Abstract
Theranostic nanoparticles integrate diagnostic and therapeutic potential, representing a promising approach in precision medicine. Accordingly, numerous inventions have been patented to protect novel formulations and methods. This review examines the evolution of patented theranostic nanoparticles, focusing on organic nanosystems, particularly polymeric and lipid nanoparticles, to assess their development, technological advances, and patentability. A scoping review approach was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines in the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and European Patent Office (EPO) database. The search included patents filed within the last ten years (2014–2024) that specifically claimed organic and/or hybrid theranostic nanoparticles. Data extraction focused on nanoparticle composition, synthesis methods, functionalization strategies, and theranostic applications. The search identified 130 patents, of which 13 met the inclusion criteria. These patents were primarily filed by inventors from the United States, Canada, Great Britain, Italy, and China. Polymeric nanoparticles were frequently engineered for targeted drug delivery and imaging, utilizing hyperbranched polyesters, sulfated polymers, or chitosan-based formulations. Lipid nanoparticles were often hybridized with inorganic nanomaterials or magnetic nanostructures to enhance their theranostic potential. While most patents detailed synthesis methods and physicochemical characterizations, only a few provided comprehensive preclinical validation, limiting their demonstrated efficacy. The analysis of recent patents highlights significant advances in the design and application of theranostic nanoparticles. However, a notable gap remains in validating these nanosystems for clinical translation. Future efforts should emphasize robust preclinical data, including in vitro and in vivo assessments, to enhance patent quality and applicability to substantiate the claimed theranostic capabilities.
1. Introduction
Theranostic nanoparticles represent a groundbreaking convergence of diagnostics and therapy, offering a multifunctional approach to disease management at the nanoscale. These systems integrate diagnostic imaging with targeted drug delivery, enabling real-time monitoring of therapeutic responses and enhancing treatment precision [1]. By leveraging nanostructures, theranostic platforms facilitate early detection, localized therapy, and continuous tracking of disease progression, contributing to a more personalized and effective medical strategy [2].
A wide range of nanostructures has been explored for theranostic applications, including micellar systems, lipid-based nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, inorganic nanocarriers, hybrid nanoparticles, and carbon-based nanomaterials [3,4,5,6]. These nanotechnological drug delivery systems allow for precise surface modifications and material engineering to enhance biocompatibility, control drug release kinetics, minimize systemic toxicity, and improve therapeutic efficacy [7]. Furthermore, theranostic nanoparticles are promising when it comes to addressing challenges such as multidrug resistance and off-target effects, particularly in oncology and cardiovascular medicine [8]. Notably, they offer novel alternatives for mitigating cardiotoxicity induced by various therapeutic agents [9].
Despite their therapeutic potential, the successful translation of theranostic nanoparticles into clinical applications is often hindered by challenges related to large-scale production, regulatory approval, and long-term safety assessments [10]. Moreover, the high complexity of these nanosystems requires continuous technological advancements to optimize stability, bioavailability, and targeting efficiency [11]. As research in this field progresses, the development of new fabrication techniques, surface functionalization strategies, and multimodal imaging capabilities further expands the possibilities for theranostics in precision medicine. Understanding these innovations through patent analysis allows for a deeper insight into the competitive landscape and the key technological breakthroughs shaping the future of nanomedicine.
Given the rapid growth of nanotheranostic technologies, patent filings have become essential for tracking technological advancements, protecting intellectual property, and driving commercial innovation. The increasing number of patents in this field reflects strong interest from academic institutions and pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies in developing cutting-edge nanoplatforms. By systematically analyzing these patents, it is possible to identify emerging trends and technological gaps that could guide future research and development efforts. This study aims to map patented inventions focusing on organic nanoparticles—particularly polymeric and lipid-based systems—designed for theranostic applications. By analyzing patent claims, formulation methodologies, and the reported advantages of these nanosystems, this work provides valuable insights into the technological landscape of nanotheranostics and its implications for future medical applications.
2. Methods
The integrative patent review was carried out based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines as a tool for the search and screening [12,13,14]. The search was conducted in March 2025 on the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and European Patent Office (EPO) databases, using the “title and abstract” and a combination of the keywords “nanoparticle*” and “theranostic*”. Code A61K was also used to filter the inventions related to medical preparations, dentistry, and hygiene. The patent documents were evaluated, and the inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied. Hence, the inventions that did not present polymeric, lipid, or hybrid lipid nanoparticles were excluded from this study, as well as the documents with more than 10 years of publication and documents not available in English. This study included inventions concerning organic nanoparticles, such as solid lipid and polymeric nanoparticles and organic–inorganic hybrid nanoparticles, such as hybrid lipid nanoparticles. The information about the patents was downloaded and exported to Microsoft Office Excel®, where data were evaluated. The graphs were generated using Google Sheets and the software GraphPad Prism version 8.0.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Information About the Patents
The search found 130 documents identified on the selected databases, WIPO and EPO, which hold documents of patents from several countries, including the United States of America, Brazil, China, among other countries [15]. Before screening, some records were excluded, such as duplicated documents, patents older than 10 years, and documents unavailable in English. Patents were screened and 56 were excluded due to being outside of scope. Hence, 76 patents were fully analyzed, from which 2 could not be retrieved. Thus, 35 documents were assessed for eligibility and 18 were excluded for claiming inorganic nanoparticles, 3 did not describe nanoparticles, and 1 did not present theranostic activity. In this sense, only 13 documents met the inclusion criteria of this study (Table 1). The flowchart of this research is shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Summary of included patents on theranostic nanoparticles of organic nature.
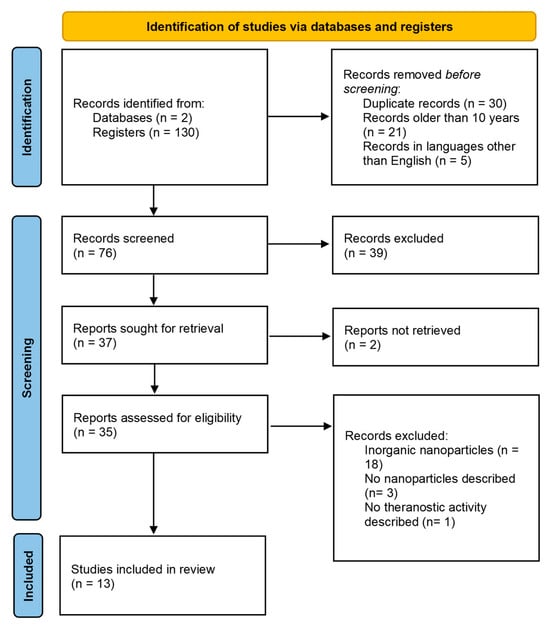
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the search on the selected databases.
