Helical Airflow Synthesis of Quinoxalines: A Continuous and Efficient Mechanochemical Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
2.2. Synthesis of 1 by S-GSF
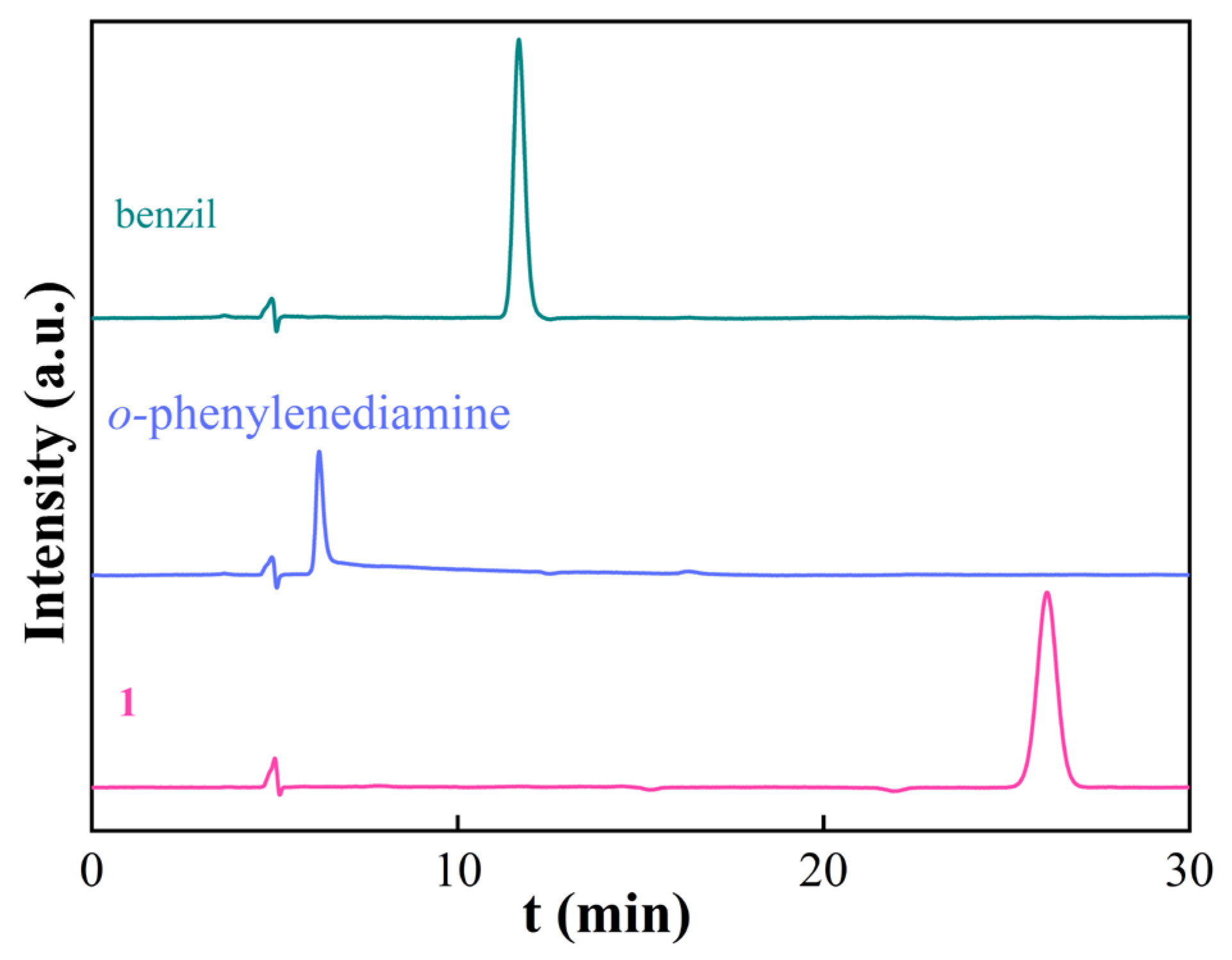
2.3. Analysis and Characterization
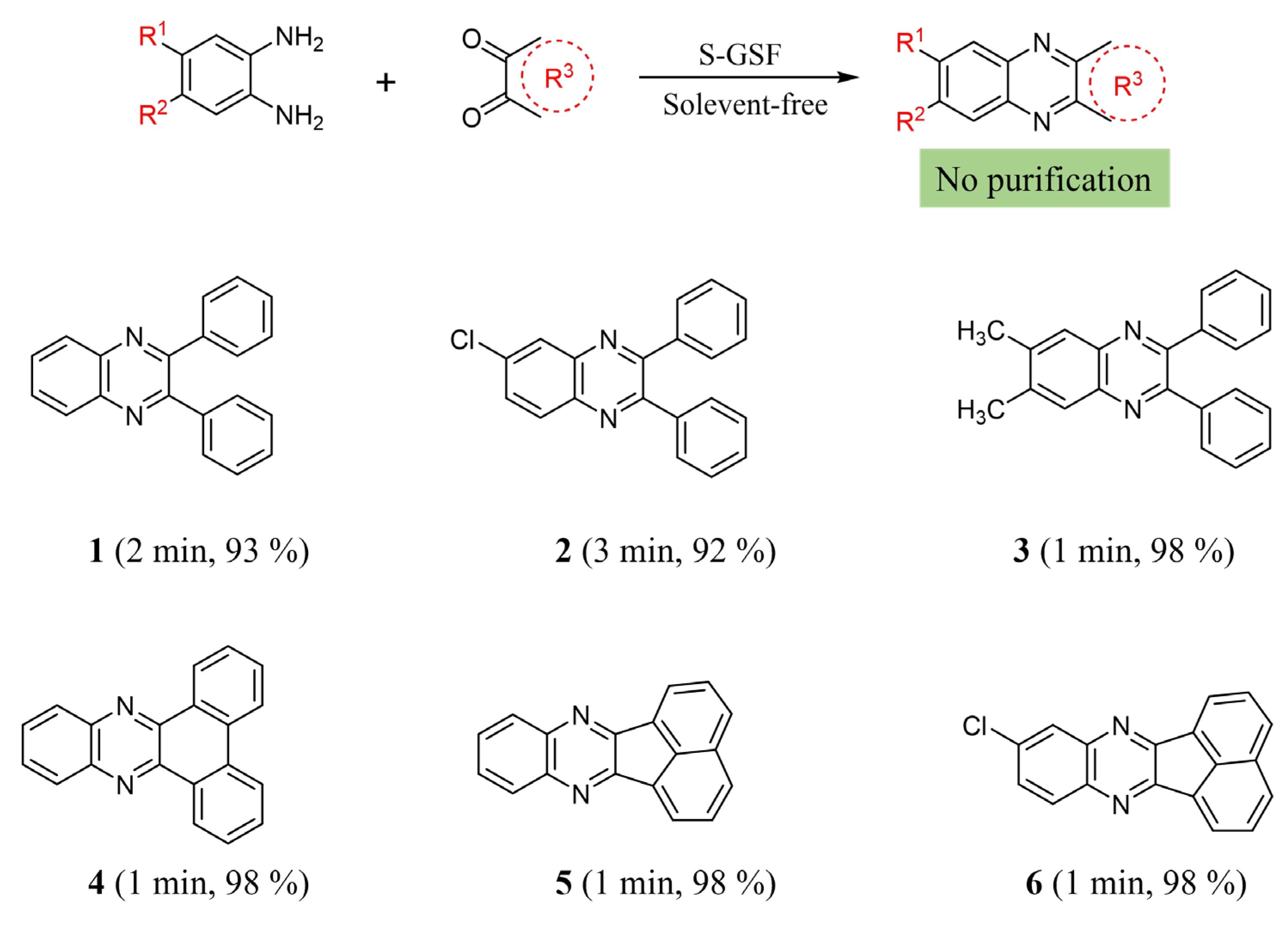
3. Results and Discussion
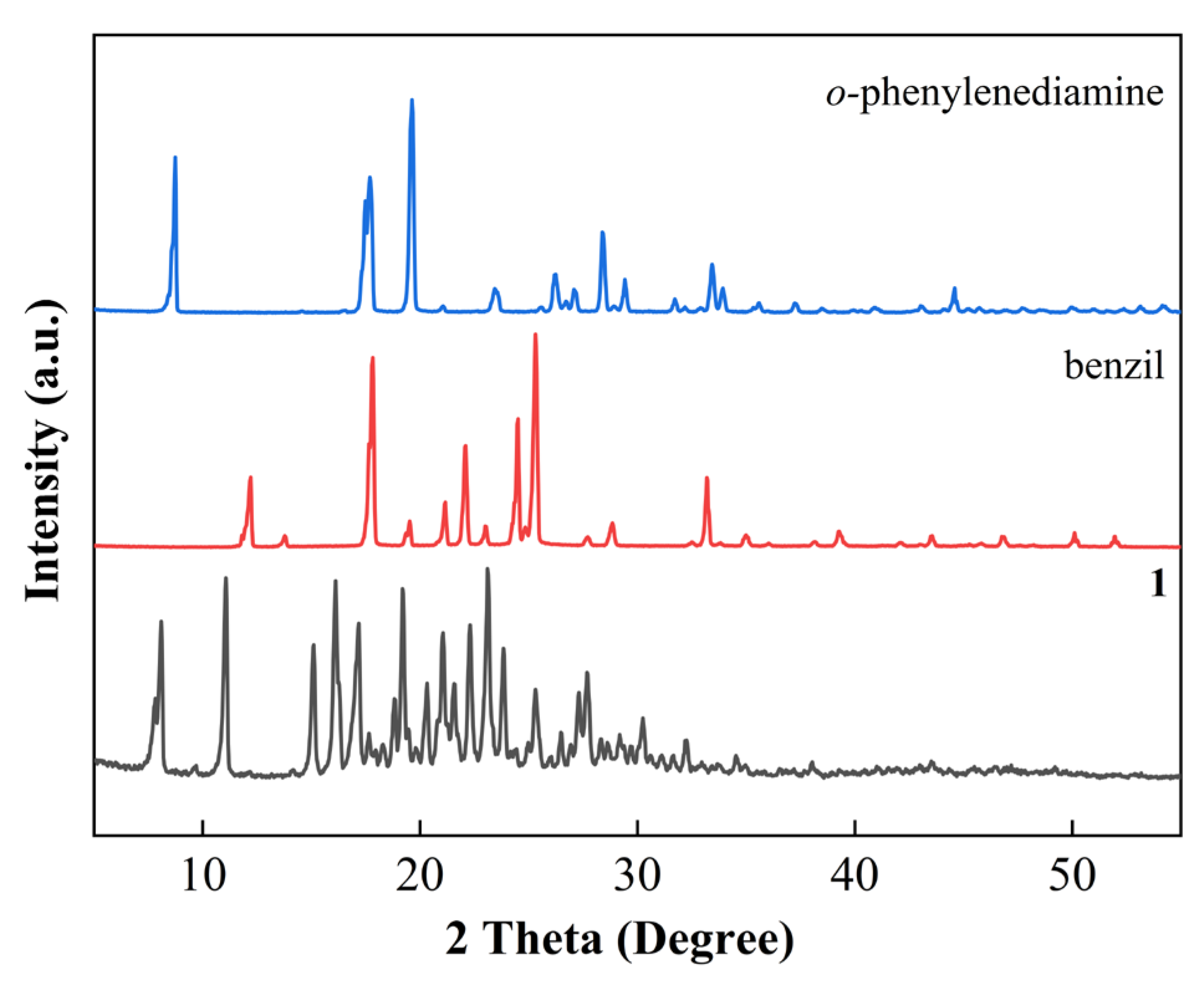
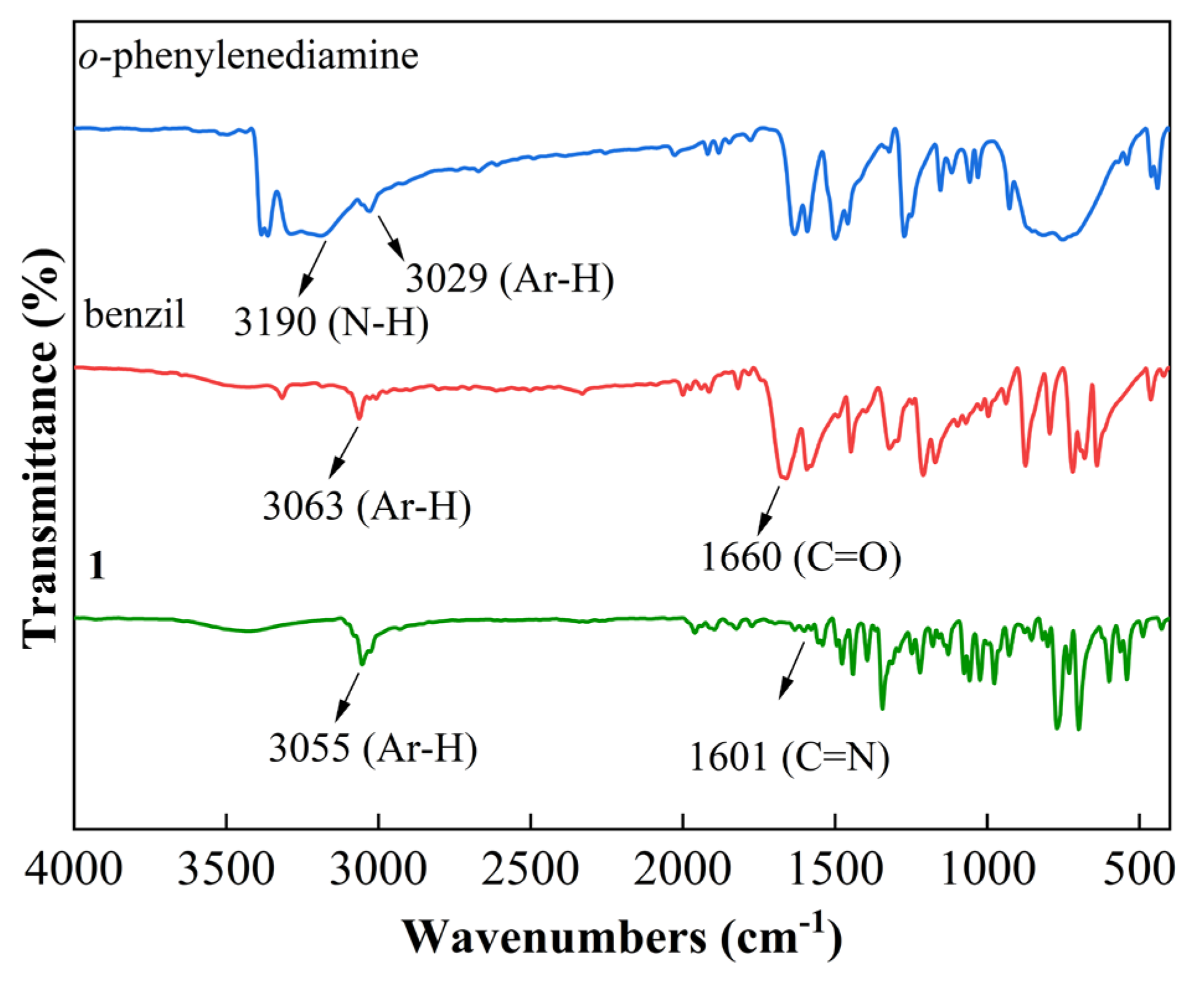
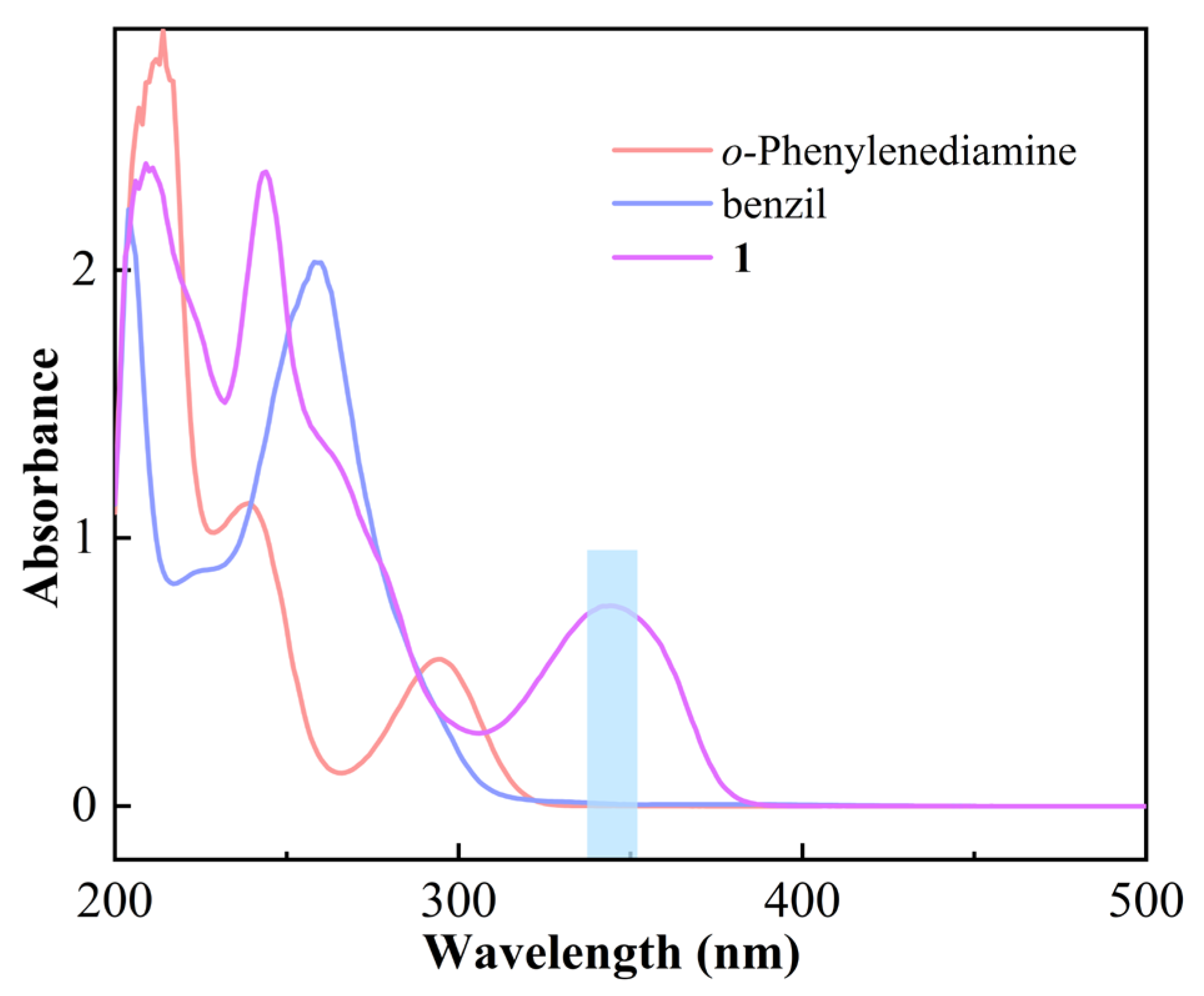
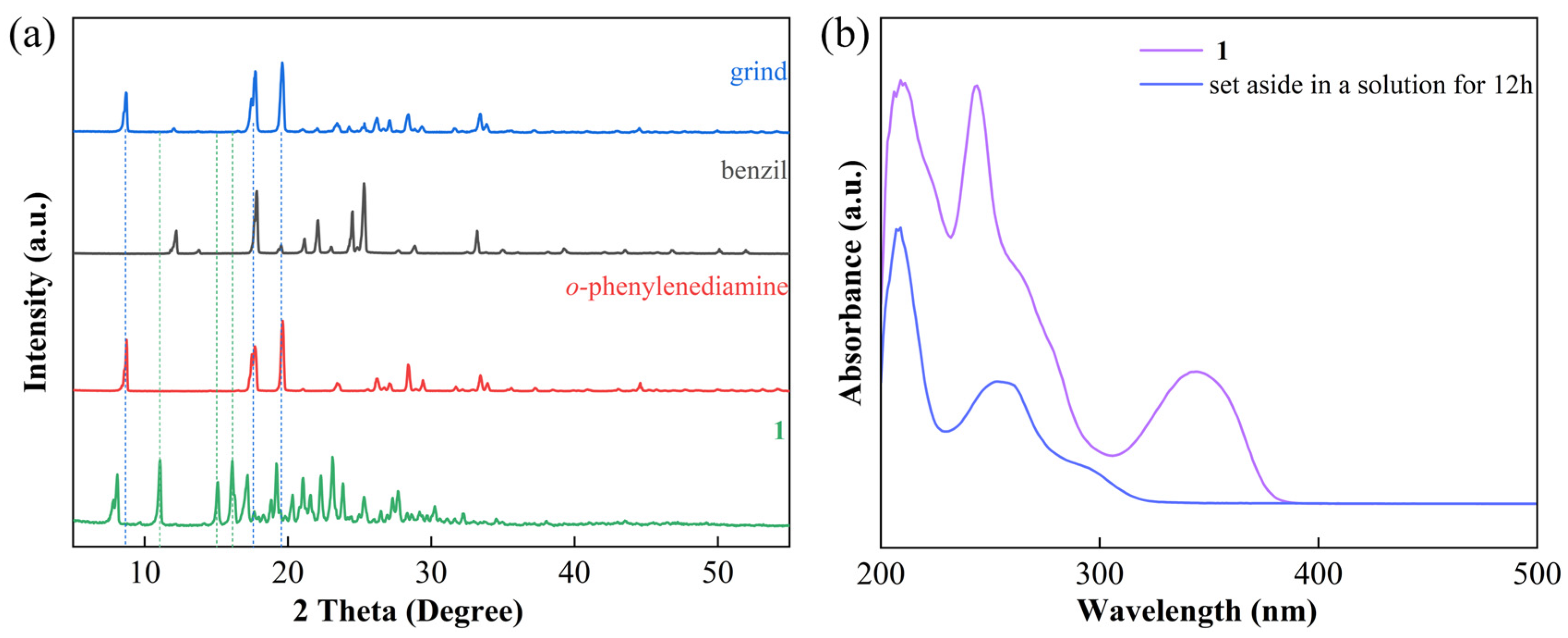
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
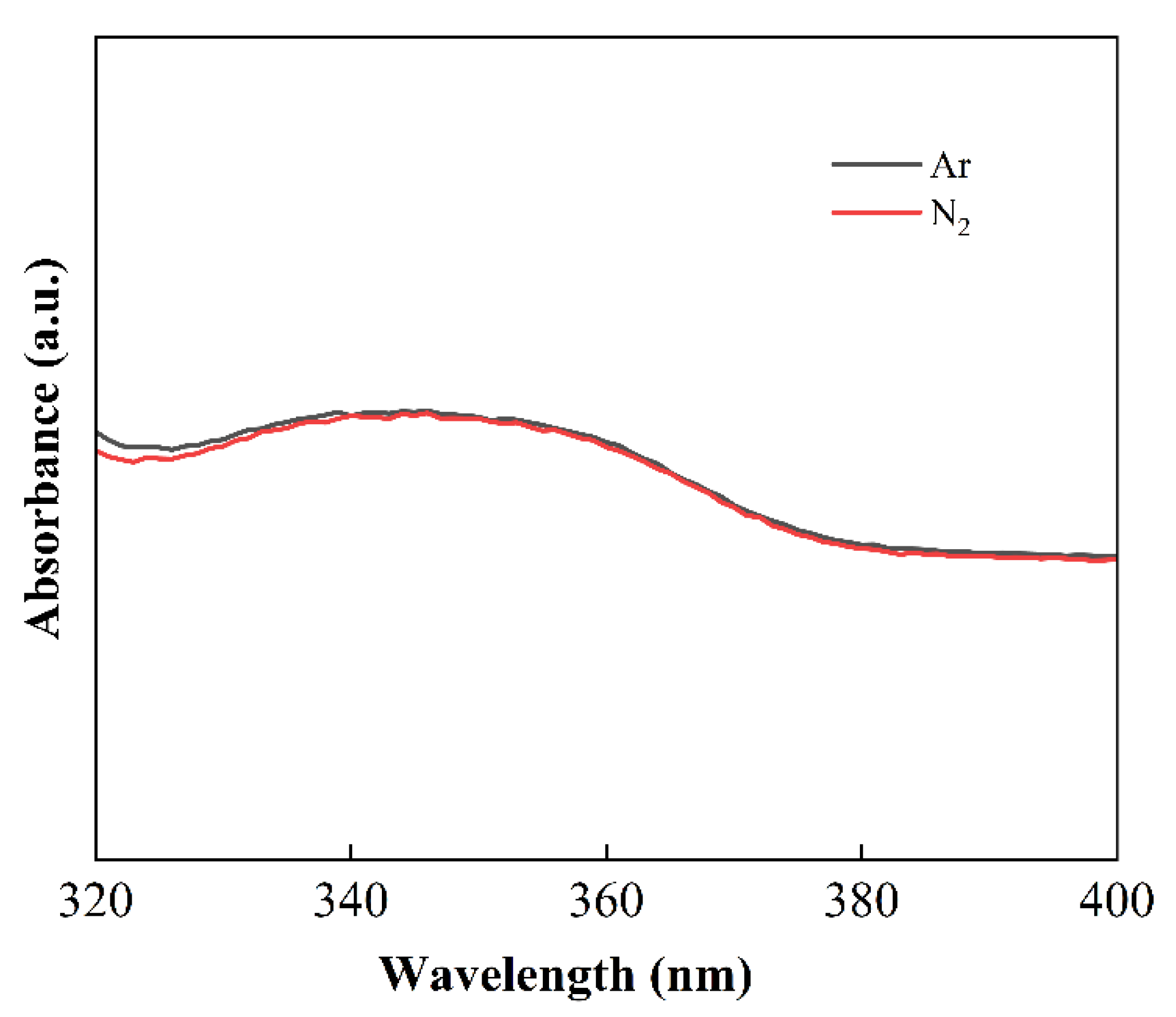
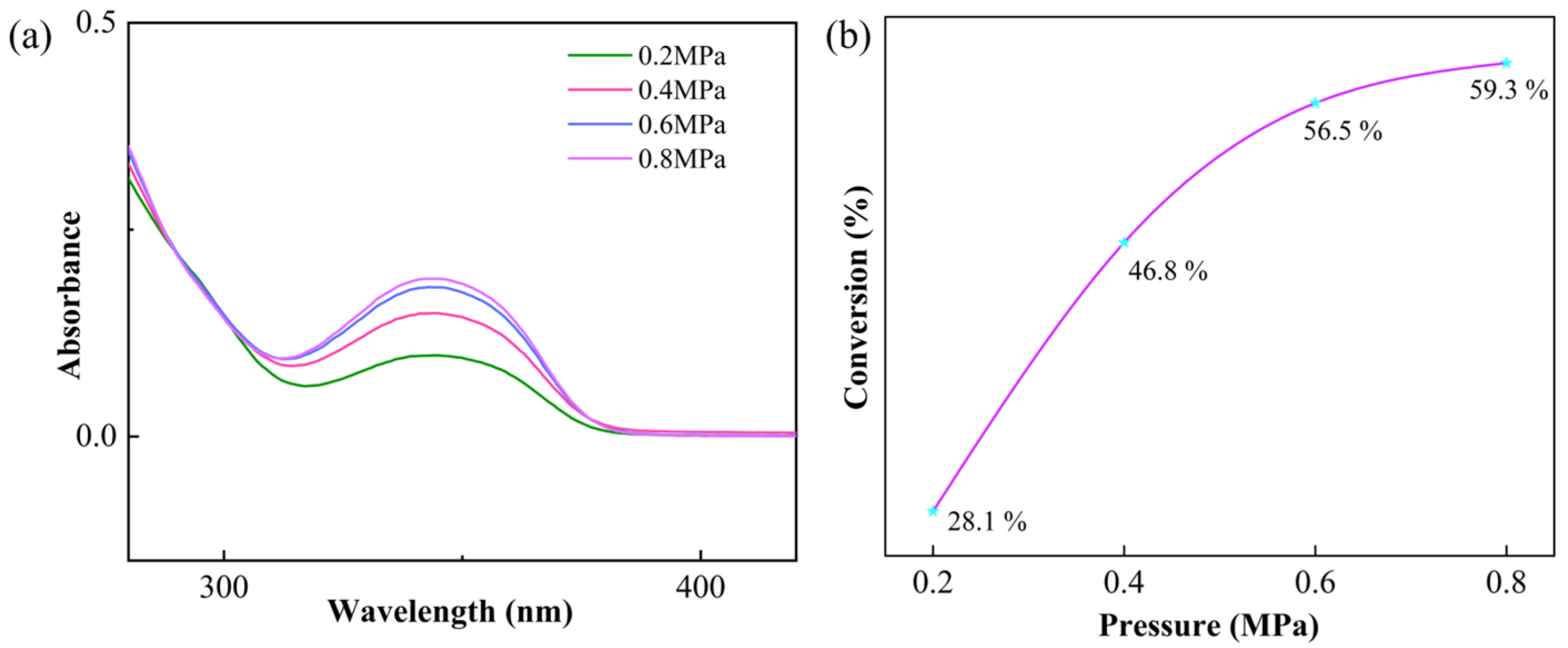
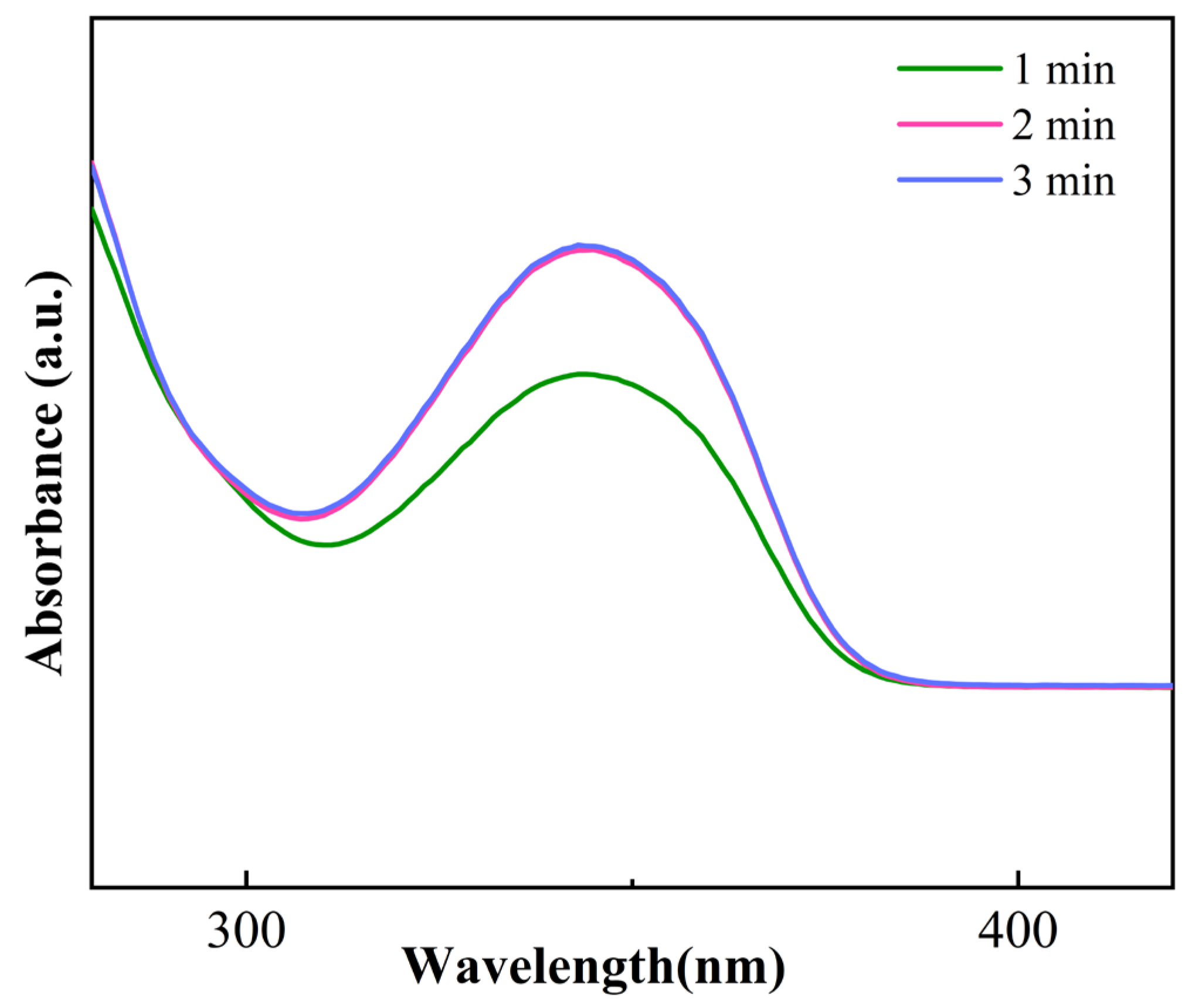
3.2. Reaction Process Analysis
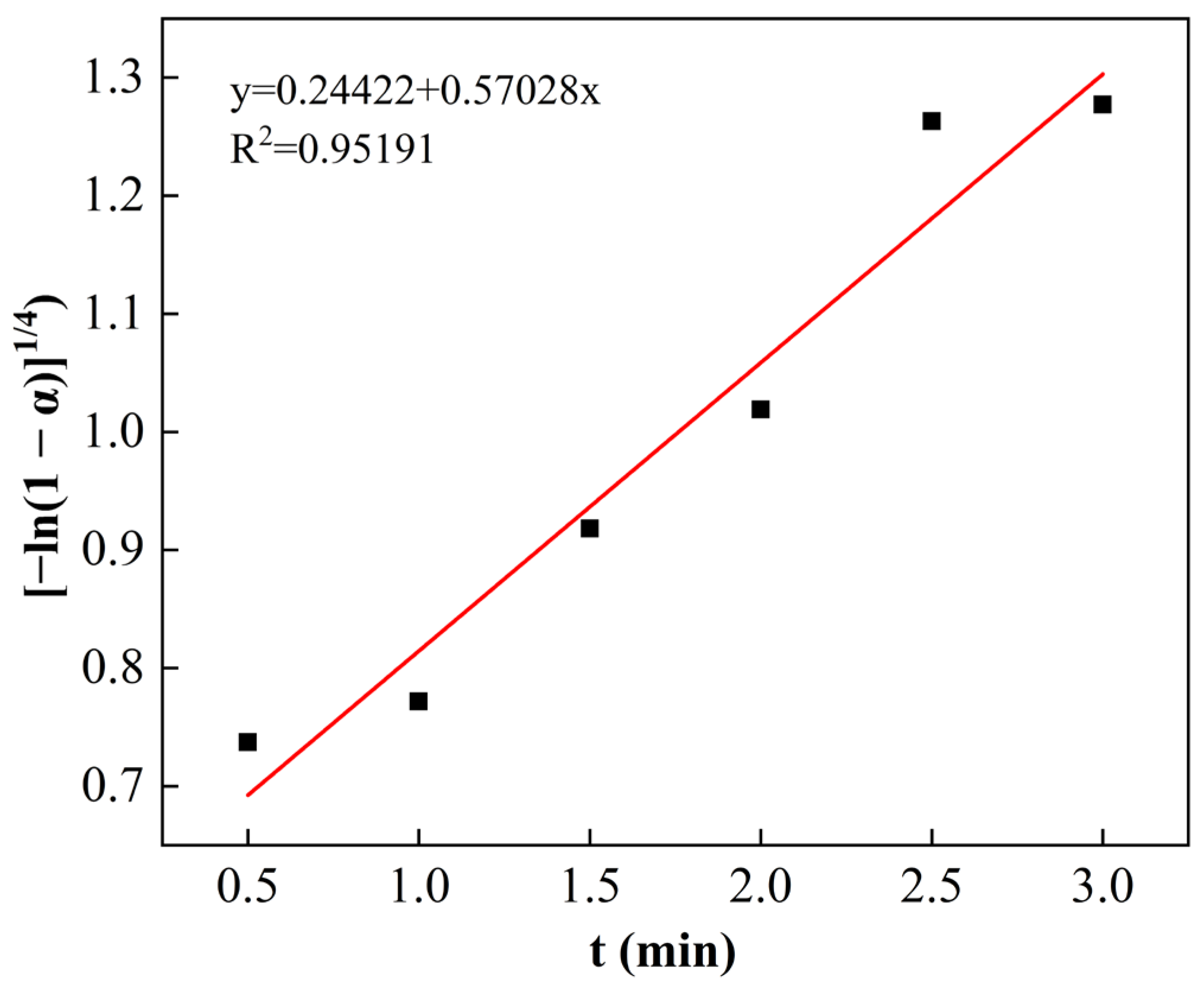
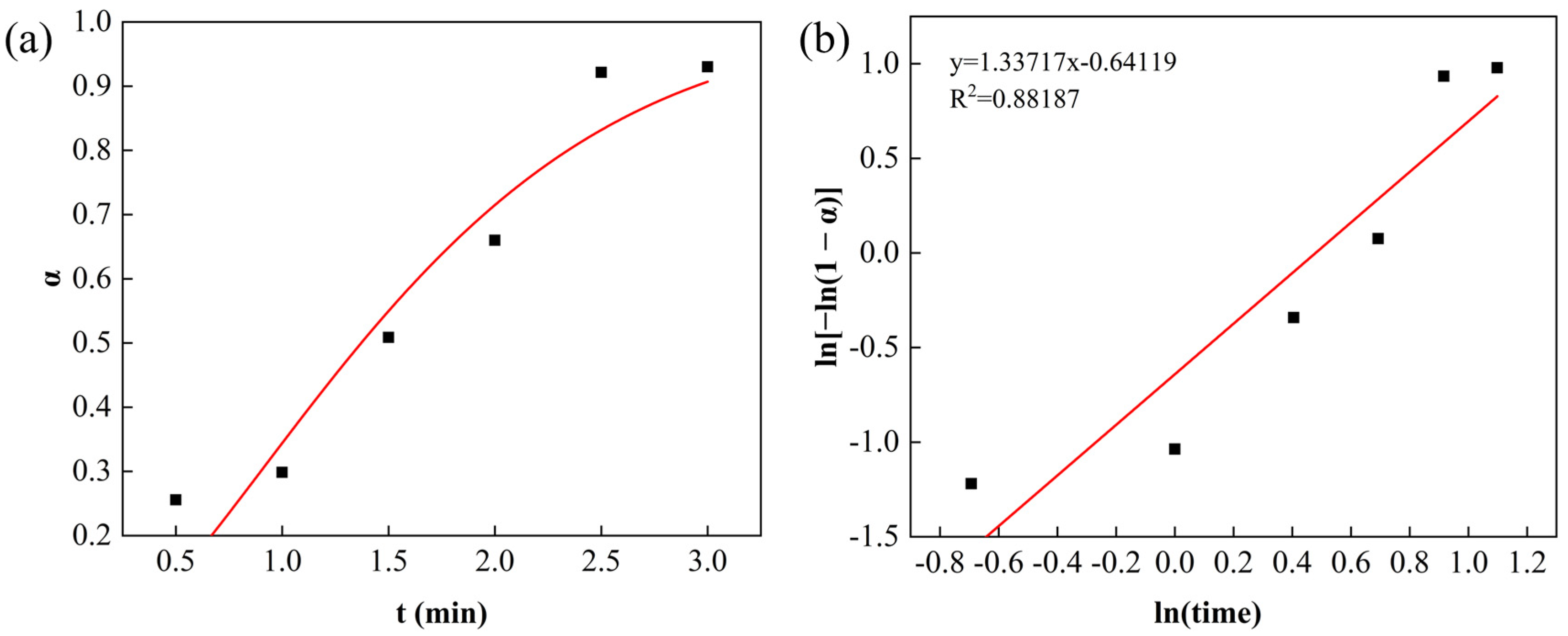
3.3. Kinetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.; Yang, R.; Xiao, Q. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Heterocyclics via Cascade Cyclization of Propargylic Alcohols. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 852–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Studer, A. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Nitrogen Heterocycles via Radical Cascade Reactions Using Isonitriles as Radical Acceptors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3505–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, P.; Carta, A.; Loriga, M.; Vitale, G.; Paglietti, G. Synthesis and in vitro Antitumor Activity of New Quinoxaline Derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewangan, D.; Nakhate, K.; Mishra, A.; Thakur, A.S.; Rajak, H.; Dwivedi, J.; Sharma, S.; Paliwal, S. Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Quinoxaline Derivatives as a Potent Antimicrobial Agent. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2019, 56, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Singh, P.; Quraishi, M.A. Quinoxaline Derivatives as Efficient Corrosion Inhibitors: Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitra, S.; Parameswari, K.; Vidhya, M.; Kalishwari, M.; Selvaraj, A. Evaluation of Quinoxalines as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acid Environment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 4593–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Obi-Egbedi, N.O. Indeno-1-One [2,3-b]quinoxaline as an Effective Inhibitor for the Corrosion of Mild Steel in 0.5M H2SO4 Solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 122, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Obi-Egbedi, N.O.; Odozi, N.W. Acenaphtho [1,2-b] Quinoxaline as a Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in 0.5M H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Dixit, R.; Sharma, S.; Dutta, S.; Yadav, S.; Arora, B.; Gawande, M.B.; Sharma, R.K. Efficient and Sustainable Co3O4 Nanocages Based Nickel Catalyst: A Suitable Platform for the Synthesis of Quinoxaline Derivatives. Mol. Catal. 