Appropriate Buffers for Studying the Bioinorganic Chemistry of Silver(I) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
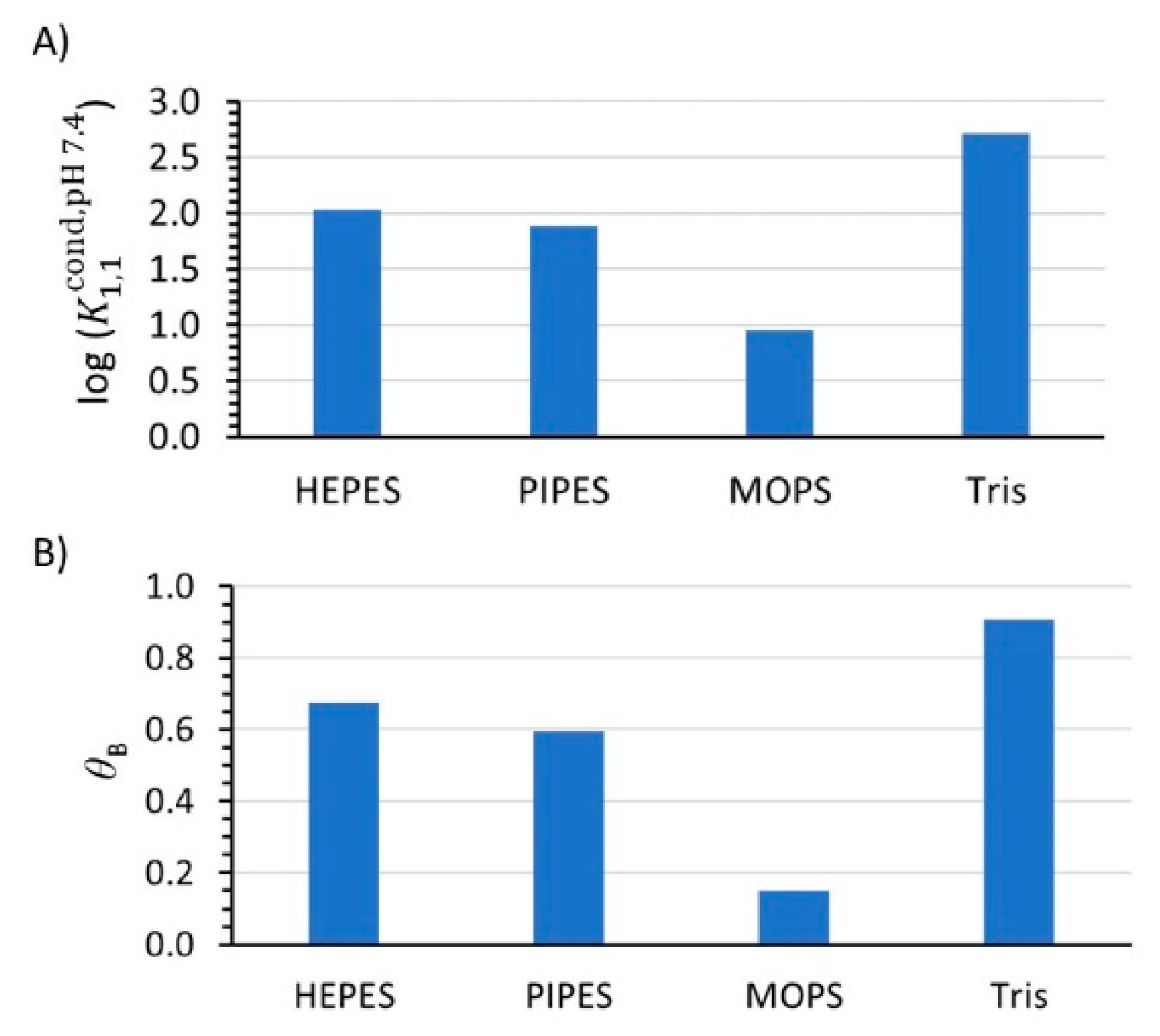
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Used to Fit Potentiometric Titrations
Appendix B. Calculation of Apparent Binding Constants of a Ligand Binding Silver
Appendix C. Calculation of Conditional Stability Constants at a Certain pH and Calculation of Percentage of Metal Bound to the Buffer θB
References
- Good, N.E.; Winget, G.D.; Winter, W.; Connolly, T.N.; Izawa, S.; Singh, R.M.M. Hydrogen Ion Buffers for Biological Research*. Biochemistry 1966, 5, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, W.J.; Braunschweiger, K.I.; Braunschweiger, W.R.; Smith, J.R.; McCormick, J.J.; Wasmann, C.C.; Jarvis, N.P.; Bell, D.H.; Good, N.E. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Anal. Biochem. 1980, 104, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.S. Buffers for enzymes. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 104, pp. 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, J.K.; Chasteen, N.D.; Harris, D.C. Radicals from “Good’s” buffers. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 173, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, M.; Bose, S.J.P.R. Inhibition of photosystem II activity by Cu++ ion. Choice of buffer and reagent is critical. Photosynth. Res. 1990, 23, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagira, K.; Hayashida, M.; Shiga, M.; Sasamoto, K.; Kina, K.; Osada, K.; Sugahara, T.; Murakami, H. Effects of organic pH buffers on a cell growth and an antibody production of human-human hybridoma HB4C5 cells in a serum-free culture. Cytotechnology 1995, 17, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Koerner, M.M.; Palacio, L.A.; Wright, J.W.; Schweitzer, K.S.; Ray, B.D.; Petrache, H.I. Electrodynamics of lipid membrane interactions in the presence of zwitterionic buffers. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRee, D.E.; Jensen, G.M.; Fitzgerald, M.M.; Siegel, H.A.; Goodin, D.B. Construction of a bisaquo heme enzyme and binding by exogenous ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12847–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, D. Replacement of the Proximal Ligand of Sperm Whale Myoglobin with Free Imidazole in the Mutant His-93.fwdarw.Gly. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 6546–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J.; Wilcox, S.K.; Ai, J.; Moënne-Loccoz, P.; Loehr, T.M.; Goodin, D.B. Replacement of the Axial Histidine Ligand with Imidazole in Cytochrome c Peroxidase. 2. Effects on Heme Coordination and Function. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.M.H.; Pinto, I.S.S.; Soares, E.V.; Soares, H.M.V.M. (Un)suitability of the use of pH buffers in biological, biochemical and environmental studies and their interaction with metal ions—A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30989–31003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, M.T.S.D.; Azenha, M.A.G.O.; Lage, O.M. Electrochemical Evidence of Surfactant Activity of the Hepes pH Buffer Which May Have Implications on Trace Metal Availability to Culturesin Vitro. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 241, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mash, H.E.; Chin, Y.-P.; Sigg, L.; Hari, R.; Xue, H. Complexation of Copper by Zwitterionic Aminosulfonic (Good) Buffers. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, M.; Bal, W. Cu(II) complexation by “non-coordinating” N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES buffer). J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawisza, I.; Rózga, M.; Poznański, J.; Bal, W. Cu(II) complex formation by ACES buffer. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 129, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.E.; Häring, U.K.; Tribolet, R.; Sigel, H. Metal Ion/Buffer Interactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 1979, 94, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, K.H.; Abel, T.H.J.; Polanyi, P.E.; Wenk, P.K.; Fischer, B.E.; Sigel, H. Metal Ion/Buffer Interactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980, 107, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabert, V.; Hologne, M.; Sénèque, O.; Crochet, A.; Walker, O.; Fromm, K.M. Model peptide studies of Ag+ binding sites from the silver resistance protein SilE. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6105–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabert, V.; Hologne, M.; Sénèque, O.; Walker, O.; Fromm, K.M. Alpha-helical folding of SilE models upon Ag(His)(Met) motif formation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10419–10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilinovich, S.M.; Panzner, M.J.; Youngs, W.J.; Leeper, T.C. Poly[[{[mu]3-2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonato}silver(I)] trihydrate]. Acta Crystallogr. E 2011, 67, m1178–m1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.N.; Kishore, N.; Lennen, R.M. Thermodynamic Quantities for the Ionization Reactions of Buffers. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2002, 31, 231–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, H.; Takahashi, K. Enthalpy and heat capacity changes for the proton dissociation of various buffer components in 0.1 M potassium chloride. Proteins 1998, 33, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Itoh, T. Reaction volume of protonic ionization for buffering agents. Prediction of pressure dependence of pH and pOH. J. Solut. Chem. 1987, 16, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.G.; Pinching, G.D. Dissociation Constants of Weak Bases from Electromotive-Force Measurements of Solutions of Partially Hydrolyzed Salts. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1949, 43, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stability Constants Available on Joint Expert Speciation System. Available online: http://jess.murdoch.edu.au/rawrxnbiny.shtml (accessed on 22 March 2020).