3.2. Annual Evaluation and Country Distribution of Patents
Over the years, different theranostic nanotechnologies have been developed, such as lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, and other approaches. The oldest patent reported, according to our criteria, was the 2015 document “Precision therapeutics” (WO2016198859), which comprised a liposome-type lipid nanoparticle. The inventors used this system as a nanotheranostic applied to cancer. Between the years 2015 and 2024, there was a great filling expressiveness in 2017 (3 patents) with a clear recession between 2019 and 2021 (Figure 2). This decline may have been impacted by the critical state of global health with the COVID-19 pandemic, which interfered with several economic sectors worldwide [29,30].
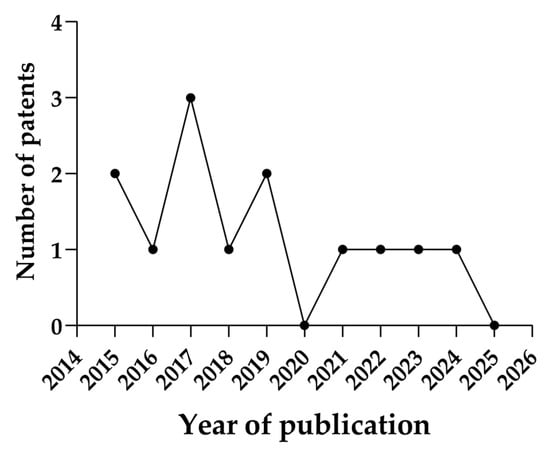
Figure 2.
Annual publication profile of the patented theranostic nanoparticles.
Nanotheranostics technologies in this period were deposited by inventors from five different countries (Figure 3): United States of America (seven patents), Canada (three patents), Great Britain (one patent), Italy (one patent) and China (one patent). The USA leads the number of patents as it has numerous policies to encourage innovation and nanotechnology since the creation of the National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI), which began in the 2000s. This initiative was conceived by the National Council of Science and Technology (NCST) [31,32]. Notwithstanding, since it was determined as criteria patents available in English, the prevalence of English-speaking countries is expected, the deposit of more patents in the worldwide office in a worldwide language such as English could enable the broad access of new technologies in development.
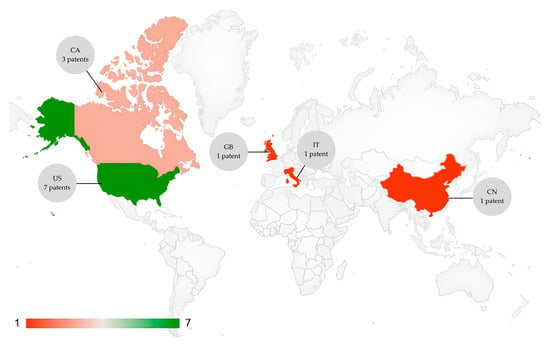
Figure 3.
Countries with inventors of organic-based theranostic nanoparticles patents.
The section below describes the patent documents related to nanotheranostics (polymeric, lipid and hybrid nanoparticles) filed by the countries up to 2024.
3.3. Polymeric Nanoparticles
Polymeric nanoparticles are versatile nanostructures due to their easy synthesis, biocompatibility, biodegradability, controlled release, protection against the environment, controllable size, shape, and surface charge, possibility of functionalization, and robust and scalable techniques used to formulate them. They also can allow for high loading efficiencies [33,34]. In addition, these systems can be obtained by many methods and materials [35]. In this context, these nanostructures may act both for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. This section will cover the polymeric nanoparticles referenced in the analyzed patents and the methods for obtaining these structures. Additionally, detailed data extracted from these documents will be presented, along with a critical perspective on the gathered information.
The patent “US20210228733” entitled “Methods and compositions for theranostic nanoparticles”, describes a hyperbranched polyester (HPBE) nanoparticle intended for theranostic approaches [17]. A hyperbranched polyester is a three-dimensional dendritic macromolecule that presents higher physical, chemical, and mechanical properties when compared to linear polymers, which is why this polymer is so attractive to developing nanoscale delivery systems [36]. In this sense, the inventors produced polymeric nanoparticles using the solvent diffusion method. In this method, the polymer and the molecule to be encapsulated are dissolved in an organic solvent; this solution is then added to a beaker containing purified water, drop-wise, with constant stirring. After this, there is a solvent displacement, causing the polymer to self-assemble, forming the polymeric nanoparticles encapsulating the molecule. The inventor’s nanoparticles were functionalized with a target ligand, which is a substrate for a solid tumor-specific cell protein. Also, the nanoparticle contains an imaging compound ligand and a therapeutic molecule encapsulated inside the core of the nanoparticle. In addition, the inventors performed assays to characterize the nanoparticles using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and mass spectroscopy, as well as to characterize the size of the nanoparticles using dynamic light scattering. The size of the nanoparticles was about 76.6 nm, which is expected for polymeric nanoparticles [37]. The inventors also presented in vitro and in vivo studies utilizing CT20p, a cytotoxic peptide, as a model molecule. The in vivo assay was performed using nude mice, wherein the nanoparticles were injected at 2 mg/kg intravenously (IV) for imaging after 24 h. The mice were euthanized before the tumors ulcerated and images were obtained for the evaluation of the tissues as well as for the comparison between the size of the tumors and the ability to regress the tumors. The images provided of the assays demonstrated that the developed polymeric nanoparticles met the initial objectives of their research, showing safety for use and yielding satisfactory results in prostate cancer models involving mice. In this regard, not only did the peptide demonstrate its efficacy on cancer treatments, this result was expected since CT20p is reported in several studies for the treatment of cancers, such as breast cancer, and it is known to promote fusion-like aggregation, mitochondrial membrane hyperpolarization, and hinder mitochondrial movement in tumor cells [38]. Additionally, this peptide can enhance ferroptosis through the production of ROS and lipid peroxidation in prostate cancer cells [39]. Also, the formulation showed as a promising theranostic agent since it was able to provide a clear image of the tumor for the diagnosis of prostate cancer in mice.
