Carbon Monoxide Therapy Using Hybrid Carbon Monoxide-Releasing/Nrf2-Inducing Molecules through a Neuroprotective Lens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Carbon Monoxide and the Nrf2 Pathway
3. Relevance of the Nrf2 Pathway
4. Therapeutic Application of CO
4.1. Inhaled Carbon Monoxide
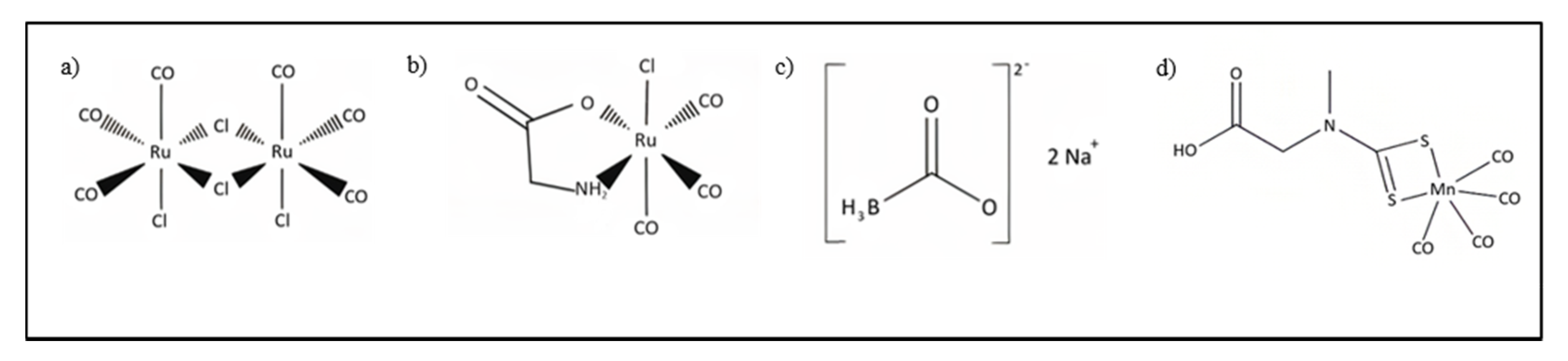
4.2. CORMs
4.3. Hybrid CORMs
4.3.1. HYCO-1 and HYCO-2
4.3.2. HYCO-4 and HYCO-10
4.3.3. HYCO-3, HYCO-6, HYCO-11, and HYCO-13
4.3.4. FumET-CORMs
4.3.5. CAI-CORMs as Nrf2 Activators
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Literature Search
References
- Ismailova, A.; Kuter, D.; Bohle, D.S.; Butler, I.S. An Overview of the Potential Therapeutic Applications of CO-Releasing Molecules. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 8547364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Zaher, A.O.; Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; Aboulhagag, N.A.; Farghaly, H.S.M.; Al-Wasei, F.M.M. The potential relationship between gasotransmitters and oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in lead-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Tissue Cell 2021, 71, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foresti, R.; Bani-Hani, M.G.; Motterlini, R. Use of carbon monoxide as a therapeutic agent: Promises and challenges. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.P.; Ryter, S.W.; Choi, A.M.K. CO as a cellular signaling molecule. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 46, 411–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, B.E. Carbon monoxide: An essential signalling molecule. In Medicinal Organometallic Chemistry; Jaouen, G., Metzler-Nolte, N., Eds.; Topics in organometallic chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 32, pp. 247–285. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Hirsch, D.J.; Glatt, C.E.; Ronnett, G.V.; Snyder, S.H. Carbon monoxide: A putative neural messenger. Science 1993, 259, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, F. The cGMP system: Components and function. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, H.; Kautza, B.; Escobar, D.; Nassour, I.; Luciano, J.; Botero, A.M.; Gordon, L.; Martinez, S.; Holder, A.; Ogundele, O.; et al. Inhaled Carbon Monoxide Protects against the Development of Shock and Mitochondrial Injury following Hemorrhage and Resuscitation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Huang, M.-H.; Jiang, J.-D.; Peng, Z.-G. Hepatitis C: From inflammatory pathogenesis to anti-inflammatory/hepatoprotective therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5297–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naggie, S.; Muir, A.J. Oral combination therapies for hepatitis C virus infection: Successes, challenges, and unmet needs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanpour, M.; Imani, F.; Safari, S.; Sanaie, S.; Soleimanpour, H.; Ameli, H.; Alavian, S.M. The Role of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in the Treatment of Patients with Hepatic Disease: A Review Article. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 6, e37822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hersi, K.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Kondamudi, N.P. Meningitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Young, N.; Thomas, M. Meningitis in adults: Diagnosis and management. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Bashir, H.; Laundy, M.; Booy, R. Diagnosis and treatment of bacterial meningitis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fredenburgh, L.E.; Kraft, B.D.; Hess, D.R.; Harris, R.S.; Wolf, M.A.; Suliman, H.B.; Roggli, V.L.; Davies, J.D.; Winkler, T.; Stenzler, A.; et al. Effects of inhaled CO administration on acute lung injury in baboons with pneumococcal pneumonia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L834–L846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenburgh, L.E.; Perrella, M.A.; Barragan-Bradford, D.; Hess, D.R.; Peters, E.; Welty-Wolf, K.E.; Kraft, B.D.; Harris, R.S.; Maurer, R.; Nakahira, K.; et al. A phase I trial of low-dose inhaled carbon monoxide in sepsis-induced ARDS. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e124039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motterlini, R.; Clark, J.E.; Foresti, R.; Sarathchandra, P.; Mann, B.E.; Green, C.J. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules: Characterization of biochemical and vascular activities. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, E17–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poulos, T.L. Heme enzyme structure and function. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 3919–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siracusa, R.; Schaufler, A.; Calabrese, V.; Fuller, P.M.; Otterbein, L.E. Carbon Monoxide: From Poison to Clinical Trials. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, M.; Damore, G.; Costa, B.; Gioannini, T.L.; Weiss, J.P.; Peri, F. Hemin and a metabolic derivative coprohemin modulate the TLR4 pathway differently through different molecular targets. Innate Immun. 2011, 17, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Free heme toxicity and its detoxification systems in human. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 157, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, S.T.; Midwinter, R.G.; Berger, B.S.; Stocker, R. Heme Oxygenase-1: A Critical Link between Iron Metabolism, Erythropoiesis, and Development. Adv. Hematol. 2011, 2011, 473709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leffler, C.W.; Parfenova, H.; Jaggar, J.H. Carbon monoxide as an endogenous vascular modulator. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1–H11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.S.; Zhuang, H.; Doré, S. Heme oxygenase-1 protects brain from acute excitotoxicity. Neuroscience 2006, 141, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Yoon, H.-J.; Cha, Y.-N.; Surh, Y.-J. Role of heme oxygenase-1 and its reaction product, carbon monoxide, in manifestation of breast cancer stem cell-like properties: Notch-1 as a putative target. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 1336–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Locascio, L.M.; Doré, S. Critical role of nrf2 in experimental ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonardo, C.C.; Doré, S. Dietary flavonoids are neuroprotective through Nrf2-coordinated induction of endogenous cytoprotective proteins. Nutr. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srisook, K.; Kim, C.; Cha, Y.-N. Molecular mechanisms involved in enhancing HO-1 expression: De-repression by heme and activation by Nrf2, the “one-two” punch. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogun, E.; Hoque, M.; Gong, P.; Killeen, E.; Green, C.J.; Foresti, R.; Alam, J.; Motterlini, R. Curcumin activates the haem oxygenase-1 gene via regulation of Nrf2 and the antioxidant-responsive element. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, J.L.; Fayad Kobeissi, S.; Oudir, S.; Haas, B.; Michel, B.; Dubois Randé, J.-L.; Ollivier, A.; Martens, T.; Rivard, M.; Motterlini, R.; et al. Design and synthesis of new hybrid molecules that activate the transcription factor Nrf2 and simultaneously release carbon monoxide. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14698–14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, N.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; et al. Carnosol as a nrf2 activator improves endothelial barrier function through antioxidative mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafer, D.; Tombes, M.B.; Shrader, E.; Ryan, A.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Dent, P.; Malkin, M. Phase I trial of dimethyl fumarate, temozolomide, and radiation therapy in glioblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdz052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Du, R.; Yin, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, G.; Cao, W. Nrf2 is essential for the anti-inflammatory effect of carbon monoxide in LPS-induced inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, K.K.; Jadeja, R.N.; Thadani, J.M.; Joshi, A.; Vohra, A.; Mevada, V.; Patel, R.; Khurana, S.; Devkar, R.V. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule A-1 attenuates acetaminophen-mediated hepatotoxicity and improves survival of mice by induction of Nrf2 and related genes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 360, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, K.K.; Jadeja, R.N.; Vyas, H.S.; Pandya, B.; Joshi, A.; Vohra, A.; Thounaojam, M.C.; Martin, P.M.; Bartoli, M.; Devkar, R.V. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-A1 improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via Nrf2 activation mediated improvement in oxidative stress and mitochondrial function. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Pae, H.-O.; Zheng, M.; Park, R.; Kim, Y.-M.; Chung, H.-T. Carbon monoxide induces heme oxygenase-1 via activation of protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase and inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis triggered by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogaki, S.; Taguchi, K.; Maeda, H.; Watanabe, H.; Ishima, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Kupffer cell inactivation by carbon monoxide bound to red blood cells preserves hepatic cytochrome P450 via anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects exerted through the HMGB1/TLR-4 pathway during resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 97, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoetzel, A.; Dolinay, T.; Vallbracht, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, H.P.; Ifedigbo, E.; Alber, S.; Kaynar, A.M.; Schmidt, R.; Ryter, S.W.; et al. Carbon monoxide protects against ventilator-induced lung injury via PPAR-gamma and inhibition of Egr-1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagao, S.; Taguchi, K.; Sakai, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Watanabe, H.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Carbon monoxide-bound hemoglobin vesicles ameliorate multiorgan injuries induced by severe acute pancreatitis in mice by their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5611–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Cao, W.; Biswal, S.; Doré, S. Carbon monoxide-activated Nrf2 pathway leads to protection against permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2011, 42, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, B.; Zhang, C.; Hu, W.; Guo, C.; Xia, Z.; Hu, W.; Qin, M.; Jiang, W.; Lv, J.; Xu, D.; et al. Nano-designed carbon monoxide donor SMA/CORM2 exhibits protective effect against acetaminophen induced liver injury through macrophage reprograming and promoting liver regeneration. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepinskas, G.; Katada, K.; Bihari, A.; Potter, R.F. Carbon monoxide liberated from carbon monoxide-releasing molecule CORM-2 attenuates inflammation in the liver of septic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G184–G191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinay, T.; Szilasi, M.; Liu, M.; Choi, A.M.K. Inhaled carbon monoxide confers antiinflammatory effects against ventilator-induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bathoorn, E.; Slebos, D.J.; Postma, D.S.; Koeter, G.H.; van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; van der Toorn, M.; Boezen, H.M.; Kerstjens, H.A.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled carbon monoxide in patients with COPD: A pilot study. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadori, M.; Seveso, M.; Besenzon, F.; Bosio, E.; Tognato, E.; Fante, F.; Boldrin, M.; Gavasso, S.; Ravarotto, L.; Mann, B.E.; et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of the carbon monoxide-releasing molecule, CORM-3, in the xenogeneic pig-to-primate context. Xenotransplantation 2009, 16, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, D.K.; McGahee, S.M.; Politte, L.C.; Duncan, G.N.; Cusin, C.; Hopwood, C.J.; Stern, T.A. Complications of carbon monoxide poisoning: A case discussion and review of the literature. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 11, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatzschneider, U. Novel lead structures and activation mechanisms for CO-releasing molecules (CORMs). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romão, C.C.; Blättler, W.A.; Seixas, J.D.; Bernardes, G.J.L. Developing drug molecules for therapy with carbon monoxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3571–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.E.; Naughton, P.; Shurey, S.; Green, C.J.; Johnson, T.R.; Mann, B.E.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R. Cardioprotective actions by a water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, e2–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abeyrathna, N.; Washington, K.; Bashur, C.; Liao, Y. Nonmetallic carbon monoxide releasing molecules (CORMs). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 8692–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Sawle, P.; Hammad, J.; Bains, S.; Alberto, R.; Foresti, R.; Green, C.J. CORM-A1: A new pharmacologically active carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Habtezion, A. Carbon monoxide-based therapy ameliorates acute pancreatitis via TLR4 inhibition. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Stone, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, C.; Yin, X.; Meng, R. CORM-2 inhibits intracerebral hemorrhage-mediated inflammation. Neurol. Res. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.J.; Jernigan, N.L.; Drummond, H.A.; McLemore, G.R.; Rimoldi, J.M.; Poreddy, S.R.; Gadepalli, R.S.V.; Stec, D.E. Renal vascular responses to CORM-A1 in the mouse. Pharmacol. Res. 2006, 54, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, K.; Cavalli, E.; Mammana, S.; Basile, M.S.; Caltabiano, R.; Pesce, A.; Puleo, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Magro, G.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1/CO axis and therapeutic intervention with the CO-releasing molecule CORM-A1, in a murine model of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 4156–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Quattrocchi, C.; Motterlini, R.; Di Marco, R.; Magro, G.; Penacho, N.; Romao, C.C.; Nicoletti, F. Prevention of clinical and histological signs of proteolipid protein (PLP)-induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice by the water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM)-A1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 163, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmer, R.D.; Richter, H.; Ford, P.C. A photochemical precursor for carbon monoxide release in aerated aqueous media. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palao, E.; Slanina, T.; Muchová, L.; Šolomek, T.; Vítek, L.; Klán, P. Transition-Metal-Free CO-Releasing BODIPY Derivatives Activatable by Visible to NIR Light as Promising Bioactive Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.; Mann, B.E.; Poole, R.K. Sulfite species enhance carbon monoxide release from CO-releasing molecules: Implications for the deoxymyoglobin assay of activity. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 427, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczara, P.; Motterlini, R.; Rosen, G.M.; Augustynek, B.; Bednarczyk, P.; Szewczyk, A.; Foresti, R.; Chlopicki, S. Carbon monoxide released by CORM-401 uncouples mitochondrial respiration and inhibits glycolysis in endothelial cells: A role for mitoBKCa channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1847, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fayad-Kobeissi, S.; Ratovonantenaina, J.; Dabiré, H.; Wilson, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Berdeaux, A.; Dubois-Randé, J.-L.; Mann, B.E.; Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R. Vascular and angiogenic activities of CORM-401, an oxidant-sensitive CO-releasing molecule. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 102, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braud, L.; Pini, M.; Wilson, J.L.; Czibik, G.; Sawaki, D.; Derumeaux, G.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R. A carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM-401) induces a metabolic switch in adipocytes and improves insulin-sensitivity on high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. Suppl. 2018, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.N.; Richard-Mohamed, M.; Sun, Q.; Haig, A.; Aboalsamh, G.; Barrett, P.; Mayer, R.; Alhasan, I.; Pineda-Solis, K.; Jiang, L.; et al. CORM-401 Reduces Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in an Ex Vivo Renal Porcine Model of the Donation After Circulatory Death. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Fan, M.; Zhu, J.; Ling, C.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Yao, Q.; Gu, Z.; et al. A multifunctional anti-inflammatory drug that can specifically target activated macrophages, massively deplete intracellular H2O2, and produce large amounts CO for a highly efficient treatment of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brieger, K.; Schiavone, S.; Miller, F.J.; Krause, K.H. Reactive oxygen species: From health to disease. Swiss Med. Wkly 2012, 142, w13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikam, A.; Ollivier, A.; Rivard, M.; Wilson, J.L.; Mebarki, K.; Martens, T.; Dubois-Randé, J.