Abstract
The potential of pretreated sugarcane bagasse (SCB) as a low-cost and renewable source to yield activated carbon (AC) for chromate CrO42− removal from an aqueous solution has been investigated. Raw sugarcane bagasse was pretreated with H2SO4, H3PO4, HCl, HNO3, KOH, NaOH, or ZnCl2 before carbonization at 700 °C. Only pretreatments with H2SO4 and KOH yield clean AC powders, while the other powders still contain non-carbonaceous components. The point of zero charge for ACs obtained from SCB pretreated with H2SO4 and KOH is 7.71 and 2.62, respectively. Batch equilibrium studies show that the most effective conditions for chromate removal are a low pH (i.e., below 3) where >96% of the chromate is removed from the aqueous solution.
Keywords:
wastewater; water treatment; Cr(VI); heavy metals; adsorption; sugarcane bagasse; activated carbon; low-cost 1. Introduction
Chromium is a naturally occurring element and the 21st most abundant element in the earth’s crust [1]. Although chromium in its metallic form was first described in 1797 [2], its technical applications were limited until the middle of the 20th century. This is due to the high toxicity of chromium compounds, which was discovered early on. However, with the advent of the modern industrialized society in the mid to late 1800s, there was a rapidly increasing need for heat- and corrosion-resistant alloys. Moreover, the textile industry, another rapidly growing sector, was actively looking into advanced chemical processes for tanning and dyeing [3,4,5,6]. In their well-known book “Handwörterbuch der reinen und angewandten Chemie” Liebig, Poggendorf and Wöhler stated about the element in 1842 [7]:
“Von dem metallischen Chrom wird noch keine Anwendung gemacht; um so wichtiger aber sind durch ihre technischen Anwendungen mehrere seiner Verbindungen geworden. Auf den Organismus wirken sie als Gifte, indessen hat man sie noch nicht als Arzneimittel anzuwenden versucht.”
“Metallic chromium is not yet used, but several of its compounds have become all the more important through their technical applications. They act as poisons on the organism, but no attempt has yet been made to use them as medicines.”
Though numerous applications have been identified and developed for metallic chromium and its salts since the days of Justus von Liebig, chromium compounds obviously remain harmful. Despite this, chromium compounds can be found in the environment all over the planet but foremost in developing countries, where high chromium levels dramatically endanger entire eco systems [1,6,8]. This is a development that could probably not have been foreseen by the scientists in Liebig’s time but needs to be faced and resolved nowadays.
In terms of toxicity, one of the main challenges of Cr is its chemical versatility. Chromium can adopt oxidation states between –II and +VI, but Cr(III) and Cr(VI) are most prominent in natural environments [6]. Cr(III) is an essential nutrient for the human body and necessary for controlling blood glucose levels and insulin action in tissues [9]. Cr(VI) is a carcinogen, highly mobile in aqueous environments, highly soluble in water, and 500 times more toxic than Cr(III) [5,10]. Because of its high water solubility and high mobility in the environment, Cr(VI) can enter the terrestrial food chain and finally end up in higher animals and humans. Once taken up, Cr(VI) causes liver and kidney damage, asthma, and skin ulcerations, along with immunotoxic, genotoxic, and neurotoxic effects, among others [3].
Plants also take up Cr(VI). Consequently, Cr(VI) can be found in plant roots, shoots, stems, leaves, and seeds [11,12]. Cr(VI) inhibits germination and affects root, stem, and leaf growth [6]. Moreover, the quality of flowers, crop yields, photosynthesis, respiration, and symbiotic nitrogen fixation are severely disturbed by Cr(VI) [11]. Therefore, the reduction of Cr(VI) levels in water bodies is a significant and large-scale problem needing reliable treatments and solutions [6,13].
Electroplating, leather tanning, dye and pigment, steel and alloy, automobile, ammunition, paint, and textile manufacturing industries are the most common sources of Cr(VI) [3,4,5,6]. Many of these industries release significant amounts of Cr(VI) into surface water bodies, which leads to critical Cr(VI) levels around these manufacturing sites [3,10].
Some of the most common methods to control Cr(VI) levels in water are ion exchange, precipitation, flocculation, reverse osmosis, electrocoagulation, electrodialysis, membrane filtration, solvent extraction, and adsorption [3,5,10,14,15]. Each of these methods has advantages and drawbacks. For instance, ion exchange, electrocoagulation, reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, and membrane filtration require a high amount of energy and regular maintenance [3,6,10]. Industries in developing countries are typically not able to manage the high costs of those treatments. Additionally, some of these treatments produce tremendous amounts of sludge as a byproduct. Deposited sludge waste then triggers secondary pollution and requires further management [6,10]. As a result, and because a large number of these manufacturing sites are located in developing countries [13,16,17], there is an ever-growing need for effective yet (very) low-cost approaches towards Cr(VI) removal.
Activated carbons (ACs) are very effective adsorbents [13,17,18], but the very high demand overall and the significant cost of ACs limit their use, especially in developing countries. Hence, low-cost adsorbents and effective yet cheap activation of suitable raw materials have become a substantial focus of science and technology [17].
Generally, the effective activation of carbonaceous raw materials involves chemical or physical modifications that significantly improve the quality of the adsorbents. The enhanced formation of micro- and mesopores, generation of large surface areas, and the addition of functional groups to the adsorbent surface are key parameters for improved performance of (low-cost) ACs [19]. Acids such as H3PO4 [20,21], H2SO4 [22,23,24], HCl [20], or HNO3 [19,25], strong bases such as KOH [21,24] or NaOH [20,21], and salts such as ZnCl2 [21,26], CaCl2 [27], or FeCl3 [21] are popular activators for AC production. Depending on the treatment, different types of materials are obtained. For instance, NaOH or HCl pretreatments reduce the silica and ash content, while H3PO4 pretreatments yield P-containing functional groups and highly microporous materials [20]. H2SO4 produces acidic surface oxygen species and increases the specific surface area [28], while HNO3 pretreatment yields cellulose nitrate groups and high pore volume [19]. ZnCl2 [26] and KOH [29] yield smaller pore sizes and higher surface areas in the ACs. Interestingly, the reasons why these different treatments produce different pore sizes are still largely unclear.
