Dispersion of Micro Fibrillated Cellulose (MFC) in Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) from Lab-Scale to Semi-Industrial Processing Using Biobased Plasticizers as Dispersing Aids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Extrusion-grade poly(lactic) acid 2003D purchased from NatureWorks (D-content: between 3% and 6%; density: 1.24 g/cm3; molecular weight of 200,000 g/mol and melt flow index of 6 g/10 min at 190 °C and 2.16 kg);
- PEG 400 purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (CAS number: 25322-68-3; MW: 400 g/mol; density: 1.12 g/cm3; water solubility: 100 mg/mL).
- LAO (trade name: Glyplast OLA 2) provided by Condensia Quimica, (Barcelona, Spain): it is a completely biodegradable and impact modifier PLA plasticiser (ester content: >99%; density: 1.10 g/cm3; viscosity (ASTM D 445): 90 mPa∙s at T = 40 °C, water content (ASTM E 203): maximum 0.1%; molecular weight: 500 g/mol [37]);
- MFC Exilva F 01-L 10% provided by Borregaard (Sarpsborg, Norway) had a solid content of 1.5–2.4% and a viscosity in H2O (2%, mPa∙s) of ≥14,000).
- MFC Celish KY100S 25% purchased from Daicel Miraizu Ltd. (Osaka, Japan) (CAS number: 9004-34-6; density: 1.27–1.61 g/cm3).
2.2. Neat MFCs Characterizations
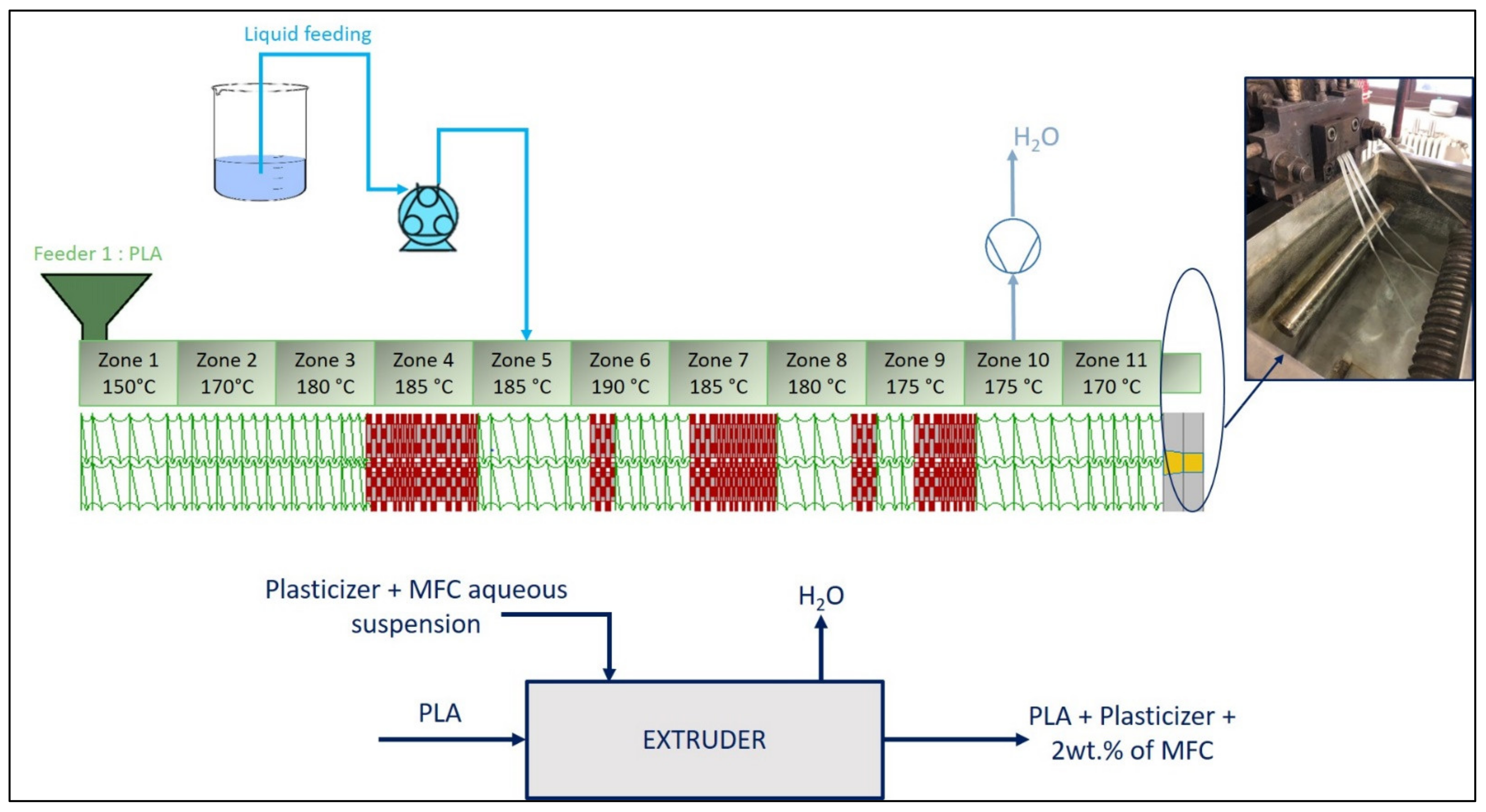
2.3. Microcompounding of Lab-Scale PLA/MFCs Composites
2.4. Scale-Up of PLA/MFCs Composites Extrusion Compounding
2.5. Mechanical Characterization
2.6. Optical Characterization
2.7. FT-IR Characterization
2.8. Thermal Characterization
2.9. Melt Flow Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
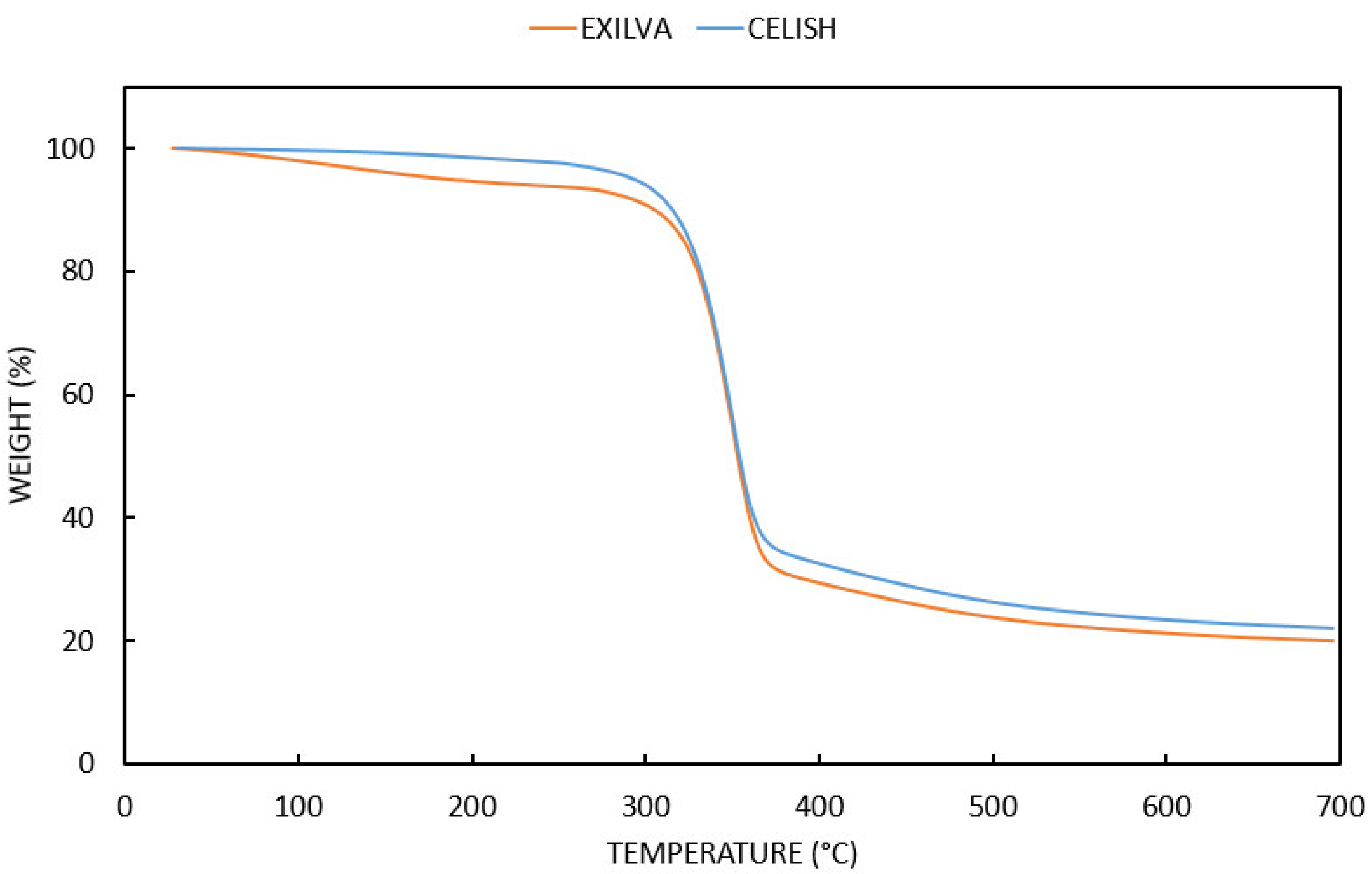
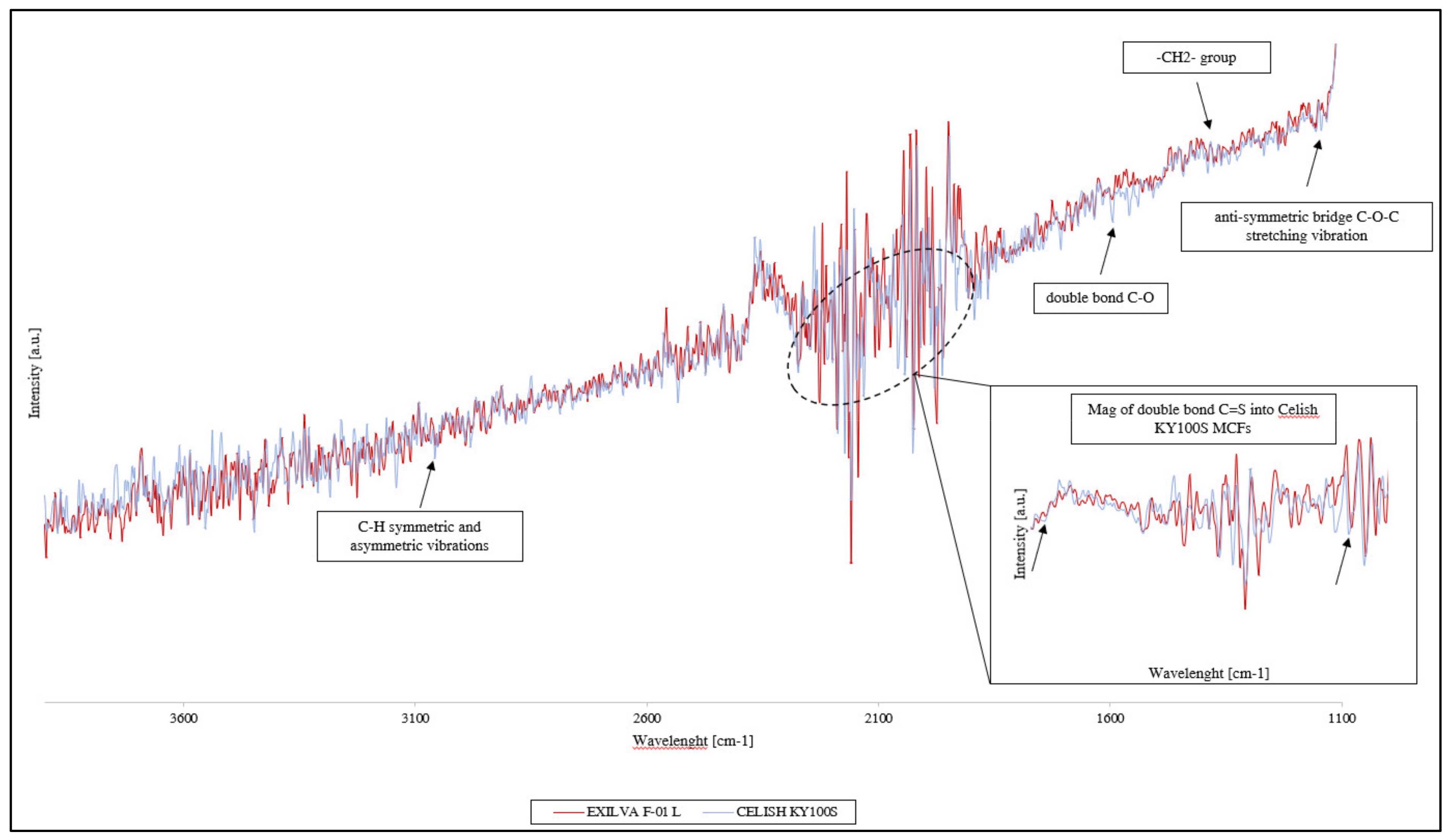
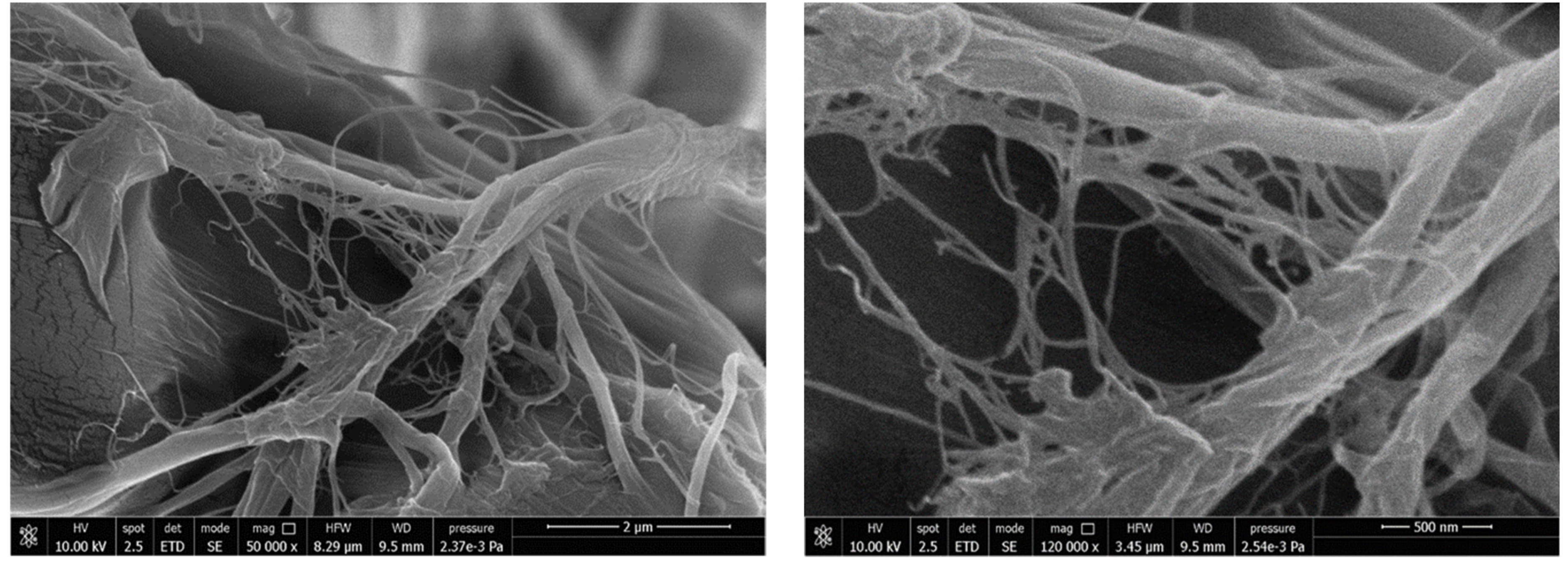
3.1. Neat MFCs Results
3.2. Lab-Scale Results
3.3. Scale-Up Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Palermo, S.; Fragalà, M.; Pappalardo, F. Characterization and Processability of Blends of Polylactide Acid with a New Biodegradable Medium-Chain-Length Polyhydroxyalkanoate. J. Polym. Environ. 2015, 23, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempi, E.; Sorrentino, G.P.; Zanoletti, A.; Alessandri, I.; Depero, L.E.; Caneschi, A. Sustainable Materials and their Contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Critical Review Based on an Italian Example. Molecules 2021, 26, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez, J.; Correa Aguirre, J.P.; Hidalgo Salazar, M.A.; Vera Mondragón, B.; Wagner, E.; Caicedo, C. Effect of Extrusion Screw Speed and Plasticizer Proportions on the Rheological, Thermal, Mechanical, Morphological and Superficial Properties of PLA. Polymers 2020, 12, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, C.; Barletta, M.; Puopolo, M.; Vesco, S. Cast extrusion of low gas permeability bioplastic sheets in PLA/PBS and PLA/PHB binary blends. Polym. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrosanto, A.; Scarfato, P.; Di Maio, L.; Nobile, M.R.; Incarnato, L. Evaluation of the Suitability of Poly(Lactide)/Poly(Butylene-Adipate-co-Terephthalate) Blown Films fro Chilled and Frozen Food Packaging Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gigante, V.; Canesi, I.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Rubber Toughening of Polylactic Acid (PLA) with Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT): Mechanical Properties, Fracture Mechanics and Analysis of Ductile-to-Brittle Behavior while Varying Temperature and Test Speed. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 115, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Morreale, M. Green composites: A brief review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Coltelli, M.B.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A. Evaluation of Mechanical and Interfacial Properties of Bio-Composites Based on Poly (Lactic Acid) with Natural Cellulose Fibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Seggiani, M. Thermo-mechanical properties of PLA/short flax fiber biocomposites. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoo, R.Z.; Ismail, H.; Chow, W.S. Thermal and Morphological Properties of Poly (Lactic Acid)/Nanocellulose Nanocomposites. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksman, K.; Aitomäki, Y.; Mathew, A.P.; Siqueira, G.; Zhou, Q.; Butylina, S.; Tanpichai, S.; Zhou, X.; Hooshmand, S. Review of the recent developments in cellulose nanocomposite processing. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigotti, D.; Checchetto, R.; Tarter, S.; Caretti, D.; Rizzuto, M.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Polylactic acid-lauryl functionalized nanocellulose nanocomposites: Microstructural, thermo-mechanical and gas transport properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 858–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaerunisaa, A.Y.; Sriwidodo, S.; Abdassah, M. Microcrystalline cellulose as pharmaceutical excipient. In Pharmaceutical Formulation Design-Recent Practices; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A. Effect of a Bio-Based Dispersing Aid (Einar® 101) on PLA-Arbocel® Biocomposites: Evaluation of the Interfacial Shear Stress on the Final Mechanical Properties. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzi, F.; Puglia, D.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Maffei, G.; Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Kenny, J.M.; Torre, L. Valorization and extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from North African grass: Ampelodesmos mauritanicus (Diss). Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessini, V.; Navarro-Baena, I.; Arrieta, M.P.; Dominici, F.; López, D.; Torre, L.; Kenny, J.M.; Dubois, P.; Raquez, J.