The (E, Z) Isomerization of C-methoxycarbonyl-N-aryl Chlorohydrazones
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. X-ray Diffraction
2.2. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
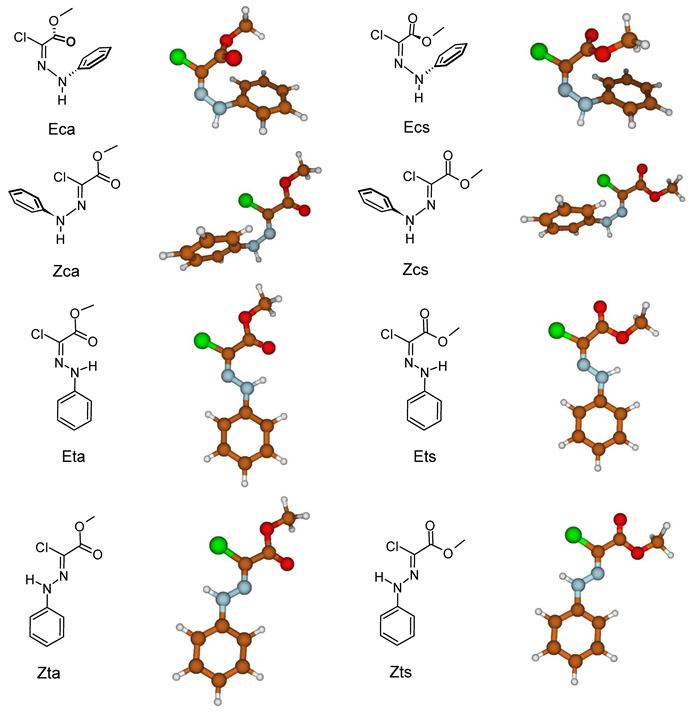
3.1. Structure and Energetics of the Isomers of Chlorohydrazones 1–7
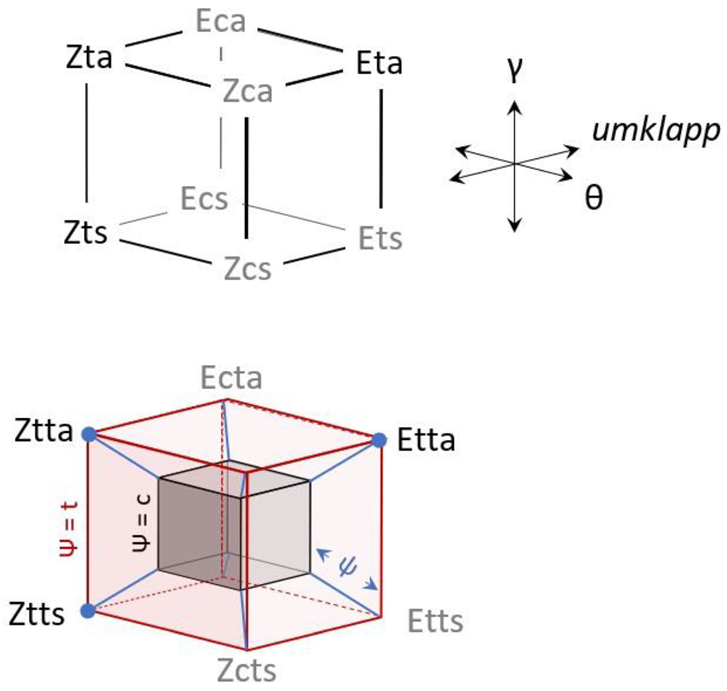
3.1.1. Generalities
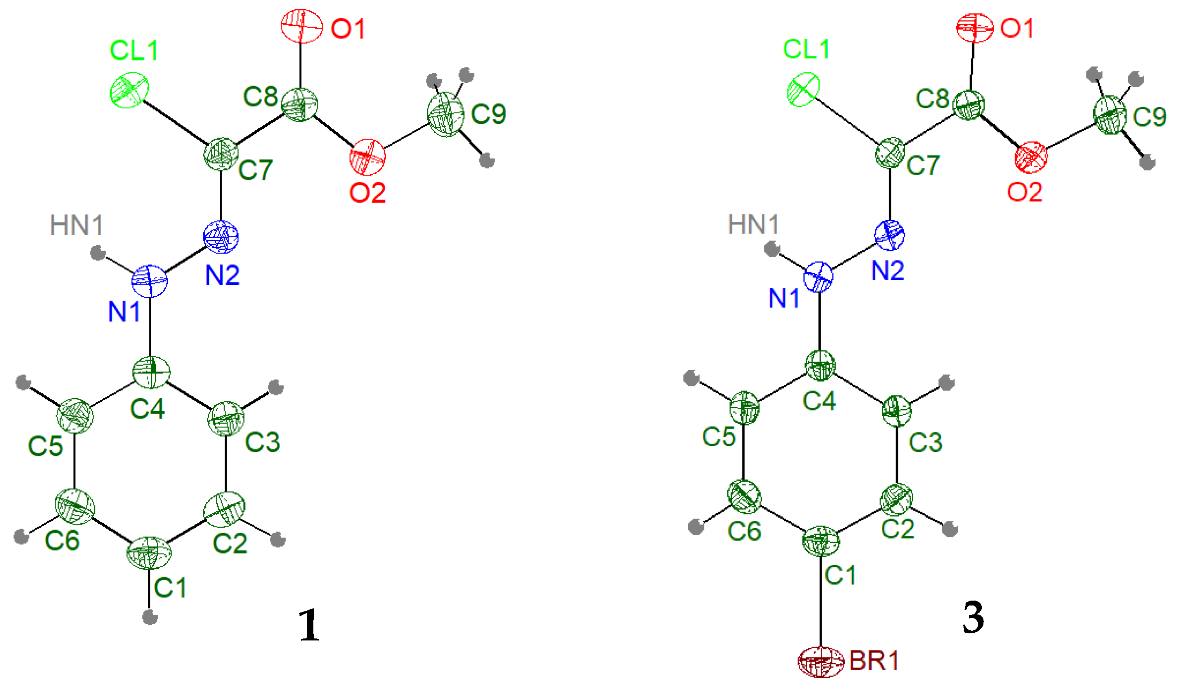
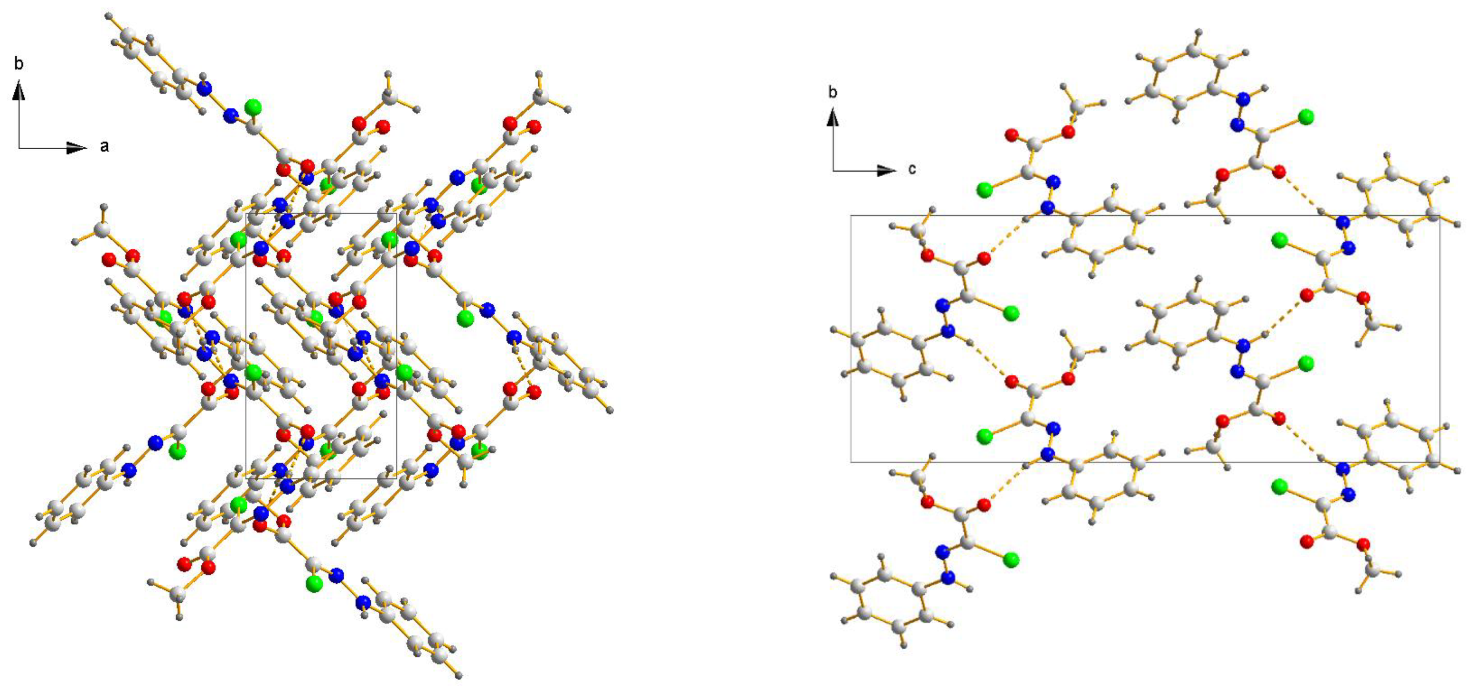
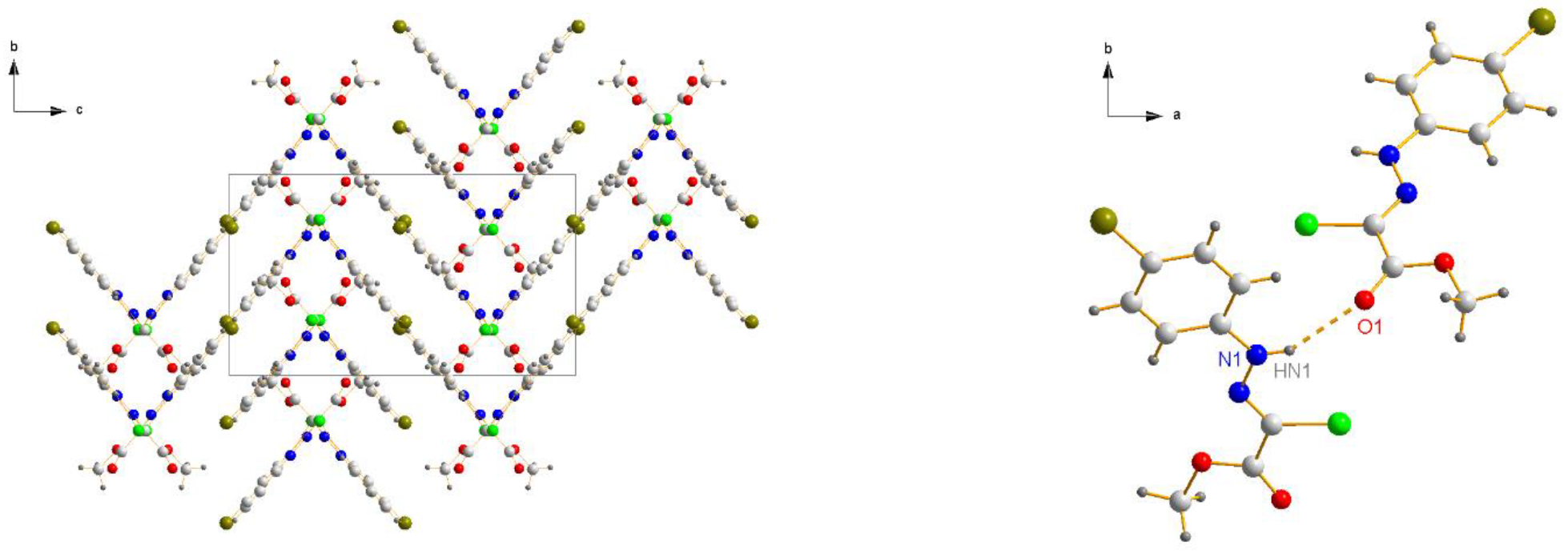
3.1.2. Crystal Structure of Chlorohydrazones 1 and 3
3.1.3. DFT Structure and Energetics of the Isomers of Chlorohydrazone 1
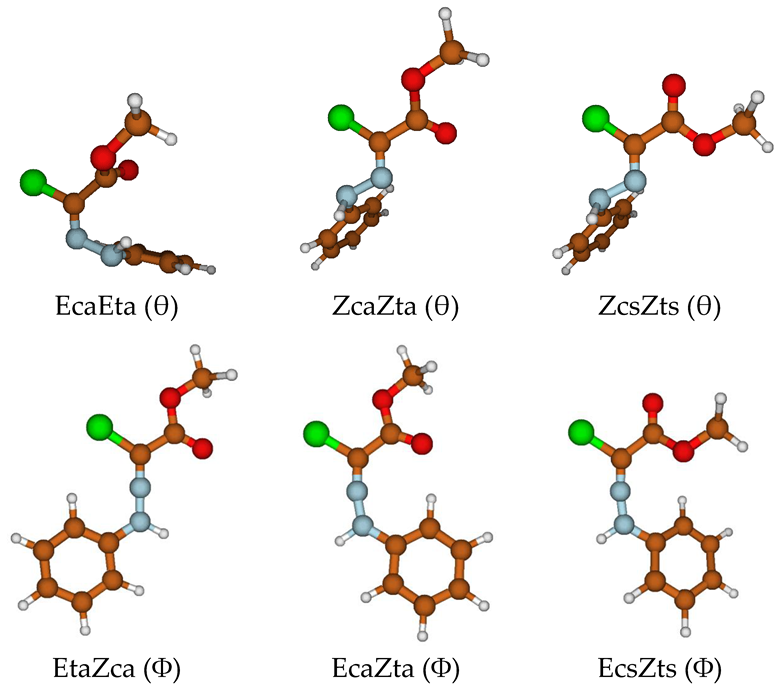
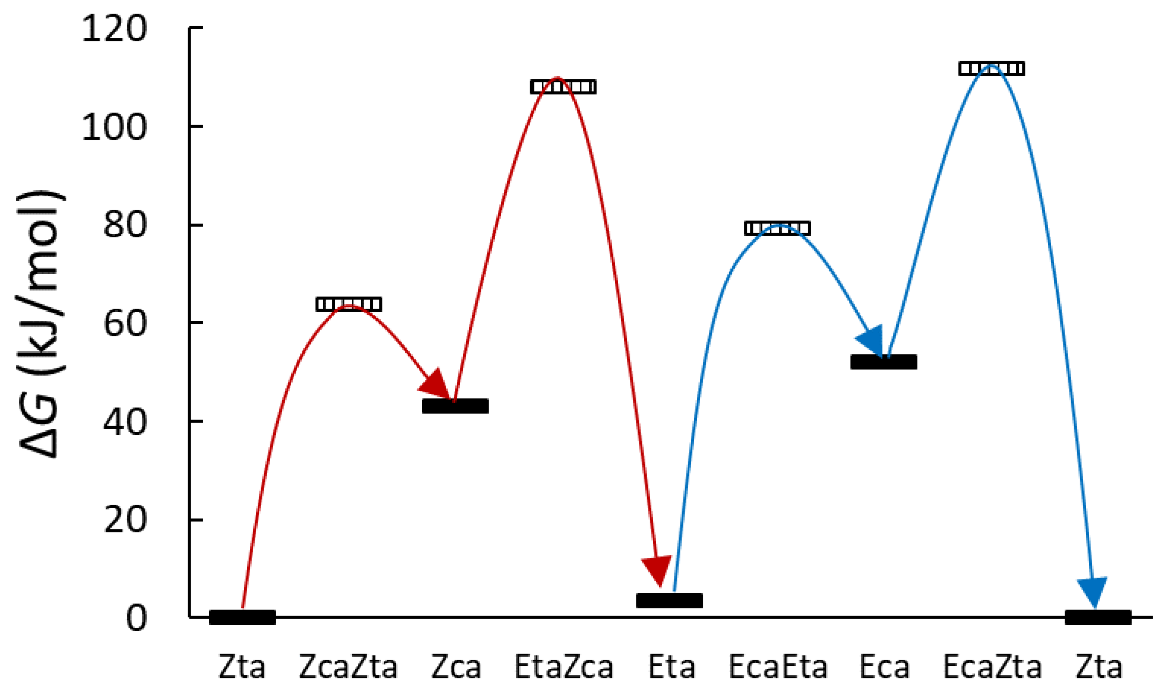
Energetics of the θ (c, t) Isomerism
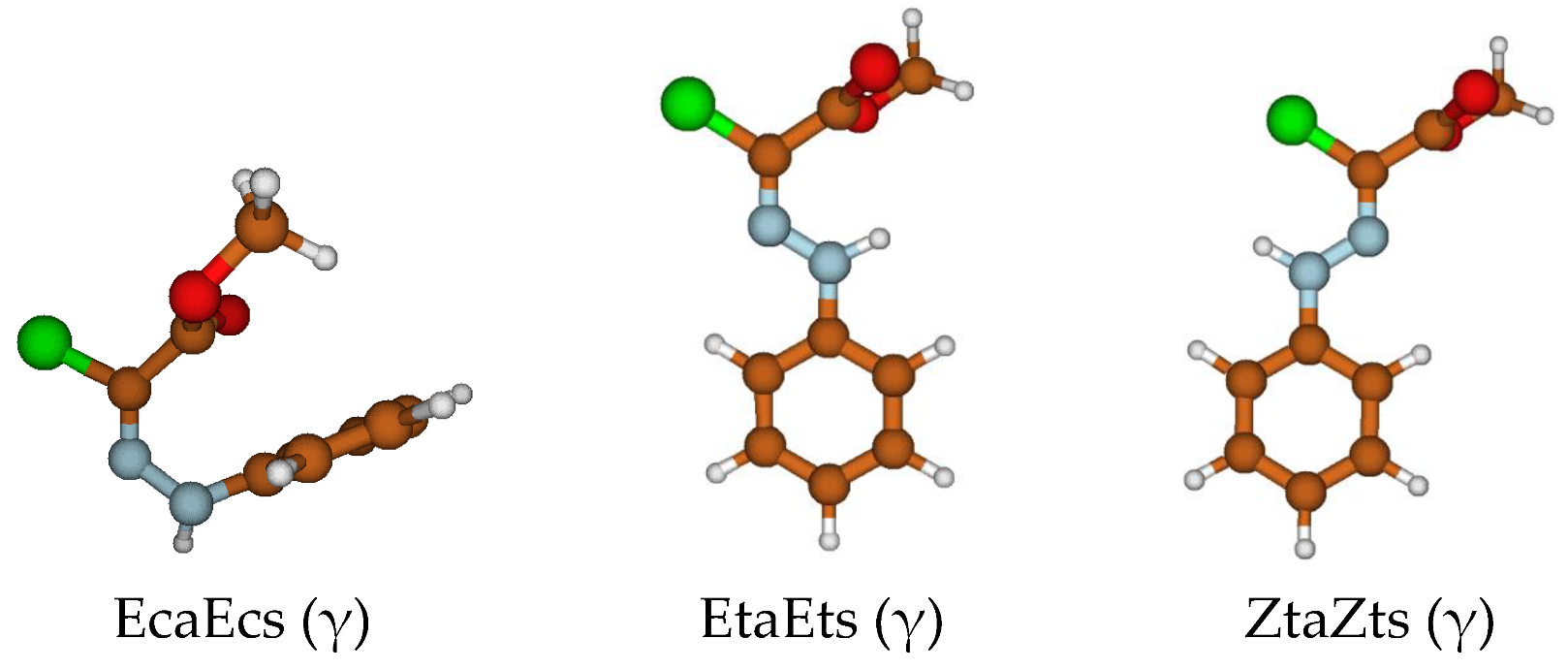
Energetics of the γ (a, s) Isomerism
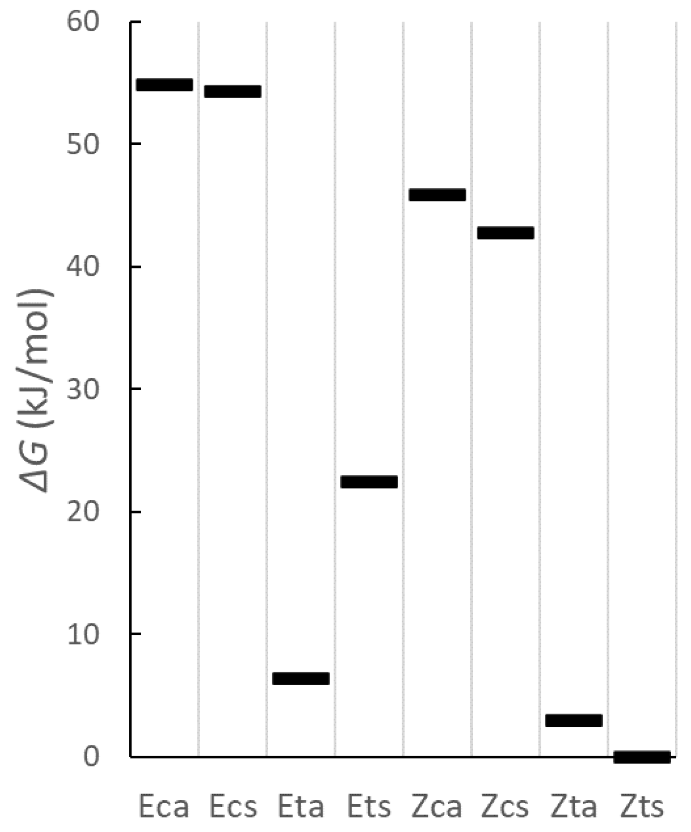
Energetics of the Φ (E, Z) Isomerism
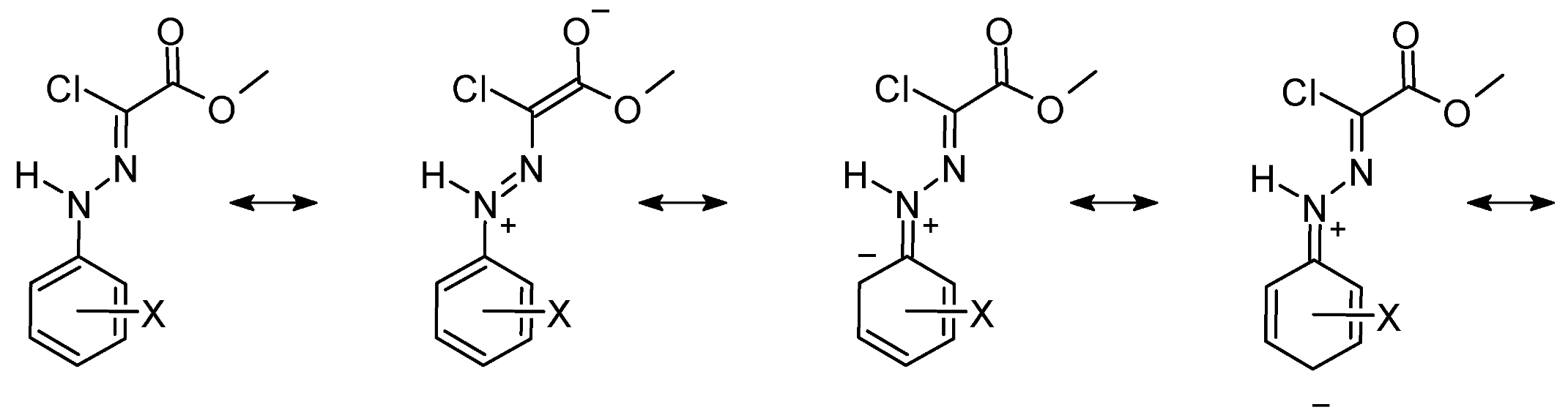
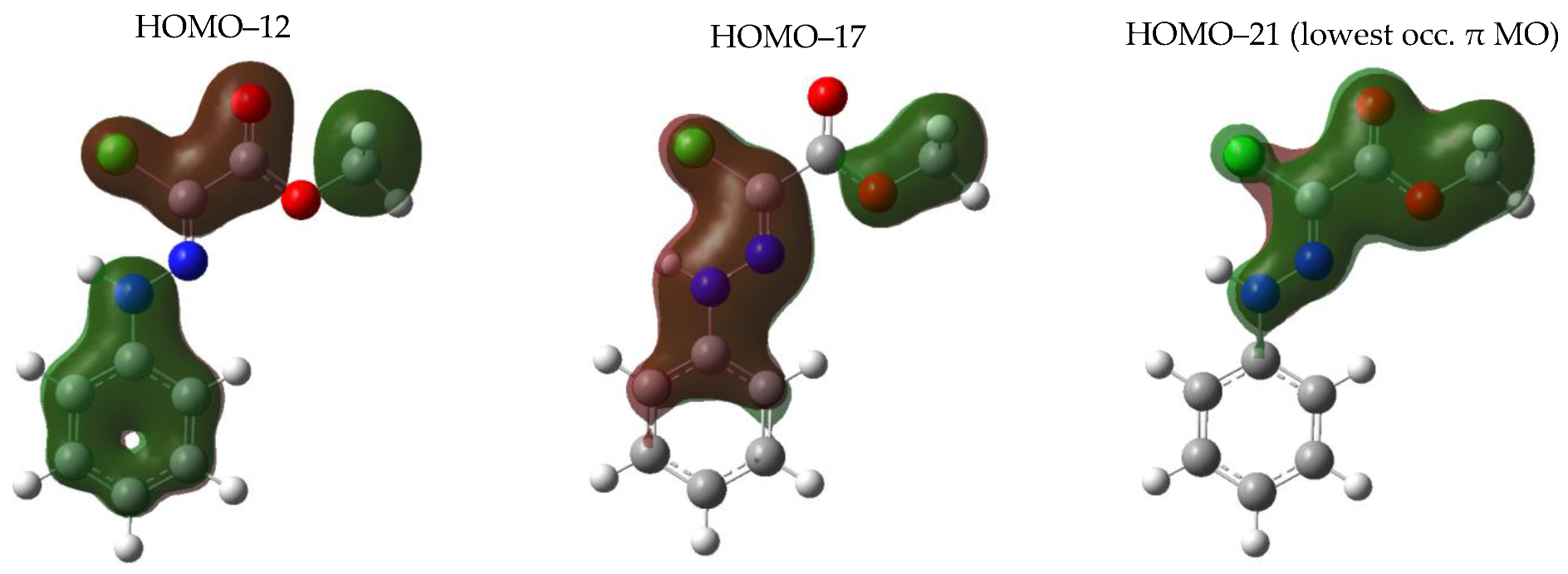
3.1.4. Electronic Structure and π Delocalization of the Isomers of Chlorohydrazone 1
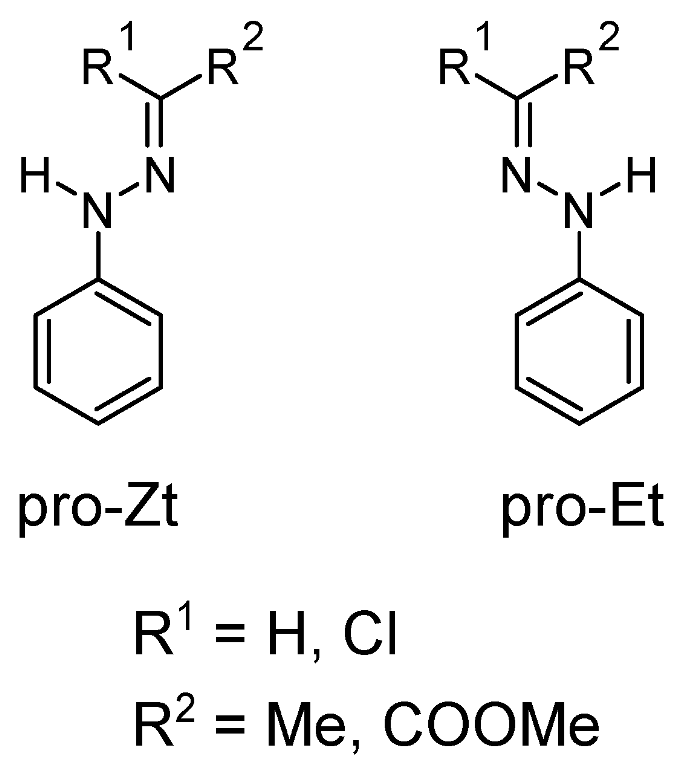
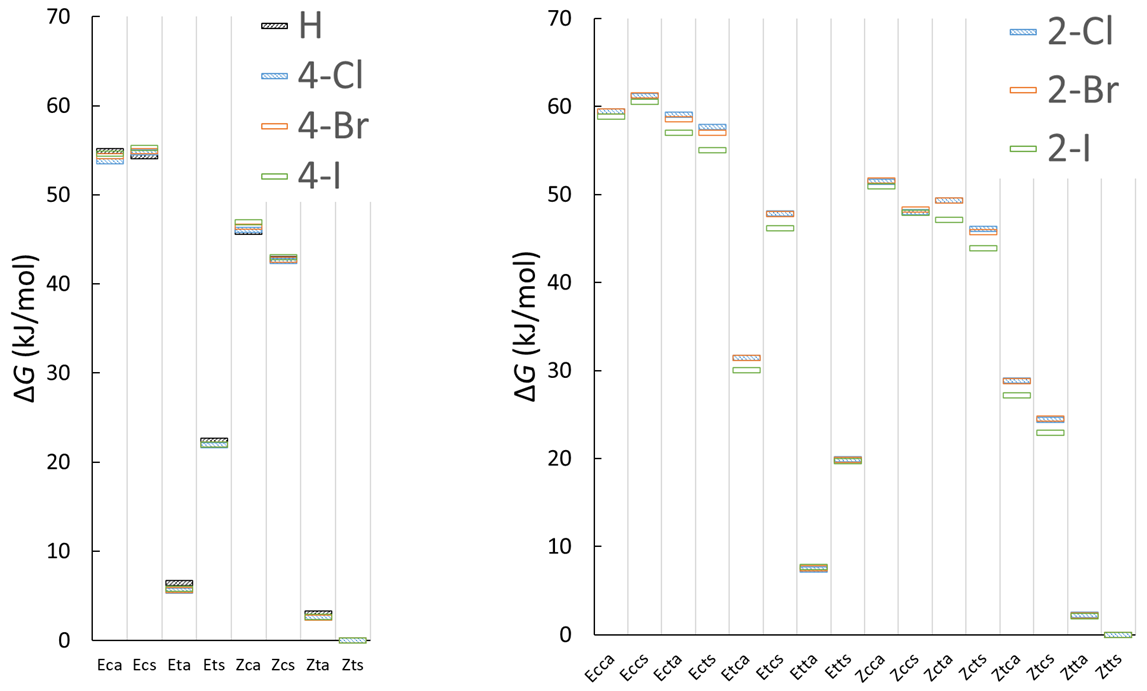
3.1.5. Structure and Energetics of the Isomers of Halogen-Substituted Chlorohydrazone 2–7
3.2. Kinetics of the Isomerization of Chlorohydrazones 1–7
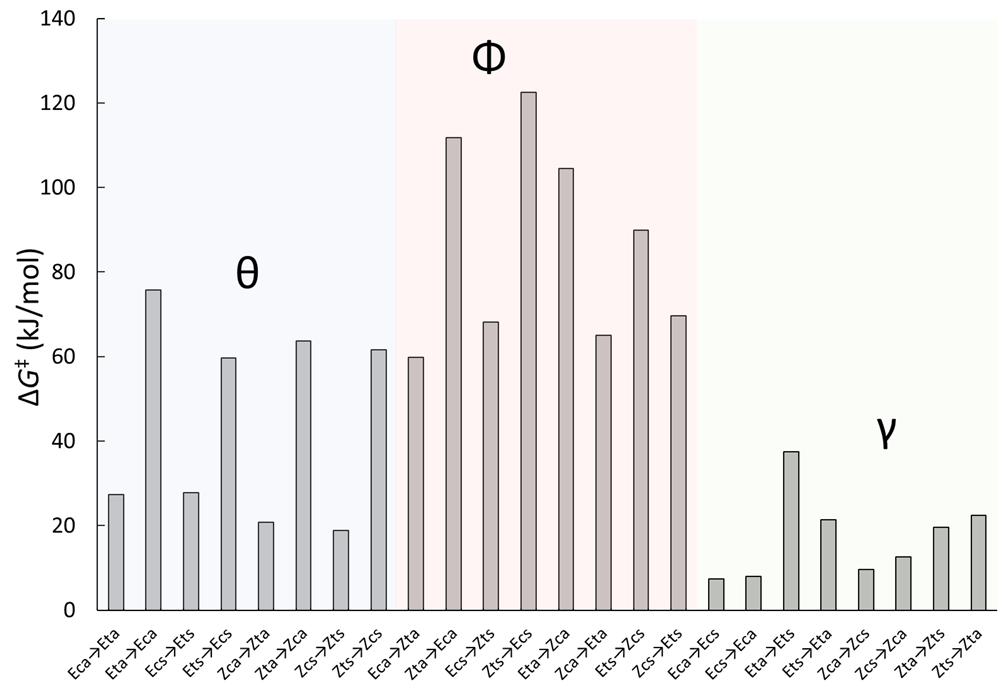
3.2.1. Generalities
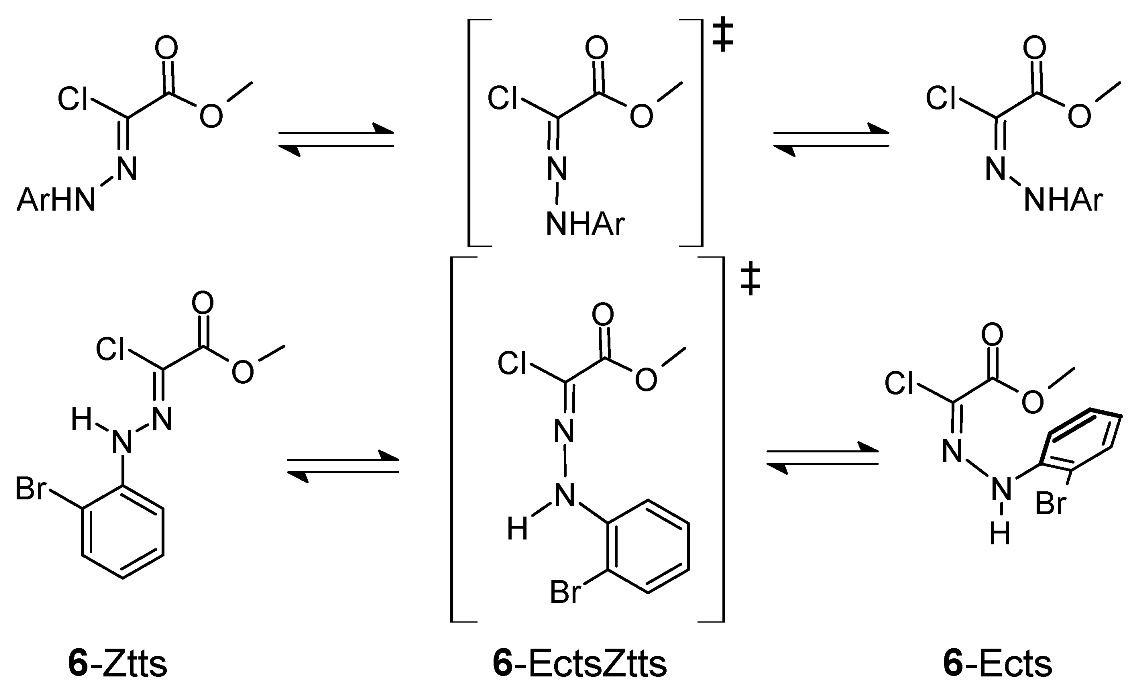
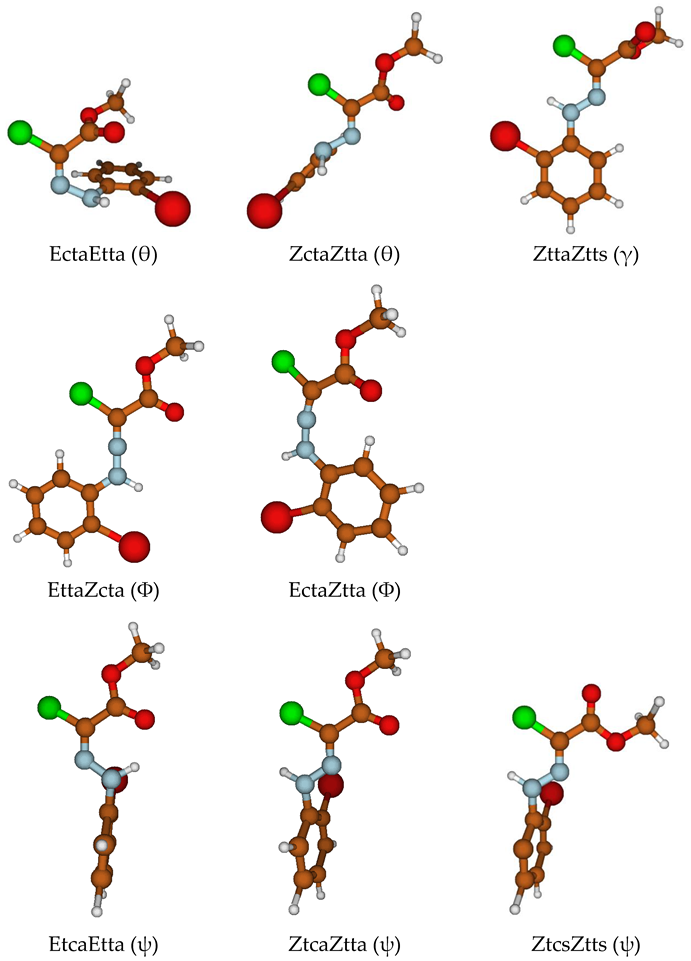
3.2.2. Isomerization Transition States of Chlorohydrazone 1
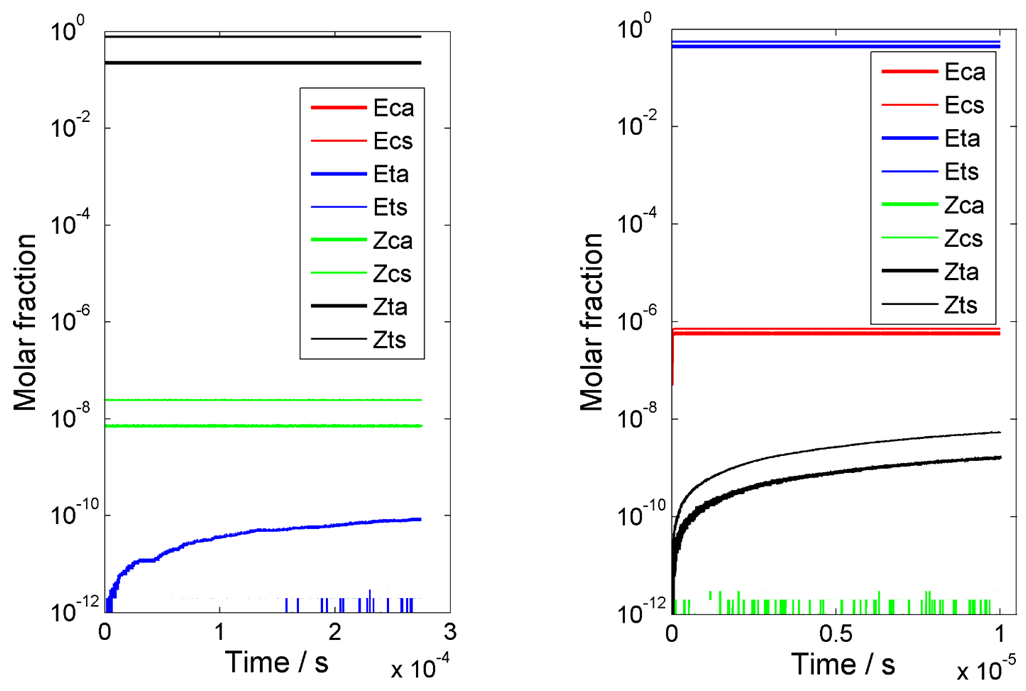
3.2.3. Umklapp Kinetics of Chlorohydrazone 1
3.2.4. Electronic Structure and π Delocalization of the Umklapp TSs of Chlorohydrazone 1
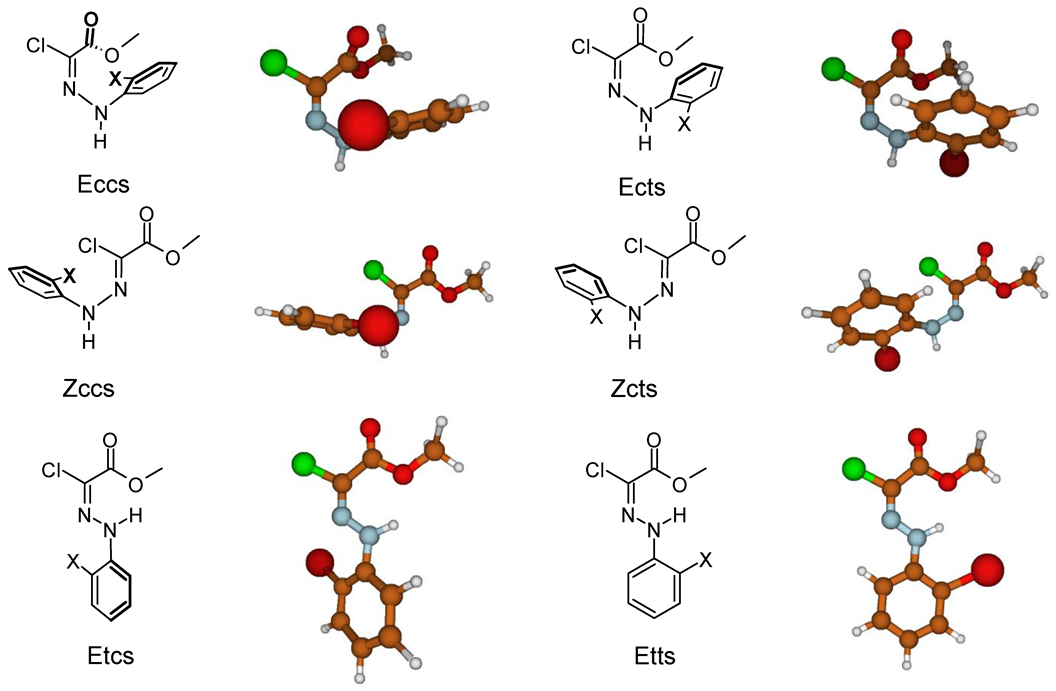
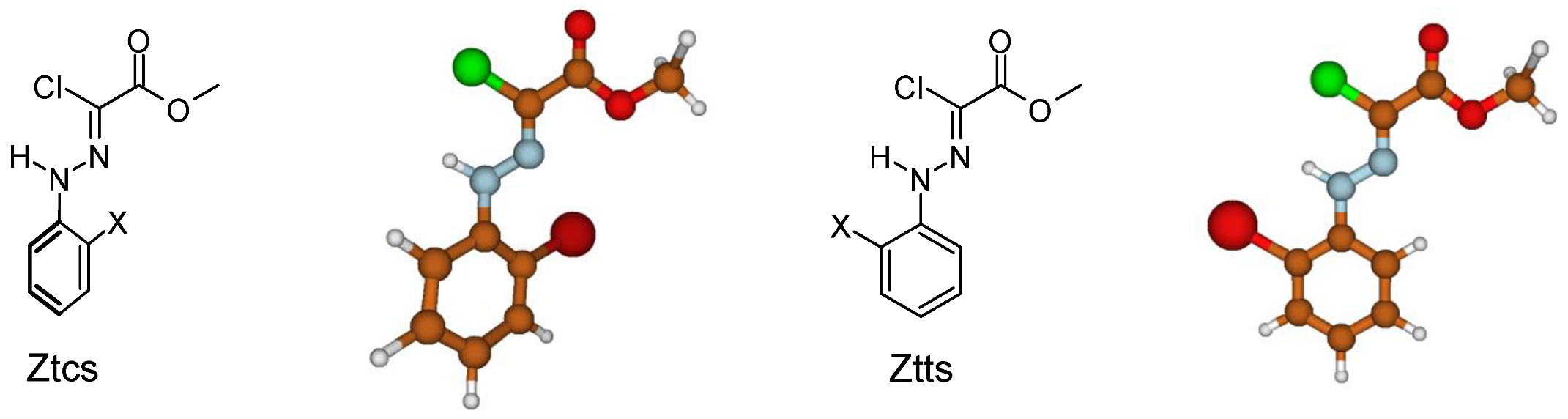
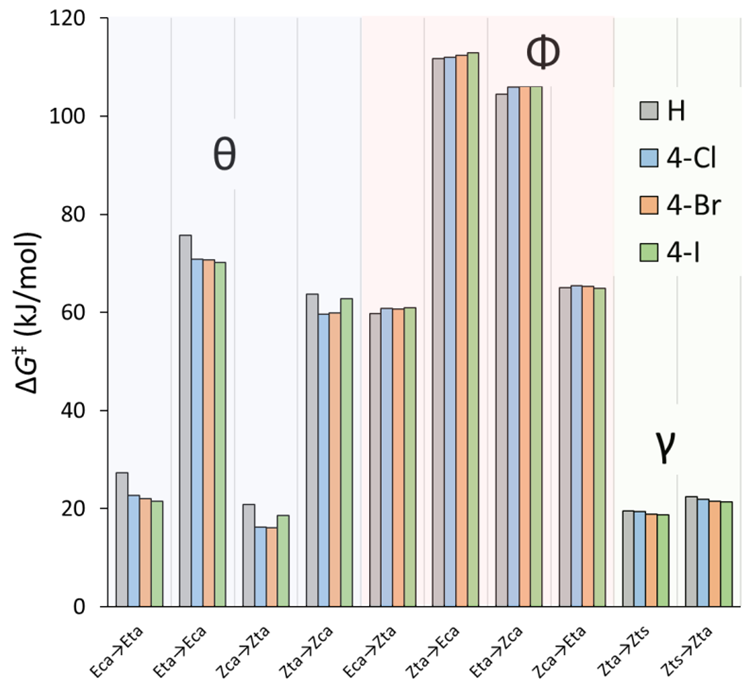
3.2.5. Isomerization Transition States of Chlorohydrazones 2–7
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, E. Uber Die Hydrazinwerbindung. Liebigs Ann. 1882, 212, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, H. The Chemistry of Imidoyl Halides; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Shawali, A.S.; Párkanyi, C. Hydrazidoyl halides in the synthesis of heterocycles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1980, 17, 833–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawali, A.S. Reactions of heterocyclic compounds with nitrilimines and their precursors. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 2731–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawali, A.S.; Abdallah, M.A. The chemistry of heterocyclic hydrazonoyl halides. In Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 63, pp. 277–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawali, A.S.; Mosselhi, M.A.N. Hydrazonoyl halides: Useful building blocks for the synthesis of arylazoheterocycles. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2003, 40, 725–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawali, A.S. A Review on bis-hydrazonoyl halides: Recent advances in their synthesis and their diverse synthetic applications leading to bis-heterocycles of biological interest. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 873–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, S.R.; Halldin, C.; Pike, V.W. A facile and regioselective synthesis of rimonabant through an enamine-directed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 2789–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawali, A.S. Hydrazonoyl halides: A bubbling fountain of biologically active compounds. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 784–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.W.; Friedman, A.R.; Steinhards, A. Herbicidal activity of phenylhydrazones and related azo compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1972, 20, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukota, S.N.; Borisenko, V.P.; Bodnar, V.N.; Zhuravskaya, N.I.; Lozinskii, M.O. Syntehsis and phytotoxicity of arylhydrazones of substituted pyruvic and a,ß-dioxobutyric acids. Fiziol. Akt. Veshchestva 1978, 10, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.E. Insecticidal Phenylhydrazone Sulfides. U.S. Patent 3,932,660, 13 January 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Folz, S.D.; Pax, R.A.; Klei, T.R.; Thomas, E.M.; Ash, K.A.; Conder, G.A.; Bennett, J.L. Development of a novel in vitro equine anthelmintic assay. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1988, 11, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Molodykh, Z.V.; Buzykin, B.I.; Kudrina, M.A.; Sysoeva, L.P.; Gazetdinova, N.G.; Neklesova, I.D.; Kitaev, Y.P. Antimicrobial activity of some acyl halide arylhydrazones and carboxylic acid arylhydrazides. Pharm. Chem. J. 1980, 14, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Hassaneen, H.M.; Elzayat, E.M.; El-Hallouty, S.M.; El-Manawaty, M.; Saleh, F.M.; Mohamed, Y.; El-Zohiry, D.; Fahmy, G.; Abdelaal, N.; et al. Biological activity, apoptotic induction and cell cycle arrest of new hydrazonoyl halides derivatives. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, A. Contact dermatitis from N-(α-chlorobenzylidene)phenylhydrazine. Contact Dermat. 1988, 18, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, A.F.; Cashman, M.P.; Scott, F.L. The kinetics of nitrilimine formation in base-catalysed hydrolysis of hydrazonyl halides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1972, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.T. Nitrile ylides and nitrile imines. In Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds: A Series of Monographs; Padwa, A., Pearson, W.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 473–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramella, P.; Grünanger, P. 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Chemistry; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984; Volume 1, pp. 291–392. [Google Scholar]
- Frohberg, P.; Drutkowski, G.; Wagner, C. Synthesis and structural assignment of oxanilo-N-arylhydrazonoyl chlorides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 2002, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Sahay, A.; Prasad, J.; Singh, K. Studies on Complex Arylhydrazones. 13. Action of Bromine on 2,3-Dioxo-2-PhenylHydrazono Butyric Acid. Asian J. Chem. 1996, 8, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Greb, L.; Lehn, J.-M. Light-driven molecular motors: Imines as four-step or two-step unidirectional rotors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13114–13117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Sahay, A.; Prasad, J.; Singh, K. Studies on Arylhydrazones. 12. Action of Bromine on Ethylhydrogen Mesoxalate Phenylhydrazones. Asian J. Chem. 1996, 8, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Landge, S.M.; Tkatchouk, E.; Benítez, D.; Lanfranchi, D.A.; Elhabiri, M.; Goddard, W.A.; Aprahamian, I. Isomerization mechanism in hydrazone-based rotary switches: Lateral shift, rotation, or tautomerization? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9812–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaton, H.G.; Willey, G.R.; Drew, M.G.B. Preparation and hydrogen bonding studies of phenylhydrazone derivatives of alloxan: Crystal and molecular structure of pyrimidine-2(1H),4(3H),5,6-tetraone 5-(2-nitrophenyl)hydrazone. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1987, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. Exploring the limit of accuracy of the global hybrid meta density functional for main-group thermochemistry, kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 1849–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunning, T.H. Gaussian Basis Sets for Use in Correlated Molecular Calculations. I. The Atoms Boron through Neon and Hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 1989, 90, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woon, D.E.; Dunning, T.H. Gaussian Basis Sets for Use in Correlated Molecular Calculations. III. The Atoms Aluminum through Argon. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Revision A.03; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mardirossian, N.; Head-Gordon, M. ωB97M-V: A combinatorially optimized, range-separated hybrid, meta-gga density functional with vv10 nonlocal correlation. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 214110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeweyher, E.; Bannwarth, C.; Grimme, S. Extension of the D3 dispersion coefficient model. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 034112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F. Software Update: The ORCA Program System—Version 5.0. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2022, 12, e1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.A.; Shepler, B.C.; Figgen, D.; Stoll, H. On the spectroscopic and thermochemical properties of ClO, BrO, IO, and their anions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 13877–13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.A. Systematically convergent basis sets with relativistic pseudopotentials. I. Correlation consistent basis sets for the post- d group 13–15 elements. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 11099–11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.A.; Figgen, D.; Goll, E.; Stoll, H.; Dolg, M. Systematically convergent basis sets with relativistic pseudopotentials. II. Small-core pseudopotentials and correlation consistent basis sets for the post- d group 16–18 elements. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 11113–11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Revilla, M.; Popelier, P.L.A.; Francisco, E.; Martín Pendás, Á. Nature of chemical interactions from the profiles of electron delocalization indices. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outeiral, C.; Vincent, M.A.; Martín Pendás, Á.; Popelier, P.L.A. Revitalizing the concept of bond order through delocalization measures in real space. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 5517–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugas, D.; Guillaumes, L.; Duran, M.; Simon, S. Delocalization indices for non-covalent interaction: Hydrogen and DiHydrogen bond. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2012, 998, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, E.O.; Khrenova, M.G.; Tsirelson, V.G. The explicit role of electron exchange in the hydrogen bonded molecular complexes. J. Comput. Chem. 2021, 42, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.T. A General method for numerically simulating the stochastic time evolution of coupled chemical reactions. J. Comput. Phys. 1976, 22, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Jin, J.; Cao, D.; Guan, R.; Chen, Q.; Sun, X. Reversible regulating of crystal structures based on isomerization of phenylhydrazones. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 12630–12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soave, R.; Colombo, P. Intermolecular C—H...O, Cl...Cl and π–π interactions in the 2-dichloromethyl derivative of vitamin K3. Acta Crystallogr. C 2013, 69, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantina, M.; Chamberlin, A.C.; Valero, R.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Consistent van Der Waals radii for the whole main group. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 5806–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommerse, J.P.M.; Price, S.L.; Taylor, R. Hydrogen bonding of carbonyl, ether,and ester oxygen atoms with alkanolhydroxyl groups. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, O.; Smolíková, J.; Jehlička, V.; Shawali, A.S. Hydrogen bonding, configuration and conformation of substituted α-oxo oximes and hydrazones. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1979, 44, 2494–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory; The International Series of Monographs on Chemistry; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Novoa, J.J. (Ed.) Intermolecular Interactions in Crystals: Fundamentals of Crystal Engineering; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wurmb-Gerlich, D.; Vögtle, F.; Mannschreck, A.; Staab, H.A. Untersuchungen