Nowadays, numerous raw materials have been identified as suitable sources for ACs for water treatment, including agricultural waste [4,30]. Popular raw materials include pomegranate peel, orange peel, banana peel, corn cobs, rice husks, sugarcane bagasse (SCB), sawdust, plant leave waste, tea leaves, cottonseed, coconut shell, and rice straw [13,16]. Further studies suggest that adsorbents prepared from raw or carbonized SCB [31,32,33,34,35], coconut shell [36], or rice husks [30,37] effectively remove metal ions and dyes.
The current study focuses on SCB as a raw material for ACs for Cr(VI) removal from water. SCB is one of the most common and cheapest agricultural wastes in the world and is a major byproduct of the sugar industry [33]. Annually, approximately 54 million tons of dry SCB are produced worldwide. To avoid further management costs, the majority of the SCB is burned directly on the sugarcane fields, causing significant air pollution [33].
However, SCB is an interesting raw material because of its high lignin and cellulose content, which is rich in carbonyl, hydroxyl, ether, phenol, amine, and sulfhydryl groups [33,38]. Being agricultural waste, raw SCB also contains impurities that often require thorough pretreatment and modification to boost the adsorption capacities of the resulting ACs [38].
The functional groups present on the surface of SCB-based ACs act as active adsorption sites that bind different heavy metal ions to the surface [35,38]. Therefore, utilizing SCB waste as a source of ACs not only combats the global wastewater crisis but also reduces the volume of agricultural waste. Hence, considering the increasing demand for a low-cost, sustainable, and easy wastewater treatment process, SCB is an attractive starting material [33].
A final reason for selecting SCB as the starting material is the fact that there are regions, such as Bangladesh, that offer a large amount of sugarcane fields and a large textile industry in close proximity. As a result, SCB as highly abundant agricultural waste and Cr(VI) contamination, which poses severe environmental and health problems, occurs in exactly the same geographic region. The current study, therefore, builds on the fact that local agricultural waste could be used to improve local water quality.
2. Materials and Methods
Chemicals and apparatus. Sulfuric acid (>95% H2SO4), zinc chloride dihydrate (ZnCl2*2 H2O), ortho-phosphoric acid (85% H3PO4), nitric acid (65% HNO3), hydrochloric acid (37% HCl), potassium hydroxide pellets (90% KOH), sodium hydroxide (98% NaOH), potassium dichromate (99% K2Cr2O7), sodium chloride (99.99% NaCl), 1,5-diphenylcarbazide, and acetone were of analytical grade quality and supplied by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). All chemicals were used without further purification.
Collection and purification of SCB. Raw SCB was collected from local sugarcane-juice vendors of Mymensingh, Bangladesh, using a white polyethylene bag for transport. The raw SCB was cut into small pieces with scissors and soaked in tap water to remove dirt and sugar. Afterwards, the SCB was washed thoroughly with distilled water until the residual water was dirt-free (i.e., clear). Next, the washed SCB was dried in a preheated oven at 110 °C for 24 h. After drying, the SCB was ground with a Philips HR3655/00 Blender until the particle size was below 0.50 mm. The particle size below 0.50 mm was ensured by passing the SCB powder through a 0.50 mm sieve (VEB Metallweberei, Neustadt/Orla). The ground SCB powders were then stored in an airtight glass bottle until further use.
Pre-carbonization treatment of SCB. A total of 25 g of the clean and dry SCB powder was mixed with 250 mL of 3M H2SO4 in a three-necked round bottom flask with a condenser in an oil bath. The oil bath was maintained at 80 °C, and the mixture was stirred at 200 rpm for 24 h. Then the mixture was filtered using vacuum filtration to separate the pretreated SCB. The SCB was then washed with hot distilled water until the pH was 6–7. After that, the powder was dried overnight at 105 °C, and the dry, treated SCB was kept in an airtight bottle until further use. The same process was used for treatment with 3M HCl, 30% (v/v) H3PO4, 30% (v/v) HNO3, 30% (w/v) ZnCl2, 1M KOH, and 1M NaOH.
Preparation of activated carbon. All SCB samples were loaded in a custom-made pyrolysis oven described previously [39], and the oven was then heated to 700 °C at 5 °C/min under Argon. The powders were kept for 1 h at 700 °C, then the oven was switched off and left overnight to cool to room temperature. After cooling, all carbonized SCB (cSCB) powders were stored in airtight bottles until further use. Table 1 summarizes all materials studied in this work.

Table 1.
Overview of cSCB powders studied in this article.
Characterization and analysis. Infrared spectroscopy was conducted at room temperature on a Nicolet iS5 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham MA, USA) with an iD7 attenuated total reflection (ATR) unit, a resolution of 1 cm−1, and 32 scans per measurement from 400–4000 cm−1.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted on a JEOL JSM-6510 (JEOL, Freising, Germany) SEM operated at 5 kV. Prior to imaging, all samples were sputter-coated with Au/Pd for 75 s and 18 mA using an SC7620 mini sputter coater (Quorum Technologies, Lewes, UK).
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) data were collected on a PANalytical Empyrean powder X-ray diffractometer in a Bragg–Brentano geometry. It is equipped with a PIXcel1D detector using Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5419 Å) operating at 40 kV and 40 mA. θ/θ scans were run in a 2θ range of 4–70° with a step size of 0.0131° and a sample rotation time of 1 s. The diffractometer is configured with a programmable divergence and anti-scatter slit and a large Ni-beta filter. The detector was set to continuous mode with an active length of 3.0061°.