- Smith, R.M.; Martell, A.E. Critical Stability Constants; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daofeng, S.; Rong, C.; Yucang, L.; Maochun, H. Self-Assembly of A Novel Sulphonate Silver(I) Complex. Chem. Lett. 2002, 31, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ma, J.-F.; Zhang, W.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.; Ping, G.-J.; Su, Z.-M. Metal–Organic Frameworks Containing Flexible Bis(benzimidazole) Ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Cao, R.; Bi, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Hong, M. Self-Assembly of Novel Silver Polymers Based on Flexible Sulfonate Ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 2004, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Our own attempts to crystallize complexes of Tris, MES or MOPS with silver were unsuccessful mostly due to the reduction of silver.
- Kumar, R.; Obrai, S.; Kaur, A.; Hundal, M.S.; Meehnian, H.; Jana, A.K. Synthesis, crystal structure investigation, DFT analyses and antimicrobial studies of silver(i) complexes with N,N,N′,N″-tetrakis(2-hydroxyethyl/propyl) ethylenediamine and tris(2-hydroxyethyl)amine. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehlman, R.J.; Verhoek, F.H. The Basic Strengths of Amines as Measured by the Stabilities of Their Complexes with Silver Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.P.; Grzybowski, A.K. 222. The stability constants of the silver complexes of some aliphatic amines and amino-acids. J. Chem. Soc. 1959, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poucke, L.C.V.; Eeckhaut, Z. Stability Constants of the Ag(I) Complexes of Some Amino-Alcohols. Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1972, 81, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepari, S.; Carunchio, V.; Castellano, P.; Messina, A. Protonation and silver(I) complex-formation equilibria of some amino-alcohols. Talanta 1997, 44, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, L.D. Stability Constants of Metal-ion Complexes. Part B. Organic Ligands. IUPAC Chem. Data Set No. 22; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Houngbossa, K.; Enea, G.B.E.O. Étude thermodynamique