MgAl-NO3 LDH: Adsorption Isotherms and Multivariate Optimization for Cr(VI) Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization
2.3. Adsorption Tests
3. Results and Discussion
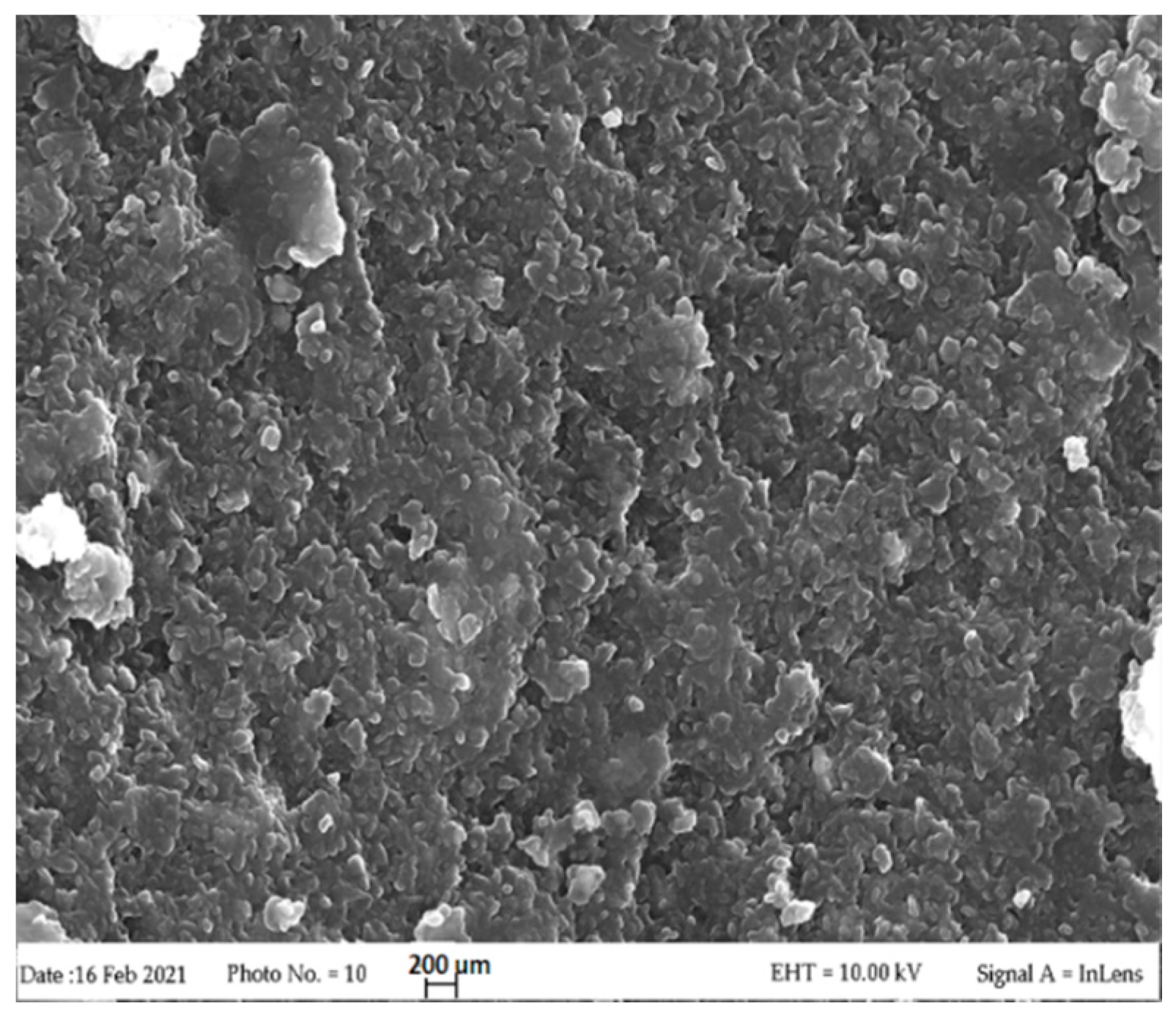
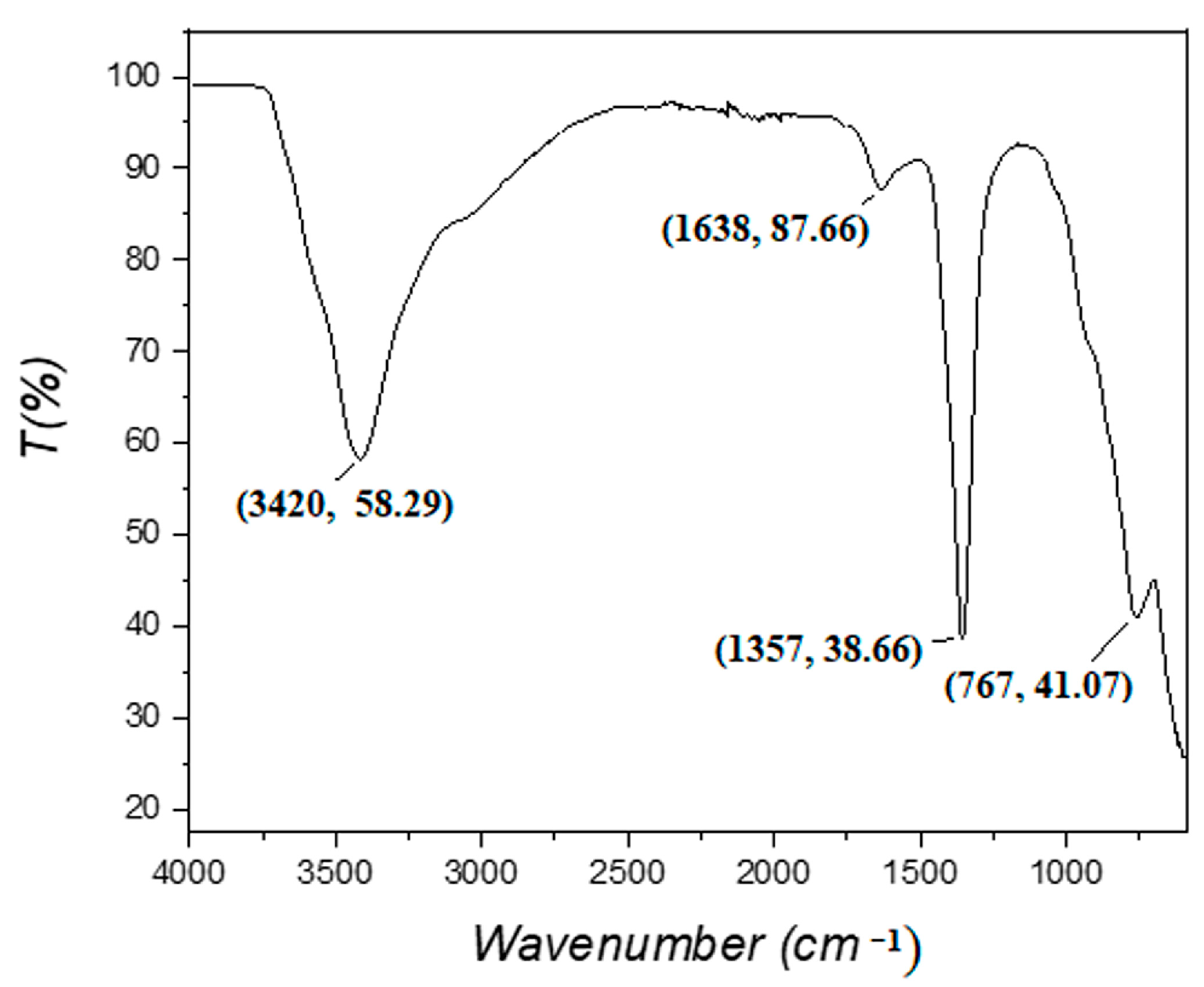
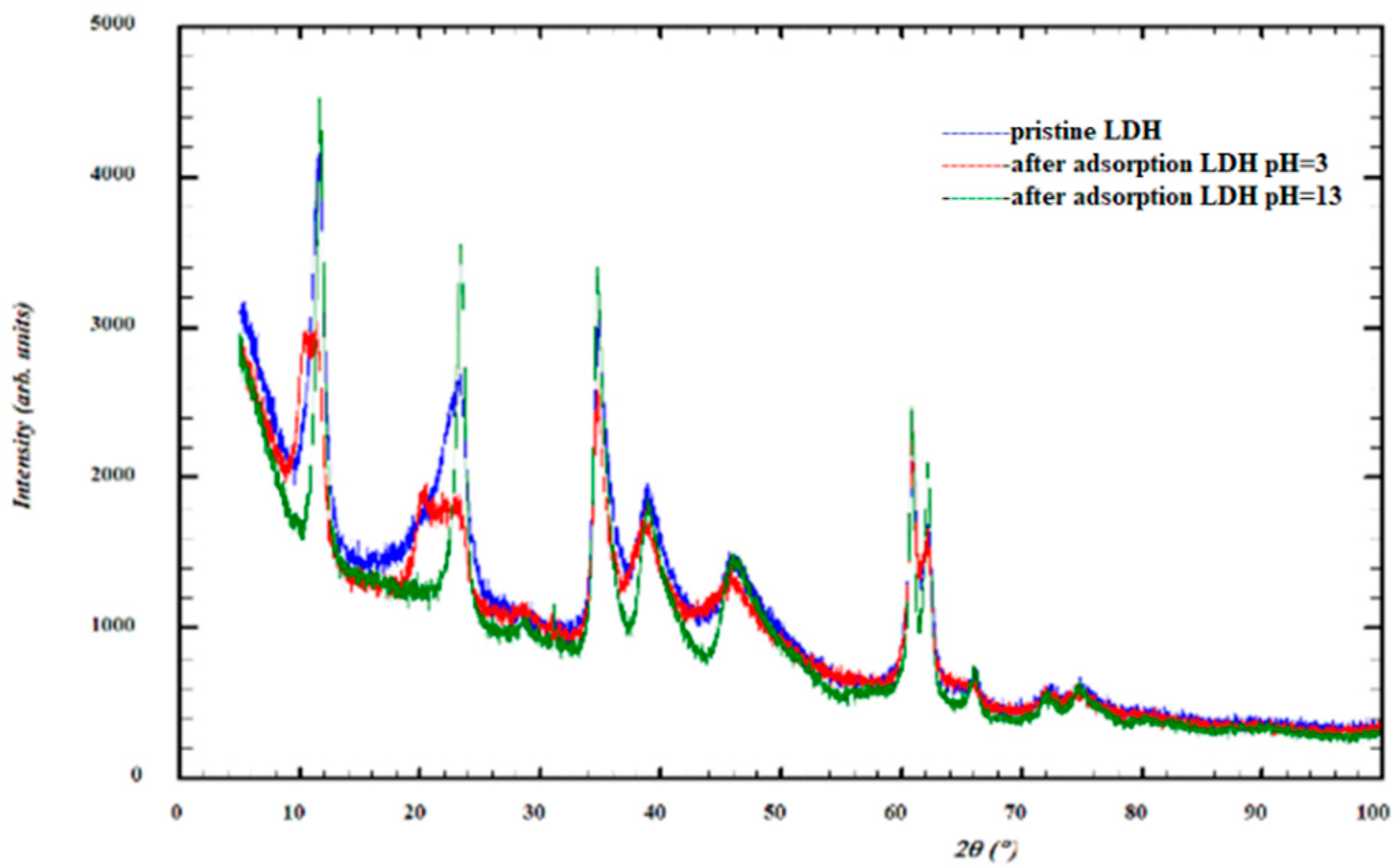