Surface area and pore sizes were determined via nitrogen sorption at 77 K using a Micromeritics Tristar (Micromeritics Instrument Corp., Norcross, GA, USA). Prior to all measurements, the materials were degassed to about 2 Pa at 353 K for 10 h. The specific surface area (SSA) was calculated via the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) approach. Average pore sizes were estimated from the adsorption branch of the isotherm using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method. The pore volume was determined at P/P0 > 0.99.
Determination of the point of zero charge, pHpzc, was performed according to published protocols [40,41]. First, 50 mL of a 0.01M NaCl solution was transferred to a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and the initial pH (pHi) was adjusted to 2–12 using (0.1 to 1M) H2SO4 and NaOH. The pH was recorded with a Digital pH meter GPH014 (PCE Instruments UK Ltd., Hamble-le-Rice, UK, refillable electrode). Then 0.15 g of cSCB was added to the solution, and the mixture was agitated on a magnetic stirrer for 24 h at 200 rpm. Thereafter the solution was vacuum–filtered with Whatman® Grade 1 filter paper (diameter 11 cm). The final pH (pHf) of the solution was measured, and ΔpH = pHf − pHi was plotted vs. pHi. The point where ΔpH and pHi are zero is pHpzc for the corresponding cSCB adsorbent.
Batch adsorption experiments. All batch adsorption studies were carried out in 50 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 25 mL of an aqueous K2Cr2O7 solution with a concentration of 1 g/L. After the addition of the cSCB adsorbent, the mixtures were placed on a magnetic stirrer and stirred at 200 rpm at 30 °C for 24 h. The suspension was filtered, and the residual concentration of Cr(VI) was determined with a Vernier® UV-VIS Spectrophotometer (Vernier Software & Tech SE, Vernier Science Education, Beaverton, OR, USA) via Method 7196A as published by the US EPA [42]. Calibration was performed with a dilution series of aqueous K2Cr2O7 with concentrations between 10 and 100 mg/L (R2 > 0.998). The impact of solution pH on adsorption was evaluated from adsorption experiments with 20 mg/L K2Cr2O7 solutions with starting pH from 1 to 11.
The fraction of Cr(VI) removed was calculated using Equation (1)
where %R is the percentage of Cr(VI) removed, while C0 and Cf are the initial and final Cr(VI) concentrations (mg/L) of the solutions before and after treatment.
The influence of the initial Cr(VI) concentration and the influence of the adsorbent dose were studied using analogous approaches by either varying the K2Cr2O7 concentration or the adsorbent dose while keeping all other conditions constant. The adsorption kinetics were studied by variation of the contact time of the adsorbent and K2Cr2O7 solution. All experiments were repeated three times, and all spectrophotometric measurements were duplicates yielding six measurements per experimental condition. Values reported are mean and standard deviations obtained from these six values.
3. Results
Figure 1 shows X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns obtained from the raw SCB and the chemically activated SCBs after pyrolysis. The XRD pattern of raw SCB shows three broad halos at 16.34 (110), 22.05 (002), and 34.68° (004) 2θ. These signals can be assigned to the presence of cellulose I [43,44].
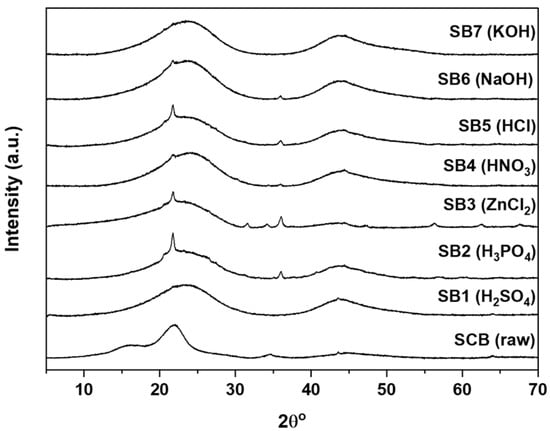
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction patterns obtained from SCB adsorbents after pyrolysis.
All pretreated and carbonized SCBs (cSCBs) only show two broad halos (not three as in the raw SCB) at around 24 and around 44° 2θ that can be assigned to graphitized carbon [20,45,46]. Moreover, sharp reflections at 21.79 (011) and 36.01° (112) 2θ in the patterns obtained from SB2, SB4, SB5, and SB6 can be assigned to cristobalite (ICDD 98-003-4933). Additional sharp reflections observed in the XRD patterns obtained from SB3 at 2θ = 31.67 (010), 36.02 (011), 56.199 (110), 62.52, (020), and 67.57° (112) 2θ can be assigned to wurtzite ZnO (ICDD 98-018-2355).
Only SB1 and SB7 (see Table 1 for assignments) show no additional reflections, indicating that there are no further crystalline (inorganic) compounds present in the materials. The halos at 2θ = 23.61 (002) and 43.82 (011) can be assigned to graphite 2H (ICDD 98-007-6767). Based on the XRD data, therefore, SB1 and SB7 are the purest carbons produced here (i.e., materials without further components visible in the XRD data). As a result, these two materials were chosen for an in-depth investigation along with the raw carbonized SCB for comparison.
Figure 2 shows representative IR spectra obtained from raw SCB, SB1, and SB7. Spectra of raw SCB show a broad peak centered at 3614 cm−1, which can be assigned to the O-H stretching vibration of intramolecular hydrogen bonds in carbohydrates and lignin [47]. Bands centered at 3029 cm−1 stem from C-H bond vibrations [48]. A small band at 1770 cm−1 can be assigned to C=O bond vibrations of aldehydes, ketones, or carboxyl groups [48,49]. Furthermore, bands at 1612 and 1525 cm−1 are attributed to the aromatic rings present in lignin and to adsorbed water, while a band at 1281 cm−1 can be assigned to C-O stretching vibrations in lignin [44,47,49].