The patent “US20160256402” entitled “Synthesis of hyperbranched amphiphilic polyester and theranostic nanoparticles thereof” prepares a polymeric nanoparticle using a hyperbranched polymer [25]. To achieve this, the inventors used the modified solvent diffusion method, where the polymer and the drug were dissolved in anhydrous dimethylformamide and added drop-wise to water under continuous stirring. This procedure led to the self-assembly of the nanoparticle and encapsulation of the drug. Dynamic light scattering was used to determine the size of 115 nm, demonstrating the success in obtaining a nanoformulation. In addition, the inventors performed an in vitro cytotoxicity assay using MTT, where they examined the potential difference of carboxylated, aminated, and folate decorated dye added to the nanoformulation. For this test, lung carcinoma cells were grown in Kaighn’s modification of Ham’s F12 medium; the cells were incubated with the nanoparticles for 3 h at controlled conditions, then, the cells were washed and absorbance was recoded. The inventors also evaluated the cellular internalization of the formulation through florescence laser-scanning confocal microscopy, the same cell line was incubated under controlled conditions, washed, and fixed for observation. The results presented by the inventors showed that the formulation exhibited cellular cytotoxicity, especially for the aminated dye which induced cell death to approximately 10% of the cell population. The cellular uptake assay demonstrated that the nanoparticles could not be internalized, remaining in the membrane of the cells. To corroborate this result, flow cytometry was performed with the same cell line which showed limited fluorescence emission, confirming the observed in the previous assay. However, it was observed that the cells incubated with aminated nanoparticles showed fluorescence emission and indeed interacts with the cellular membrane.
The patent “WO2024229271” entitled “Nanoparticle-based Theranostic Platform for Diagnosis and Treatment of Senescence-related Pathologies” describes a polymeric nanoparticle designed for diagnosing and treating senescence-related diseases [18]. However, the inventors did not specify the method for obtaining the polymeric nanoparticles; instead, they claimed to use a sulfated polymer with free hydroxyl and sulfate moieties capable of targeting P-selectin. They claim that the polymeric nanoparticles are configured to selectively target senescent cells in the tumor microenvironment and state that the described method can prevent or mitigate metastasis. The inventors also claim that the nanoparticles can carry a senomorphic drug and include an infrared dye in their structure due to functionalization. Although it is a promising nanoformulation, the inventors did not provide the necessary data to demonstrate the benefits of their formulation for theranostic purposes, nor did they detail the characterization of their nanoparticles; nonetheless, they claim that the polymeric nanoparticles range in size from 20 to 200 nm. The lack of information in their document undermines the patent, as they must prove the benefits of their invention, which weakens the patent and decreases the likelihood of the invention being granted.
The patent “US20190381471” entitled “Process for the Preparation of Double Crosslinked Core-Shell Polymeric Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging and Theranostic Applications” describes a polymeric nanoparticle obtained through coacervation [21]. In this document, the inventors solubilized chitosan in an aqueous solution with acetic acid; then, Gadolinium DTPA (Gd-DTPA) was added, and the pH was stabilized from 4.5 to 5. Next, an oil phase was created by dissolving Span 80® (0.5–1% wt/v) in 45 mL of mineral oil to form an emulsion. A coacervant phase was prepared with hyaluronic acid (0.1% wt/v) in a water solution. The coacervant phase was then added dropwise to the previously prepared emulsion while maintaining constant stirring to allow for phase separation. The final dispersion was homogenized, and, after all the steps, the final solution was collected and diluted in ethanol, filtered through an ISOPORE filter membrane, ultracentrifuged, and the final nanoparticles were concentrated to 10 mg/mL. The inventors characterized the nanoparticles using a transmission electron microscope and a scanning electron microscope. Additionally, to investigate crosslinking within the nanoparticles, they performed an FTIR study. The analysis showed that the obtained nanoparticles had a nanometric size (40–500 nm) and exhibited crosslink interactions between the polymers used. The absence of in vitro or in vivo studies to assert the effectiveness of the formulation weakens the patent as the inventors did not prove that their invention can be used for the claimed purpose.
The inventors of this patent also have published articles concerning nanoparticles for multimodal imaging. Hence, despite not presenting any in vivo or in vitro studies in their patent, they performed such studies indicating the efficacy of the crosslinked nanoparticles, especially in treating lymphoma in murine models, using the peptide A20-36, which can be used for detecting A20 cells in lymphoma tumors [40]. Thus, the inventors attested that their invention is effective and suitable for theranostic purposes [41].
The patent “US20150078995” entitled “Nanoparticles/theranostic vehicles” relates to a polymeric nanoparticle used for theranostic purposes, more specifically, for the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [26]. In this document, the formulation of nanoparticles uses chitosan as the polymer and a contrast agent Magnevist® by conjugation of these ingredients. After this, the system was lyophilized for later use. Then, cyclophosphamide was entrapped in the Magnevist®-conjugated chitosan using ionic gelation with pentasodium tripolyphosphate, and the surface was functionalized with putrescein modified anti-amyloid IgG4.1. The produced theranostic nanovehicle was separated from the cyclophosphamide by ultracentrifugation. The formulation was 239 nm (hydrodynamic diameter) and showed a zeta potential of 11.9 mV. The inventors performed in vitro studies to evaluate the uptake of the nanoformulation on the blood–brain barrier. This experiment was conducted by pre-incubating the bovine brain microvascular endothelia with fluorescein isothiocyanate for 30 min, then, the formulation was incubated for 60 min under controlled conditions. Then, the formulation was removed, the cells were washed, harvested, fixed, and analyzed under a microscope. An increase in uptake was observed in the cells treated with the formulation. In addition, the in vivo test was performed to evaluate the brain distribution of the nanostructure. To do so, B6/SJL mice were treated with 100 µCi of the formulation via femoral vein. At pre-determined time points, blood was collected and assayed for radioactivity. Furthermore, the ability to target cerebrovascular vessels was determined by administering 45 mg to the nanovehicles via external carotid to 2 years old transgenic or age-matched WT mice. The images provided showed that the nanovehicles were able to cross the blood–brain barrier and were adequately biodistributed in the tissue, mainly when combined with DutchAβ40 protein.