-L.; Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R. Diverse Nrf2 Activators Coordinated to Cobalt Carbonyls Induce Heme Oxygenase-1 and Release Carbon Monoxide in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Nikam, A.; Manin, S.; Ollivier, A.; Wilson, J.L.; Djouadi, S.; Muchova, L.; Martens, T.; Rivard, M.; Foresti, R. HYCO-3, a dual CO-releaser/Nrf2 activator, reduces tissue inflammation in mice challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Redox Biol 2019, 20, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, A.; Foresti, R.; El Ali, Z.; Martens, T.; Kitagishi, H.; Motterlini, R.; Rivard, M. Design and Biological Evaluation of Manganese- and Ruthenium-Based Hybrid CO-RMs (HYCOs). ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ali, Z.; Ollivier, A.; Manin, S.; Rivard, M.; Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R. Therapeutic effects of CO-releaser/Nrf2 activator hybrids (HYCOs) in the treatment of skin wound, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanski, S.; Stamellou, E.; Jaraba, J.T.; Storz, D.; Krämer, B.K.; Hafner, M.; Amslinger, S.; Schmalz, H.G.; Yard, B.A. Enzyme-triggered CO-releasing molecules (ET-CORMs): Evaluation of biological activity in relation to their structure. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.; Göderz, A.-L.; Braumüller, H.; Neudörfl, J.M.; Röcken, M.; Wieder, T.; Schmalz, H.-G. Methyl Fumarate-Derived Iron Carbonyl Complexes (FumET-CORMs) as Powerful Anti-inflammatory Agents. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1927–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Carradori, S.; Angeli, A.; Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T.; Guglielmi, P.; Coletti, C.; Paciotti, R.; Schweikl, H.; Maestrelli, F.; et al. Dual Carbonic Anhydrase IX/XII Inhibitors and Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecules Modulate LPS-Mediated Inflammation in Mouse Macrophages. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrino, E.; Milazzo, L.; Micheli, L.; Vullo, D.; Angeli, A.; Bozdag, M.; Nocentini, A.; Menicatti, M.; Bartolucci, G.; di Cesare Mannelli, L.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors with Carbon Monoxide Releasing Properties for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7233–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallorini, M.; Berardi, A.C.; Ricci, A.; Passeri, C.A.L.; Zara, S.; Oliva, F.; Cataldi, A.; Carta, F.; Carradori, S. Dual acting carbon monoxide releasing molecules and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors differentially modulate inflammation in human tenocytes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronesi, A.; Pecoraro, V.; Zauli, S.; Ottone, M.; Leonardi, G.; Lauriola, P.; Trenti, T. Use of carboxyhemoglobin as a biomarker of environmental CO exposure: Critical evaluation of the literature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 25798–25809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Coco, M.; Perciavalle, V.; Garotta, G.; Romao, C.C.; Nicoletti, F. Therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavicchioli, F.; Cesarotti, I.M.; Fangman, M.; Lua, J.; Hautamaki, R.; Doré, S. Carbon Monoxide Therapy Using Hybrid Carbon Monoxide-Releasing/Nrf2-Inducing Molecules through a Neuroprotective Lens. Chemistry 2021, 3, 800-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030057
Cavicchioli F, Cesarotti IM, Fangman M, Lua J, Hautamaki R, Doré S. Carbon Monoxide Therapy Using Hybrid Carbon Monoxide-Releasing/Nrf2-Inducing Molecules through a Neuroprotective Lens. Chemistry. 2021; 3(3):800-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavicchioli, Flavia, Izzy M. Cesarotti, Madison Fangman, Josh Lua, Raymond Hautamaki, and Sylvain Doré. 2021. "Carbon Monoxide Therapy Using Hybrid Carbon Monoxide-Releasing/Nrf2-Inducing Molecules through a Neuroprotective Lens" Chemistry 3, no. 3: 800-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030057
APA StyleCavicchioli, F., Cesarotti, I. M., Fangman, M., Lua, J., Hautamaki, R., & Doré, S. (2021). Carbon Monoxide Therapy Using Hybrid Carbon Monoxide-Releasing/Nrf2-Inducing Molecules through a Neuroprotective Lens. Chemistry, 3(3), 800-817. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3030057