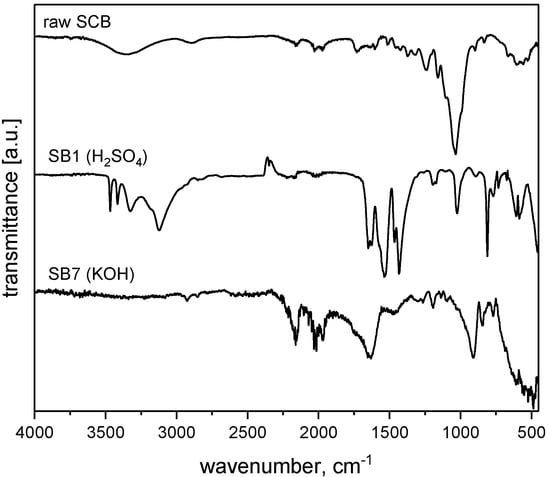
Figure 2.
IR spectra obtained from raw SCB, SB1, and SB7 after pyrolysis. IR spectra of all materials can be found in the Supporting Information. While the spectra vary from material to material, all IR bands can be assigned to C-C, C=C, C=O, and C-H vibrations stemming from the organic and carbonized components of the materials. SB6 and SB7 exhibit rather noisy spectra, but also here, all bands and shoulders can be assigned to vibrations in the activated carbonaceous material.
IR spectra of SB1 show bands at 3323 and 1526 cm−1, which correspond to the N-H stretching vibration of amines and amides along with nitro groups [50]. A band at 3118 cm−1 originates from C-H stretching vibrations, while a band at 1428 cm−1 can be attributed to C-H deformation vibrations [47,51]. Bands at 2390 and 1636 cm−1 indicate the presence of aromatic C=C bonds and C=O bonds in carboxyl groups [13,52]. Furthermore, the presence of aromatic moieties and amines in SB1 is further corroborated by bands at 1192 and 1024 cm−1 [34,50,51,53].
IR spectra of SB7 show a broad signal centered at 3375 cm−1, which indicates the presence of O-H bonds, including hydrogen bonding [54]. A band at 1635 cm−1 again indicates the presence of C=O bonds, likely from ketones, aldehydes, or carboxylates [26]. Further bands between 1200 and 1100 cm−1 can be assigned to C-O vibrations in ether, alcohol, phenol, acid, or ester moieties [54], while a broad and poorly resolved group of bands at around 618 cm−1 is from C-H and C-C stretching vibrations [52].
Figure 3 shows representative scanning electron microscopy (SEM) data obtained from raw SCB, SB1, and SB7. SEM images of SCB show a large variety of particle sizes with numerous different morphologies. The surface of the particles is rather dense without much substructure.
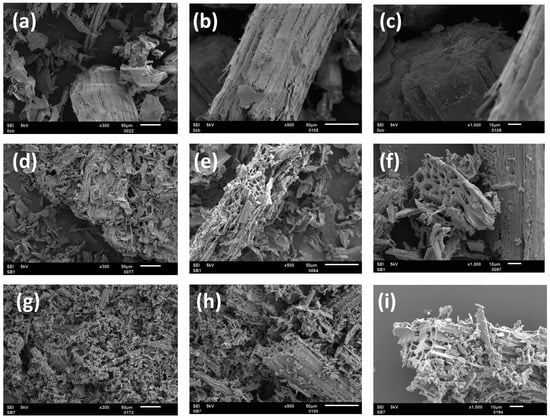

Figure 3.
SEM images of SCB (a–c), SB1 (d–f), and SB7 (g–i) at different magnifications.
SB1 is quite different from raw SCB. SB1 exhibits a very broad size distribution along with a fraction of smaller particles with sharper edges than those observed in SCB. Moreover, all particles also exhibit some surface roughness, and there are also large particles with micrometer-sized pores. All particles show cracks and appear to have a larger fraction of open surface than raw SCB. The opening and surface roughening can be assigned to the pre-activation with H2SO4 combined with thermal treatment that removes lignin and inorganic components, which leaves pores and cavities on the adsorbent surface (and likely also inside the powders), consistent with previous studies [13,22,52].
Likewise, SB7 is quite different from SCB. Again, smaller particles are visible. They appear finer and somewhat smaller than in SB1, but overall, the material exhibits a very broad particle size distribution. Additionally, SB7 exhibits sharp edges of the particles, and cracks and pores are visible in all particles.
Figure 4 shows complementary nitrogen sorption data for the three materials, SCB, SB1, and SB7. All datasets are very similar and only show a very limited N2 uptake and a correspondingly small surface area of all materials. SCB is essentially non-porous (note that nitrogen sorption does not detect macropores, which are visible in the SEM images). The surface area determined for SB1 is 6–8 m2/g, and SB7 has a surface area of around 30 m2/g. Overall, these data indicate that the materials are essentially macroporous powders with negligible mesopore and micropore fractions.
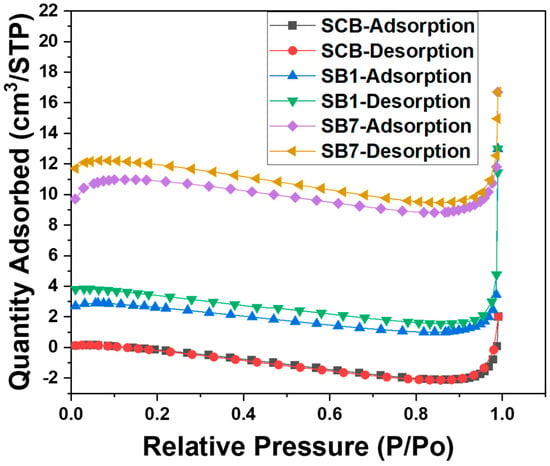
Figure 4.