-M.; Peponi, L. Effect of the addition of polyester-grafted-cellulose nanocrystals on the shape memory properties of biodegradable PLA/PCL nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 152, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Behrooz, R.; Ghasemi, I.; Yassar, R.S.; Long, F. Development of nanocellulose-reinforced PLA nanocomposite by using maleated PLA (PLA-g-MA). J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2018, 31, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battegazzore, D.; Bocchini, S.; Alongi, J.; Frache, A.; Marino, F. Cellulose extracted from rice husk as filler for poly (lactic acid): Preparation and characterization. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Reimer, C.; Wang, T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of the Biocomposites of Miscanthus Biocarbon and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV). Polymers 2020, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonoobi, M.; Harun, J.; Mathew, A.P.; Oksman, K. Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhani, A.; Hosseinzadeh, J.; Ashori, A.; Dadashi, S.; Takzare, Z. Preparation and characterization of modified cellulose nanofibers reinforced polylactic acid nanocomposite. Polym. Test. 2014, 35, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, A.; Kochumalayil, J.J.; Nilsson, C.; Fogelström, L.; Gamstedt, E.K. Toward an alternative compatibilizer for PLA/cellulose composites: Grafting of xyloglucan with PLA. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P.; Bondeson, D.; Kvien, I. Manufacturing process of cellulose whiskers/polylactic acid nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melilli, G.; Carmagnola, I.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Pirri, F.; Ciardelli, G.; Sangermano, M.; Hakkarainen, M.; Chiappone, A. DLP 3D Printing Meets Lignocellulosic Biopolymers: Carboxymethyl Cellulose Inks for 3D Biocompatible Hydrogels. Polymers 2020, 12, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchosa, N.; Zhou, Q. Water redispersible cellulose nanofibrils adsorbed with carboxymethyl cellulose. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4349–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Hietala, M.; Oksman, K. One-step twin-screw extrusion process of cellulose fibers and hydroxyethyl cellulose to produce fibrillated cellulose biocomposite. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8105–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, D.; Mathew, A.; Oksman, K. Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline celluloseby acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 2006, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Tye, Y.Y.; Leh, C.P.; Saurabh, C.K.; Ariffin, F.; Mohammad Fizree, H.; Mohamed, A.; Suriani, A.B. Cellulose reinforced biodegradable polymer composite film for packaging applications. Bionanocompos. Packag. Appl. 2017, 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Haafiz, M.K.M.; Hassan, A.