The patent “US20230076792” entitled “Sequential targeting in crosslinking nano-theranostics for treating brain tumors” describes crosslinked nanoparticles and telodendrimers [22]. The polymeric nanoparticles were obtained through film formation, in which the polymer was dissolved in a polar solvent and the solvent was evaporated to form a thin film. After this step, the film was rehydrated with a PBS buffer and sonicated for 30 min. The telodendrimers were added to bond with the nanoparticles, resulting in crosslinked nanoparticles. The inventors obtained nanoparticles that ranged in size from 149 to 172 nm, with a loading rate of 87.5 to 92.6%. Additionally, tests were performed in vitro and in vivo, and orthotopic brain tumor models were established on female SCID mice. The mice were injected with the formulation in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg. After 24 h, the mice were injected with Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Dextran to mark the blood vessel at 2 min before euthanasia. Images were obtained to evaluate the effect of the nanoparticles and verify the ability to cross the blood–brain barrier. The images provided in the document demonstrated that the formulation is highly effective in treating brain tumors, showing a potential to cross the blood–brain barrier. In addition, it shows imaging potential, making it suitable for diagnostic and treatment purposes. Because of its reduced size, the crosslinked nanoparticles are addressed to be used in brain cancer; however, crossing the blood-brain barrier is not an easy task. Accordingly, a possibility for the success in this study might be the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, since very small particles can cross some biological barriers in tumor cells, allowing for the passive diffusion of the molecules [42].
In addition, the formulation was proven to be effective against ovarian cancer by preventing premature drug leakage and facilitating programmed-responsive drug release. The inventors published an article showing that the crosslinked nanoparticles show a potential application for ovarian cancer; however, the paper did not show the formulation’s ability in the diagnosis field [43].
The patent “US20190233567” entitled “Polymeric nanoparticles useful in theranostics” shows a formulation of polymeric nanoparticles for cancer treatment. For this purpose, the inventors used a free radical dispersion method to prepare the nanoparticles [28]. The polymerization was performed by dissolving the starch in distilled water and heating the mix for 30 min. After cooling and purging oxygen with nitrogen, other excipients were added to the formulation under stirring. After 15 min, the reaction was started by adding the required amounts methacrylic acid and N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide. Reaction happened for 8 h to ensure complete conversion. The suspension was washed with water and extracted with methanol followed by ultracentrifugation to remove unreacted material. Subsequently, the particles were freeze-dried and stored. The nanoparticles presented a particle size ranging 100–200 nm. Doxorubicin was used as a drug model and gadolinium as contrast agent. An in vitro assay using human breast cancer cells was conducted to evaluate the uptake of the nanoparticles by the cells using fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. Also, the efficacy of doxorubicin and the nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin were evaluated against breast cancer cell lines for 24 h and 48 h, and the cell viability were inferred by an MTT assay. The results provided in the document suggest the nanoparticle uptake by the wild type and multidrug resistant cells. In the absence of nanoparticle incubation, the cells showed no signal of fluorescence and the incubation of the nanoparticles for 4 h demonstrated a larger number of fluorescent foci, representing that membrane bond vesicles formed. For cellular viability, the treatment elicited cytotoxicity for both free doxorubicin and nanoparticles loaded on the wild type cells in a dose-dependent manner, which may imply that the nanoencapsulation of doxorubicin does not affect its cytotoxic activity.
Finally, the patent “US20210268129” titled “Theranostic Radiophotodynamic Therapy Nanoparticles” describes a polymeric nanoparticle designed to encapsulate a nanoscintillator, a radioluminescent material at the nanoscale [24]. To produce the nanoparticles, the polymer (PEG-PLGA) was dissolved in acetonitrile. Protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) and the nanoscintillator were added to an organic phase and then introduced into water. The mixture was vacuum evaporated to eliminate the organic phase and centrifuged, after which, the nanoparticles were washed with water. The nanoparticles were characterized by a size ranging from 75 to 125 nm and a polydispersity index of 0.3. The inventors performed in vivo studies to assert the theranostic potential of the nanoformulation. For this purpose, PC3 implanted NOD-SCID-gamma mice models were adopted. The mice were injected with 500 mg/kg intravenously and images were acquired to evaluate the contrast enhancement and uptake of the nanoparticles on the tumor. In addition, therapeutic studies were conducted and assessed the tumor response via caliper-based tumor size measurements over time until endpoints of tumor size, wet ulceration, or poor animal health were reached. Tumor size measurements demonstrated no differences in tumor growth or survival in the control and nanoparticle only groups, and significantly slower growth characteristic in the nanoformulation.
The nanoparticles described in this section for theranostic purposes are innovative delivery systems for diagnosis and therapeutics. However, the lack of information about their effectiveness is a crucial drawback that needs to be overcome.
All claimed nanoparticles have performed characterization assays, which is an important feature to explore. However, information about the therapeutic and diagnostic sides is also very important to confirm the advantages of these systems in the theranostic field.
Also, the nanoparticles described in this section match the size and polydispersity index expected for this kind of nanoparticle. Normally, it is expected that nanoparticles for medical use will have a size smaller than 200 nm [44]. Furthermore, all the inventors successfully presented the methods for obtaining the nanoparticles, utilizing methodologies ranging from solvent displacement to coacervation.
Moreover, the majority of patents claim the use of synthetic polymers. These polymers can be fabricated into various shapes and have a wide range of physical and chemical properties [45]. Due to the advantages provided by synthetic polymers, they are usually chosen to ease the lab bench to market process.
The patents described in this section claimed the use of polymeric nanoparticles. All formulations used biocompatible polymers, which offer safe and efficient drug delivery [46,47,48]. Furthermore, the inventors used the nanoparticles versatile surface modification properties to address the known limitations of theranostics such as overcoming biological barriers. On the other hand, the inventions still lack proof of concept of this benefit, regardless of how nanoparticles have shown this ability in research studies [49].
Based on searching the literature, we can disclose that from the documents described in this section, only two can be corroborated by peer-reviewed papers regarding the theranostic potentials of such formulations.
