Abstract
Intercellular gap junction (GJ) contacts formed by the coupling of connexin (Cx) hemichannels (HCs) embedded into the plasma membranes of neighboring cells play significant role in the development, signaling and malfunctions of mammalian tissues. Understanding and targeting GJ functions, however, calls for finding valid Cx subtype-specific inhibitors. We conjecture the lack of information about binding interactions between the GJ interface forming extracellular EL1 and EL2 loops and peptide mimetics designed to specifically inhibit Cx43HC coupling to Cx43GJ. Here, we explore active spots at the GJ interface using known peptide inhibitors that mimic various segments of EL1 and EL2. Binding interactions of these peptide inhibitors and the non-peptide inhibitor quinine has been modelled in combination with the use of blind docking molecular mechanics (MM). The neuron-specific Cx36HC and astrocyte-specific Cx43HC subtypes were modelled with a template derived from the high-resolution structure of Cx26GJ. GJ-coupled and free Cx36HC and Cx43HC models were obtained by dissection of GJs (GJ-coupled) followed by 50 ns molecular dynamics (free). Molecular mechanics (MM) calculations were performed by the docking of inhibitors, explicitly the designed Cx43 EL1 or EL2 loop sequence mimetics (GAP26, P5 or P180–195, GAP27, Peptide5, respectively) and the Cx36 subtype-specific quinine into the model structures. In order to explore specific binding interactions between inhibitors and CxHC subtypes, MM/Generalized Born Surface Area (MM/GBSA) ΔGbind values for representative conformers of peptide mimetics and quinine were evaluated by mapping the binding surface of Cx36HC and Cx43HC for all inhibitors. Quinine specifically contacts Cx36 EL1 residues V54-C55-N56-T57-L58, P60 and N63. Blocking the vestibule by the side of Cx36HC entry, quinine explicitly interacts with the non-conserved V54, L58, N63 residues of Cx36 EL1. In addition, our work challenges the predicted specificity of peptide mimetics, showing that the docking site of peptides is unrelated to the location of the sequence they mimic. Binding features, such as unaffected EL2 residues and the lack of Cx43 subtype-specificity of peptide mimetics, suggest critical roles for peptide stringency and dimension, possibly pertaining to the Cx subtype-specificity of peptide inhibitors.
1. Introduction
Gap junctions (GJs) formed by the coupling of various connexin (Cx) subtype hemichannels (CxHCs, connexons) maintain adhesion and conduction between adjacent cells [1,2,3]. They are recognized as critical players in the development and disease of mammalian tissues [4,5,6] (and reference cited). All Cx subtypes contain two extracellular loops (EL1 and EL2) which are supposed to participate in GJ formation [7]. Previously, Warner et al. [8] conjectured HC coupling to GJ and conserved amino acid (AA) motifs, with QPG of EL1 being among the residues that possibly intervene HC coupling to GJ. Significantly, the consensus sequence of the conserved AAs of EL1 DEQSxFxCNTxQPGCxNVCYDxx highlights sequences of fully (bold) or in at least 50% identical residues in all of some twenty human Cx proteins [9]. One third of EL1 AAs (x) are less conserved, providing opportunity for subtype-specific inhibitor design. An exposed tetrapeptide sequence within the EL2 sequence has also been emphasized concerning the specificity of inter-connexon interaction [10,11].
As a result, several EL1 or EL2 mimicking peptides targeted to inhibit the coupling of HC to GJ have been developed [12,13,14,15]. Unexpectedly, GJ inhibitor peptide mimetics do block CxGJ-facilitated intercellular communications, but in unanticipated ways [16]. We and others [2] have sought to develop a more detailed understanding of HC coupling to GJ, first made apparent at the molecular level by the discovery of the X-ray structure of Cx26 GJ at 3.5 Å resolution [17].
As major subclasses of GJs shaping brain signaling, the astrocytic and neuronal GJs are formed by astrocytic Cx43 and neuronal connexin36 (Cx36) [18]. Indeed, GJs consisting of Cx43 protomer chains participate in long-range synchronized neural activity, underlying epilepsy [19,20] or slow-wave sleep [21]. Our undertaking expects insights into the structural quality associated with Cx43 versus Cx36 selectivity of peptide mimetic inhibitors. It is conceivable that, being identical with various sequences of EL1 or EL2 of Cx43 (P5, GAP26 or Peptide5, GAP27, P180-195, respectively; Figure 1), the peptide mimetic inhibitors designed to date shall meet the criteria of Cx43 subtype selectivity. Importantly, however, the literature relating the functional relevance of peptide mimetics does not validate the specificity [14,15,22,23,24,25,26]. Furthermore, the subtype specificity of these peptides is also challenged by the fact that the protein segments they mimic are widely shared by other Cx subtypes, as outlined above. Furthermore, subtype selectivity of another widely accepted selective GJ inhibitor, the Cx36-specific (R)-(6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)((2S,4S,8R)-8-vinylquinuclidin-2-yl)methanol (quinine) has not been strengthened either [6,27,28,29,30]. We hypothesize that Cx subtype-specific coupling of HC to GJ shall become true by undertaking the validation of the binding of mimetic peptides and quinine at the extracellular interface of Cx43HC and/or Cx36HC.