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Fazita, M.R.N.; Islam, M.S.; Inuwa, I.M.; Marliana, M.M.; Hussin, M.H. Exploring the effect of cellulose nanowhiskers isolated from oil palm biomass on polylactic acid properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Garcia, M.D.; Lagaron, J.M. On the use of plant cellulose nanowhiskers to enhance the barrier properties of polylactic acid. Cellulose 2010, 17, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentano, I.; Fortunati, E.; Burgos, N.; Dominici, F.; Luzi, F.; Fiori, S.; Jiménez, A.; Yoon, K.; Ahn, J.; Kang, S.; et al. Processing and characterization of plasticized PLA/PHB blends for biodegradable multiphase systems. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, V.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Vannozzi, A.; Panariello, L.; Fusco, A.; Trombi, L.; Donnarumma, G.; Danti, S.; Lazzeri, A. Flat Die Extruded Biocompatible Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS) Based Films. Polymers 2019, 11, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darie-Niţə, R.N.; Vasile, C.; Irimia, A.; Lipşa, R.; Râpə, M. Evaluation of some eco-friendly plasticizers for PLA films processing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiza, M.; Benaniba, M.T.; Quintard, G.; Massardier-Nageotte, V. Biobased additive plasticizing Polylactic acid (PLA). Polimeros 2015, 25, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloser, E.; Gray, D.G. Surface grafting of cellulose nanocrystals with poly (ethylene oxide) in aqueous media. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13450–13456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; An, X.; Zhu, X.; Ni, Y. Adsorption of polyethylene glycol (PEG) onto cellulose nano-crystals to improve its dispersity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Eblagon, K.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical Applications. C 2021, 7, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, N.M.; Wei, L.; Sabo, R.C.; Reiner, R.R.; Matuana, L.M. Effect of freeze-drying on the morphology of dried cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) and tensile properties of poly (lactic) acid-CNC composites. In Proceedings of the ANTEC® 2018-society of plastics engineers. 5p, Orlando, FL, USA, 7–10 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, M.V.G.; Borsoi, C.; Lavoratti, A.; Zanini, M.; Zattera, A.J.; Santana, R.M.C. Drying techniques applied to cellulose nanofibers. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Umemura, K.; Kawai, S. Kinetic analysis of color changes in cellulose during heat treatment. J. Wood Sci. 2012, 58, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacche, S.D.; Vitale, A.; Bongiovanni, R. Photocuring of epoxidized cardanol for biobased composites with microfibrillated cellulose. Molecules 2019, 24, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Qi, X.; He, Y.; Tan, D.