über Schiffsche Basen, VI. Protonenresonanz-Untersuchungen zur syn-anti-Isomerisierung von Iminen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1967, 708, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerek, F.; Ostrogovich, G.; Simon, Z. Mechanism of the uncatalysed syn–anti-isomerization of imine systems. Part IV. A theoretical study of the influence of substituents. J. Chem. Soc. B 1971, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, J.; Guirado, A. A Theoretical study of topomerization of imine systems: Inversion, rotation or mixed mechanisms? J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Fabián, E.; Moscardó, F. Cyclobutadiene automerization and rotation of ethylene: Energetics of the barriers by using spin-polarized wave functions. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, D. Kinetics of consecutive reactions: First reaction, first-order; second reaction, zeroth order. J. Chem. Educ. 1998, 75, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

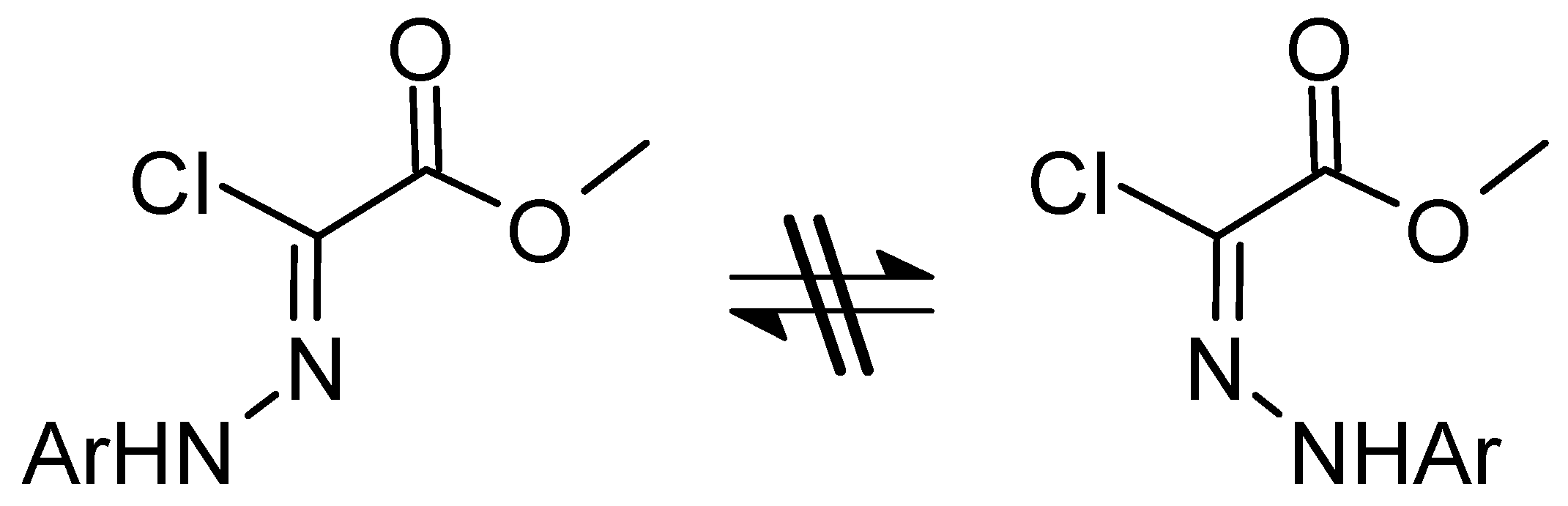
| Definition | Typical Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Φ | C=N–N | ≈120°, Z | ≈240°, E |
| θ | C–N–N–Ar | ≈0°, c(isoid) | ≈180°, t(ransoid) |
| ψ | N–N–Cipso–Cortho | ≈0°, c(isoid) | ≈180°, t(ransoid) |
| γ | Cl–C–C=O | ≈0°, s(yn) | ≈180°, a(nti) |
| ΔG (kJ/mol) | Rel. Pop. | |
|---|---|---|
| Eca | 54.9 | 1.7 · 10−10 |
| Ecs | 54.3 | 2.2 · 10−10 |
| Eta | 6.4 | 0.06 |
| Ets | 22.4 | 8.6 · 10−5 |
| Zca | 45.9 | 6.7 · 10−9 |
| Zcs | 42.8 | 2.3 · 10−8 |
| Zta | 3.0 | 0.22 |
| Zts | 0.0 | 0.73 |
| C=N | N-N | N-Cipso | Φ | θ | ψ | δΣ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eca | 1.259 | 1.362 | 1.433 | 238.2 | −38.9 | −33.7 | 15.3 |
| Ecs | 1.260 | 1.362 | 1.431 | 237.3 | −40.1 | −29.0 | 14.8 |
| Eta | 1.277 | 1.314 | 1.402 | 237.4 | 178.9 | 0.9 | 0.0 |
| Ets | 1.271 | 1.317 | 1.401 | 235.1 | 178.8 | 1.3 | 0.0 |
| Zca | 1.262 | 1.351 | 1.433 | 123.7 | −49.7 | −23.8 | 16.1 |
| Zcs | 1.263 | 1.356 | 1.434 | 123.0 | −51.0 | −23.8 | 17.0 |
| Zta | 1.268 | 1.314 | 1.402 | 121.4 | 181.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Zts | 1.268 | 1.317 | 1.401 | 121.1 | 180.6 | 1.3 | 0.0 |
| XRD (Zts) | 1.270(2) | 1.321(2) | 1.402(2) | 121.65(16) | 178.04(18) | −0.3(3) | 0.2 |
| N-N | |
|---|---|
| H2N–NH2 | 1.476 |
| H2N–NHPh | 1.407 |
| HN=NH (Z) | 1.233 |
| HN=NH (E) | 1.235 |
| HN=NPh (Z) a | 1.236 |
