [52]. The aforementioned research on COX inhibition, however, shows that inhibiting CYP4F2 may reduce some anti-inflammatory properties of vitamin E analogs. The competing properties of pre- and post-CYP4F2 metabolites means that practical supplementation in cattle would need to determine which specific balance of analog function is most beneficial to animals and will add a layer of complexity to research.
5. Safety of In Vivo Supplementation
Non-α-tocopherol analogs of vitamin E are used to treat, mitigate, and prevent inflammatory conditions in non-bovine species. Nevertheless, limited research has sought to understand such applications in dairy cattle [23]. One of the reasons for this is a justified concern for causing adverse effects by supplementing vitamin E analogs, especially tocotrienols [10]. In mice injected subcutaneously with δ-tocotrienol and γ-tocotrienol, doses above 200 mg/kg of body weight, an amount 4–20 times greater than that used for most in vivo studies, caused severe skin irritation. Aside from this cutaneous reaction, mice tolerated 200 mg/kg of δ-tocotrienol and γ-tocotrienol without measurable or visible impact on internal organs [53].
A human profiling study showed that individuals with greater plasma γ-tocopherol had reduced plasma α-tocopherol and β-carotene concentrations in addition to increased plasma F2-isoprostane [54], detailing correlation and not direct causation. In this study by Abdulla et al. the group of participants containing those with the greatest plasma γ-tocopherol concentrations had >2.47 μg/mL, a concentration similar to that of cattle fed γ-tocopherol by Qu et al., which averaged between 2 and 3.5 μg/mL after dietary supplementation [26,54]. Similarities between these studies suggest comparisons; however, as a profile of a general human population rather than a clinical trial, it cannot be determined if, in humans, γ-tocopherol directly increased oxidative stress and reduced vitamin concentrations or was associated with an unknown confounding variable, such as patient diet. Certainly, many studies have shown that the dose at which non-α-tocopherols cause in vitro cytotoxic effects is much lower in various cell types than that of α-tocopherol; the concentrations at which non-α-tocopherol analogs have bioactivity, however, are consistently lower than that of α-tocopherol as well [49,55,56].
Although cytotoxicity of all vitamin E analogs should be assessed, there has not yet been any indication of detrimental effects of non-α-tocopherols supplemented dietarily in ruminants [22,28,33]. Supplementation of tocopherol mixes in goats, sheep, and cattle up to at least 18 mg/kg of total tocopherol have not revealed adverse outcomes nor increases in oxidative stress or immune suppression (Table 1) [22,30,33]. Vitamin mixes containing significant amounts of tocotrienols or the parenteral administration of non-α-tocopherol have not yet been evaluated in ruminants. Promisingly, parenteral injection of α-tocopherol has not been associated with injection site hypersensitivity reactions or other adverse effects [8,37].

Table 1.
Ruminant feeding trials using tocopherol mixes as dietary supplements, supplement parameters, and major outcomes 1.
Thus far, the limited number of feeding trials in cattle using mixed tocopherols have not garnered the same positive results as those seen in humans. Although feeding mixed tocopherols to beef calves slightly reduced LPS-induced liver inflammation and oxidant damage, supplementing mid-lactation dairy cows with a tocopherol mix did not elicit as beneficial of results [28,30]. Mid-lactation cows were studied by Qu et al. to avoid the dramatic shifts of transition period inflammatory responses [28]. When supplemented with a tocopherol mix at a very similar dose to that of a human supplementation trial (~10 mg/kg of body weight), neutrophils of mid-lactations cows challenged with LPS did not show a difference in inflammatory gene expression between those from supplemented and un-supplemented cows. This differs from the results of the related human trial in which LPS stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) had reduced interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α expression when derived from supplemented humans compared to un-supplemented [18]. A lack of differential response to LPS may be due to the difference in response to LPS by neutrophils compared to PBMCs.