3.4. Lipid Nanoparticles and Liposomes
Lipid nanoparticles are widely studied as delivery systems, particularly in the development of vaccines. These nanosystems consist of lipids, which are small amphiphilic or hydrophobic molecules that have structural, signaling, and energy storage functions in cellular physiology. Their structural similarity to cellular membranes makes this type of nanostructure an attractive platform for developing theranostic agents, as it can evade the immune system. With this in mind, this section will describe the inventions related to lipid nanoparticles, focusing on how they were obtained and critically discussing the information contained in these documents.
The document “WO2016198859” titled “Precision Therapeutics” describes a liposomal formulation obtained through film formation [20]. In this method, the inventors added the lipid stock solution to a flask and the solvent was slowly evaporated under vacuum to ensure thin and even film formation. Afterward, the film was hydrated in ammonium sulfate and plunged into liquid nitrogen, followed by hot water to fragment the film. The suspension was then sonicated and extruded through a polycarbonate membrane. The inventors reported that the liposomes were characterized by size and polydispersity index, and that doxorubicin was quantified using HPLC. Additionally, they conducted cell cultures and in vivo assays; however, the results of these tests are not presented in the document. Nonetheless, the inventors claimed that the liposomes can reach tumor cells and emit fluorescence, indicating that the theranostic purpose can be demonstrated given that doxorubicin is an anticancer agent.
Additionally, the document “US20200147078” titled “Theranostic Agents” describes a lipid nanoparticle created by adding TPA-T-TQ and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-phosphoethanolamine–N-[Methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] to tetrahydrofuran and deionized water [23]. The mixture was sonicated for 2 min, and the remaining tetrahydrofuran was evaporated overnight, yielding a colloidal suspension of nanoparticles. The inventors succeeded in obtaining nanoparticles measuring 60–80 nm in size. Furthermore, they conducted in vivo assays with xenograft 4T1 tumor-bearing nude mice. The results presented in the document suggest the formulation’s effectiveness with breast cancer; however, the inventors did not disclose information about the dosages or administration of the nanoparticles. This lack of information compromises the quality and credibility of the document since this is an important information, and its absence can make further experiments irreproducible. On the other hand, the inventors evaluated the ability of the formulation to capture images of tumors in the animals using laser irradiation at 808 nm. The images presented in the document show that the formulation improved the visualization of the structures when compared to a saline solution; thus, demonstrating its potential as a diagnosis tool.
Finally, the document “US20240041768” entitled “Multifunctional pO2/pH-sensitive theranostic liposome nanocarriers and methods of using same” describes a formulation of liposomes [27]. This formulation was produced by ethanol injection and thin film hydration. Pioglitazone was used as drug model, mixed with the lipid mixture and dissolved in 2 mL of anhydrous ethanol, sonicated and filtered through a 0.22 syringe filter. Then, the solution was mixed with 10 mL of pH 7.2 saline through opposite ends of a T-junction, and the resulting translucent liposome suspension was filtered to remove ethanol and any unencapsulated ingredients of the formulation, such as contrast agents. The size and charge of the nanoparticles were determined by dynamic light scattering and presented a hydrodynamic size between 30 nm and 100 nm. Despite declaring that surface charge was determined, the inventors did not present the data of the zeta potential of the formulation. As for the biological assays, the document did not detail how the in vitro assay was performed, only showing the result of release in different pH media, presenting as parameters. The fluorescence intensity better enhanced in pH 6.85 after 7 days of experiment. The omission of this information on biological tests affects its credibility since the experiments described cannot be reproduced elsewhere, limiting the robustness of the employed methods of the document.
In this type of nanostructure, lipid nanoparticles are synthesized with fluorescent lipids, which is an important method to ensure diagnostic objectives. These lipids have a fluorophore attached to their structure, enabling the fluorescent properties of these molecules. Additionally, they exhibit photostability and do not degrade easily. The fluorophore in these lipids can also emit light in the visible spectrum, allowing for their use in diagnostic applications.
Additionally, lipid nanoparticles are very attractive platforms for developing new technological products due to their advantages, such as ease of formulation, self-assembly methods of obtention, high bioavailability, biocompatibility, capacity to carry substantial payloads, and modulation of biological characteristics [50]. These advantages can explain the use of this nanosystem in the cited documents once it is known that theranostic agents have difficulty ensuring the safety of the formulation, and this type of system can minimize the side effects of theranostics [51].
However, some of the nanoparticles claimed in this section are actually liposomes. This drug delivery system is composed of natural or synthetic phospholipids sterols and polysaccharides, organized in bilayers, and dispersed in an aqueous medium [52,53]. They can be categorized as nanovesicles, with its core or membrane encapsulating drugs, which is the case of the aforementioned patent.
The lipid nanoparticles addressed in this section prove that these nanosystems can be used as a valuable tool to theranostic approaches. The inventions that presented preclinical trials demonstrated that lipid nanoparticles are indeed effective for the goal claimed by the inventors, but the absence of detail in some documents represents a fragility that needs to be overcome to ensure the reproducibility, quality, and robustness of the patented products. Thus, it is expected that novel formulations protected by intellectual property can focus on improving the material on the documents so their patents can become a valuable scientific source.
Interestingly, none of the patents described in this section could be corroborated by peer-reviewed articles from the inventors of such formulations.
3.5. Hybrid Lipid Nanoparticles
Hybrid lipid nanoparticles are complexes comprised of a mixture of lipids and other compounds such as inorganic nanoparticles that confer unique properties inherent to both materials [54]. The hybridization of lipid and inorganic nanoparticles has proven to be a potential technique that helps in obtaining efficient medical images and treatments [55]. In this perspective, this section addresses in detail the patent documents of these hybrid lipid complexes as nanotheranostics.