| HN=NPh (E) b | 1.232 |
| N≡N | 1.091 |
| R1 | R2 | ΔG(Z–E) (kJ/mol) | Z Fraction a |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | Me | 1.7 | 67% |
| H | COOMe b | –22.5 | 0% |
| Cl | Me | 24.9 | 100% |
| Cl | COOMe b,c | 2.0 | 69% |
| 1-Zts | 1-Zta | 1-Ets | 1-Eta | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| C=O | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.075 |
| C–O | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.062 | 0.002 |
| C=N | N-N | N-Cipso | Φ | θ | ψ | δΣ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zts | 1.268 | 1.311 | 1.393 | 121.13 | 179.95 | 179.79 | 0.0 |
| XRD (Zts) | 1.277(3) | 1.329(2) | 1.397(3) | 120.02(18) | 173.19(19) | 178.1(2) | –0.6 |
| Isomerization | From | To | ΔG‡ (kJ/mol) | k (s−1) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotation, γ | Eca | Ecs | 7.4 | 3.2 · 1011 |
| Ecs | Eca | 7.9 | 2.6 · 1011 | |
| Eta | Ets | 37.4 | 1.7 · 106 | |
| Ets | Eta | 21.4 | 1.1 · 109 | |
| Zca | Zcs | 9.6 | 1.3 · 1011 | |
| Zcs | Zca | 12.7 | 3.7 · 1010 | |
| Zta | Zts | 19.5 | 2.4 · 109 | |
| Zts | Zta | 22.5 | 7.1 · 108 | |
| Rotation, θ | Eca | Eta | 27.3 | 1.0 · 108 |
| Eta | Eca | 75.8 | 0.33 | |
| Ecs | Ets | 27.8 | 8.4 · 107 | |
| Ets | Ecs | 59.7 | 2.2 · 102 | |
| Zca | Zta | 20.8 | 1.4 · 109 | |
| Zta | Zca | 63.7 | 43 | |
| Zcs | Zts | 18.8 | 3.2 · 109 | |
| Zts | Zcs | 61.6 | 100 | |
| Umklapp, Φ (θ) | Eca | Zta | 59.8 | 210 |
| Zta | Eca | 111.7 | 1.6 · 10−7 | |
| Ecs | Zts | 68.1 | 7.2 | |
| Zts | Ecs | 122.5 | 2.2 · 10−9 | |
| Eta | Zca | 104.5 | 3.1 · 10−6 | |
| Zca | Eta | 65.0 | 25 | |
| Ets | Zcs | 89.9 | 1.1 · 10−3 | |
| Zcs | Ets | 69.6 | 4.0 |
| Isomerization | TS | C=N | N-N | Φ | θ | ψ | δΣ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotation, γ | EcaEcs | 1.259 | 1.346 | 235.5 | 0.0 | −113.4 | 2.6 |
| EtaEts | 1.259 | 1.347 | 240.3 | 170.4 | 16.3 | 5.5 | |
| ZcaZcs | 1.254 | 1.382 | 120.1 | −64.7 | −7.9 | 23.4 | |
| ZtaZts | 1.257 | 1.332 | 121.2 | 175.3 | 9.5 | 1.1 | |
| Rotation, θ | EcaEta | 1.257 | 1.436 | 243.6 | −54.1 | −34.6 | 18.4 |
| EcsEts | 1.258 | 1.436 | 243.6 | −54.8 | −33.0 | 18.5 | |
| ZcaZta | 1.252 | 1.428 | 115.6 | 121.0 | −31.4 | 31.4 | |
| ZcsZts | 1.256 | 1.427 | 115.3 | 118.8 | −25.5 | 31.1 | |
| Umklapp, Φ (θ) | EcaZta | 1.225 | 1.281 | 191.0 | 0.9 | −1.9 | 0.1 |
| EcsZts | 1.222 | 1.282 | 187.5 | −17.5 | −19.1 | 0.4 | |
| EtaZca | 1.220 | 1.276 | 179.8 | −30.7 | 1.1 | 0.0 | |