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Simultaneous reinforcing and toughening of polyurethane via grafting on the surface of microfibrillated cellulose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, Z.; Svedberg, A. Controlled retention and drainage of microfibrillated cellulose in continuous paper production. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 13796–13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar Ciftci, G.; Larsson, P.A.; Riazanova, A.V.; Øvrebø, H.H.; Wågberg, L.; Berglund, L.A. Tailoring of rheological properties and structural polydispersity effects in microfibrillated cellulose suspensions. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9227–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.A.; Riazanova, A.V.; Cinar Ciftci, G.; Rojas, R.; Øvrebø, H.H.; Wågberg, L.; Berglund, L.A. Towards optimised size distribution in commercial microfibrillated cellulose: A fractionation approach. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.-C.; Wu, Q.; Song, K.; Lee, S.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y. Cellulose nanoparticles: Structure–morphology–rheology relationships. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Rigid filler toughening in PLA-Calcium Carbonate composites: Effect of particle surface treatment and matrix plasticization. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 113, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatto, M.; Salmini, E.; Castiello, S.; Coltelli, M.B.; Conzatti, L.; Stagnaro, P.; Andreotti, L.; Bronco, S. Plasticized and nanofilled poly(lactic acid)-based cast films: Effect of plasticizer and organoclay on processability and final properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4947–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Jiménez, A.; González-Martínez, C.; Chiralt, A. Influence of plasticizers on thermal properties and crystallization behaviour of poly(lactic acid) films obtained by compression moulding. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiardo, M.; Frisoni, G.; Scandola, M.; Rimelen, M.; Lips, D.; Ruffieux, K.; Wintermantel, E. Thermal and mechanical properties of plasticized poly(L-lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haafiz, M.K.M.; Hassan, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Inuwa, I.M.; Islam, M.S.; Jawaid, M. Properties of polylactic acid composites reinforced with oil palm biomass microcrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Gao, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L. Nanocomposites of poly (lactic acid) reinforced with cellulose nanofibrils. BioResources 2010, 5, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Kvien, I.; Tanem, B.S.; Oksman, K. Characterization of cellulose whiskers and their nanocomposites by atomic force and electron microscopy. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3160–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Pan, H.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, H.; Dong, L. A study on the mechanical, thermal properties and crystallization behavior of poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic poly(propylene carbonate) polyurethane blends. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 46183–46194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyholzer, C.; Tingaut, P.; Zimmermann, T.; Oksman, K. Dispersion and Reinforcing Potential of Carboxymethylated Nanofibrillated Cellulose Powders Modified with 1-Hexanol in Extruded Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W.; Xiao, H. Dispersion Properties of Nanocellulose: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, M.; El Kissi, N.; Dufresne, A. Cellulose nanocrystals and related nanocomposites: Review of some properties and challenges. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudharsan Reddy, K.; Prabhakar, M.N.; Kumara Babu, P.; Venkatesulu, G.; Kumarji Rao, U.S.; Chowdoji Rao, K.; Subha, M.C.S. Miscibility Studies of Hydroxypropyl Cellulose/Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in Dilute Solutions and Solid State. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popa, E.E.; Rapa, M.; Popa, O.; Mustatea, G.; Popa, V.I.; Mitelut, A.C.; Popa, M.E. Polylactic acid/cellulose fibres based composites for food packaging applications. Mater. Plast 2017, 54, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, K.; Csóka, L. Plasticized Biodegradable Poly(lactic acid) Based Composites Containing Cellulose in Micro- and Nanosize. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 329379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Ji, C.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, J. Structure and properties of Polylactic acid biocomposite films reinforced with cellulose Nanofibrils. Molecules 2020, 25, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, L.; Gazzano, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Righetti, M.C. Constrained amorphous interphase in poly(l-lactic acid): Estimation of the Tensile elastic modulus. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20890–20902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicogna, F.; Coiai, S.; De Monte, C.; Spiniello, R.; Fiori, S.; Franceschi, M.; Braca, F.; Cinelli, P.; Fehri, S.M.K.; Lazzeri, A.; et al. Poly(lactic acid) plasticized with low-molecular-weight polyesters: Structural, thermal and biodegradability features. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, S.; Liu, X.; Gu, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of plasticized poly (lactic acid) and its influence on the properties of composite materials. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oguz, O.; Candau, N.; Demongeot, A.; Citak, M.K.; Cetin, F.N.; Stoclet, G.; Michaud, V.; Menceloglu, Y.Z. Poly(lactide)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites by high-shear mixing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, V.; Cinelli, P.; Righetti, M.C.; Sandroni, M.; Polacco, G.; Seggiani, M.; Lazzeri, A. On the use of biobased waxes to tune thermal and mechanical properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates– bran biocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, N.A.A.; Ariff, Z.M.; Ariffin, A.; Jikan, S.S. Study on effect of filler loading on the flow and swelling behaviors of polypropylene-kaolin composites using single-screw extruder. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
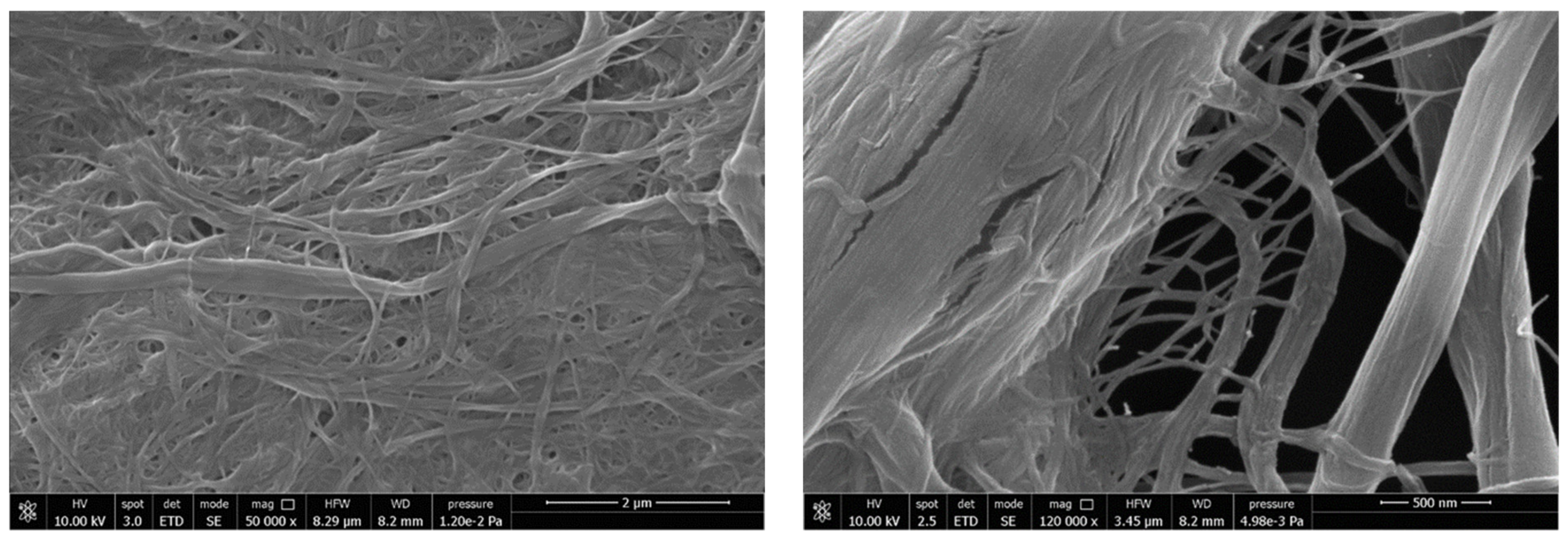
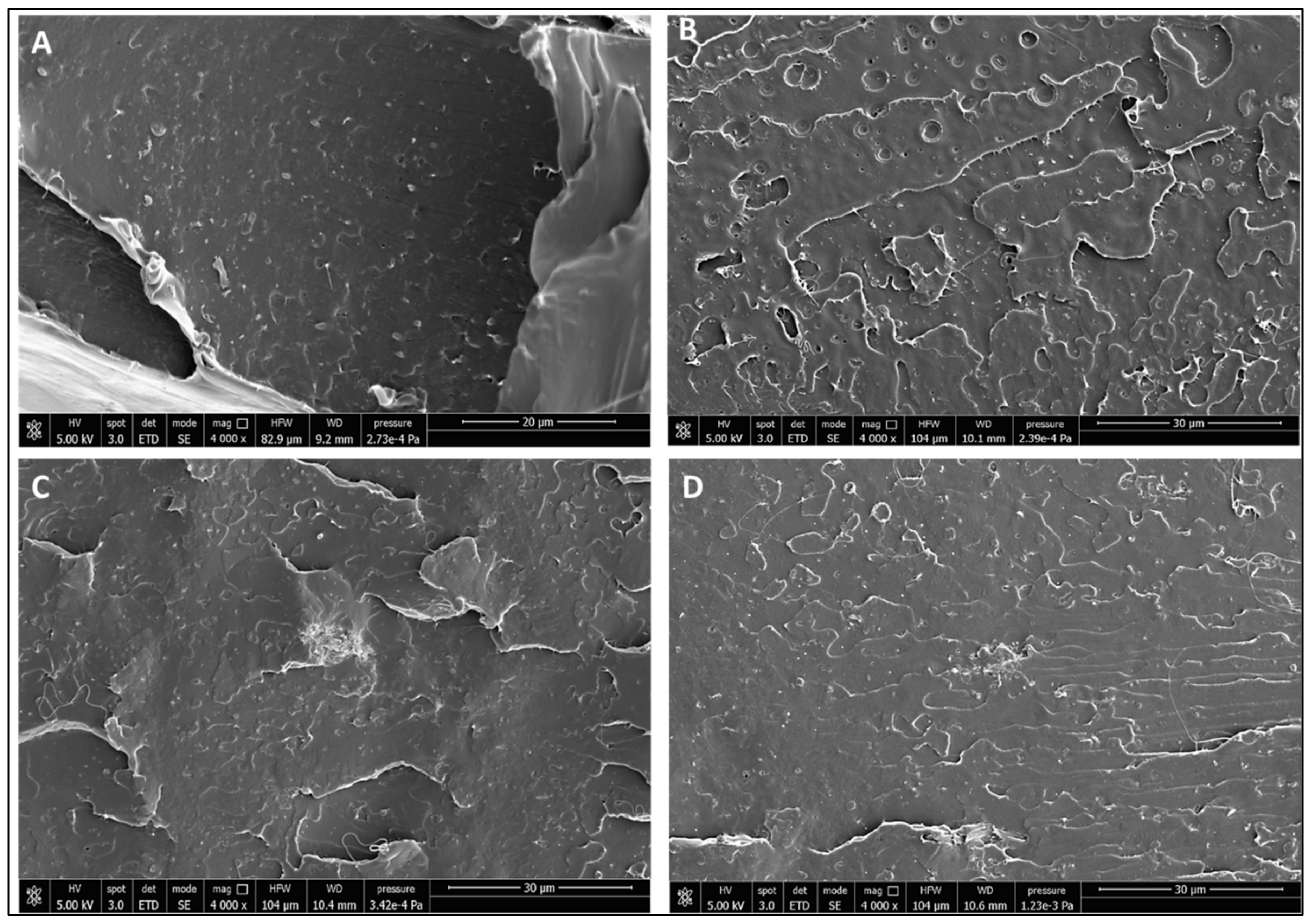
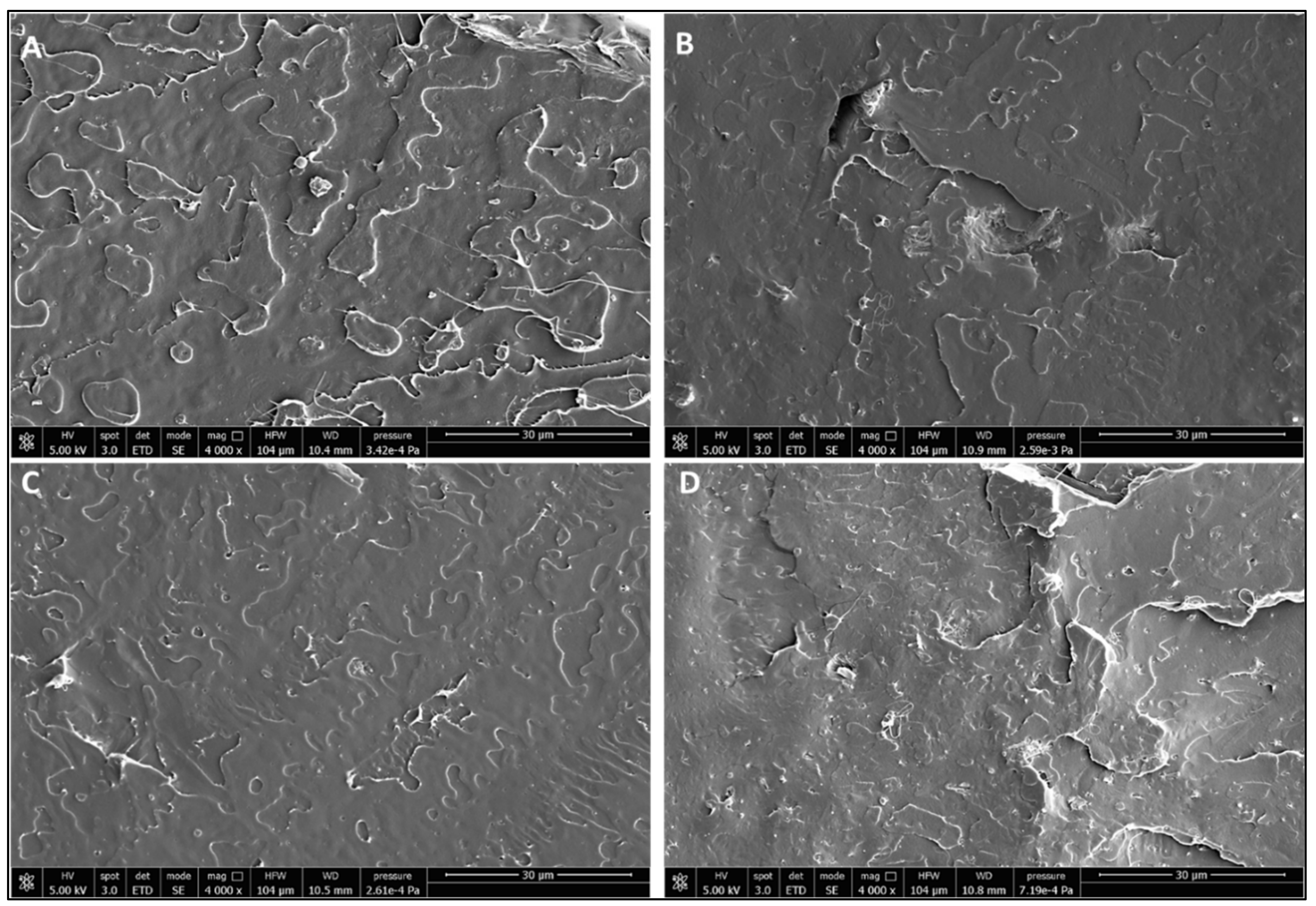
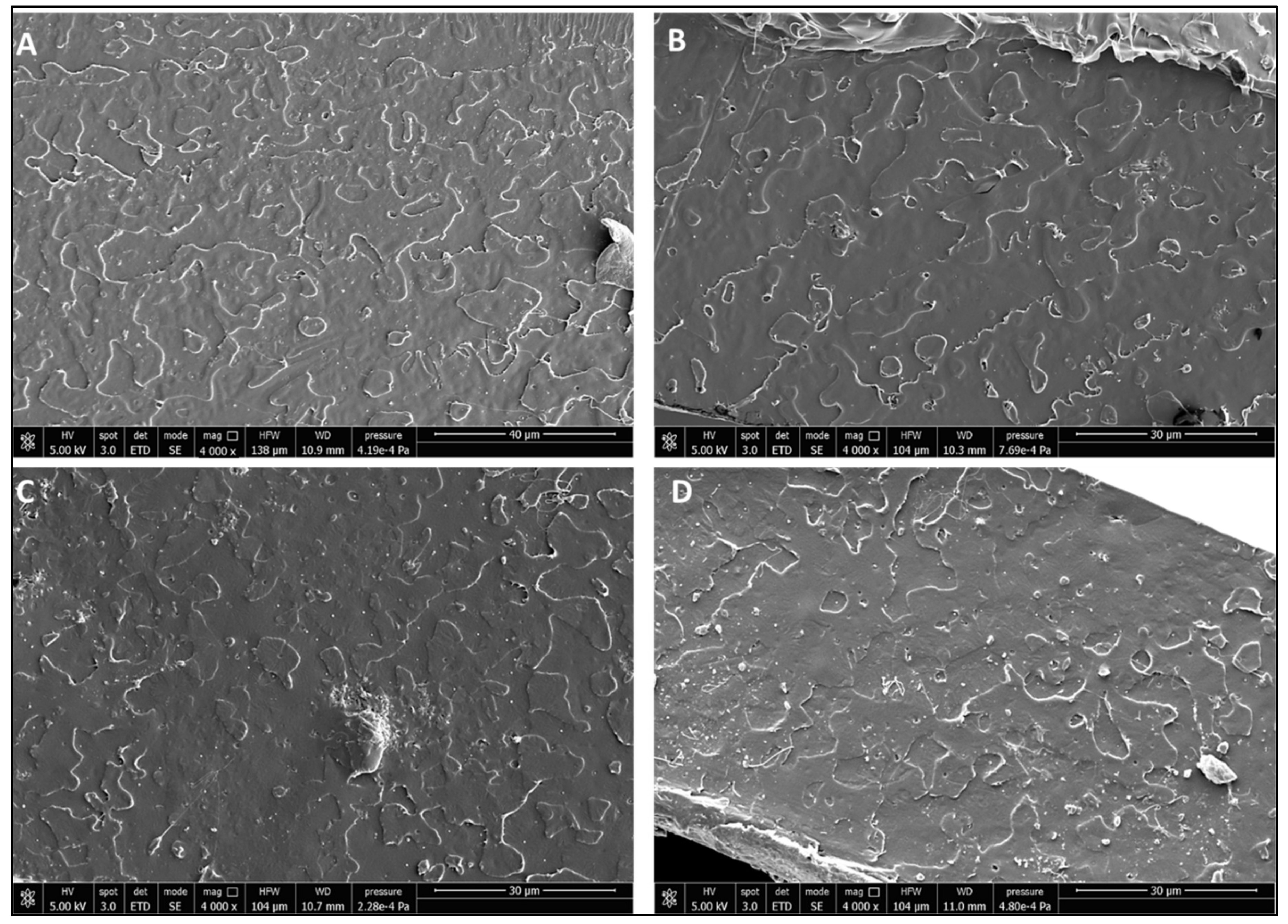


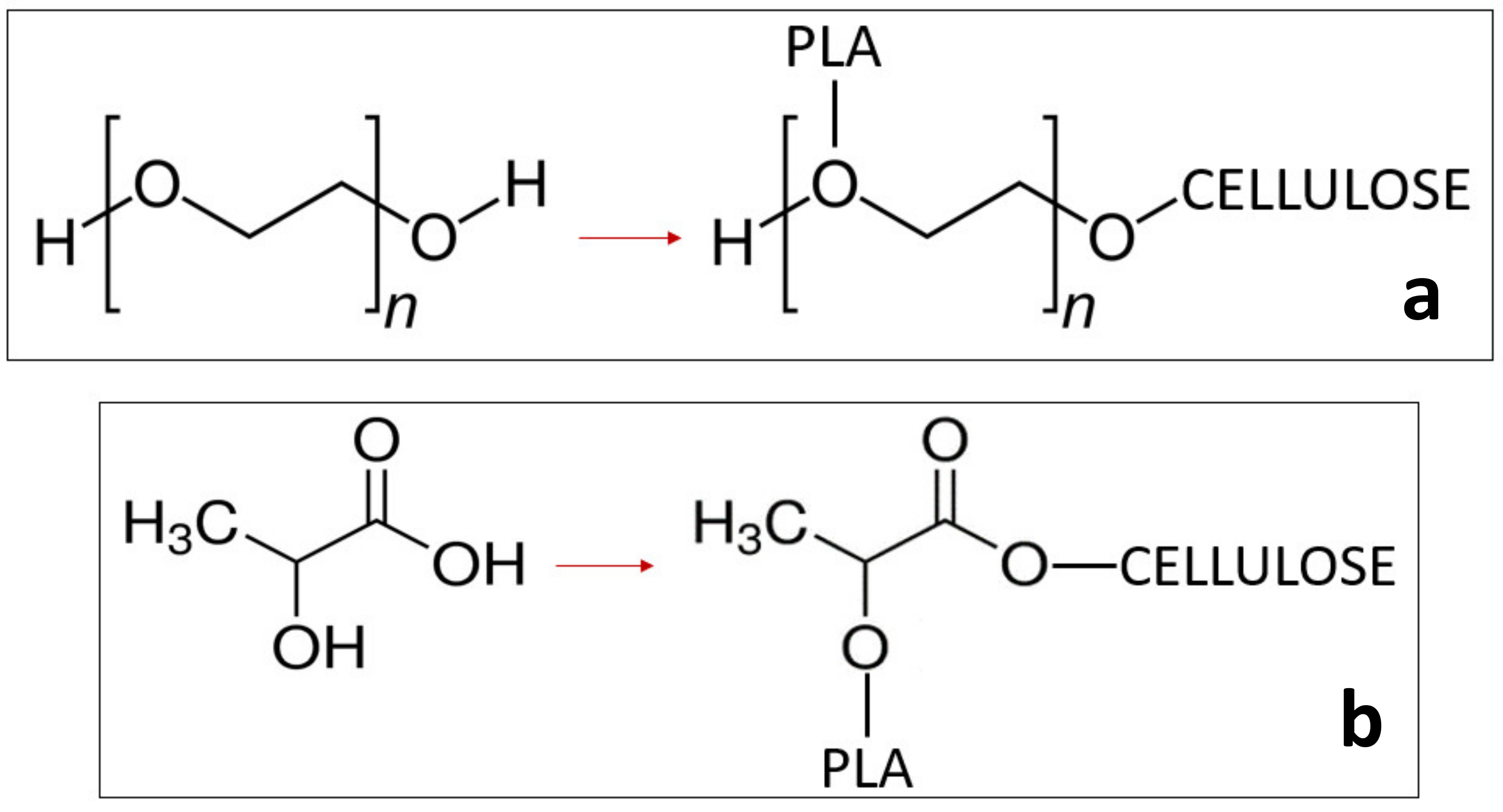


| Formulation | Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | Poly(ethylene glycol) 400 (PEG 400; wt %) | Oligomeric Acid Lactic 2 (OLA 2; wt % | Exilva F-01 L wt % | CELISH KY100S wt % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA_PEG_5 | 95 | 5 | / | / | / |
| PLA_PEG_10 | 90 | 10 | / | / | / |
| PLA_PEG_15 | 85 | 15 | / | / | / |
| PLA_OLA_5 | 95 | / | 5 | / | / |
| PLA_OLA_10 | 90 | / | 10 | / | / |
| PLA_OLA_15 | 85 | / | 15 | / | / |
| PLA_PEG_5_EX | 93.1 | 4.9 | / | 2 | / |
| PLA_PEG_10_EX | 88.2 | 9.8 | / | 2 | / |
| PLA_PEG_15_EX | 83.3 | 14.7 | / | 2 | / |
| PLA_OLA_5_EX | 93.1 | 4.9 | / | 2 | / |
| PLA_OLA_10_EX | 88.2 | 9.8 | / | 2 | / |
| PLA_OLA_15_EX | 83.3 | 14.7 | / | 2 | / |
| PLA_PEG_5_CE | 93.1 | / | 4.9 | / | 2 |
| PLA_PEG_10_CE | 88.2 | / | 9.8 | / | 2 |
| PLA_PEG_15_CE | 83.3 | / | 14.7 | / | 2 |
| PLA_OLA_5_CE | 93.1 | / | 4.9 | / | 2 |
| PLA_OLA_10_CE | 88.2 | / | 9.8 | / | 2 |
| PLA_OLA_15_CE | 83.3 | / | 14.7 | / | 2 |
| Formulation | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | σbreak (MPa) | εbreak (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA_PEG_5 | 2.47 ± 0.48 | 23.87 ± 2.72 | 11.98 ± 0.31 |
| PLA_OLA_5 | 2.51 ± 0.02 | 24.03 ± 2.74 | 19.8 ± 0.98 |
| PLA_PEG_5_EX | 3.31 ± 0.02 | 53.12 ± 3.33 | 3.92 ± 0.18 |
| PLA_OLA_5_EX | 3.06 ± 0.80 | 53.16 ± 1.10 | 2.92 ± 0.11 |
| PLA_PEG_5_CE | 2.76 ± 0.33 | 46.68 ± 4.46 | 3.76 ± 0.09 |
| PLA_OLA_5_CE | 3.07 ± 0.50 | 51.66 ± 2.04 | 3.15 ± 0.10 |
| PLA_PEG_10 | 2.07 ± 0.31 | 23.05 ± 2.62 | 18.1 ± 0.52 |
| PLA_OLA_10 | 2.15 ± 0.28 | 21.63 ± 1.11 | 42.78 ± 0.87 |
| PLA_PEG_10_EX | 3.39 ± 0.03 | 46.49 ± 2.14 | 4.61 ± 0.27 |
| PLA_OLA_10_EX | 3.17 ± 0.13 | 49.63 ± 1.44 | 3.36 ± 0.04 |
| PLA_PEG_10_CE | 2.97 ± 0.44 | 46.80 ± 3.15 | 3.88 ± 0.02 |
| PLA_OLA_10_CE | 3.68 ± 0.17 | 51.59 ± 2.77 | 3.23 ± 0.04 |
