The Impact of Low-Temperature Inactivation of Protease AprX from Pseudomonas on Its Proteolytic Capacity and Specificity: A Peptidomic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of the LTI Condition
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Peptide Extraction
2.5. LC-MS/MS-Based Peptidomic Analysis
2.6. Peptide and Protein Identification and Quantification
2.7. Data Analysis
2.8. Enzyme Predictions
2.9. Frequency of Amino Acids in the P1 and P1′ Position
2.10. Bitterness Predictions
3. Results
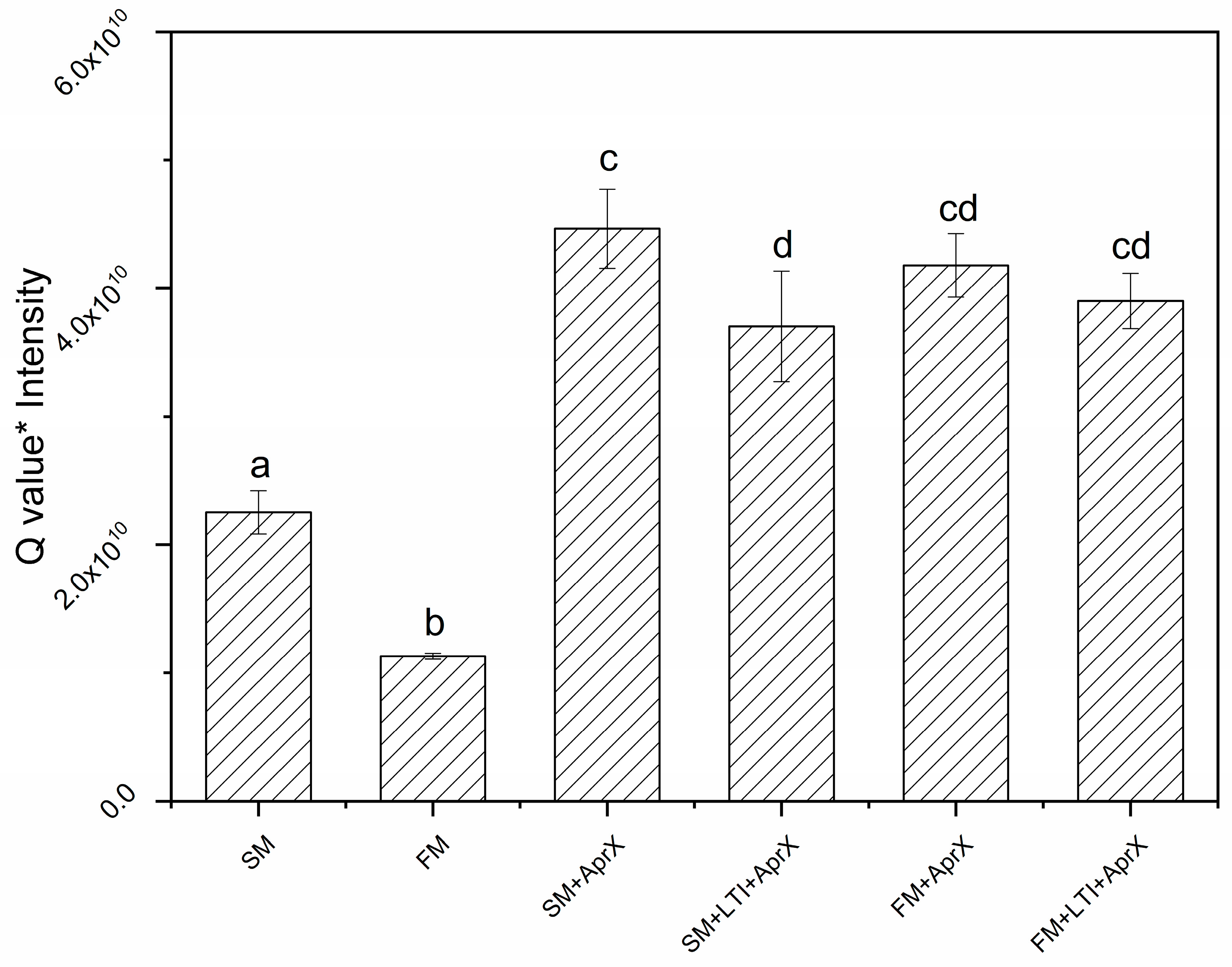
3.1. Determination of Appropriate LTI Conditions
3.2. Proteins Being Hydrolyzed
3.3. Peptides Formed by AprX
3.3.1. Peptide Mapping
3.3.2. Cleavage at P1 and P1′ Positions
3.4. Effects of LTI
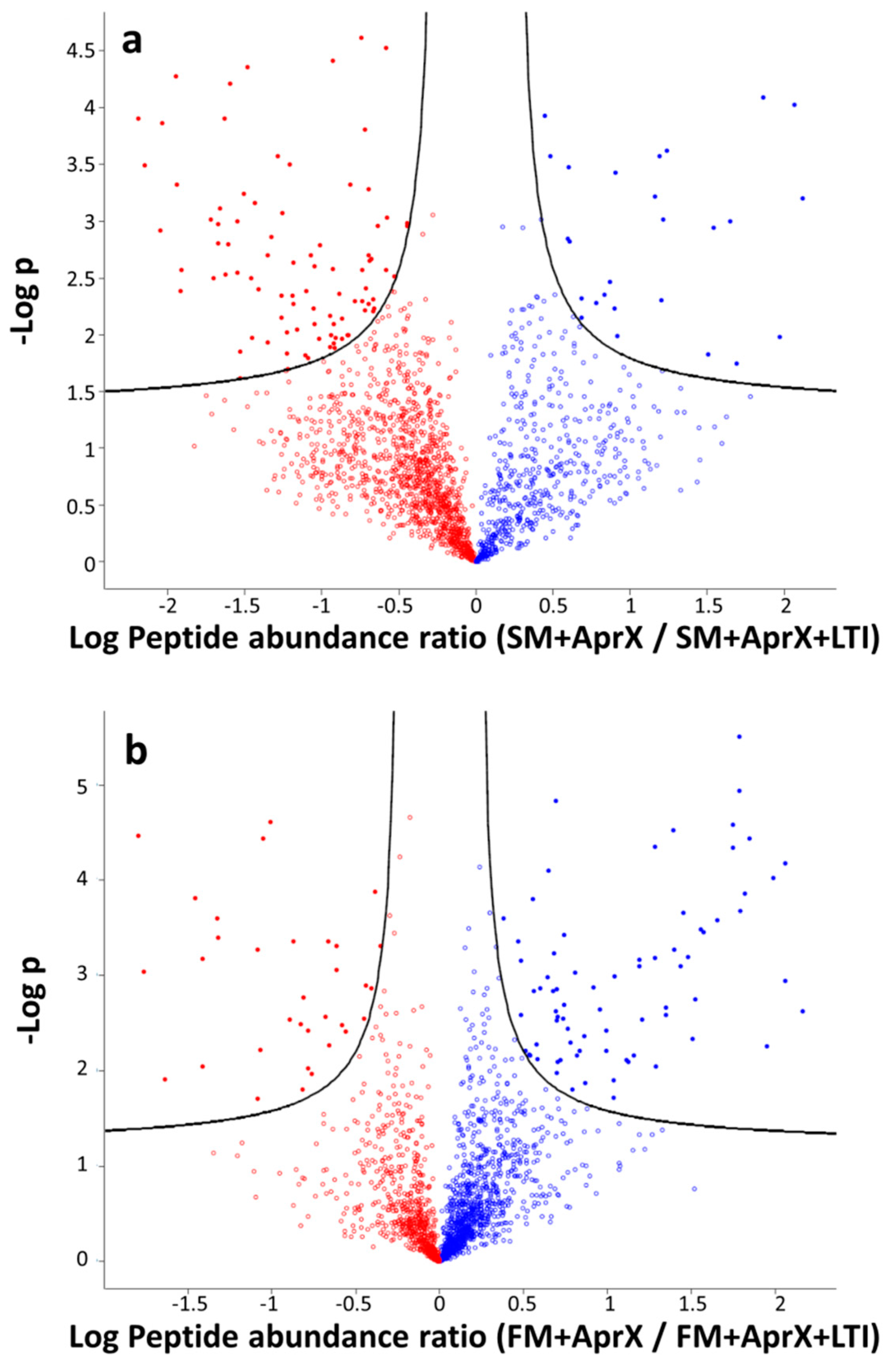
3.4.1. Comparison of Peptide Profiles
3.4.2. Bitterness Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sørhaug, T.; Stepaniak, L. Psychrotrophs and Their Enzymes in Milk and Dairy Products: Quality Aspects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decimo, M.; Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M. Characterization of Gram-Negative Psychrotrophic Bacteria Isolated from Italian Bulk Tank Milk. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M2081–M2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Liu, T.; Flint, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, G.; He, G. Psychrotrophic Bacterial Populations in Chinese Raw Dairy Milk. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Neubeck, M.; Baur, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Stoeckel, M.; Kranz, B.; Stressler, T.; Fischer, L.; Hinrichs, J.; Scherer, S.; Wenning, M. Biodiversity of Refrigerated Raw Milk Microbiota and Their Enzymatic Spoilage Potential. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 211, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bijl, E.; Hettinga, K. Destabilization of UHT Milk by Protease AprX from Pseudomonas Fluorescens and Plasmin. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, M.; Lidolt, M.; Stressler, T.; Fischer, L.; Wenning, M.; Hinrichs, J. Heat Stability of Indigenous Milk Plasmin and Proteases from Pseudomonas: A Challenge in the Production of Ultra-High Temperature Milk Products. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, V.; Xiao, Y. The Shelf Life of Heat-Treated Dairy Products. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 125, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbairn, D.J.; Law, B.A. Proteinases of Psychrotrophic Bacteria: Their Production, Properties, Effects and Control. J. Dairy Res. 1986, 53, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglinière, F.; Matéos, A.; Tanguy, G.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Rousseau, F.; Robert, B.; Beaucher, E.; Gaillard, J.L.; Amiel, C. Proteolysis of Ultra High Temperature-Treated Casein Micelles by AprX Enzyme from Pseudomonas Fluorescens F Induces Their Destabilisation. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 31, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, N.A.; Carraro, L.; Fasolato, L.; Balzan, S.; Lucchini, R.; Novelli, E.; Cardazzo, B. Characterisation of the Thermostable Protease AprX in Strains of Pseudomonas Fluorescens and Impact on the Shelf-Life of Dairy Products: Preliminary Results. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2016, 5, 6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matéos, A.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Baglinière, F.; Jardin, J.; Gaucheron, F.; Dary, A.; Humbert, G.; Gaillard, J.-L. Proteolysis of Milk Proteins by AprX, an Extracellular Protease Identified in Pseudomonas LBSA1 Isolated from Bulk Raw Milk, and Implications for the Stability of UHT Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 49, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schokker, E.P.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Mechanism and Kinetics of Inactivation at 40–70 °C of the Extracellular Proteinase from Pseudomonas Fluorescens 22F. J. Dairy Res. 1998, 65, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barach, J.T.; Adams, D.M.; Speck, M.L. Stabilization of a Psychrotrophic Pseudomonas Protease by Calcium against Thermal Inactivation in Milk at Ultrahigh Temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barach, J.T.; Adams, D.M.; Speck, M.L. Mechanism of Low Temperature Inactivation of a Heat-Resistant Bacterial Protease in Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1978, 61, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, F.B.; Adams, D.M.; Speck, M.L. Inactivation of Heat Resistant Proteases in Normal Ultra-High Temperature Sterilized Skim Milk by a Low Temperature Treatment. J. Dairy Sci. 1978, 61, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.; Klostermeyer, H. Heat Inactivation of Exogenous Proteinases from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Z. Lebensm.-Unters. Forsch. 1984, 179, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diermayr, P.; Kroll, S.; Klostermeyer, H. Mechanisms of Heat Inactivation of a Proteinase from Pseudomonas Fluorescens Biotype I. J. Dairy Res. 1987, 54, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, C.; Rentschler, E.; Krewinkel, M.; Merz, M.; von Neubeck, M.; Wenning, M.; Scherer, S.; Stoeckel, M.; Hinrichs, J.; Stressler, T. Thermostability of Peptidases Secreted by Microorganisms Associated with Raw Milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 56, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, F.M. Lipases and Proteinases in Milk. Occurence, Heat Inactivation and Their Importance for the Keeping Quality of Milk Products. Neth. Milk Dairy J. 1983, 1, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Rauh, V.M.; Sundgren, A.; Bakman, M.; Ipsen, R.; Paulsson, M.; Larsen, L.B.; Hammershoj, M. Plasmin Activity as a Possible Cause for Age Gelation in UHT Milk Produced by Direct Steam Infusion. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 38, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Jansson, T.; Le, T.T.; Jensen, S.; Eggers, N.; Rauh, V.; Sundekilde, U.K.; Sørensen, J.; Andersen, H.J.; Bertram, H.C. Correlation between Sensory Properties and Peptides Derived from Hydrolysed-Lactose UHT Milk during Storage. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 68, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, H.R.; Zadow, J.G. The Effect of Low-Temperature-Inactivation Treatment on Age Gelation of UHT Whole Milk. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1985, 40, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Kocak, H.R.; Zadow, J.G. The Effect of Lactose Hydrolysis and Subsequent Low-Temperature-Inactivation Treatment on Age Gelation of UHT Whole Milk. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1989, 44, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Cao, X.; Yue, X. Peptidomics as a Tool to Analyze Endogenous Peptides in Milk and Milk-Related Peptides. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, D.C.; Citerne, F.; Tian, T.; Silva, V.L.M.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Frese, S.A.; Robinson, R.C.; Mills, D.A.; Barile, D. Peptidomic Analysis Reveals Proteolytic Activity of Kefir Microorganisms on Bovine Milk Proteins. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Toro, M.; Nielsen, S.D.-H.; Kragh, M.L.; Xiao, Y.; Hansen, L.T.; Rauh, V.; Wiking, L.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B. Peptidomic Fingerprints of Stored UHT Milk Inoculated with Protease Extracts from Different Pseudomonas Strains Relative to AprX Expression and Visible Spoilage. Dairy 2023, 4, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, S.; Pica, V.; Masotti, F.; Cattaneo, S.; Brasca, M.; de Noni, I.; Silvetti, T. Proteolytic Traits of Psychrotrophic Bacteria Potentially Causative of Sterilized Milk Instability: Genotypic, Phenotypic and Peptidomic Insight. Foods 2021, 10, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaucher, I.; Tanguy, G.; Fauquant, J.; Jardin, J.; Rousseau, F.; Robert, B.; Madec, M.N.; Gaucheron, F. Proteolysis of Casein Micelles by Pseudomonas Fluorescens CNRZ 798 Contributes to the Destabilisation of UHT Milk during Its Storage. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2011, 91, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.M.; Barach, J.T.; Speck, M.L. Effect of Psychrotrophic Bacteria from Raw Milk on Milk Proteins and Stability of Milk Proteins to Ultrahigh Temperature Treatment. J. Dairy Sci. 1976, 59, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, P.; Brasca, M.; Rosi, V.; Morandi, S.; Ferranti, P.; Picariello, G.; Pellegrino, L. Bacterial Proteolysis of Casein Leading to UHT Milk Gelation: An Applicative Study. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Deng, Y.; Tu, Y.; Niu, H.; Cai, W.; Han, X. Whey Protein Influences the Production and Activity of Extracellular Protease from Pseudomonas Fluorescens W3. LWT 2022, 154, 112865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingess, K.A.; De Waard, M.; Boeren, S.; Vervoort, J.; Lambers, T.T.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Hettinga, K. Human Milk Peptides Differentiate between the Preterm and Term Infant and across Varying Lactational Stages. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3769–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Boeren, S.; de Vries, S.C.; van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Filter-Aided Sample Preparation with Dimethyl Labeling to Identify and Quantify Milk Fat Globule Membrane Proteins. J. Proteom. 2011, 75, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant Enables High Peptide Identification Rates, Individualized p.p.b.