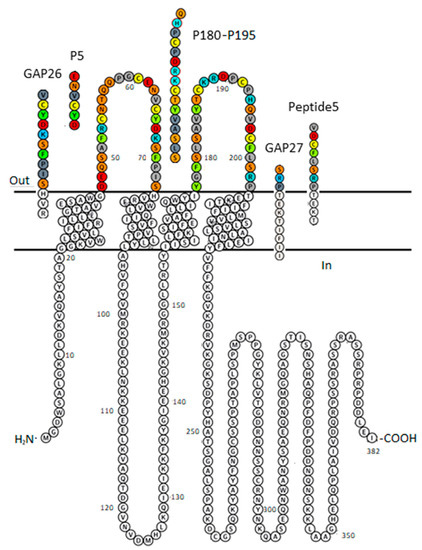
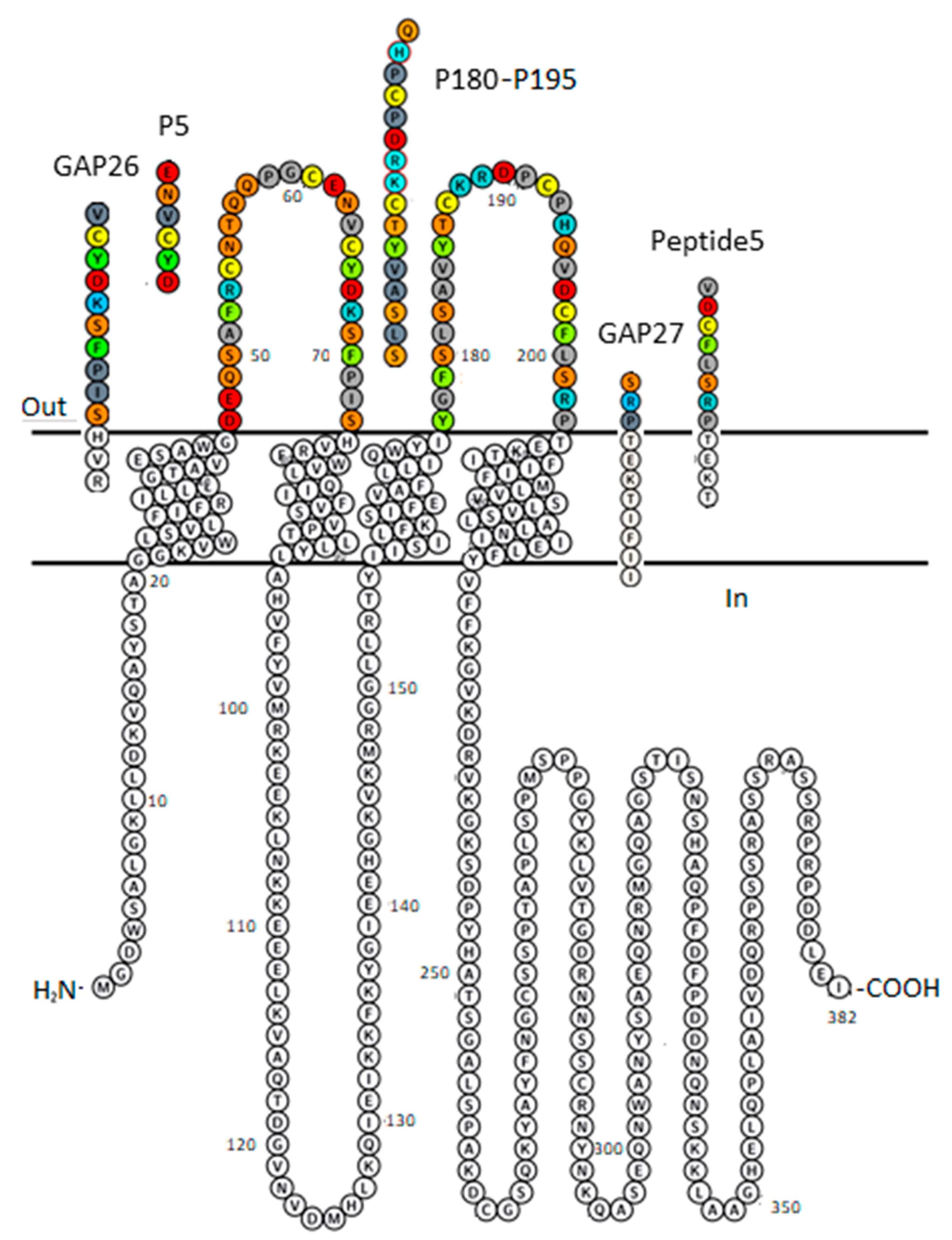
Figure 1.
Plot of Cx43 protomer explaining sequence identity of peptide inhibitors GAP26, P5, GAP27, P180–195 and Peptide5. The membrane-embedded residues, including four transmembrane (TM) helices are recognized using the “positioning proteins in membrane” (PPM) server by the “orientation of proteins in membrane” (OPM) database [31]. AA colour code: aromatic—green; hydrophobic—gray; basic—blue; acidic—red; polar neutral—orange; Cys—lemon. Figure was generated by Protter [32].
We began this study by identifying the contact area between the peptide inhibitors and GJ-coupled and free Cx36/Cx43 connexon models using an iterative blind docking approach that did not require existing experimental binding data [33]. By blind docking peptide sequence mimetics, we also explored the valid binding area. Calculations of the Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area (MM/GBSA) ΔGbind values were performed [34] on the 30 best scoring poses of the blind docking trials to fit CxHC peptide inhibitors and quinine. This method has proved to be a powerful tool to predict binding affinities and identify the correct binding poses for protein–peptide complexes [35].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Homology Modelling of Homomeric GJs Formed by Cx36 or Cx43
Homomeric GJ models built up exclusively by Cx36 or Cx43 protomers were constructed using the X-ray structure (2zw3) of homologous Cx26 GJ [17] as a template and the Swiss-Model server facility [36]. This initial PDB structure includes a whole GJ, explicitly chains A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L, shaping the extracellular (interface) and transmembrane (TM) regions, except the large intracellular region, due to its potentially disordered nature. Sequences of cytosolic residues, without experimentally determined coordinates in the crystal structure, were utilized to connect individual TM helices intracellularly using the built-in protocol of Swiss-Model server. Our model GJ structures enfold two hexameric HCs that are formed by apposed protomer chains A-B-C-D-E-F coupled with chains G-H-I-J-K-L. Since there are no significant insertions or deletions among Cx subtypes in the extracellular and TM regions, the built-in automated alignment of Swiss-Model was used for creating individual homology models. The modelling server puts on hydrogen atoms and arranges amino acid (AA) sidechains so that no clashes appear in the structure. Otherwise, the alpha carbon backbone of homomeric GJs formed by Cx36 or Cx43 resembles the Cx26 structure, reflecting the 6-fold symmetry. Due to these preparatory steps, homology models were ready for the separation of the A-F chains from the whole of GJ (A-L). Hence, homomeric Cx36GJ and Cx43GJ models were used to cut off solo connexons, i.e., Cx36HC or Cx43HC. To this end, G-L protomer chains of both Cx36 and Cx43 GJs were removed by means of Schrödinger’s Maestro module [37]. The remaining A-F chains, representing the GJ-coupled model of Cx36HC and Cx43HC, are characterized by their extracellular front (Figure 2A) and top (Figure 2B) views.