de la complexation de ‘l’argent par la pipérazine et quelques-uns de ses dérivés en milieu aqueux. Thermochim. Acta 1973, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrzykowski, D.; Pilarski, B.; Jacewicz, D.; Chmurzyński, L. Investigation of metal–buffer interactions using isothermal titration calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
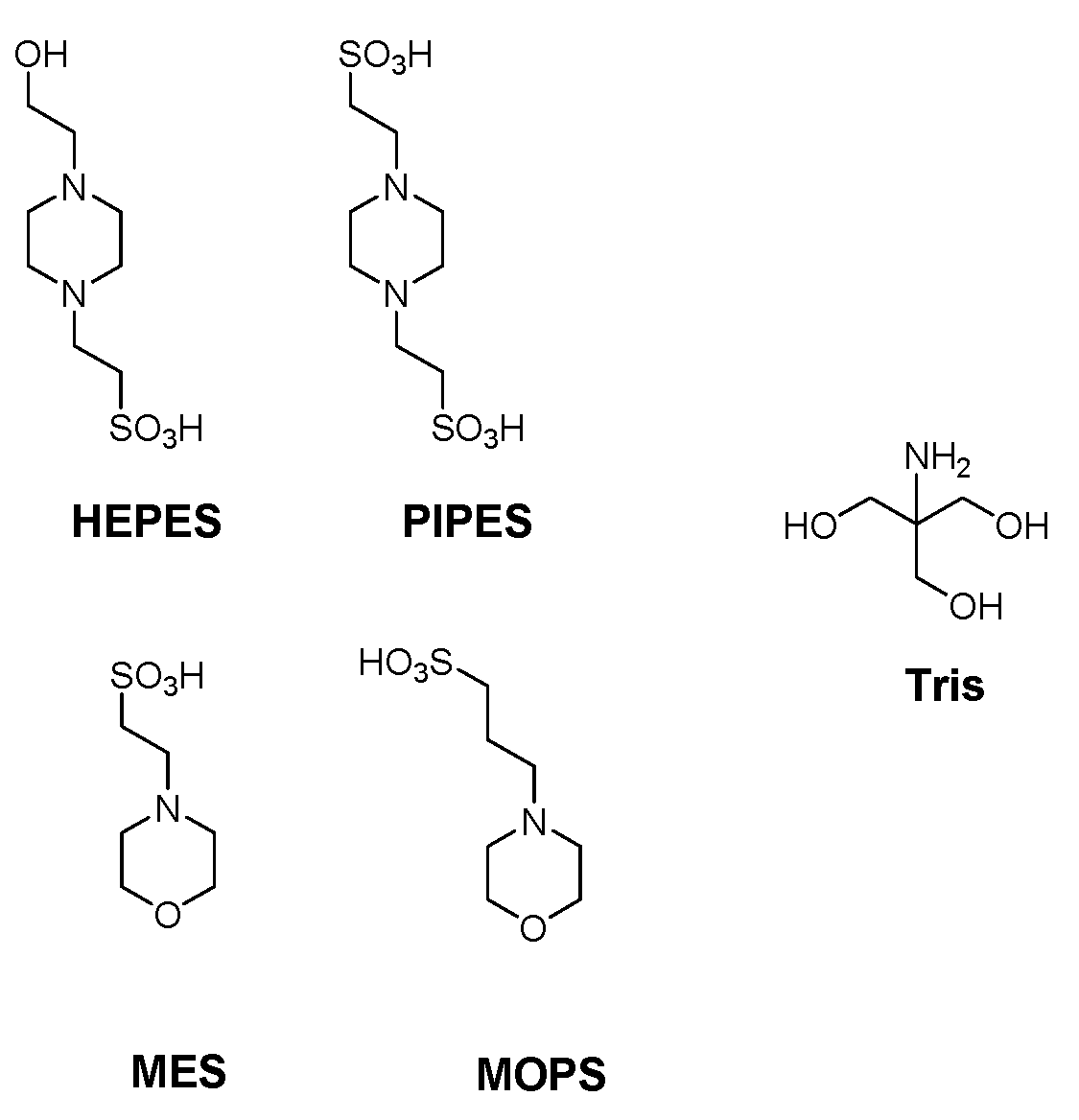
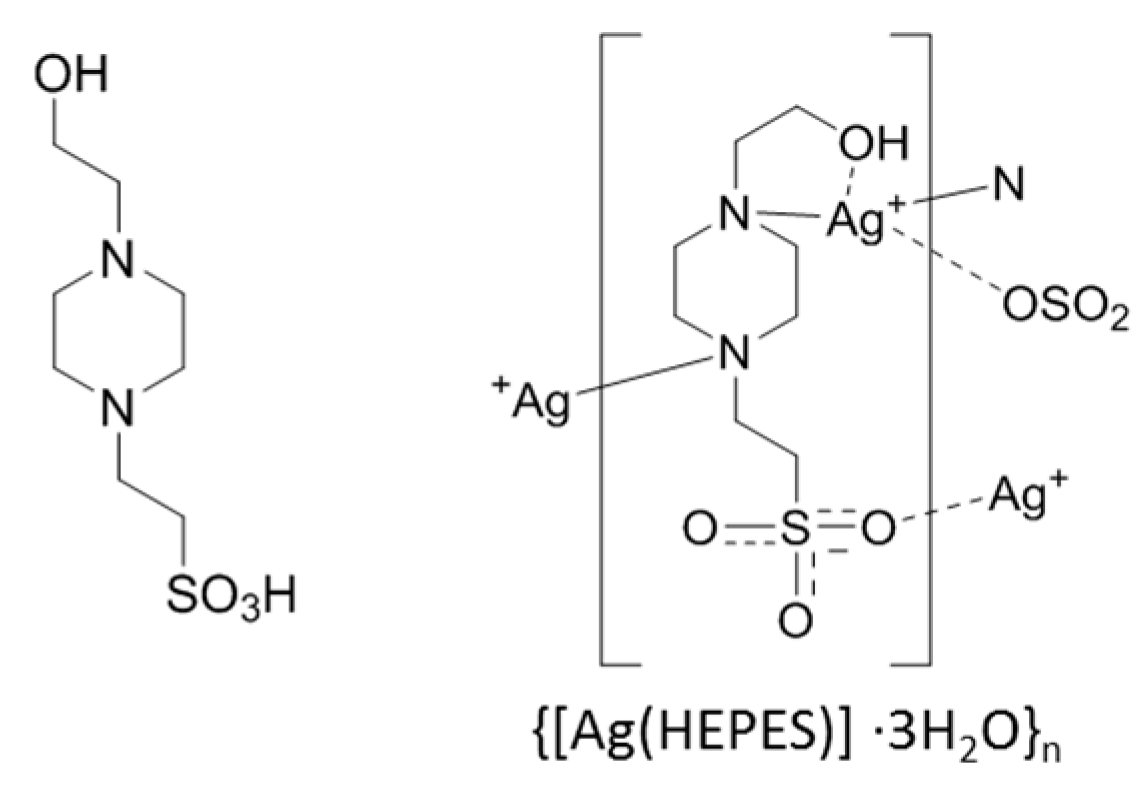
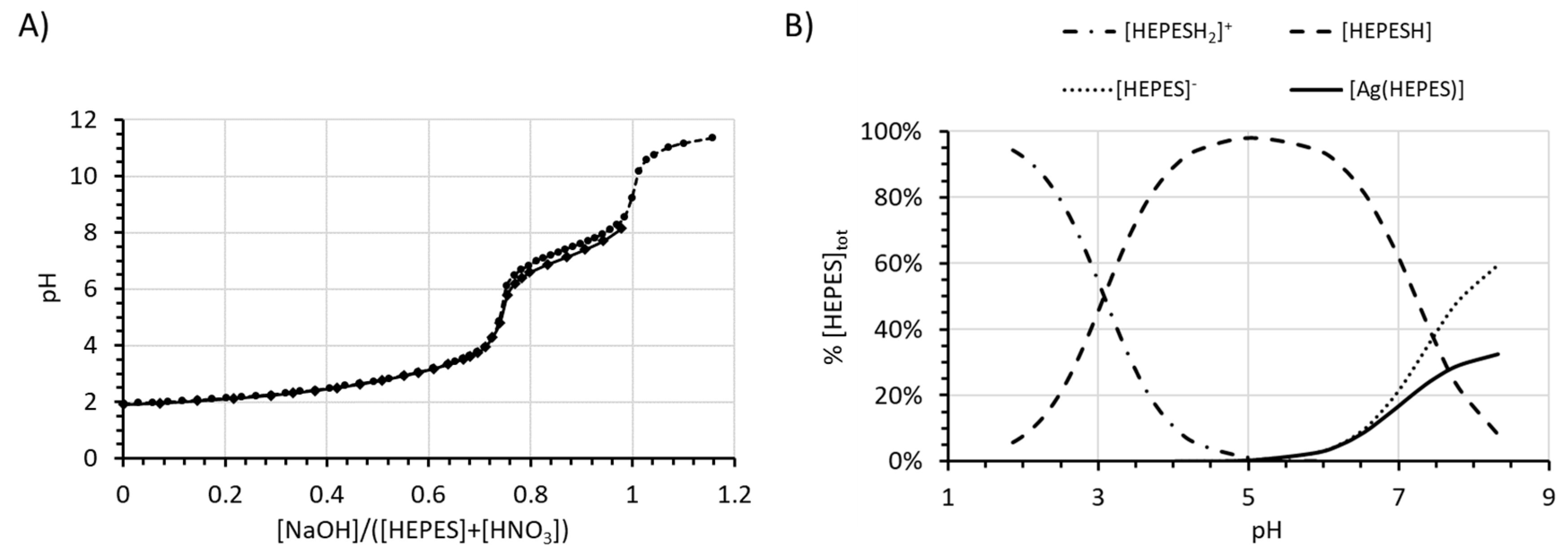
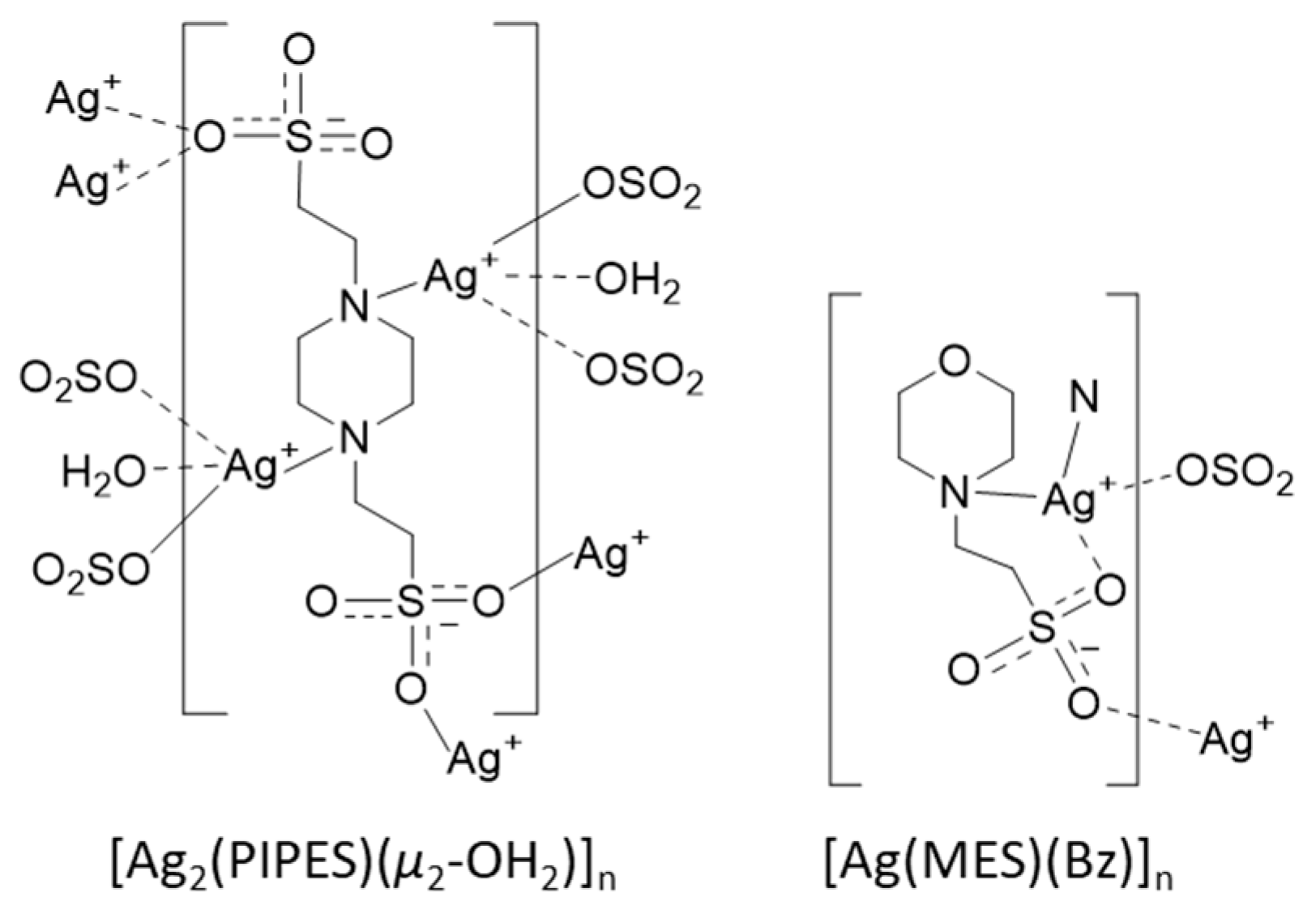
| Buffer | pKan (23 °C) a | pKan Literature (25 °C) | log() (23 °C) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEPES | 7.46(1), 3.07(2) | 7.45(1) [23], 3.0(1) [24] | 2.36(2) |
| PIPES | 6.65(1), 2.54(2), 1.3(4) | 6.71(1) [23] | 1.95(3) |
| MOPS | 7.03(1) | 7.09(1) [23] | 1.1(1) |
| MES | 6.00(2) | 6.07(1) [23] | 1.69(8) |
| Tris | 8.24(1) | 8.08(1) [25] | 3.1(2), 6.5 (1) |
| log ( ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| log() | 6.4 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 |
| [L] = 10 μM, [B] = 0.4 mM | 6.38 (−0.3%) | 3.98 (−0.4%) | 2.98 (−0.6%) | 1.98 (−0.9%) |
| [L] = 100 μM, [B] = 4 mM | 6.25 (−2.3%) | 3.85 (−3.7%) | 2.85 (−4.9%) | 1.85 (−7.3%) |
| [L] = 500 μM, [B] = 20 mM | 5.92 (−7.5%) | 3.52 (−11.9%) | 2.52 (−15.9%) | 1.52 (−23.8%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babel, L.; Bonnet-Gómez, S.; Fromm, K.M. Appropriate Buffers for Studying the Bioinorganic Chemistry of Silver(I). Chemistry 2020, 2, 193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2010012
Babel L, Bonnet-Gómez S, Fromm KM. Appropriate Buffers for Studying the Bioinorganic Chemistry of Silver(I). Chemistry. 2020; 2(1):193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabel, Lucille, Soledad Bonnet-Gómez, and Katharina M. Fromm. 2020. "Appropriate Buffers for Studying the Bioinorganic Chemistry of Silver(I)" Chemistry 2, no. 1: 193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2010012
APA StyleBabel, L., Bonnet-Gómez, S., & Fromm, K. M. (2020). Appropriate Buffers for Studying the Bioinorganic Chemistry of Silver(I). Chemistry, 2(1), 193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2010012