3.1. LDH Characterization
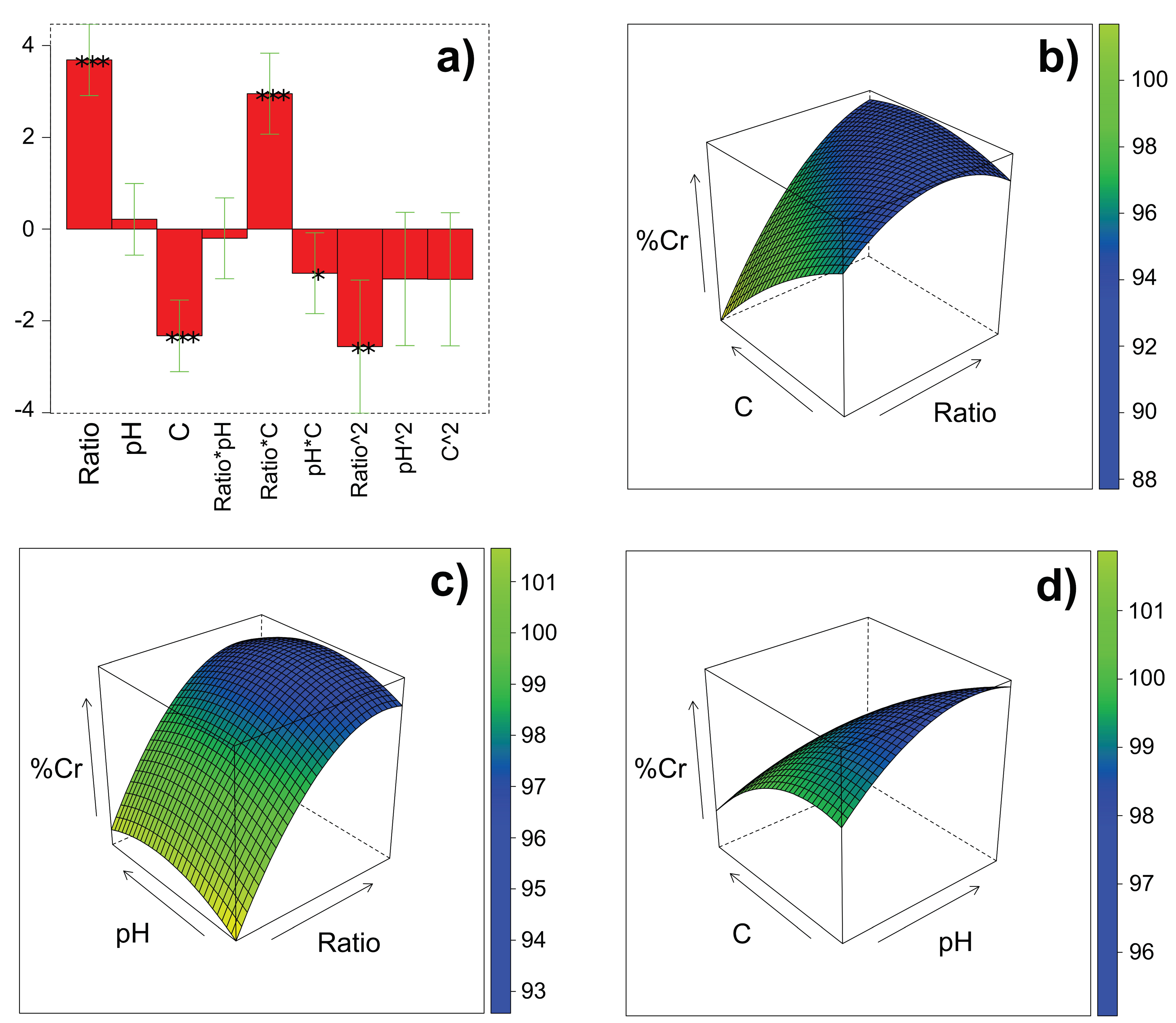
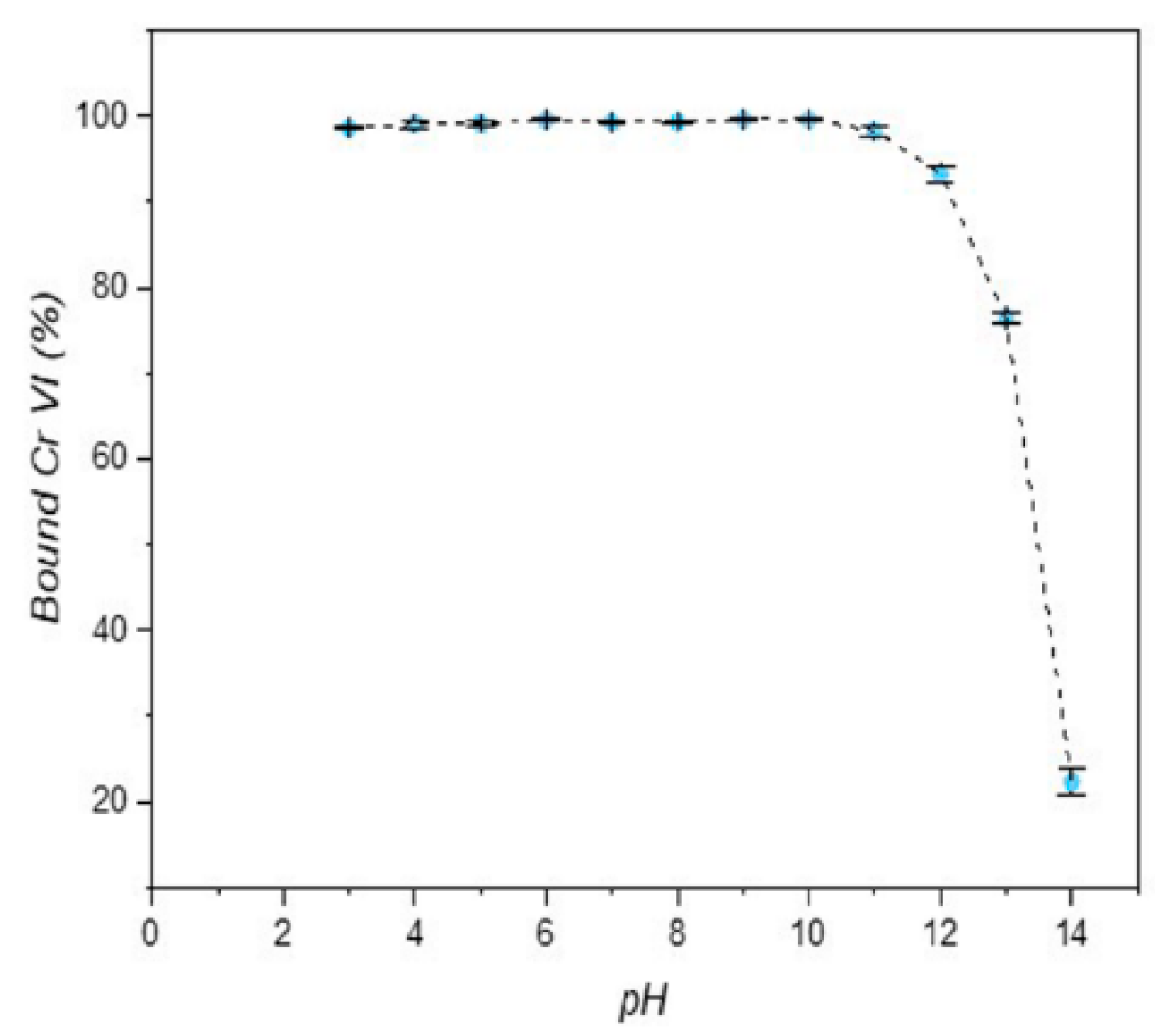
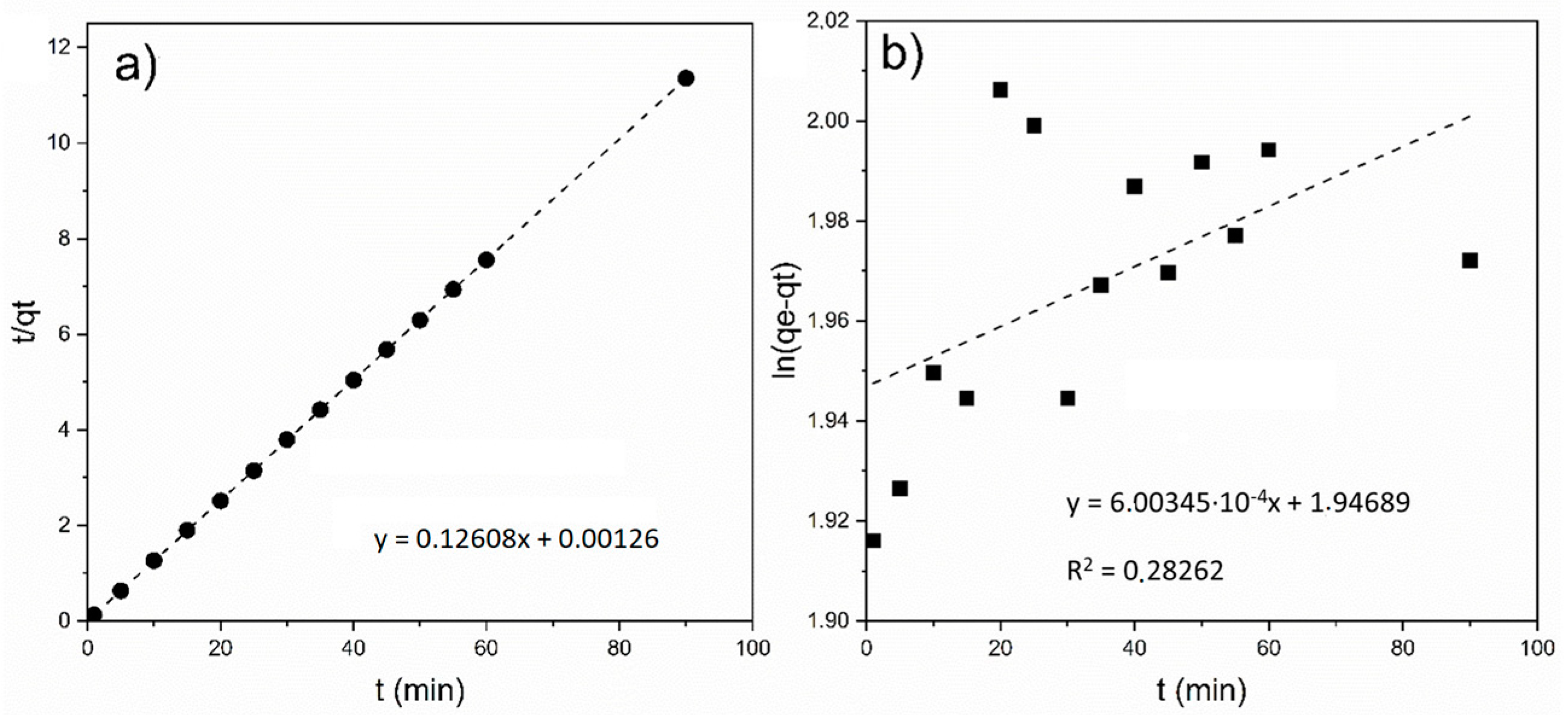
3.2. Adsorption Tests
4. Conclusions
- The synthesis of MgAl-nitrate LDH is simple, reproducible and provides good yield.
- To plan the experimental setup, applying an experimental design (DOE) dramatically reduces the number of experimental tests and yields an appreciation of the whole behavior of the system.
- The ratio (mass of LDH)/(solution volume) identified for optimal adsorption of chromium corresponds to 10 gL−1. Foreseeing a large-scale use of the adsorbent, this value represents the better compromise between adsorption capability and the cost effectiveness of the process.
- As the kinetic, it has demonstrated an almost instantaneous removal of chromium. The Langmuir isotherm adequately describes the absorption kinetics.
- Among the different adsorption parameters investigated, the solution’s pH value has no influence on the efficiency of the process, as long as the pH is between 3 and 12. As predicted, the chromium adsorption increases for high LDH/solution volume ratios and low concentrations of Cr(VI).The maximum adsorption capacity is 27.397 mg/g at neutral conditions.
- The percentage of chromium absorbed (with a ratio of 10 gL−1 of LDH) under the studied conditions is 100 mass% up to an initial concentration of about 300 ppm. This performance can meet remediation needs in the majority of cases where it could be applied.