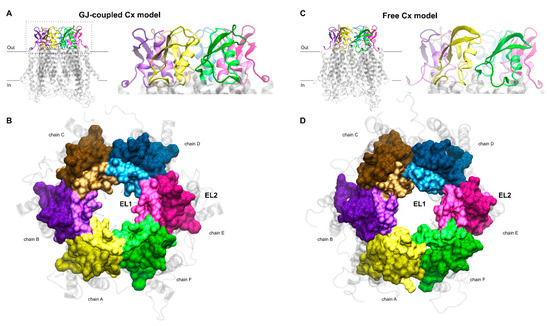
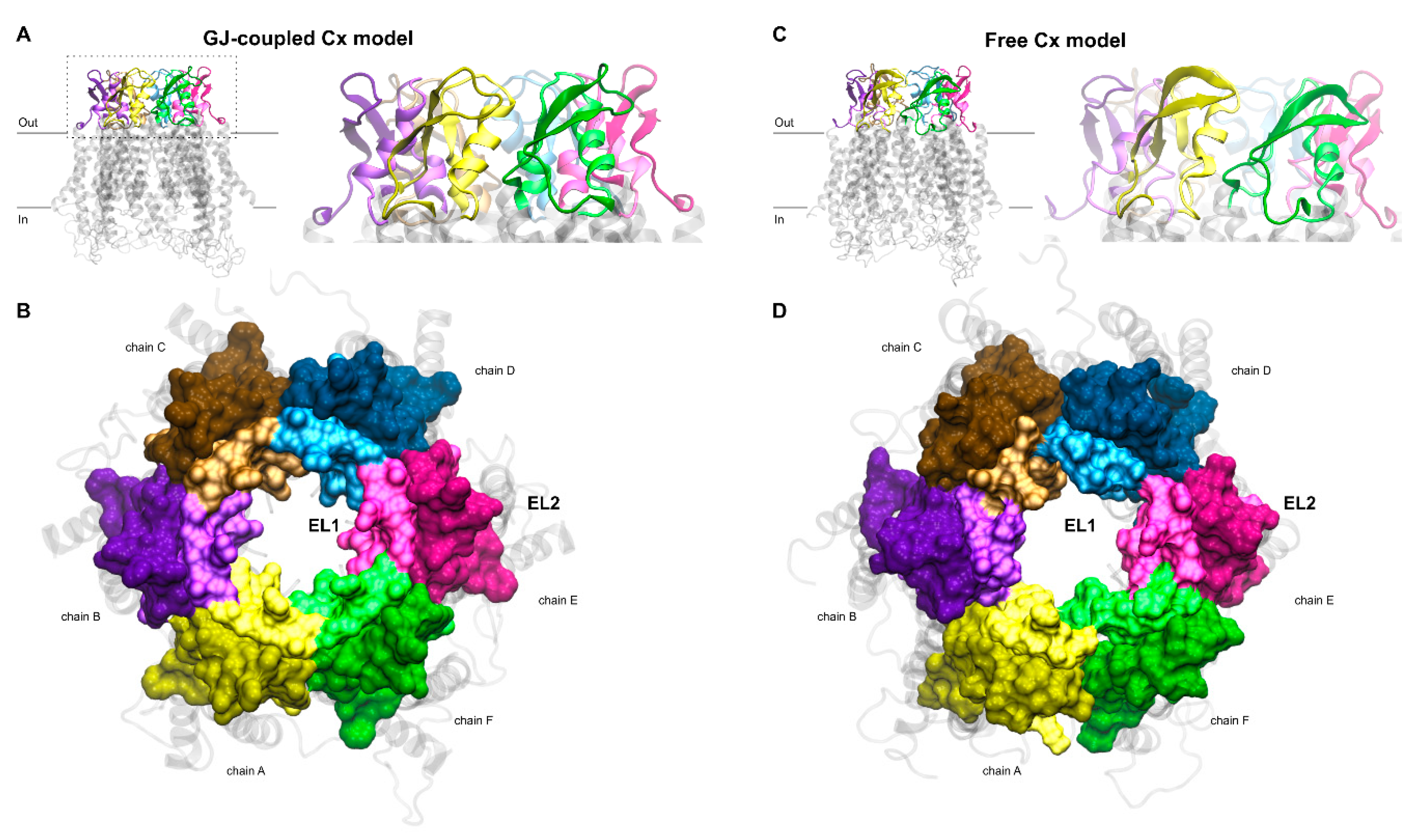
Figure 2.
(A,B) Gap junction (GJ)-coupled homology model of Cx43HC with extracellular loops shown in cartoon representation in front view (A) and surf representation in top view (B). For the latter, the z-axis of the coordinate system was set up to point towards the channel. EL1 and EL2 loops of each chain, depicted using the “positioning proteins in membrane” (PPM) server by the “orientation of proteins in membrane” (OPM) database [31] as detailed in Section 2.2, are colored by lighter and darker versions of the same color, respectively. Color codes for the different chains are as follows: yellow (A), violet (B), brown (C), blue (D), magenta (E), green (F). TM helices and intracellular segments are shown in transparent light gray cartoon representation. (C,D) Free connexon models were obtained from the homology model of GJ-coupled Cx43HC (A,B) by applying 50 ns molecular dynamics to the hemichannel. Views and color codes are the same as in A–B.
Since this structure represents the conformation of connexins in the full GJ form and peptides are expected to interact with the hemichannel form, we applied 50 ns molecular dynamics (MD) to allow the protein adopting the free hemichannel-like form not to resemble the prior presence of the apposed connexon (G-L chains). Molecular dynamics (MD) calculations were performed using the Desmond software package obtained from DE Shaw Research [37]. Cx36HC and Cx43HC transmembrane regions were defined according to Section 2.2. These HCs were then prepared via the Protein Preparation Wizard, and membranes were added using the System Builder menu by placing the membrane on the pre-aligned structure obtained from PPM. The model was relaxed before simulation and molecular dynamics was run at 300 K for a total simulation time of 50 ns at the supercomputer facility of the Governmental Agency for IT Development (KIFU), Hungary. The resulting free Cx36HC and Cx43HC model structures (Figure 2C,D) were used to dock mimetic peptides.
2.2. Determination of the Position of TM Regions
Successful prediction of inhibitor binding at extracellular CxHC areas necessitates the realistic arrangement of membrane bilayers. Explicitly, the claim concerns the genuine arrangement of extracellular loops EL1 and EL2 of CxHC subtypes, critically depending on the valid position of the membrane bilayer. Initially, the determination of the position of TM regions was focused on the primary sequence of the Cx43 protein. According to Delvaeye et al. [15], we also sampled the sequence-based prediction of TM regions based on Uniprot’s TM assignment as being 14–36, 77–99, 155–177, 209–231. These data were based on the prediction of the Transmembrane Protein Topology with a Hidden Markov Model (TMHMM) server [38], although the prediction of the first TM region of Cx43 was mistakenly identified as 14–36, and is currently under correction (Uniprot—personal communication). When TM regions were assigned according to 3D structures of our CxHC models, a significantly different TM1 region 21–46 was obtained, using the “positioning proteins in membrane” (PPM) server by the “orientation of proteins in membrane” (OPM) database [31]. To clarify the issue of real membrane boundaries determining extracellular EL1/EL2 domains, a series of sequence-based predictions of the TM regions from the CCTOP server [39] were weighed against the 3D structure-based predictions of the TM regions from the PPM server by the OPM database [31] in addition to an earlier TMDET server [40]. The procedure of the 3D structure-based assessments of the TM regions via the PPM and OPM approach seems to provide more detailed information about the membrane-embedded amino acids (AAs). This way, the membrane boundaries were determined, providing the consensus Cx36-membrane embedded amino acids (AAs) 3–9, 12, 23–49, 67, 71–95/94, 198, 200–225/198–225, 246–274/273. These AAs comprise secondary structures such as TM helices 23–49, 75–92/95, 200–220, 247–273. Similarly, the embedded AAs of Cx43 display comparable arrangement of AAs 3–9, 12/12–13, 21–46, 48, 71–94, 154–180, 202, 204–230, 232 shaping TM helices 21–46, 74–93, 156–176, 204–229/230.
TM domains, characterized by two shorter and two longer TM helices in succession together with the embedded residues near the N-terminal, are recognized. It is worth mentioning that structural motifs of CxHCs [2,17,41,42] (also this work) may reveal similar mechanistic clues such as the ball-and-chain inactivation in the K+ channel [43]. In fact, the ball-and-chain mechanism was further confirmed by the recently determined 3D structure of Cx26 [44].
2.3. Topological Arrangements of Cx43 EL1 and EL2 Sequences Identical with EL1-Mimetic GAP26 and EL2-Mimetic GAP27 or P180-195
The question arises as to whether the peptide mimetics designed to specifically inhibit Cx43HC coupling to Cx43GJ shall act along the GJ-interface surface. Figure 3 shows that AA residues of GAP26 (blue), GAP27 (red) and P180–195 (green) shape extracellular Cx43HC interfaces. Explicitly, the AAs corresponding to mimetic peptides GAP26, GAP27 and P180–195 are principally located at interfaces between inner EL1 and outer EL2 or at the peripheral boundary interface of EL2 (Figure 3). The arrangement illustrates that permutations of the vertical inter-loop interface joined with the horizontal loop-periphery interface are beyond the most exposed EL1 loop sequences, lying on the front of the CxHC coupling reaction. These findings conclusively suggest that the location of interfaces identified by matching AA sequences of designed peptide mimetics argue against the notion that mimetics could directly inhibit connexon coupling to GJ. Notably, EL1 sequences contiguous to channel forming TM helices take the shape of a vestibule by the side of HC entry.
