Reversible Mussel-Inspired Adhesive from Strong and Tough Dynamic Covalent Crosslinking Polymer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
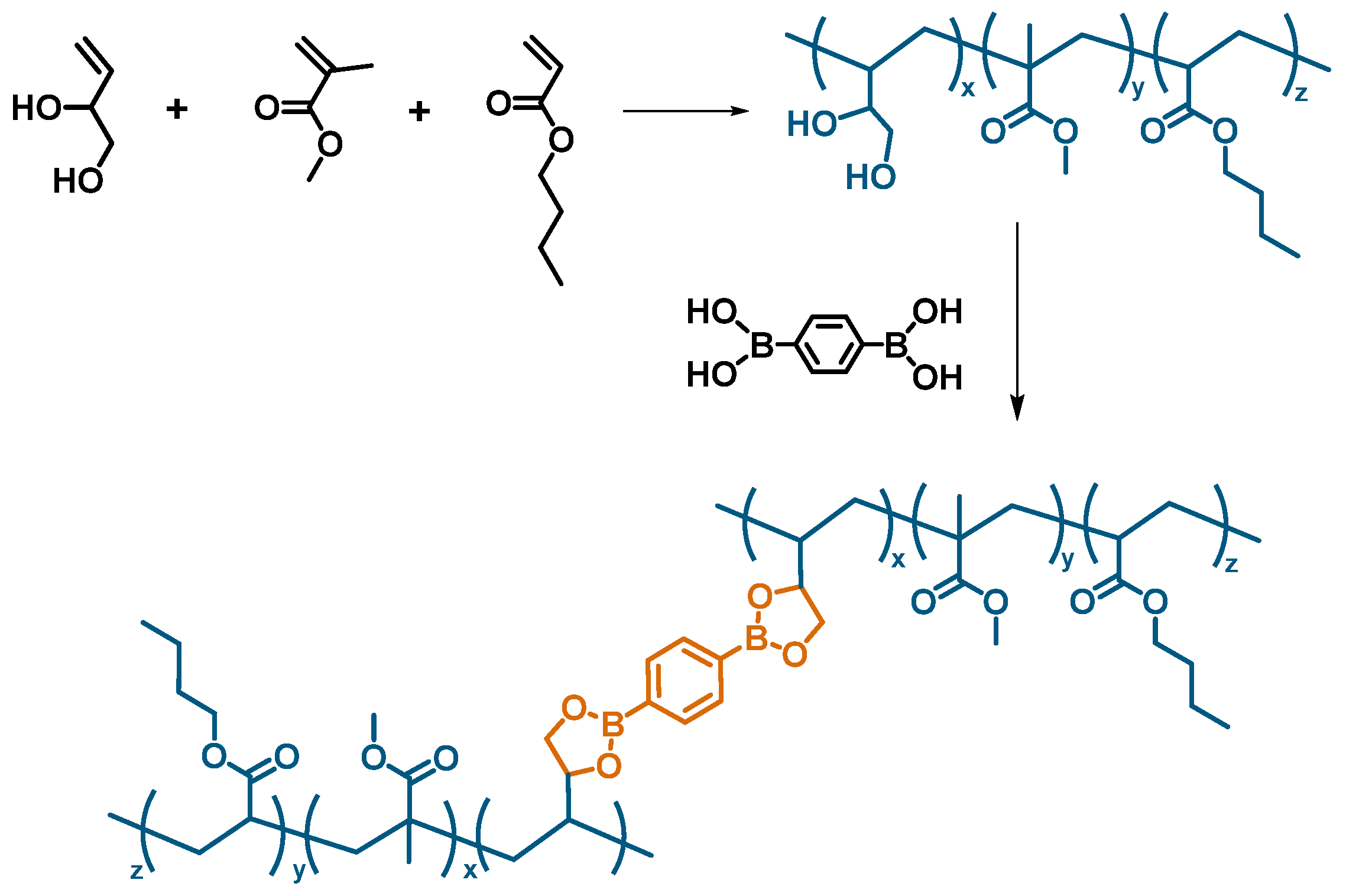
2.2. Synthesis of the Adhesive
2.3. General Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
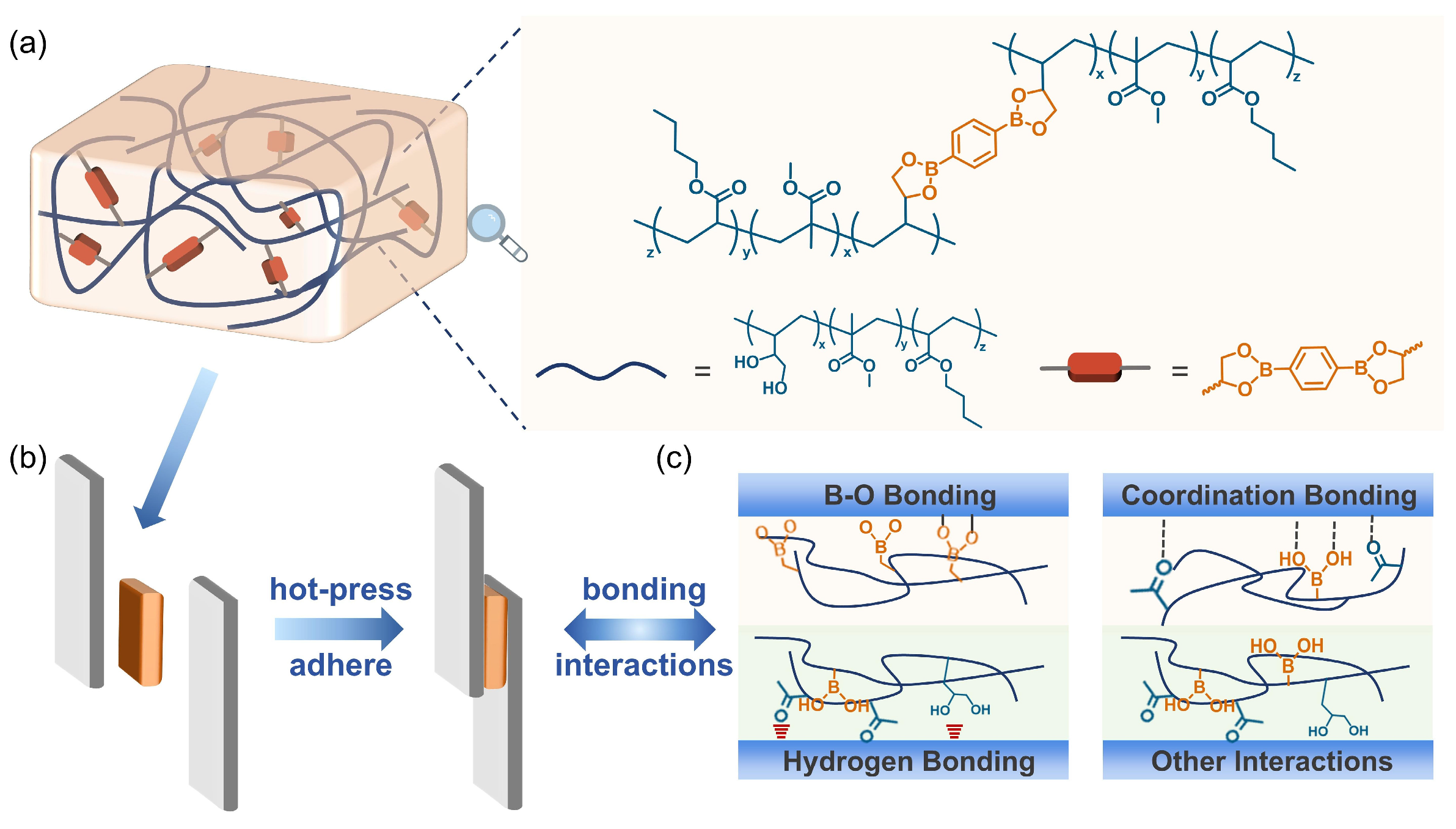
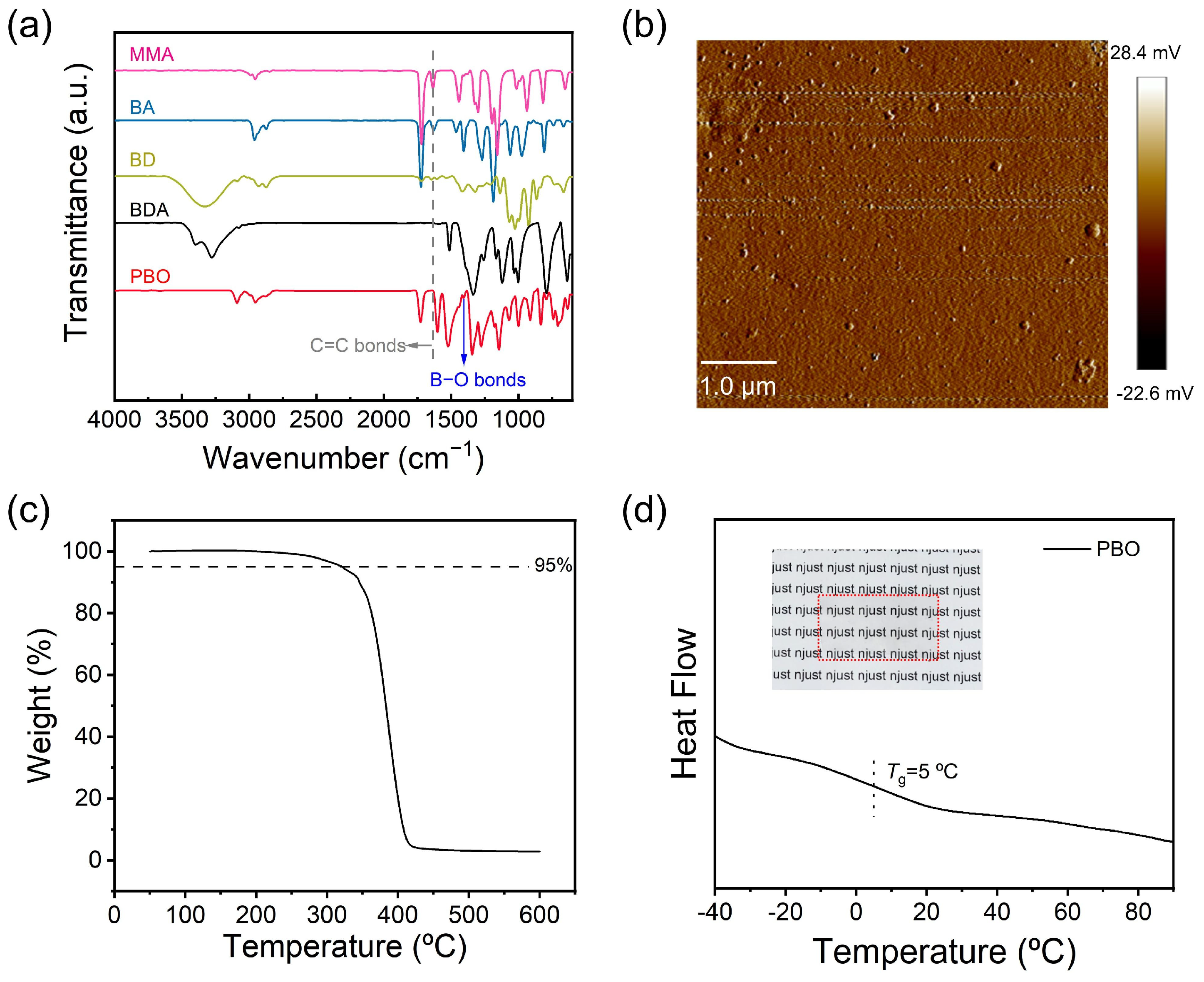
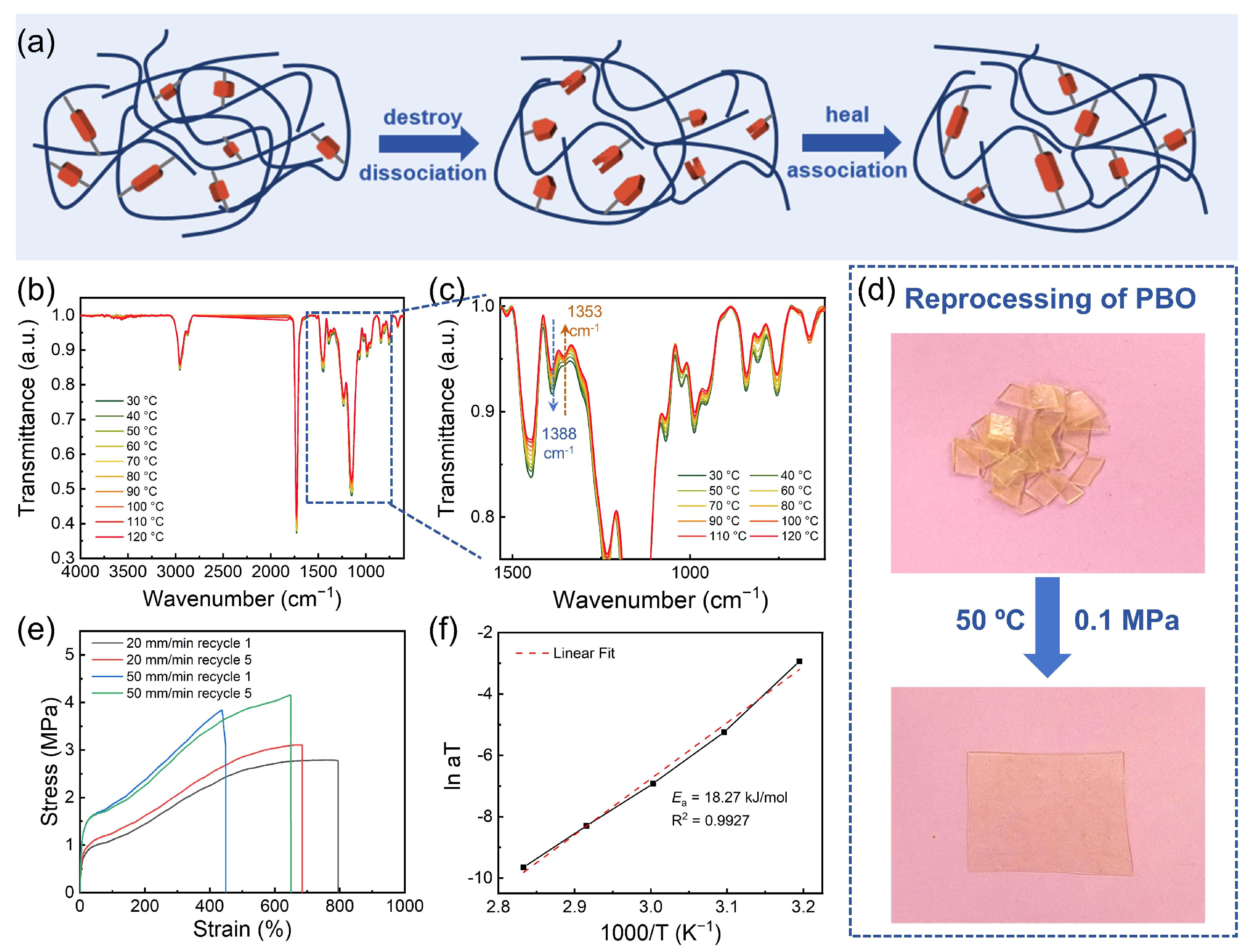
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Adhesive
3.2. Mechanical Property of the Adhesive PBO
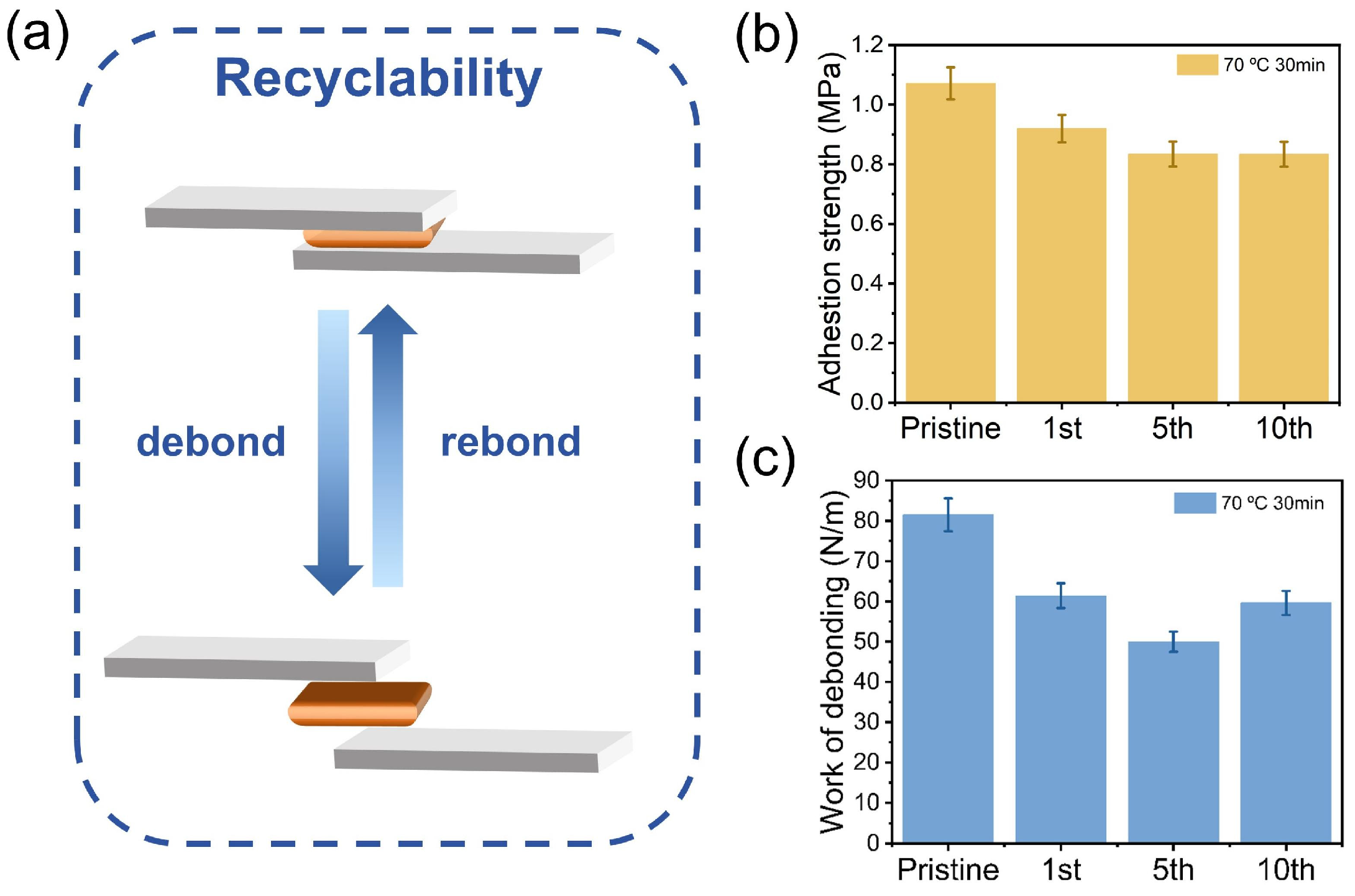
3.3. Recyclability of the Adhesive PBO
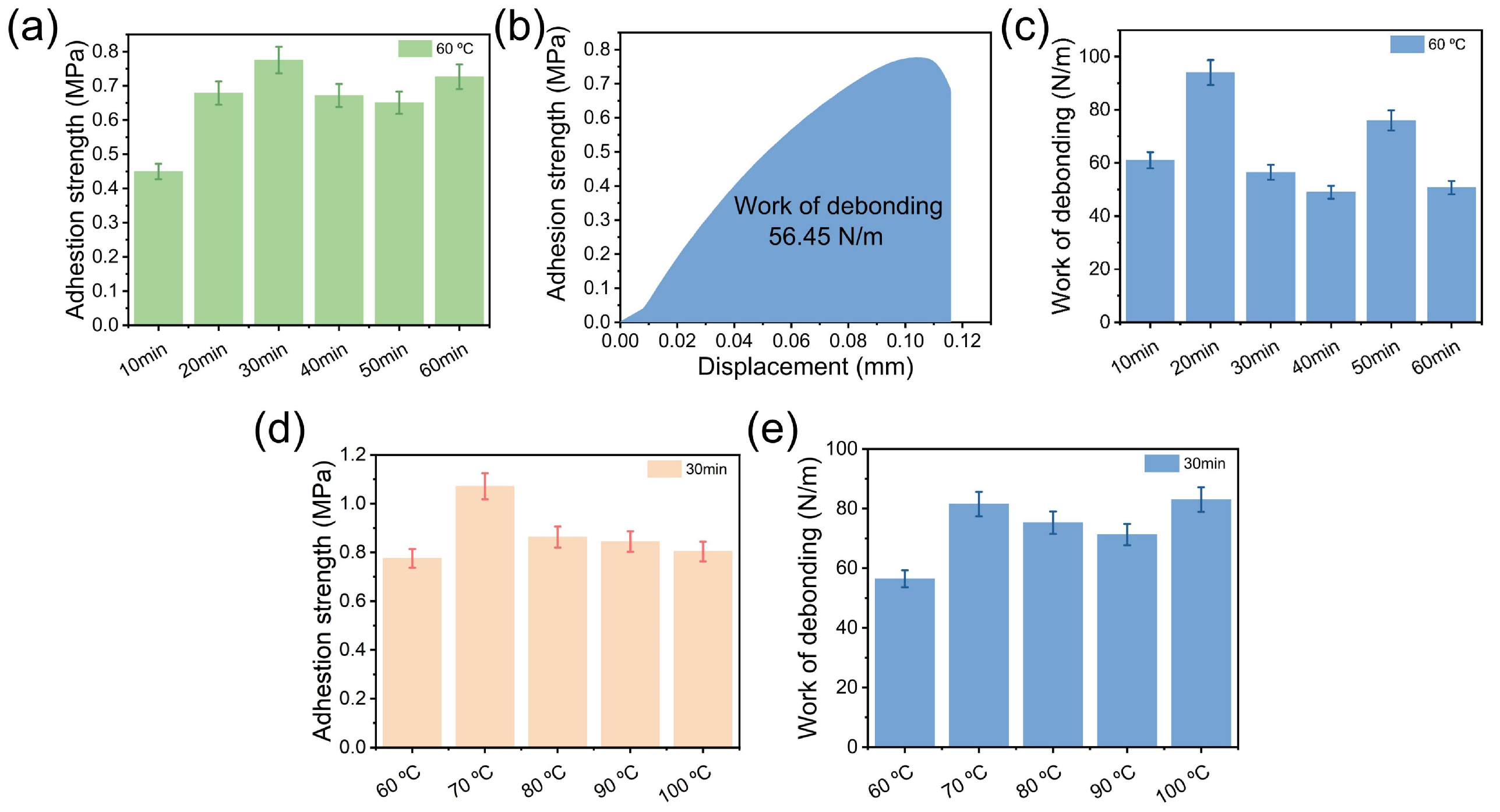
3.4. Adhesion Performance of the Adhesive PBO
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| mfps | mussel foot proteins |
| DOPA | 3,4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine |
| MMA | methyl methacrylate |
| BA | butyl acrylate |
| BD | 3-butene-1,2-diol |
| BDA | benzene-1,4-diboronic acid |
| AIBN | azodiisobutyronitrile |
| PBO | the name of the prepared adhesive |
References
- Zhao, Y.; Song, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, Y. Supramolecular Adhesive Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5604–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bai, R.; Suo, Z. Topological Adhesion of Wet Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, J.; Yang, J.; Suo, Z. Covalent Topological Adhesion. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, A.; Dhinojwala, A.; Joy, A. Design principles for creating synthetic underwater adhesives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 13321–13345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Bowland, C.; Ge, S.; Acharya, S.R.; Kim, S.; Cooper, V.R.; Chen, X.C.; Irle, S.; Sokolov, A.P.; Savara, A.; et al. Design of tough adhesive from commodity thermoplastics through dynamic crosslinking. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabk2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gong, J.P. Bioinspired Underwater Adhesives. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, T.; Xiang, L.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Zeng, H. Adhesive Coacervates Driven by Hydrogen-Bonding Interaction. Small 2020, 16, 2004132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Wan, X.; Dai, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Recent Progress of Spider-Silk-Inspired Adhesive Materials. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 1453–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, M.G.; Putnam, A.A.; North, M.A.; Wilker, J.J. Weak bonds in a biomimetic adhesive enhance toughness and performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4762–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Mussel-inspired hydrogels: From design principles to promising applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3605–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X. Mussel-Inspired Hydrogels for Self-Adhesive Bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord Forooshani, P.; Lee, B.P. Recent approaches in designing bioadhesive materials inspired by mussel adhesive protein. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Liu, W. Recent advances in wet adhesives: Adhesion mechanism, design principle and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 116, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.K. Perspectives on Mussel-Inspired Wet Adhesion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10166–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogsgaard, M.; Nue, V.; Birkedal, H. Mussel-Inspired Materials: Self-Healing through Coordination Chemistry. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Ding, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ren, C.; Xu, W. Hydrogels for underwater adhesion: Adhesion mechanism, design strategies and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 11823–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Peng, Y.; Tu, X.; Du, P.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Facile Preparation of Mussel-Inspired Polyurethane Hydrogel and Its Rapid Curing Behavior. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12495–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Bae, H.; Ahn, J.; Kang, T.; Seo, D.-G.; Hwang, D.S. Catechol-thiol-based dental adhesive inspired by underwater mussel adhesion. Acta Biomater. 2020, 103, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, J.M.; Börner, H.G. Accessing the Next Generation of Synthetic Mussel-Glue Polymers via Mussel-Inspired Polymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6408–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Lu, S.; Xiao, H.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Wu, H. Mussel-inspired conductive hydrogel with self-healing, adhesive, and antibacterial properties for wearable monitoring. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5798–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Yu, J. Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Li, F.; He, S.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; He, J.; Ruan, R.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H. Mussel- and Barnacle Cement Proteins-Inspired Dual-Bionic Bioadhesive with Repeatable Wet-Tissue Adhesion, Multimodal Self-Healing, and Antibacterial Capability for Nonpressing Hemostasis and Promoted Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Weng, L.-T.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhao, C.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive and Tough Hydrogel Based on Nanoclay Confined Dopamine Polymerization. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Li, S.; Pei, M.; Yang, H.; Gu, S.; Tao, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Dopamine-Modified Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Adhesives with Fast-Forming and High Tissue Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18225–18234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Xu, Z.-K. Revisiting the adhesion mechanism of mussel-inspired chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz-Poseu, J.; Mancebo-Aracil, J.; Nador, F.; Busqué, F.; Ruiz-Molina, D. The Chemistry behind Catechol-Based Adhesion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 696–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cholewinski, A.; Yang, F.; Zhao, B.; Pinnaratip, R.; et al. Catechol-functionalized hydrogels: Biomimetic design, adhesion mechanism, and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, W.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y. Versatile Polydopamine Platforms: Synthesis and Promising Applications for Surface Modification and Advanced Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.A.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, F.; Hong, S.; Lee, H. Material-Independent Surface Chemistry beyond Polydopamine Coating. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, G.; Geng, D.; Zhu, C.; Bai, J. A Pseudo-Mytilus Edulis Foot Protein-Based Hydrogel Adhesive with Osteo-Vascular-Immune Coupling Effects for Osteoporotic Bone-Implant Integration. Adv. Mater. 2025, e11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, S.D.; Davidson, M.G.; van den Elsen, J.M.H.; Fossey, J.S.; Jenkins, A.T.A.; Jiang, Y.-B.; Kubo, Y.; Marken, F.; Sakurai, K.; Zhao, J.; et al. Exploiting the Reversible Covalent Bonding of Boronic Acids: Recognition, Sensing, and Assembly. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromwell, O.R.; Chung, J.; Guan, Z. Malleable and self-Healing covalent polymer networks through tunable dynamic boronic ester bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6492–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Oh, D.X.; Park, J. Recent progress in self-healing polymers and hydrogels based on reversible dynamic B–O bonds: Boronic/boronate esters, borax, and benzoxaborole. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 14630–14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Zhao, P.C.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, J.L.; Li, C.H. An underwater long-term strong adhesive based on boronic esters with enhanced hydrolytic stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, A.P.; Sumerlin, B.S.; Sutti, A. Bulk network polymers with dynamic B–O bonds: Healable and reprocessable materials. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 694–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-H.; Wang, D.-P.; Zuo, J.-L.; Li, C.-H. A Tough and Self-Healing Polymer Enabled by Promoting Bond Exchange in Boronic Esters with Neighboring Hydroxyl Groups. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jin, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Shi, S.Q.; Li, J. Bioinspired hyperbranched protein adhesive based on boronic acid-functionalized cellulose nanofibril and water-soluble polyester. Compos. Part B 2021, 219, 108943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Fu, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, L.; Zhang, M.; Song, F.; Zhou, Y. A multifunctional cardanol-based room-temperature phosphorescent material with multi-stimulus-responsive shape-memory for anti-counterfeiting and encryption. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 6363–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ma, H.; Li, M.; Qin, R.; Li, P. Electroconductive hydrogels for bioelectronics: Challenges and opportunities. FlexMat 2024, 1, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, S.; Sun, F.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, Z.; Fu, J. Ultra-Robust and Tough Epoxy Resin Enabled by Pulley Mechanism-Based Curing Agent for Strong and Reversible Adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, e17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xie, D.; Qu, Q.; Rojas, O.J.; Hu, G.; et al. Starfish-Inspired Synergistic Reinforced Hydrogel Wound Dressing: Dual Responsiveness and Enhanced Bioactive Compound Delivery for Advanced Skin Regeneration and Management. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 10180–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; He, R.; et al. High-Conductivity, Self-Healing, and Adhesive Ionic Hydrogels for Health Monitoring and Human-Machine Interactions Under Extreme Cold Conditions. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2412726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Shao, Y.; Luo, B.; Liu, T.; Zhao, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chi, M.; Gao, C.; et al. Compliant Iontronic Triboelectric Gels with Phase-Locked Structure Enabled by Competitive Hydrogen Bonding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, R.; Li, W.; Sun, W.; Yan, Y.; Xiang, X.; Fang, J.; Liao, Y.; Xie, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Silk fibroin hydrogel adhesive enables sealed-tight reconstruction of meniscus tears. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Lin, F.; Guo, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Wu, T.; Huang, H.; Chi, Z.; Yang, Z. Stable and ultralong room-temperature phosphorescent copolymers with excellent adhesion, resistance, and toughness. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.-T.; Huang, F. Multiple hydrogen bonding driven supramolecular architectures and their biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1592–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jia, B.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Qiao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, B. Multiple bonds crosslinked antibacterial, conductive and antioxidant hydrogel adhesives with high stretchability and rapid self-healing for MRSA infected motion skin wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
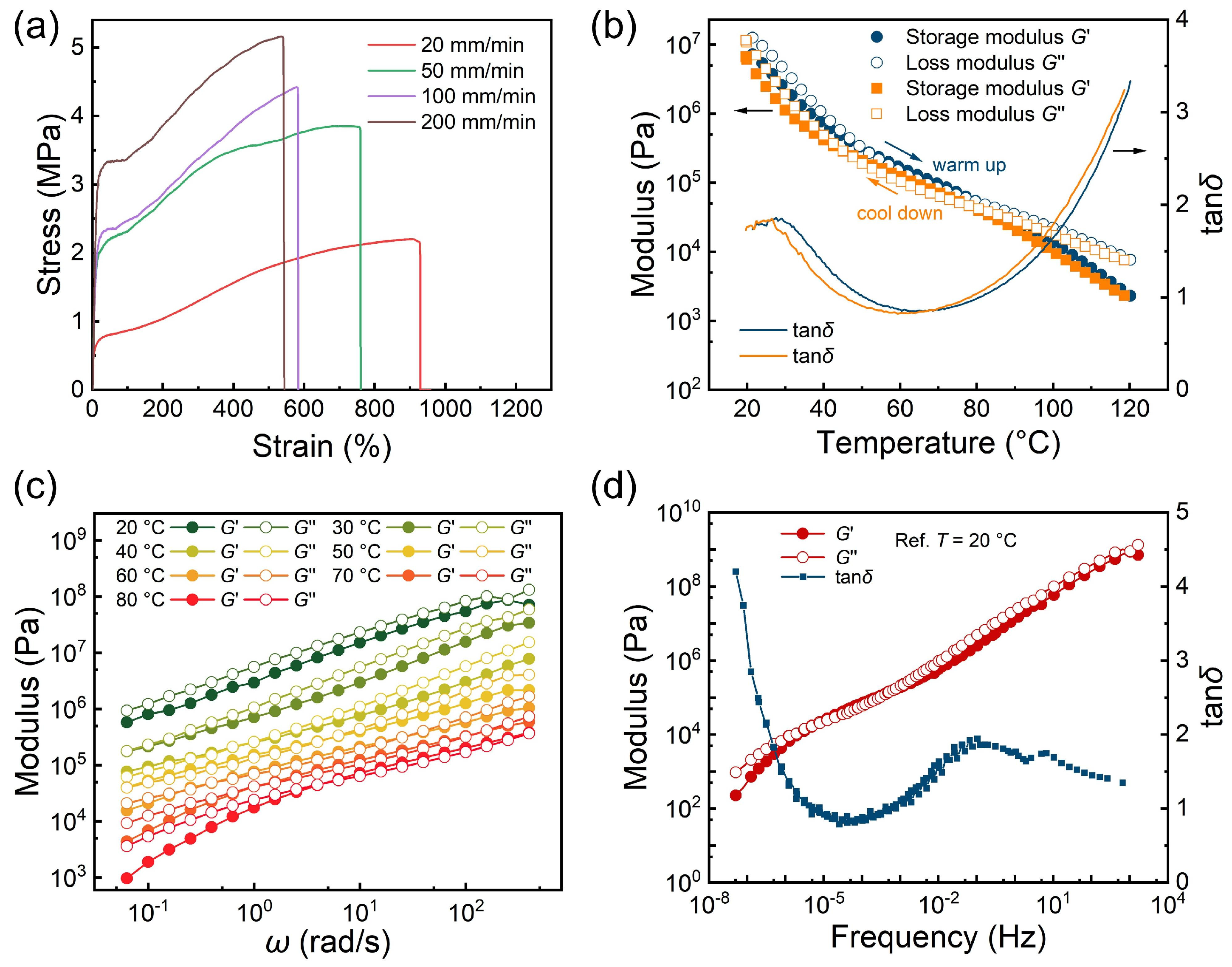

| Tensile Rate (mm/min) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Maximum Stress (MPa) | Maximum Strain (%) | Toughness (MJ/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 40.68 ± 0.32 | 2.21 ± 0.17 | 930 ± 10 | 14.80 ± 0.19 |
| 50 | 31.74 ± 0.28 | 3.85 ± 0.28 | 757 ± 19 | 24.30 ± 0.14 |
| 100 | 22.67 ± 0.45 | 4.42 ± 0.12 | 579 ± 15 | 19.14 ± 0.30 |
| 200 | 22.20 ± 0.23 | 5.15 ± 0.06 | 540 ± 7 | 22.52 ± 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.-H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, D.; Fu, J. Reversible Mussel-Inspired Adhesive from Strong and Tough Dynamic Covalent Crosslinking Polymer. Chemistry 2025, 7, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7060186
Zhao Z-H, Li Q, Zhou Y, Zeng Y, Yang D, Fu J. Reversible Mussel-Inspired Adhesive from Strong and Tough Dynamic Covalent Crosslinking Polymer. Chemistry. 2025; 7(6):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7060186
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zi-Han, Qikun Li, Yingpeng Zhou, Yinghong Zeng, Dandan Yang, and Jiajun Fu. 2025. "Reversible Mussel-Inspired Adhesive from Strong and Tough Dynamic Covalent Crosslinking Polymer" Chemistry 7, no. 6: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7060186
APA StyleZhao, Z.-H., Li, Q., Zhou, Y., Zeng, Y., Yang, D., & Fu, J. (2025). Reversible Mussel-Inspired Adhesive from Strong and Tough Dynamic Covalent Crosslinking Polymer. Chemistry, 7(6), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7060186