Given the predisposition for transition cattle to face dysfunctional inflammation compared to mid-lactation cows, a more practical study may focus on animals in the transition period when inflammatory responses to LPS may indeed be aberrant and potentially excessive. Alternatively, the species’ different responses may be explained by blood γ-tocopherol concentrations being about one-third less in supplemented cattle than that of humans despite similar supplementation concentrations, suggesting absorption, metabolism, or storage of vitamin E may differ significantly between the two species.
Several reasons may explain why cattle have less of an increase in circulating tocopherols despite similar supplementation to humans. One such explanation is the vehicle used for supplementation that may influence gastrointestinal bioavailability. Additionally, as analogs of vitamin E are packaged into lipoproteins, differential liver activity, likely lower in cattle compared to humans, would result in a lower release from bovine liver compared to humans. Because of this, it may be necessary to supplement vitamin E analog mixes either in greater concentrations to cattle or to use parenteral administration, avoiding any reductions in gastrointestinal bioavailability.
6. Future Directions
The use of vitamin E analogs in other mammalian species has revealed that not all vitamin E analogs have equivalent biological activities. Each has unique antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities that vary by species, cell type, and other physiological conditions. Rather than trying to identify a single best analog to supplement alongside α-tocopherol, taking a broader approach to supplementation with a mixture of analogs likely offers the greatest benefits. Based upon this and the disproportionate prevalence of oxidative stress and dysfunctional inflammation at transition, the use of a mixed analog supplement should be evaluated for targeted supplementation. Peak plasma concentrations tocopherols are reached after only five days of feeding in adult dairy cattle and just 38 hours after oral dosing of Nelore steers [26,57]. This suggests that long-term dietary supplementation is likely not necessary. Peak concentrations of blood α-tocopherol have been reported at similarly short periods after parenteral administration, notably after seven days when injected subcutaneously or only one to two days if given intramuscularly [8,58]. Unfortunately, a time course for liver accumulation was not undertaken in these studies.
Based on the kinetics of α-tocopherol, results from LeBlanc et al. and Jensen et al. suggest that supplementing vitamin E analog mixes would likely reach peak blood concentrations in a short period of time [8,58]. This indeed makes it realistic to use feeding or parenteral injection of vitamin E analogs in a targeted manner to animals in the transition period or early lactation when concentrations of α-tocopherol are typically lower than average in blood and tissues. Thus, ample reason exists to move forward with greater use of vitamin E analogs in disease models to begin to discern what benefits they may afford to dairy cattle or what harm could be caused if inflammatory responses are overly constrained. With reported safety at specific doses, in vivo supplementation could begin while monitoring for adverse effects to determine what impacts analog mixes may have on the redox balance or inflammation.
The most significant obstacle that this research will face is the preferential metabolism of non-α-tocopherol analogs. Without interventions to slow metabolism, benefits to supplementation will be limited by the rapid breakdown of non-α-tocopherol analogs. The previously mentioned inhibitor of CYP4F2, sesamin, has been used in human clinical trials and shown to increase the circulating concentrations of non-α-tocopherols [59]. Given that the relative contribution of the post-CYP4F2 metabolites of vitamin E analogs is only beginning to be uncovered, utilizing an incomplete inhibitor such as sesamin may reduce the chances of fully inhibiting the production of these downstream metabolites and preventing their potentially beneficial activities. For these reasons, supplementation of sesamin, sesame oils, or other partial CYP4F2 inhibitors alongside a vitamin E analog mix is likely to provide additive beneficial effects.
7. Conclusions
The use of vitamin E analogs as dietary supplements in cattle remains relatively unexplored despite evidence that such analogs may be able to contribute to the antioxidant potential and positive growth parameters of cattle and calves. Mixed tocopherols have been supplemented safely in both cows, calves, and other ruminant species, justifying further research into their safety and biological activities in dairy cattle. With an ever greater emphasis on the prevention of disease and non-antimicrobial based therapeutics, analogs of vitamin E present an intriguing potential disease mitigation strategy.