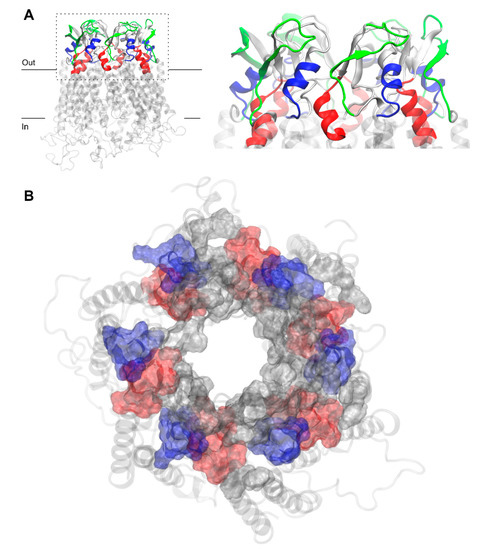
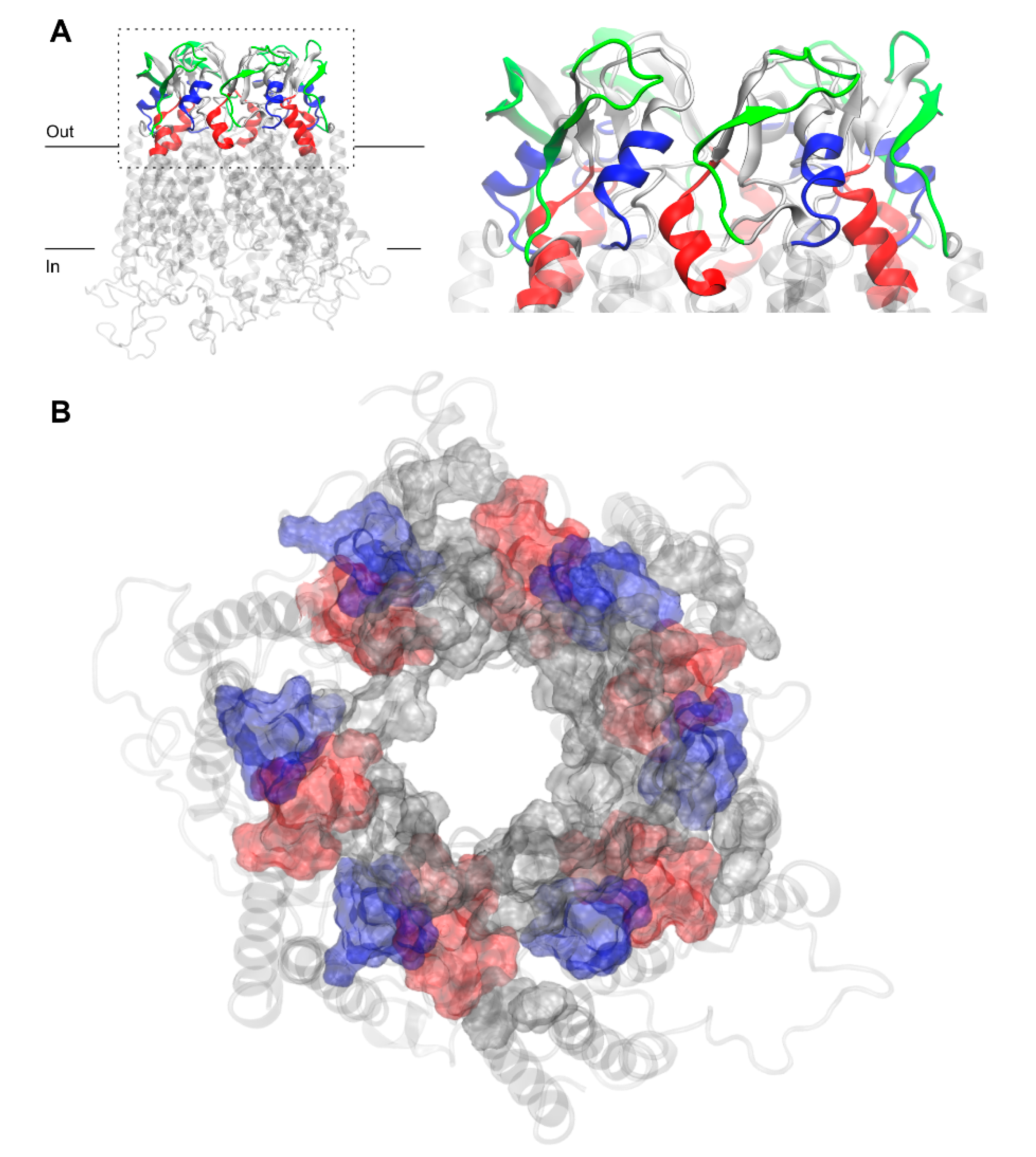
Figure 3.
Residues of free Cx43HC model corresponding to three commonly used peptide mimetic inhibitors derived from different EL1 and EL2 sequences, GAP26 (blue), GAP27 (red) and P180–195 (green) in front (A) and top (B) views with z-axis pointing towards the channel. P180–195 labeling was removed from (B) for clarity. Peptide residues are shown in surf representation on the extracellular region of Cx43. Other residues of EL1 and EL2, not corresponding to peptide mimetic inhibitors, are shown in gray surf. The membrane-embedded residues, including four TM helices recognized using the PPM server by OPM database [31], are shown in the transparent light gray cartoon.
2.4. Validation of Blind Docking Procedure via Optimization of MM/GBSA ΔGbind Values
Docking calculations were performed using the Schrödinger Small-Molecules Drug Discovery Suite 2020-1 software package [45]. The in silico calculations were performed based on the recommendations of Tubert-Brohman et al. [46] for peptide docking with increased accuracy. The Glide SP-Peptide mode was used for docking with subsequent MM/GBSA ΔGbind ranking calculations [34]. The structures of the connexins Cx36 and Cx43 were prepared using the Protein Preparation Wizard program, while the quinine structure was prepared using the Ligprep module. Two binding area definitions were used around the EL1–EL2 loop regions, and docking grids suitable for peptide docking were generated (Figure 4). The ligand diameter midpoint box sizes were increased from the default to values between 30 and 40 Angströms to cover the whole binding site region. During the Glide SP-Peptide mode docking calculations, sampling was enhanced by a factor of 2 and the expanded sampling option was used as well. Because of the increased volume of the binding site region, instead of the default number 1000, the 3000 best poses were used for energy minimization to assure an exhaustive search of the possible binding poses. The Schrödinger peptide docking protocol uses an initial Macromodel conformational search instead of the Confgen conformational search performed by the Ligand docking protocol. To model the peptide docking procedure, a Macromodel conformational search was performed on all ligand structures. The resulting conformers were clustered into five structurally different clusters. Based on visual inspection, only representative structures for the first three clusters were taken into account during docking calculations with the “Canonicalize input conformation” Glide option turned off. The MM/GBSA ΔGbind calculations were performed on the best 30 poses. The resulting poses from the two docking grids were combined and analyzed together.
