Using the Two-Phase Emission Detector RED-100 at NPP to Study Coherent Elastic Neutrinos Scattering off Nuclei
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Exposition of the RED-100 Detector with Liquid Xenon as the Working Medium at Kalinin NPP
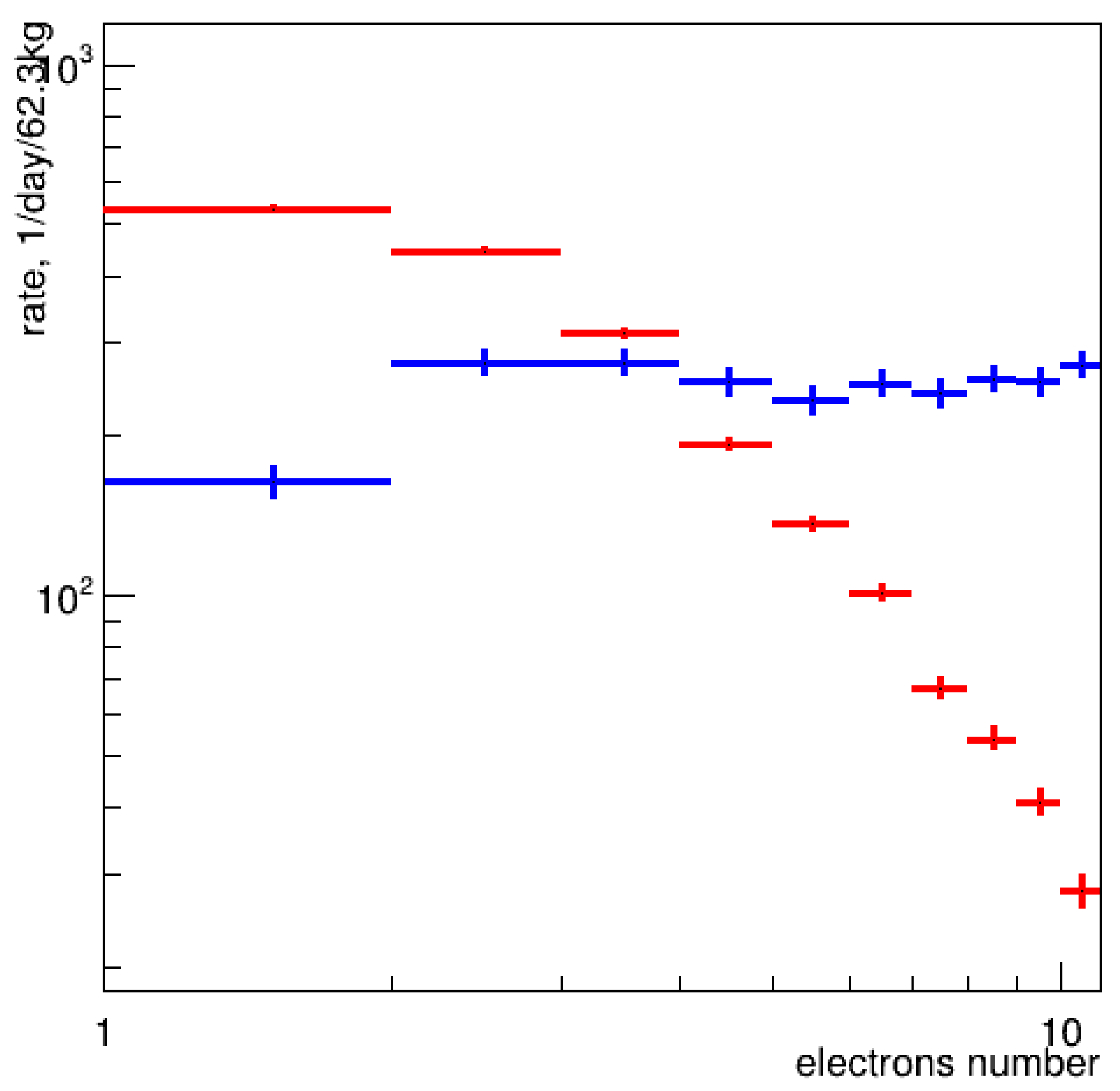
3. Observation of Single-Electron Noise Imitating CEvNS Signals
- Subsurface electrons trapped by a potential barrier at the phase boundary (a relatively weak source with characteristic times on the order of the lifetime of excess electrons before being captured by electronegative impurities).
- The working volume of the detector itself, filled with liquid xenon after irradiation with ionizing radiation (a relatively intense source with characteristic times in the millisecond range).
