Deep Brain Stimulation for Major Depression and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder—Discontinuation of Ongoing Stimulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
3. Review of the Literature
3.1. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
3.2. Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD)
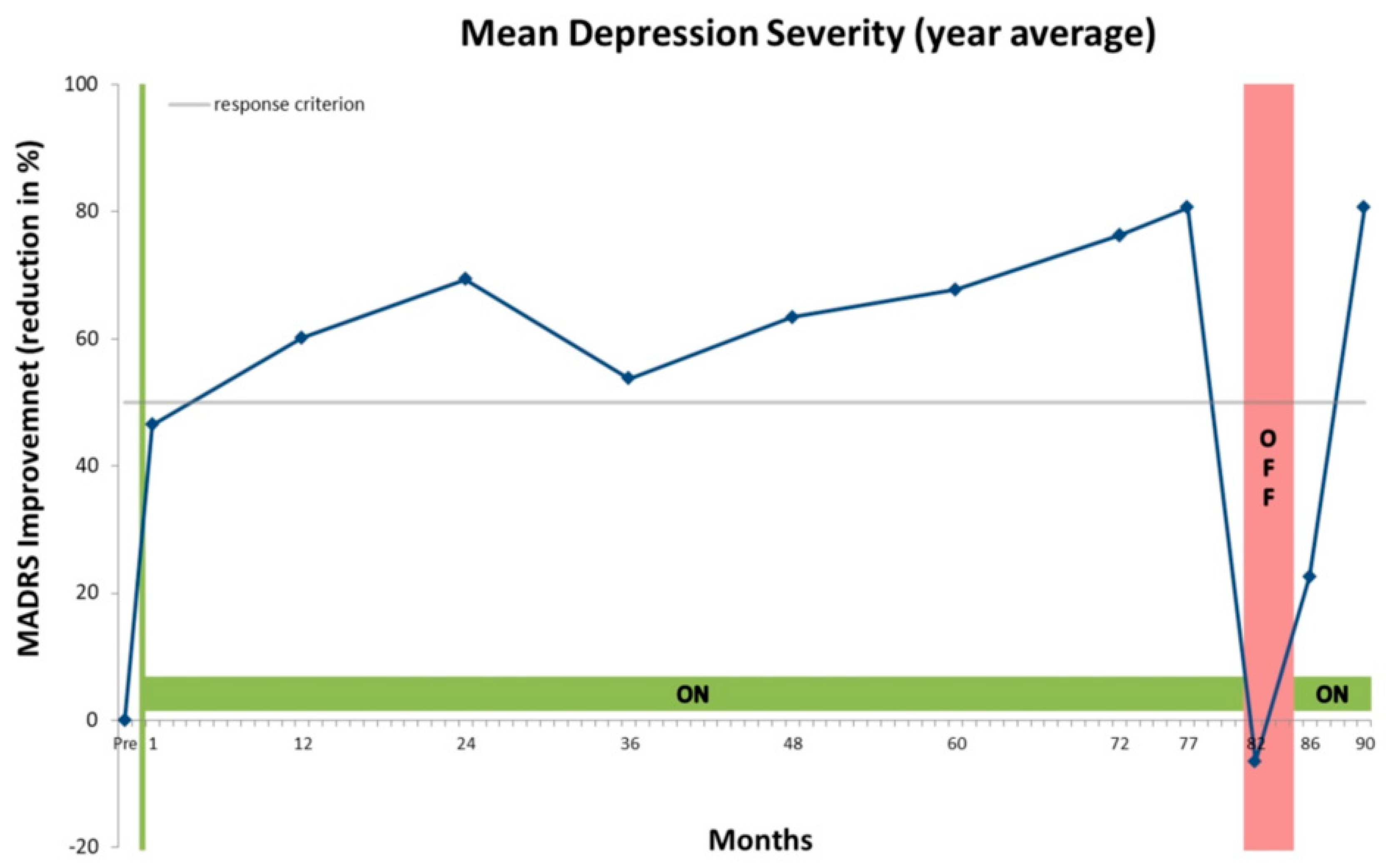
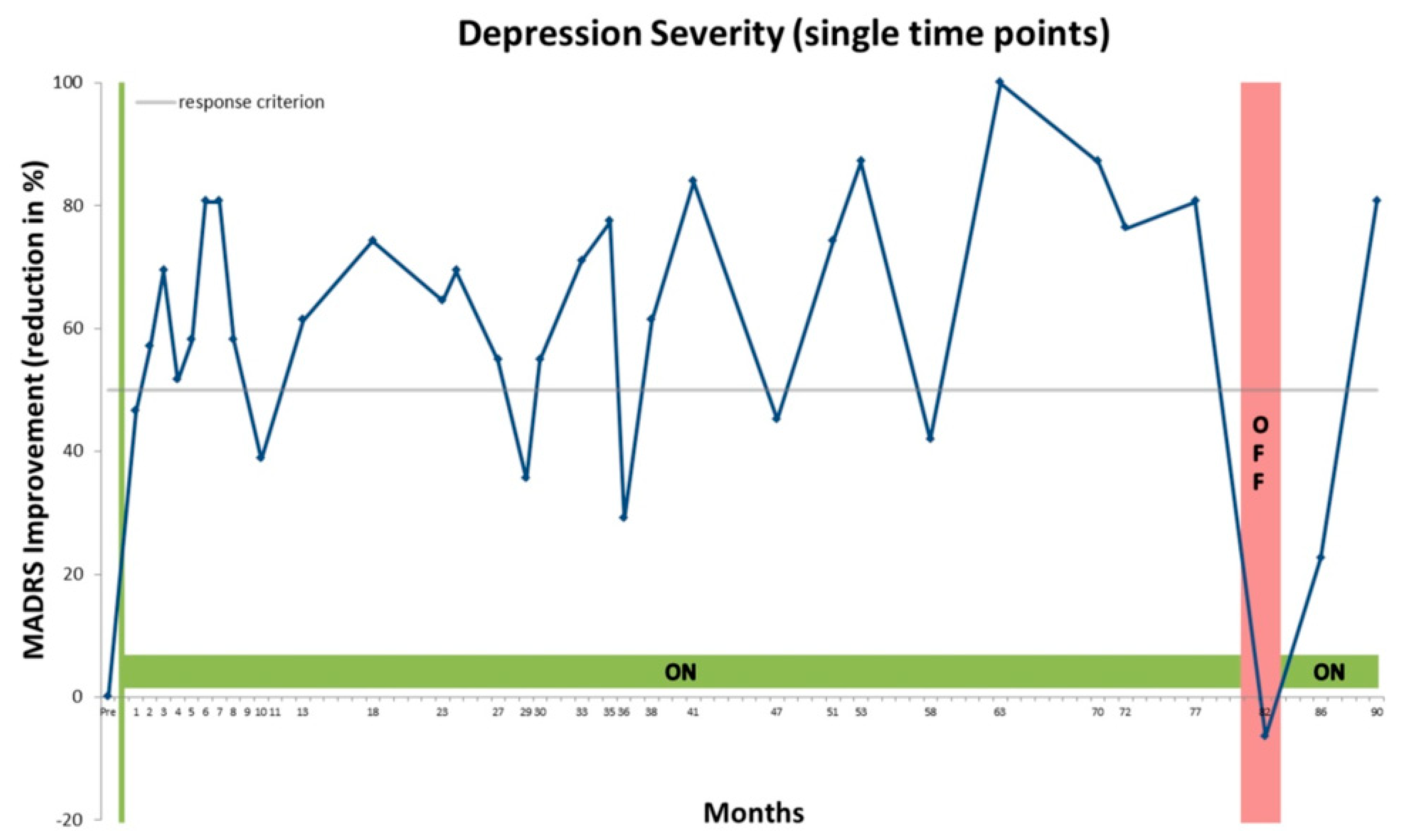
4. Case Presentation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benabid, A.L.; Pollak, P.; Gross, C.; Hoffmann, D.; Benazzouz, A.; Gao, D.M.; Laurent, A.; Gentil, M.; Perret, J. Acute and long-term effects of subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 1994, 62, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, P.; Benabid, A.-L.; Gross, C.; Gao, D.M.; Laurent, A.; Benazzouz, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Gentil, M.; Perret, J. Effects of the stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson disease. Rev. Neurol. 1993, 149, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P.; Chabardes, S.; Chang, J.W.; Matthews, K.; McIntyre, C.C.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Schulder, M.; et al. Deep brain stimulation: Current challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temperli, P.; Ghika, J.; Villemure, J.-G.; Burkhard, P.R.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Vingerhoets, F.J.G. How do parkinsonian signs return after discontinuation of subthalamic DBS? Neurology 2003, 60, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariz, M.I.; Johansson, F. Hardware failure in parkinsonian patients with chronic subthalamic nucleus stimulation is a medical emergency. Mov. Disord. 2001, 16, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuneier, J.; Barbe, M.T.; Dohmen, C.; Maarouf, M.; Wirths, J.; Fink, G.R.; Timmermann, L. Malignant deep brain stimulation-withdrawal syndrome in a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1640–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Krishnan, S.; Kesavapisharady, K.K.; Kishore, A. Malignant Subthalamic Nucleus-Deep Brain Stimulation Withdrawal Syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2016, 3, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Deuschl, G.; Falk, D.; Mehdorn, M.; Witt, K. Uncoupling of dopaminergic and subthalamic stimulation: Life-threatening DBS withdrawal syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariz, M. Once STN DBS, Always STN DBS?-Clinical, Ethical, and Financial Reflections on Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2016, 3, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfhde/hde.cfm?id=H050003 (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Drobisz, D.; Damborská, A. Deep brain stimulation targets for treating depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, P.J.; Lee, S.; Jimenez-Shahed, J.; Goodman, W.K.; Viswanathan, A.; Sheth, S.A. Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Evolution of Surgical Stimulation Target Parallels Changing Model of Dysfunctional Brain Circuits. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisely, S.; Hall, K.; Siskind, D.; Frater, J.; Olson, S.; Crompton, D. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 3533–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisely, S.; Li, A.; Warren, N.; Siskind, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation for depression. Depress. Anxiety 2018, 35, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borders, C.; Hsu, F.; Sweidan Alexander, J.; Matei, E.S.; Bota, R.G. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: A review of results by anatomical target. Ment. Illn. 2018, 10, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crowell, A.L.; Riva-Posse, P.; Holtzheimer, P.E.; Garlow, S.J.; Kelley, M.E.; Gross, R.E.; Denison, L.; Quinn, S.; Mayberg, H.S. Long-Term Outcomes of Subcallosal Cingulate Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wal, J.M.; van der Bergfeld, I.O.; Lok, A.; Mantione, M.; Figee, M.; Notten, P.; Beute, G.; Horst, F.; Munckhof, P.; van den Schuurman, P.R.; et al. Long-term deep brain stimulation of the ventral anterior limb of the internal capsule for treatment-resistant depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bewernick, B.H.; Kayser, S.; Gippert, S.M.; Switala, C.; Coenen, V.A.; Schlaepfer, T.E. Deep brain stimulation to the medial forebrain bundle for depression- long-term outcomes and a novel data analysis strategy. Brain Stimul. 2017, 10, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D. Evaluation of Electromagnetic Incompatibility Concerns for Deep Brain Stimulators. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2008, 40, 299–303. [Google Scholar]
- Vora, A.K.; Ward, H.; Foote, K.D.; Goodman, W.K.; Okun, M.S. Rebound symptoms following battery depletion in the NIH OCD DBS cohort: Clinical and reimbursement issues. Brain Stimul. 2012, 5, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videnovic, A.; Metman, L.V. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: Prevalence of adverse events and need for standardized reporting. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, T.E.; Bewernick, B.H.; Kayser, S.; Mädler, B.; Coenen, V.A. Rapid effects of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouizerate, B.; Martin-Guehl, C.; Cuny, E.; Guehl, D.; Amieva, H.; Benazzouz, A.; Fabrigoule, C.; Bioulac, B.; Tignol, J.; Burbaud, P. Deep brain stimulation for OCD and major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, B.D.; Malone, D.A.; Friehs, G.M.; Rezai, A.R.; Kubu, C.S.; Malloy, P.F.; Salloway, S.P.; Okun, M.S.; Goodman, W.K.; Rasmussen, S.A. Three-year outcomes in deep brain stimulation for highly resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, W.K.; Foote, K.D.; Greenberg, B.D.; Ricciuti, N.; Bauer, R.; Ward, H.; Shapira, N.A.; Wu, S.S.; Hill, C.L.; Rasmussen, S.A.; et al. Deep brain stimulation for intractable obsessive compulsive disorder: Pilot study using a blinded, staggered-onset design. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooms, P.; Blankers, M.; Figee, M.; Mantione, M.; Munckhof, P.; van den Schuurman, P.R.; Denys, D. Rebound of affective symptoms following acute cessation of deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beszłej, J.A.; Siwicki, D.; Fila-Witecka, K.; Wieczorek, T.; Piotrowski, P.; Weiser, A.; Tabakow, P.; Rymaszewska, J. Deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder—Case report of two patients. Psychiatr. Pol. 2019, 53, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttin, B.J.; Gabriëls, L.A.; Cosyns, P.R.; Meyerson, B.A.; Andréewitch, S.; Sunaert, S.G.; Maes, A.F.; Dupont, P.J.; Gybels, J.M.; Gielen, F.; et al. Long-term electrical capsular stimulation in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, J.L.; Curtis, G.C.; Sagher, O.; Albucher, R.C.; Harrigan, M.; Taylor, S.F.; Martis, B.; Giordani, B. Deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, L.; Polosan, M.; Jaafari, N.; Baup, N.; Welter, M.-L.; Fontaine, D.; Du Montcel, S.T.; Yelnik, J.; Chéreau, I.; Arbus, C.; et al. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation in severe obsessive-compulsive disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, D.; Mantione, M.; Figee, M.; Munckhof, P.; van den Koerselman, F.; Westenberg, H.; Bosch, A.; Schuurman, R. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, D.A.; Dougherty, D.D.; Rezai, A.R.; Carpenter, L.L.; Friehs, G.M.; Eskandar, E.N.; Rauch, S.L.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Machado, A.G.; Kubu, C.S.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, S.H.; Giacobbe, P.; Rizvi, S.J.; Placenza, F.M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Mayberg, H.S.; Lozano, A.M. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: Follow-up after 3 to 6 years. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkl, A.; Schneider, G.-H.; Schönecker, T.; Aust, S.; Kühl, K.-P.; Kupsch, A.; Kühn, A.A.; Bajbouj, M. Antidepressant effects after short-term and chronic stimulation of the subgenual cingulate gyrus in treatment-resistant depression. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 249, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkl, A.; Aust, S.; Schneider, G.-H.; Visser-Vanderwalle, V.; Horn, A.; Kühn, A.A.; Kuhn, J.; Bajbouj, M. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subcallosal Cingualte Gyrus in Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression: A double-blind randomized controlled study and long-term follow-up in eight patients. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 227, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, D.R.; Haber, S.N.; Tyrka, A.R.; Bernier, J.A.; Rassmussen, S.A.; Greenberg, B.D. Reversible increase in smoking after withdrawal of ventral capsule/ventral striatum deep brain stimulation in a depressed smoker. J. Addict. Med. 2012, 6, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.; Honey, C.R.; Hurwitz, T.A.; Ilcewicz-Klimek, M.; Woo, C.; Lam, R.W.; Berman, N. Deep brain stimulation interruption and suicidality. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 116, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, H.M.; Meyer, D.M.; Bewernick, B.H.; Spanier, S.; Coenen, V.A.; Schlaepfer, T.E. Discontinuation of Superolateral Medial Forebrain Bundle Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression Leads to Critical Relapse. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, e23–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayberg, H.S.; Lozano, A.M.; Voon, V.; McNeely, H.E.; Seminowicz, D.; Hamani, C.; Schwalb, J.M.; Kennedy, S.H. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron 2005, 45, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigdemont, D.; Portella, M.; Pérez-Egea, R.; Molet, J.; Gironell, A.; Diego-Adeliño, J.; de Martín, A.; Rodríguez, R.; Àlvarez, E.; Artigas, F.; et al. A randomized double-blind crossover trial of deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus in patients with treatment-resistant depression: A pilot study of relapse prevention. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2015, 40, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeld, I.O.; Mantione, M.; Hoogendoorn, M.L.C.; Ruhé, H.G.; Notten, P.; Laarhoven, J.; van Visser, I.; Figee, M.; Kwaasteniet, B.P.; de Horst, F.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Ventral Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule for Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewernick, B.H.; Hurlemann, R.; Matusch, A.; Kayser, S.; Grubert, C.; Hadrysiewicz, B.; Axmacher, N.; Lemke, M.; Cooper-Mahkorn, D.; Cohen, M.X.; et al. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzheimer, P.E.; Kelley, M.E.; Gross, R.E.; Filkowski, M.M.; Garlow, S.J.; Barrocas, A.; Wint, D.; Craighead, M.C.; Kozarsky, J.; Chismar, R.; et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, T.E.; Bewernick, B.H.; Kayser, S.; Hurlemann, R.; Coenen, V.A. Deep brain stimulation of the human reward system for major depression-rationale, outcomes and outlook. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Pollo, A.; Lopiano, L.; Lanotte, M.; Vighetti, S.; Rainero, I. Conscious Expectation and Unconscious Conditioning in Analgesic, Motor, and Hormonal Placebo/Nocebo Responses. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado, R.; Constantoyannis, C.; Mandat, T.; Kumar, A.; Schulzer, M.; Stoessl, A.J.; Honey, C.R. Expectation and the placebo effect in Parkinson’s disease patients with subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volonté, M.A.; Garibotto, V.; Spagnolo, F.; Panzacchi, A.; Picozzi, P.; Franzin, A.; Giovannini, E.; Leocani, L.; Cursi, M.; Comi, G.; et al. Changes in brain glucose metabolism in subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for advanced Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, R.; Voges, J.; Weisenbach, S.; Kalbe, E.; Burghaus, L.; Ghaemi, M.; Lehrke, R.; Koulousakis, A.; Herholz, K.; Sturm, V.; et al. Subthalamic nucleus stimulation restores glucose metabolism in associative and limbic cortices and in cerebellum: Evidence from a FDG-PET study in advanced Parkinson’s disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figee, M.; Luigjes, J.; Smolders, R.; Valencia-Alfonso, C.-E.; Wingen, G.; van Kwaasteniet, B.; de Mantione, M.; Ooms, P.; Koning, P.P.; de Vulink, N.; et al. Deep brain stimulation restores frontostriatal network activity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Blanco, A.; Serra-Blasco, M.; Pérez-Egea, R.; Diego-Adeliño, J.; de Carceller-Sindreu, M.; Puigdemont, D.; Molet, J.; Álvarez, E.; Pérez, V.; Portella, M.J. Immediate cerebral metabolic changes induced by discontinuation of deep brain stimulation of subcallosal cingulate gyrus in treatment-resistant depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 173, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, P.P.; de Figee, M.; Endert, E.; Storosum, J.G.; Fliers, E.; Denys, D. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder is associated with cortisol changes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kilian, H.M.; Bewernick, B.H.; Klein, M.; Meyer, D.M.; Spanier, S.; Reinacher, P.C.; Coenen, V.A.; Schlaepfer, T.E. Deep Brain Stimulation for Major Depression and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder—Discontinuation of Ongoing Stimulation. Psych 2020, 2, 174-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2030015
Kilian HM, Bewernick BH, Klein M, Meyer DM, Spanier S, Reinacher PC, Coenen VA, Schlaepfer TE. Deep Brain Stimulation for Major Depression and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder—Discontinuation of Ongoing Stimulation. Psych. 2020; 2(3):174-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2030015
Chicago/Turabian StyleKilian, Hannah M., Bettina H. Bewernick, Margaretha Klein, Dora M. Meyer, Susanne Spanier, Peter C. Reinacher, Volker A. Coenen, and Thomas E. Schlaepfer. 2020. "Deep Brain Stimulation for Major Depression and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder—Discontinuation of Ongoing Stimulation" Psych 2, no. 3: 174-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2030015
APA StyleKilian, H. M., Bewernick, B. H., Klein, M., Meyer, D. M., Spanier, S., Reinacher, P. C., Coenen, V. A., & Schlaepfer, T. E. (2020). Deep Brain Stimulation for Major Depression and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder—Discontinuation of Ongoing Stimulation. Psych, 2(3), 174-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/psych2030015