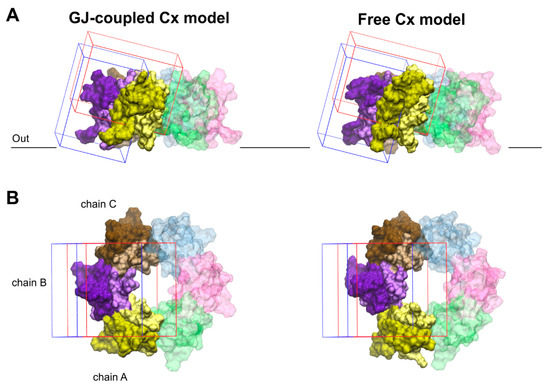
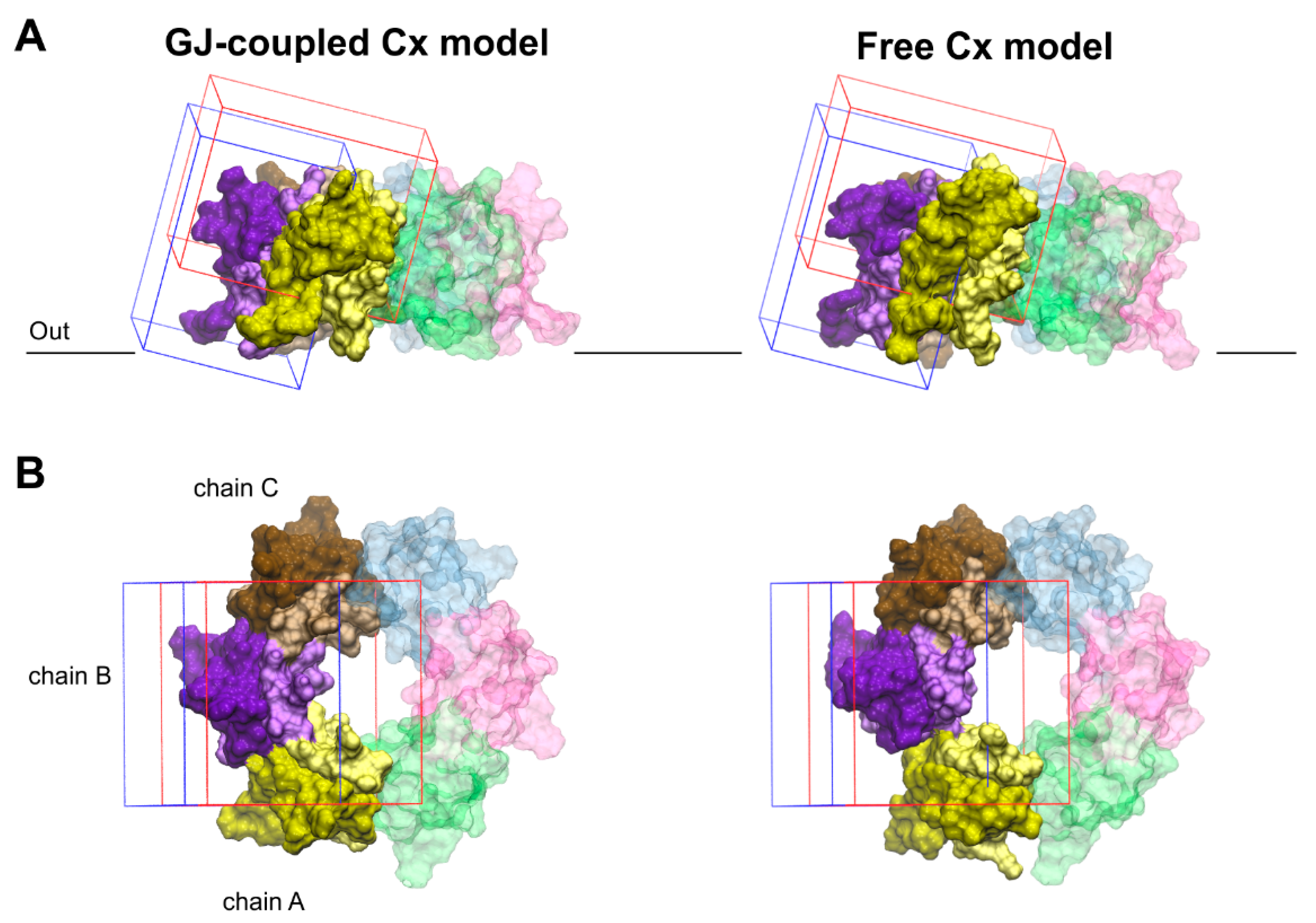
Figure 4.
Validation of blind docking search for the binding crevices of Cx inhibitors. Front (A) and top (B) views of boundaries limiting docking grids in the GJ-coupled (left) and the free (right) connexon models. The grid positioned at the water-facing, outer side of EL2 is shown in blue. The other grid, covering the EL1–EL2 interface as well as the top region of the pore-facing EL1 and water-facing EL2 loops, is shown in red. The significant overlap between the two grids allows cross-validation of docking results. Only EL1 and EL2 loops of Cx43 are displayed. EL1 and EL2 loops of each chain are colored by lighter and darker versions of the same color, respectively. Color codes for the different chains are as follows: yellow (A), violet (B), brown (C), blue (D), magenta (E), green (F). Chains not included in the docking grids (D–F) are displayed in transparent colors. For the position of the outer membrane, see legends to Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 and Section 2.2.