-Range Mass Accuracies and Proteome-Wide Protein Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, I.; Hine, B.; Smolenksi, G.; Hettinga, K.; Zhang, L.; Wheeler, T.T. Proteomics Data in Support of the Quantification of the Changes of Bovine Milk Proteins during Mammary Gland Involution. Data Brief 2016, 8, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus Computational Platform for Comprehensive Analysis of (Prote)Omics Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance Analysis of Microarrays Applied to the Ionizing Radiation Response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Guerrero, A.N.; Davey, N.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Shields, D.C.; Khaldi, N. EnzymePredictor: A Tool for Predicting and Visualizing Enzymatic Cleavages of Digested Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 6056–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, I.; Berger, A. On the Size of the Active Site in Proteases. I. Papain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1967, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ney, K.H. Voraussage Der Bitterkeit von Peptiden Aus Deren Aminosäurezu-Sammensetzung. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1971, 147, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, T.; Jensen, H.B.; Sundekilde, U.K.; Clausen, M.R.; Eggers, N.; Larsen, L.B.; Ray, C.; Andersen, H.J.; Bertram, H.C. Chemical and Proteolysis-Derived Changes during Long-Term Storage of Lactose-Hydrolyzed Ultrahigh-Temperature (UHT) Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11270–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, B.; Schäfer, J.; Atamer, Z.; Hinrichs, J. The Heat Stability of Indigenous and Bacterial Enzymes in Milk. In Agents of Change; Food Engineering Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglinière, F.; Tanguy, G.; Salgado, R.L.; Jardin, J.; Rousseau, F.; Robert, B.; Harel-Oger, M.; Vanetti, M.C.D.; Gaucheron, F. Ser2 from Serratia Liquefaciens L53: A New Heat Stable Protease Able to Destabilize UHT Milk during Its Storage. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.C.; Guerrero, A.; Parker, E.A.; Garay, L.A.; Bhandari, A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Barile, D.; German, J.B. Peptidomic Profile of Milk of Holstein Cows at Peak Lactation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 62, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.C.; Weinborn, V.; de Moura Bell, J.M.L.N.; Wang, M.; Parker, E.A.; Guerrero, A.; Hettinga, K.A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; German, J.B.; Barile, D. Comprehensive Peptidomic and Glycomic Evaluation Reveals That Sweet Whey Permeate from Colostrum Is a Source of Milk Protein-Derived Peptides and Oligosaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Fox, P.F. Heat-Induced Changes in Casein, Including Interactions with Whey Proteins. In Heat-Induced Changes in Milk; International Diary Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 1995; pp. 86–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ebner, J.; Baum, F.; Pischetsrieder, M. Identification of Sixteen Peptides Reflecting Heat and/or Storage Induced Processes by Profiling of Commercial Milk Samples. J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, B.A.; Andrews, A.T.; Sharpe, M.E. Gelation of Ultra-High-Temperature-Sterilized Milk by Proteases from a Strain of Pseudomonas Fluorescens Isolated from Raw Milk. J. Dairy Res. 1977, 44, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, P.; Rosi, V.; Fortina, M.G.; Sindaco, M.; Ricci, G.; Pellegrino, L. Biochemical, Microbiological, and Structural Evaluations to Early Detect Age Gelation of Milk Caused by Proteolytic Activity of Pseudomonas Fluorescens. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeren, T.H.M.; van Riel, J.A.M. Milk Proteinase, Its Isolation and Action of Alpha 2-and Beta-Casein. Milchwissenschaft 1979, 34, 528–531. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, C. Structure and Stability of Bovine Casein Micelles. In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 43, pp. 63–151. ISBN 0065-3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuknytė, M.; Decimo, M.; Colzani, M.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M.; Cattaneo, S.; Aldini, G.; De Noni, I. Extracellular Thermostable Proteolytic Activity of the Milk Spoilage Bacterium Pseudomonas Fluorescens PS19 on Bovine Caseins. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4188–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, F.A.; Dell’Aica, M.; Sickmann, A.; Zahedi, R.P. Why Phosphoproteomics Is Still a Challenge. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Z.; Du, M.; Bai, Y. Purification and Properties of a Heat-Stable Enzyme of Pseudomonas Fluorescens Rm12 from Raw Milk. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Uluko, H.; Liu, L.; Pang, X.; Lv, J. Investigation of Protease Production by Pseudomonas Fluorescens BJ-10 and Degradation on Milk Proteins. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, D.C.; Smink, C.J.; Robinson, R.C.; Tian, T.; Guerrero, A.; Parker, E.A.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Hettinga, K.A.; Underwood, M.A.; Lebrilla, C.B. Endogenous Human Milk Peptide Release Is Greater after Preterm Birth than Term Birth1–3. J. Nutr. 2014, 145, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’donoghue, A.J.; Eroy-Reveles, A.A.; Knudsen, G.M.; Ingram, J.; Zhou, M.; Statnekov, J.B.; Greninger, A.L.; Hostetter, D.R.; Qu, G.; Maltby, D.A. Global Identification of Peptidase Specificity by Multiplex Substrate Profiling. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Boeren, S.; Zhao, L.; Bijl, E.; Hettinga, K. The Impact of Low-Temperature Inactivation of Protease AprX from Pseudomonas on Its Proteolytic Capacity and Specificity: A Peptidomic Study. Dairy 2023, 4, 150-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010011
Zhang C, Boeren S, Zhao L, Bijl E, Hettinga K. The Impact of Low-Temperature Inactivation of Protease AprX from Pseudomonas on Its Proteolytic Capacity and Specificity: A Peptidomic Study. Dairy. 2023; 4(1):150-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunyue, Sjef Boeren, Liming Zhao, Etske Bijl, and Kasper Hettinga. 2023. "The Impact of Low-Temperature Inactivation of Protease AprX from Pseudomonas on Its Proteolytic Capacity and Specificity: A Peptidomic Study" Dairy 4, no. 1: 150-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010011
APA StyleZhang, C., Boeren, S., Zhao, L., Bijl, E., & Hettinga, K. (2023). The Impact of Low-Temperature Inactivation of Protease AprX from Pseudomonas on Its Proteolytic Capacity and Specificity: A Peptidomic Study. Dairy, 4(1), 150-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010011