| PLA_PEG_15 | 1.63 ± 0.78 | 18.48 ± 0.2 | 30.45 ± 5.26 |
| PLA_OLA_15 | 1.64 ± 0.4 | 20.02 ± 0.54 | 49.95 ± 1.22 |
| PLA_PEG_15_EX | 3.53 ± 0.07 | 43.18 ± 2.44 | 5.52 ± 0.28 |
| PLA_OLA_15_EX | 3.45 ± 0.43 | 44.76 ± 1.13 | 3.56 ± 0.14 |
| PLA_PEG_15_CE | 3.54 ± 0.30 | 47.06 ± 3.79 | 3.88 ± 0.04 |
| PLA_OLA_15_CE | 3.81 ± 0.23 | 42.98 ± 2.04 | 3.62 ± 0.08 |
| Formulation | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | σbreak (MPa) | εbreak (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA_OLA_15* | 0.73 ± 0.01 | 8.03 ± 0.89 | 178.3 ± 18.2 |
| PLA_PEG_15* | 1.15 ± 0.05 | 10.85 ± 1.51 | 149.6 ± 21.3 |
| PLA_PEG_15_EX* | 2.16 ± 0.19 | 19.84 ± 1.04 | 23.91 ± 3.06 |
| PLA_OLA_15_EX* | 2.50 ± 0.16 | 28.44 ± 2.22 | 11.84 ± 4.52 |
| PLA_PEG_15_CE* | 2.11 ± 0.14 | 19.32 ± 2.37 | 11.79 ± 0.13 |
| PLA_OLA_15_CE* | 2.13 ± 0.07 | 29.03 ± 1.39 | 15.16 ± 2.65 |
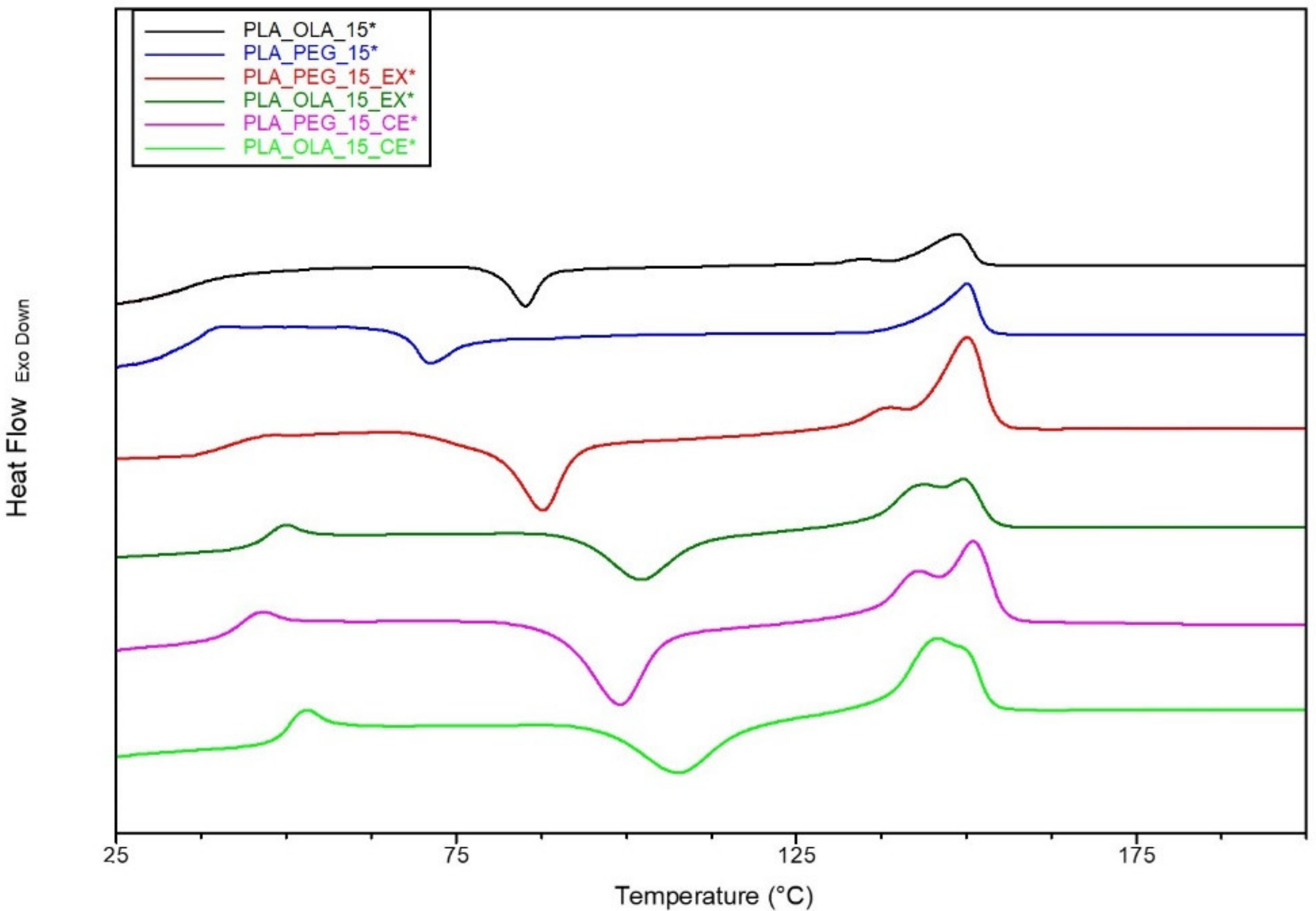
| Figure | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | Tm (°C) | ΔH°cc (J/g) | ΔH°m (J/g) | Xcc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA_OLA_15* | 35.6 | 85.2 | 148.8 | 6.1 | 7.2 | 1.4 |
| PLA_PEG_15* | 37.2 | 70.9 | 150 | 5.8 | 10.8 | 6.3 |
| PLA_PEG_15_EX* | 40.5 | 87.6 | 150 | 20.9 | 28.3 | 9.5 |
| PLA_OLA_15_EX* | 45 | 102.2 | 149.4 | 14.9 | 22.2 | 9.4 |
| PLA_PEG_15_CE* | 43.3 | 99 | 150.9 | 25.7 | 32.9 | 9.2 |
| PLA_OLA_15_CE* | 50.4 | 107.9 | 148.3 | 18.7 | 25.7 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molinari, G.; Gigante, V.; Fiori, S.; Aliotta, L.; Lazzeri, A. Dispersion of Micro Fibrillated Cellulose (MFC) in Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) from Lab-Scale to Semi-Industrial Processing Using Biobased Plasticizers as Dispersing Aids. Chemistry 2021, 3, 896-915. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030066
Molinari G, Gigante V, Fiori S, Aliotta L, Lazzeri A. Dispersion of Micro Fibrillated Cellulose (MFC) in Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) from Lab-Scale to Semi-Industrial Processing Using Biobased Plasticizers as Dispersing Aids. Chemistry. 2021; 3(3):896-915. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolinari, Giovanna, Vito Gigante, Stefano Fiori, Laura Aliotta, and Andrea Lazzeri. 2021. "Dispersion of Micro Fibrillated Cellulose (MFC) in Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) from Lab-Scale to Semi-Industrial Processing Using Biobased Plasticizers as Dispersing Aids" Chemistry 3, no. 3: 896-915. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030066
APA StyleMolinari, G., Gigante, V., Fiori, S., Aliotta, L., & Lazzeri, A. (2021). Dispersion of Micro Fibrillated Cellulose (MFC) in Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) from Lab-Scale to Semi-Industrial Processing Using Biobased Plasticizers as Dispersing Aids. Chemistry, 3(3), 896-915. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030066