Nitrogen sorption isotherms obtained from SCB, SB1, and SB7. Adsorption and desorption branches are identified separately. The somewhat unusual shape of the isotherms with a decrease at intermediate pressures can be assigned to the very low surface areas of all materials studied here.
The rather low surface areas observed for these materials are comparable with many other examples from the literature [14,16,18,19]. Many ACs made from agricultural waste show surface areas on the order of 10 to ca. 100 m2/g. This likely stems from the fact that all these ACs are essentially based on carbohydrates and that the original materials have micrometer-sized features in the plants. Apparently, most treatments are not able to open up significant amounts of micro- or mesopores, but rather the treatments seem to modify the surfaces chemically, which in turn then alters the adsorption behavior.
Numerous studies have shown that pH is a crucial parameter when it comes to adsorption [4,55,56]. Figure 5a illustrates the adsorption efficiency of SB1 and SB7 vs. the initial solution pH. SB1 removes ca. 96% of the chromate within 24 h at pH 1–3. This is confirmed by visual inspection: solutions treated with SB1 at pH 1–3 show essentially no remaining color, Figure 5b, indicating an almost complete Cr(VI) removal. At pH 4 and higher, the fraction of Cr(VI) that is removed decreases and reaches ca. 20% at pH 9 and higher.
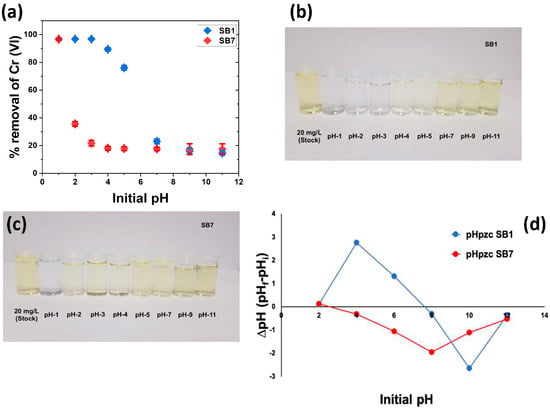
Figure 5.
(a) Cr(VI) removal vs. initial pH for SB1 and SB7 (C0 = 20 mg/L, m = 0.1 g, V = 25 mL, t = 24 h, T = 30 °C, rpm = 200). (b) Solution color vs. pH for treatment with SB1. (c) Solution color vs. pH for treatment with SB7. (d) Determination of pHpzc for SB1 and SB7 (C0 = 0.01 M NaCl, m = 0.15 g, V = 50 mL, t = 48 h, T = 25 , rpm = 200).
In contrast, SB7 only shows a high removal rate of ca. 96% Cr(VI) at pH 1. Already at pH 3, the removal rate drops to below 40% and reaches ca. 20% at pH 4. Again, this is corroborated by visual inspection: solutions treated at pH 2 and higher are still yellow, indicating incomplete Cr(VI) removal, Figure 5c.
To better quantify and understand this observation, the point of zero charge (pHpzc) was determined, Figure 5d. The pHpzc is 7.71 for SB1, showing that the surface is positively charged below pH ca. 7.7. In contrast, the pHpzc of SB7 is 2.62, indicating that SB 7 is only positively charged below ca. pH 2.6, which is much lower than what is observed for SB1.
Figure 6 shows the effect of the initial Cr(VI) concentration with the SB1 adsorbent at an initial pH of 3. After 24 h, the highest Cr(VI) removal rate is observed at low concentrations. Generally, the removal rate decreases with increasing initial Cr(VI) concentration. This is consistent with previous data [4,13,50,56].
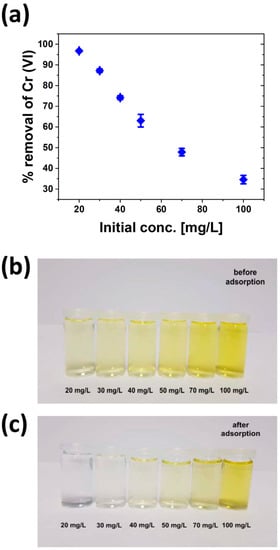
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of initial SB1 concentration on Cr(VI) removal (pH = 3, mSB1 = 0.1 g, V = 25 mL, t = 24 h, T = 30 °C, rpm = 200). (b) Color of the Cr(VI) solutions before treatment with SB1. (c) Color of the Cr(VI) solutions after treatment with SB1.
Figure 7 shows the effects of the adsorbent dose on Cr(VI) removal. Generally, Cr(VI) removal increases as the adsorbent dose increases. At a dose of 0.1 g/25 mL and higher, no further color changes (or changes in the absorption data) are observed. The solution is essentially colorless, and >96% of the Cr(VI) is removed from the solution. Therefore, 0.1 g/25 mL was subsequently used for further batch experiments.
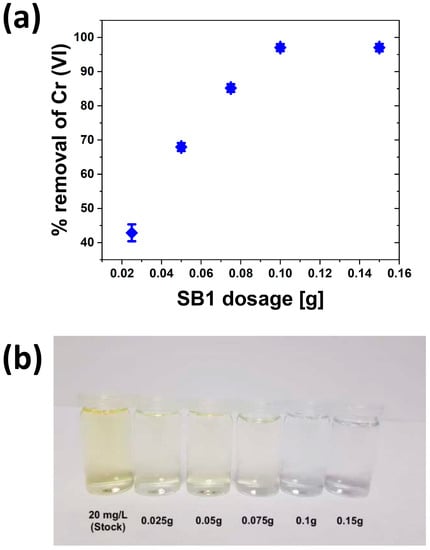
Figure 7.
(a) SB1 dose vs. Cr(VI) removal (C0(Cr) = 20 mg/L, pH = 3, V = 25 mL, t = 24 h, T = 30 °C, rpm = 200). (b) Photograph of the solutions after treatment with increasing adsorbent dose.