Funding
This work was funded by Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grants Program (2017-38420-26759 and 2017-67015-26676), the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, an endowment from the Matilda R. Wilson Fund (Detroit, MI, USA), and the Michigan Alliance for Animal Agriculture.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge the late Lorraine M. Sordillo, within whose lab this work was performed and whose dedication to unraveling the mystery of oxylipids in cattle spawned the research careers of now pioneers in the field. The author would also like to acknowledge Jaimie Strickland for assistance with editing and hours of discussion on the intersection of oxylipids, oxidative stress, and ruminant nutrition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Sordillo, L.M.; Mavangira, V. The nexus between nutrient metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation in transition cows. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Aitken, S.L. Impact of oxidative stress on the health and immune function of dairy cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC, National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle: Seventh Revised Edition; The National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; 405p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, I. Reevaluation of vitamin E supplementation of dairy cows: Bioavailability, animal health and milk quality. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2012, 6, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.P.; Stabel, J.R. Decreased plasma retinol, alpha-tocopherol, and zinc concentration during the periparturient period: Effect of milk fever. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, H.; Danicke, S.; Meyer, U.; Rehage, J.; Frank, J.; Sauerwein, H. Tocopherols and tocotrienols in serum and liver of dairy cows receiving conjugated linoleic acids or a control fat supplement during early lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7034–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erskine, R.J.; Bartlett, P.C.; Herdt, T.; Gaston, P. Effects of parenteral administration of vitamin E on health of periparturient dairy cows. JAVMA-J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 211, 466–469. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, S.J.; Duffield, T.F.; Leslie, K.E.; Bateman, K.G.; TenHag, J.; Walton, J.S.; Johnson, W.H. The effect of prepartum injection of vitamin E on health in transition dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, J.S.; Weiss, W.P.; Todhunter, D.A.; Smith, K.L.; Schoenberger, P.S. Bovine neutrophil responses to parenteral vitamin E. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Ozer, N.K. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, S.; Miyaji, M.; Nakano, M.; Ishizaki, H.; Matsuyama, H.; Katoh, K.; Roh, S.G. Changes in the expression of alpha-tocopherol-related genes in liver and mammary gland biopsy specimens of peripartum dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5277–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.J.; Mavangira, V.; Gandy, J.C.; Sordillo, L.M. Production of 15-F2t-isoprostane as an assessment of oxidative stress in dairy cows at different stages of lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9287–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmolz, L.; Birringer, M.; Lorkowski, S.; Wallert, M. Complexity of vitamin E metabolism. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, R.J.; Nielen, M.; Newbold, J.R.; Jansen, E.H.; Jelinek, H.F.; van Werven, T. Vitamin E supplementation during the dry period in dairy cattle. Part II: Oxidative stress following vitamin E supplementation may increase clinical mastitis incidence postpartum. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5696–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, R.J.; Nielen, M.; Stegeman, J.A.; Dobbelaar, P.; Newbold, J.R.; Jansen, E.H.; van Werven, T. Vitamin E supplementation during the dry period in dairy cattle. Part I: Adverse effect on incidence of mastitis postpartum in a double-blind randomized field trial. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5684–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal-Eldin, A.; Appelqvist, L.A. The chemistry and antioxidant properties of tocopherols and tocotrienols. Lipids 1996, 31, 671–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbank, A.J.; Duran, C.G.; Pan, Y.; Burns, P.; Jones, S.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, C.; Jenkins, S.; Wells, H.; Alexis, N.; et al. Gamma tocopherol-enriched supplement reduces sputum eosinophilia and endotoxin-induced sputum neutrophilia in volunteers with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1231–1238.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiser, J.; Alexis, N.E.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, W.; Robinette, C.; Roubey, R.; Peden, D.B. In vivo gamma-tocopherol supplementation decreases systemic oxidative stress and cytokine responses of human monocytes in normal and asthmatic subjects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Christen, S.; Shigenaga, M.K.; Ames, B.N. gamma-tocopherol, the major form of vitamin E in the US diet, deserves more attention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, T.J.; Parker, R.S. Influence of major structural features of tocopherols and tocotrienols on their omega-oxidation by tocopherol-omega-hydroxylase. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, A.; Arita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kiyose, C.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Affinity for alpha-tocopherol transfer protein as a determinant of the biological activities of vitamin E analogs. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, K.D.; Sabow, A.B.; Aghwan, Z.A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Samsudin, A.A.; Alimon, A.R.; Sazili, A.Q. Serum fatty acids, biochemical indices and antioxidant status in goats fed canola oil and palm oil blend. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E: Metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities and their role in disease prevention and therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, E.; Pei, R.; Guo, Y.; Masterjohn, C.; Ballard, K.D.; Taylor, B.A.; Taylor, A.W.; Traber, M.G.; Volek, J.S.; Bruno, R.S. Greater gamma-tocopherol status during acute smoking abstinence with nicotine replacement therapy improved vascular endothelial function by decreasing 8-iso-15(S)-prostaglandin F2α. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.H.; Kastelic, J.; Hart, E.B. The effect of mixed tocopherols on milk and butterfat production of the dairy cow. J. Nutr. 1948, 36, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y. The Effect of Feeding Mixed Tocopherl Oil on Body Accumulation and Immune Cell Functions in Lactating Holstein Dairy Cows. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, J.D.; Hill, T.M.; Dennis, T.S.; Suarez-Mena, F.X.; Hu, W.; Kahl, S.; Elsasser, T.H. Effects of mixed tocopherols added to milk replacer and calf starter on intake, growth, and indices of stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 9769–9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Elsasser, T.H.; Kahl, S.; Garcia, M.; Scholte, C.M.; Connor, E.E.; Schroeder, G.F.; Moyes, K.M. The effects of feeding mixed tocopherol oil on whole-blood respiratory burst and neutrophil immunometabolic-related gene expression in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4332–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.J.; Sordillo, L.M. Vitamin E analogs limit in vitro oxidant damage to bovine mammary endothelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7154–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsasser, T.H.; Kahl, S.; Lebold, K.M.; Traber, M.G.; Shaffer, J.; Li, C.-J.; Block, S. Short-term alpha- or gamma-delta-enriched tocopherol oil supplementation differentially affects the expression of proinflammatory mediators: Selective impacts on characteristics of protein tyrosine nitration in vivo. Vet. Sci. Dev. 2013, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, L.; Blais, S.; Desrosiers, C.; Zhao, X.; Lacasse, P. Nitric oxide production during endotoxin-induced mastitis in the cow. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2574–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasimanickam, R.K.; Kasimanickam, V.R. Effect of tocopherol supplementation on serum 8-epi-prostaglandin F2 alpha and adiponectin concentrations, and mRNA expression of PPARgamma and related genes in ovine placenta and uterus. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Ames, B.N. Gamma-tocopherol, but not alpha-tocopherol, decreases proinflammatory eicosanoids and inflammation damage in rats. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Itoh, N.; Hayakawa, M.; Piga, R.; Cynshi, O.; Jishage, K.; Niki, E. Lipid peroxidation induced by carbon tetrachloride and its inhibition by antioxidant as evaluated by an oxidative stress marker, HODE. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 208, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, M.L.; Wagner, J.G.; Kala, A.; Mills, K.; Wells, H.B.; Alexis, N.E.; Lay, J.C.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; et al. Vitamin E, gamma-tocopherol, reduces airway neutrophil recruitment after inhaled endotoxin challenge in rats and in healthy volunteers. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 60, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, G.C.; Monteiro, P.L., Jr.; Prata, A.B.; Guardieiro, M.M.; Pinto, D.A.; Fernandes, G.O.; Wiltbank, M.C.; Santos, J.E.; Sartori, R. Effect of injectable vitamin E on incidence of retained fetal membranes and reproductive performance of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2437–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Reis, J.C.; Papasian, C.J.; Morrison, D.C.; Qureshi, N. Tocotrienols inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages of female mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.G.; Birmingham, N.P.; Jackson-Humbles, D.; Jiang, Q.; Harkema, J.R.; Peden, D.B. Supplementation with gamma-tocopherol attenuates endotoxin-induced airway neutrophil and mucous cell responses in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 68, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muid, S.; Froemming, G.R.; Rahman, T.; Ali, A.M.; Nawawi, H.M. Delta- and gamma-tocotrienol isomers are potent in inhibiting inflammation and endothelial activation in stimulated human endothelial cells. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 31526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Yin, X.; Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E and 13′-carboxychromanol, a long-chain vitamin E metabolite, inhibit leukotriene generation from stimulated neutrophils by blocking calcium influx and suppressing 5-lipoxygenase activity, respectively. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, P.; Bureau, F.; Degand, G.; Lekeux, P. Imbalance between lipoxin A4 and leukotriene B4 in chronic mastitis-affected cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavangira, V.; Gandy, J.C.; Zhang, C.; Ryman, V.E.; Daniel Jones, A.; Sordillo, L.M. Polyunsaturated fatty acids influence differential biosynthesis of oxylipids and other lipid mediators during bovine coliform mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6202–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.J.; Mavangira, V.; Sordillo, L.M. Invited review: Cytochrome P450 enzyme involvement in health and inflammatory-based diseases of dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavangira, V.; Brown, J.; Gandy, J.C.; Sordillo, L.M. 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid alters endothelial cell barrier integrity independent of oxidative stress and cell death. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020, 149, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.J.; Sordillo, L.M. Inhibition of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid biosynthesis by vitamin E analogs in human and bovine cytochrome P450 microsomes. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, S.M.; Leonard, S.W.; Taylor, A.W.; Birringer, M.; Edson, K.Z.; Rettie, A.E.; Traber, M.G. omega-Hydroxylation of phylloquinone by CYP4F2 is not increased by alpha-tocopherol. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Brown, J.M.; Chung, S. Gamma-tocotrienol attenuates the aberrant lipid mediator production in NLRP3 inflammasome-stimulated macrophages. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 58, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, M.L.; Abdul Hafid, S.R.; Cheng, H.M.; Nesaretnam, K. Tocotrienols suppress proinflammatory markers and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages. Lipids 2009, 44, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Yin, X.; Lill, M.A.; Danielson, M.L.; Freiser, H.; Huang, J. Long-chain carboxychromanols, metabolites of vitamin E, are potent inhibitors of cyclooxygenases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20464–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Hodgson, J.M.; Clarke, M.W.; Indrawan, A.P.; Barden, A.E.; Puddey, I.B.; Croft, K.D. Inhibition of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid synthesis using specific plant lignans: In vitro and human studies. Hypertension 2009, 54, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Toyoshima, K.; Yamashita, K. Dietary sesame seeds elevate alpha- and gamma-tocotrienol concentrations in skin and adipose tissue of rats fed the tocotrienol-rich fraction extracted from palm oil. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2892–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.N.; Pessu, R.L.; Chakraborty, K.; Villa, V.; Lombardini, E.; Ghosh, S.P. Acute toxicity of subcutaneously administered vitamin E isomers delta- and gamma-tocotrienol in mice. Int. J. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, K.A.; Um, C.Y.; Gross, M.D.; Bostick, R.M. Circulating gamma-Tocopherol Concentrations Are Inversely Associated with Antioxidant Exposures and Directly Associated with Systemic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Adults. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazlan, M.; Sue Mian, T.; Mat Top, G.; Zurinah Wan Ngah, W. Comparative effects of alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocotrienol against hydrogen peroxide induced apoptosis on primary-cultured astrocytes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 243, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, C.C.; Parker, R.S. The cytotoxicity of vitamin E is both vitamer- and cell-specific and involves a selectable trait. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3335–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borher, J.R.; Goncalves, L.A.; de Felicio, P.E. alpha- and gamma-tocopherol levels in Nelore steer blood plasma after a single oral treatment of soybean oil deodorizer distillate (SODD). Meat Sci. 2002, 61, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.K.; Lashkari, S.; Kristensen, N.B. Pharmacokinetics of alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers in plasma and milk of cows following a single dose injection of all-rac-alpha-tocopheryl acetate. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Kang, Y.P.; Wang, N.H.; Jou, H.J.; Wang, T.A. Sesame ingestion affects sex hormones, antioxidant status, and blood lipids in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).