| EtsZcs | 1.220 | 1.276 | 179.1 | 163.2 | 1.1 | 0.0 |
| ΔG‡ (kJ/mol) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isomerization | From | To | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Rotation, γ | Zta | Zts | 19.4 | 18.9 | 18.8 |
| Zts | Zta | 22.0 | 21.5 | 21.4 | |
| Rotation, θ | Eca | Eta | 22.7 | 22.0 | 21.5 |
| Eta | Eca | 70.9 | 70.7 | 70.2 | |
| Zca | Zta | 16.2 | 16.1 | 18.6 | |
| Zta | Zca | 59.7 | 59.9 | 62.9 | |
| Umklapp, Φ (θ) | Eca | Zta | 60.8 | 60.6 | 61.0 |
| Zta | Eca | 112.0 | 112.4 | 112.9 | |
| Eta | Zca | 105.9 | 106.0 | 106.1 | |
| Zca | Eta | 65.4 | 65.3 | 65.0 |
| ΔG‡ (kJ/mol) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
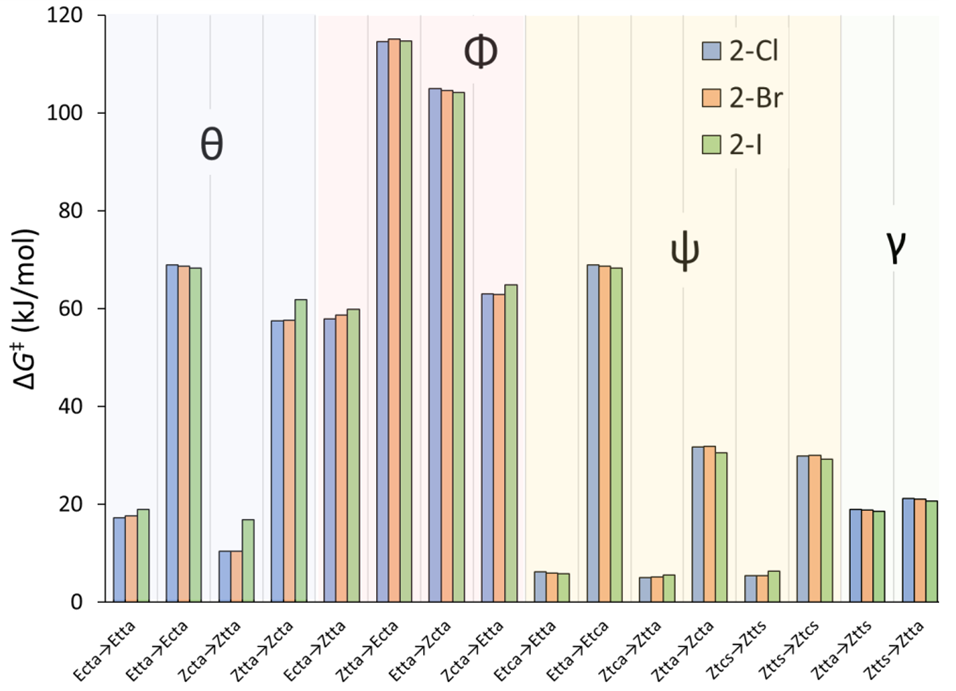
| Isomerization | From | To | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Rotation, γ | Ztta | Ztts | 18.9 | 18.8 | 18.5 |
| Ztts | Ztta | 21.2 | 21.0 | 20.6 | |
| Rotation, θ | Ecta | Etta | 17.3 | 17.6 | 19.0 |
| Etta | Ecta | 68.9 | 68.7 | 68.3 | |
| Zcta | Ztta | 10.4 | 10.4 | 16.9 | |
| Ztta | Zcta | 57.4 | 57.6 | 61.8 | |
| Rotation, ψ | Etca | Etta | 6.1 | 5.9 | 5.8 |
| Etta | Etca | 68.9 | 68.7 | 68.3 | |
| Ztca | Ztta | 5.0 | 5.2 | 5.5 | |
| Ztta | Ztca | 31.7 | 31.8 | 30.6 | |
| Ztcs | Ztts | 5.4 | 5.4 | 6.3 | |
| Ztts | Ztcs | 29.9 | 29.9 | 29.2 | |
| Umklapp, Φ (θ) | Ecta | Ztta | 57.8 | 58.7 | 59.8 |
| Ztta | Ecta | 114.6 | 115.1 | 114.7 | |
| Etta | Zcta | 104.9 | 104.6 | 104.2 | |
| Zcta | Etta | 63.0 | 62.8 | 64.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molteni, G.; Cargnoni, F.; Soave, R.; Ponti, A. The (E, Z) Isomerization of C-methoxycarbonyl-N-aryl Chlorohydrazones. Chemistry 2022, 4, 1624-1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040106
Molteni G, Cargnoni F, Soave R, Ponti A. The (E, Z) Isomerization of C-methoxycarbonyl-N-aryl Chlorohydrazones. Chemistry. 2022; 4(4):1624-1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040106
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolteni, Giorgio, Fausto Cargnoni, Raffaella Soave, and Alessandro Ponti. 2022. "The (E, Z) Isomerization of C-methoxycarbonyl-N-aryl Chlorohydrazones" Chemistry 4, no. 4: 1624-1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040106
APA StyleMolteni, G., Cargnoni, F., Soave, R., & Ponti, A. (2022). The (E, Z) Isomerization of C-methoxycarbonyl-N-aryl Chlorohydrazones. Chemistry, 4(4), 1624-1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry4040106