Figure 8 shows the effect of contact time on Cr(VI) removal. The data show a monotonous increase in Cr(VI) removal up to ca. 8 h. After that, the Cr(VI) removal is much slower and finally levels off at ca. 96% at around 24 h.
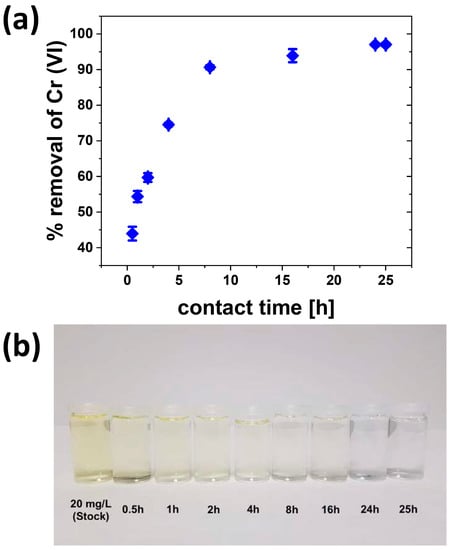
Figure 8.
(a) Contact time vs. Cr(VI) removal (C0(Cr) = 20 mg/L, pH = 3, m = 0.1 g, V = 25 mL, t = 24 h, T = 30 °C, rpm = 200). (b) Photograph of solutions after treatment.
4. Discussion
As stated in the introduction, low-cost and low-tech approaches towards Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions are highly important. The current study proposes a new approach based on activated carbons from sugarcane bagasse, a high-volume agricultural waste. In particular, we have identified two promising materials (SB1 and SB7) that are clean carbon materials that effectively remove dichromate from an aqueous solution. Both materials show a strong pH dependence on Cr(VI) removal: while SB1 removes up to 96% of Cr(VI) up to pH 3, SB7 is only effective at pH 1, Figure 5a.
This behavior can be assigned to the different points of zero charge in the two materials, Figure 5d. Considering the pHpzc of 2.62 that is observed for SB7, these data indicate that already at pH 2, the charge density and overall charge of the SB7 surface is too low to produce a strong interaction between the adsorbent surface and the chromate or dichromate ions in solution. In contrast, the much higher pHpzc of ca. 7.2 of SB7 suggests that here a much larger window of positive charge exists, and thus, there is a much wider pH window where the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged adsorbent surface and the dissolved anions is effective. Such an observation is consistent with previous studies [4,55,56,57,58]. Similarly, low pHpzc values are also consistent with the literature; these effects have been assigned to surface adsorption of OH- from the pretreatment, with hydroxides then being released and acting as a buffer and lowering the pHpzc [59].
Once the pH is high enough to supersede the pHpzc, the surface of the adsorbent is negatively charged. This should result in electrostatic repulsion between adsorbent and anions in solution, which drives the adsorption capacities down at higher pH. Likely, the remaining low adsorption of below 20% is then due to effects such as hydrogen bonding or direct interaction with individual surface groups such as amines.
These data clearly show that acid treatment is more attractive in the current case because this treatment keeps the pHpzc higher and thus provides a material that is effective in Cr(VI) removal from pH 1–3, similar to a previous study showing that net negative charges are advantageous for Cr(VI) removal [23]. Evaluation of the surface areas, Figure 4, also shows that the dominating effect is indeed the pHpzc and not the surface areas, as they are very low in all cases investigated here.
As an interesting and technologically relevant observation, it must be noted that the pH of Cr(VI) containing industrial effluent occurs mostly at around 3 [4,60,61] or even below 3 [62]. As a result, especially SB1 is a prime candidate for direct use without any further modifications for Cr(VI) removal from industrial wastewaters. The one remaining challenge is the fact that the Cr(VI) concentrations in real wastewaters are often much higher than even the highest concentration studied here, Figure 6. Moreover, the adsorbent doses and contact times may need to be adjusted to account for a large-scale, real-life system and may therefore be different from the contact times studied here, Figure 7 and Figure 8. There is thus a further need to improve the materials and the overall process to be able to directly use the SB1 material for Cr(VI) removal, but in spite of this, the ease of production, the very good performance under near-realistic pH conditions, and the low cost of the raw materials make the materials and the process an attractive candidate for further development.