2021, 504, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassagne, F.; Chevallier, F.; Roisnel, T.; Dorcet, V.; Mongin, F.; Domingo, L. A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study of the Ammonium Bifluoride Catalyzed Regioselective Synthesis of Quinoxalines and Pyrido[2,3-b]pyrazines. Synthesis 2015, 47, 2680–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, M.; Bazzar, M.; Ramzanian, S.F.; Tajbakhsh, M. Sulfonated nanoClay Minerals as a Recyclable Eco-Friendly Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoxaline Derivatives in Green Media. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 88–89, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, C.; Gao, W.-C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yue, J.; Tang, B. Nickel-Catalyzed Borrowing Hydrogen Annulations: Access to Diversified N-Heterocycles. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 7844–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Gravel, E.; Jawale, D.V.; Doris, E.; Namboothiri, I.N.N. Synthesis of Quinoxalines by a Carbon Nanotube–Gold Nanohybrid-Catalyzed Cascade Reaction of Vicinal Diols and Keto Alcohols with Diamines. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh Naidu, B.; Venkateswarlu, K. WEPA: A Reusable Waste Biomass-Derived Catalyst for External Oxidant/Metal-Free Quinoxaline Synthesis via Tandem Condensation–Cyclization–Oxidation of α-Hydroxy Ketones. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 6215–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godino-Ojer, M.; Shamzhy, M.; Čejka, J.; Pérez-Mayoral, E. Basolites: A Type of Metal Organic Frameworks Highly Efficient in the One-Pot Synthesis of Quinoxalines from α-Hydroxy Ketones under Aerobic Conditions. Catal. Today 2020, 345, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithambaram, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Shen, X.; Gaenzler, F.; Suib, S.L. Manganese Octahedral Molecular Sieves Catalyzed Tandem Process for Synthesis of Quinoxalines. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Venegas, M.; Juaristi, E. Mechanochemical and Mechanoenzymatic Synthesis of Pharmacologically Active Compounds: A Green Perspective. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8881–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-W. Mechanochemical Organic Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyreva, E. Mechanochemistry of Inorganic and Organic Systems: What Is Similar, What Is Different? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Adams, C.J.; Bolm, C.; Braga, D.; Collier, P.; Friščić, T.; Grepioni, F.; Harris, K.D.M.; Hyett, G.; Jones, W.; et al. Mechanochemistry: Opportunities for New and Cleaner Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 413–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, B.; Peng, R. Continuous, Solvent-Free, and Mechanochemical Synthesis of N-Acylhydrazone Derivatives by Spiral Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, W.; Huang, J.; Jin, B.; Peng, R. Low-Temperature Continuous Mechanochemical Synthesis of Hydantoin-Based Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients by Spiral Gas–Solid Two-Phase Flow. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 17739–17748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawam, A.; Flanagan, D.R. Solid-State Kinetic Models: Basics and Mathematical Fundamentals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 17315–17328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, Z.T.; Prasannakumar, G.; Das, A.; Biswas, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Banerjee, M. A Facile, Catalyst-Free Mechano-Synthesis of Quinoxalines and Their In-Vitro Antibacterial Activity Study. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| E-Factor b | PMI c | AE (%) d | |
|---|---|---|---|
| using S-GSF | 0.26 | 1.26 | 88.68 |
| in solution [11] a | 1.98 | 3.59 | 61.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, B.; Peng, R. Helical Airflow Synthesis of Quinoxalines: A Continuous and Efficient Mechanochemical Approach. Chemistry 2025, 7, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040121
Zhang J, Xiao Z, Huang Q, Zhao Y, Jin B, Peng R. Helical Airflow Synthesis of Quinoxalines: A Continuous and Efficient Mechanochemical Approach. Chemistry. 2025; 7(4):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040121
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiawei, Zeli Xiao, Qi Huang, Yang Zhao, Bo Jin, and Rufang Peng. 2025. "Helical Airflow Synthesis of Quinoxalines: A Continuous and Efficient Mechanochemical Approach" Chemistry 7, no. 4: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040121
APA StyleZhang, J., Xiao, Z., Huang, Q., Zhao, Y., Jin, B., & Peng, R. (2025). Helical Airflow Synthesis of Quinoxalines: A Continuous and Efficient Mechanochemical Approach. Chemistry, 7(4), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040121