2.5. Mapping Binding Interactions of Inhibitory Peptide Mimetics and Quinine in Model CxHC Structures
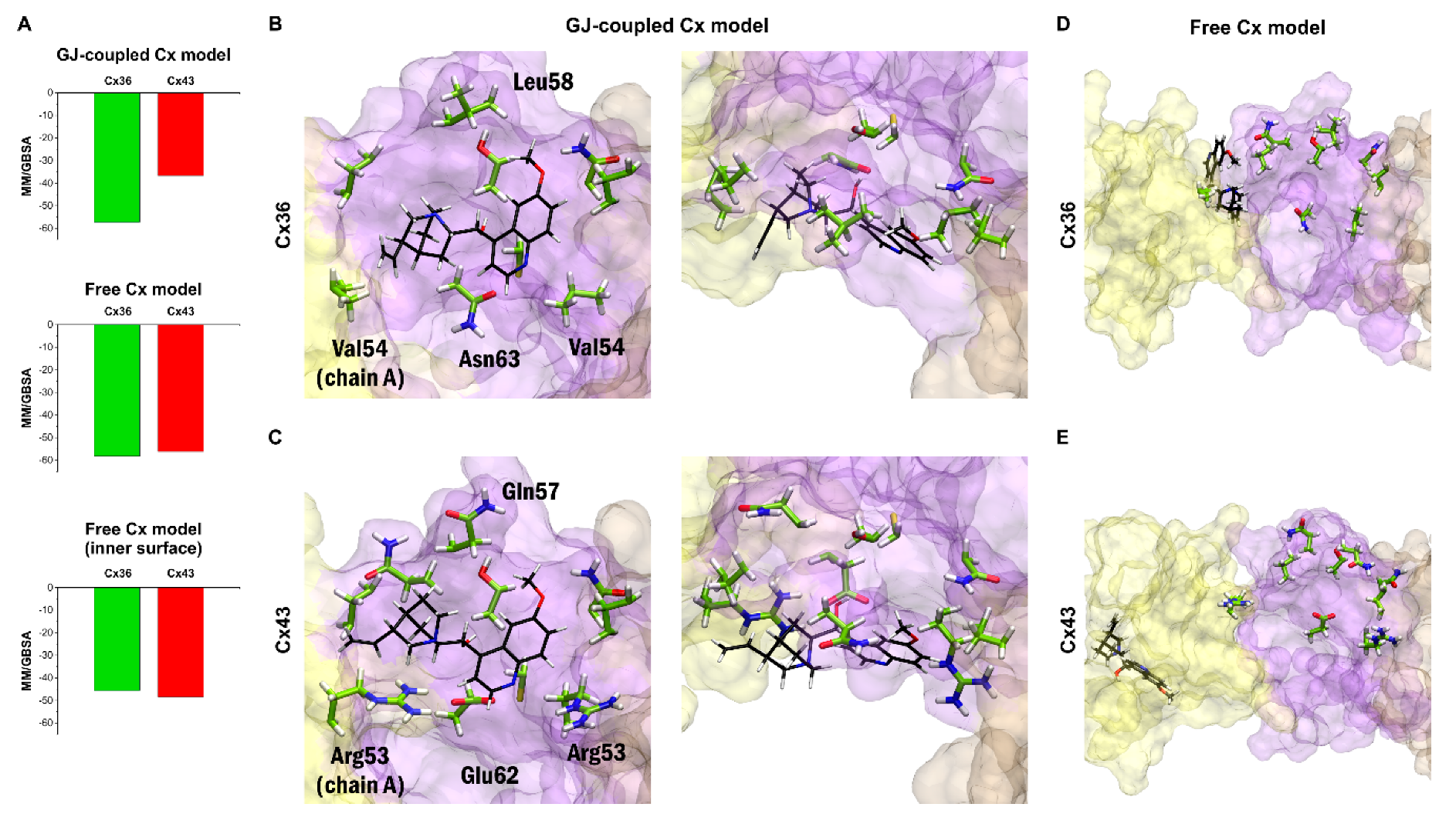
MM/GBSA ΔGbind values obtained for the best 30 blind docking runs (see previous paragraph) for quinine and each peptide mimetic inhibitors have been evaluated. The best MM/GBSA ΔGbind values obtained from docking quinine to Cx36 or Cx43 GJ-coupled models indicate that quinine prefers binding to Cx36 over Cx43 (Figure 5A–C). However, docking quinine into the free Cx36HC and Cx43HC structures did not show subtype-specificity (Figure 5A,D,E). In this structure, quinine was not able to dock onto the same surface identified in docking to the GJ-coupled Cx36 structure, and instead preferred docking to the outer surface of the extracellular region (Figure 5D,E). Filtering the docking results for poses on the inner surface still did not reveal any subtype-specific interaction (Figure 5A, bottom). These data suggest that quinine shall exert its subtype-specificity by entering the GJ from the cytosol. Altogether, the claimed subtype-specificity of neuronal-type Cx36GJ inhibitor quinine [6,27,28,29,30] has been substantiated by molecular modelling of binding at the GJ-coupled, but not in the free Cx36HC versus Cx43HC model structures (Figure 5).
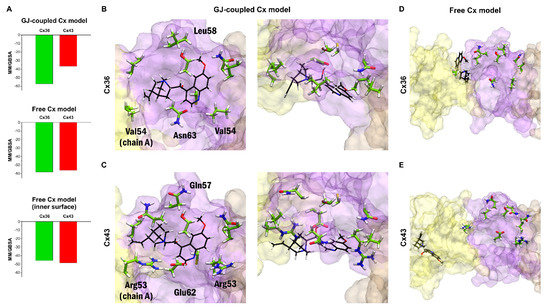
Figure 5.
Docking results confirm Cx36-specificity of quinine in the GJ-coupled connexin model. (A) Best MM/GBSA ΔGbind scores of quinine after docking to Cx36 or Cx43 in the GJ-coupled model (top), in the free connexin model (middle) and filtering the results of the free connexin model to the inner surface (bottom). (B,C) Best docking conformation of quinine in Cx36 (B) and Cx43 (C) GJ-coupled models in side view from inside the pore (left) and top view (right) based on MM/GBSA ΔGbind values. Quinine is shown in sticks (black). Residue sidechains in the vicinity (<4 Angström) of quinine are shown in stick (green). Residues not conserved between Cx36 and Cx43 are labeled. Only EL1 and EL2 loops of Cx36 and Cx43 A-C chains are displayed. Color codes for the different chains are as follows: yellow (A), violet (B), brown (C). For the definition of the position of the EL1 and EL2 see Section 2.2. (D,E) Best docking conformation of quinine in Cx36 (D) and Cx43 (E) free connexon models in side view from inside the pore. The same residues as in A–B are shown and labeled. Note that the best docking site identified in the GJ-coupled connexon structure is not available anymore in the free connexon model. Quinine is docked fully (Cx43) or partly (Cx36) to the outer surface of the connexon and is visible only due to the transparent representation of chain A.
Bulky quinuclidine and quinoline moieties present four stereo-centers and give the impression of stiffness and conformational restraint, leaving its conformation basically unaltered when fitting in the GJ-coupled Cx36HC vestibule. How does quinine get in the vestibule? We may consider steric interactions between non-conserved EL1 residues V54 (A chain) or L58 (B chain) and quinuclidine or quinoline moieties, respectively, forcing quinine to enter the vestibule. In that way, quinine may contact non-conserved N63 (B chain), and conserved C62 (B-chain) within 4 Angströms, enabling polar/redox interactions to occur (Figure 5B). By contrast, the matching non-conserved vestibular residues of Cx43 EL1 R53 (A chain), R53 (B chain), Q57 (B chain) and E62 (B chain) are not contacting quinine (Figure 5C).
The findings from docking quinine to the extracellular EL1–EL2 interface of GJ-coupled models of Cx36/Cx43 subtypes indicate that quinine preferentially binds to Cx36HC versus Cx43HC. By contrast, quinine does not distinguish between Cx36HC and Cx43HC when docked to the free CxHCs (Figure 5). The “quinine paradox” highlights that quinine subtype-specificity shall depend on conformations acquired during GJ formation from connexon subtypes. In addition, the GJ-coupled state should be open, allowing the diffusion of quinine from the cytosol to the extracellular vestibule.