5. Conclusions
Sugarcane bagasse (SCB) is a suitable raw material for the fabrication of activated carbons for Cr(VI) removal from synthetic wastewater at conditions that are reminiscent of real wastewaters from tanning and other industries. Pretreatments with KOH and H2SO4 remove impurities from the raw materials. After carbonization of these pretreated raw materials, effective adsorbents for Cr(VI) removal at low pH can be obtained. Acid activation yields materials that can be used between pH 1 and 3 with good to excellent removal rates; materials obtained from KOH-treated SCB only remove Cr(VI) at a very low pH of 1. Overall, pretreated SCB is a cheap and abundant carbon source that can effectively be converted to AC to remove Cr(VI) from wastewater.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemistry5020077/s1. IR spectra of SB1 to SB7.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A., A.B. and A.T.; methodology, all authors; software, R.A. and A.D.-R.; validation, all authors (R.A., I.B., F.O., C.G., A.D.-R., P.H., A.B., A.T.); formal analysis, all authors except F.O.; investigation, all authors; resources, A.B., P.H. and A.T.; data curation, all authors; writing—original draft preparation, R.A, A.B. and A.T.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, R.A., A.D.-R., P.H. and C.G.; supervision, A.B. and A.T.; project administration, A.B. and A.T.; funding acquisition, A.B., P.H. and A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Potsdam (grant #53170000, #53140000).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the current article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ertani, A.; Mietto, A.; Borin, M.; Nardi, S. Chromium in Agricultural Soils and Crops: A Review. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Nwankwo, W.; Osibote, O.A.; Paumo, H.K.; Ama, O.M.; Adetunji, C.O.; Siloko, I.U. Effect of hexavalent chromium on the environment and removal techniques: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Sarkar, A.; Sen, S. Removal of chromium from industrial effluents using nanotechnology: A review. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itankar, N.; Patil, Y. Management of hexavalent chromium from industrial waste using low-cost waste biomass. Procd. Soc. Behav. 2014, 133, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.M.; Shrivastava, V.S. Photocatalytic degradation of Chromium (VI) from wastewater using nanomaterials like TiO2, ZnO, and CdS. Appl. Nanosci. 2011, 1, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium pollution in European water, sources, health risk, and remediation strategies: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, J.; Poggendorff, J.C.; Wöhler, F. Chrom. In Handwörterbuch der Reinen und Angewandten Chemie, 1st ed.; Vieweg und Sohn: Braunschweig, France, 1842; Volume 2, pp. 264–284. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Gu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, J. Carcinogenicity of chromium and chemoprevention: A brief update. Oncotargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4065–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschinsky, N.; Kottwitz, K.; Freund, B.; Dresow, B.; Fischer, R.; Nielsen, P. Bioavailability of chromium(III)-supplements in rats and humans. Biometals 2012, 25, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur-E-Alam, M.; Mia, M.A.S.; Ahmad, F.; Rahman, M.M. An overview of chromium removal techniques from tannery effluent. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambulska, U.Y.; Bayliak, M.M.; Lushchak, V.I. Chromium(VI) toxicity in legume plants: Modulation effects of rhizobial symbiosis. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8031213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H. Chromium as an Environmental Pollutant: Insights on Induced Plant Toxicity. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 375843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Kuang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, M. Removal of hexavalent chromium in aquatic solutions by pomelo peel. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Moisy, P.; Banerji, A.; Hesemann, P.; Taubert, A. Monitoring and Management of Anions in Polluted Aqua Systems: Case Studies on Nitrate, Chromate, Pertechnetate and Diclofenac. In Progress and Prospects in the Management of Oxoanion Polluted Aqua Systems; Oladoja, N., Unuabonah, E.I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 293–348. [Google Scholar]
- Lofu, A.; Mastrorilli, P.; Dell’Anna, M.M.; Mali, M.; Sisto, R.; Vignola, R. Iron(II) modified natural zeolites for hexavalent chromium removal from contaminated water. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Arya, D.K.; Singh, N.; Vats, H.K. Removal of Cr (VI) Using Low Cost Activated Carbon Developed by Agricultural Waste. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 10, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Q. Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, J.; Bin Shahid, U.; Hijab, M.; Mackey, H.; McKay, G. Production and applications of activated carbons as adsorbents from olive stones. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2019, 9, 775–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademiluyi, F.T.; David-West, E.O. Effect of Chemical Activation on the Adsorption of Heavy Metals Using Activated Carbons from Waste Materials. ISRN Chem. Eng. 2012, 2012, 674209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Cao, Q.; Liu, X. The performance of phosphoric acid in the preparation of activated carbon-containing phosphorus species from rice husk residue. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5008–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedia, J.; Peñas-Garzón, M.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Belver, C. Review on Activated Carbons by Chemical Activation with FeCl3. J. Carbon Res. 2020, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, L.W.; Teng, T.T.; Ahmad, A.; Morad, N.; Wong, Y.S. A novel pretreatment method of lignocellulosic material as adsorbent and kinetic study of dye waste adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 218, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, R.; Philip, L.; Chandraraj, K. Biosorption of chromium species by aquatic weeds: Kinetics and mechanism studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.C.; Wu, P.H.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Preparation of novel activated carbons from H2SO4-Pretreated corncob hulls with KOH activation for quick adsorption of dye and 4-chlorophenol. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkady, M.; Shokry, H.; Hamad, H. New activated carbon from mine coal for adsorption of dye in simulated water or multiple heavy metals in real wastewater. Materials 2020, 13, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, L.; Zeng, J. Cr(VI) adsorption performance and mechanism of an effective activated carbon prepared from bagasse with a one-step pyrolysis and ZnCl2 activation method. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4921–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.A.; Lade, H.S.; Patil, S.M.; Govindwar, S.P. Low cost CaCl2 pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for enhancement of textile dyes adsorption and subsequent biodegradation of adsorbed dyes under solid state fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Tian, F.; Sun, F.; Liang, C.; You, W.; Han, C.; Li, C. Activated carbons chemically modified by concentrated H2SO4 for the adsorption of the pollutants from wastewater and the dibenzothiophene from fuel oils. Langmuir 2003, 19, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsom, M.; Autthanit, C. Preparation of sludge-derived KOH-activated carbon for crude glycerol purification. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Garg, U.; Singh, D.; Garg, V.K. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using pre-consumer processing agricultural waste: A case study of rice husk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Nadeem, R.; Iqbal, M.; Manzoor, Q. Biosorption of chromium onto native and immobilized sugarcane bagasse waste biomass. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harripersadth, C.; Musonge, P.; Makarfi Isa, Y.; Morales, M.G.; Sayago, A. The application of eggshells and sugarcane bagasse as potential biomaterials in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 34, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, T.C.A.; da Silva, I.Z.; Rubio, A.J.; Bergamasco, R.; Gasparotto, F.; de Souza Paccola, E.A.; Yamaguchi, N.U. Sugarcane bagasse as an efficient biosorbent for methylene blue removal: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusto, L.A.R.; Pissetti, F.L.; Castro, T.S.; Magalhães, F. Preparation of Activated Carbon from Sugarcane Bagasse Soot and Methylene Blue Adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.M.; Nasir, M.; Imran, M.; Bakhat, H.F.; Rabbani, F.; Sajjad, M.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Ahmad, S.; Song, L. Biosorption potential of natural, pyrolysed and acid-assisted pyrolysed sugarcane bagasse for the removal of lead from contaminated water. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushawish, A.; Almanassra, I.W.; Backer, S.N.; Jaber, L.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Sayed, E.T.; Alawadhi, H.; Shanableh, A.; Atieh, M.A. High-efficiency removal of hexavalent chromium from contaminated water using nitrogen-doped activated carbon: Kinetics and isotherm study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elham, A.; Hossein, T.; Mahnoosh, H. Removal of Zn(II) and Pb (II) ions Using Rice Husk in Food Industrial Wastewater. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2010, 14, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, T.S.; Azam, S.M.G.G.; El-Gawad, A.M.A.; Gaglione, S.A.; Bonanomi, G. Sugarcane bagasse: A potential low-cost biosorbent for the removal of hazardous materials. Clean Technol. Environ. 2017, 19, 2343–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, I.; Guenter, C.; Duarte-Rodrigues, A.; Paasch, S.; Hesemann, P.; Taubert, A. Carbon adsorbents from spent coffee for removal of methylene blue and methyl orange from water. Materials 2021, 14, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeydouni, G.; Rodriguez Couto, S.; Nourmoradi, H.; Basiri, H.; Amoatey, P.; Esmaeili, S.; Saeidi, S.; Keishams, F.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Khaniabadi, Y.O. H2SO4-modified Aloe vera leaf shells for the removal of P-chlorophenol and methylene blue from aqueous environment. Toxin Rev. 2020, 39, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Heydari, R.; Nourmoradi, H.; Basiri, H.; Basiri, H. Low-cost sorbent for the removal of aniline and methyl orange from liquid-phase: Aloe Vera leaves wastes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. SW-846 Test Method 7196A: Chromium, Hexavalent (Colorimetric). 1992. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/7196a.pdf. (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Evans, S.K.; Wesley, O.N.; Nathan, O.; Moloto, M.J. Chemically purified cellulose and its nanocrystals from sugarcane baggase: Isolation and characterization. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh Negi, Y.; Choudhary, V.; Kant Bhardwaj, N. Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals Produced by Acid-Hydrolysis from Sugarcane Bagasse as Agro-Waste. J. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, S.; Niu, J. Crystallite Structure Characteristics and Its Influence on Methane Adsorption for Different Rank Coals. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 20762–20772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-H.; Wazir, A.H.; Yang, K.S.; Bang, Y.H.; Kim, S.R.; Info, A. Molecular structure effects of the pitches on preparation of activated carbon fibers from electrospinning Review Articles. Carbon Lett. 2011, 12, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, G.; Bahurudeen, A.; Appari, S. Thermochemical Conversion of Sugarcane Bagasse: Composition, Reaction Kinetics, and Characterisation of By-Products. Sugar Tech 2020, 23, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, R.C.; Mendes, F.M.; Perrone, C.C.; Sant’Anna, C.; de Souza, W.; Abud, Y.; Bon, E.P.; Ferreira-Leitão, V. Structural evaluation of sugar cane bagasse steam pretreated in the presence of CO2 and SO2. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohtashami, S.-A.; Asasian Kolur, N.; Kaghazchi, T.; Asadi-kesheh, R.; Soleimani, M. Optimization of sugarcane bagasse activation to achieve adsorbent with high affinity towards phenol. Turkish J. Chem. 2018, 42, 1720–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.K.; Shahi, G.; Meena, V.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, R.S.; Rai, B.N. Removal of hexavalent chromium Cr (VI) using activated carbon prepared from mango kernel activated with H3PO4. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2016, 2, S63–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savou, V.; Grause, G.; Kumagai, S.; Saito, Y.; Kameda, T.; Yoshioka, T. Pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse pretreated with sulfuric acid. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labied, R.; Benturki, O.; Eddine Hamitouche, Y.; and Donnot, A. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by activated carbon obtained from a waste lignocellulosic material (Ziziphus jujuba cores): Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1066–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabassi, F.; Casu, B.; Perlin, A.S. Infrared absorption and raman scattering of sulfate groups of heparin and related glycosaminoglycans in aqueous solution. Carbohyd. Res. 1978, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedin, K.C.; Martins, A.C.; Cazetta, A.L.; Pezoti, O.; Almeida, V.C. KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon: Adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene Blue removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksabye, P.; Thiravetyan, P.; Nakbanpote, W.; Chayabutra, S. Chromium removal from electroplating wastewater by coir pith. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.T.; Nguyen, V.P.; Ouakouak, A.; Nieva, A.; Doma, B.T., Jr.; Nguyen Tran, H.; Chao, H.-P. Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Water by Biochar and Activated Carbon Prepared through Hydrothermal Carbonization and Pyrolysis: Adsorption-Coupled Reduction Mechanism. Water 2019, 11, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Tiwari, P.N. Removal and Recovery of Chromium(VI) from Industrial Waste Water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 69, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, P.; Blanco, C.; Granda, M. The adsorption of chromium (VI) from industrial wastewater by acid and base-activated lignocellulosic residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, B.; Mestre, A.S.; Carvalho, A.P.; Pires, J. Activated carbon derived from cork powder waste by KOH activation: Preparation, characterization, and VOCs adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 5841–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Mostafa, M.G.; Biswas, T.K.; Mandal, A.; Saha, A.K. Characterization of the Effluents from Leather Processing Industries. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genawi, N.M.; Ibrahim, M.H.; El-Naas, M.H.; Alshaik, A.E. Chromium removal from tannery wastewater by electrocoagulation: Optimization and sludge characterization. Water 2020, 12, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgiç, A.; Çimen, A. Removal of chromium(vi) from polluted wastewater by chemical modification of silica gel with 4-acetyl-3-hydroxyaniline. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37403–37414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