The patent “US20200170946” entitled “Nanoparticle-lipid composite carriers and uses thereof” describes a lipid nanoparticle designed to transport magnetic nanostructures (MNS) and other therapeutic agents [19]. These lipid nanoparticles are synthesized by mixing citrate MNS with the cationic lipid dimethyldioctadecyl ammonium bromide in a chloroform dispersion, followed by adding Milli-Q water to emulsify the mixture. It is then left overnight at room temperature for self-assembly. The mixture undergoes centrifugation to remove excess MNS, and the residual surfactants and lipids are removed using a dialysis bag for two days in water. The mixture is subsequently filtered to eliminate any precipitation. The resulting hydrodynamic size is 180 nm, with a zeta potential of 28 mV. To validate the nanosystem as an effective drug delivery carrier, curcumin was utilized as a model drug, with nearly 80% of the drug being incorporated into the system. To assess biocompatibility, a cell viability assay was conducted, revealing that the cells were not adversely affected by the increased concentration of nanoparticles, indicating the formulation’s biocompatibility. Additionally, the uptake study demonstrated that the formulation enhances cellular uptake with increasing concentrations. The inventors also incorporated paclitaxel into the nanoparticles to showcase the therapeutic effect of this anticancer agent; this test revealed that the formulation with paclitaxel exhibited in vitro toxicity associated with the drug loaded in the nanoparticles. Finally, the formulation displayed a greater contrast enhancement property, confirming its theranostic purpose.
The patent “WO2023150892” entitled “Hybrid lipid nanoparticle comprising an inorganic particle and an agent of interest” describes a hybrid nanoparticle system that consists of a lipid nanoparticle designed to carry an inorganic nanoparticle [16]. The inventors used a lipid mixture made of 1,2-dioleoyl-3-dimethylammonium-propane (DODAP), 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DSPC), cholesterol (Chol), and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy-(polyethylene-glycol)-2000] (PEG-DSPE) (molar ratio of 10/49/40/1) in 100% ethanol, resulting in a 10 mg/mL solution. The lipid solution was mixed with an aqueous dispersion of gold nanoparticles. The mixture was extruded using syringes and a T-junction. The ethanol was removed from the dispersions by dialysis in a buffer solution. Once the dialysis was complete, the formed hybrid nanoparticles were characterized by their mean diameter, polydispersity index (PdI), and zeta potential. The inventors observed a mean diameter ranging from 87 to 114 nm and a polydispersity index from 0.06 to 0.23; these values depended upon the gold-to-lipid ratio, with an increase in the number of particles/µmol resulting in growth in size and PdI of the nanoparticles. The inventors also incorporated a therapeutic agent into the nanoparticles and evaluated the size and PdI of the formulations, which underwent a slight alteration in mean size, changing to 115–135 nm, while the PdI remained in the range of 0.08–0.12. Additionally, an entrapment efficiency (EE) analysis yielded a value of 81–91%. Finally, an irradiation protocol was employed to assess the ability to release the therapeutic agent using a femtosecond laser. This test demonstrated that irradiation enhanced the release of the therapeutic agent. The inventors of this patent also authored a published article on this formulation. Their research paper did not provide further in vitro and/or in vivo data. In fact, the article solely detailed the development and physicochemical characteristics of the formulation. Hence, they showed that the nanoparticles have simple synthesis and can encapsulate inorganic nanoparticles and anticancer drugs, prospecting their suitability for drug delivery and imaging purposes [56].
The inventions above highlight promising advances such as theranostic nanotechnologies based on metallic–lipid hybrid systems. The hybridization of lipid nanoparticles with those of an inorganic nature gives the complex imaging properties without the loss of biocompatibility and drug entrapment efficiency. The ability to entrap active pharmaceutical ingredients and respond to external stimuli, such as laser irradiation, promotes uniqueness and versatility to these nanoformulations [57,58]. In this way, organic/inorganic hybrid systems pave the way for personalized medicine, allowing optimized nanotheranostic capabilities in a single nanosystem.
As presented in this section, hybrid lipid nanoparticles are a promising nanosystem to be used in therapy and diagnosis. The patents described in this topic were sufficiently detailed and demonstrated the potential of these nanostructures to the claimed objective. However, in this study, only 2 out of 13 patents were for hybrid lipid nanoparticles, which represents a gap in the patenting of these nanostructures. Once these nanoformulations begin to be more patented, information about their methods of obtention, animal trials, scalability, and reproducibility will be further described and can improve the scientific data available for robust discussions. Finally, only one patent from the two described in this section was corroborated by a scientific publication in a peer-reviewed journal for further assessment of the formulation’s potential as a theranostic nanoparticle.
4. Challenges in Clinical Translation of Organic-Based Nanotheranostics
The patent data presented in this study present organic-based theranostic nanostructures. The process of this nanosystem, from development to reaching the market, is a challenge faced by researchers and has a long way to go to become the standard choice in clinical treatment. Furthermore, for a patent to be conceded, it needs to meet some criteria: novelty, inventive activity, and industrial scalability. These conditions sometimes cause ambiguity on the patent offices, since it is up to each patent examiner to determine if the document possesses these characteristics; a standardization of this criteria could be beneficial for the quality of the patents deposited worldwide.
Nanostructures such as organic-based nanoparticles represent a huge breakthrough in modern medicine as they have unique properties like large specific surface area, stability, dispersibility and an important feature: the ability to control drug delivery [8,59]. Another interesting characteristic is the potential to assist in the detection and identification of abnormalities at a molecular level, helping in diagnosis purposes [60]. Hence, these nanostructures are advantageous nanosystems for therapy and diagnostic purposes; however, to date there is no approved product with this appeal.
Nevertheless, nanoparticles can present some drawbacks, for instance, some nanoparticles can show cytotoxicity, risk of recrystallization, and poor encapsulation. Additionally, one key point that hinders the production of these nanosystems at larger scales is the high cost involved in their development [61].
As previously discussed, an important aspect to take into consideration in patenting is performing studies to attest the efficacy of the formulations. Assays on the physicochemical characteristics of these nanomedicines and how they behave in human disease pathophysiology is crucial to attest to the real theranostic potential of formulations, since some platforms that have good therapeutic efficacy might not be good as diagnostic tools [62].
Nowadays, some strategies can be adopted to optimize the design and development of nanoparticles and predict interactions with biological components and important cellular barriers. For instance, software and artificial intelligence (AI) tools can be applied to the research and production of these platforms [62,63]. Also, an association between private and academic initiatives can reduce the gap in clinical translation and shorten the process for these technologies to reach the market.
Another important aspect is the regulation of the nanostructure innovations. A well-written, standardized, and global legislation about intellectual property of nanosystems can assure the evenness on the information provided in patent documents. This would be important to secure the information provided by these documents.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed the state of nanometric organics (polymeric and lipid nanoparticles) and hybrid organic–inorganics (hybrid lipid nanoparticles) for theranostics. The patents described in the segments of this paper show that these nanoparticles can be obtained and used for this purpose through the functionalization of nanoparticle surfaces, alterations to the membrane, and the loading of imaging and/or anticancer drugs. Among the number of nanoparticle formulations already in the market, the U.S. leads the search for novel nanotheranostics from a patent perspective.