- By comparing the performance of the investigated MgAl nitrate with other similar LDHs operating in similar chemical—physical conditions, it seems that the nitrate anion can be exchanged more easily than the carbonate. Only the ternary NiMgAl LDH shows a better adsorption capacity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium Pollution in European Water, Sources, Health Risk, and Remediation Strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.K.; Yu, S.; Chang, H.J.; Cho, H.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Chae, B.G. Lead chromate detected as a source of atmospheric Pb and Cr (VI) pollution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, H. Lifting the veil: Unpacking the discourse of water scarcity in Jordan. Eviron. Sci. Policy 2018, 89, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermatas, D.; Panagiotakis, I.; Mpouras, T.; Tettas, K. The Origin of Hexavalent Chromium as a Critical Parameter for Remediation of Contaminated Aquifers. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haounati, R.; Alakhras, F.; Ouachtak, H.; Saleh, T.A.; Al-Mazaideh, G.; Alhajri, E.; Jada, A.; Hafid, N.; Addi, A.A. Synthesized of Zeolite@Ag2O Nanocomposite as Superb Stability Photocatalysis Toward Hazardous Rhodamine B Dye from Water. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouachtak, H.; Akhouairi, S.; Haounati, R.; Addi, A.A.; Jada, A.; Taha, M.L.; Douch, J. 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid removal from water by goethite modified natural sand column fixed-bed: Experimental study and mathematical modeling. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 194, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, C.; Bai, L.; Sun, X. One-step preparation of lignin-based magnetic biochar as bifunctional material for the efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Congo red: Performance and practical application. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Bai, L.; Han, C.; Sun, X. Ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) by chitosan coated biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron aerogel from aqueous solution: Application performance and reaction mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, A.M.; Carbone, C.; Fortunato, M.; Fabiano, B.; Reverberi, A.P. ZnAl-SO4 Layered Double Hydroxide and Allophane for Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Fe(III) Adsorption in Wastewater: Structure Comparison and Synergistic Effects. Materials 2022, 15, 6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, S.; Magro, M.; Baratella, D.; Salviulo, G.; Ugolotti, J.; Filip, J.; Petr, M.; Tucek, J.; Zoppellaro, G.; Zboril, R.; et al. Smart synthetic maghemite nanoparticles with unique surface properties encode binding specificity toward AsIII. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140175–140186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, S.; Magro, M.; Carbone, C.; Baratella, D.; Ugolotti, J.; Ianni, M.C.; Badocco, D.; Canepa, M.; Zboril, R.; Vianello, F.; et al. Environmental implications of one-century COPRs evolution in a single industrial site: From leaching impact to sustainable remediation of CrVI polluted groundwater. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131211–131221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaya Valdivia, A.E.; Montaño Osorio, C.; Vargas Rodríguez, Y.M. Preparation of Activated Carbon from Co_eeWaste as an Adsorbent for the Removal of Chromium (III) from Water. Optimization for an Experimental Box-Behnken Design. Chemistry 2020, 2, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, A.M.; Vecchio Ciprioti, S.; Fortunato, M.; Catauro, M. Thermal behavior and antibacterial studies of a carbonate Mg–Al-based layered double hydroxide (LDH) for in vivo uses. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 5297–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, J.; Hyla, J.; Maziarz, P.; Rybka, K.; Leiviskä, T. Performance of Halloysite-Mg/Al LDH Materials for Aqueous As(V) and Cr(VI) Removal. Materials 2019, 12, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shang, J.; Deng, F. Enhanced adsorption properties of organic ZnCr-LDH synthesized by soft template method for anionic dyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48236–48252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, A.; Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Layered Double Hydroxides and Environment: An Overview. In Advanced Materials for Agriculture, Food, and Environmental Safety; Tiwari, A., Syväjärvi, M., Eds.; WILEY-Scrivener Publisher: Austin, TX, USA, 2014; Chapter 1; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.T.; Kameda, T.; Kumagai, S.; Yoshioka, T. Adsorption isotherms and kinetics of arsenic removal from aqueous solution by Mg–Al layered double hydroxide intercalated with nitrate ions. Reac. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2017, 120, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Son, S.; Bae, S.; Kim, T.H.; Hwang, Y. Particle size and interlayer anion effect on chromate adsorption by MgAl-layered double hydroxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 225, 106552–106563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.-H.; Lim, T.-T.; Banas, A.; Dong, Z. Sorption characteristics and mechanisms of oxyanions and oxyhalides having different molecular properties on Mg/Al layered double hydroxide nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarks, P.; Cenzual, K. Pearson’s Crystal Data-Crystal Structure Database for Inorganic Compounds; ASM international: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- King, G.; Schwarzenbach, L.D. Xtal3.7 System; Hall, S.R., du Boilay, D.J., Olthof-Hazekamp, R., Eds.; University of Western: Crawley, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Petalaa, E.; Dimosa, K.; Douvalisc, A.; Bakasc, T.; Tucekb, J.; Zbořil, R.; Karakassidesa, M.A. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on mesoporous silica: Characterization and reactivity for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Wien, Austria, 2014; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Leardi, R.; Melzi, C.; Polotti, G. CAT (Chemometric Agile Tool). 2017. Available online: http://gruppochemiometria.it/index.php/software (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Bas, D.; Boyaci, I.H. Modeling and Optimization i: Usability of Response Surface Methodology. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Zhao, N.; Xia, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of Mg-Al layered double hydroxides (LDHs) from natural brucite and Al(OH)3. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 3897–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccalon, E.; Gorrasi, G.; Nocchetti, M. Layered double hydroxides are still out in the bloom: Syntheses, applications and advantages of three-dimensional flower-like structures. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102284–102302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, B.; Caponigro, V.; Ardini, F. Experimental Design Step by Step: A Practical Guide for Beginners. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Ng, J.C.Y.; McKay, G. Kinetics of Pollutant Sorption by Biosorbents: Review. Sep. Purif. Methods 2000, 29, 189–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L. Comparison between linear and non-linear forms of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetic models for the removal of methylene blue by activated carbon. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, A.M.; Carbone, C.; Consani, S.; Fortunato, M.; Parodi, N. Layered Double Hydroxides for Remediation of Industrial Wastewater from a Galvanic Plant. Crystals 2020, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Zhub, X.; Zhua, B.; Jianga, C.; Lea, Y.; Yua, J. Superb adsorption capacity of hierarchical calcined Ni/Mg/Al layered double hydroxides for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment | Ratio (g/L) | pH | C (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 4 | 100 |
| 2 | 15 | 4 | 100 |
| 3 | 5 | 8 | 100 |
| 4 | 15 | 8 | 100 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 300 |
| 6 | 15 | 4 | 300 |
| 7 | 5 | 8 | 300 |
| 8 | 15 | 8 | 300 |
| 9 | 15 | 6 | 200 |
| 10 | 10 | 8 | 200 |
| 11 | 10 | 6 | 300 |
| 12 | 5 | 6 | 200 |
| 13 | 10 | 4 | 200 |
| 14 | 10 | 6 | 100 |
| 15 | 10 | 6 | 200 |
| LDH Composition | Solid/Liquid Ratio (g/L) | Solution Cr(VI) Concentration (ppm) | qe (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgAl-NO3 | 10 | 300 | 27.397 | This work |
| MgAl-CO3 * | 5 | 87 | 2.37 | [32] |
| NiMgAl-CO3 | 0.5 | 100 | 32.5 | [33] |
| MgAl-CO3 | 1 | 100 | 11.55 | [18] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardinale, A.M.; Carbone, C.; Molinari, S.; Salviulo, G.; Ardini, F. MgAl-NO3 LDH: Adsorption Isotherms and Multivariate Optimization for Cr(VI) Removal. Chemistry 2023, 5, 633-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010045
Cardinale AM, Carbone C, Molinari S, Salviulo G, Ardini F. MgAl-NO3 LDH: Adsorption Isotherms and Multivariate Optimization for Cr(VI) Removal. Chemistry. 2023; 5(1):633-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardinale, Anna Maria, Cristina Carbone, Simone Molinari, Gabriella Salviulo, and Francisco Ardini. 2023. "MgAl-NO3 LDH: Adsorption Isotherms and Multivariate Optimization for Cr(VI) Removal" Chemistry 5, no. 1: 633-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010045
APA StyleCardinale, A. M., Carbone, C., Molinari, S., Salviulo, G., & Ardini, F. (2023). MgAl-NO3 LDH: Adsorption Isotherms and Multivariate Optimization for Cr(VI) Removal. Chemistry, 5(1), 633-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010045