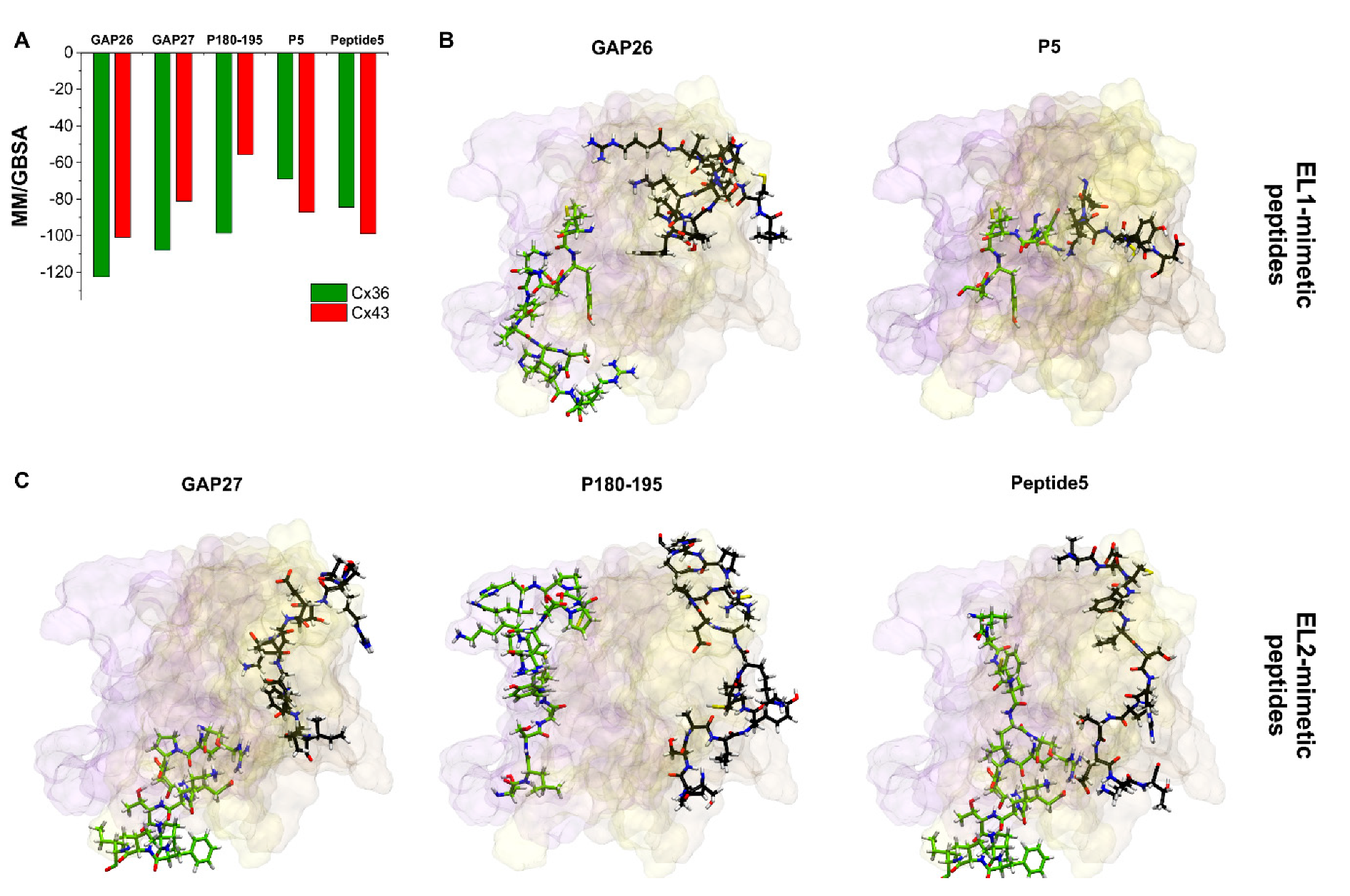
The best MM/GBSA ΔGbind scores of peptide mimetic inhibitors after docking to the free Cx36HC or Cx43HC models indicate that most peptides bind to both Cx36 and Cx43 subtypes (Figure 6A), although the Cx43 EL2 sequence mimetic P180–195 seems to be rather Cx36 subtype-specific. Importantly, however, binding surfaces of peptide mimetic inhibitors do not correspond to the sequence mimicked by the particular peptides (Figure 6B,C). In fact, the possible appearance of novel binding hotspots for Cx43 peptide mimetic inhibitors has already been predicted just by the reduced accessibility of the pertinent EL1–EL2 regions (see Section 2.3, Figure 3). Peptides mimicking the EL1 loop (GAP26, P5) or the EL2 loop (GAP27, P180–195, peptide 5) all bind at the inner EL1 surface and the EL1–EL2 interface (Figure 6B,C), irrespective of the derivation of their sequences. Indeed, the subtype specificity of these peptides is also challenged by the fact that the protein segments they mimic are widely shared by other Cx subtypes, as previously introduced. Consequently, these structural and docking data suggest that the rationale behind the design of peptidomimetics may not be valid for connexin gap junction proteins.
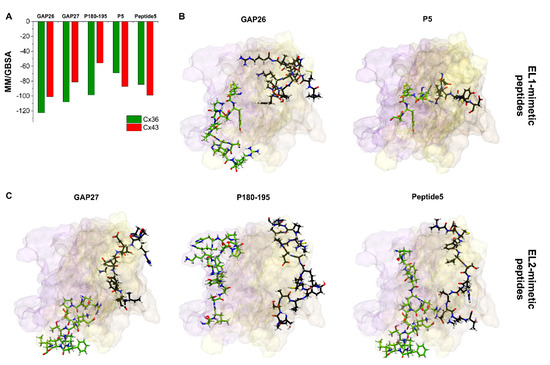
Figure 6.
Docking positions of peptide mimetic inhibitors do not correspond to the mimicked sequences. (A) Best MM/GBSA ΔGbind values of peptide mimetic inhibitors after docking to Cx36 or Cx43 free connexon models. (B,C) Best docking conformations of peptide inhibitors (black) and mimicked Cx43 sequence (green) are shown as sticks from front view in the free Cx43HC structure. Only EL1 and EL2 loops of Cx43 A–C chains are displayed. Color codes for the different chains are as follows: yellow (A), violet (B), brown (C). For the definition of the position of the EL1 and EL2 see Section 2.2.
Our present understanding is that the particular reduction in the extracellular conformational freedom of connexons during GJ formation increases the connexon subtype-specificity of quinine. The principle predicts the “quinine paradox” (see above) but does not explain the lack of subtype-specificity in the case of the EL1/EL2 sequence mimetic peptides. Checking up the position of EL1/EL2 sequences mimicked by peptide mimetics reveals, however, that the GAP26/GAP27 matching segments are buried in the connexon structure both in the GJ-coupled and the free Cx43HC (Figure 3). Of note, the P180–195 matching EL2 segment comprising three basic (K, R, H) and one acidic (D) AAs (cf. Figure 1) may lead to a partially protonated peripheral surface at physiological pH, explaining the relatively weak P180–195 interaction by the Cx43HC setting (Figure 6A). Instead, peptide mimetics seem docking to more variable EL1 surface (Figure 6), thus gaining flexible contact areas for binding. Peptide binding to these surface hotspots may be size-dependent but not particularly subtype structure-specific.