4. Liquid Argon as Alternative Media for Observation of CEvNS at NPP
- The significant difference in the decay times of the singlet and triplet components of argon radiation can be used as an additional tool for selecting useful signals against the background.
- A relatively higher probability of detecting double events (a scintillation signal followed by an electroluminescence signal), which can also be used to improve the separation of useful events and background.
- The operating temperature of the argon target is approximately −186 °C versus −108 °C for the xenon target, i.e., the RED-100 cryogenic system should ensure the performance of the detector at lower (by about 80 °C lower) temperatures.
- The need to use a shifter for the spectrum of argon scintillation and electroluminescent radiation is due to the insensitivity of the HAMAMATSU R11410-20 photomultipliers (PMs) used in the RED-100 detector to the relatively short (about 130 nm) wavelength range of argon radiation.
5. Preparation of RED-100/Ar Experiment
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Membership of the RED-100 Collaboration
Affiliations
- Institute of Nuclear Physics and Technology, National Research Nuclear University MEPhI, 115409 Moscow, Russia
- Research and Education Center for Advanced Studies, National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, 634050 Tomsk, Russia
- National Research Center ”Kurchatov Institute”, 123182 Moscow, Russia
- Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RAS, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia
- Faculty of Physics, Novosibirsk State University, 630090 Novosibirsk, Russia
- Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, 141980 Dubna, Russia
- The P.N. Lebedev Physical Institute, 119991 Moscow, Russia
- Institute for Nuclear Research, 117312 Moscow, Russia
- *
- Correspondence: aibolozdynya@mephi.com
References
- Freedman, D.Z. Coherent effects of a weak neutral current. Phys. Rev. D 1974, 9, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeliovich, V.D.; Frankfurt, L.L. Isotopic and chiral structure of neutral current. JETP Lett. 1974, 19, 145–147. Available online: http://jetpletters.ru/ps/1776/article_27044.shtml (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Akimov, D.; Albert, J.B.; An, P.; Awe, C.; Barbeau, P.S.; Becker, B.; Belov, V.; Brown, A.; Bolozdynya, A.; Cabrera-Palmer, B.; et al. Observation of coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering. Science 2017, 357, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmann, C.; Bernstein, A. Two-phase emission detector for measuring coherent neutrino-nucleus scattering. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2004, 51, 2151–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, E.; Bolotnikov, A.E.; Bolozdynya, A.I.; Doke, T. Noble Gas Detectors; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimov, D.; Bondar, A.; Burenkov, A.; Buzulutskov, A. Detection of reactor antineutrino coherent scattering off nuclei with a two-phase noble gas detector. J. Instrum. 2009, 4, P06010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard, J.; Johnston, J.; Kavanagh, B.J. Prospects for exploring New Physics in Coherent Elastic Neutrino-Nucleus Scattering. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelyan, L.A. Neutrino laboratory in the atomic plant (fundamental and applied researches). In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics: Neutrino 77, Elbrus Mountains, Russia, 18–24 June 1977; pp. 383–387. Available online: https://enpl.mephi.ru/download/articles/Neutrino77.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Bernstein, A.; Baldwin, G.; Boyer, B.; Goodman, M.; Learned, J.; Lund, J.; Reyna, D.; Svoboda, R. Nuclear security applications of antineutrino detectors: Current capabilities and future prospects. Sci. Glob. Secur. 2010, 18, 127–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, V.; Brudanin, V.; Egorov, V.; Filosofov, D.; Fomina, M.; Gurov, Y.; Korotkova, L.; Lubashevskiy, A.; Medvedev, D.; Pritula, R. The νGeN experiment at the Kalinin Nuclear Power Plant. J. Instrum. 2015, 10, P12011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.T.-K. Taiwan EXperiment On NeutrinO—History, status and prospects. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2018, 16, 1830014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnolet, G.; Baker, W.; Barker, D.; Beck, R.; Carroll, T.J.; Cesar, J.; Cushman, P.; Dent, J.B.; De Rijck, S.; Dutta, B.; et al. Background studies for the MINER Coherent Neutrino Scattering reactor experiment. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2017, 853, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angloher, G.; et al. [NUCLEUS Collaboration]. Exploring CEνNS with NUCLEUS at the Chooz nuclear power plant. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Status of the CHILLAX Detector Development. Talk at the Magnificent CEνNS 2021 Workshop, Online, 6–7 October 2021. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/1075677/contributions/4556726/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Bonet, H.; et al. [CONUS Collaboration]. Constraints on elastic neutrino nucleus scattering in the fully coherent regime from the CONUS experiment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 041804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaresi, J.; Collar, J.I.; Hossbach, T.W.; Kavner, A.R.L.; Lewis, C.M.; Robinson, A.E.; Yocum, K.M. First results from a search for coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering at a reactor site. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 072003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salagnac, T.; Billar, J.; Colas, J.; Chaize, D.; De Jesus, M.; Dumoulin, L.; Filippini, J.-B.; Gascon, J.; Juillard, A.; Lattaud, H.; et al. Optimization and performance of the CryoCube detector for the future RICOCHET low-energy neutrino experiment. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, L.J.; Peinado, E.; et al. [CEνNS Theory Group at IF-UNAM]; Alfonso-Pita, E. et al. [SBC Collaboration]. Physics reach of a low threshold scintillating argon bubble chamber in coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering reactor experiments. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, L091301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimov, D.Y.; Alexandrov, I.S.; Alyev, R.R.; Belov, V.A.; Bolozdynya, A.I.; Etenko, A.V.; Galavanov, A.V.; Glagovsky, E.M.; Gusakov, Y.V.; Khromov, A.V.; et al. The RED-100 experiment. J. Instrum. 2022, 17, T11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimov, D.Y.; Alexandrov, I.S.; Belov, V.A.; Bolozdynya, A.I.; Etenko, A.V.; Galavanov, A.V.; Gusakov, Y.V.; Khromov, A.V.; Konovalov, A.M.; Kovalenko, A.G.; et al. Electronic noise generated by cosmic muons in the two-phase xenon emission detector RED-100. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2023, 1, 1–9. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Akimov, D.Y.; Alexanderov, I.S.; Belov, V.A.; Bolozdynya, A.I.; Etenko, A.V.; Galavanov, A.V.; Gusakov, Y.V.; Khromov, A.V.; Konovalov, A.M.; Kovalenko, A.G.; et al. The RED-100 two-phase emission detector. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2017, 60, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, P.; Kamdin, K. Two distinct components of the delayed single electron noise in liquid xenon emission detectors. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, P02032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerib, D.S.; Alsum, S.; Araujo, H.M.; Bai, X.; Balaithy, J.; Baxter, A.; Bernard, E.P.; Bernstein, A.; Biesiadzinski, T.P.; Boulton, E.M.; et al. Investigation of background electron emission in the LUX detector. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 092004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrapak, A.G.; Volykhin, K.F. Negative ions in liquid xenon. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1999, 88, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimov, D.; et al. [COHERENT Collaboration]. First measurement of coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering on argon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidgard, J.J. Pulse Shape Discrimination Studies in Liquid Argon for the DEAP-1 Detector. Master’s Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, April 2008. Available online: http://deap3600.ca/student-thesis/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Bondar, A.; Buzulutskov, A.; Dolgov, A.; Grishnyaev, E.; Nosov, V.; Oleynikov, V.; Polosatkin, S.; Shekhtman, L.; Shemyakina, E.; Sokolov, A. Measurement of the ionization yield of nuclear recoils in liquid argon using a two-phase detector with electroluminescence gap. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, C05010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kimura, M.; Yorita, K. Development of a high-light-yield liquid argon detector using tetraphenyl butadiene and silicon photomultiplier array. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2021, 2022, 043H01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, G.; Al Kharusi, S.; Angelico, E.; Anton, G.; Arnquist, I.J.; Badhrees, I.; Bane, J.; Belov, V.; Bernard, E.P.; Bhatta, T.; et al. nEXO: Neutrinoless double beta decay search beyond 1028 years half-life sensitivity. J. Phys. G 2022, 49, 015104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collaboration, R.-1. Using the Two-Phase Emission Detector RED-100 at NPP to Study Coherent Elastic Neutrinos Scattering off Nuclei. Physics 2023, 5, 492-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5020034
Collaboration R-1. Using the Two-Phase Emission Detector RED-100 at NPP to Study Coherent Elastic Neutrinos Scattering off Nuclei. Physics. 2023; 5(2):492-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollaboration, RED-100. 2023. "Using the Two-Phase Emission Detector RED-100 at NPP to Study Coherent Elastic Neutrinos Scattering off Nuclei" Physics 5, no. 2: 492-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5020034
APA StyleCollaboration, R.-1. (2023). Using the Two-Phase Emission Detector RED-100 at NPP to Study Coherent Elastic Neutrinos Scattering off Nuclei. Physics, 5(2), 492-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics5020034