Despite the promising results of some documents, not all patents show that their formulations can achieve what is claimed. This weakens the patent and leaves the reader blind from the true potential of the invention. Furthermore, some inventions did not present data on biological studies. This is unfortunate since the biological assays can prove the effectiveness of the patented nanosystems; however, such assays require resources, especially for academic research, which is a difficulty faced by researchers over the world. Associations of academic and private institutions can be advantageous for both and boost the arrival of new products to the market.
Thus, it is highly encouraged that inventions not only describe the methods and formulation specifications but also provide information about the conducted assays and preclinical results to demonstrate that their product is ready for use by the end user. This would allow for increased patentability, especially in recent years, where the market has become more competitive.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, original draft writing: D.T.F.; formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing, visualization: J.A.M.; formal analysis, investigation, writing, review and editing, visualization: D.D.; writing—review and editing; conceptualization, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, É.d.N.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance code 001.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Blasco-Navarro, C.; Alonso-Moreno, C.; Bravo, I. From Traditional Nanoparticles to Cluster-Triggered Emission Polymers for the Generation of Smart Nanotheranostics in Cancer Treatment. J. Nanotheranostics 2025, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccetti, M.; Pariano, M.; Schoubben, A.; Giovagnoli, S.; Ricci, M. Biologics, theranostics, and personalized medicine in drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 201, 107086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajbhiye, K.R.; Salve, R.; Narwade, M.; Sheikh, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Gajbhiye, V. Lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles: A custom-tailored next-generation approach for cancer therapeutics. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Peng, S.; Cao, J.; Tan, H.; Zhao, H.; Bai, J. Advances in the variations and biomedical applications of stimuli-responsive nanodrug delivery systems. Nanotechnology 2024, 35, 132001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uredat, S.; Gujare, A.; Runge, J.; Truzzolillo, D.; Oberdisse, J.; Hellweg, T. A review of stimuli-responsive polymer-based gating membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 2732–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.; Chandra, S. Inorganic hybrid nanoparticles in cancer theranostics: Understanding their combinations for better clinical translation. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 18, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurul, F.; Turkmen, H.; Cetin, A.E.; Topkaya, S.N. Nanomedicine: How nanomaterials are transforming drug delivery, bio-imaging, and diagnosis. Next Nanotechnol. 2025, 7, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, B.K.; Singh, V.V.; Solanki, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Ruokolainen, J.; Kesari, K.K. Smart Nanomaterials in Cancer Theranostics: Challenges and Opportunities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 14290–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, A.; Challa, R.R.; Vallamkonda, B.; Satti, P.; Mehata, A.K.; Priya, V.; Kumar, S.; Muthu, M.S. Nanomedicine And Nanotheranostics: Special Focus on Imaging of Anticancer Drugs Induced Cardiac Toxicity. Nanotheranostics 2024, 8, 473–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Salamat, S.; Beiram Zadeh, Z.; Tanhaei, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Theranostic polymeric nanoparticles as a new approach in cancer therapy and diagnosis: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology in Healthcare and Medicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, J.A.C., Jr.; Santos, A.M.; Oliveira, A.M.S.; Santos, A.B.; Araújo, A.A.d.S.; Frank, L.A.; Serafini, M.R. Use of nanotechnology applied to sunscreens: Technological prospection based on patents. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 91, 105245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezar, S.V.S.; Santos, A.B.; Santos, A.M.; Brito, J.R.L.R.; Menezes, P.d.P.; Serafini, M.R. Patents on the move: The therapeutic future of liquid crystals in cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 97, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WIPO. World Intellectual Property Organization; WIPO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cullis, P.; Kulkarni, J.; Jigaltsev, I.; Tam, Y.Y.; Uzel, A.; Kafshgari, M.H.; Meunier, M. Hybrid Lipid Nanoparticle Comprising an Inorganic Particle and an Agent of Interest. WO/2023/150892, 17 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, A.; Figueroa, J.M.P.; Santra, S.; Kaittanis, C.; Santiesteban, O.; Grimm, J.; Sessions, H. Methods and Compositions for Theranostic Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent No. 10,973,925, 13 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Barthet, V.; Hinterleitner, C.; Heller, D.A.; Lowe, S. Nanoparticle-Based Theranostic Platform for Diagnosis and Treatment of Senescence-Related Pathologies. WO/2024/229271, 7 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dravid, V.P.; Nandwana, V. Nanoparticle-Lipid Composite Carriers and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent No. 11,510,872, 29 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thanou, M.; Wright, M.; Centelles, M.; Miller, A.D.; Gedroyc, W. Precision Therapeutics. 2015. WO/2016/198859, 15 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Torino, E.; Netti, P. Process for the Preparation of Double Crosslinked Core-Shell Polymeric Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging and Theranostic Applications. U.S. Patent No. 11,311,853, 26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Lin, T.-Y. Sequential Targeting in Crosslinking Nano-Theranostics for Treating Brain Tumors. U.S. Patent Application No. 17/785,765, 9 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Ding, D.; Qi, J. Theranostic Agents. 2017. U.S. Patent No. 11,389,446, 14 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dinakaran, D.; Moore, R.; Lewis, J.; Narain, R.; Kumar, P.; Usmani, N. Theranostic Radiophotodynamic Therapy Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent Application No. 17/255,424, 2 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J.M.; Santra, S. Synthesis of Hyperbranched Amphiphilic Polyester and Theranostic Nanoparticles Thereof. U.S. Patent 20160256402A1, 2 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Karunya, K.K. Nanoparticles/Theranostic Vehicles. U.S. Patent No. 09,950,002, 19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, M. Multifunctional pO2/pH-Sensitive Theranostic Liposome Nanocarriers and Methods of Using Same. U.S. Patent Application No. 18/357,810, 8 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.X. Polymeric Nanoparticles Useful in Theranostics. U.S. Patent No. 10,233,277, 19 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WIPO. World Intellectual Property Indicators Report: Global Patent Filings Reach; WIPO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McKibbin, W.; Fernando, R. The global economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Econ. Model. 2023, 129, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanotechnology at NIH; NIH: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016.