3. Conclusions
The validation of connexon binding interactions suggests that the design principle of peptide mimetics based on selected primary EL1/EL2 sequences may fail in predicting the mechanism of inhibitory action. Instead, we put forward the new rationale of modelling 3D binding hotspots. Of note, quinone moieties of antimalarial therapeutics quinine and hydroxychloroquine may substantiate a search for medications to treat COVID-19 via furthering the awareness of a possible relationship between connexons and COVID-19. To this end, future studies should be set up for both in silico molecular docking of additional antimalarial drugs to Cx36HC connexon subtype and testing hits against COVID-19.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Á.S., L.H., and J.K.; modelling, Á.S.; blind docking, C.M.; mapping of binding surface, L.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K. and L.H.; supervision, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants of the Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office VEKOP-2.1.1-15-2016-00156, OTKA K124558 and OTKA K115698.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Nielsen, M.S.; Axelsen, L.N.; Sorgen, P.L.; Verma, V.; Delmar, M.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H. Gap Junctions. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1981–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.; Yue, B.; Aoyama, H. Crucial Motifs and Residues in the Extracellular Loops Influence the Formation and Specificity of Connexin Docking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Grima, R. Single-Cell Variability in Multicellular Organisms. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, D.W.; Lampe, P.D. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Connexins. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.E.; Kwak, B.R. An Overview of the Focus of the International Gap Junction Conference 2017 and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Ceja, L.; Salazar-Sánchez, J.C.; Ortega-Ibarra, J.; Morales-Villagrán, A. Connexins-Based Hemichannels/Channels and Their Relationship with Inflammation, Seizures and Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G.; Werner, R.; Levine, E.; Rabadan-Diehl, C. Mutational Analysis of Gap Junction Formation. Biophys. J. 1992, 62, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, A.; Clements, D.K.; Parikh, S.; Evans, W.H.; DeHaan, R.L. Specific Motifs in the External Loops of Connexin Proteins Can Determine Gap Junction Formation between Chick Heart Myocytes. J. Physiol. 1995, 488, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, E.C.; Berthoud, V.M. The Family of Connexin Genes. In Connexins: A Guide; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone, R.; White, T.W.; Paul, D.L. Expression of Chimeric Connexins Reveals New Properties of the Formation and Gating Behavior of Gap Junction Channels. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.L. Emerging Issues of Connexin Channels: Biophysics Fills the Gap. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2001, 34, 325–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard Evans, W.; Leybaert, L. Mimetic Peptides as Blockers of Connexin Channel-Facilitated Intercellular Communication. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2007, 14, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, F.; Oshima, A.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Scheuring, S. Two-Dimensional Kinetics of Inter-Connexin Interactions from Single-Molecule Force Spectroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 412, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leybaert, L.; Lampe, P.D.; Dhein, S.; Kwak, B.R.; Ferdinandy, P.; Beyer, E.C.; Laird, D.W.; Naus, C.C.; Green, C.R.; Schulz, R. Connexins in Cardiovascular and Neurovascular Health and Disease: Pharmacological Implications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 396–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvaeye, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Bultynck, G.; Leybaert, L.; Krysko, D.V. Therapeutic Targeting of Connexin Channels: New Views and Challenges. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 1036–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, G. Gap Junction-Mimetic Peptides Do Work, but in Unexpected Ways. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2007, 14, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Suga, M.; Yamashita, E.; Oshima, A.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of the Connexin 26 Gap Junction Channel at 3.5 A Resolution. Nature 2009, 458, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermietzel, R.; Meier, C. Gap Junction Expression in Brain Tissues with Focus on Development. In Gap Junctions in Development and Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 83–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kékesi, O.; Ioja, E.; Szabó, Z.; Kardos, J.; Héja, L. Recurrent Seizure-like Events Are Associated with Coupled Astroglial Synchronization. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Vincze, R.; Péter, M.; Szabó, Z.; Kardos, J.; Héja, L.; Kovács, Z. Connexin 43 Differentially Regulates Epileptiform Activity in Models of Convulsive and Non-Convulsive Epilepsies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, Z.; Héja, L.; Szalay, G.; Kékesi, O.; Füredi, A.; Szebényi, K.; Dobolyi, Á.; Orbán, T.I.; Kolacsek, O.; Tompa, T.; et al. Extensive Astrocyte Synchronization Advances Neuronal Coupling in Slow Wave Activity in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6018. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, B.R.; Jongsma, H.J. Selective Inhibition of Gap Junction Channel Activity by Synthetic Peptides. J. Physiol. 1999, 516, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.E.M.; Wall, C.; Griffith, T.M. Effects of Connexin-Mimetic Peptides on Gap Junction Functionality and Connexin Expression in Cultured Vascular Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, M.; Locovei, S.; Keane, R.W.; Dahl, G. Modulation of Membrane Channel Currents by Gap Junction Protein Mimetic Peptides: Size Matters. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 293, C1112–C1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Carroll, S.J.; Alkadhi, M.; Nicholson, L.F.B.; Green, C.R. Connexin43 Mimetic Peptides Reduce Swelling, Astrogliosis, and Neuronal Cell Death after Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2008, 15, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Griffin, J.M.; Harris, P.W.R.; Chan, S.H.C.; Nicholson, L.F.B.; Brimble, M.A.; O’Carroll, S.J.; Green, C.R. Characterizing the Mode of Action of Extracellular Connexin43 Channel Blocking Mimetic Peptides in an in Vitro Ischemia Injury Model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, M.; Hopperstad, M.G.; Spray, D.C. Quinine Blocks Specific Gap Junction Channel Subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10942–10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajda, Z.; Szupera, Z.; Blazsó, G.; Szente, M. Quinine, a Blocker of Neuronal Cx36 Channels, Suppresses Seizure Activity in Rat Neocortex in Vivo. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Ceja, L.; Ventura-Mejía, C. Differential Effects of Trimethylamine and Quinine on Seizures Induced by 4-Aminopyridine Administration in the Entorhinal Cortex of Vigilant Rats. Seizure 2010, 19, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Pérez, J.; Manjarrez-Marmolejo, J.; Rodríguez-Balderas, C.; Castro, N.; Ballesteros-Zebadua, P. Quinine and Carbenoxolone Enhance the Anticonvulsant Activity of Some Classical Antiepileptic Drugs. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM Database and PPM Web Server: Resources for Positioning of Proteins in Membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasits, U.; Ahrens, C.H.; Müller, S.; Wollscheid, B. Protter: Interactive Protein Feature Visualization and Integration with Experimental Proteomic Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciemny, M.; Kurcinski, M.; Kamel, K.; Kolinski, A.; Alam, N.; Schueler-Furman, O.; Kmiecik, S. Protein–Peptide Docking: Opportunities and Challenges. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods to Estimate Ligand-Binding Affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, G.; Wang, E.; Chen, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Hou, T. Assessing the Performance of MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods. 9. Prediction Reliability of Binding Affinities and Binding Poses for Protein-Peptide Complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 10135–10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C.; Schwede, T. Automated Comparative Protein Structure Modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: A Historical Perspective. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, S162–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Klepeis, J.L.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; et al. Scalable Algorithms for Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Commodity Clusters. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; Von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology with a Hidden Markov Model: Application to Complete Genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, L.; Reményi, I.; Tusnády, G.E. CCTOP: A Consensus Constrained TOPology Prediction Web Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W408–W412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusnády, G.E.; Dosztányi, Z.; Simon, I. TMDET: Web Server for Detecting Transmembrane Regions of Proteins by Using Their 3D Coordinates. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1276–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, W.; Ramachandran, J.; Alsamarah, A.; Luo, Y.; Harris, A.L.; Contreras, J.E. Mechanism of Gating by Calcium in Connexin Hemichannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7986–E7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, P.N.T.; Ennis, P.D. Calcium-Mediated Changes in Gap Junction Structure: Evidence from the Low Angle x-Ray Pattern. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 97, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Sukomon, N.; Flood, E.; Rheinberger, J.; Allen, T.W.; Nimigean, C.M. Ball-and-Chain Inactivation in a Calcium-Gated Potassium Channel. Nature 2020, 580, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.K.; Jagielnicki, M.; McIntire, W.E.; Purdy, M.D.; Dharmarajan, V.; Griffin, P.R.; Yeager, M. A Steric “Ball-and-Chain” Mechanism for PH-Mediated Regulation of Gap Junction Channels. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Small-Molecules Drug Discovery Suite 2020-1; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tubert-Brohman, I.; Sherman, W.; Repasky, M.; Beuming, T. Improved Docking of Polypeptides with Glide. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).