- De Souza, M.L.; Oliveira, D.D.; Ribeiro, P.L.L.; de Paula Pereira, N.; Druzian, J.I. Nanoemulsions for Cosmetic Applications: What Innovation Status? Recent. Pat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 12, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.A. Theranostic Polymeric Nanoparticles for Cancer. BioNanoScience 2023, 13, 1609–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Carreiró, F.; Oliveira, A.M.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization, Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Molecules 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, S.F.; Bharadwaj, P.; Leblond Chain, J.; Roullin, V.G. Purification processes of polymeric nanoparticles: How to improve their clinical translation? J. Control Release 2023, 360, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alregeb, F.; Khalili, F.; Sweileh, B.; Ali, D.K. Synthesis and Characterization of Chelating Hyperbranched Polyester Nanoparticles for Cd(II) Ion Removal from Water. Molecules 2022, 27, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdal, Z.D.; Gültekin, Y.; Vural, İ.; Takka, S. Development and characterization of polymeric nanoparticles containing ondansetron hydrochloride as a hydrophilic drug. J. Drug Dev. Technol. 2022, 74, 103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Bassiouni, R.; Sparrow, N.A.; Iketani, A.; Boohaker, R.J.; Moskowitz, C.; Vishnubhotla, P.; Khaled, A.S.; Oyer, J.; Copik, A.; et al. The CT20 peptide causes detachment and death of metastatic breast cancer cells by promoting mitochondrial aggregation and cytoskeletal disruption. Cell Death Disease 2014, 5, e1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Lu, L.; Shi, X.; Lovell, J.F.; Zeng, X.; Hu, W.; Jin, H. Irradiated microparticles suppress prostate cancer by tumor microenvironment reprogramming and ferroptosis. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, D.N.; Dhinasekaran, D.; Rebecca, P.N.B.; Rajendran, A.R. Optical Biosensors for Detection of Cancer Biomarkers: Current and Future Perspectives. J. Biophotonics 2024, 17, e202400243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torino, E.; Auletta, L.; Vecchione, D.; Orlandella, F.M.; Salvatore, G.; Iaccino, E.; Fiorenza, D.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Sandomenico, A.; Albanese, S.; et al. Multimodal imaging for a theranostic approach in a murine model of B-cell lymphoma with engineered nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Seven, E.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles. J. Control Release 2018, 270, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirescu, V.A.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Therapies: An Up-To-Date Overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Xue, X.; Zhang, D.; Du, H.; Shen, Y.; Ramachandran, M.; et al. Programmed-response cross-linked nanocarrier for multidrug-resistant ovarian cancer treatment. J. Control Release 2023, 357, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitz, M.F. Applications of synthetic polymers in clinical medicine. Biossurf. Biotribol. 2015, 1, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, M.A.; Nayanathara, U.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Such, G.K. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 5505–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Bakr, M.M.; ElMeshad, A.N. Surface-functionalised polymeric nanoparticles for breast cancer treatment: Processes and advances. J. Drug Target. 2024, 32, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, K.; Srinivasan, S.; Shanmugam, A. Review of the efficacy of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 5, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mehta, A.; Tong, Z.; Esser, L.; Voelcker, N.H. Development of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Blood-Brain Barrier Transfer-Strategies and Challenges. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhayalan, M.; Wang, W.; Riyaz, S.U.M.; Dinesh, R.A.; Shanmugam, J.; Irudayaraj, S.S.; Stalin, A.; Giri, J.; Mallik, S.; Hu, R. Advances in functional lipid nanoparticles: From drug delivery platforms to clinical applications. 3 Biotech. 2024, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmiladevi, P.; Girigoswami, K.; Haribabu, V.; Girigoswami, A. Nano-enabled theranostics for cancer. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2876–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.A.; Cruz, Y.F.d.; Girão, Í.C.; Souza, F.J.J.d.; Oliveira, W.N.d.; Alencar, É.d.N.; Amaral-Machado, L.; Egito, E.S.T.d. Beyond Traditional Sunscreens: A Review of Liposomal-Based Systems for Photoprotection. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Jaber, A.M.; Abdelghany, S.; Atwan, R.; Shalan, N.; Abdelnabi, H.; Odeh, F.; El-Tanani, M.; Alshaer, W. Liposome bilayer stability: Emphasis on cholesterol and its alternatives. J. Liposome Res. 2024, 34, 178–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, K.M.; Shon, Y.-S. Hybrid lipid–nanoparticle complexes for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadinoiu, A.N.; Rata, D.M.; Atanase, L.I.; Daraba, O.M.; Gherghel, D.; Vochita, G.; Popa, M. Aptamer-Functionalized Liposomes as a Potential Treatment for Basal Cell Carcinoma. Polymers 2019, 11, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musielak, M.; Potoczny, J.; Boś-Liedke, A.; Kozak, M. The Combination of Liposomes and Metallic Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Nanostructures in the Therapy and Medical Imaging—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Cullis, P.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Hybrid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Gold Nanoparticles and a Weak Base Drug. Langmuir 2022, 38, 7858–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, A.; Sándor, N.; Szenti, I.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Juhász, K.; Rónavári, A.; Kachal, E.; Kutus, B.; Kónya, Z.; Balogi, Z. Highly Stable Antitumor Silver-Lipid Nanoparticles Optimized for Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virlan, M.J.; Miricescu, D.; Radulescu, R.; Sabliov, C.M.; Totan, A.; Calenic, B.; Greabu, M. Organic Nanomaterials and Their Applications in the Treatment of Oral Diseases. Molecules 2016, 21, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilnawaz, F.; Acharya, S.; Sahoo, S.K. Recent trends of nanomedicinal approaches in clinics. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikdouz, A.; Namarvari, N.; Ghasemi Shayan, R.; Hosseini, A. Comprehensive comparison of theranostic nanoparticles in breast cancer. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Naziris, N.; Demetzos, C. Lipid Nanoparticles as Platforms for Theranostic Purposes: Recent Advances in the Field. J. Nanotheranostics 2022, 3, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragelle, H.; Fabienne, D.; Véronique, P.; Robert, L.; Anderson, D.G. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems: A commercial and regulatory outlook as the field matures. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).